Service Features
Last updated:2025-01-09 15:50:07
TDSQL-C for MySQL provides the serverless service to meet your database requirements in specific business scenarios, helping you reduce costs and increase efficiency. This document describes the major features of the serverless service.
Feature | Description |
Resource scaling range (CCU) | You can adjust the range of elastic CCU scaling. The serverless cluster will automatically increase or decrease the number of CCUs within this range based on the actual business load. |
Elastic policy | The serverless cluster will continuously monitor your CPU, memory, and other workloads and trigger automatic scaling policies according to certain rules. |
Automatic start/stop | The serverless service allows you to customize the automatic pause time of the instance when there is no connection. When a task connection is established, the instance will be automatically started in seconds. |
Resource Scaling Range (CCU)
TDSQL-C Compute Unit (CCU) is the computing and billing unit for the Serverless Edition. A CCU is approximately equal to 1 CPU core and 2 GB memory. The number of CCUs used in each billing cycle is the greater of the number of CPU cores used by the database and 1/2 of the memory size.
You need to set the scaling range for the serverless service. For more information, see Compute Unit.
The minimum capacity configuration of the Serverless service supports setting to 0.25 CCUs. We recommend that when setting the elastic range for the first time, set the minimum capacity configuration to 1 CCUs and select a higher value for the maximum capacity configuration. A smaller capacity configuration allows your cluster to be reduced to the maximum extent when it is completely idle to avoid incurring additional costs. A larger capacity configuration can maximize expansion when your cluster load is too heavy, helping you to stably survive business peak periods.
Note:
If your business requires fast scale-out to a very high capacity, consider increasing the value of the minimum capacity.
To adjust the resource scaling range, log in to the console and make the change based on the actual view mode.
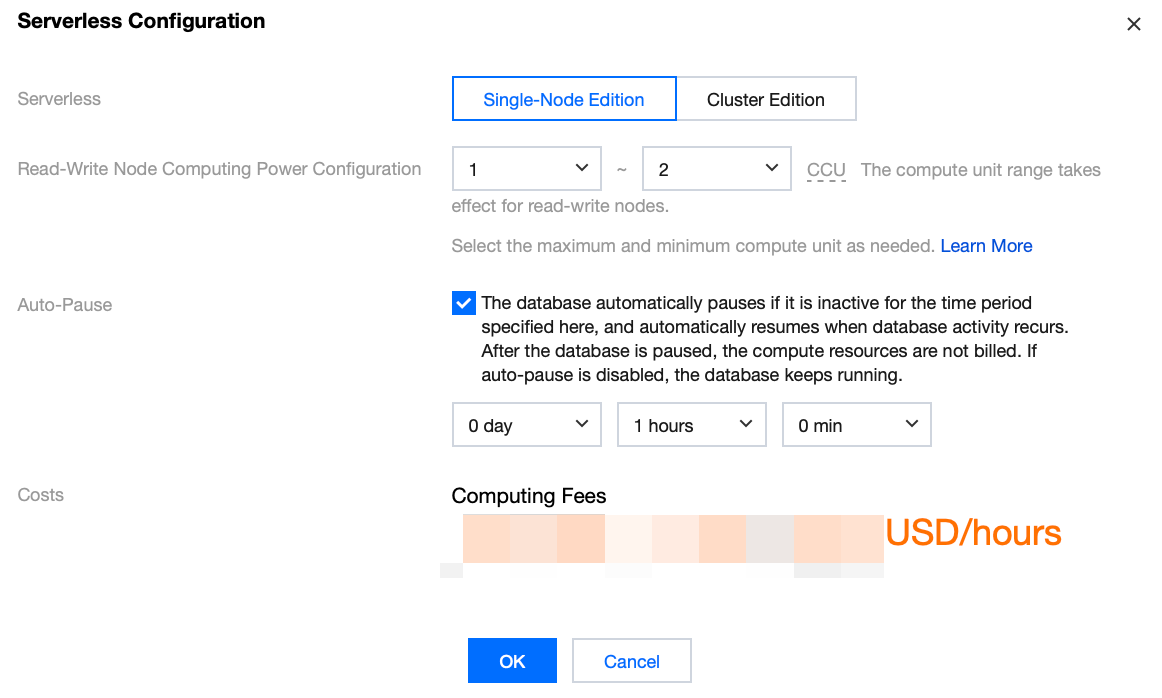
Within the Cluster Management Page, click on Serverless Configuration located at the top right corner, and proceed to modify the computing power settings in the pop-up window. Adjustments will take effect immediately, seamlessly integrating without impacting operations.

In the Operation column under Cluster Management > Instance List, click More > Adjust Configurations. Adjustments will take effect immediately, seamlessly without impacting operations.
Elastic Policy
The elastic policy of the serverless service is implemented by monitoring the computing layer. By monitoring the business load, the system automatically scales computing resources and bills the resources consumed at that moment. When there is no database request, the monitoring service will repossess computing resources and notify the access layer. When you access the cluster again, the access layer will wake up the cluster to make it accessible.
Initially, the elastic policy of the serverless service will limit the CPU and memory resources to the maximum specifications based on the capacity range you selected during purchase, greatly reducing the time impact and usage restrictions caused by CPU and memory scaling. When the cluster triggers the automatic scaling load threshold, the buffer pool will be adjusted within seconds in advance based on the monitoring data. Under this scheme, the CPU can be scaled in an imperceptible manner when you use the database, and no instance OOM events will occur due to the connection surge.
Note:
When Serverless is used, due to its inherent flexible elasticity, cross-server scale-out may occur. To avoid the impact of cross-server scale-out on your business, it is recommended to use database proxy to prevent disconnection issues caused by cross-server momentary disconnection. It is also recommended that your business has a reconnection mechanism to reduce the impact of cross-server scale-out.
Currently, only vertical scaling is allowed for read-only nodes, with no support for horizontal scaling.
Automatic Pause/Start
Note:
The serverless service will be automatically paused when there is no user connection. If your business needs to use
event_scheduler to trigger SQL regularly, we recommend you not enable the auto-pause feature.To enable or disable the auto-pause feature, you may perform the corresponding actions based on the actual view mode.
Within the Cluster Management Page, click on Serverless Configuration located at the upper right corner. In the pop-up window, either check or uncheck the option for automatic suspension.

Click More > Adjust Configurations in the Operation column in Instance List > Read-Write Instance on the target cluster management page.
After this feature is enabled, you need to set the auto-pause time, which is one hour by default. The database will be automatically paused if it has no active connections and CPU usage during this time. After the pause, the computing resources will not be billed, and the storage resources will be billed by the actual usage.
If this feature is disabled, the database will keep running. When there are no active connections and CPU usage, the database will be billed based on the minimum CCU you configure. This is suitable for scenarios where your business has a heartbeat connection.
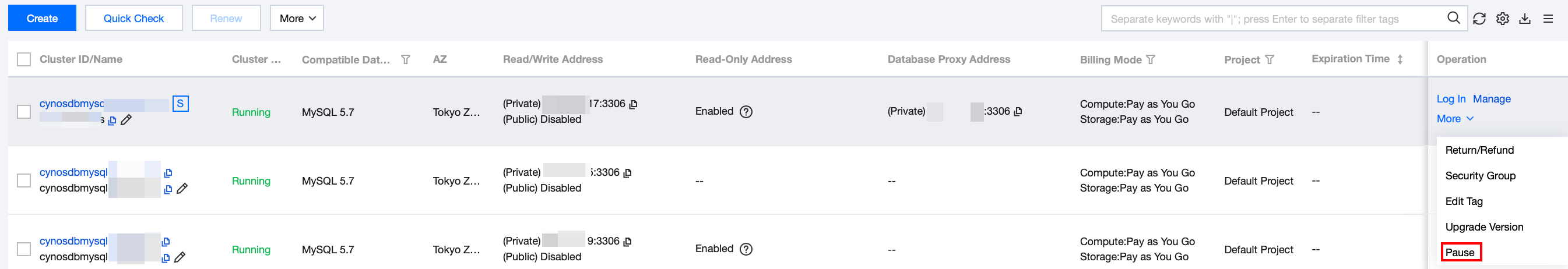
Manual Pause
You can also manually pause specified databases in the console based on the actual view mode.

Manual Restart After Suspension
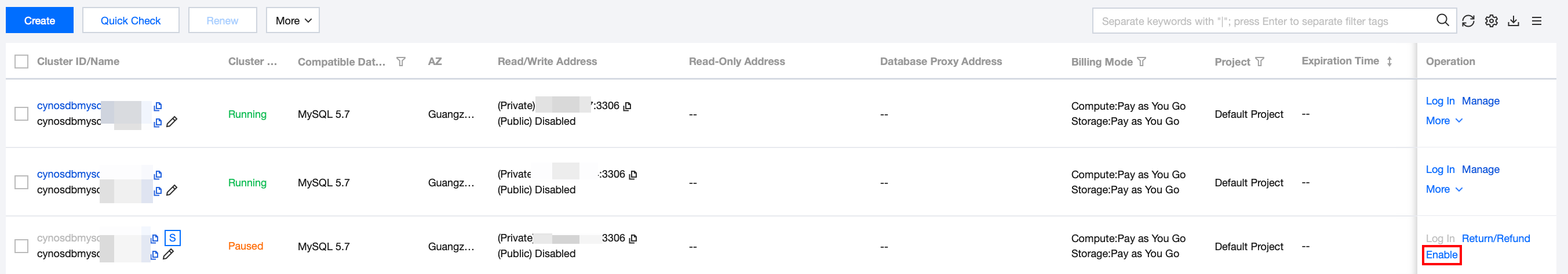
You cannot use the features in the console for a paused serverless database until it is automatically started or its serverless data is manually started based on the actual view mode.

Forwarding requests without interrupting the connection
When a paused database is accessed, the system will automatically start it in seconds, so you don't need to configure a reconnection mechanism.
The access layer of TDSQL-C for MySQL has a resumption perceptron module to implement request forwarding. After the perceptron shakes hands with the client, the TDSQL-C for MySQL cluster will be resumed, without interrupting the user connection. Then, it will shake hands with the cluster and forward layer-4 packets.
The overall process uses two random challenge numbers for authentication, so that the perceptron can verify the username and password without storing them. This ensures the security of the user password and eliminates the inconsistency issue of stored passwords.
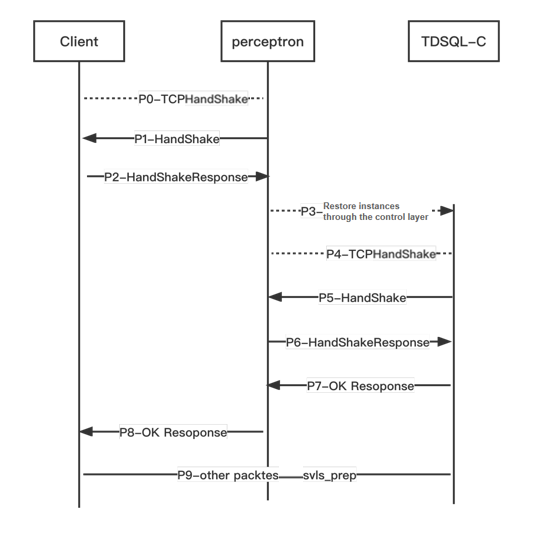
When the instance is paused, if a connection is initiated to it, the MySQL client will first perform a TCP handshake (P0) with the perceptron. After the TCP handshake is completed, the perceptron will send "random number A" to the client for challenge (P1). The MySQL client will use its own account and password and "random number A" to calculate and reply with its own "login response A" (P2). As the perceptron does not store the user's account and password, it cannot verify whether "login response A" is correct, but it can tell whether the client is a MySQL client or not (it is a classifier in the machine learning field, and distinguishing between different types of clients is one of the reasons why it is named perceptron). The verification of "login response A" will be completed by the computing layer of TDSQL-C for MySQL. After the perceptron wakes up TDSQL-C through control (P3), the next step of the login verification process will begin.
After handshaking with perceptron TCP (P4), TDSQL-C will regard the perceptron as a general MySQL client, so it will send "random number B" (P5) to the perceptron for challenge. The perceptron's reply is a special MySQL packet (P6). First, it uses "random number B" and its own authentication mechanism to calculate "login response B" and puts it into the packet; then, it adds "random number A" and "login response A" to the packet. TDSQL-C will perform two checks after receiving the special response packet: it will first check the correctness of "random number B" and "login response B" and the authenticity of the perceptron, and if the check is passed, it will check the correctness of "random number A" and "login response A", and if the check is also passed, it will log in as the user and reply to the perceptron that the login is successful (P7). Then, the perceptron will reply to the user that the login is successful (P8).
When the cluster is paused, only the route of the perceptron will be retained. After the cluster is resumed, the system will retain the routes of both the perceptron and TDSQL-C and set the route weight of the perceptron to 0, so that new connections can be directly made to TDSQL-C, while existing connections to the perceptron can still communicate.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

