Task Insights
Last updated:2025-04-17 15:22:36
Task insights are made from the task perspective, helping you quickly identify the completed tasks for analysis and providing optimization suggestions.
Prerequisites
1. SuperSQL SparkSQL and Spark job engines:
1. For engines purchased after July 18, 2024, task insights are enabled by default.
2. For Spark kernel versions prior to July 18, 2024, the engine kernel should be upgraded to enable task insights. For details on upgrading, see How to Enable Insights.
3. Standard Spark engine:
1. For engines purchased after December 20, 2024, task insights are supported by default.
2. For engines purchased before December 20, 2024, manual activation of task insights is not supported. Submit a ticket to contact after-sales service for activation.
Other types of engines do not support task insights currently.
Directions
Log in to the DLC Console, select the Insight Management feature, and switch to the task insights page.
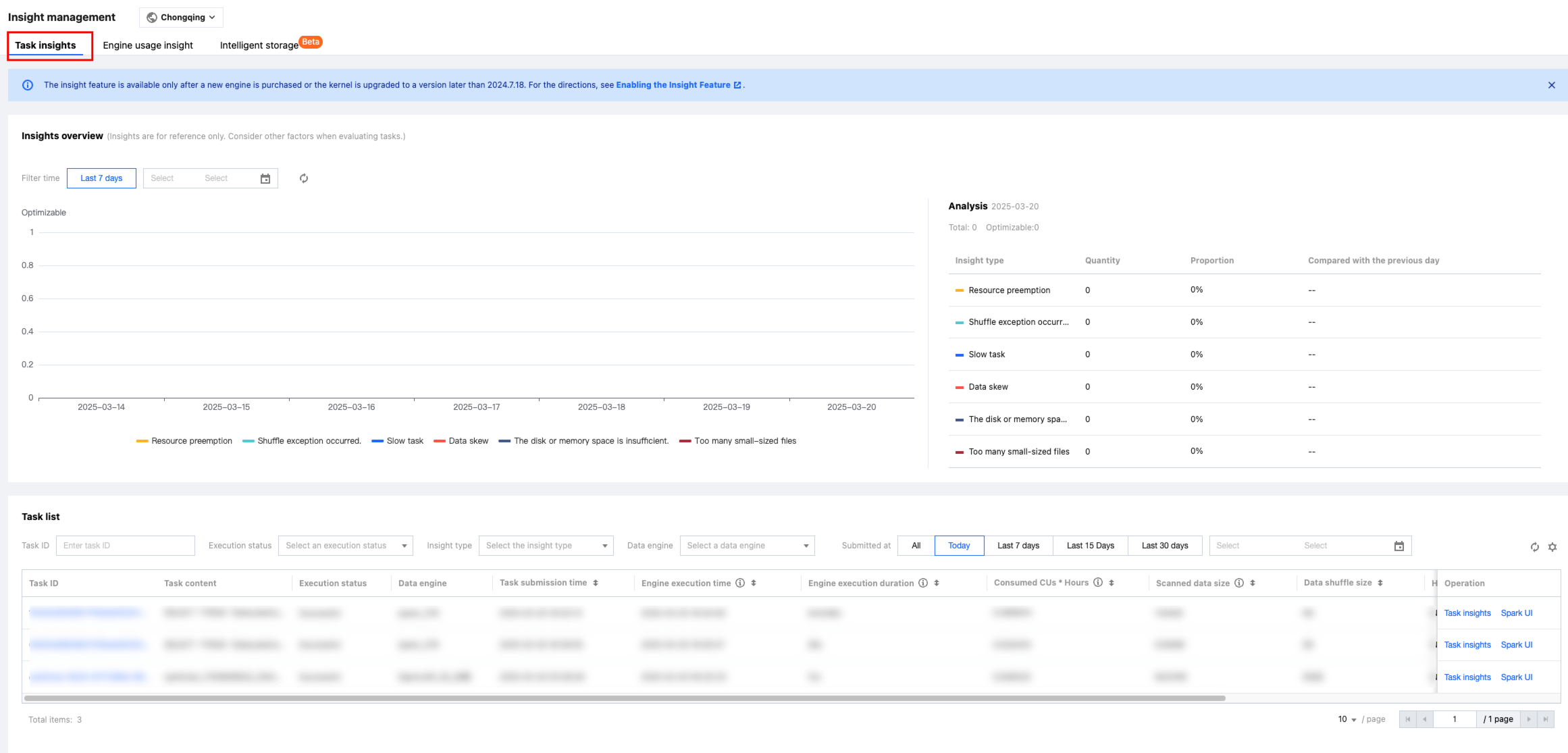
Insights Overview
Daily-level statistics offer insights into the distribution and trend of tasks requiring optimization, providing a more intuitive understanding of daily tasks.
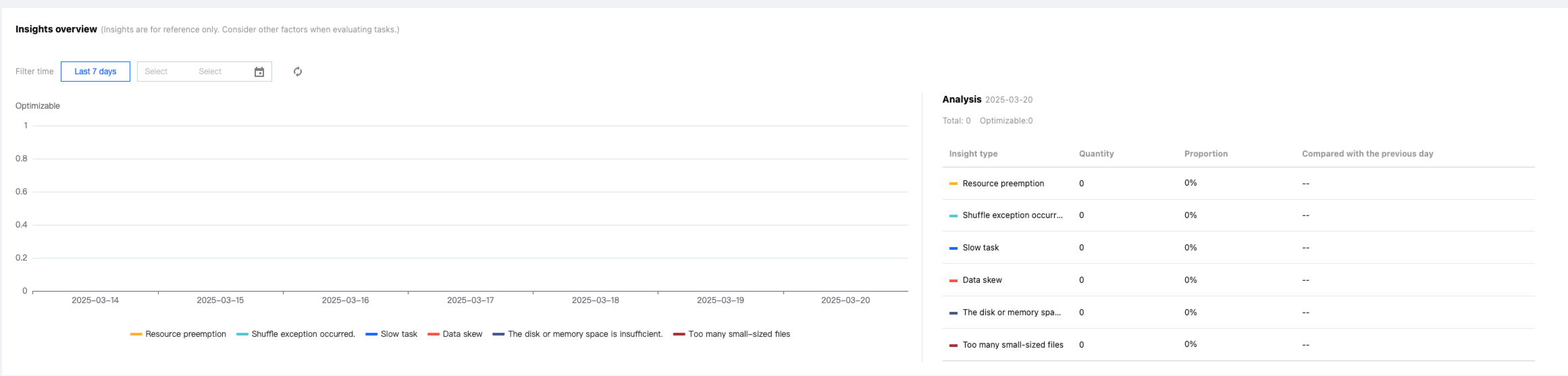
Task Insights
The task insights feature supports analyzing the summary metrics of each executed task and identifying the possible optimization issues.
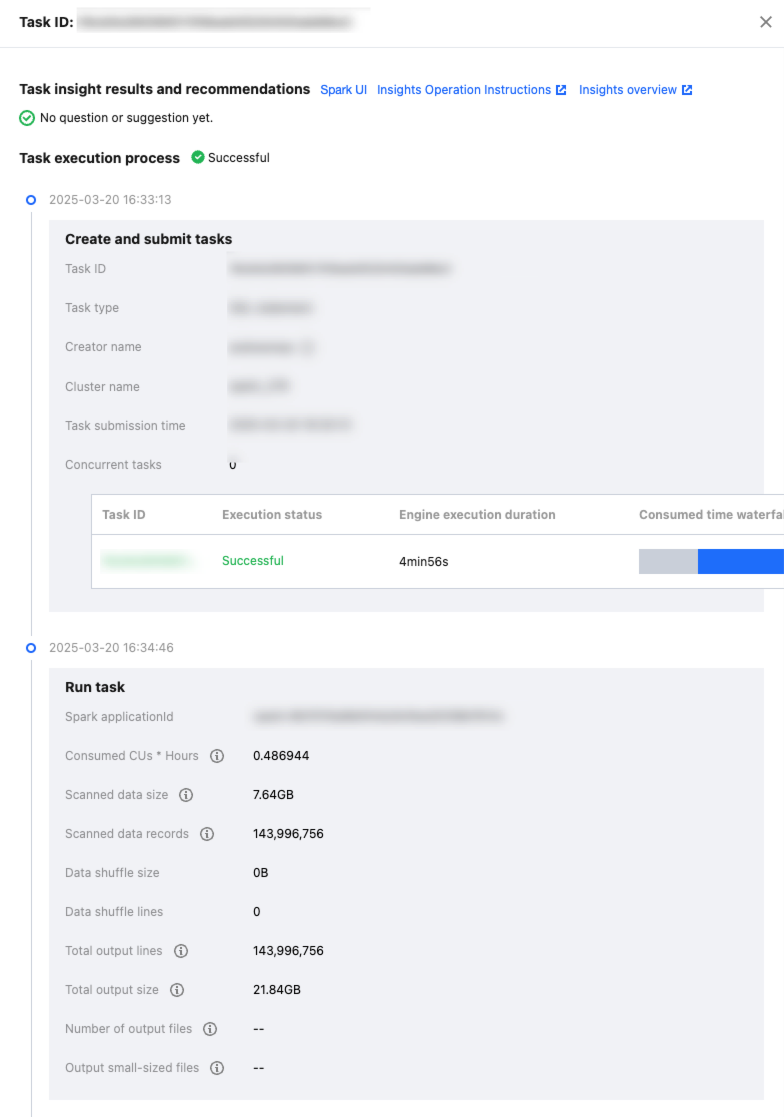
After a task is completed, users only need to select the task to be analyzed and click Task Insights in the operation column to view the details.
Based on the actual execution of the current task, DLC task insights leverage data analysis and algorithmic rules to provide the corresponding optimization recommendations.
How to Enable the Insights Feature?
Upgrading Kernel Image for Existing SuperSQL Engines
Note:
For engines purchased after July 18, 2024, or existing engines upgraded to kernel versions after July 18, 2024, Insights are automatically enabled. You can skip this step.
Directions
1. Go to the SuperSQL Engine list page and select the engine for which you want to enable the insights feature.
2. On the engine details page, click Kernel version management > Version upgrade (default upgrade to the latest kernel version).
Overview of Key Insight Metrics
Metric Name | Metric Definition |
Engine execution time | Reflects the time the first task was executed on the Spark engine (the time when the task first preempted the CPU for execution). |
Execution time within the engine | Reflects the time actually required for computing, namely, the time taken from the start of the first task execution in a Spark task to the completion of the Spark task. More specifically, it is the sum of the duration from the start of the first task to the completion of the last task for each Spark stage. This sum does not include the queuing time of the task before it starts (that is, excluding other time such as the time required for scheduling between task submission and the start of execution of the Spark task), nor include the time spent waiting for task execution due to insufficient executor resources between multiple Spark stages during the task execution process. |
Queuing time (time spent waiting for execution) | Specifies the time taken from task submission to the start execution of the first Spark task. The time taken may include the cold startup duration of the first execution of the engine, the queuing time caused by the concurrent limit of the configuration task, the time waiting for executor resources due to full resources within the engine, and the time taken to generate and optimize the Spark execution plan. |
Consumed CU*H | Specifies the sum of the CPU execution duration of each core of the Spark Executor used in computing, per hour (not equivalent to the duration of starting machines in the cluster, because the machines may not participate in task computing after they start. Eventually, the cluster's CU fee is subject to the bill). In the Spark scenario, it approximately equals to the sum of the execution durations of the Spark task (seconds) / 3600 (per hour). |
Data scan size | The amount of physical data read from storage by this task. In the Spark scenario, it approximately equals to the sum of the Stage Input Size in Spark UI. |
Total output size | The size of the records output after this task processes the data. In the Spark scenario, it approximately equals to the sum of the Stage Output Size in Spark UI. |
Data shuffle size | In the Spark scenario, it approximately equals to the sum of the Stage Shuffle Read Records in Spark UI. |
Number of output files | (This metric requires the Spark engine kernel to be upgraded to a version after November 16, 2024)The total number of files written by tasks through statements such as insert. |
Number of output small files | (This metric requires the Spark engine kernel to be upgraded to a version after November 16, 2024)Small files are defined as output files with a size less than 4 MB (controlled by the parameter spark.dlc.monitorFileSizeThreshold, default 4 MB, configurable at the engine or task level). This metric represents the total number of small files written by tasks through statements such as insert. |
Parallel task | Displays the parallel execution of tasks, making it easier to analyze affected tasks (up to 200 entries). |
Overview of Insight Algorithms
Insight Type | Algorithm Description (Continuously Improving and Adding New Algorithms) |
Resource preemption | SQL execution task delay time is greater than 1 minute after stage submission, or delay exceeds 20% of the total runtime (the threshold formula dynamically adjusts based on task runtime and data volume). |
Shuffle exception | Stage execution encounters shuffle-related error stack information. |
Slow task | Task duration in a stage is greater than twice the average duration of other tasks in the same stage (the threshold formula dynamically adjusts based on task runtime and data volume). |
Data skew | Task shuffle data is greater than twice the average shuffle data size of other tasks (the threshold formula dynamically adjusts based on task runtime and data volume). |
Disk or memory insufficiency | Error stack information during stage execution includes OOM, insufficient disk space, or COS bandwidth limitation errors related to disk or memory insufficiency. |
Excessive small file output | (This insights type requires the Spark engine kernel to be upgraded to a version after November 16, 2024)See the metric number of output small files in the list, and the presence of excessive small file output is determined if any of the following conditions are met: 1. Partitioned tables: The number of small files written out by a partition exceeds 200. 2. Non-partitioned tables: The total number of output small files exceeds 1000. 3. If partitioned or non-partitioned tables output more than 3,000 files with an average file size less than 4 MB. |
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

