Enabling Data Optimization
Last updated:2026-01-30 16:08:47
In big data scenarios, frequent fragmented writes can generate a large number of small files, which can severely degrade performance. Based on extensive production experience, Data Lake Compute (DLC) offers efficient, simple, and flexible data optimization capabilities to handle near-real-time scenarios with large data volumes.
Note:
1. In Upsert scenarios, a large number of small files and snapshots can be created. It’s important to configure data optimization before writing data to prevent the need for extensive resources to handle the backlog of small files later on.
2. Data optimization capabilities currently only support DLC native tables.
3. Currently, the data optimization capability is only supported for DLC native tables (Iceberg).
4. The first execution of a data optimization task may be slow, depending on the size of the existing data and the chosen engine resource specifications.
5. It is recommended to separate the data optimization engine from the business engine to avoid the situation where data optimization jobs and business jobs compete for resources, causing delays in business jobs.
Configuring Data Optimization via the DLC Console
Data optimization policies in DLC can be configured at the database, and data table levels. If no specific data optimization policy is set for a database or data table, it will inherit the policy from the upper-level. When configuring data optimization, users need to select an engine to execute the optimization tasks. If the user does not currently have a data engine, they can see Purchasing Dedicated Data Engine for purchase. DLC data governance supports both Spark SuperSQL and Spark job engines.
Note:
1. Data optimization policies are only available for data catalogs, databases, and data tables with a connection type of DataLakeCatalog.
2. If a user chooses the Super SQL Spark job engine as the data optimization resource, DLC will create 1 to 2 optimization jobs on this engine.
3. It is recommended to properly enable scaling for all data optimization task engines.
Data catalog Configuration Steps
You can configure a data optimization policy for a data catalog through the data catalog editing capability.
1. Enter the Metadata Management module in the DLC console. Select and configure a data catalog with a connection type of DataLakeCatalog.
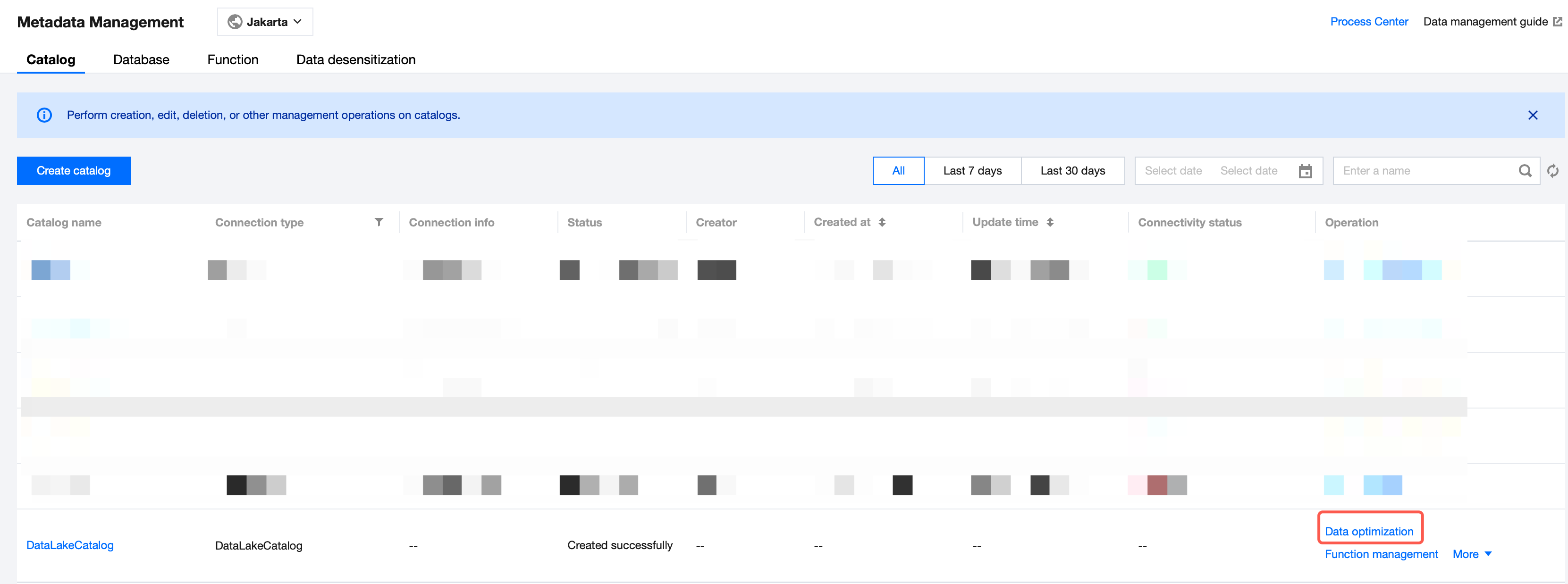
2. Click Data optimization. Once confirmed, the data optimization policy will automatically apply to the data catalog.
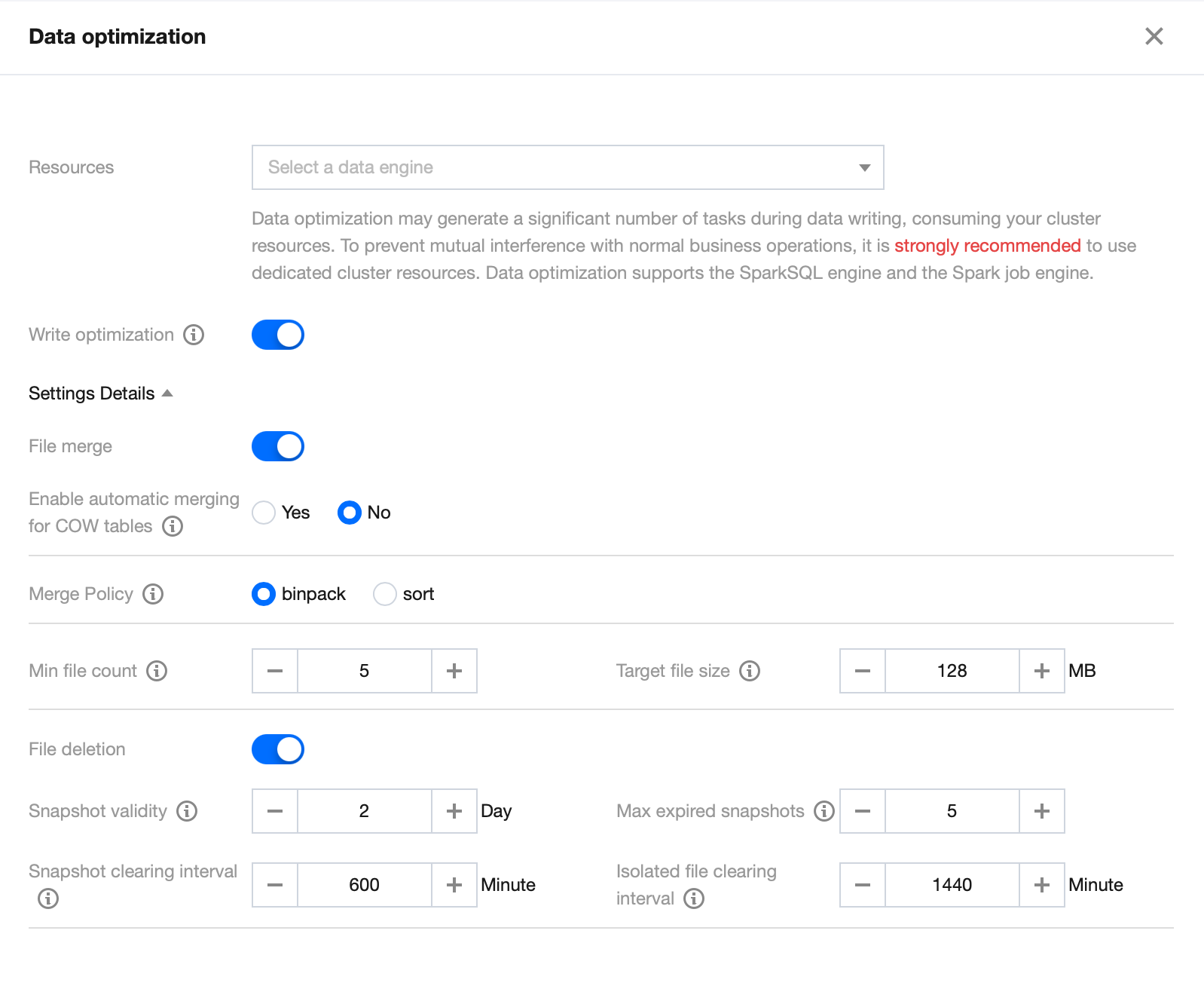
Database Configuration Steps
If you want to configure a data optimization policy for a specific database, you can use DLC's database editing feature to set up data optimization for that database.
1. Enter the Data Management module in the DLC console, and navigate to the Database page. Access the database list under DataLakeCatalog.
2. Open the Database page, click Data Optimization Configuration. Once confirmed, the data optimization policy will automatically apply to the database.
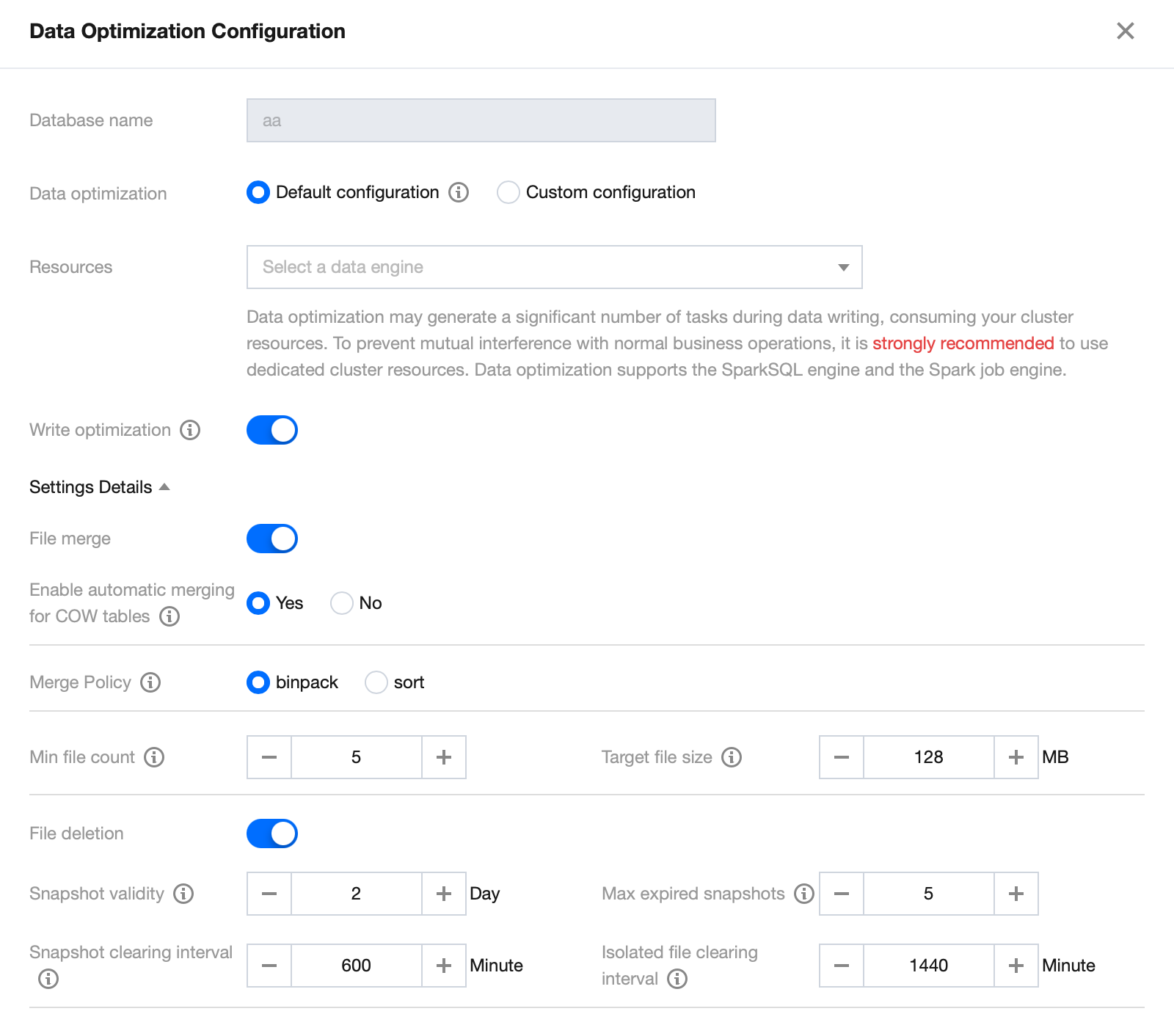
Data Table Configuration Steps
If you want to configure a data optimization policy for a specific data table, you can use DLC's data table editing feature to set up data optimization for that table.
1. Enter the Metadata Management module in the DLC console. In the database list, click to select a database. Enter the Data table list page and click Create native table.
2. Open the Create Native Table page, configure the corresponding optimization resources, and confirm. The data optimization policy will then automatically apply to that data table.
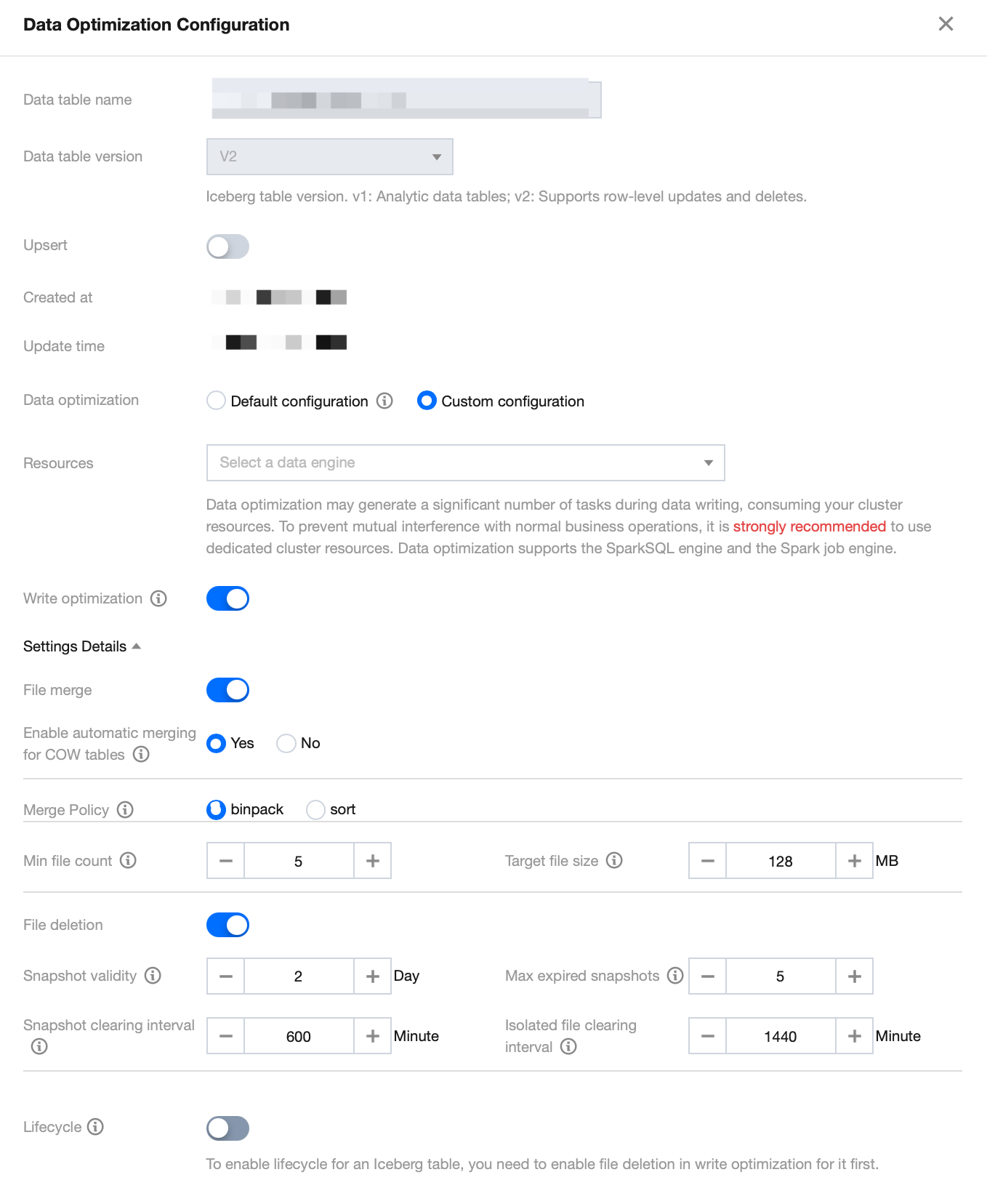
3. For already created tables, you can click Data Optimization Configuration to edit the existing data optimization policy for the data table.
Note:
When you create or edit a data table, the default display will show the data optimization policy inherited from the upper-level data table. To customize the data optimization policy, select Custom Configuration and configure the data optimization resources and policies.
Configuring Data Optimization Through Attribute Fields
Note:
Only databases and data tables support configuring data optimization through attribute field configurations.
In addition to the above visualization method for configuring data optimization, you can also manually specify database and table field attributes through ALTER TABLE/DATABASE for configurations. The example SQL reference is as follows:
// for table govern policyALTER TABLE`DataLakeCatalog`.`wd_db`.`wd_tb`SETTBLPROPERTIES ('smart-optimizer.inherit' = 'none','smart-optimizer.written.enable' = 'enable')// for database govern policyALTER DATABASE`DataLakeCatalog`.`wd_db`SETDBPROPERTIES ('smart-optimizer.inherit' = 'none','smart-optimizer.written.enable' = 'enable')
The attribute values for data optimization can all be modified using the ALTER statement. The definitions of attribute values are as follows:
Attribute Value | Meaning | Default Value | Value Description |
smart-optimizer.inherit | Inherit Upper-Level Policy | default | none: Does not inherit default: Inherits |
smart-optimizer.written.enable | Enable Write Optimization | disable | disable: Disabled enable: Enabled |
smart-optimizer.written.advance.compact-enable | (Optional) Advanced Write Optimization Parameter - Small File Merging | enable | disable: Disabled enable: Enabled |
smart-optimizer.written.advance.delete-enable | (Optional) Advanced Write Optimization Parameter - Data Cleaning | enable | disable: Disabled enable: Enabled |
smart-optimizer.written.advance.min-input-files | (Optional) Minimum Quantity of Input Files for Merging | 5 | When the number of files under a table or partition exceeds the minimum file count, the platform will automatically check and initiate file optimization merging. File optimization merge can significantly improve analysis and query performance. A larger minimum file number increases resource load, while a smaller one allows for more flexible execution and more frequent tasks. A value of 5 is recommended. |
smart-optimizer.written.advance.target-file-size-bytes | (Optional) Target Merge Size | 134217728 (128 MB) | During file optimization merging, the platform will attempt to merge files to this target size. The recommended value is 128 MB. |
smart-optimizer.written.advance.retain-last | (Optional) Snapshot Expiration Time (in days): | 5 | When the existence time of a snapshot exceeds this value, the platform will mark the snapshot as expired. The longer the snapshot expiration time, the slower the snapshot cleanup and more storage space will be occupied. |
smart-optimizer.written.advance.before-days | (Optional) Quantity of Expired Snapshots to Retain | 2 | Expired snapshots exceeding this number will be cleaned up. The more expired snapshots are saved, the more storage space is used. A value of 5 is recommended. |
smart-optimizer.written.advance.expired-snapshots-interval-min | (Optional) Snapshot Expiration Execution Cycle | 600 (10 hour) | The platform periodically scans and expires snapshots. A shorter execution cycle makes snapshot expiration more responsive but may consume more resources. |
smart-optimizer.written.advance.cow-compact-enable | (Optional) Enable COW Table (V1 Table or V2 Non-Upsert Table) Merging | disable | When this configuration item is enabled, the system will automatically create file merging tasks for COW tables. Note: COW tables usually have large amounts of data. Merging files may consume considerable resources. You can decide whether to enable file merging for COW tables based on resource availability and table size. |
smart-optimizer.written.advance.strategy | (Optional) File Merging Policy | binpack | binpack (default merge policy): Merges data files meeting the merge conditions into larger data files using an append method.
sort: The sort policy merges files by sorting based on specified fields. You can choose fields that are frequently used in query conditions according to your business scenario. This can improve query performance after merging. |
smart-optimizer.written.advance.sort-order | (Optional) Sort Order Configuration for Sort Merge Policy | - | If no sorting policy is configured, Upsert tables will use the upsert key- values (defaulting to the first two keys) sorted in ASC NULLS LAST order. If no sorting policy is found for COW table sort merging, the binpack default merge policy will be used. |
smart-optimizer.written.advance.remove-orphan-interval-min | (Optional) Orphan File Cleanup Execution Cycle | 1440 (24 hour) | The platform periodically scans and cleans up orphan files. A shorter execution cycle makes orphan file cleanup more responsive but may consume more resources. |
smart-optimizer.lifecycle.enable | Whether to enable data lifecycle | disable | disable: indicates it is disabled. enable: indicates it is enabled. This takes effect only for data table configurations. |
smart-optimizer.lifecycle.expiration | Expiration time of data lifecycle, in days | - | The expiration time of data lifecycle. Data exceeding the specified expiration time may be removed by the lifecycle task. |
smart-optimizer.lifecycle.expired-field | Expired field of data lifecycle | - | The expired field of data lifecycle. This field is used to check whether the data lifecycle takes effect. This field should be in time format and is recommended to be configured as a partition field. |
smart-optimizer.lifecycle.expired-field-format | Format of the expired field of data lifecycle | - | The format of the effective field of data lifecycle. Supported formats include yyyy-MM-dd, yyyyMMdd, yyyyMMddHH, and yyyyMM. |
Optimization Recommendations
The DLC backend regularly collects metrics for native tables (Iceberg) and combines these metrics with practical tutorials to provide optimization suggestions for native tables. There are 4 categories of optimization suggestion items, including basic configurations for table use cases, data optimization suggestions, and suggestions for data storage distribution items.
Optimization Recommendation Check Items | Sub-Check Items | Meaning | Business Scenario | Optimization Recommendation |
Basic Table Attribute Configuration Check | Metadata Governance Enabled | Check if metadata governance is enabled to prevent metadata inflation caused by frequent table writes. | append/merge into/upsert | Recommended to enable. |
| Bloom Filter Configuration | Check if bloom filter is set. Enabling bloom filter for MOR tables helps quickly filter deletes files and improves query and deletes file merge performance. | upsert | Must be enabled. |
| Key Metrics Attributes Configuration | Check if metrics are set to full. Enabling this attribute will record all metrics information, avoiding incomplete metrics records due to long table locations. | append/merge into/upsert | Must be enabled. |
Data Optimization Configuration Check | Small File Merging | Check if small file merging is enabled. | merge into/upsert | Must be enabled. |
| Snapshot Expiration | Check if snapshot expiration is enabled. | append/merge into/upsert | Recommended to enable. |
| Orphan File Removal | Check if orphan file removal is enabled. | append/merge into/upsert | Recommended to enable. |
Recent Governance Tasks Check Items | Recent Governance Tasks Check Items | If data governance is enabled for the table, the system tracks the execution of data governance tasks. Multiple consecutive timeouts or failures in tasks indicate a need for optimization. | append/merge into/upsert | Recommended to enable. |
Data Storage Distribution | Average File Size | Collect summary information from snapshots and calculate the average file size. If the average file size is less than 10 MB, it indicates a need for optimization. | append/merge into/upsert | Recommended to enable. |
| Metadata File Size | Collect the size of the metadata.json file. If this file exceeds 10 MB, it indicates a need for optimization. | append/merge into/upsert | Recommended to enable. |
| Quantity of Table Snapshots | Collect the quantity of table snapshots. If the number of snapshots exceeds 1000, it indicates a need for optimization. | append/merge into/upsert | Recommended to enable. |
Recommendations for Optimizing Basic Table Attribute Configuration
Checking and Configuring Metadata Governance
Step 1 Check Method
Use show TBLPROPERTIES to view table attributes and check if "write.metadata.delete-after-commit.enabled" and "write.metadata.previous-versions-max" are configured.
Step 2 Configuration Method
If the check in Step 1 shows that these attributes are not configured, you can configure them using the following Alter table DDL commands.
ALTER TABLE`DataLakeCatalog`.`axitest`.`upsert_case`SETTBLPROPERTIES('write.metadata.delete-after-commit.enabled' = 'true','write.metadata.previous-versions-max' = '100');
Note:
To enable automatic metadata governance, set the attribute "write.metadata.delete-after-commit.enabled" to true. You can set the number of retained historical metadata according to your actual conditions. For example, setting "write.metadata.previous-versions-max" to 100 will keep a maximum of 100 historical metadata.
Checking and Setting Bloom Filter
Step 1 Check Method
Use show TBLPROPERTIES to view table attributes and check if "write.parquet.bloom-filter-enabled.column.{column}" is set to true.
Step 2 Configuration Method
If the check in Step 1 shows that these attributes are not configured, you can configure them using the following Alter table DDL commands.
ALTER TABLE`DataLakeCatalog`.`axitest`.`upsert_case`SETTBLPROPERTIES('write.parquet.bloom-filter-enabled.column.id' = 'true');
Note:
It is recommended to enable bloom filters in upsert scenarios and set them based on the upsert primary key. If there are multiple primary keys, it is recommended to set bloom filters for the first two primary key fields.
After the bloom filter fields are updated, if there are upstream processes like inlong/oceans/flink writing data, you need to restart the upstream import jobs.
Checking and Configuring Key Table Metrics
Step 1 Check Method
Use show TBLPROPERTIES to view table attributes and check if "write.metadata.metrics.default" is set to "full".
Step 2 Configuration Method
If the check in Step 1 shows that these attributes are not configured, you can configure them using the following Alter table DDL commands.
ALTER TABLE`DataLakeCatalog`.`axitest`.`upsert_case`SETTBLPROPERTIES('write.metadata.metrics.default' = 'full');
Data Optimization Configuration Recommendations
Step 1 Check Method
Check via SQL
Use show TBLPROPERTIES to view table attributes and check if data optimization is configured. For reference on data optimization attribute values, see DLC Native Table Core Capabilities.
Visual Check via DLC Console
Enter the Data Management module in the DLC console, navigate to the Database page, select the database, go to the Data Table list, select the table to check, and enter Data Optimization Configuration.
Step 2 Configuration Method
Recent Data Governance Optimization Task Recommendations
Checking if Data Governance is Functioning Properly
Step 1 Check Method
Enter the Data Management module in the DLC console, navigate to the Database page, select the database, go to the Data Table list, click the data table name, enter Optimized Monitoring, select Today's Optimization under Optimization Task, and check for any failed tasks in the last three hours. If there are any, this check fails. Select the failed task and check the Execution Results in View Details.
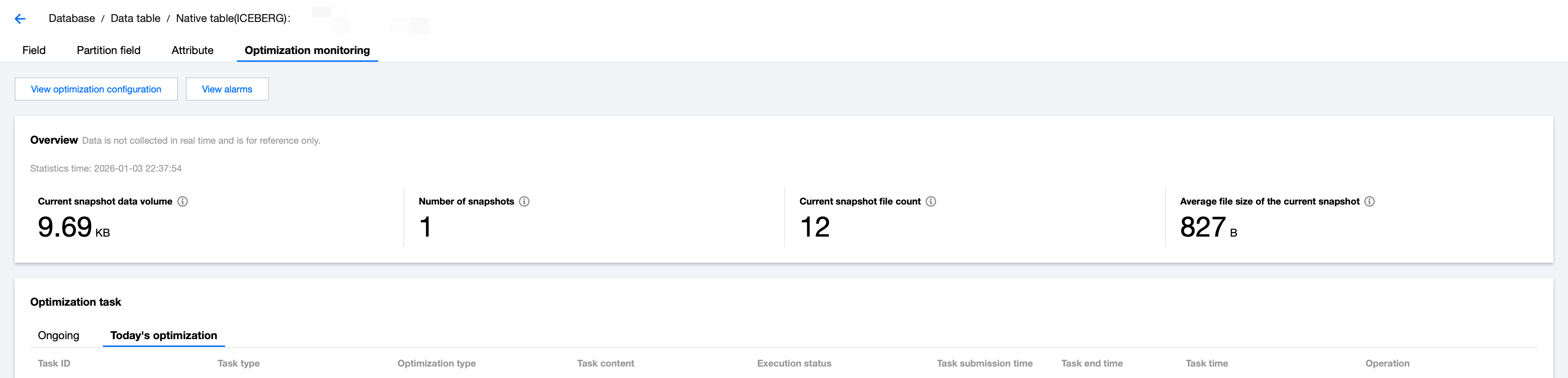
Step 2 Fix Method
Summary of reasons and solutions for data optimization task failures.
1. The task failed due to errors in the data governance configuration.
The sort-merge policy was enabled, but the sorting rules were incorrectly configured or nonexistent.
The engine configured for data governance changed, causing the governance task to fail due to the absence of a suitable engine.
2. The task has timed out.
Note:
After fixing the issues, wait for three hours to check if the recent data optimization tasks have resumed normal operation.
Data Storage Distribution Optimization Recommendations
Note:
This check usually fails when there is a large amount of data. It is recommended to handle it manually before considering adding it to data optimization governance.
It is recommended to use a more efficient Spark job engine for processing.
When manually merging small files, configure the target-file-size-bytes parameter according to the business scenario. For upsert writes, it is recommended not to exceed 134,217,728 bytes (128 MB). For append/merge into writes, it is recommended not to exceed 536,870,912 bytes (512 MB).
When executing snapshot expiration with a Spark job engine, consider increasing the max_concurrent_deletes parameter.
Handling Failed Data File Average Size Check
Step 1 Summary of Causes
The average size of the data file is too small, which usually occurs in the following situations:
The table partitions are too fine-grained, resulting in only a small amount of data per partition.
When INSERT INTO or OVERWRITE is used for table writes, upstream data is scattered, especially if the upstream data is also partitioned with small amounts of data in each partition.
When using MERGE INTO to write to an MOR table without merging small files.
When using UPSERT writes without performing small file merging.
Step 2 Fix Method
Use the following SQL to manually perform small file merging.
CALL `DataLakeCatalog`.`system`.`rewrite_data_files`(`table` => 'test_db.test_tb',`options` => map('delete-file-threshold','10','max-concurrent-file-group-rewrites', --Adjust based on available resources. Higher concurrency uses more resources but speeds up merging.'5','partial-progress.enabled','true','partial-progress.max-commits','10','max-file-group-size-bytes','10737418240','min-input-files','30','target-file-size-bytes','134217728'))
Handling Failed Metadata File Size Check
Step 1 Summary of Causes
The MetaData file is too large, usually caused by having too many data files, often due to the following reasons:
The table has been performing APPEND writes for a long time, with each write generating many scattered files.
The table is an MOR table and has been using MERGE INTO writes for a long time but hasn't enabled small file merging.
The table has not performed snapshot expiration for a long time, leading to a large number of historical snapshot data files.
The partitions of the table are large, and there are many small files within each partition.
Step 2 Fix Method
See the manual implementation of small file merging.
Use the following SQL to manually clean up expired snapshots.
--use spark Job engine expired snapshot referenceCALL `DataLakeCatalog`.`system`.`expire_snapshots`(`table` => 'test_db.test_tb',`retain_last` => 5,`stream_results` => true,`older_than` => TIMESTAMP '2024-01-10 13:02:40.407', --expiration time based on actual snapshot of table`max_concurrent_deletes` => 50);--use spark sql engine expired snapshot referenceCALL `DataLakeCatalog`.`system`.`expire_snapshots`(`table` => 'test_db.test_tb',`retain_last` => 5,`stream_results` => true,`delete_by_executor` => true,`older_than` => TIMESTAMP '2024-01-10 13:02:40.407', --expiration time based on actual snapshot of table`max_concurrent_deletes` => 4)
Aggregate files to some extent based on the business scenario to avoid writing too scattered files.
If data is written via `insert into` or `insert overwrite`, you can automatically add the `rebalance` operation in the following ways (engine needs to be upgraded to 2025-07-11 or higher version):
`spark.sql.adaptive.insert.repartition`: This parameter defaults to `false` and needs to be set manually to `true`. As an engine-level global static configuration, it is only applicable to Hive tables (not suitable for I
Handling Failed Snapshot Quantity Check
Step 1 Summary of Causes
Snapshots have not been expired for a long time.
The checkpoint interval for upsert writes is not set correctly, resulting in a large number of snapshots.
Step 2 Fix Method
Use snapshot expiration SQL to expire old snapshots.
Adjust the checkpoint interval for Flink writes. For DLC native tables, it is recommended to set the checkpoint interval for upsert writes to 3-5 minutes.
Typical Case Configuration Reference for Data Optimization
Case 1: Not Enabling File Merging and Only Enabling File Cleanup
Applicable Scenario
Data tables are written in append mode, including insert into/overwrite with the Spark engine and offline writes with Flink/InLong. Since files are already aggregated to a relatively large size while being written in this case, there is no need to use data optimization for data merging. Therefore, you only need to enable file cleanup.
Configuration Reference
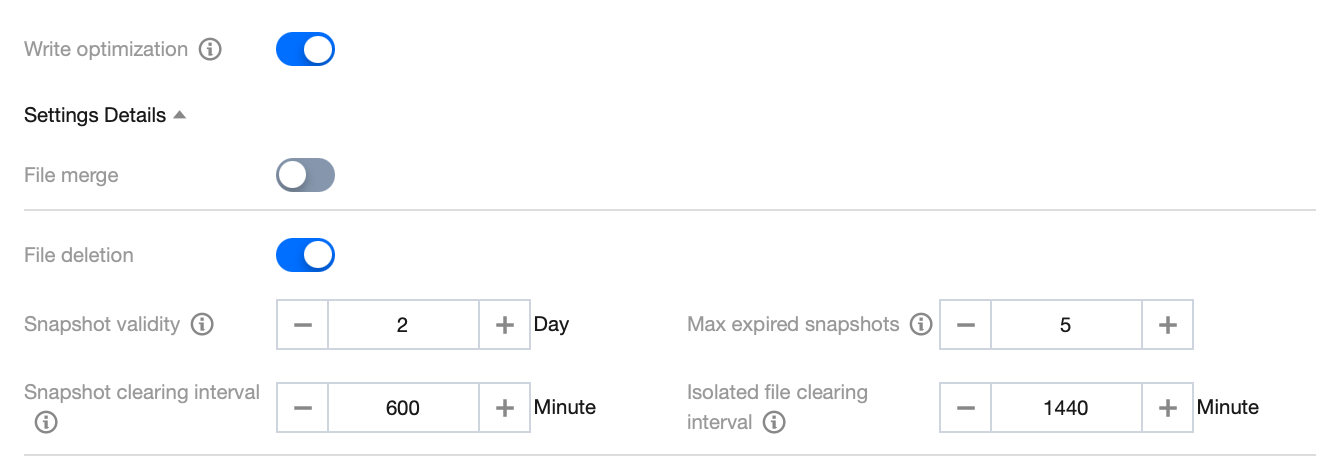
Note:
1. If you found that the file written in append mode is relatively small, you can also enable file merging based on the actual situation and adjust the target file size accordingly. It is recommended to configure the size of the table catalog file written in append mode as 512 MB.
2. If users need to build an index, file merging can be enabled, and the merging policy is configured as sort.
Case 2: Enabling File Merging and File Cleanup Simultaneously
Applicable Scenario
Data tables are in version V2 and are written in upsert and merge into modes. Typically, they are written in Flink/InLong Upsert mode. Since Deletes files will be written in this case, data optimization is required for processing in advance. Otherwise, query performance will be affected.
Configuration Reference
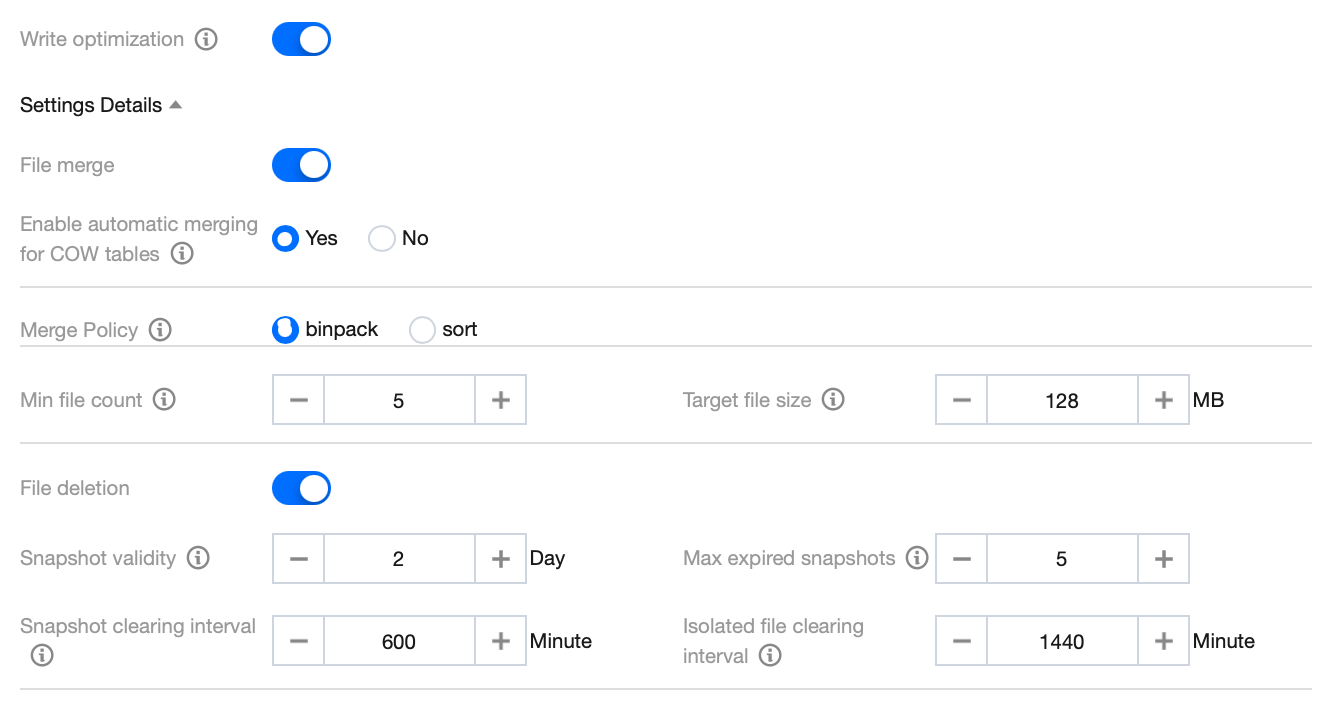
Note:
If users need to build an index, file merging can be enabled, and the merging policy is configured as sort.
Case 3: Inheriting the Data Optimization Policy from the Upper Level and Enabling Table-Level Lifecycle Individually
Applicable Scenario
Users have table lifecycle configuration requirements.
Configuration Reference
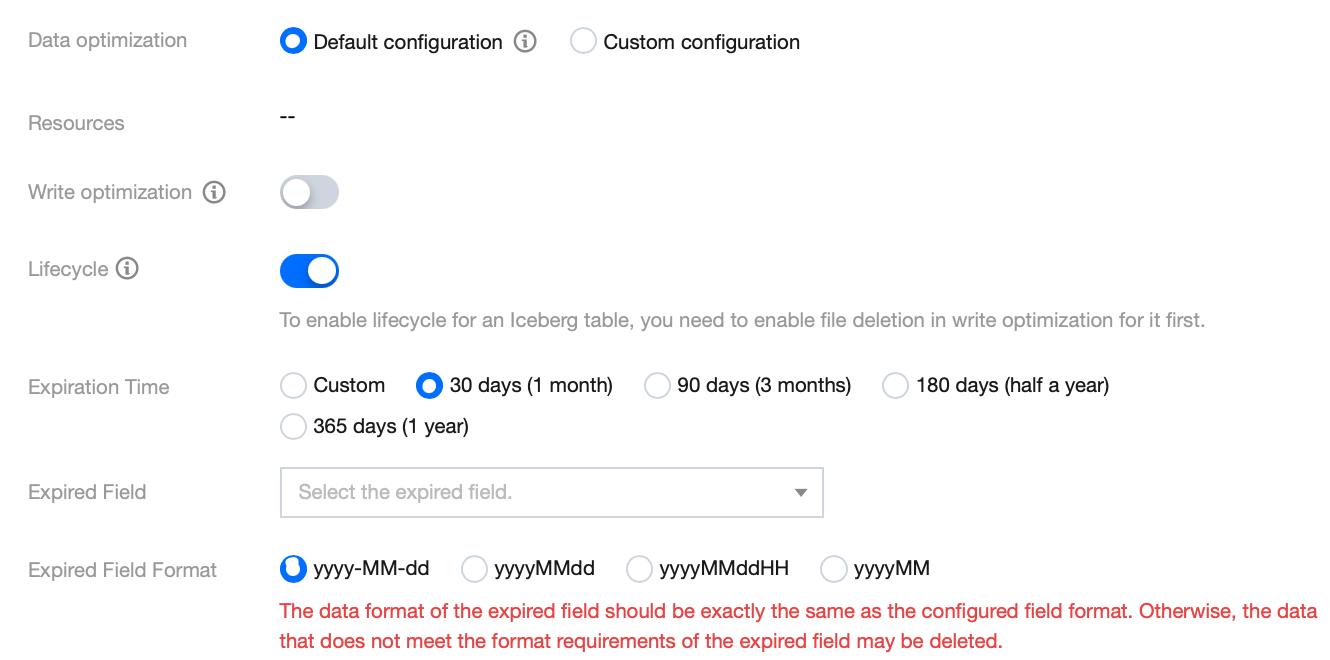
Note:
Lifecycle configurations and data optimization configurations can be independently configured. Users can set data optimization configurations at the database level and lifecycle configurations at the table level, thereby reducing the need to independently configure data optimization policies for each table.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

