Python SDK
Last updated:2026-01-05 11:20:33
Scenarios
This document introduces how to use an open-source SDK (taking the Python SDK as an example) to send and receive messages, so as to help you better understand the complete process of sending and receiving messages.
Prerequisites
You have obtained the related client connection parameters as instructed in SDK Overview.
Operation Steps
Step 1: Adding Dependencies
1. According to the RabbitMQ official website, it is recommended to use Pika. First, it is required to install Pika in the client environment.
python -m pip install pika --upgrade
2. Import Pika when creating a client.
import pika
Step 2: Producing Messages
Create, compile, and run the message production program messageProducer.py.
import pika# Use the username and password to create a login credential object.credentials = pika.PlainCredentials('rolename', 'eyJr***')# Create a connection.connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='111.222.333.44', port=5672, virtual_host='Vhostname', credentials=credentials))# Establish a channel.channel = connection.channel()# Declare an exchange.channel.exchange_declare(exchange='ExchangeName', exchange_type="ExchangeType")routingKeys = ['aaa.bbb.ccc', 'aaa.bbb.ddd', 'aaa.ccc.zzz', "xxx.yyy.zzz"]for routingKey in routingKeys:# Send a message to the specified exchange.# When messages are sent without specifying an exchange, it is required to specify a message queue. The routing_key parameter represents the Routing Key when the specified exchange is used; it represents the name of the message queue when no exchange is specified.channel.basic_publish(exchange='direct_exchange',routing_key=routingKey,body=(routingKey + 'This is a new direct message.').encode(),properties=pika.BasicProperties(delivery_mode=2, # Set message persistence.))print('send success msg to rabbitmq')connection.close()
Parameter | Description |
rolename | Username. Enter the username created in the console. |
eyJr*** | User password. Enter the password specified during user creation in the console. |
host | Cluster access address, which can be obtained from the Client Access module on the basic cluster information page. |
port | Cluster access address port, which can be obtained from the Client Access module on the basic cluster information page. |
virtual_host | Vhost name, which can be obtained from the vhost list in the console. |
direct_exchange | Exchange name, which can be obtained from the exchange list in the console. |
routingKeys | Message routing rule, which can be obtained from the Binding Key column of the binding relationship list in the console. |
Step 3: Consuming Messages
Create, compile, and run the message consumption program messageConsumer.py.
import osimport pikaimport sysdef main():# Use the username and password to create a login credential object.credentials = pika.PlainCredentials('rolename', 'eyJr***')# Create a connection.connection = pika.BlockingConnection(pika.ConnectionParameters(host='111.222.333.44', port=5672, virtual_host='Vhostname', credentials=credentials))# Establish a channel.channel = connection.channel()# Declare a message queue.channel.queue_declare(queue='route_queue1', exclusive=True, durable=True)# Bind a message queue to an exchange and specify a Routing Key.routing_keys = ['aaa.bbb.ccc', 'aaa.bbb.ddd']for routingKey in routing_keys:channel.queue_bind(exchange='direct_exchange', queue="route_queue1", routing_key=routingKey)# Set to receive only one unacknowledged message.channel.basic_qos(prefetch_count=1)# Message consumption logic.def callback(ch, method, properties, body):print(" [Consumer1(Direct 'aaa.bbb.ccc'/'aaa.bbb.ddd')] Received (%r)" % body)# Manually reply with acknowledgment.ch.basic_ack(delivery_tag=method.delivery_tag)# Create a consumer to consume messages in the message queue.channel.basic_consume(queue='route_queue1',on_message_callback=callback,auto_ack=False) # Set to non-automatic acknowledgment.print(" [Consumer1(Direct 'aaa.bbb.ccc'/'aaa.bbb.ddd')] Waiting for messages. To exit press CTRL+C")channel.start_consuming()if __name__ == '__main__':try:main()except KeyboardInterrupt:print('Interrupted')try:sys.exit(0)except SystemExit:os._exit(0)
Parameter | Description |
rolename | Username. Enter the username created in the console. |
eyJr*** | User password. Enter the password specified during user creation in the console. |
host | Cluster access address, which can be obtained from the Client Access module on the basic cluster information page. |
port | Cluster access address port, which can be obtained from the Client Access module on the basic cluster information page. |
virtual_host | Vhost name, which can be obtained from the vhost list in the console. |
direct_exchange | Exchange name, which can be obtained from the exchange list in the console. |
route_queue1 | Queue name, which can be obtained from the queue list in the console. |
routingKey | Message routing rule, which can be obtained from the Binding Key column of the binding relationship list in the console. |
Step 4: Viewing Messages
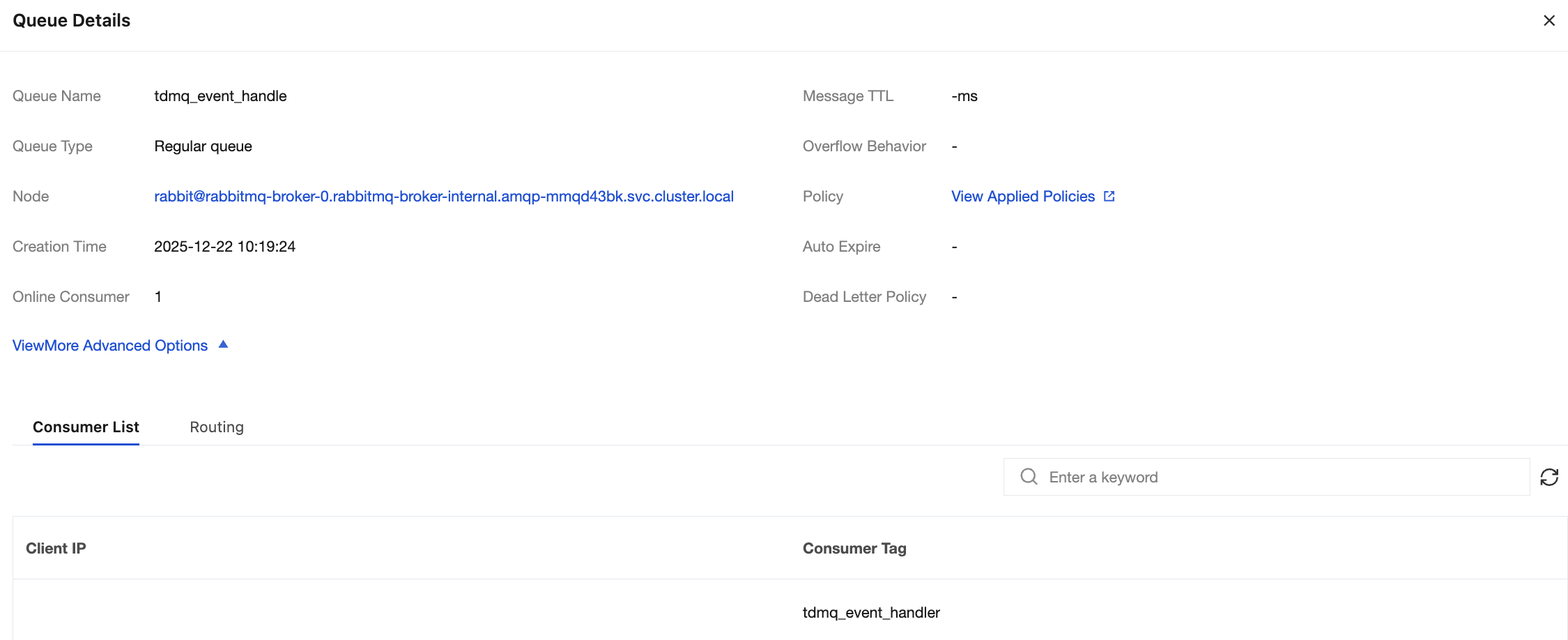
If you want to confirm whether the message is successfully sent to TDMQ for RabbitMQ, you can log in to the console and choose Cluster Management > Queue to go to the basic information page to view the details of consumers accessing the cluster.
Note:
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

