Exception Diagnosis
Last updated:2026-02-11 21:09:40
The exception diagnosis feature provides users with real-time performance monitoring, health inspections, fault diagnostics, and optimization for database instances. Users can intuitively perceive the real-time operational status of database instances, locate real-time performance exceptions, and perform system optimization based on optimization suggestions. Exception diagnosis supports viewing real-time and historical diagnostic information for instances or shards.
Overview
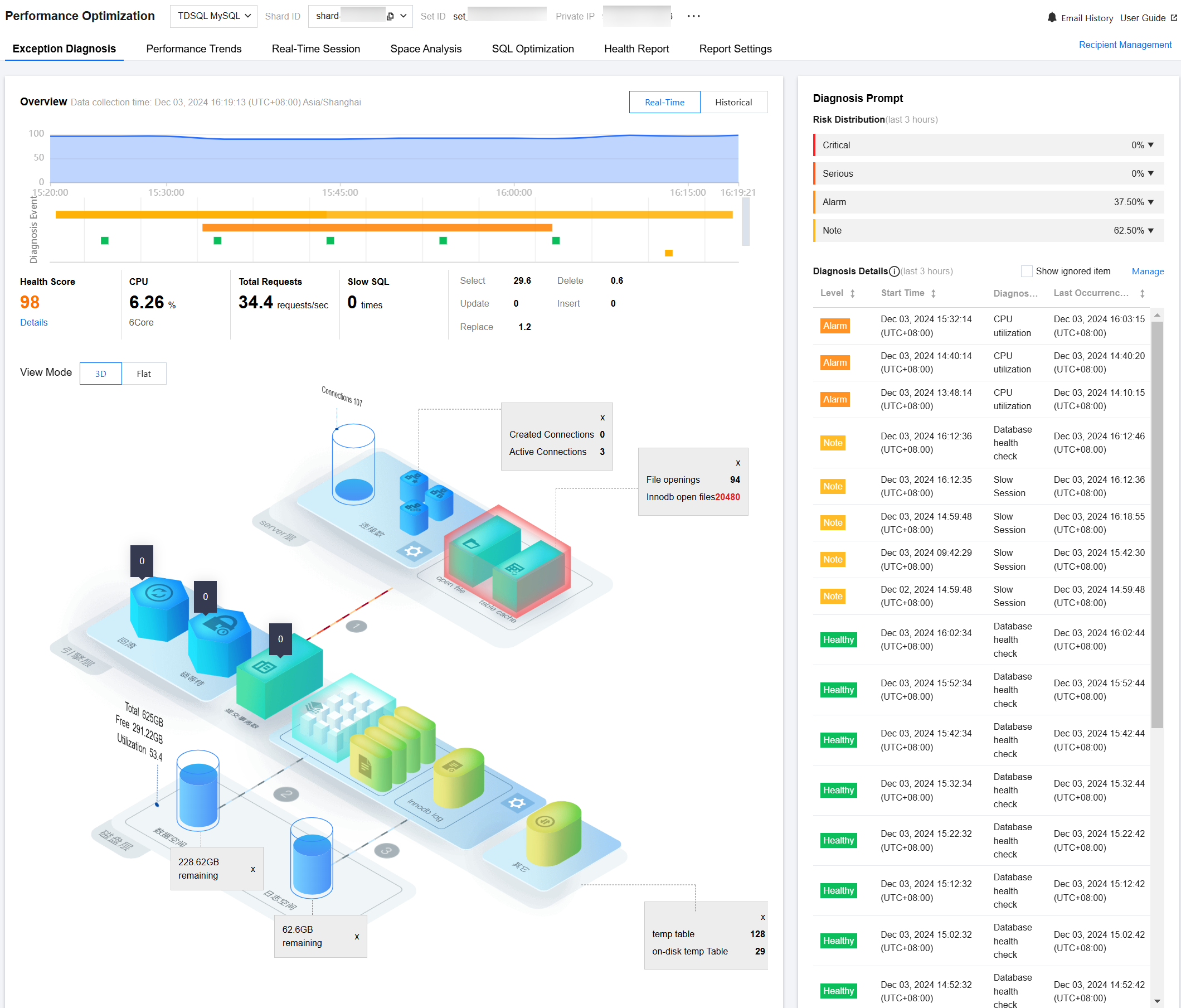
View Diagnostic Information
1. Log in to the DBbrain Console.
2. In the left sidebar, select Performance Optimization.
3. At the top, select the corresponding instance ID or shard ID, and select the Exception Diagnosis tab.
4. On the right side of the page, select to view real-time or historical diagnosis information.
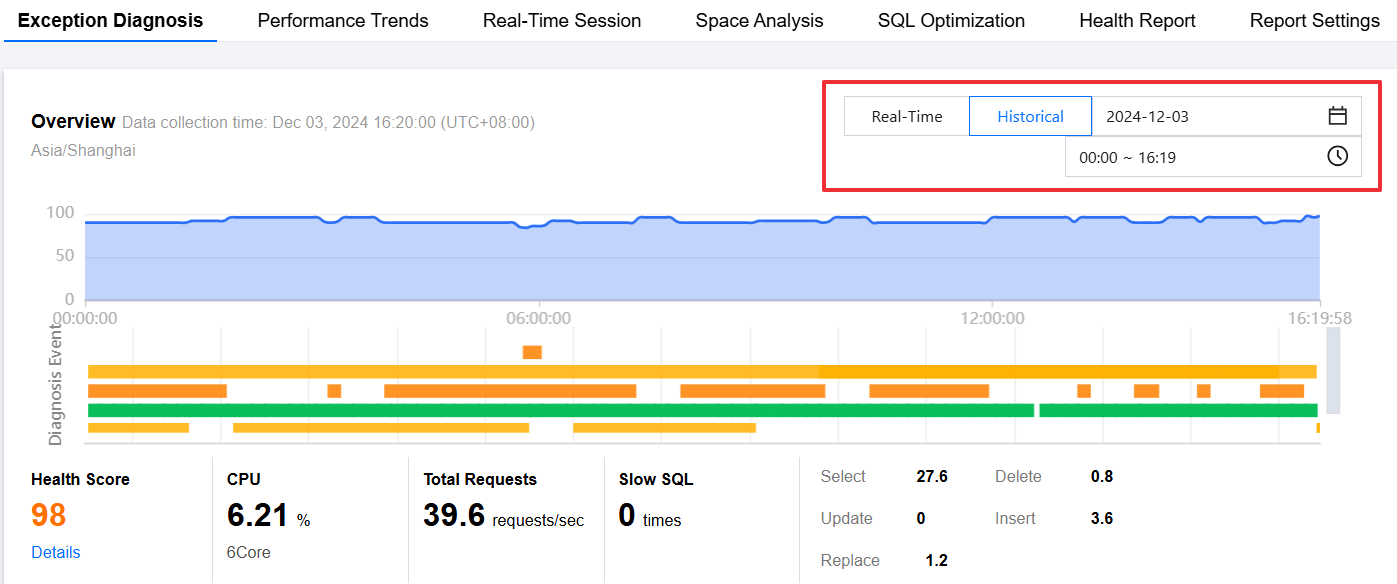
5. View the health score trend chart within the selected timeline, the diagnosed exception events, and the 3D topology or flat view.
View health score trend chart
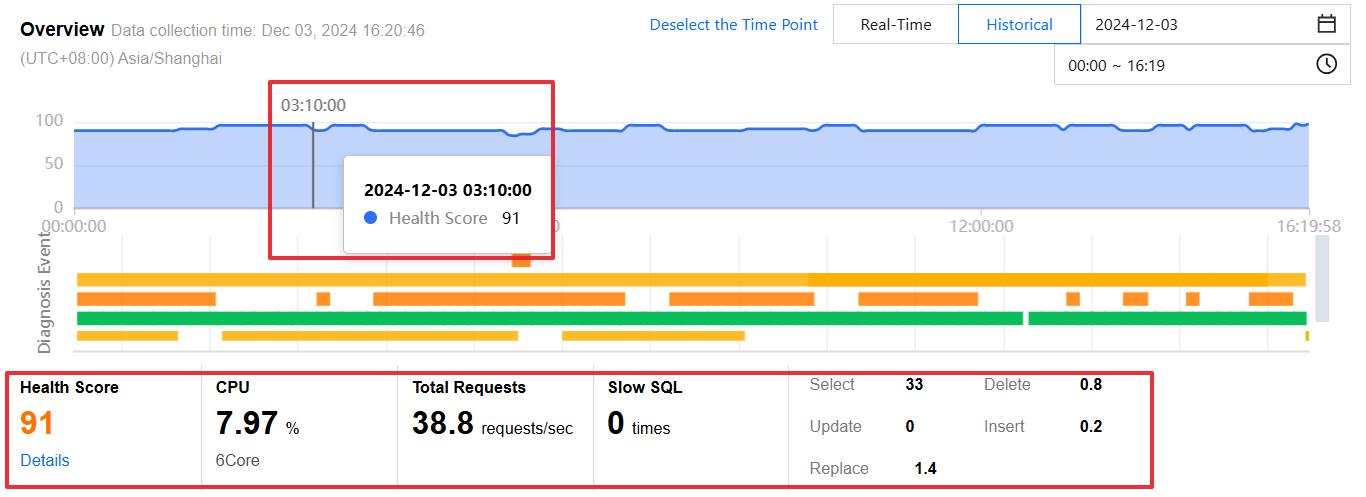
Click any point on the trend chart to display the health score at that time, and the following information will be displayed below:
The health score, CPU, memory, total number of requests, the number of slow query, and the number of execution times per second of SQL statement type will be displayed for that time point.
Click Details under the health score to enter the Health Report page and view the health score, score details, and health report.
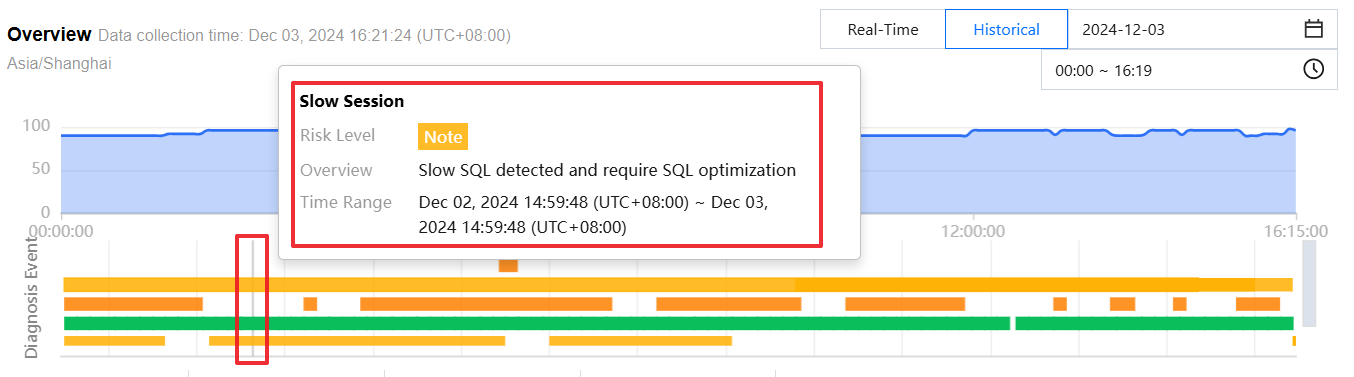
View diagnosis event bar chart
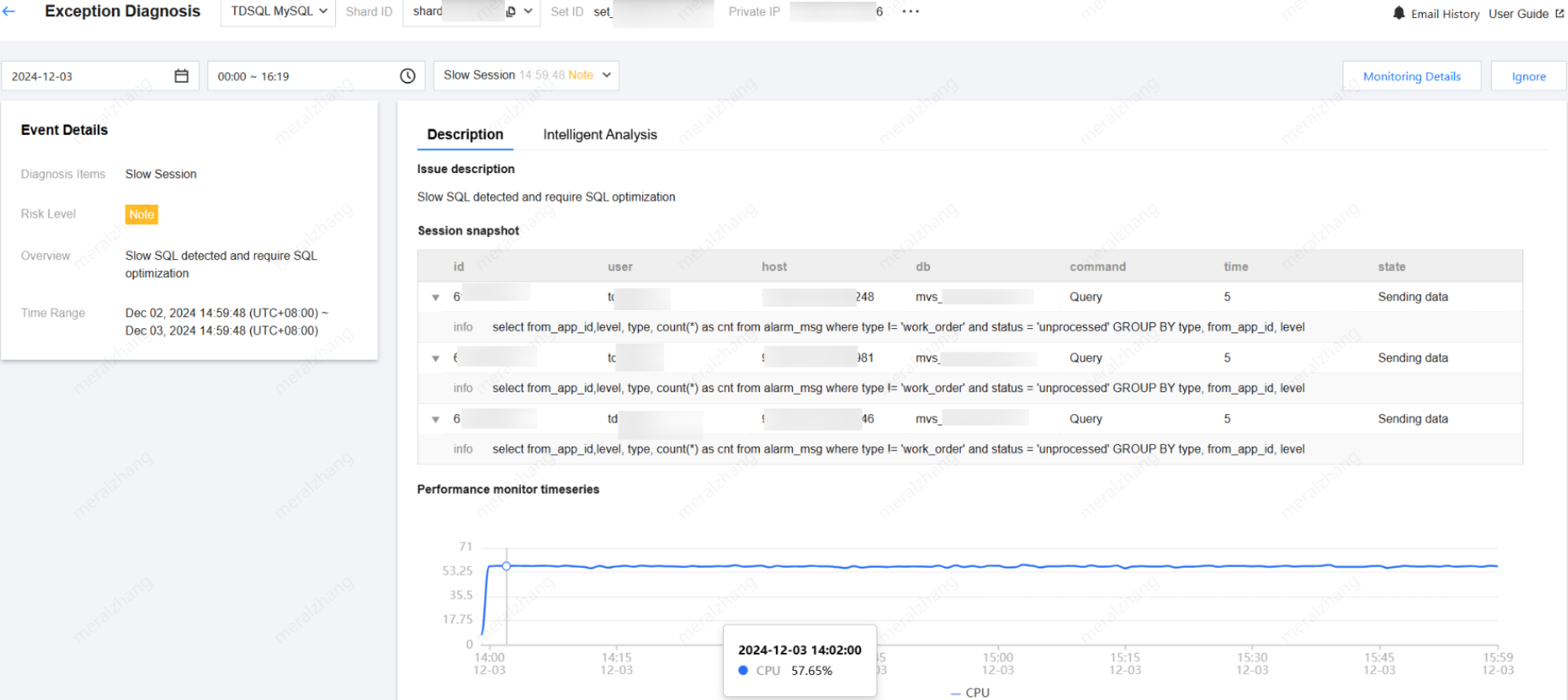
Hover over the diagnostic event bar chart to display information such as risk level, overview, and start/end time. Click the bar chart to enter the event details page and view information including event details, on-site descriptions, intelligent analysis, and optimization suggestions. For details on viewing event details, see Exception Alarms.
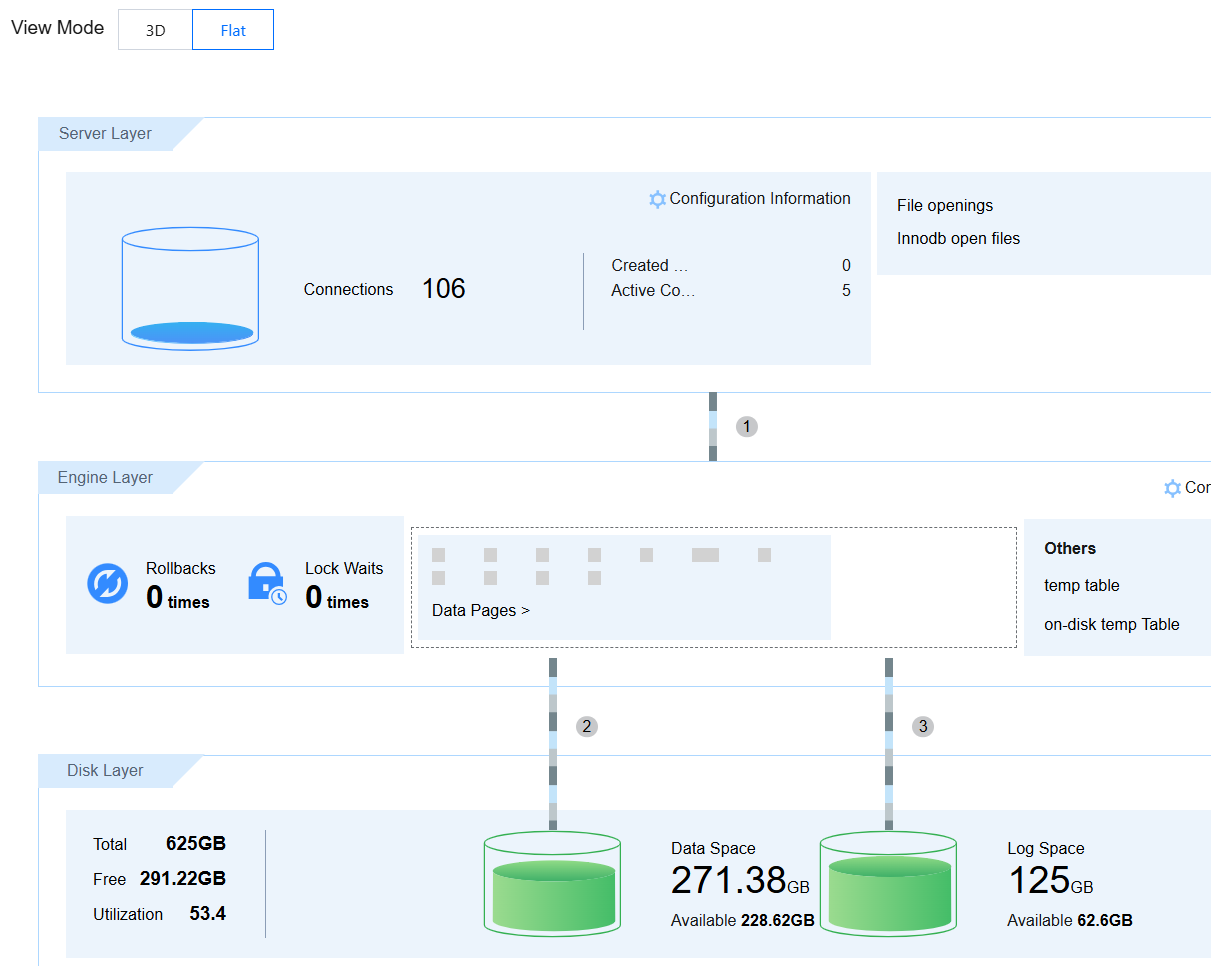
Viewing the view
Select 3D or Flat to view the view. The view will display relevant information such as the disk layer (including data space, log space, and parameter values), engine layer (the number of rollback times, the number of lock wait times, and parameter values), and server layer (connection counts and parameter values). You can click to view configuration information and hover over the connection number to display related data.
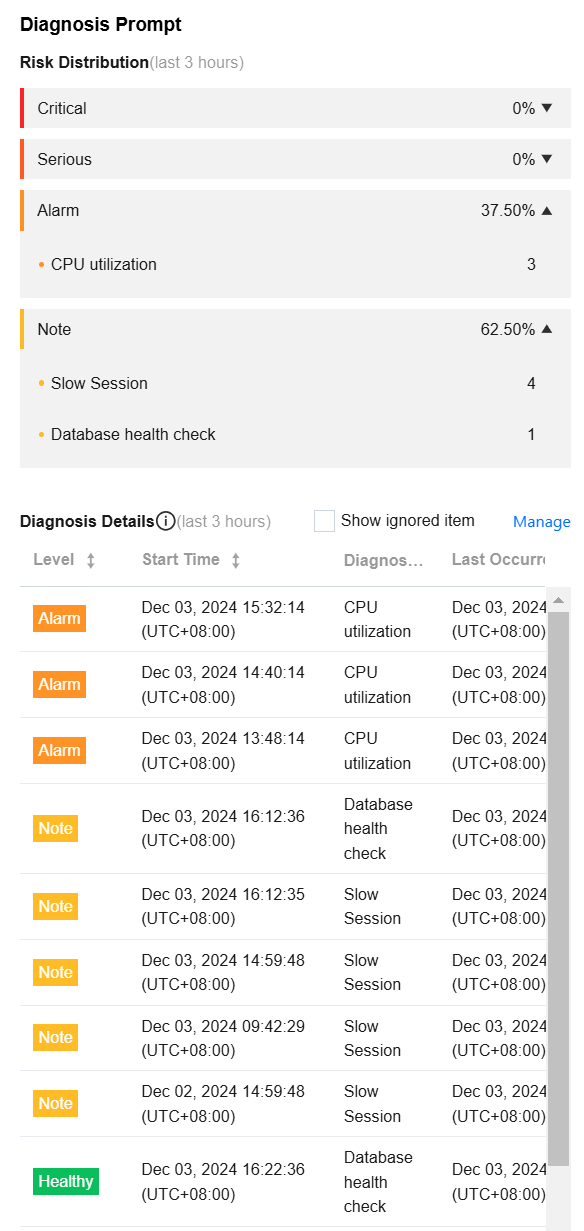
Viewing the Diagnostic Prompts
1. Log in to the DBbrain Console.
2. In the left sidebar, select Performance Optimization.
3. At the top, select the corresponding instance ID or shard ID, and select the Exception Diagnosis tab.
4. On the right side of the page, select to view real-time or historical diagnosis information.
Real-time: Select Real-time to display the risk distribution and diagnosis details for the last three hours.
History: Select History to display the risk distribution and diagnosis details for the selected time period.
5. View the diagnostic prompts for the selected time range.
Viewing Diagnostic Event Details
In the Diagnosis Prompt, click the row of a specific event alarm or hover over the event alarm and click View to enter the event details page and view the event details.
Event details mainly include event details, on-site descriptions, intelligent analysis, and optimization suggestions. The event details displayed vary depending on the diagnosis type, refer to the actual display.
Event details: Include the diagnosis item, start/end time, risk level, and overview.
On-site descriptions: Include snapshots and performance trends of external phenomena of exception events (or health inspection events).
Intelligent analysis: Analyzes the root cause of the performance exception and locates the specific operation.
Optimization suggestions: Provide optimization guidance, including but not limited to SQL optimization (index recommendations and rewrite suggestions), resource configuration optimization, and parameter tuning.
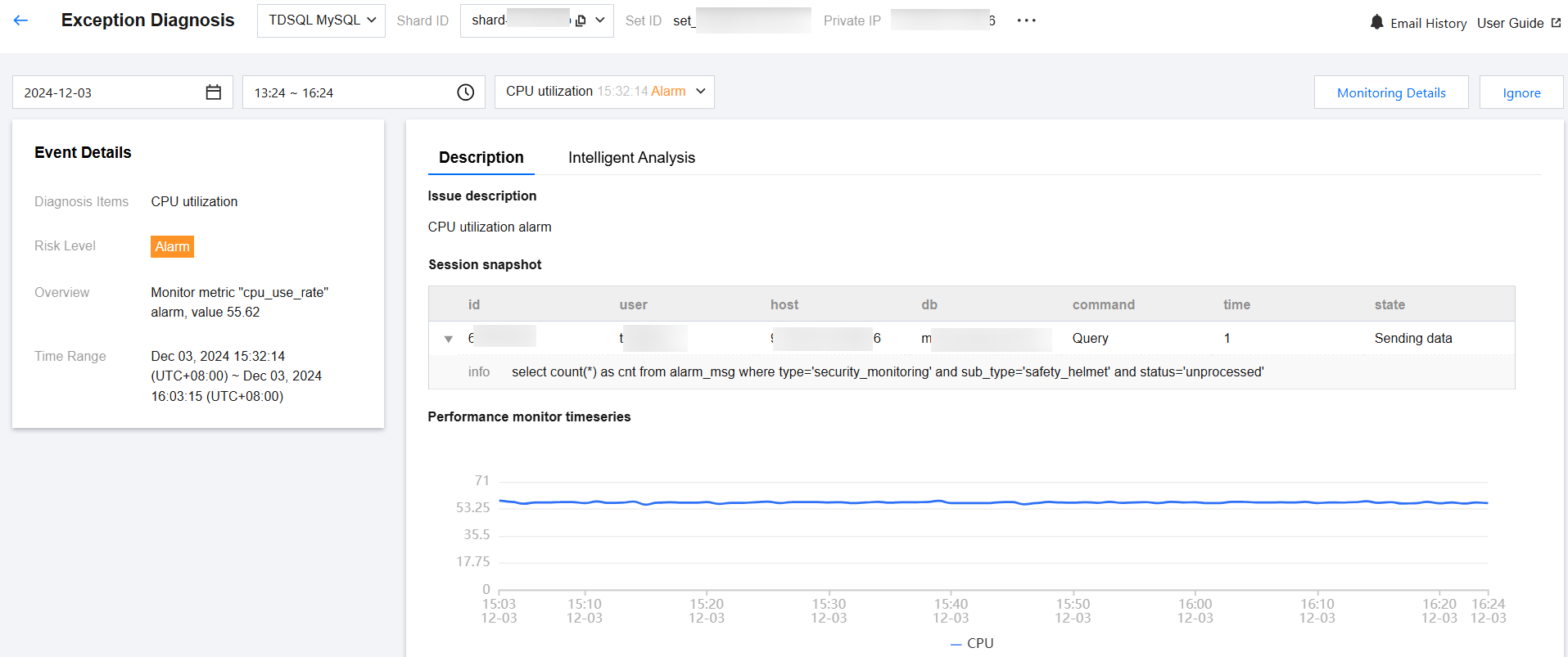
Ignore/Unignore alarms
In the Diagnosis Details, hover over the event alarm and click Ignore and select Ignore This or Ignore This Type, then click OK. Ignoring alarms is also supported on the event details page.
Note:
This feature is only applicable to exception alarms for diagnostic items that are not Health Inspections.
Ignore This: Only ignore this alarm.
Ignore This Type: Ignore exception alarms generated from the same root cause.
Ignored diagnostic events will be grayed out. To unignore, click Unignore.
Diagnostic Item Description
Diagnostic items are part of intelligent diagnosis and fall into four categories: performance, availability, reliability, and maintainability. Each diagnostic item belongs to only one category.
Diagnostic Item Name | Diagnosis Item Category | Description | Risk Level Classification |
Connectivity check | Availability | Unable to establish a connection to the database. | Critical |
Slow insertion, update, or deletion | Performance | The insert, update, or delete operations take a long time to complete. | Serious: caused by a lock wait. Warning: not caused by a lock wait. |
Slow SQL | Performance | Optimization is required for slow query statements. | Note |
Row lock wait | Performance | There are transactions with excessive lock wait time. | Severe |
Pending transactions | Performance | Some transactions remain uncommitted for a long time. | Critical |
Long transactions | Performance | Long transaction duration | Critical: transaction duration > 60 Serious: 60 ≥ transaction duration > 30 Alarm: transaction duration ≤ 30 |
Transactions with too large SQL execution interval | Performance | The transaction contains SQL with an excessively large execution interval. | Critical: SQL execution interval in a transaction > 10 Serious: 10 ≥ SQL execution interval in a transaction > 5 Alarm: SQL execution interval in a transaction ≤ 5 |
Too many SQL statements in a transaction | Performance | Too many SQL statements in a transaction | Alarm: the number of SQL statements in a transaction > 1000 Note: 1000 > the number of SQL statements in a transaction ≥ 3 |
Rows affected by large transactions | Performance | The transaction inserts, deletes, or modifies a large number of rows. | Alarm: rows affected by large transactions > 1000 Note: 1000 > rows affected by large transactions ≥ 100 |
Transactions with too long SQL response time | Performance | The transaction contains SQL with too long response time. | Critical: transaction response time > 30 Serious: 30 ≥ transaction response time > 15 Alarm: 15 ≥ transaction response time > 5 Note: transaction response time ≤ 5 |
Transactions with SQL errors | Performance | The transaction contains SQL errors. | Critical |
Unexpected transaction commit | Performance | The transaction is unexpectedly implicitly committed. | Critical |
Auto-commit transactions without restoration | Performance | Auto-commit transaction mode without restoration. | Critical |
DDL statement waiting for Metadata Lock | Performance | There are threads waiting for Metadata Lock and are under the process of DDL statement execution. | Severe |
Insert, update, and delete statements waiting for Metadata Lock | Performance | There are threads waiting for Metadata Lock and are under the process of IUD statement execution. | Severe |
Select statement waiting for Metadata Lock | Performance | There are threads waiting for Metadata Lock and are under the process of SELECT statement execution. | Severe |
Deadlock | Reliability | Database deadlock | Critical |
Read-only lock | Performance | There are threads waiting for global read-only locks. | Critical |
SQL statement waiting for Metadata Lock | Performance | There are threads waiting for Metadata Lock and are under the process of non-DDL, IUD, and SELECT statements execution. | Alarm |
Waiting for flush tables | Performance | There are threads waiting for the flush table status. | Critical: the number of active session > 30 Serious: 30 > the number of active session > 20 Alarm: the number of active session < 20 |
Active sessions | Performance | The number of active sessions is three times greater than the CPU specification of a database instance. | Note |
High concurrency/stress requests | Performance | High concurrency or stress requests are generated. | Critical: CPU utilization > 80 Serious: 80 > CPU utilization > 60 Alarm: 60 > CPU utilization > 40 |
Excessive precompiled statements | Performance | An excessive number of unclosed precompiled statements (16,382 is the default maximum value allowed by MySQL.). | Critical: the number of precompiled statements > 16,382 Serious: 16,382 > the number of precompiled statements > 14,695 Alarm: 14695 > the number ofprecompiled statements > 11,505 Note: the number of precompiled statements < 11,505 |
Disk space utilization | Reliability | Disk utilization is too high. | Critical: disk utilization > 95 Serious: 95 > disk utilization > 90 Alarm: 90 > the number of precompiled statements > 85 Note: 85 > the number of precompiled statements > 80 |
CPU Utilization | Performance | CPU utilization is too high. | Critical: CPU utilization > 80 Serious: 80 > CPU utilization > 60 Alarm: 60 > CPU utilization > 40 |
Low Table open cache hit rate | Performance | Low Table open cache hit rate | Alarm |
High-risk accounts | Maintainability | Anonymous accounts and accounts without passwords exist. | Note |
Large tables | Maintainability | A single table exceeds 10% of the instance's disk specification. | Critical: space occupied by a single table > 40% of disk capacity Serious: 40% of disk capacity > space occupied by a single table > 30% of disk capacity Alarm: 30% of disk capacity > space occupied by a single table > 20% of disk capacity Note: 20% of disk capacity > space occupied by a single table > 10% of disk capacity |
Replication I/O thread interruption | Reliability | Primary-secondary interruption, replication I/O thread interruption | Critical: interruption not caused by a restart Note: interruption caused by a restart |
Replication SQL thread interruption | Reliability | Primary-secondary interruption, replication SQL thread interruption | Critical: interruption not caused by a restart |
Replication latency caused by DDL | Reliability | Primary-secondary replication latency caused by DDL (including primary-read-only latency and primary-secondary database latency) | Critical: read-only latency > 10 minutes Serious: read-only latency < 10 minutes or secondary database latency > 10 minutes Alarm: secondary database latency < 10 minutes |
Replication delay caused by transactions | Reliability | Primary-secondary replication latency caused by transactions (including primary-read-only latency and primary-secondary database latency) | Critical: read-only latency > 10 minutes Serious: read-only latency < 10 minutes or secondary database latency > 10 minutes Alarm: secondary database latency < 10 minutes |
Replication latency caused by global read-only lock | Reliability | Primary-secondary replication latency caused by the global read-only lock (including primary-read-only latency and primary-secondary database latency) | Critical: read-only latency > 10 minutes Serious: read-only latency < 10 minutes or secondary database latency > 10 minutes Alarm: secondary database latency < 10 minutes |
Auto-increment key exhaustion | Availability | Auto-increment value exceeds 80% of the maximum auto-increment primary key value. | Critical: The auto-increment value exceeds 80% of the maximum value. |
Replication Delay | Availability | Primary-secondary replication latency (including primary-read-only latency and primary-secondary database latency) | Critical: read-only latency > 10 minutes Serious: read-only latency < 10 minutes or secondary database latency > 10 minutes Alarm: secondary database latency < 10 minutes |
Primary/Secondary Switch | Availability | A switch occurs between the primary and secondary instances. | Critical |
Full Table Scan | Availability | An operation that does not use an index in the query but scans the entire table. | Critical: rows scanned during a full table scan > 10 * N (where N is the configured value for the number of rows scanned during a full table scan, default value: 500). Serious: 10 * N > rows scanned during a full table scan > 5 * N (where N is the configured value for the number of rows scanned during a full table scan, default value: 500). Alarm: 5 * N > rows scanned during a full table scan ≥ N (where N is the configured value for the number of rows scanned during a full table scan, default value: 500). |
Execution plan changes | Availability | Used to detect execution plan changes of the same SQL template statement, which may cause sudden performance degradation. | Critical: current SQL query_cost / previous SQL query_cost > 10 Serious: 10 > current SQL query_cost / previous SQL query_cost > 5 Alarm: 5 > current SQL query_cost / previous SQL query_cost > 1 Note: current SQL query_cost / previous SQL query_cost < 1 |
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

