Overview
Last updated:2025-07-30 10:03:36
TDSQL-C for MySQL supports the global database (GD), helping enterprises build a GD architecture with high availability, low latency, and strong consistency. This document introduces the features of the GD.
Note:
The GD feature is currently in the beta testing phase. If you want to experience it, submit a ticket for application.
What Is the GD?
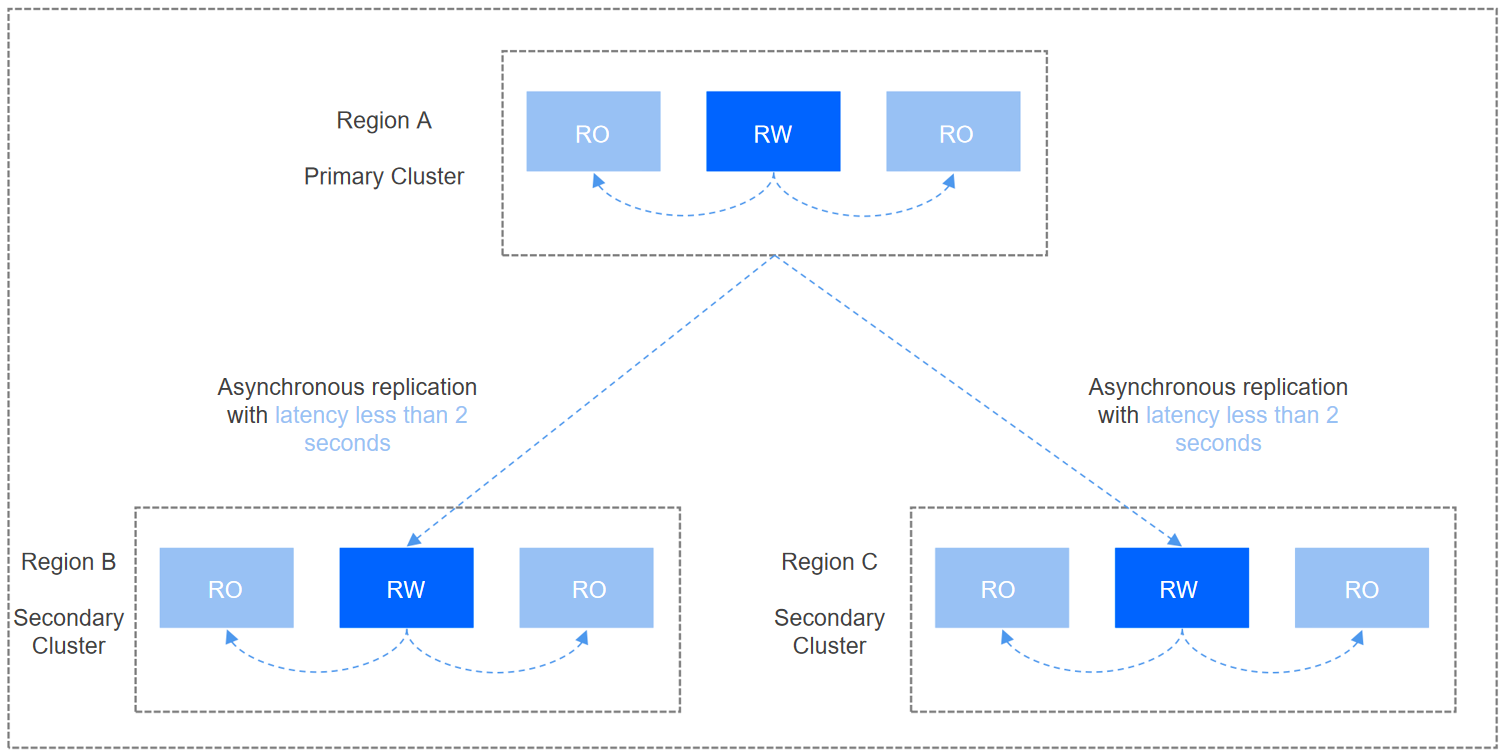
The GD is a network composed of multiple TDSQL-C for MySQL clusters distributed across various regions. In this network, data of all clusters remains synchronized, and each cluster can provide read services, while write requests are forwarded to the primary cluster for processing.
Feature Background
As the digital transformation of enterprises accelerates, an increasing number of users are migrating their core business systems to the cloud. During this process, the volume of user data experiences exponential growth, and business logic becomes increasingly complex. Although TDSQL-C for MySQL, with its cloud-native architecture, can meet the needs of most business scenarios, traditional deployment mode based on a single AZ is gradually revealing limitations in global operational scenarios. When users need to deploy business systems across multiple regions, single-AZ architectures often struggle to meet the real-time query demands across regions.
To address this challenge, traditional solutions usually use third-party data synchronization tools that establish connections between clusters in different regions to achieve data synchronization. However, such solutions face numerous pain points in practical application: first, the speed of data synchronization is limited by network bandwidth and tool performance, making it difficult to meet requirements of low-latency business scenarios; second, the introduction of third-party tools increases extra procurement and maintenance costs; and more importantly, these solutions have technical bottlenecks in terms of data real-time performance and consistency, making it hard to adapt to meet the strict timeliness requirements of core business systems.
To fundamentally resolve the above issues, TDSQL-C for MySQL has introduced the GD feature. This feature is specifically designed for global business scenarios and achieves cross-region data collaboration through a cloud-native architecture, fundamentally overcoming the limitations of traditional solutions and providing a full-stack solution for enterprises to build a high-performance, highly available global database system.
Feature Strengths
No modification of business code required: You can directly expand from intra-city deployment to multi-region deployment.
Cross-region read-write separation and proximity reading: Read requests in the GD are sent directly to the local cluster, while write requests are forwarded to the primary cluster.
Flexible configuration: The primary and secondary clusters have independent configurations, such as cluster specifications and parameter values, which are allowed for independent configurations.
Cross-region low-latency synchronization: With multi-channel physical replication, the global synchronization latency is less than 2 seconds even under high load conditions.
Use Cases
The typical use case supported by the GD feature is multi-site active-active. Below is an introduction to the business architecture and deployment process in the multi-site active-active scenario.
Business Architecture in the Multi-Site Active-Active Scenario
In the traditional network architecture, if a business system uses a single-region database for deployment (with the primary database located in one region), applications in other regions need to access the database across regions. Due to network latency and bandwidth fluctuations, long-distance data interactions can significantly increase query response time and may even result in timeout errors, directly affecting the end user's experience. By using the GD, data under it can be interconnected, allowing all global regions to access the same database. Read requests are sent to the local cluster whenever possible, while write requests are forwarded to the primary cluster for processing. With the features of cross-region low-latency synchronization, cross-region read-write separation, and local proximity reading provided by the GD, it can ensure that the latency for applications in various regions accessing the database is less than 2 seconds.
Typical industries: such as gaming, cross-border e-commerce, finance, and new retail (store).
Introduction of business architecture:
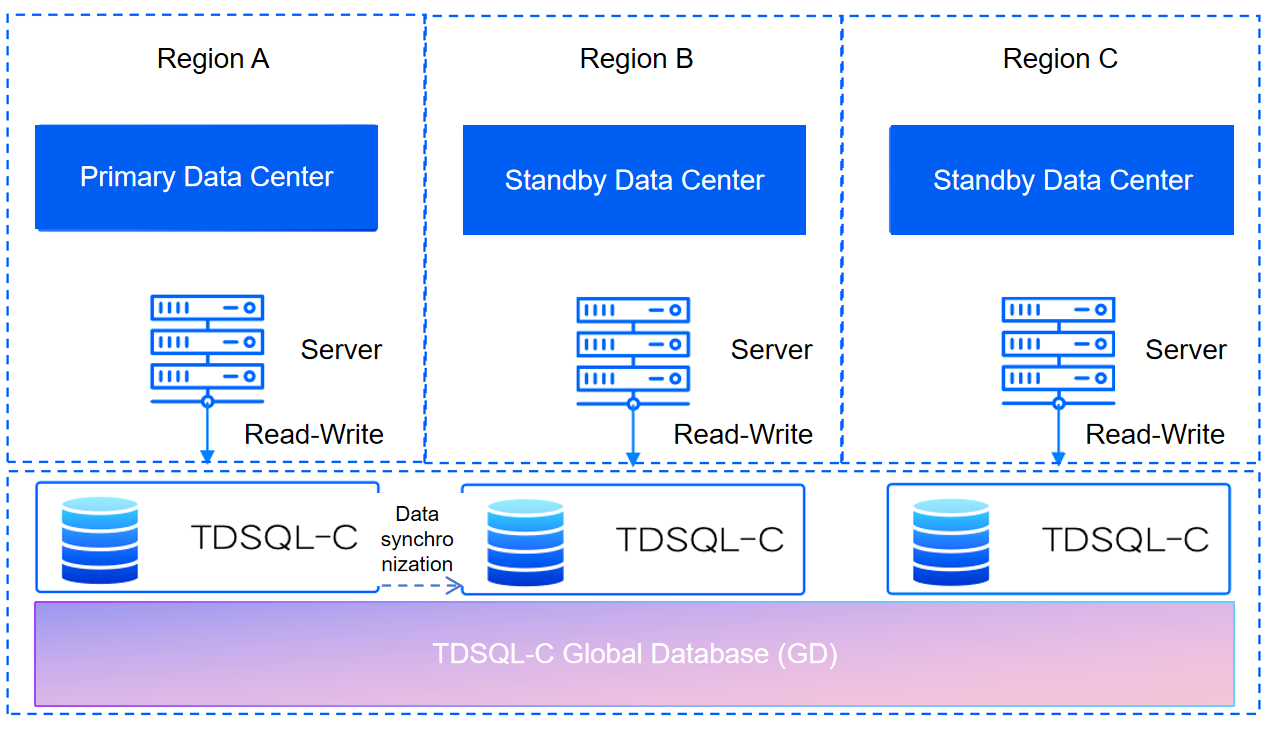
Applications in each region directly perform read and write operations on the databases nearby their respective regions, with write requests being forwarded to the primary cluster for processing.
In the GD, both the primary cluster and secondary clusters provide independent cluster addresses. You can connect to the nearest cluster address based on the region where the application is located for access.
Cluster specifications in region B and region C do not need to be consistent with those in region A and can be chosen flexibly.
Deployment Process in the Multi-Site Active-Active Scenario
1. Create a GD and select the existing cluster as the primary cluster in the GD. For detailed directions, see Creating a GD.
2. Add a new cluster as the secondary cluster in the GD. For detailed directions, see Adding Secondary Clusters.
3. Connect to the GD. For detailed directions, see Connecting to the GD.
Introduction of Supported Modes and Versions
Supported instance mode: provisioned resource. Serverless clusters are not supported currently.
Supported versions: include kernel minor version TDSQL-C for MySQL 8.0 3.1.16.100 and later versions. For the upgrade of the kernel minor version, see Upgrading the Kernel Minor Version.
Billing Instructions for Features
Currently, the cross-region traffic transmission for the GD feature is free of charge. You only need to pay for the fees associated with each cluster. For details on cluster pricing, see Product Pricing.
Introduction of Feature Limitations
Currently, this feature only supports the TDSQL-C for MySQL 8.0 version.
A GD contains a primary cluster and up to 2 secondary clusters.
Before the GD feature is enabled for the primary cluster, the database proxy needs to be enabled, which is enabled for the secondary cluster by default. During the period of enabling the GD feature, it is not supported to disable the database proxy.
The primary cluster and secondary cluster share a set of global parameters.
To enable the GD feature, the specification of the read-write instance is required to be 4 cores or higher.
Supported Regions and AZs
Region | AZ |
Shanghai | Shanghai Zone 2 |
Singapore | Singapore Zone 4 |
References
Features
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

