Accessing Self-Built Databases on User Local IDC, Local IDC, and Virtual Machines of Other Cloud Vendors
Last updated: 2025-07-23 17:39:12
Accessing Self-Built Databases on User Local IDC, Local IDC, and Virtual Machines of Other Cloud Vendors
Last updated: 2025-07-23 17:39:12
This document introduces how to access other self-built databases (self-built databases on user local IDC, local IDC, and virtual machines of other cloud vendors) to TencentDB for DBbrain. By accessing self-built databases, you can enable autonomous services such as Monitoring and Alarm, Performance Optimization, and Database Management provided by DBbrain.
Connection Method
Agent-Based Access (recommended): Deploy the DBbrain Agent on the database host to automatically detect your database. This supports all autonomous services provided by DBbrain. Strengths include:
Data transmission is encrypted.
The Agent automatically collects and temporarily stores data, ensuring no data loss even if the connection to the server is lost.
Communication between the server side and the Agent requires authentication, and SQL statements sent to the Agent include verification.
It is capable of collecting host resource information and slow logs, supporting slow log analysis.
Direct Access: No need to deploy the DBbrain Agent. Simply enter the database account and password under the condition of network connectivity to quickly access your database. This method supports some of the autonomous services provided by DBbrain and is suitable for accessing fewer self-built databases.
Note:
For a feature comparison of the two access methods, see the Feature Comparison.
DBbrain currently supports the following types of other self-built databases (self-built databases on user local IDC, local IDC, and virtual machines of other cloud vendors): MySQL.
Prerequisites
Ensure the firewall on the self-managed database server (located in on-premises IDC, local data center, or third-party cloud VMs) has opened TCP port 8899 for Agent communication.
Agent-Based Access Process
Entering the Access Page
1. Log in to the DBbrain console.
2. In the left sidebar, select Instance Overview.
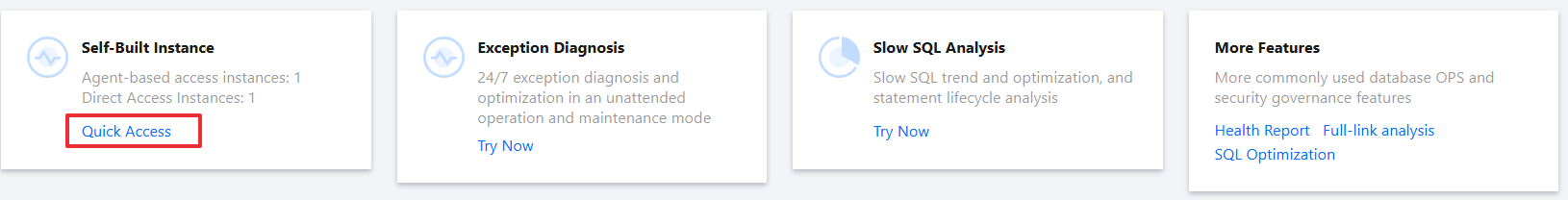
3. At the top of the page, in the Self-Built Instance card, click Quick Access to enter the Self-Built Database Instance Access page.
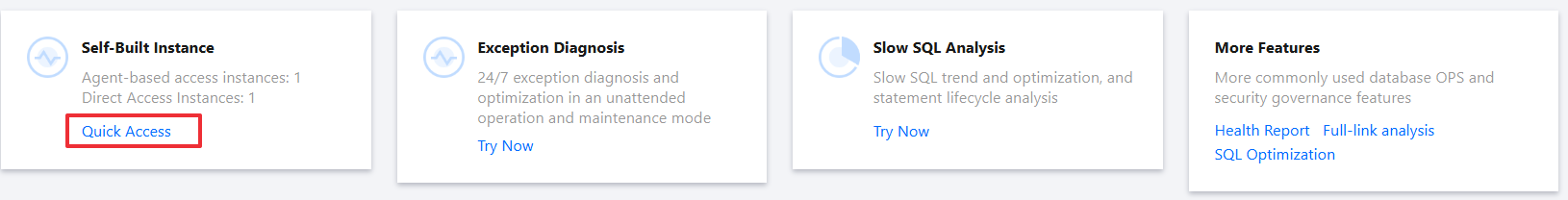
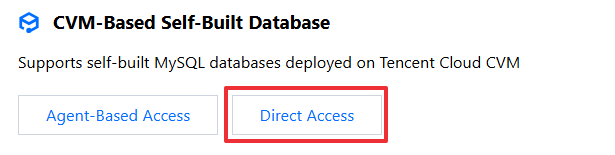
4. In the CVM-Based Self-Built Database module, click Agent-Based Access to start the access process.
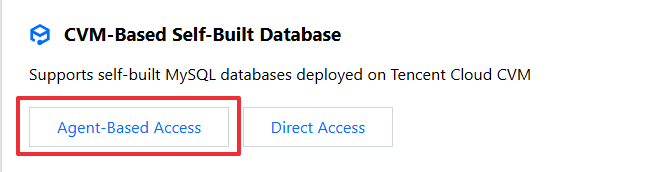
Accessing Other Self-Built Databases
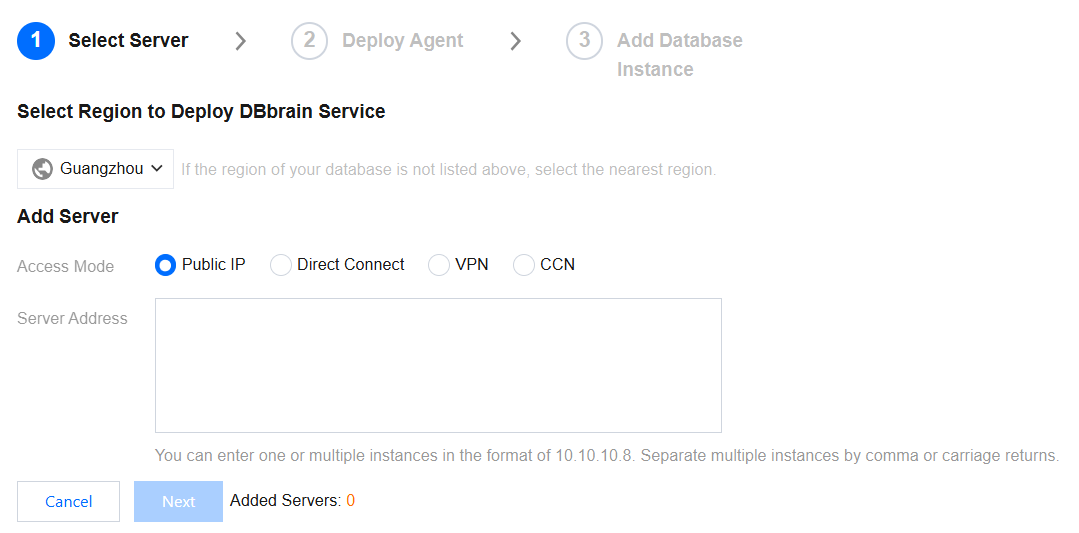
Step 1: Selecting Host
On the Select Server Instance page, add the host with a self-built database, and then click Next to proceed to the Agent deployment.
Select Region to Deploy DBbrain Service: Currently supports Guangzhou, Beijing, Shanghai, and Chengdu. If the region where the user's database is located is not within these regions, it is recommended to select the nearest one.
Add Server: Supports adding hosts through public IP addresses, DC, VPN access, and Cloud Connect Network.
Step 2: Deploying Agent
On the Agent Deployment page, the previously selected hosts and their Agent statuses are displayed.
1. On the Agent Deployment page, select a host, click Deploy in the Operation column, or select multiple hosts, click Batch Deploy at the top left of the list to deploy the Agent on the host.
Note:
If the Agent is not deployed on the host, the Agent status will be displayed as --.
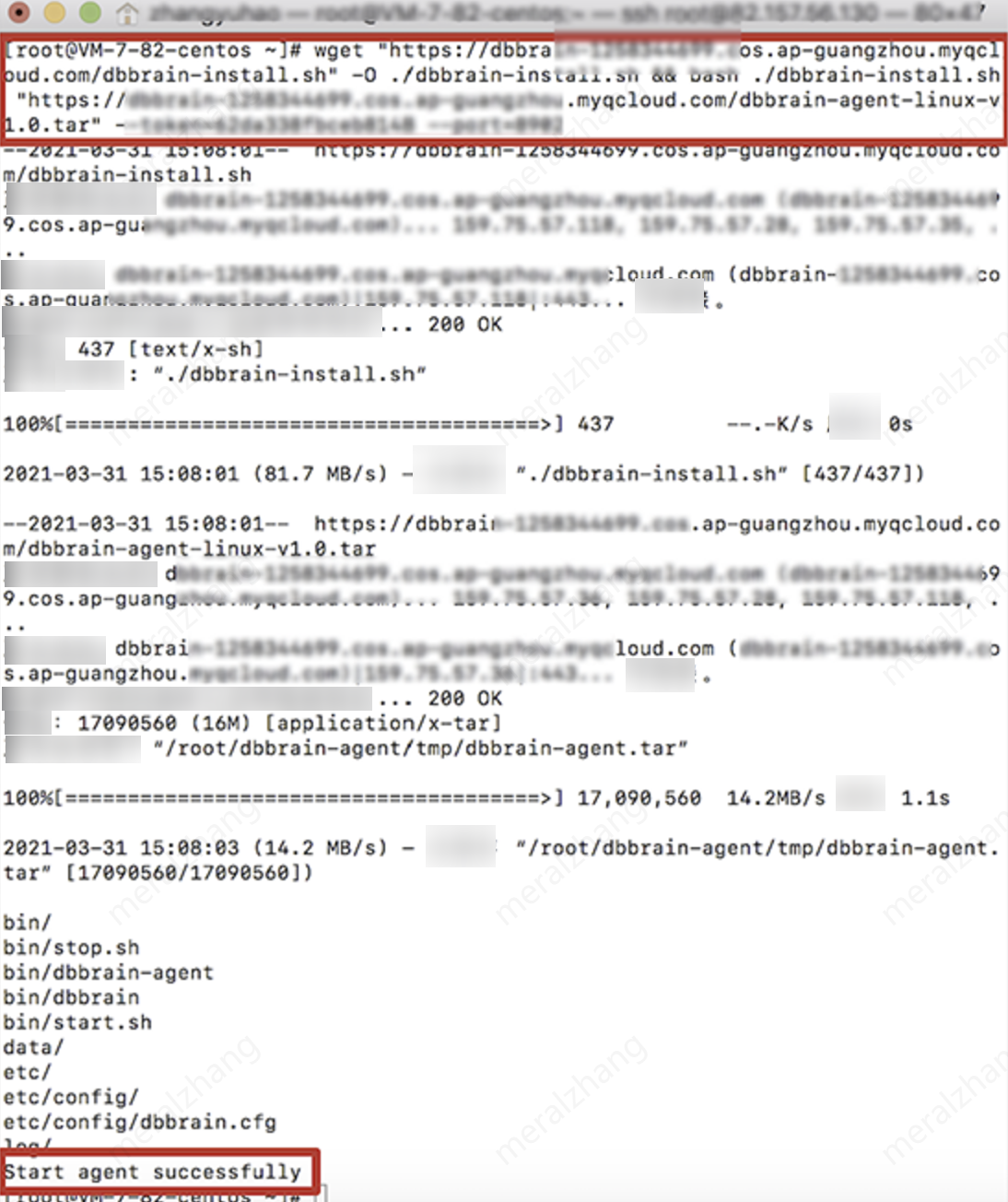
2. In the pop-up dialog box, select the Agent port, click Deploy, and the Agent deployment command will be generated according to the selected port number.
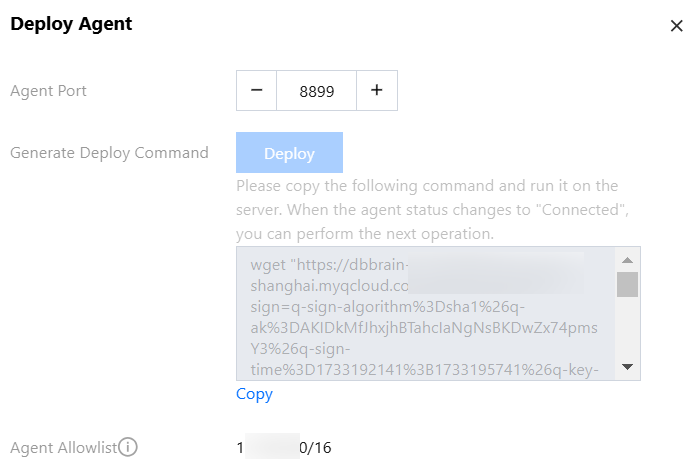
3. Copy the generated Agent deployment command and run it on the host. If
Start agent successfully appears, it means the Agent has been successfully deployed. Return to the Deployment page to see the Agent status change to Connect normal.4. The Agent status and corresponding operation instructions:
Agent Status | Status Description | Operation | Operating Instructions: |
-- | The Agent is not deployed on the host. | Deploy | Click Deploy to deploy the Agent on the host. |
In Deployment | Agent deployment is in progress. | View | Click View to see the port number and Agent command of the deploying Agent. |
| | Reset | Click Reset to recover the Agent status to --, supporting scenarios where users want to change the Agent port number and redeploy the Agent. |
Connect normal | The Agent has been successfully deployed on the host and is under normal monitoring and collection. The self-built database in this host can use the autonomous services provided by DBbrain normally. | View | Click View to see the port number and Agent command of the deployed Agent. |
| | Stop | Click Stop to pause the connection of the Agent in normal connection status. |
| | Reset | Click Reset to recover the Agent status to --, supporting scenarios where users want to change the Agent port number and redeploy the Agent. |
Failed to connect. | View | Click View to see the port number and Agent command of the Agent. | |
| | Reset | Click Reset to recover the Agent status to --, allowing you to change the Agent port number and redeploy the Agent. |
Paused connection | The Agent has been successfully deployed on the host but is currently in a paused status for monitoring data collection. | View | Click View to see the port number and Agent command of the Agent. |
| | Reconnecting | Click Reconnect to start the paused Agent and recover it to the connect normal status. |
| | Reset | Click Reset to recover the Agent status to --, supporting scenarios where users want to change the Agent port number and redeploy the Agent. |
5. After at least one Agent is in Connect normal status, click Next to proceed to the next step and add a database.
Step 3: Adding Database
On the Add Database Instance page, it shows the host with the Agent successfully deployed and its database status from the previous step.
1. On the Add Database Instance page, select Database Type.
2. Select a host, click Add in the Operation column, or select multiple hosts, click Batch Add Database at the top left of the list to add databases to the hosts with the Agent successfully deployed.
Note:
For hosts with the Agent successfully deployed, if no database is added, the database status is displayed as --.
3. In the pop-up dialog box, fill in the database port number, account, password, and database configuration, and click OK to complete the database addition.
Note:
If there is a database account authorization exception, see Database Account Authorization Exception.
The database account configuration is as follows:
Parameter Name | Parameter Description |
Port | The database port number detected by the DBbrain Agent (If there are multiple databases in the host, you can click Add Port to manually add the database port number to access multiple self-built databases on the same host simultaneously.). |
Account | The account of the self-built database (If the account has not been created, you need to click Generate Authorization Command first, then copy and execute the generated authorization command on the database.). |
Password | The corresponding password for the self-built database. |
Database Configuration | Includes CPU, memory, and disk resources allocated by the host to the self-built database. DBbrain calculates performance metrics based on the provided configuration details. |
The database account authorization is as follows:
Permission | Description |
PROCESS | View all connection processes. It is used for displaying real-time session processes. |
REPLICATION SLAVE, REPLICATION CLIENT | View the status of the primary/secondary databases, and view relaylog and binlog events of the secondary database. It is used for diagnosing primary-secondary replication exceptions. |
SHOW DATABASES, SHOW VIEW, RELOAD, SELECT | Default read permissions for databases and tables, as well as refresh permissions. |
4. Return to the Add Database Instance page, and click Done. Databases with a Connect normal status can successfully access DBbrain's autonomous services.
5. In the left sidebar, select Instance Management, and at the top, select the corresponding self-built database type to view and manage the accessed self-built database.
Direct Access Process
Entering the Access Page
1. Log in to the DBbrain console.
2. In the left sidebar, select Instance Overview.
3. At the top of the page, in the Self-Built Instance card, click Quick Access to enter the Self-Built Database Instance Access page.
4. In the CVM-Based Self-Built Database module, click Direct Access to start the access process.
Accessing Other Self-Built Databases
Step 1: Selecting Host
On the Select Server Instance page, add the host with a self-built database, and then click Next to proceed to the Agent deployment.
Select Region to Deploy DBbrain Service: Currently supports Guangzhou, Beijing, Shanghai, and Chengdu. If the region where the user's database is located is not within these regions, it is recommended to select the nearest one.
Add Server: Supports adding hosts through public IP addresses, DC, VPN access, and Cloud Connect Network.
Step 2: Adding Database
On the Add Database Instance page, it shows the selected host and its database status from the previous step.
1. On the Add Database Instance page, select Database Type.
2. Select a host, click Add in the Operation column, or select multiple hosts, click Batch Add Database at the top left of the list to add databases to the hosts with the Agent successfully deployed.
Note:
For hosts with the Agent successfully deployed, if no database is added, the database status is displayed as --.
3. In the pop-up dialog box, fill in the database port number, account, password, and database configuration, and click OK to complete the database addition.
Note:
If there is a database account authorization exception, see Database Account Authorization Exception.
The database account configuration instructions:
Parameter Name | Parameter Description |
Port | The database port number detected by the DBbrain Agent (If there are multiple databases in the host, you can click Add Port to manually add the database port number to access multiple self-built databases on the same host simultaneously.). |
Account | The account of the self-built database (If the account has not been created, you need to click Generate Authorization Command first, then copy and execute the generated authorization command on the database.). |
Password | The corresponding password for the self-built database. |
Database Configuration | Includes CPU, memory, and disk resources allocated by the host to the self-built database. DBbrain calculates performance metrics based on the provided configuration details. |
The database account authorization is as follows:
Permission | Description |
PROCESS | View all connection processes. It is used for displaying real-time session processes. |
REPLICATION SLAVE, REPLICATION CLIENT | View the status of the primary/secondary databases, and view relaylog and binlog events of the secondary database. It is used for diagnosing primary-secondary replication exceptions. |
SHOW DATABASES, SHOW VIEW, RELOAD, SELECT | Default read permissions for databases and tables, as well as refresh permissions. |
4. Return to the Add Database Instance page, and click Done. Databases with a Connect normal status can successfully access DBbrain's autonomous services.
5. In the left sidebar, select Instance Management, and at the top, select the corresponding self-built database type to view and manage the accessed self-built database.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

