Integration with Web Application Firewall
Last updated:2025-07-30 15:58:16
CAPTCHA provides seamless integration with WAF functionality. Users who use both CAPTCHA and WAF services can apply CAPTCHA verification results to their WAF security policies.
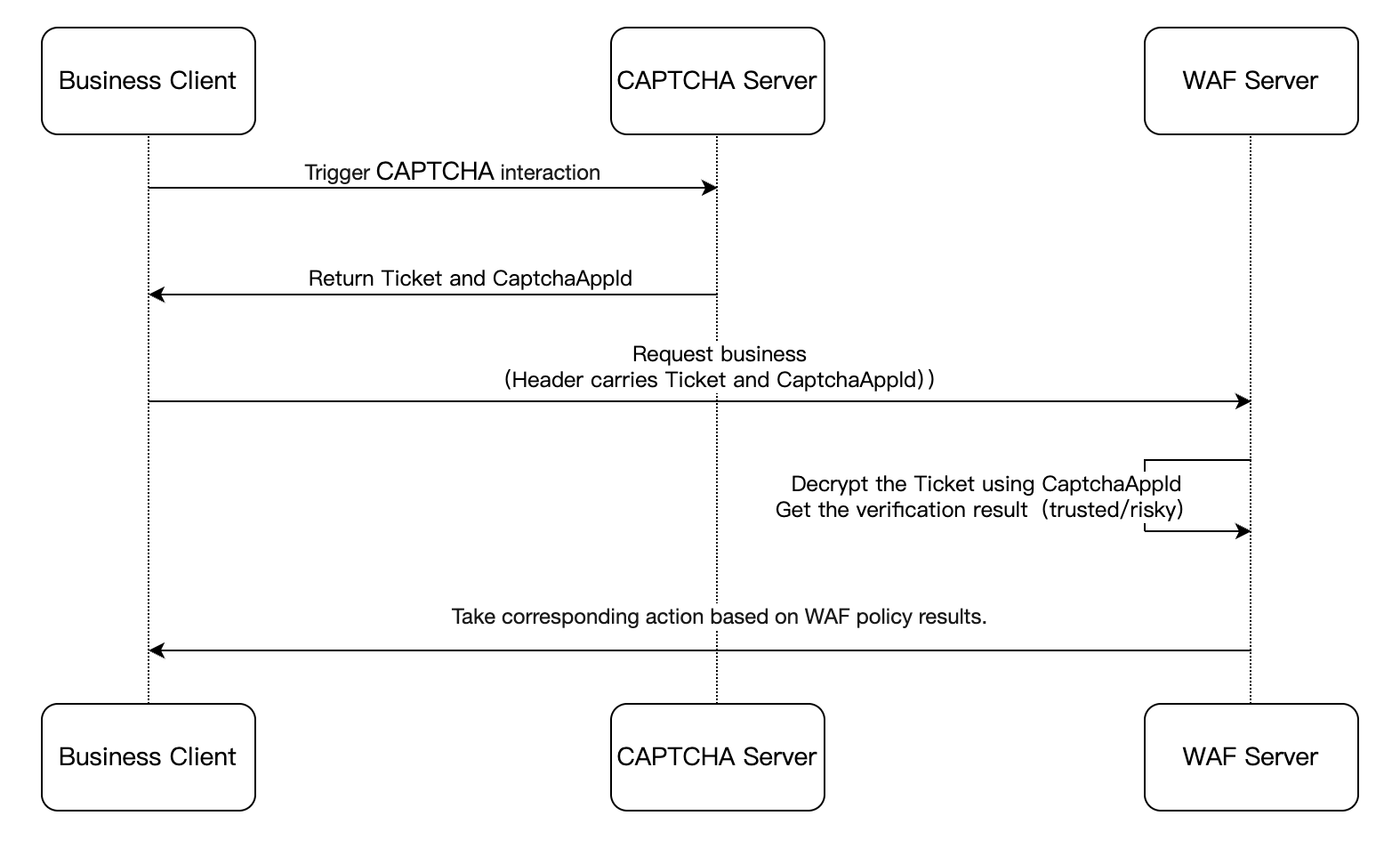
The process is as follows:
1. The business client triggers Captcha interaction and requests to load the CAPTCHA.
2. After the user completes the verification, the CAPTCHA server returns a user verification ticket (Ticket).
3. The business client adds the Ticket and CaptchaAppId to the HTTP request headers and sends them, along with the business request, to the WAF server.
4. The WAF server decrypts the Ticket using the CaptchaAppId. Based on the verification result, the WAF service provider can enforce appropriate security policies according to customer requirements.See WAF document for details.
After decrypting the Ticket, the parameters are described as follows:
Parameter | Type | Description |
CaptchaAppid | Integer | CaptchaAppId of CAPTCHA. |
EvilLevel | Integer | This parameter returns the result of imperceptible verification. 0: The request is trusted. 100: The request is malicious. |
EvilBitmap | Integer | The return value is a decimal number and needs to be converted to a binary number for use. The binary bits and the corresponding major categories of risk control interception policies are as follows: 0: Second-dial proxy IP anomaly. 1: IP address short-term aggregation anomaly (multiple verification attempts initiated within a short period). 2: CaptchaAppId + IP address short-term aggregation anomaly (multiple verification attempts initiated within a short period). 3: CaptchaAppId + IP + device short-term aggregation anomaly (multiple verification attempts initiated within a short period). 4: Traffic characteristic anomaly (e.g., abnormal TCP protocol stack information). 5: Data parameter anomaly (e.g., abnormal browser parameters). 6: Honeypot anomaly (execution of logic that should not be executed). 7: Behavioral clustering anomaly. Note: Example: If EvilBitmap returns 34, converting it to binary yields 100010. The 1st and 5th bits are set to 1, indicating that the corresponding risk control interception policies are: IP address short-term aggregation anomaly and data parameter anomaly. |
DeviceRiskCategory | String | Return value descriptions: 101: Comprehensive score risk. 102: Simulated mouse trajectory risk. Suspected machine-simulated mouse movements (browser only). 201: Malicious request risk. Suspected use of tools to initiate malicious requests. 301: Emulator risk. Suspected use of an emulator. 401: Device tampering risk. Suspected tampering with device hardware information. 501: Suspected black market device risk. Suspected use of devices associated with black or gray market activities. 601: Behavioral risk. Suspected use of automated operations. 701: Browser risk. Suspected browser tampering. |
GetCaptchaTime | Integer | The timestamp when the frontend obtains the CAPTCHA. |
SubmitCaptchaTime | Integer | The time when the CAPTCHA is submitted. |
CreateTime | Integer | The time when the ticket was generated. |
Usid | String | The unique request ID. Usid is required for locating a problem. |
Score | Integer | Risk score.The score ranges from 0 to 100(e.g., 20, 70, 90). A higher score indicates a greater probability that the interaction was initiated by a bot or represents a bot attack. A lower score indicates a greater probability that the interaction was performed by a real human user. Notes: The return value is 0 by default when no risk assessment is performed. |
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

