To provide you with an enhanced database service experience, after extensive and in-depth validation by the Tencent Cloud Database team—including stability testing, ecosystem compatibility assessment, and future technology evolution forecasting—we have decided to strategically upgrade our database system. As part of this upgrade, the TDSQL (MariaDB) will be merged into the TencentDB for MySQL service. Starting from Q3 2025, TDSQL (MariaDB) will be integrated into the TencentDB for MySQLservice framework. For new instance purchases, it is recommended to prioritize TencentDB for MySQL. Existing TDSQL (MariaDB) instances will continue to be supported without service interruption; however, to achieve a better service experience, we recommend migrating your data to TencentDB for MySQL using the DTS service.
Functional Differences between TDSQL (MariaDB) and TencentDB for MySQL:
Key Differences:
Read-Write Splitting: TencentDB for MySQL implements read-write splitting through a database proxy service, enabling a read-write separation architecture. TDSQL (MariaDB) natively supports read-write splitting, with all standby instances defaulting to read-only mode.
SQL Rate Limiting: TencentDB for MySQL supports limiting the concurrent execution of specific SQL statements by setting SQL keywords, preventing performance degradation caused by high-concurrency SQL. TDSQL (MariaDB) does not support SQL rate limiting.
Architecture: TencentDB for MySQL supports four architectures: single-node (cloud disk), dual-node (one primary, one standby), three-node (one primary, two standbys), and cloud disk version (one primary, multiple standby cloud disks). TDSQL (MariaDB) supports one primary with one or two standby nodes.
Hotspot Updates: MySQL kernel versions 5.7/8.0 significantly optimize update operations on hotspot rows for scenarios involving frequent updates or flash sales. When hotspot update auto-detection is enabled, the system automatically detects single-row hotspot updates and queues concurrent update operations to reduce performance degradation caused by extensive row locking. MariaDB 10.0/10.1 kernels do not support hotspot updates.
Flashback Query: MySQL kernel versions 5.7/8.0 implement flashback query functionality on the InnoDB engine to address operational errors during database maintenance. This feature allows quick querying of historical data at a specified point in time using simple SQL statements, eliminating the need for complex rollback or cloning operations. It significantly reduces data query and recovery time, especially suitable for minor data changes and urgent fault recovery scenarios, thereby helping to restore data quickly and ensure business continuity. MariaDB 10.0/10.1 kernels do not support flashback queries.
Differences between TDSQL (MariaDB) Kernel and TXSQL Kernel: Compatibility of TencentDB for MariaDB with MySQL 5.6
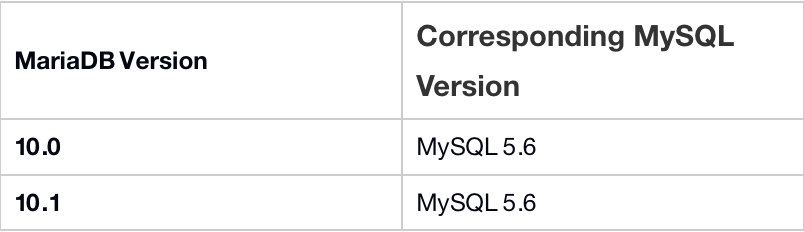
See compatible notes here: Compatibility Notes
MariaDB 10.0 Kernel Exclusive Features:
Multi-Engine Support:
XtraDB: Optimizes thread scheduling (reducing contention), buffer pool management (multi-threaded flushing), and monitoring (SHOW ENGINE XTRADB STATUS).
TokuDB: Supports fractal tree indexes, suitable for high compression and write-intensive scenarios (requires manual installation).
Aria: A crash-safe replacement for MyISAM engine supporting transactional operations (CREATE TABLE ... ENGINE=Aria).
Virtual Columns: MariaDB 10.0 supports virtual columns, which enable the creation of functional indexes based on virtual columns, effectively improving database analytical and statistical computation performance.
MariaDB 10.1 Kernel Exclusive Features:
Thread Pool: Built-in thread pool (thread_pool) optimizes high-concurrency connection management by reducing context switches.
![]()