Notebook 探索
最后更新时间:2025-09-19 17:27:00
说明:
功能概述
WeData 全新推出 Notebook 探索功能,支持通过 Jupyter Notebook 读取腾讯云大数据引擎 EMR 和 DLC 的数据,借助交互式数据分析,进行数据探索和机器学习。
目前 Notebook 探索已上线国内站北京、上海、广州、新加坡、硅谷地域,以及国际站新加坡、法兰克福地域。

功能特性
一键创建工作空间
无需手动安装 Python 环境和配置环境依赖,支持一键创建 Notebook 工作空间,包含完整的 Jupyter Notebook 环境和常用的依赖包。
用户和资源隔离
每个用户在不同项目下独享工作空间,各个工作空间的存储和计算资源相互隔离,用户的任务、文件资源不会相互干扰。
联动大数据引擎底座
支持绑定 EMR 和 DLC 大数据引擎,可以直接读取大数据存算引擎中的数据进行交互式探查、算法模型训练和数据预测性分析。
内置实践教程
Notebook 工作空间内置了大数据系列教程,支持用户开箱即用,快速上手体验。
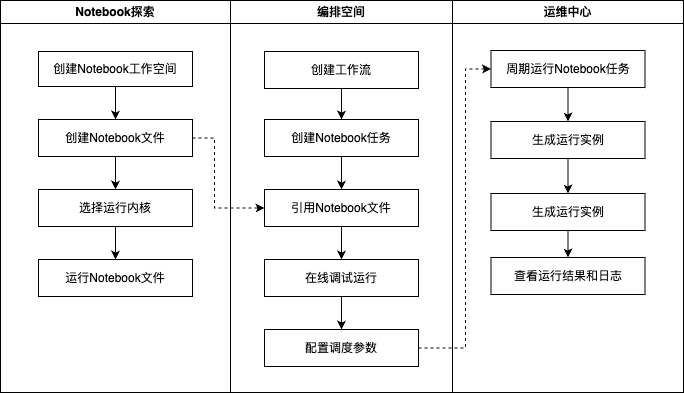
整体使用流程
用户在 WeData 使用 Notebook 的全流程如下图所示:
操作步骤
创建 Notebook 工作空间
1. 登录 数据开发治理平台 WeData 控制台。
2. 单击左侧菜单中的项目列表,找到需要操作 Notebook 探索功能的目标项目。
3. 单击项目名称进入项目
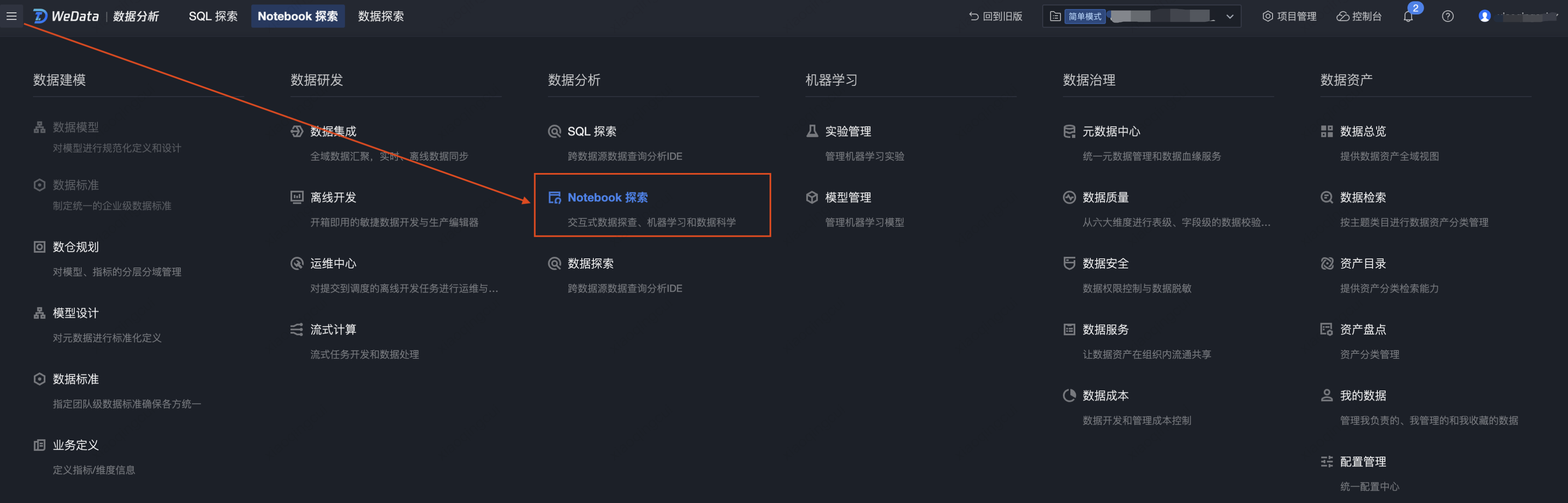
4. 单击页面左上角展开顶部菜单,进入数据分析 > Notebook 探索模块。

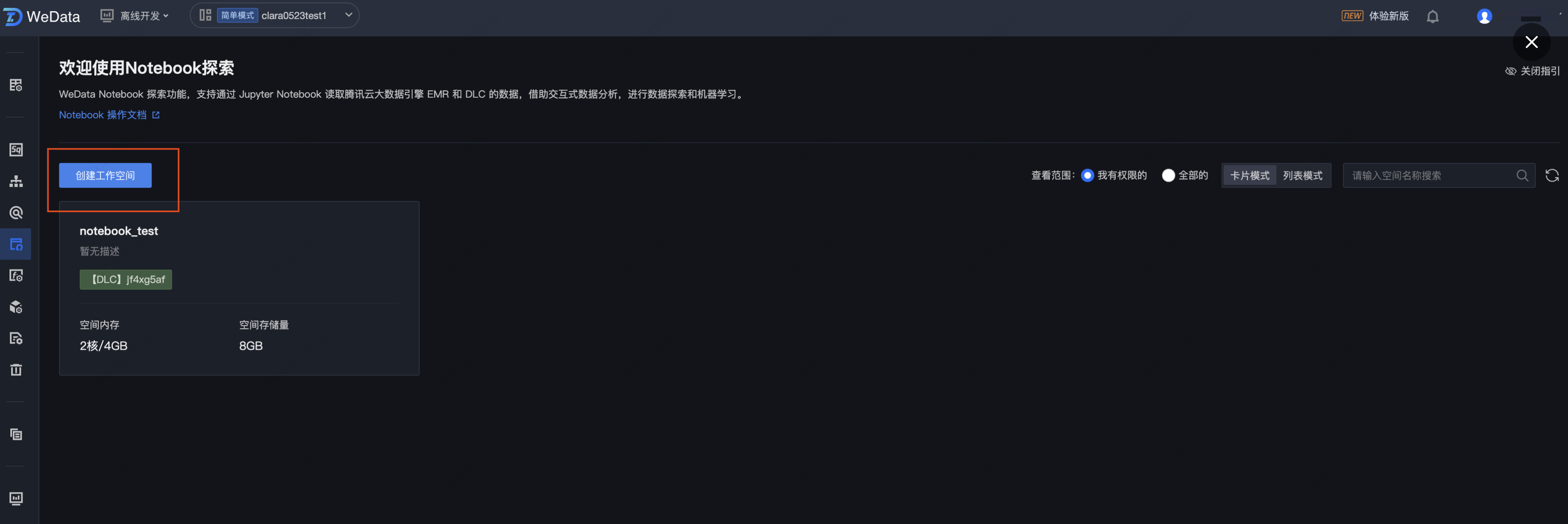
5. 进入 Notebook 探索列表页,单击创建工作空间。

6. 进入工作空间配置页面,进行基本信息和资源配置信息设置。
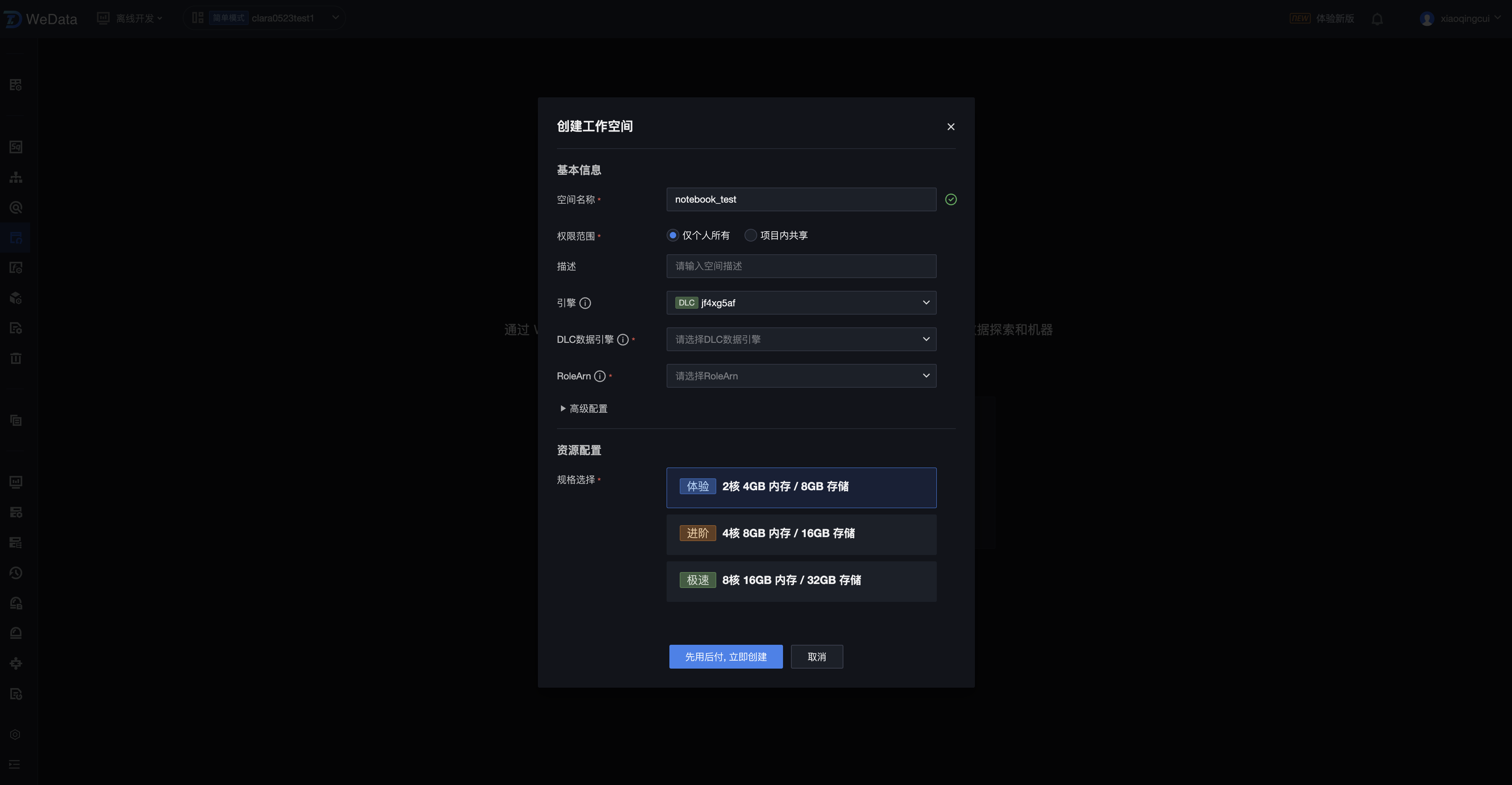

属性项名称 | 属性项说明 | 是否必填 |
基本信息 | 配置 Notebook 工作空间的基本信息,用于创建 Notebook 工作空间实例 | |
空间名称 | Notebook 工作空间名称,支持中文、英文、数字、下划线、中划线,长度不超过32字符 | 是 |
空间模板 | 选择不同模板会在初始化过程中导入不同配置。可选择Jupyter Notebook 导入标准Notebook示例模板或 选择 Deepseek 系列来导入具体模型。 | 是 |
权限范围 | 如果选择“仅个人所用”,则只有当前用户可以进入该工作空间;如果选择“项目内共享”,则项目下的所有成员均可以进入该空间进行协作开发 | 是 |
描述 | Notebook 工作空间描述,支持中文、英文、数字、特殊字符等,长度不超过255字符 | 否 |
引擎 | 支持选择当前项目绑定的 EMR 或 DLC 存算引擎,选择后将与该存算引擎进行预连通,在 Notebook 任务中可以使用 PySpark 的方式进行访问 | 否 |
网络 | 当选择 EMR 引擎时,需要进一步选择网络配置用于进行网络打通,默认使用 EMR 引擎所在的 VPC 和子网 | 是 |
DLC 数据引擎 | 当选择 DLC 引擎时,需要进一步选择该项目下绑定的一个 DLC 数据引擎,用于执行 DLC PySpark 任务。 说明: 仅支持 DLC Spark 作业类型的计算资源。 | 是 |
机器学习 | 如果您选择的 DLC 数据引擎中含有“机器学习”类型的资源组,则会出现该选项,并默认选中。 如果您选择的 DLC 数据引擎中没有“机器学习”类型的资源组,则不会出现该选项,如需使用,请前往 DLC 进行创建。 | 否 |
RoleArn | 当选择 DLC 引擎时,需要进一步选择 RoleArn,用于授权数据存储 COS 的访问权限 说明: RoleArn 为 DLC 引擎访问对象存储 COS 的数据访问策略(CAM role arn),需要用户在 DLC 进行配置。 | 是 |
高级配置 | 可以选择使用 MLflow 管理 Notebook 探索中的实验、数据和模型,该功能目前需要开通白名单使用 | |
MLflow 服务 | 勾选后,则在 Notebook 任务中使用 MLflow 函数创建实验和机器学习,均会上报到 MLflow 服务中,后续可以在机器学习-实验管理、模型管理中进行查看。 | 否 |
资源配置 | 配置工作空间的存储和计算资源,用于执行 Notebook 任务运行、文件存储 | |
规格选择 | 支持的规格包括: 2核 4GB内存 / 8GB存储(体验版) 4核 8GB内存 / 16GB存储(进阶版) 8核 16GB内存 / 32GB存储(专业版) 32核 64GB内存 / 32GB存储 (极速版) | 是 |
工作空间启停管理
启动工作空间
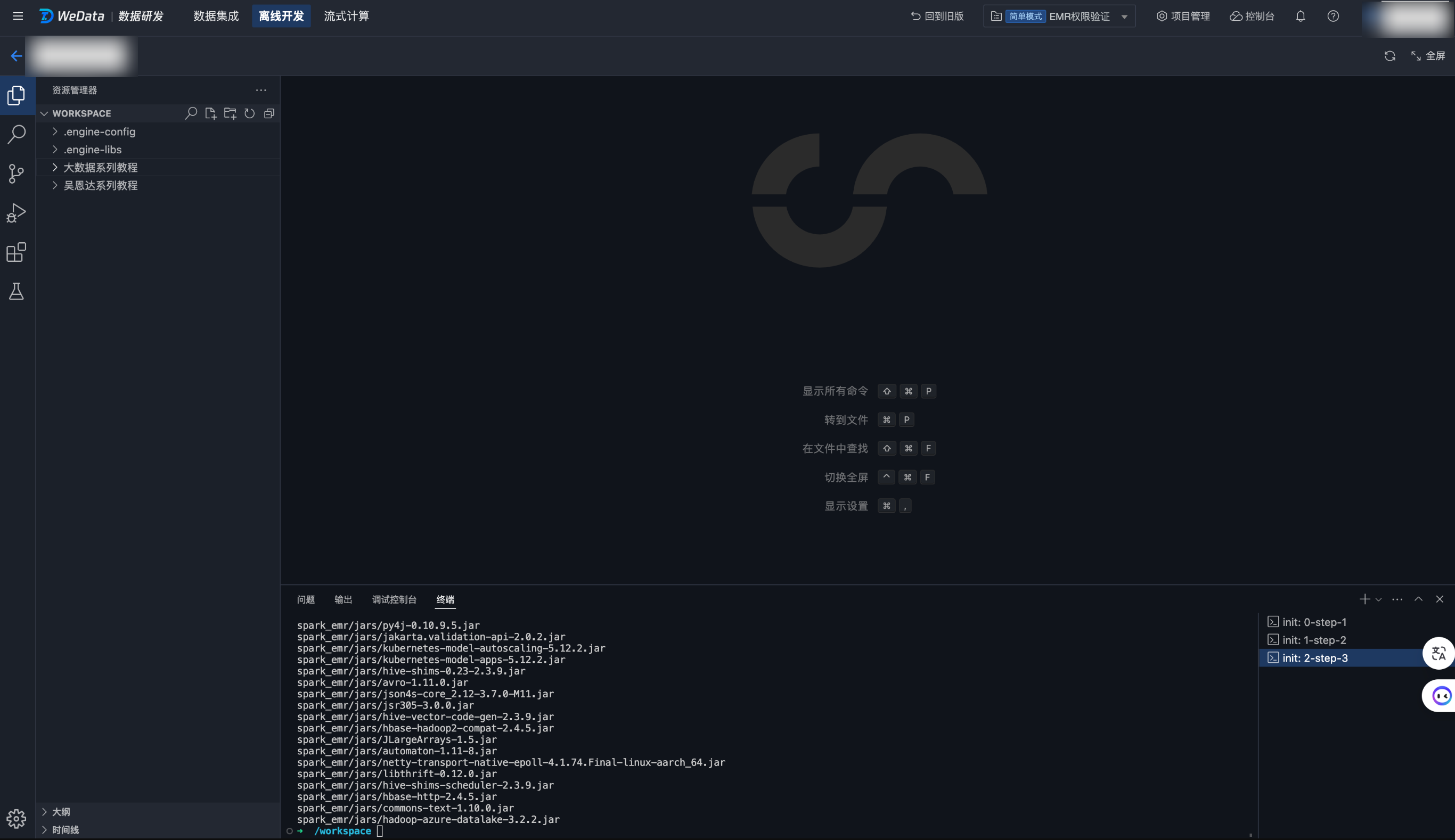
1. 单击立即创建,进入 Notebook 工作空间启动页面。
2. 启动过程中,将为您进行 PySpark 环境配置,并安装 numpy、pandas、scikit-learn 等常用 Python 包,安装过程需要一定时间,请耐心等待直至安装完成。
3. Notebook 工作空间进入如下页面,表示已经启动成功,可以开始 Notebook 任务的创建。

工作空间退出
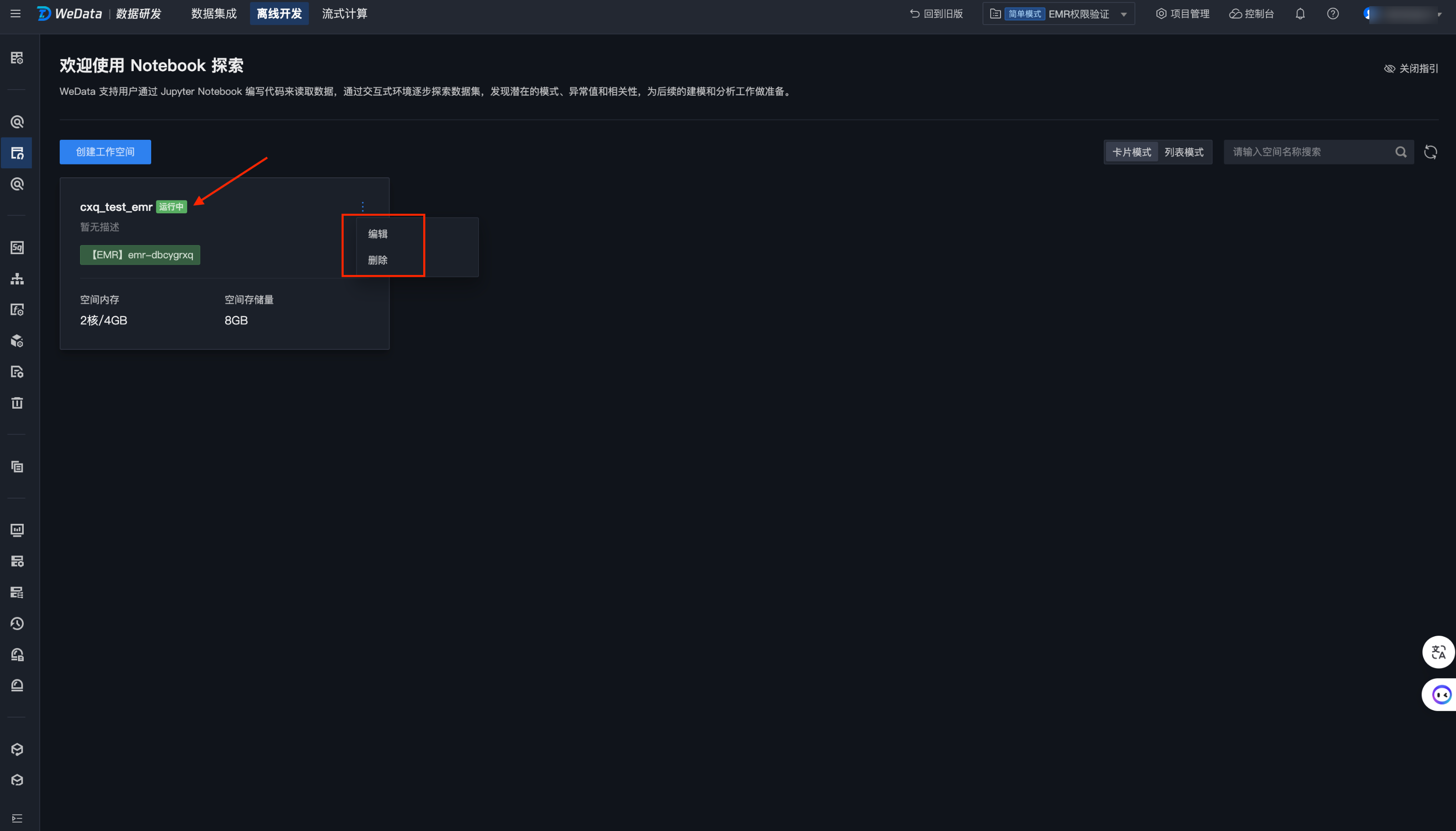
1. 单击左上方退出按钮,则会退出当前工作空间,回到了列表页面。
退出后的工作空间将在十分钟后自动停止,停止状态的工作空间再次启动将恢复开发环境和数据。

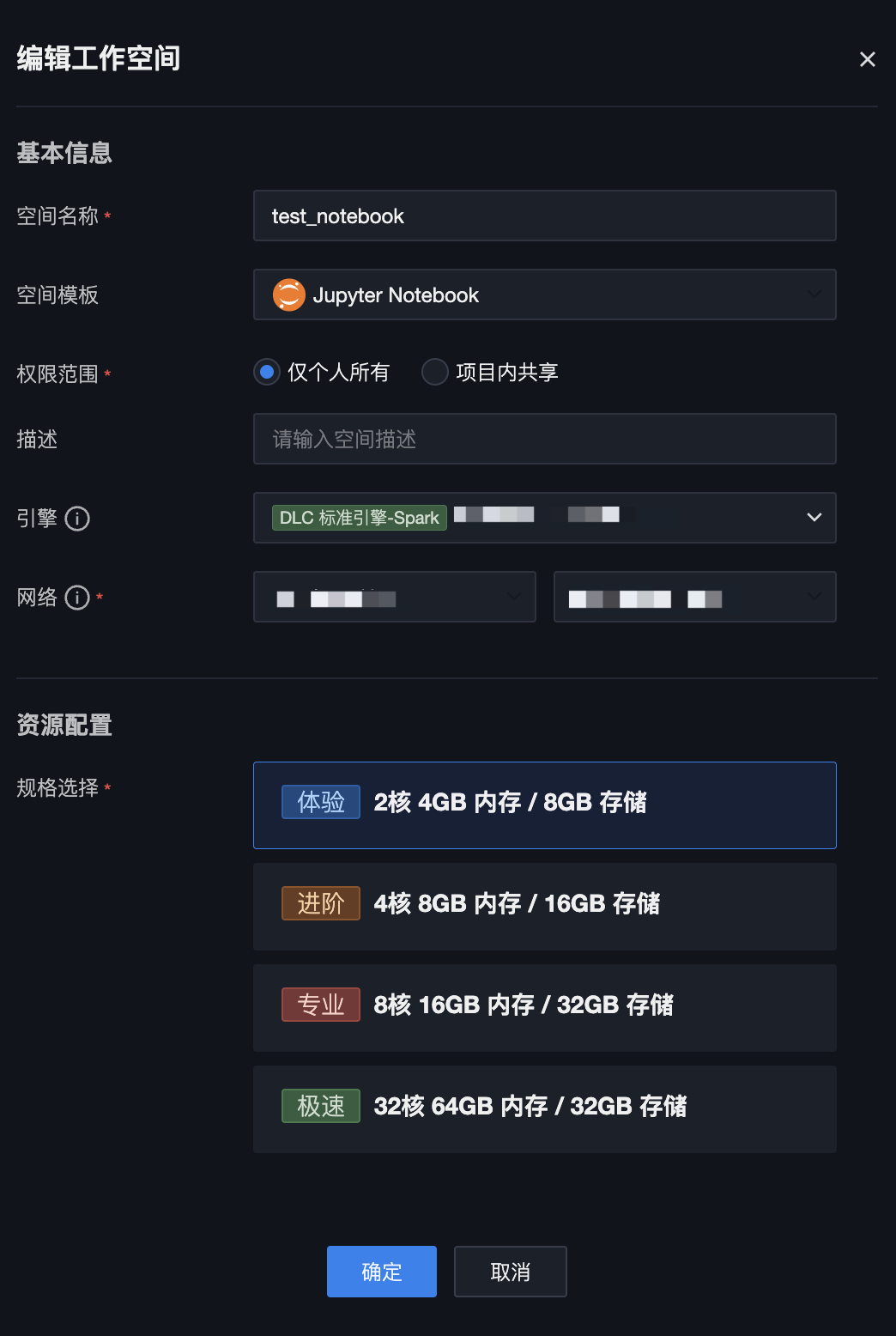
编辑工作空间
单击列表页编辑按钮,支持对当前工作空间的配置信息进行修改。支持修改的配置项包括:空间名称、描述、资源配置。
删除工作空间
单击列表页删除按钮,支持删除当前工作空间。
创建和运行 Notebook 文件
1. 创建 Notebook 文件
在左侧资源管理器可以创建文件夹和 Notebook 文件。
注意:
Notebook文件需要以(.ipynb)结尾。
2. 选择运行内核
进入 Notebook文件,单击左上角选择内核,在弹出的下拉选项中选择内核。
说明:
在 Jupyter Notebook 中,内核(Kernel)是执行代码的后端程序,它负责处理代码单元的执行、计算结果的返回以及与用户界面的交互。
WeData Notebook目前支持两种内核类型,分别为:
Python Environment:Jupyter Notebook 默认的 IPython 内核,支持 Python 代码执行。预置 Python 3.10 版本,可选择内置的 python 3.8 或 python 3.11 版本,或安装其它 python 版本使用。
DLC 资源组:由腾讯云大数据提供的 DLC 远程内核,可将 Python 任务提交到 DLC 资源组中进行运行。
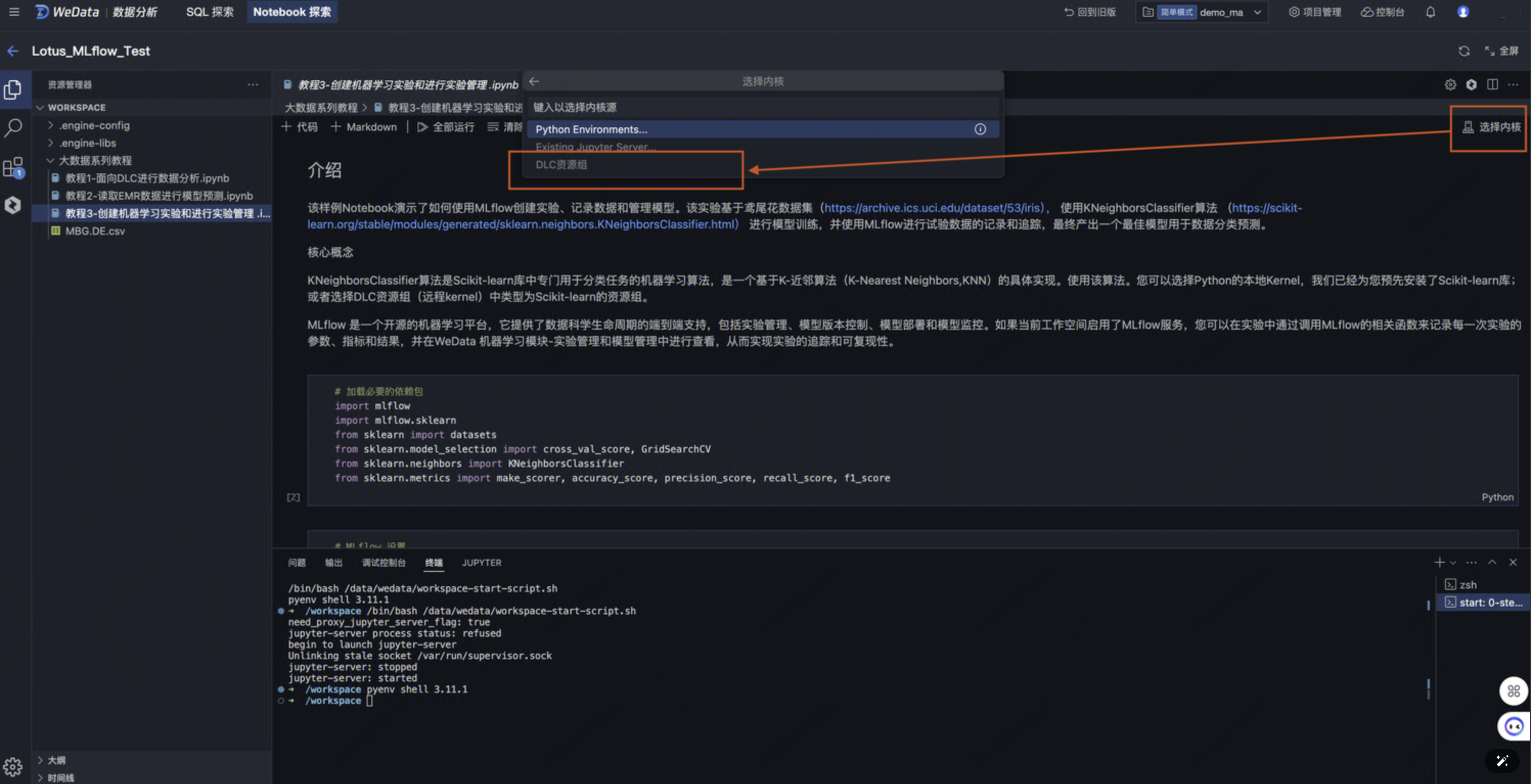
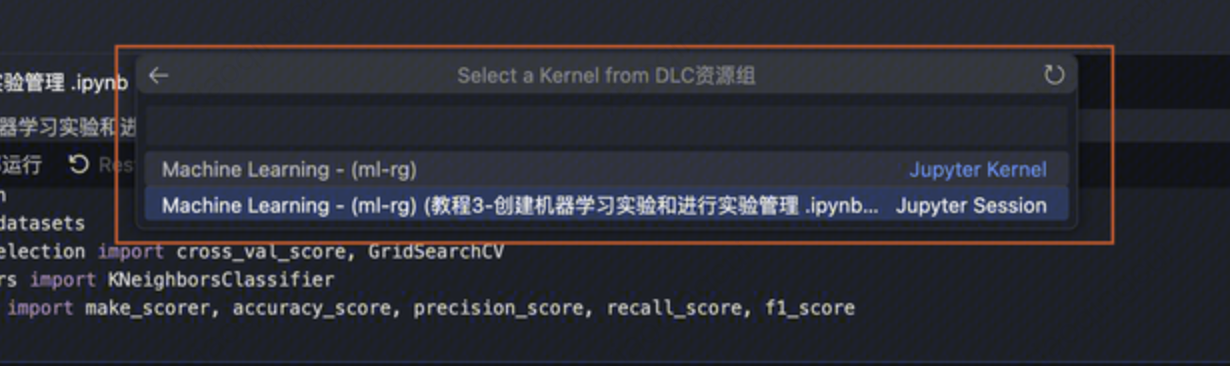
如果选择了 DLC 资源组,在下一级选项中选择 DLC 数据引擎中的某个机器学习资源组实例。
3. 运行 Notebook 文件
单击运行,则会生成一个 Notebook 内核实例并开始运行代码,运行结果显示在每一个 cell 的下方。
周期性调度 Notebook 任务
创建 Notebook 任务
1. 进入项目,并打开菜单数据研发 > 离线开发。


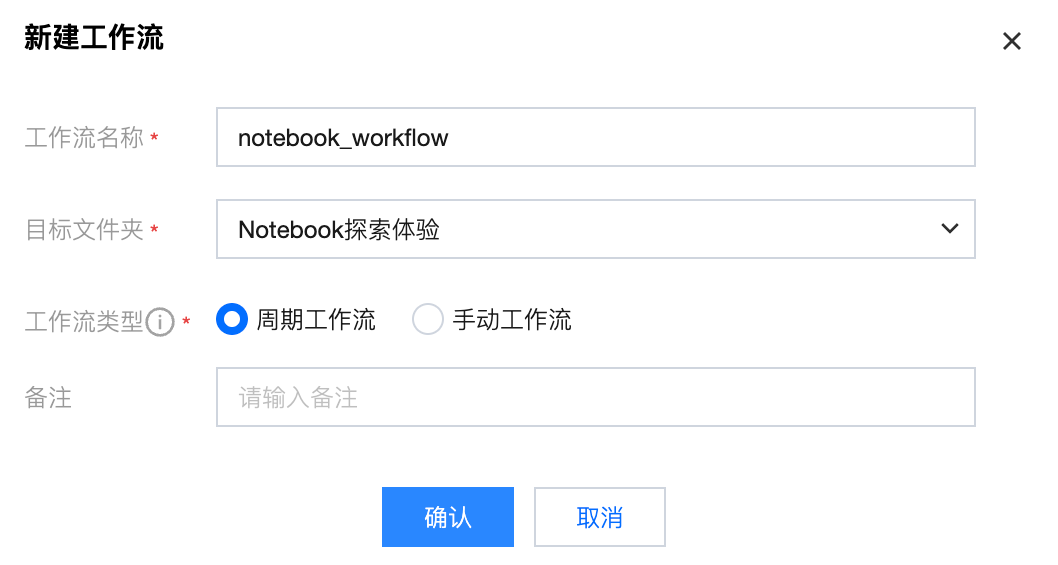
2. 在左侧目录单击新建工作流,并且配置工作流属性信息,包括工作流名称、所属文件夹等。


3. 在工作流中创建任务,任务类型为通用-Notebook 探索,在新建任务页面配置任务基本属性,包括任务名称、任务类型等。
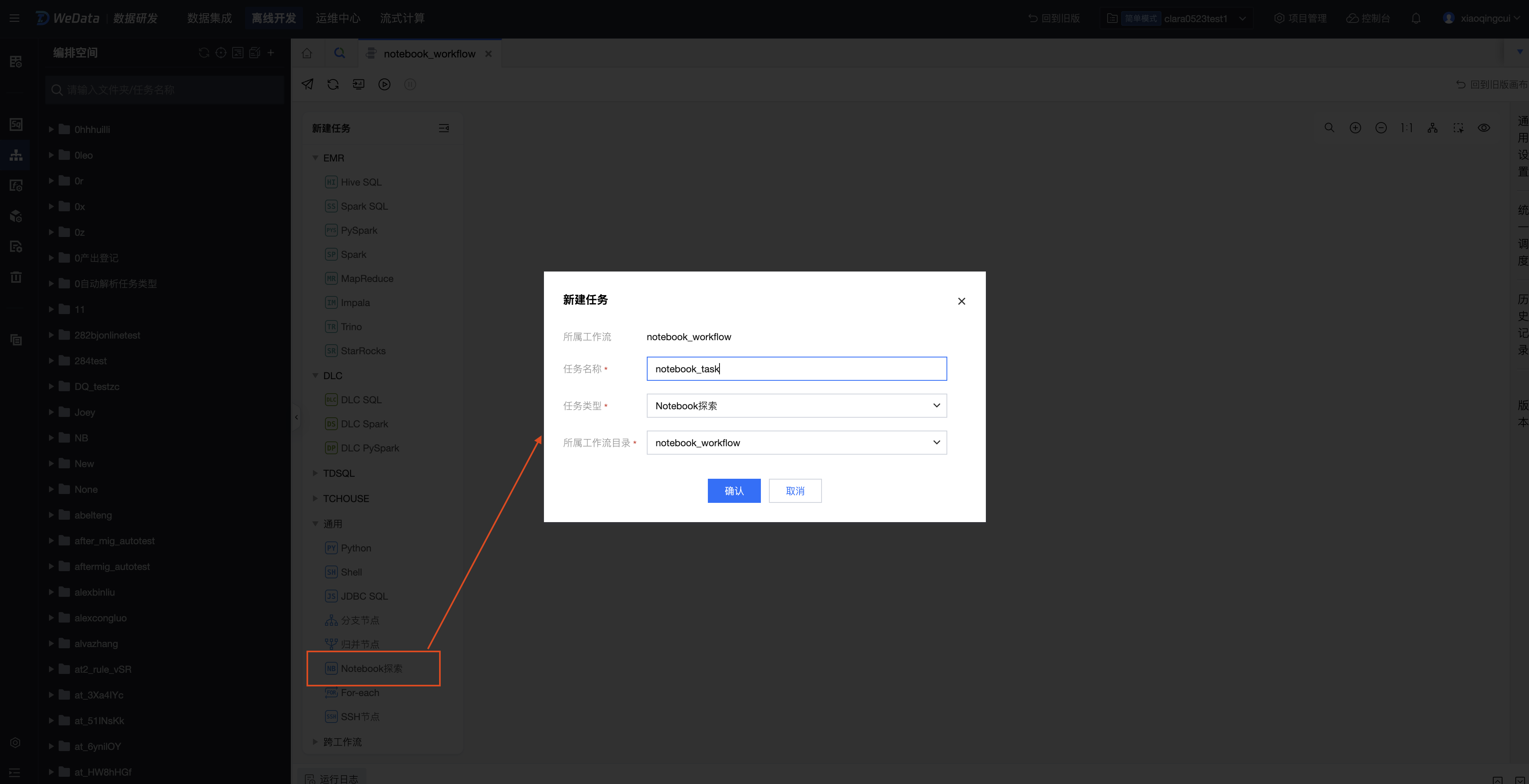

配置和运行 Notebook 任务
在 Notebook 任务配置页面,对某个 Notebook 工作空间中的文件进行引用。
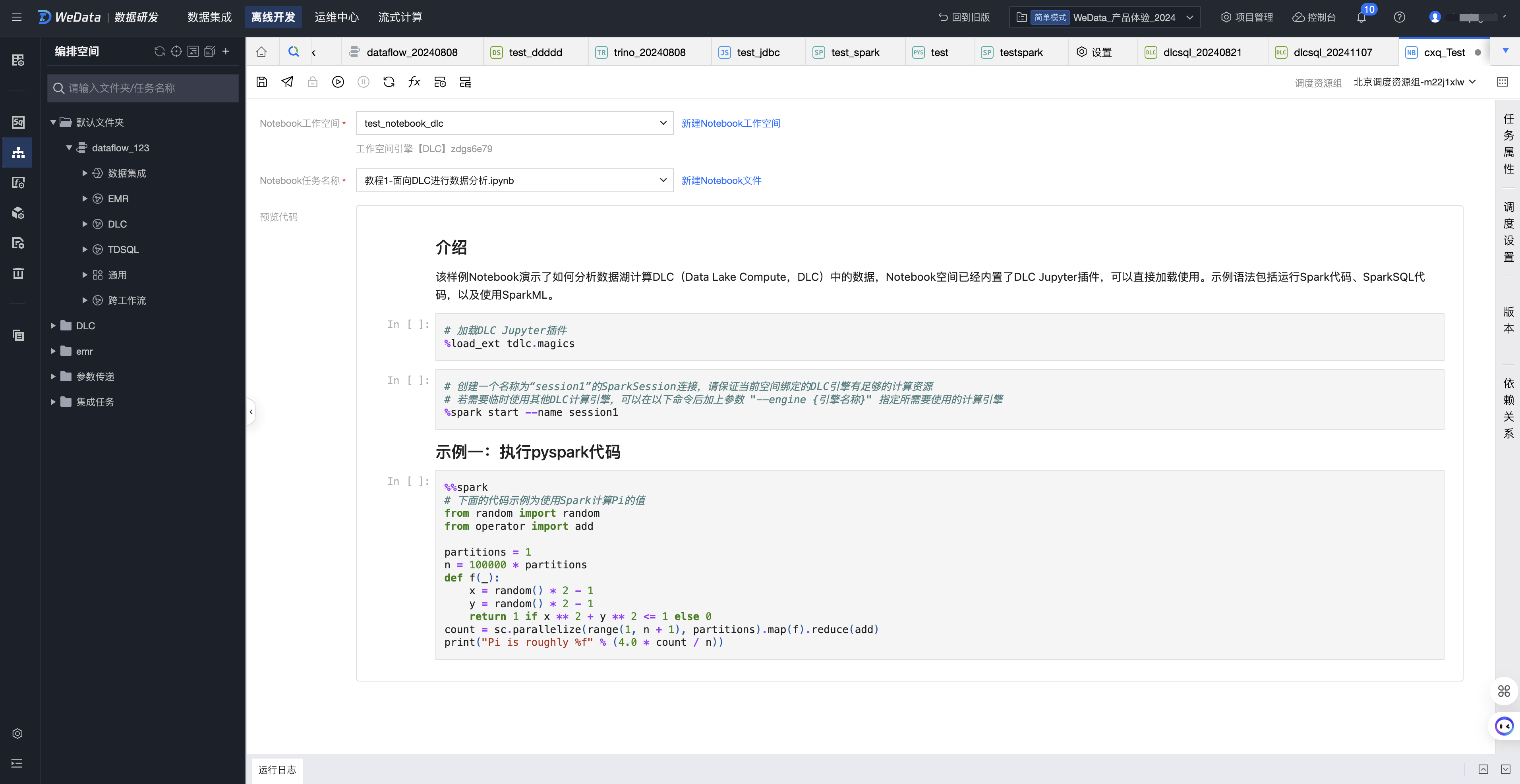
1. 选择 Notebook 工作空间
可以下拉选择当前项目中的所有 Notebook 工作空间。
2. 选择 Notebook 文件
可以下拉选择当前 Notebook 工作空间中的所有文件。备注:如果当前用户没有该 Notebook 工作空间的权限,则无法进入该工作空间进行操作。
3. 预览代码
选择 Notebook 文件后,在下方可以预览 Notebook 文件具体内容。
4. 运行 Notebook 任务
在右上角选择调度资源组,单击运行可以对当前 Notebook 文件进行在线运行,下方可以查看运行日志、运行代码和运行结果。
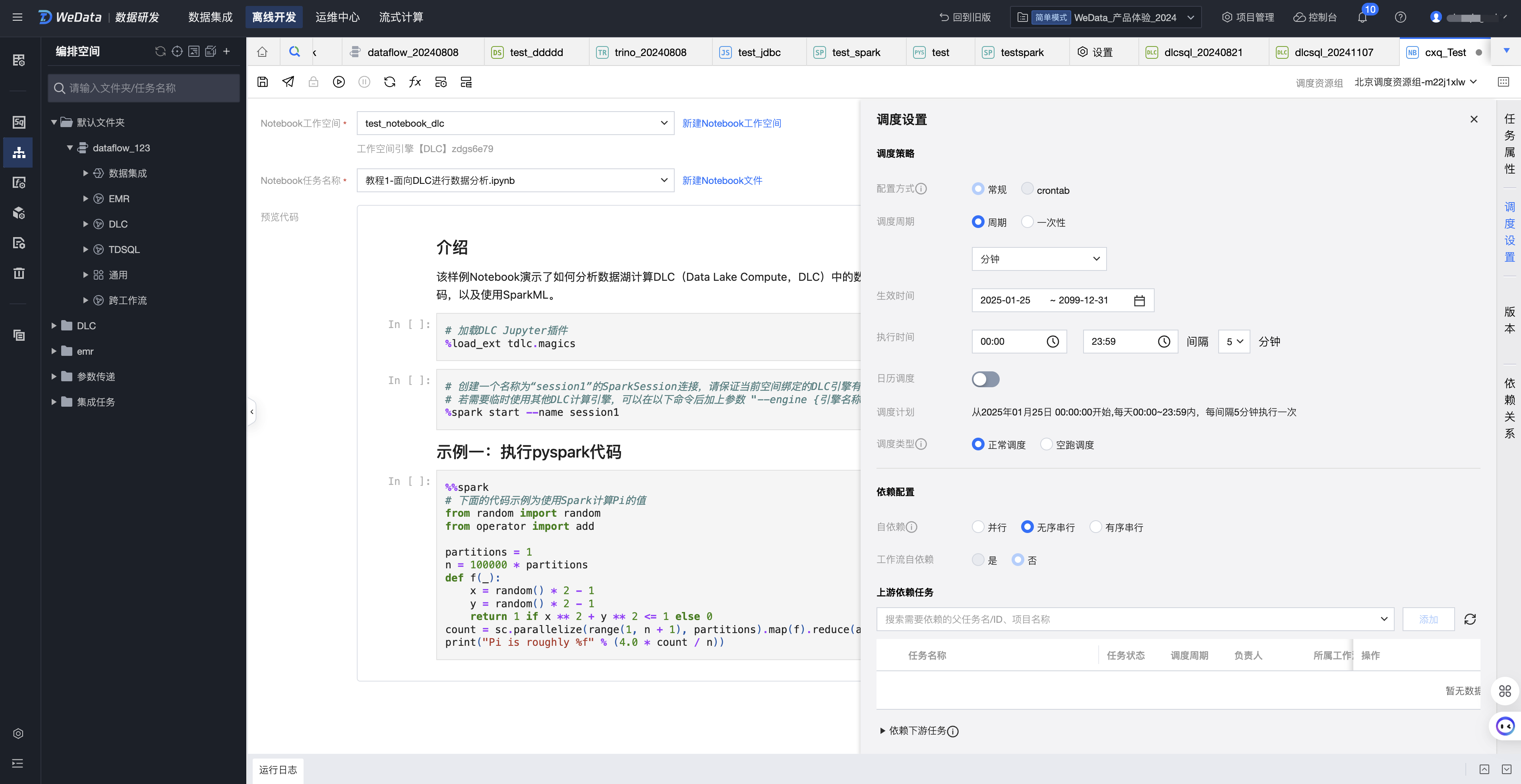
配置调度
1. 单击右侧调度配置,设置当前 Notebook 任务的调度周期,例如,下图设置为每5分钟运行一次。

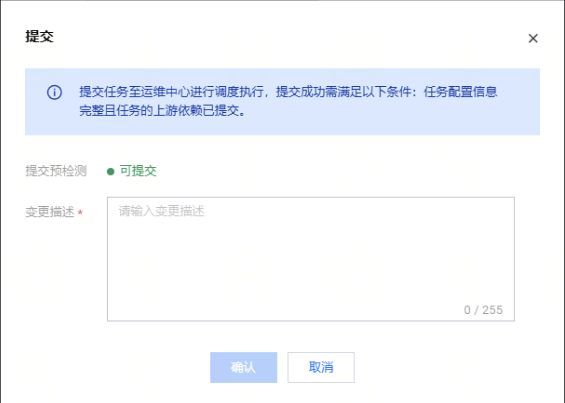
2. 单击提交按钮,将当前任务提交至周期调度。
任务运维
1. 进入数据研发 > 运维中心。
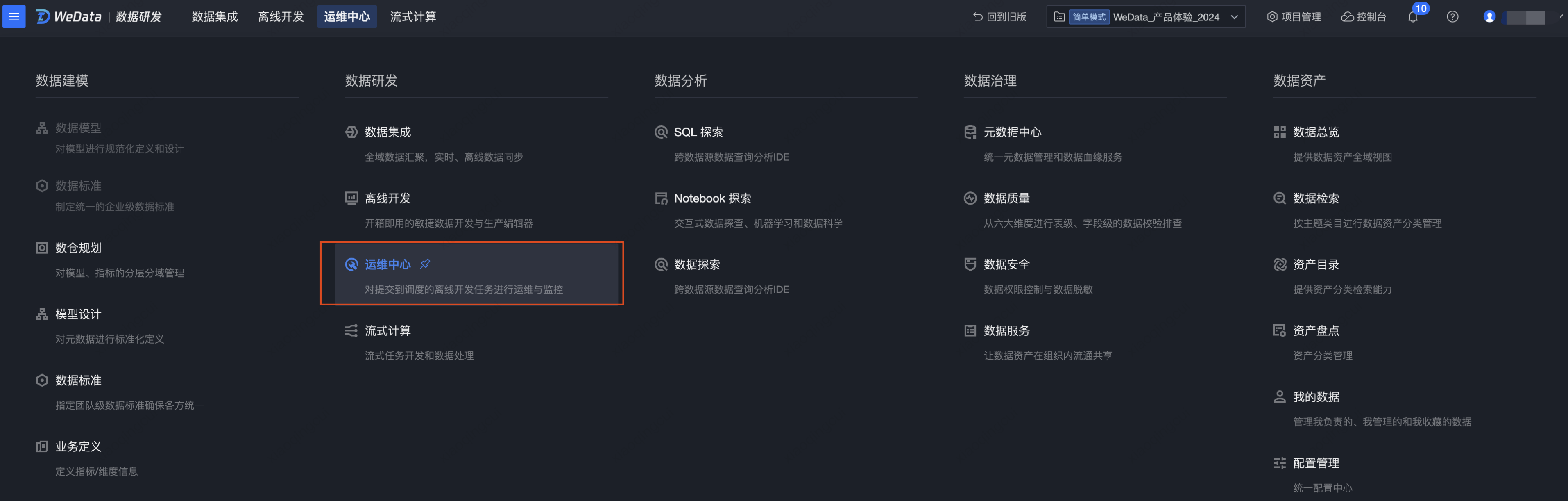
2. 任务运维
单击任务运维,可以看到提交至调度的工作流和工作流中的任务节点。
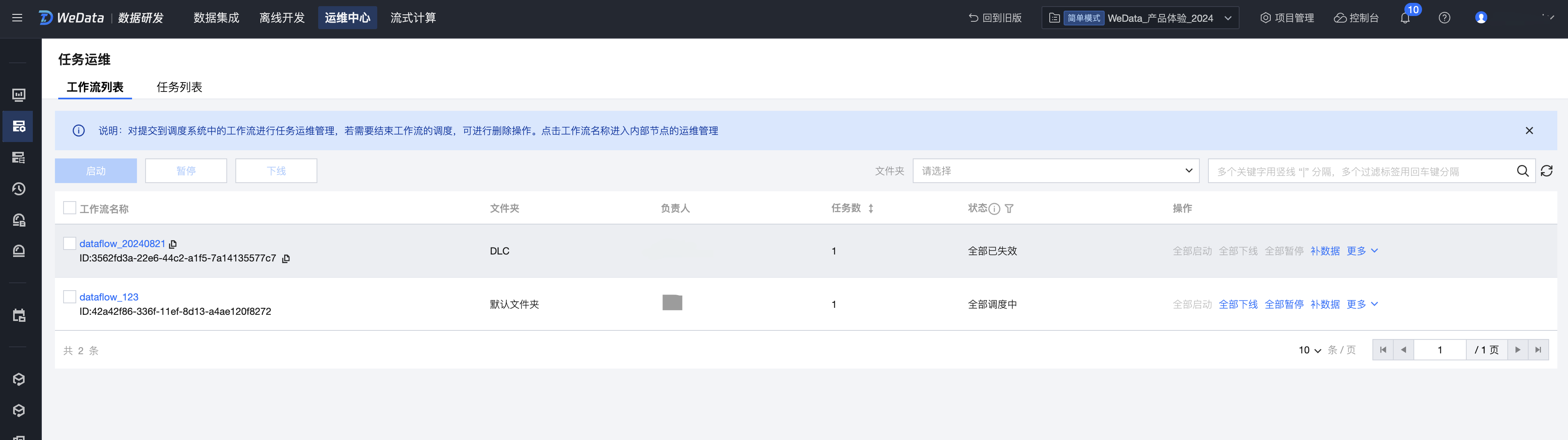
3. 实例运维
单击实例运维,可以查看上述工作流产生的每一个周期实例。
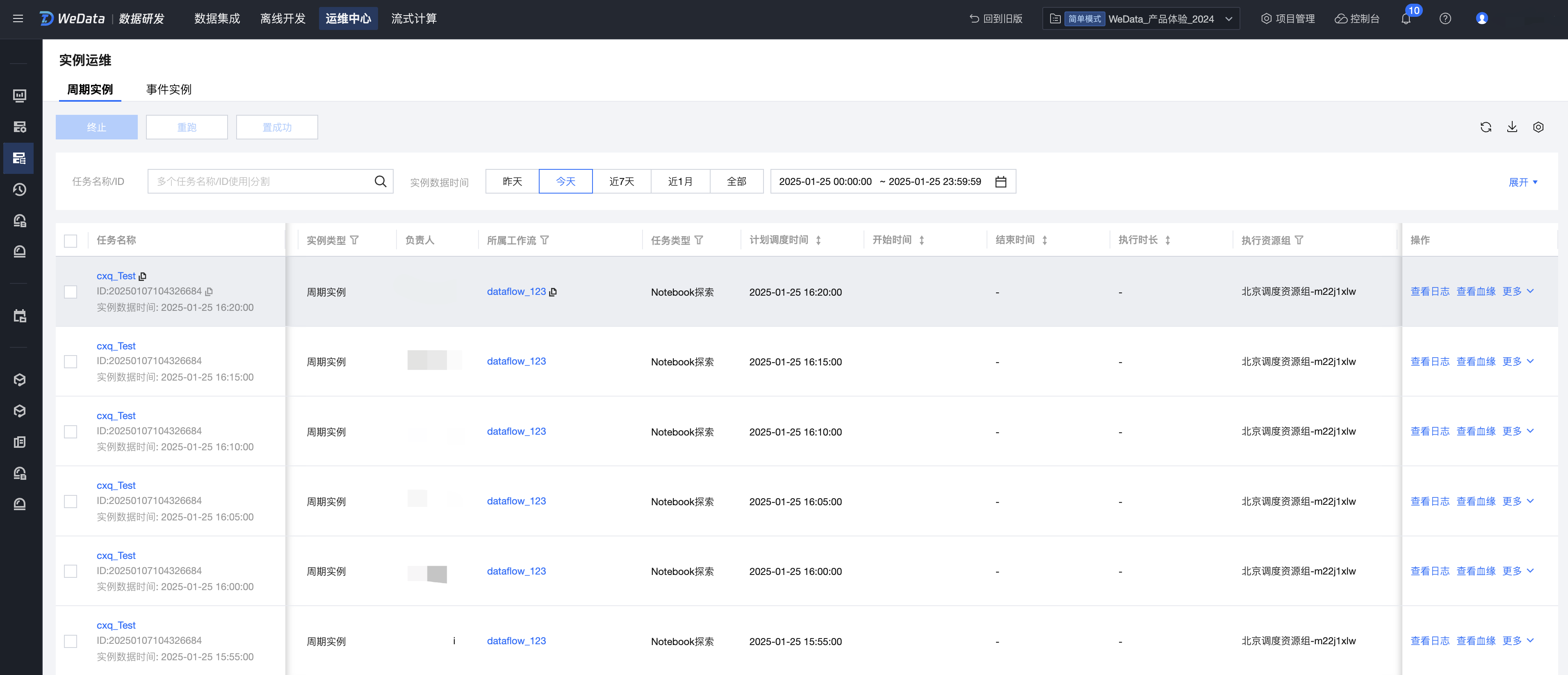
4. 进入实例详情,可以查看运行的日志和结果。
实践教程
Notebook 工作空间内置了开箱即用的大数据系列教程,用户可以快速上手体验。
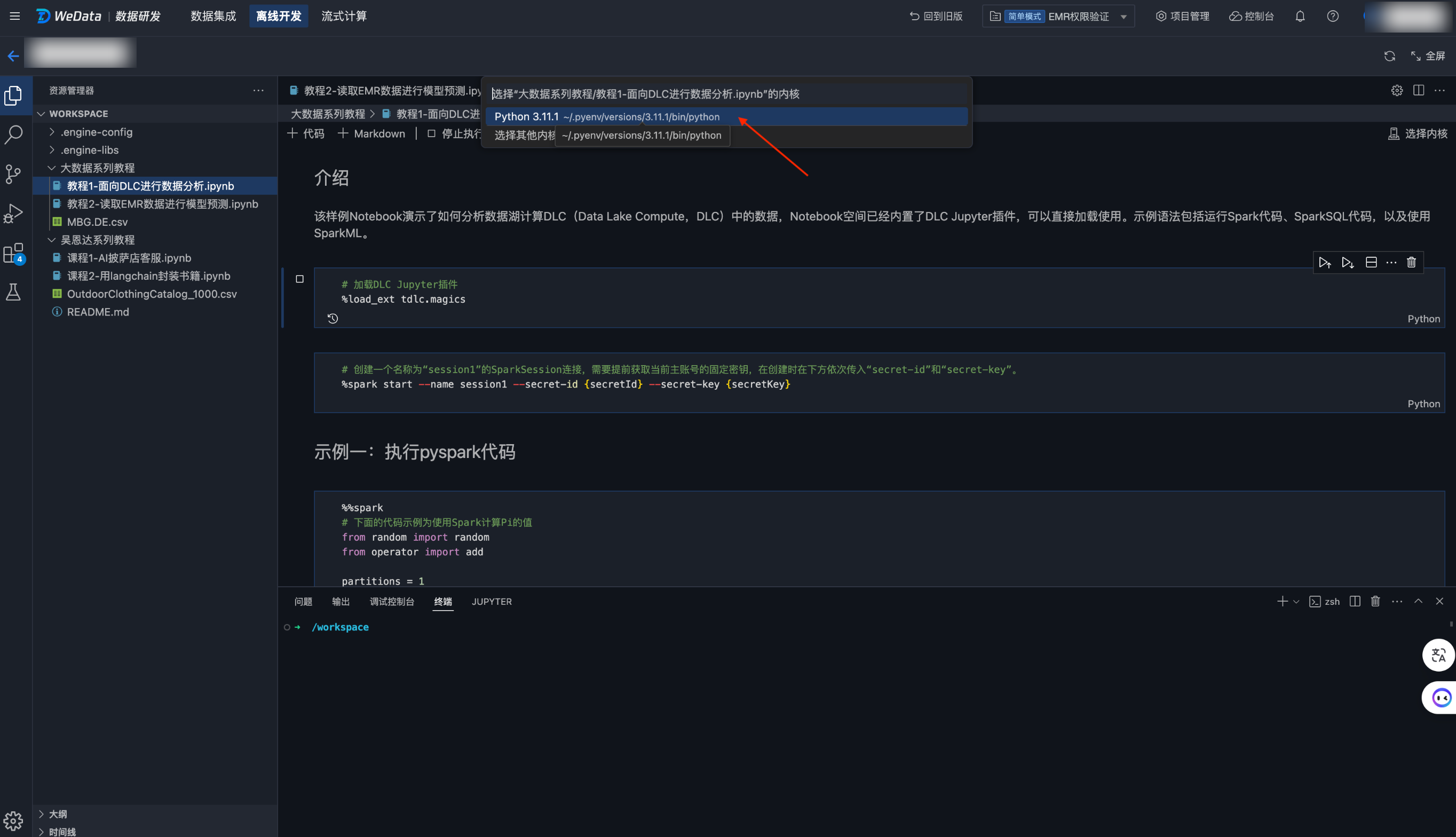
教程一 使用 DLC Jupyter 插件进行数据分析
该样例 Notebook 演示了如何分析数据湖计算 DLC(Data Lake Compute,DLC)中的数据,Notebook 空间已经内置了 DLC Jupyter 插件,可以直接加载使用。示例语法包括运行 Spark 代码、SparkSQL 代码,以及使用 SparkML。
注意:
使用该教程,Notebook 工作空间需要绑定 DLC 引擎,且不勾选“使用机器学习资源组”;内核需要选择 Python Environment,WeData Notebook 将用 Jupyter 插件的方式与 DLC 进行交互。

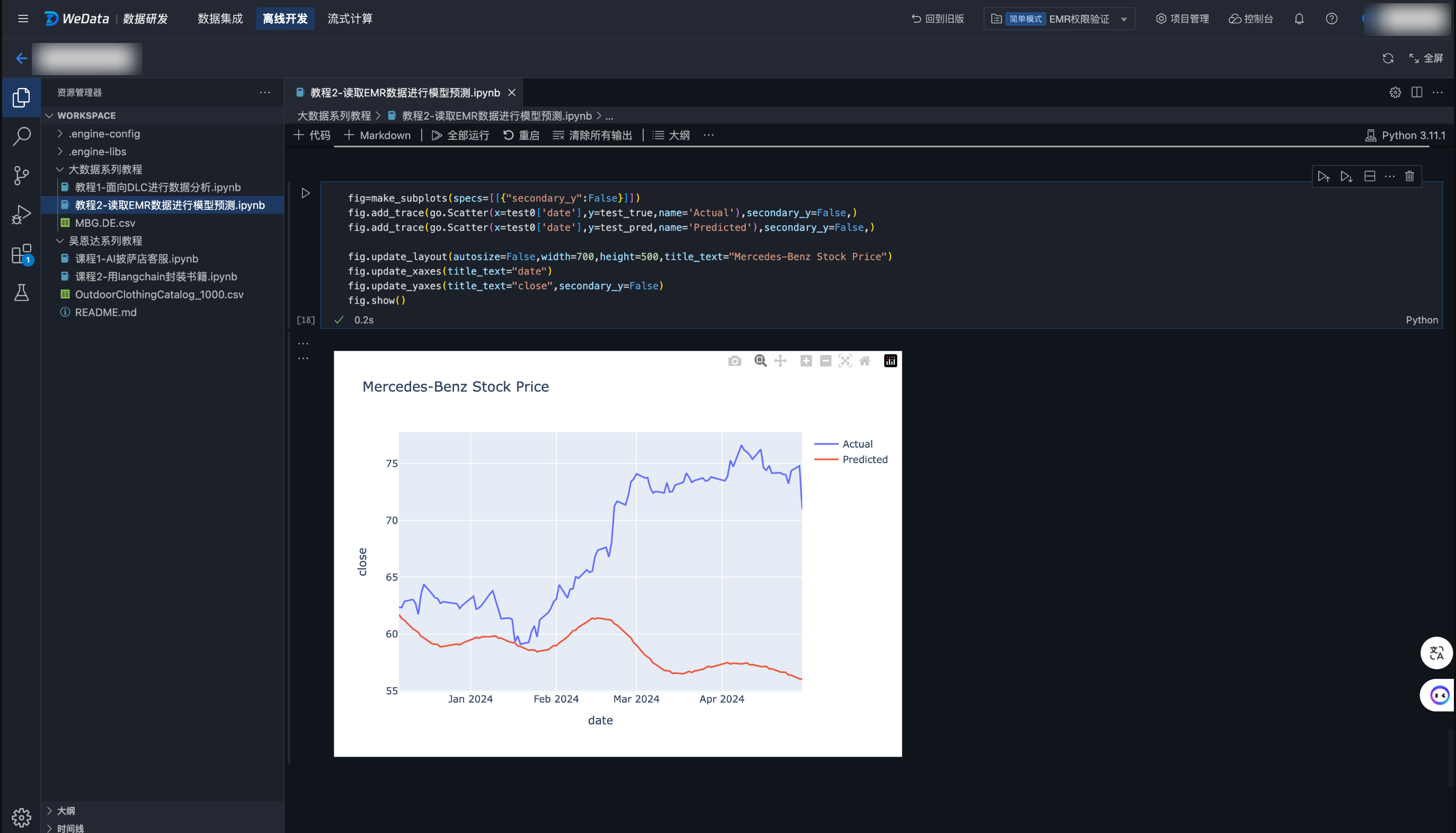
教程二 读取 EMR 数据进行模型预测
1. 该样例 Notebook 演示了如何创建 EMR-Hive 表,并且将本地数据导入到 EMR-Hive 表中。然后从 EMR-Hive 表中读取数据并转化成 pandas DataFrame 进行数据准备。
2. 完成数据准备后,您可以使用 Prophet 时间序列算法来训练一个预测模型,最后进行模型准确性的评估和预测。
注意:
使用该教程,Notebook 工作空间需要绑定EMR引擎。

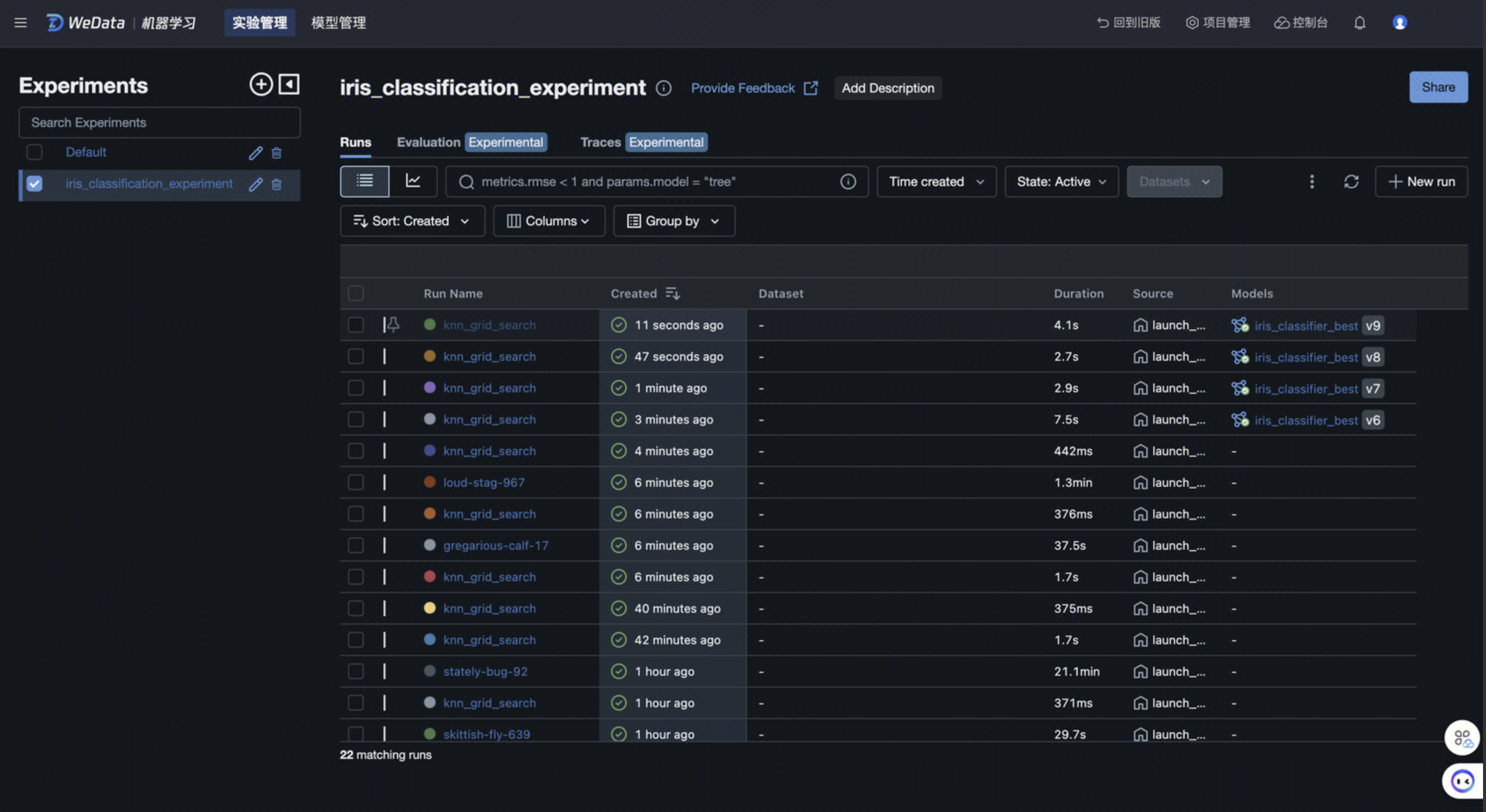
教程三 创建机器学习实验和进行实验管理
该样例 Notebook 演示了如何使用 MLflow 创建实验、记录数据和管理模型。该实验基于 鸢尾花数据集, 使用 KNeighborsClassifier 算法 进行模型训练,并使用 MLflow 进行实验数据的记录和追踪,最终产出一个最佳模型用于数据分类预测。
注意:
使用该教程,Notebook 工作空间需要绑定 DLC 引擎,且勾选“使用机器学习资源组”;内核需要选择 DLC 资源组,WeData Notebook 将会把 Notebook 文件远程提交到 DLC 到执行。
MLflow 是一个开源的机器学习平台,它提供了数据科学生命周期的端到端支持,包括实验管理、模型版本控制、模型部署和模型监控。如果当前工作空间启用了 MLflow 服务,您可以在实验中通过调用 MLflow 的相关函数来记录每一次实验的参数、指标和结果,并在 WeData 机器学习模块 > 实验管理和模型管理中进行查看,从而实现实验的追踪和可复现性。
文档反馈

