SDK for Python
Terakhir diperbarui:2025-07-15 18:32:08
Overview
This document describes how to use open-source SDK to send and receive messages by using the SDK for Python as an example and helps you better understand the message sending and receiving processes.
Prerequisites
You have created the required resources as instructed in Resource Creation and Preparation.
Directions
Step 1. Prepare the environment
As RocketMQ-client Python is lightweight wrapper around rocketmq-client-cpp, you need to install
librocketmq first.Note:
Currently, the Python client only supports Linux and macOS operating systems. It doesn't support Windows systems.
When using Python SDK, note the underlying chip architecture type (x86 or ARM) supported by the installed Python. For example, using a Python version with
'64bit','ELF' (x86_64 architecture) may cause errors on macOS systems with ARM chips.1. Install
librocketmq 2.0.0 or later as instructed in Install librocketmq.2. Run the following command to install
rocketmq-client-python.pip install rocketmq-client-python
Step 2. Produce messages
Create, compile, and run a message production program.
from rocketmq.client import Producer, Message# Initialize the producer and set the producer group information. Be sure to use the full name of the group, such as `rocketmq-xxx|namespace_python%group1`.producer = Producer(groupName)# Set the service addressproducer.set_name_server_address(nameserver)# Set permissions (role name and token)producer.set_session_credentials(accessKey, # Role tokensecretKey, # Role name'')# Start the producerproducer.start()# Assemble messages. The topic name can be copied on the **Topic** page in the console.msg = Message(topicName)# Set keysmsg.set_keys(TAGS)# Set tagsmsg.set_tags(KEYS)# Message contentmsg.set_body('This is a new message.')# Send messages in sync moderet = producer.send_sync(msg)print(ret.status, ret.msg_id, ret.offset)# Release resourcesproducer.shutdown()
Note:
Parameter | Description |
groupName | Copy the producer group name from the Group Management page on the console. 4.x virtual cluster/dedicated cluster: Concatenate the namespace name here, format namespace full name%group name, such as MQ_INSTxxx_aaa%GroupTest.4.x generic cluster/5.x cluster: No need to concatenate here, just fill in the Group name. 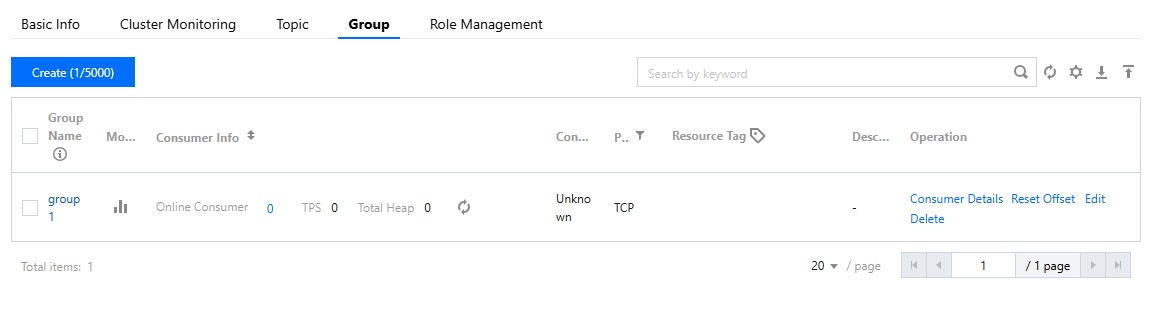 |
nameserver | Get the cluster access address from the access information module on the console cluster basic information page. 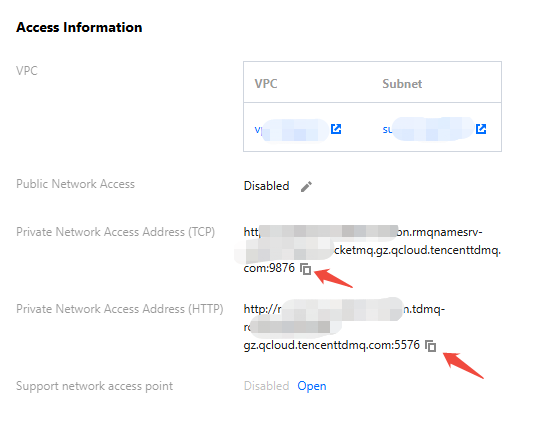 |
secretKey | Role name, copied from the SecretKey column on the Role Management page in the console. |
accessKey | Role token, copied from the AccessKey column on the Role Management page in the console. 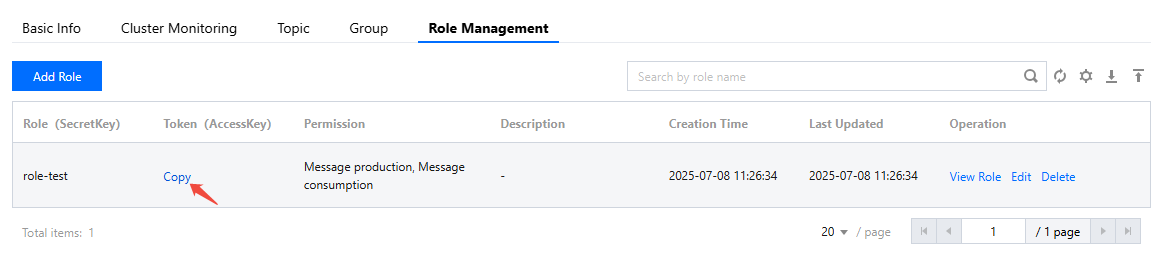 |
namespace | Copy the namespace name from the namespace page in the console. If you use a 4.x generic cluster or 5.x cluster, fill in the Cluster ID here. 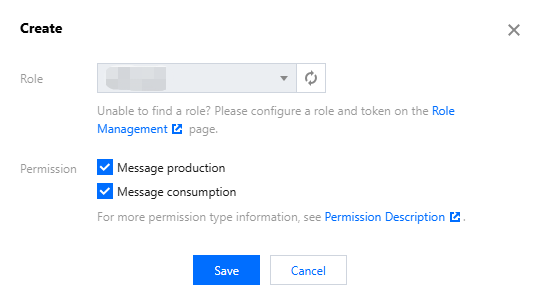 |
topicName | Topic name, which can be copied on the Topic management page in the console. 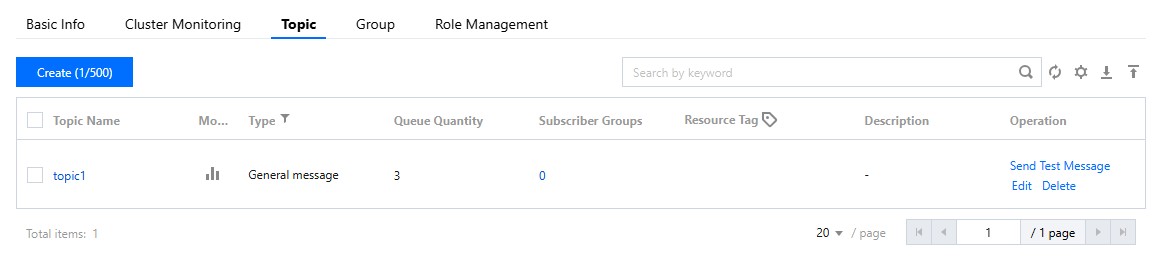 |
TAGS | A parameter used to set the message tag. |
KEYS | A parameter used to set the message key. |
There are certain defects in the message production of the open-source Python client, causing uneven load among different queues of the same Topic. For more information, see [RocketMQ document](https://github.com/apache/rocketmq-client-python/issues /128!cac28b204e4c02765f18ecd741ed1628).
Step 3. Consume messages
Create, compile, and run a message consumption program.
import timefrom rocketmq.client import PushConsumer, ConsumeStatus# Message processing callbackdef callback(msg):# Simulate the business processing logicprint('Received message. messageId: ', msg.id, ' body: ', msg.body)# Return CONSUME_SUCCESS if the consumption is successfulreturn ConsumeStatus.CONSUME_SUCCESS# Return the consumption status if the consumption is successful# return ConsumeStatus.RECONSUME_LATER# Initialize the consumer and set the consumer group informationconsumer = PushConsumer(groupName)# Set the service addressconsumer.set_name_server_address(nameserver)# Set permissions (role name and token)consumer.set_session_credentials(accessKey, # Role tokensecretKey, # Role name'')# Subscribe to a topicconsumer.subscribe(topicName, callback, TAGS)print(' [Consumer] Waiting for messages.')# Start the consumerconsumer.start()while True:time.sleep(3600)# Release resourcesconsumer.shutdown()
Note:
Parameter | Description |
namespace | Copy the namespace name from the namespace page in the console. If you use a 4.x generic cluster or 5.x cluster, fill in the Cluster ID here. |
groupName | Copy the name of consumer group from the Group Management page on the console. 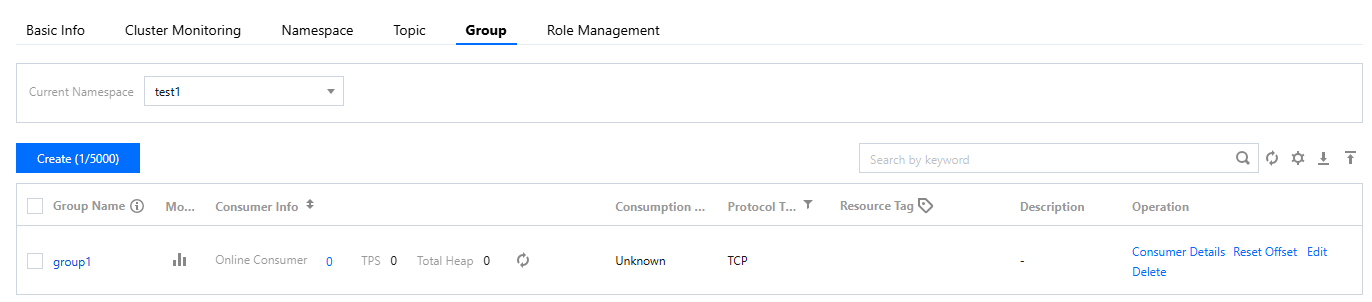 |
nameserver | Get the cluster access address from the access information module on the console cluster basic information page. 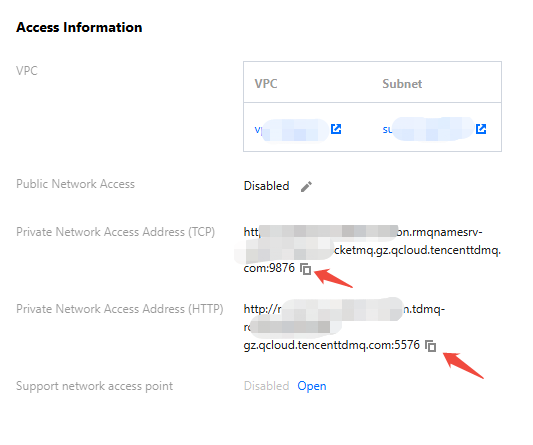 |
secretKey | Role name, copied from the SecretKey column on the Role Management page in the console. |
accessKey | Role token, copied from the AccessKey column on the Role Management page in the console. 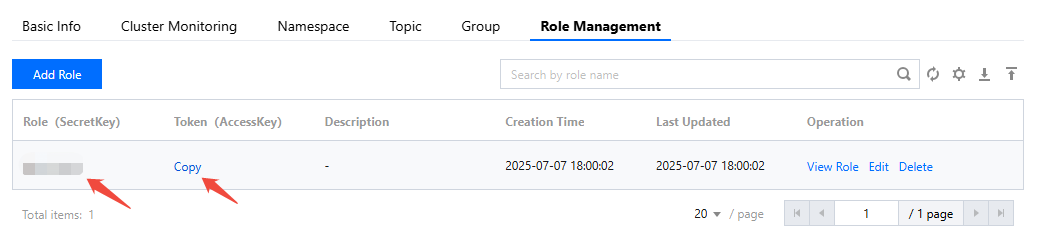 |
topicName | Copy the Topic name from the Topic management page in the console. 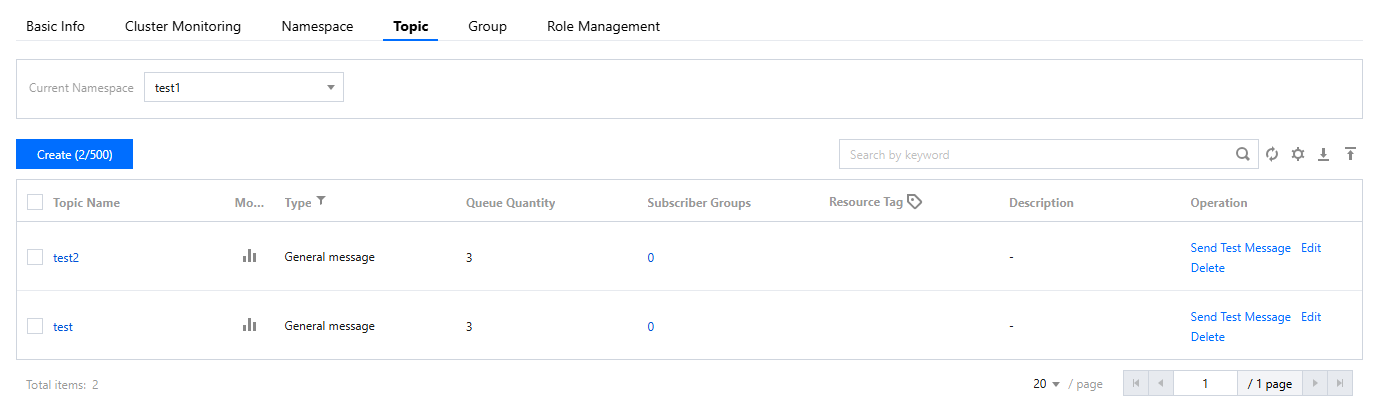 |
Step 4. View consumption details
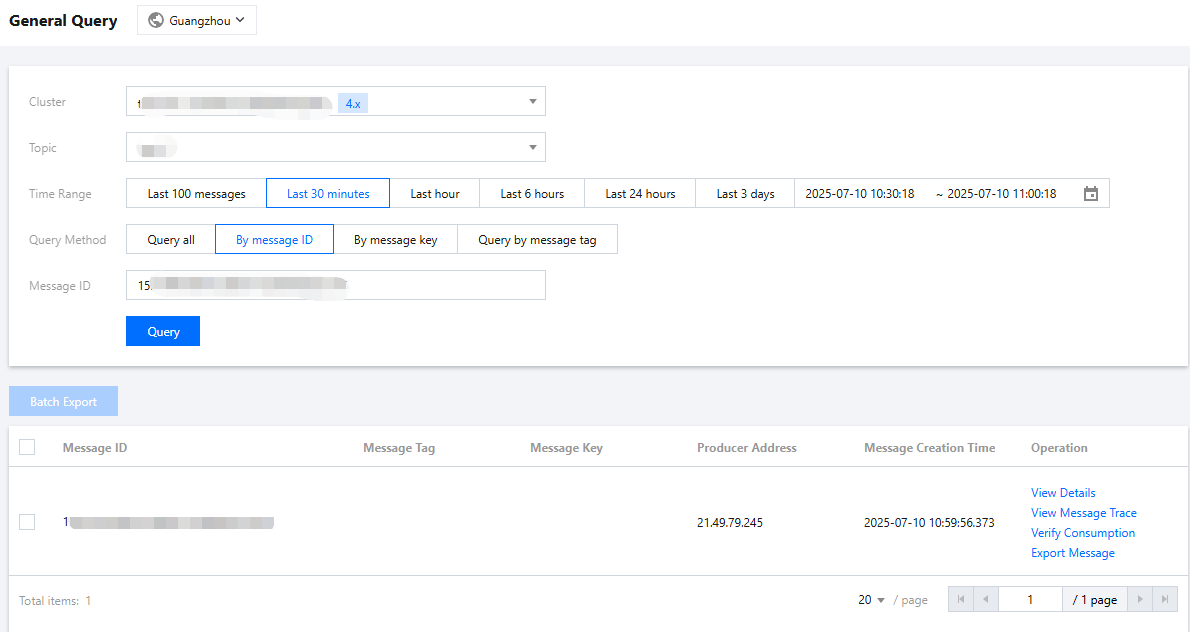
After sending the completion message, you will get a message ID (messageID). You can query the just-sent message, as well as the message details and trace, on the console Message Query > Comprehensive Query page.
Note
Above is a brief introduction to message publishing and subscription. For more information, see Demo or RocketMQ-Client-Python Sample.
Apakah halaman ini membantu?
Anda juga dapat Menghubungi Penjualan atau Mengirimkan Tiket untuk meminta bantuan.
Ya
Tidak
masukan
