Configure RabbitMQ Persistence
Last updated:2026-01-04 15:02:28
RabbitMQ stores messages in memory by default. Once a node crashes or restarts, these messages are lost.
To prevent this situation, RabbitMQ provides a persistence feature that saves messages to the disk, ensuring that messages are not lost even if the server encounters issues. Persistence includes exchange persistence, queue persistence, and message persistence.
After message persistence is enabled, messages are stored in both memory and the disk. Only when memory is insufficient will RabbitMQ remove certain messages from memory and retain them solely on the disk. Note that persistence reduces RabbitMQ performance because the read-write speed of the disk is much slower than that of memory. In comparison, lazy queues write messages directly to the disk, instead of storing them in both memory and the disk.
Constraints and Limitations
Non-persistent queues and exchanges will be lost after a service restart and need to be recreated.
Messages not marked as persistent will be lost after a service outage. Even messages declared as persistent may still be lost if a service interruption occurs during the disk write process. Only messages successfully persisted to the disk can be recovered after a restart.
Only Managed Edition clusters require configuring persistence. Serverless Edition clusters have persistence enabled by default and do not require configuring persistence.
Configuring Exchange Persistence
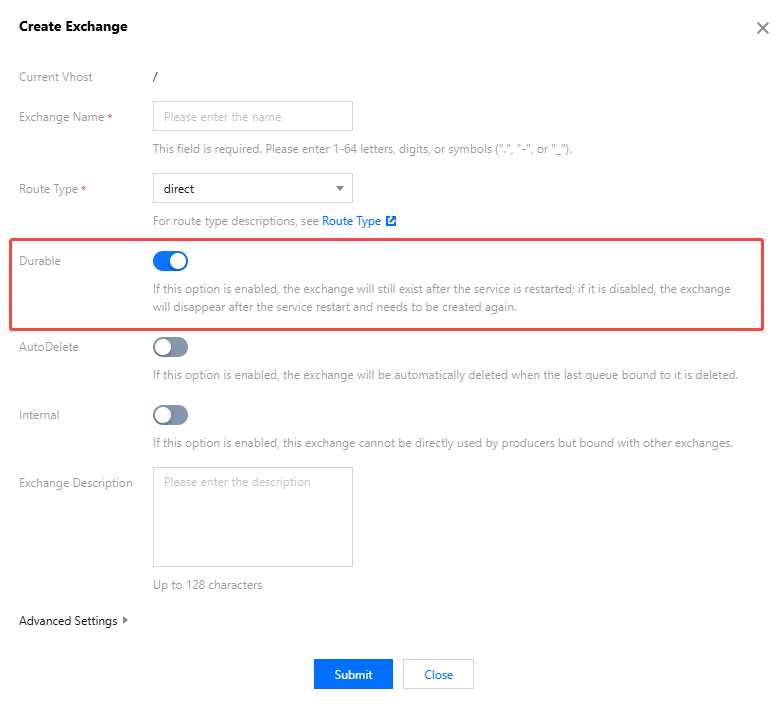
When creating an exchange, enable Durable in the parameter settings. For specific steps, see Creating an Exchange.
Configuring Queue Persistence
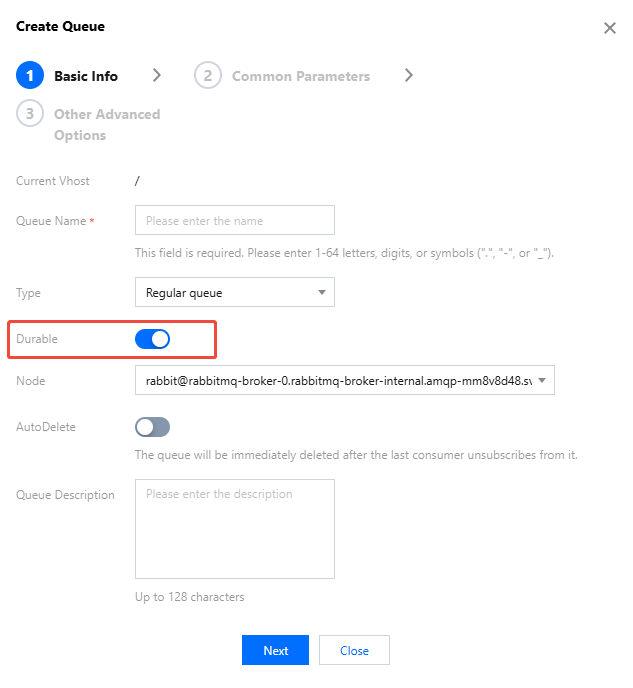
When creating a queue, enable Durable in Basic Information. For specific steps, see Creating a Queue.
Configuring Message Persistence
After a queue is set as persistent, persistent messages can be sent to it from the client.
Below is a Java client example, implemented by setting the
MessageProperties parameter to PERSISTENT_TEXT_PLAIN.import com.rabbitmq.client.MessageProperties;channel.basicPublish("", "test_queue",MessageProperties.PERSISTENT_TEXT_PLAIN, message.getBytes());
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

