Using Apache Airflow to Schedule DLC Engine to Submit Tasks
Last updated:2025-05-22 15:45:02
Using Apache Airflow to Schedule DLC Engine to Submit Tasks
Last updated: 2025-05-22 15:45:02
This document introduces DLC's support for the Apache Airflow scheduling tool and provides examples demonstrating how to use Apache Airflow to run different types of DLC engine tasks.
Overview
Apache Airflow is an open-source scheduling tool developed by Airbnb, written in Python. It defines and schedules a set of interdependent tasks using Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs). Apache Airflow supports sub-tasks written in Python and offers various operators to execute tasks, such as Bash commands, Python functions, SQL queries, and Spark jobs, providing high flexibility and scalability. Widely used in fields like data engineering, data processing, and workflow automation, Apache Airflow allows users to easily monitor and manage the state and execution of workflows through its rich features and visual interface. For more information about Apache Airflow, see Apache Airflow.
Prerequisites
1. Prepare the Apache Airflow environment.
2. Install and start Apache Airflow. For detailed steps on installation and startup, see Quick Start.
3. Install the jaydebeapi dependency package, pip install jaydebeapi.
4. Prepare the DLC environment.
5. Enable the DLC engine service.
6. If using the standard Spark engine, prepare the Hive JDBC driver. Click to download hive-jdbc-3.1.2-standalone.jar.
7. If using the standard Presto engine, prepare the Presto JDBC driver. Click to download presto-jdbc-0.284.jar.
8. If using the SuperSQL engine, prepare the DLC JDBC driver. Click to download the JDBC driver.
Key Steps
Creating Connection and Scheduling Tasks
In the Apache Airflow working directory, create a dags directory. Inside the dags directory, create a scheduling script and save it as a .py file. For example, in this document, the scheduling script is created as /root/airflow/dags/airflow-dlc-test.py as shown below:
import timefrom datetime import datetime, timedeltaimport jaydebeapifrom airflow import DAGfrom airflow.operators.python_operator import PythonOperatorjdbc_url='jdbc:dlc:dlc.tencentcloudapi.com?task_type=SparkSQLTask&database_name={dataBaseName}&datasource_connection_name={dataSourceName}®ion={region}&data_engine_name={engineName}'user = 'xxx'pwd = 'xxx'dirver = 'com.tencent.cloud.dlc.jdbc.DlcDriver'jar_file = '/root/airflow/jars/dlc-jdbc-2.5.3-jar-with-dependencies.jar'def createTable():sqlStr = 'create table if not exists db.tb1 (c1 int, c2 string)'conn = jaydebeapi.connect(dirver, jdbc_url, [user, pwd], jar_file)curs = conn.cursor()curs.execute(sqlStr)rows = curs.rowcount.realif rows != 0:result = curs.fetchall()print(result)curs.close()conn.close()def insertValues():sqlStr = "insert into db.tb1 values (111, 'this is test')"conn = jaydebeapi.connect(dirver,jdbc_url, [user, pwd], jar_file)curs = conn.cursor()curs.execute(sqlStr)rows = curs.rowcount.realif rows != 0:result = curs.fetchall()print(result)curs.close()conn.close()def selectColums():sqlStr = 'select * from db.tb1'conn = jaydebeapi.connect(dirver, jdbc_url, [user, pwd], jar_file)curs = conn.cursor()curs.execute(sqlStr)rows = curs.rowcount.realif rows != 0:result = curs.fetchall()print(result)curs.close()conn.close()def get_time():print('Current time is:', datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))return time.time()default_args = {'owner': 'tencent', # owner's name'start_date': datetime(2024, 11, 1), # the first execution start time, in UTC'retries': 2, # number of retry attempts on failure'retry_delay': timedelta(minutes=1), # retry interval on failure}dag = DAG(dag_id='airflow_dlc_test', # DAG ID, should consist only of letters, numbers, and underscoresdefault_args=default_args, # externally defined parameters in dic formatschedule_interval=timedelta(minutes=1), # defines the frequency at which the DAG runs; can be configured for days, weeks, hours, minutes, seconds, or millisecondscatchup=False # when executing the DAG, all tasks scheduled from the start time up to the present will be executed. The default value is True.)t1 = PythonOperator(task_id='create_table',python_callable=createTable,dag=dag)t2 = PythonOperator(task_id='insert_values',python_callable=insertValues,dag=dag)t3 = PythonOperator(task_id='select_values',python_callable=selectColums,dag=dag)t4 = PythonOperator(task_id='print_time',python_callable=get_time,dag=dag)t1 >> t2 >> [t3, t4]
Parameter description:
Parameters | Description |
jdbc_url | JDBC connection address and configuration parameters. For more details, see Hive JDBC Access, Presto JDBC Access, and DLC JDBC Access. |
user | SecretId |
pwd | SecretKey |
dirver | Load the JDBC driver. For more details, see Hive JDBC Access, Presto JDBC Access, and DLC JDBC Access. |
jar_file | The storage path of the driver JAR package. Replace it with the absolute path where the corresponding engine's JDBC driver JAR package is stored. For more details, see Hive JDBC Access, Presto JDBC Access, and DLC JDBC Access. |
Running Scheduled Tasks
You can access the Web interface, navigate to the DAGs tab, locate the submitted scheduling workflow, and start the scheduling.
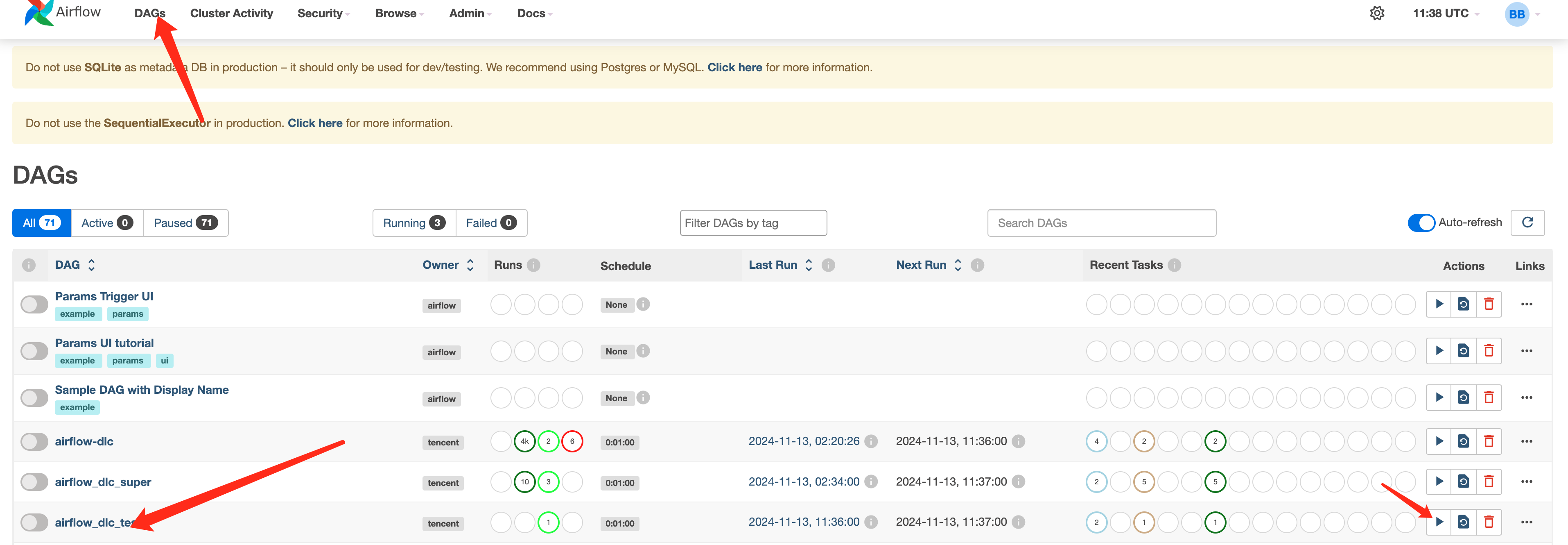
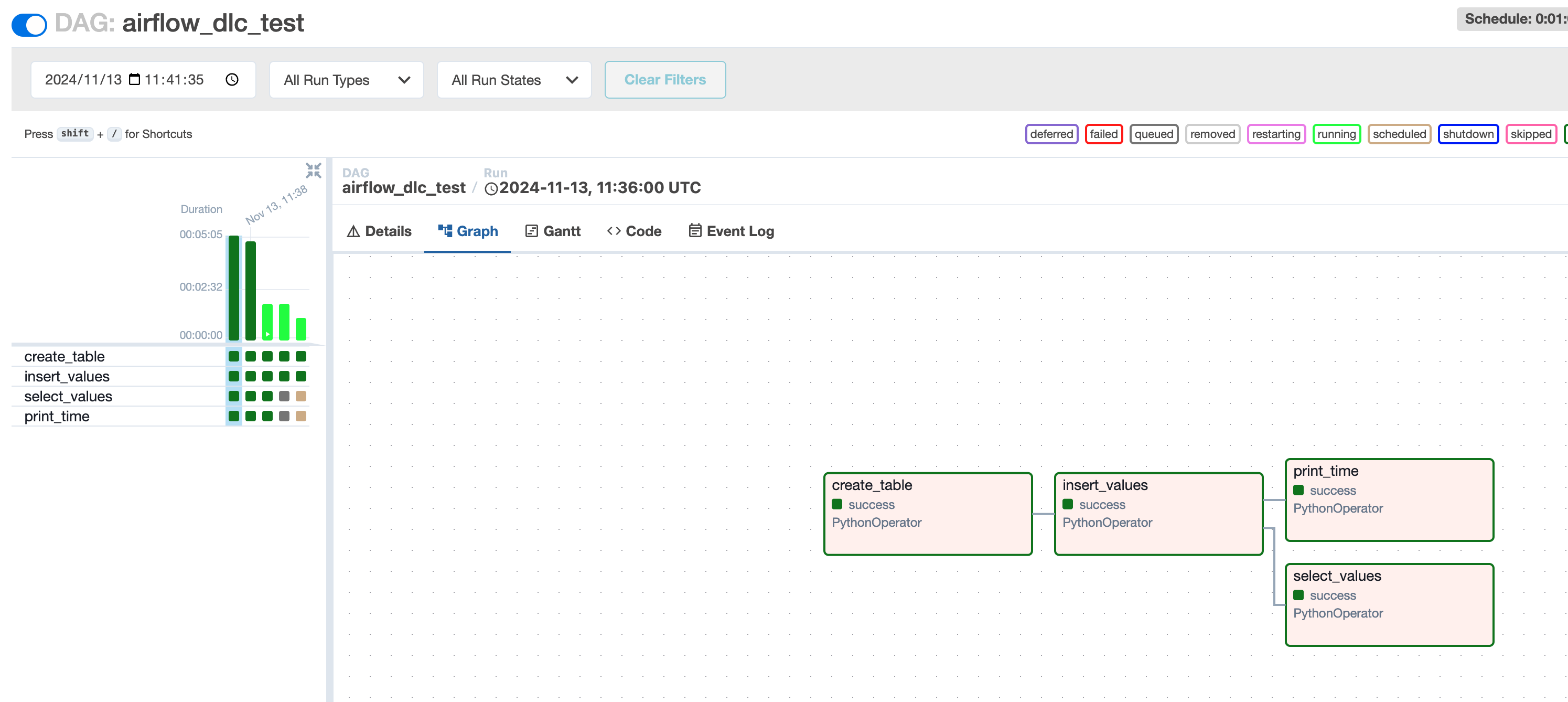
Viewing Task Execution Results
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

