Public Network Access Instructions
Last updated:2025-12-05 18:42:45
Overview
This document provides a detailed description of the solutions for implementing public network access in Cloud Dedicated Zone (CDZ).
Solution Comparison
CDZ provides three distinct architecture solutions to ensure secure and efficient public network access for your business. The following is a detailed comparison of these solutions to help you select the most suitable one based on your actual business scenarios:
Solution | |||
Solution Description | Access the public network through the public network product in the (primary) region where your CDZ is located. | Access the public network through the self-owned Internet Data Center (IDC). | Access the public network through the local public network cluster in CDZ. |
Scenarios | General scenarios. | A local public network egress exists. | High network performance, large-scale traffic egress, and self-owned public network resources are required. |
Prerequisites | Supported by default. | Deployment of a Direct Connect (DC) gateway is required during CDZ activation. The self-owned IDC and public network access capability are required. | Self-owned IP ranges are usually required. Confirmation of the need to deploy the local public network cluster in CDZ during CDZ activation is required |
Core Path | Use the public network capabilities of the region where your CDZ is located. | CVM in CDZ → Direct Connect (DC) → Private network of the self-owned IDC → Public network cluster in the IDC → the Internet. | Use the local public network cluster to access the Internet. |
Billing Rule | Pay for the resources of Elastic IP (EIP) and Cloud Load Balancer (CLB) in the public cloud based on actual consumption. | Committed use fee of the DC gateway cluster in CDZ. | Committed use fee of the local public network cluster in CDZ. |
Complexity | Low (simple cloud configuration) | High (requiring proper configuration of the DC gateway and network interconnection with the local IDC) | Low (provided by Tencent Cloud) |
[Common] Solution 1: Accessing the Public Network Through the Product Network Product in the (Primary) Region Where Your CDZ Is Located
Scenarios
This solution is suitable for scenarios where no local public network cluster is deployed in the CDZ environment and traffic forwarding through the self-owned IDC is not required. In this case, the Internet access can be achieved by using the public network capabilities of the primary region of Tencent Cloud. This solution offers high flexibility in deployment and is applicable to most general scenarios, especially the following scenarios:
Requirement for rapid business launch: The need to quickly establish public network access capabilities without going through complex local egress deployment processes.
No IDC infrastructure: Enterprises do not have self-built IDCs, or their existing IDCs cannot access the public network.
Operational agility and elasticity: The need to use EIP or public network CLB resources on the cloud, and take advantage of their benefits such as on-demand configuration, flexible scaling, and convenient maintenance.
Prerequisite Dependencies
A connection between CDZ and the primary region is established. DC is supported by default.
The traffic for public network access cannot exceed the bandwidth supported by DC.
Network Architecture
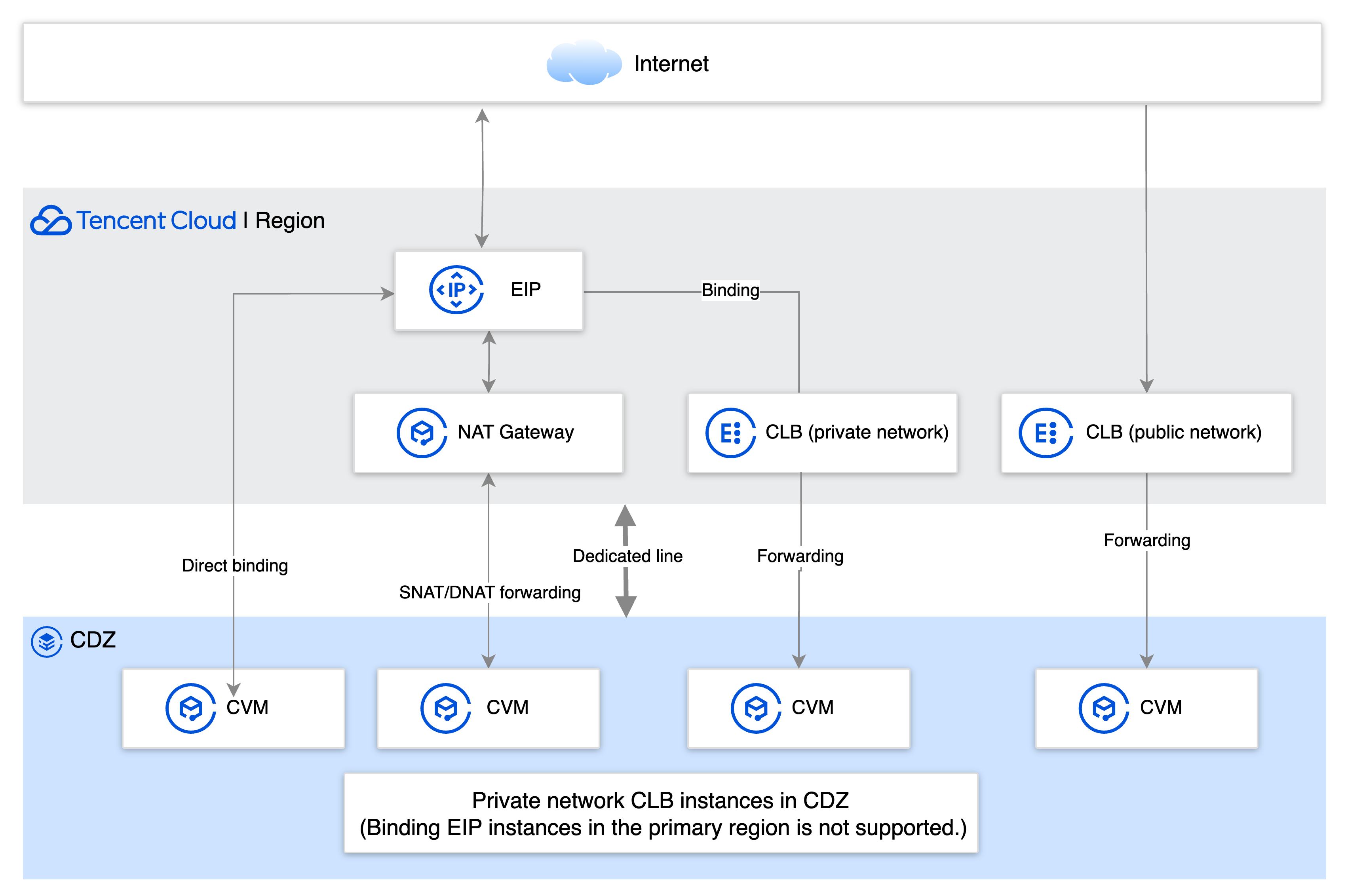
Operation Process
We provide 4 sub-solutions based on the inbound and outbound scenarios.
Solution | [Recommended] A | [Recommended] B | [Recommended] C | D |
Solution Description | Bind EIP to CVM. | Bind NAT Gateway to CVM. | Regional public network CLB. | Regional private network CLB and EIP. |
Billing Mode |
Scenarios
This solution is suitable for business scenarios where an EIP needs to be directly provided for the CVM instance in CDZ. Public network traffic is forwarded to the interior of CDZ through the EIP of the primary region.
Operation Process
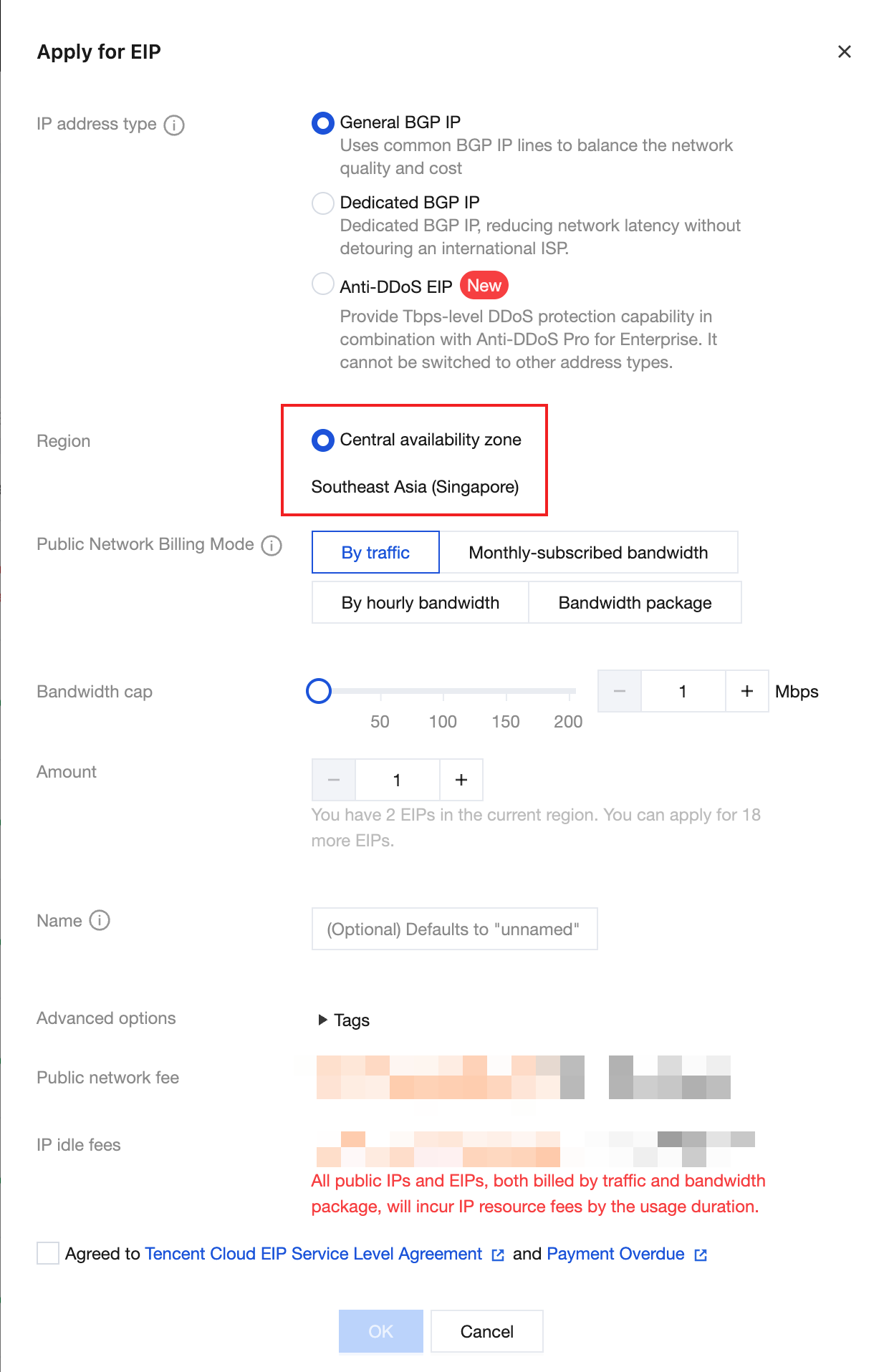
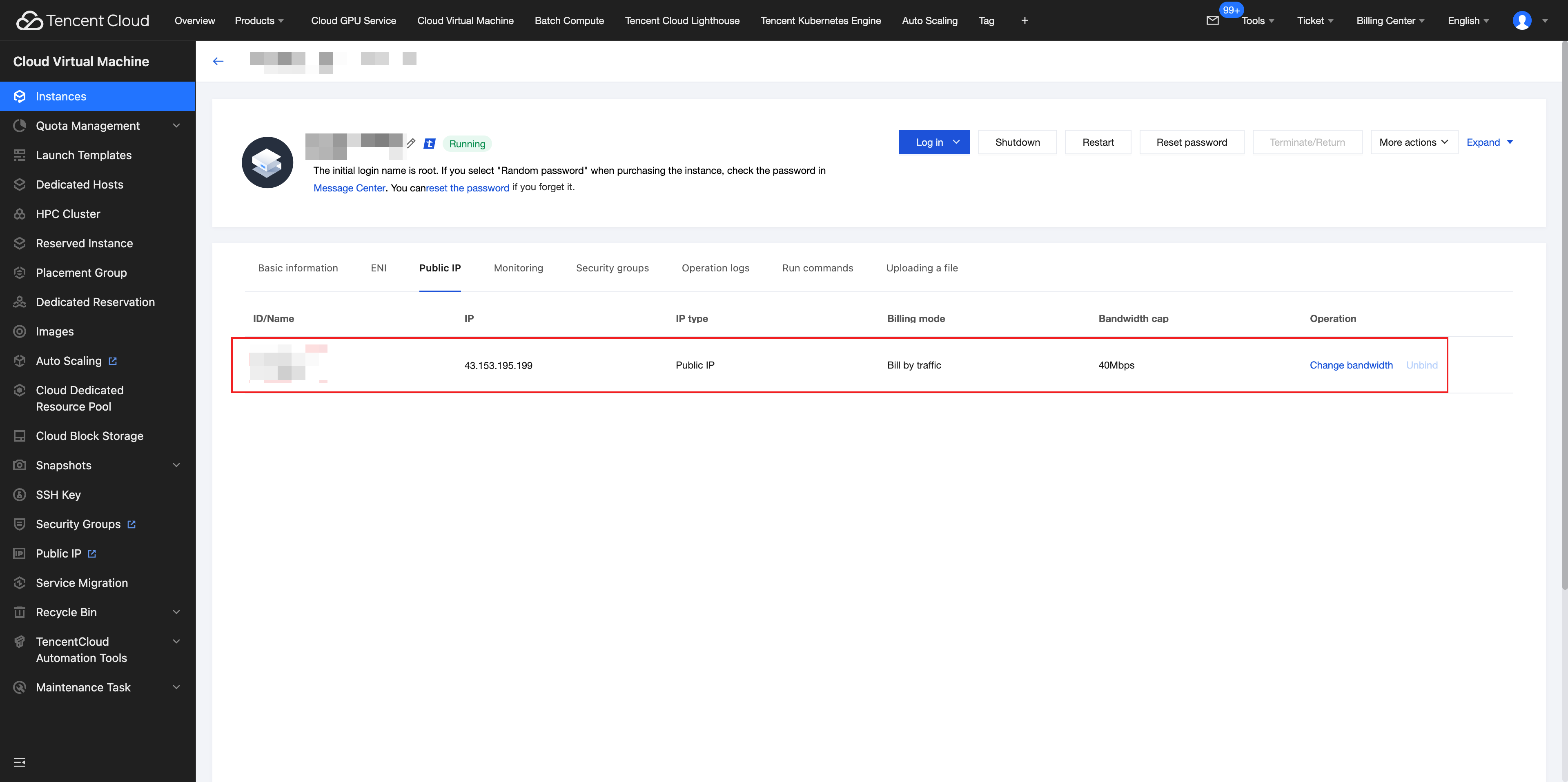
1. Apply for an EIP: On the Public IP page in the console, apply for an EIP in the central AZ of CDZ's primary region. For detailed operations, see Applying for an EIP.
2. Bind an EIP:
2.1 Log in to the CVM console.
2.2 Select the CVM instance in CDZ to which you want to bind the EIP.
2.3 On the instance details page, choose IP/NIC > Bind Elastic IP.
2.4 Select the applied EIP to complete the binding.
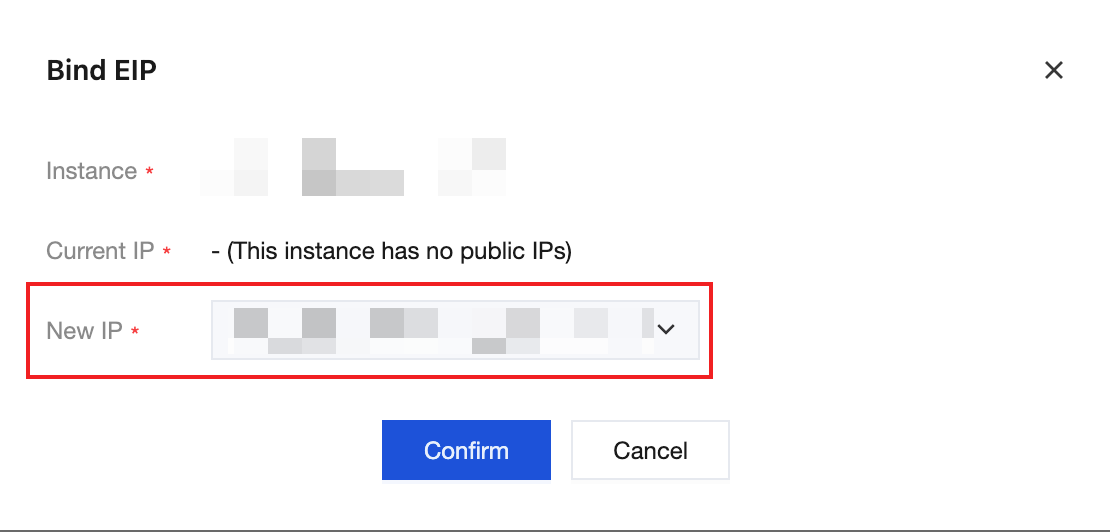
3. Verify the binding result: Confirm the EIP is successfully bound on the instance details page.
4. Test public network connectivity: Log in to the CVM instance from the console and use the
ping command to test public network connectivity.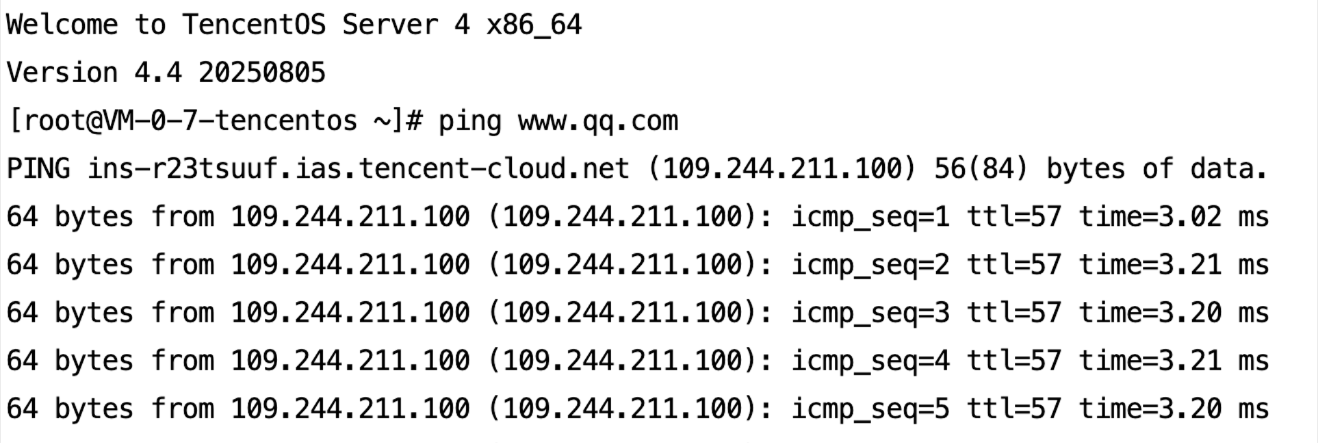
Scenarios
This sub-solution is suitable for users who expect to access the public network without exposing the private IP addresses of their CVM instances. The public network NAT Gateway provides public network access capabilities for multiple CVM instances (without EIPs) in a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). It also supports mapping EIPs and ports to the private IP addresses and ports of the CVM instances, enabling public network access to CVM instances in the VPC.
Tencent Cloud NAT Gateway supports multiple features, including Source Network Address Translation (SNAT), Destination Network Address Translation (DNAT), gateway traffic control, traffic alarms, Bandwidth Package, security protection, and automatic disaster recovery. It features high performance, large capacity, and cross-availability zone disaster recovery capabilities.
Operation Process
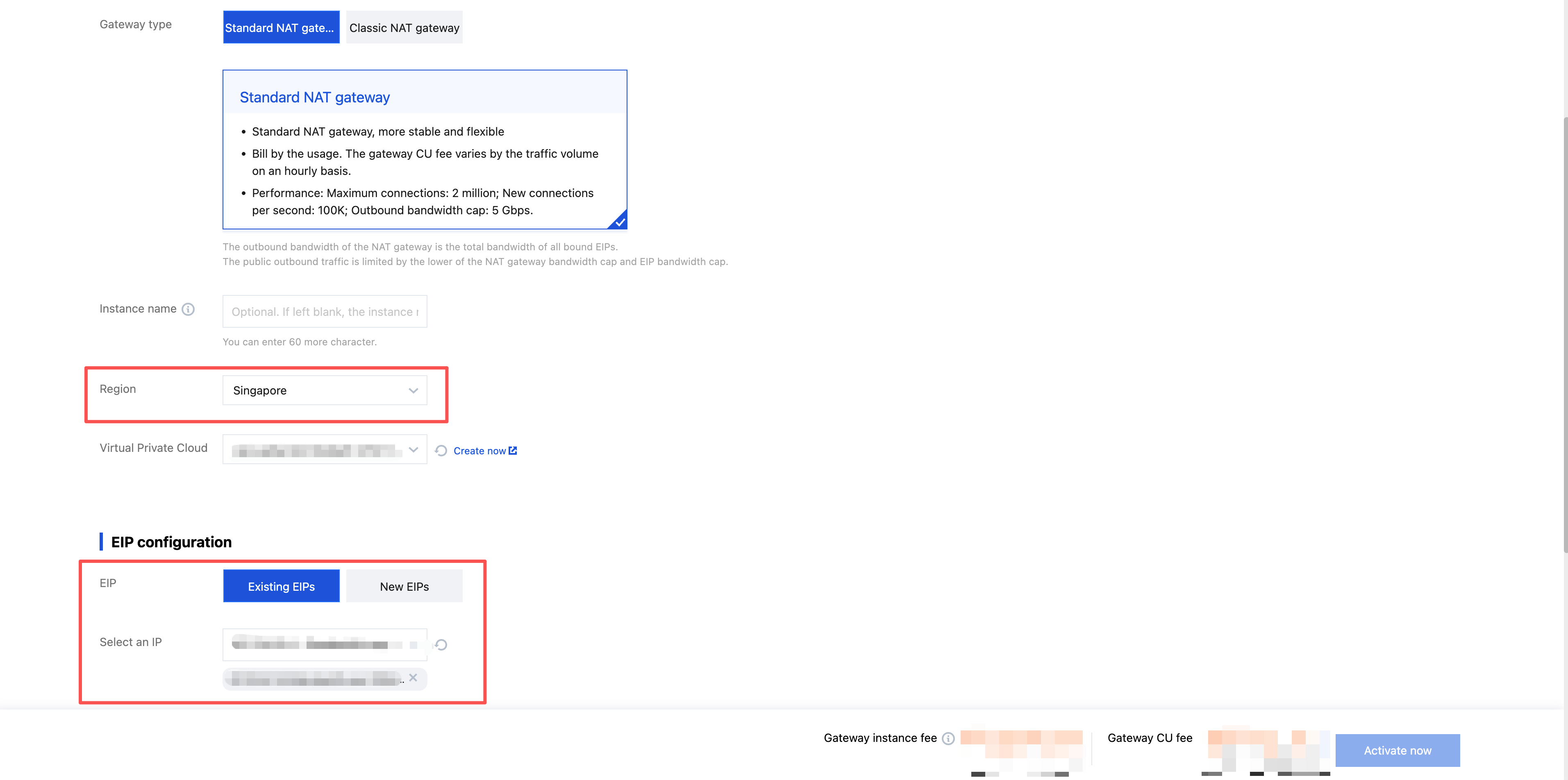
1. Create a NAT Gateway and bind an EIP:
1.1 Log in to the NAT Gateway console, select a region, and click Create.
1.2 Create a public network NAT Gateway with the configuration as follows:
Region: Select the CDZ primary region.
VPC: The selected VPC must include the CDZ subnet.
EIP:
Existing EIP: Use an existing EIP under your account.
Create an EIP: An EIP is automatically assigned by the system to the NAT Gateway.
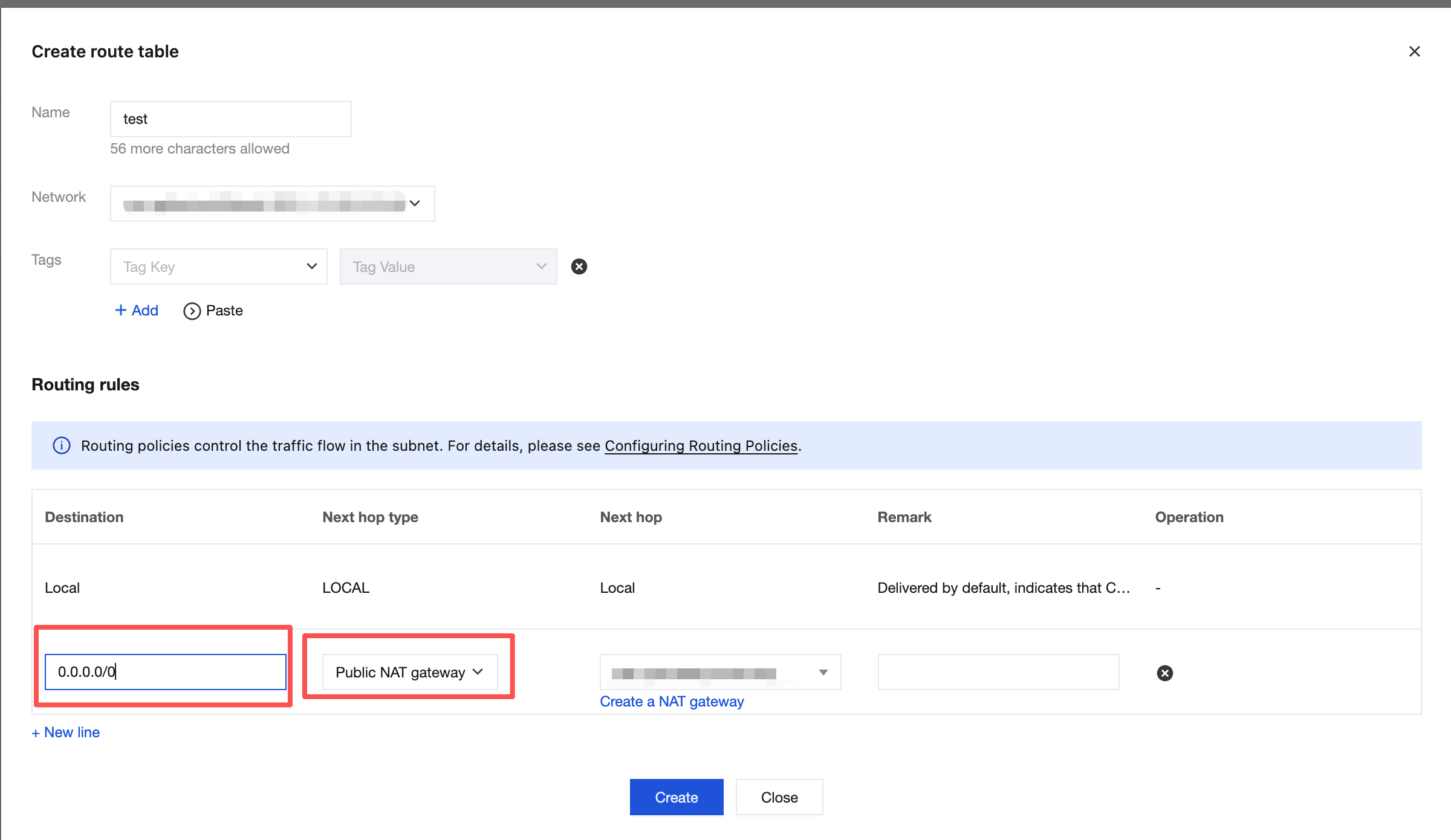
2. Configure a route pointing to the NAT Gateway: From the NAT instance list, access the subnet routing table of the VPC where the instance is located, and add a routing rule:
Destination: Enter 0.0.0.0/0.
Next Hop Type: Select Public NAT Gateway.
Next Hop: Select the NAT Gateway created in the previous step.
3. Configure SNAT rules: You can configure SNAT rules for the NAT Gateway to provide public network access for CVM instances in the VPC. When the NAT Gateway is bound to multiple EIPs, you can specify EIPs for public network access for the CVM instances in different groups based on the SNAT rules. For detailed operations, see Configuring a Route Pointing to the NAT Gateway.
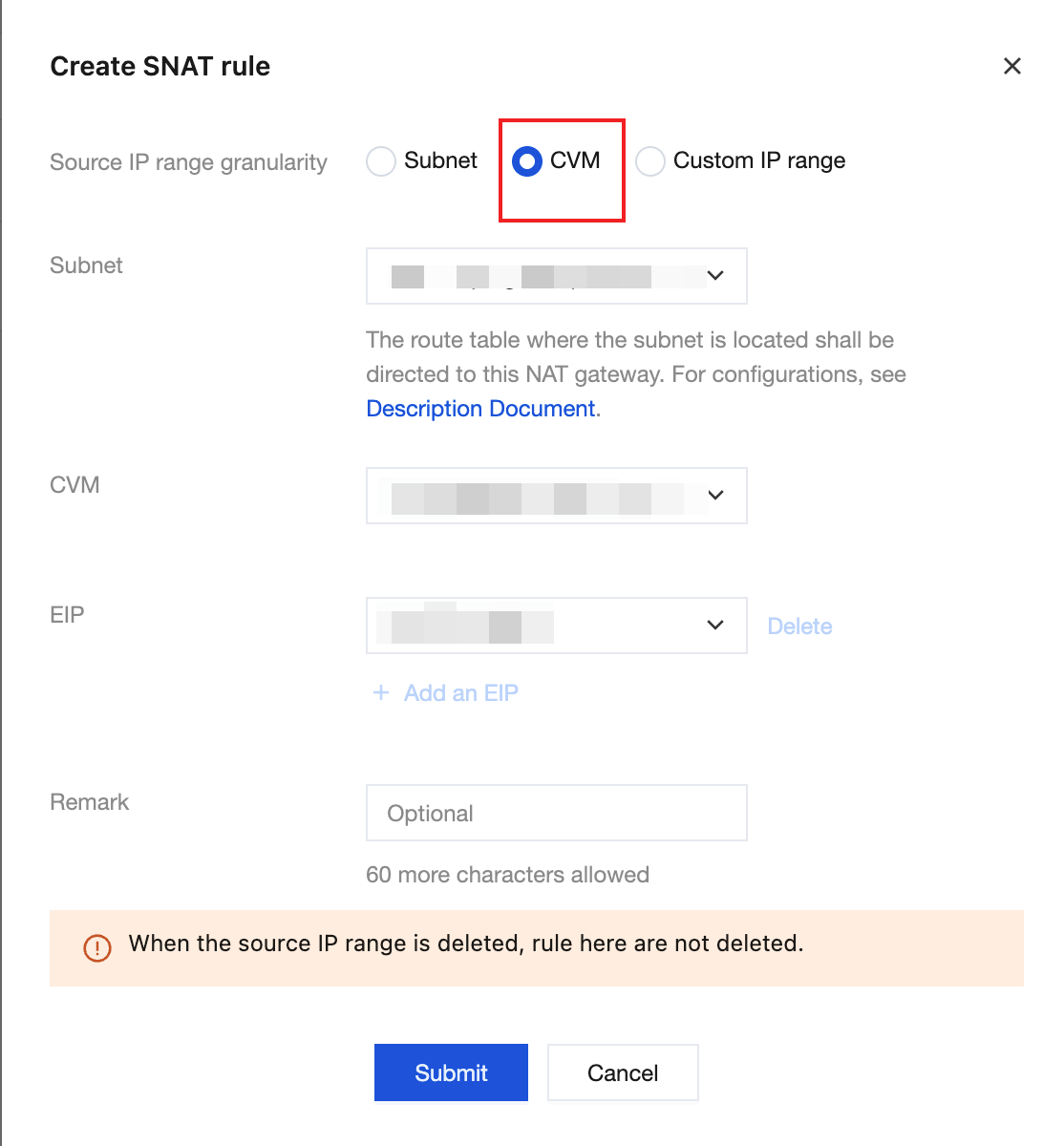
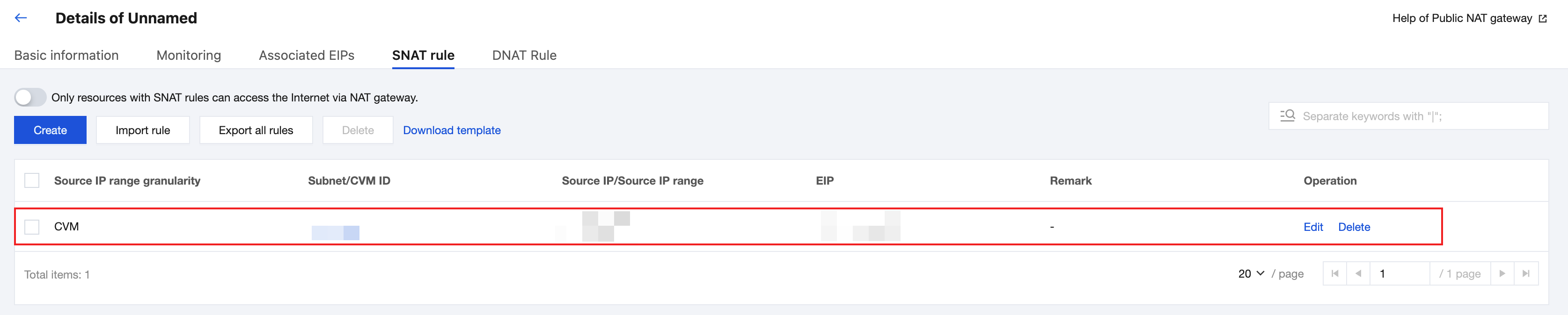
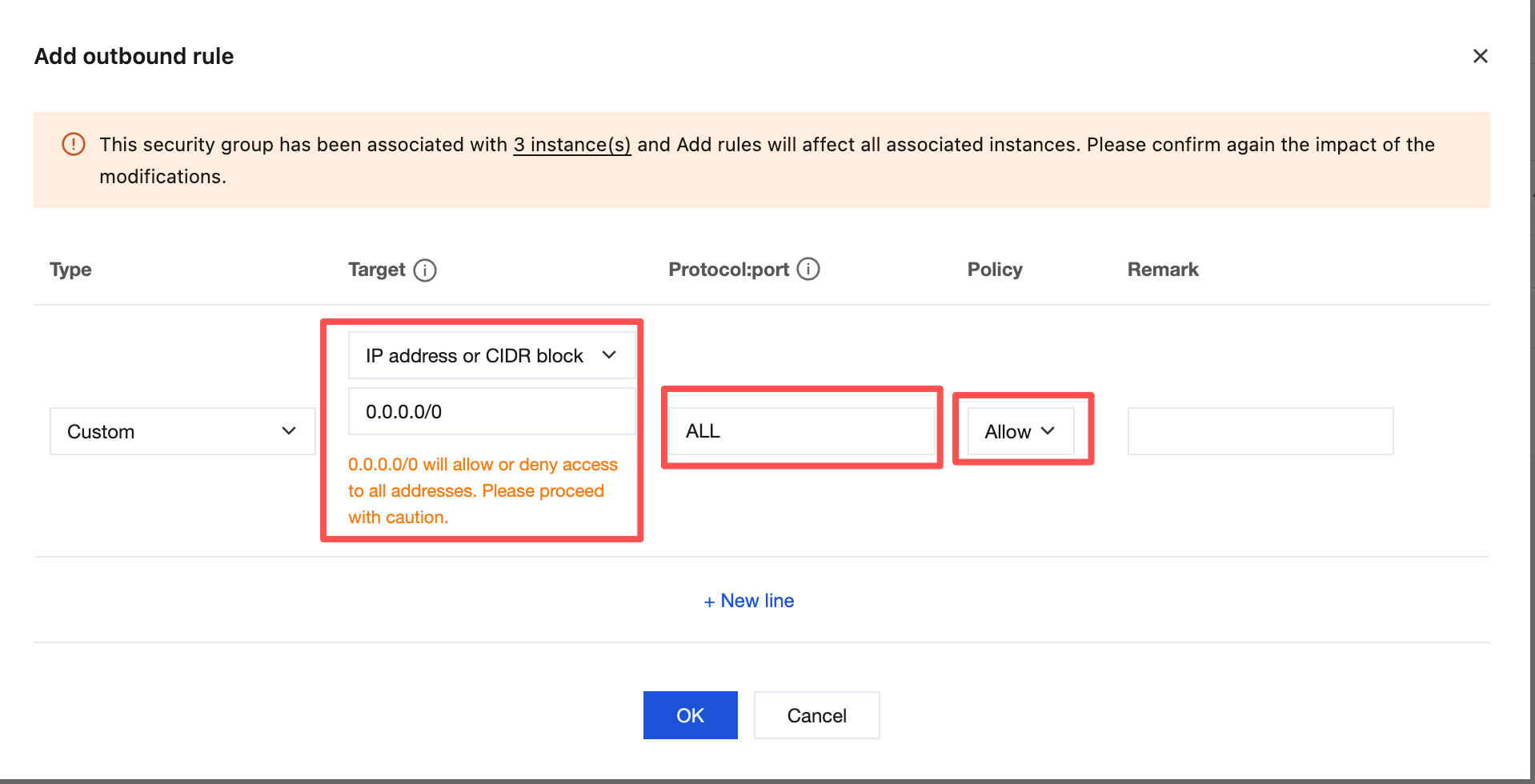
4. Configure outbound rules: Allow outbound ports (such as TCP:80/443) in the CVM security group.
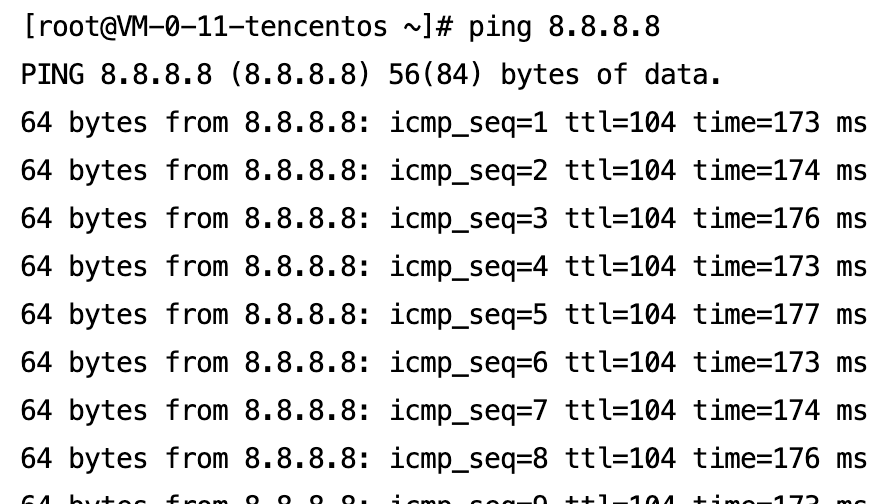
5. Test the public network connectivity: Log in to the CVM in the CDZ and use the ping command to test public network connectivity.
6. Configure DNAT rules: The port forwarding table is a configuration table on the NAT Gateway for configuring the DNAT feature. It maps the private IP address, protocol, and port of instances (such as CVM, ENI, CLB, and cloud database instances) in the VPC to a public IP address, protocol, and port, making resources on the CVM instances accessible from the public network. For detailed operations, see Managing DNAT Rules.
Elastic IP and Exposed Port: Select the EIP bound to the NAT Gateway and the externally exposed port.
Private IP and Port: Specify the private IP address of the CVM instance and the service listening port.
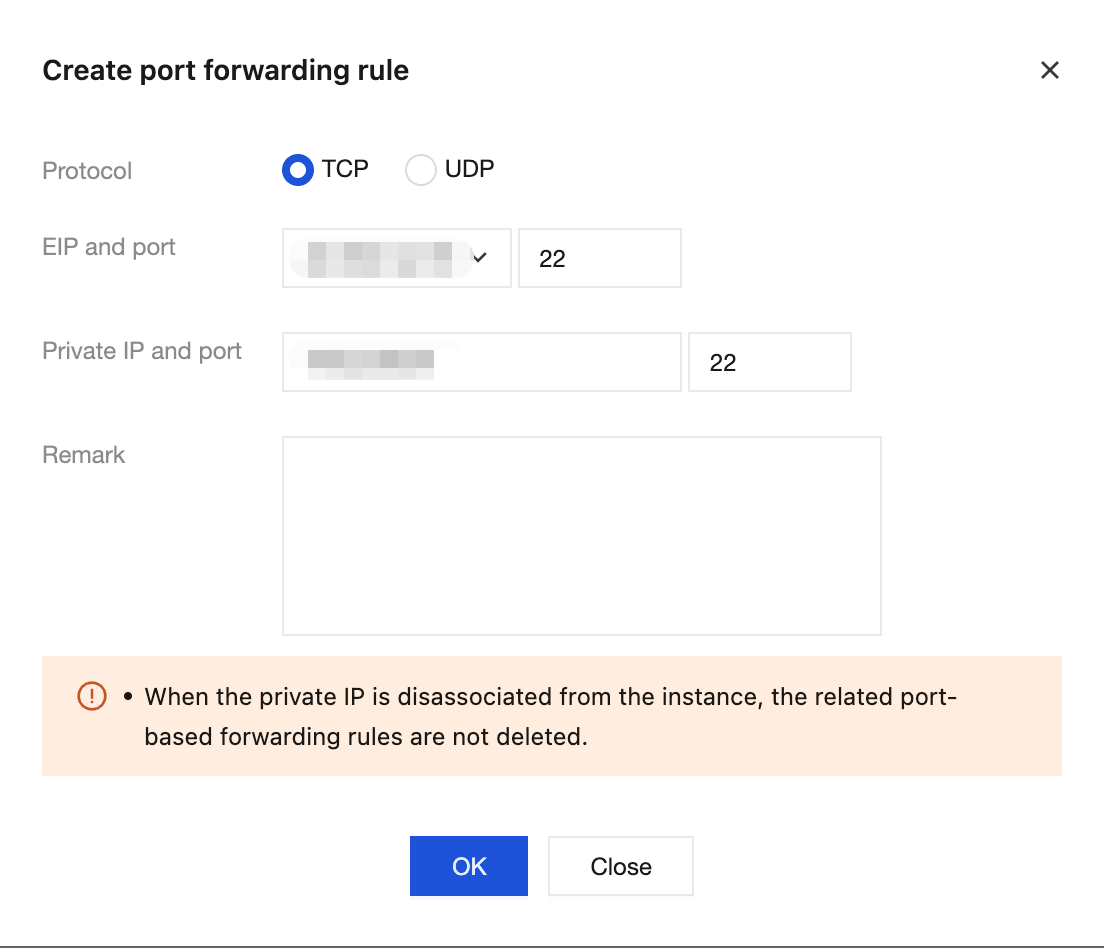
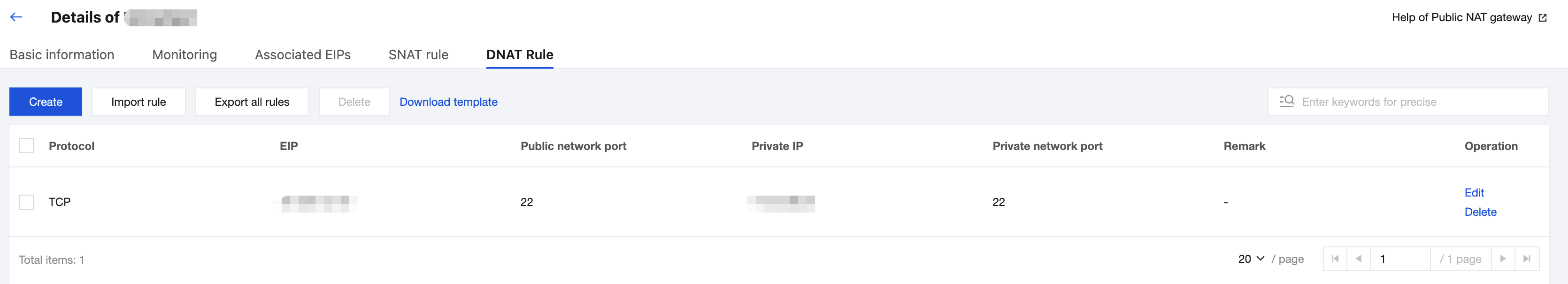
7. Test access to the EIP of the NAT Gateway by using the nc (Netcat) command for connectivity testing.

Note:
The DNAT capability of CLB instances in a VPC is a unique feature of the public network NAT Gateway - standard NAT Gateway. To use this capability, you can submit a ticket to apply.
Scenarios
This sub-solution is suitable for web services or API services that require high-availability public network access capability. By creating a public network CLB instance in the primary region and adding CVM instances in a CDZ as backend servers, it enables public network access and traffic distribution.
Operation Process
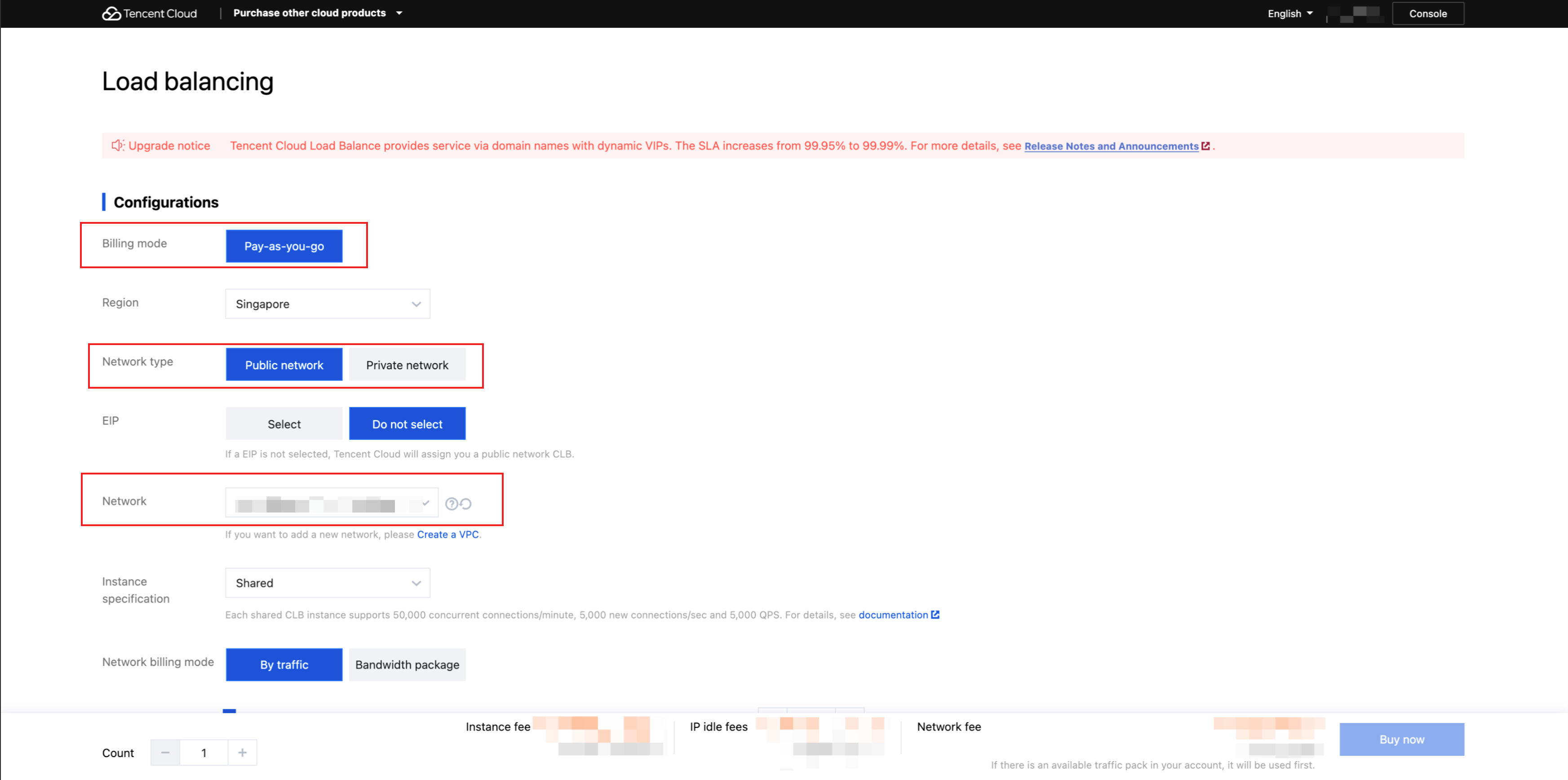
1. Create a public network CLB instance: Log in to the CLB console, create a new public network CLB instance in the CDZ primary region. On the CLB console page, click Create and configure the CLB instance as follows:
Network Type: Select Public Network.
Region: Select the region where the CDZ is located.
EIP:
Not Select Elastic IP: An EIP is automatically assigned by the system to the CLB instance. The EIP is strongly bound to the CLB instance and will be released when the CLB instance is deleted.
Elastic IP: Use an existing EIP in your own account. The IP address exists as an independent EIP resource and is decoupled from the CLB instance.
Associated Network: Select a VPC that includes the CDZ subnet to use the public network CLB instance in the region (Region-CLB) and support EIP binding for public network access.
2. Configure a listener: On the CLB instance management page, click Configure Listener in the Operation column of the target CLB instance to create a listener.
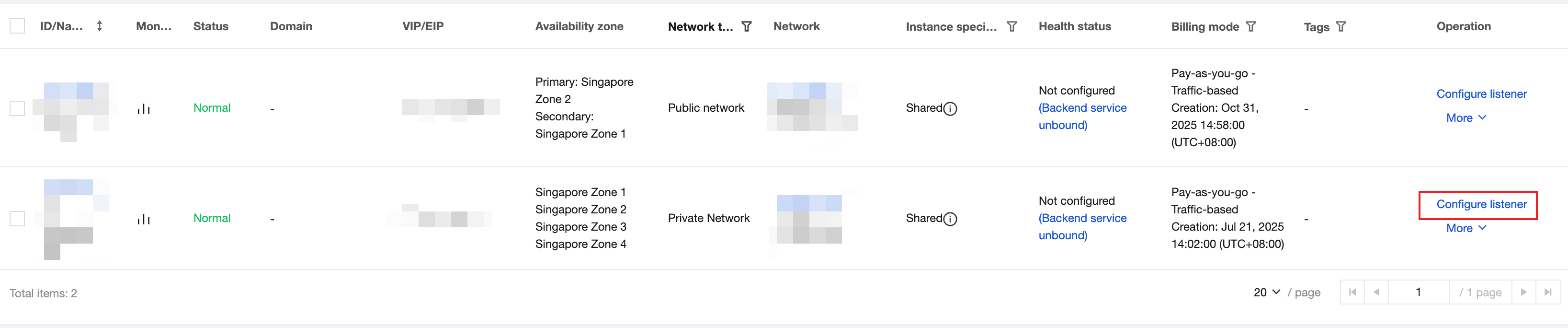
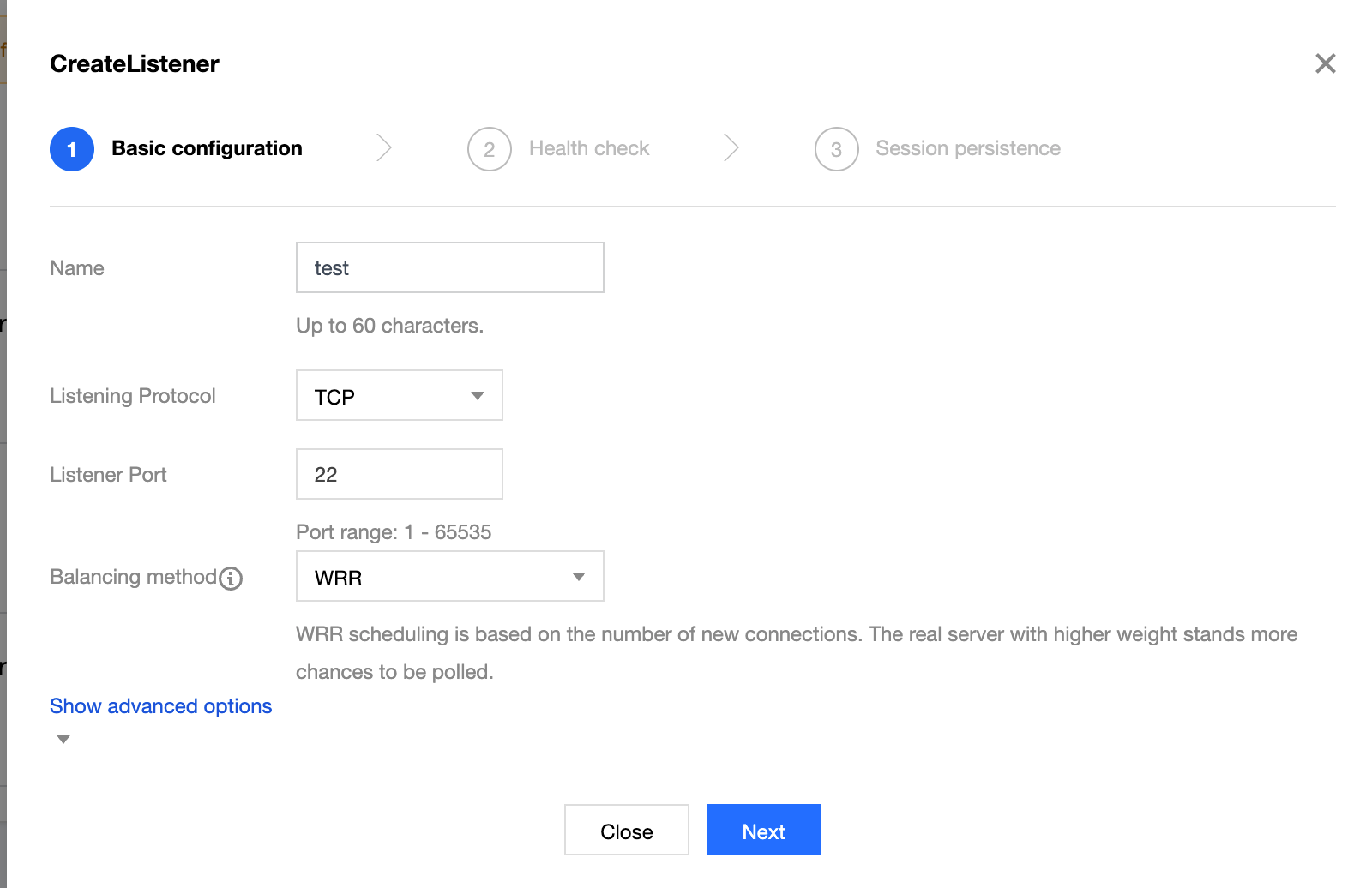
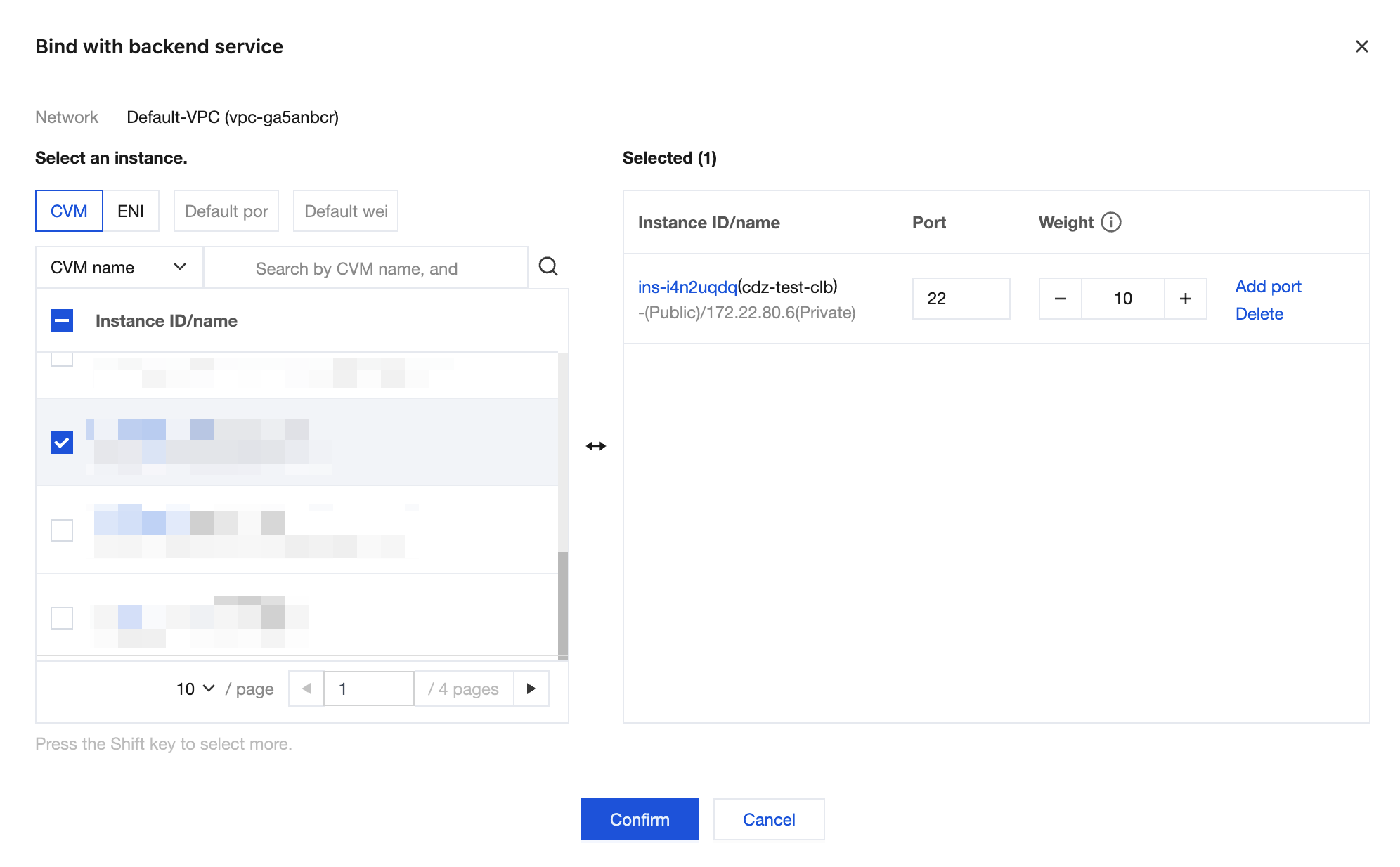
3. Bind CVM instances: Select the created listener, click Bind to bind the backend service, select and add CVM instances in the CDZ in sequence, and configure ports and weights.
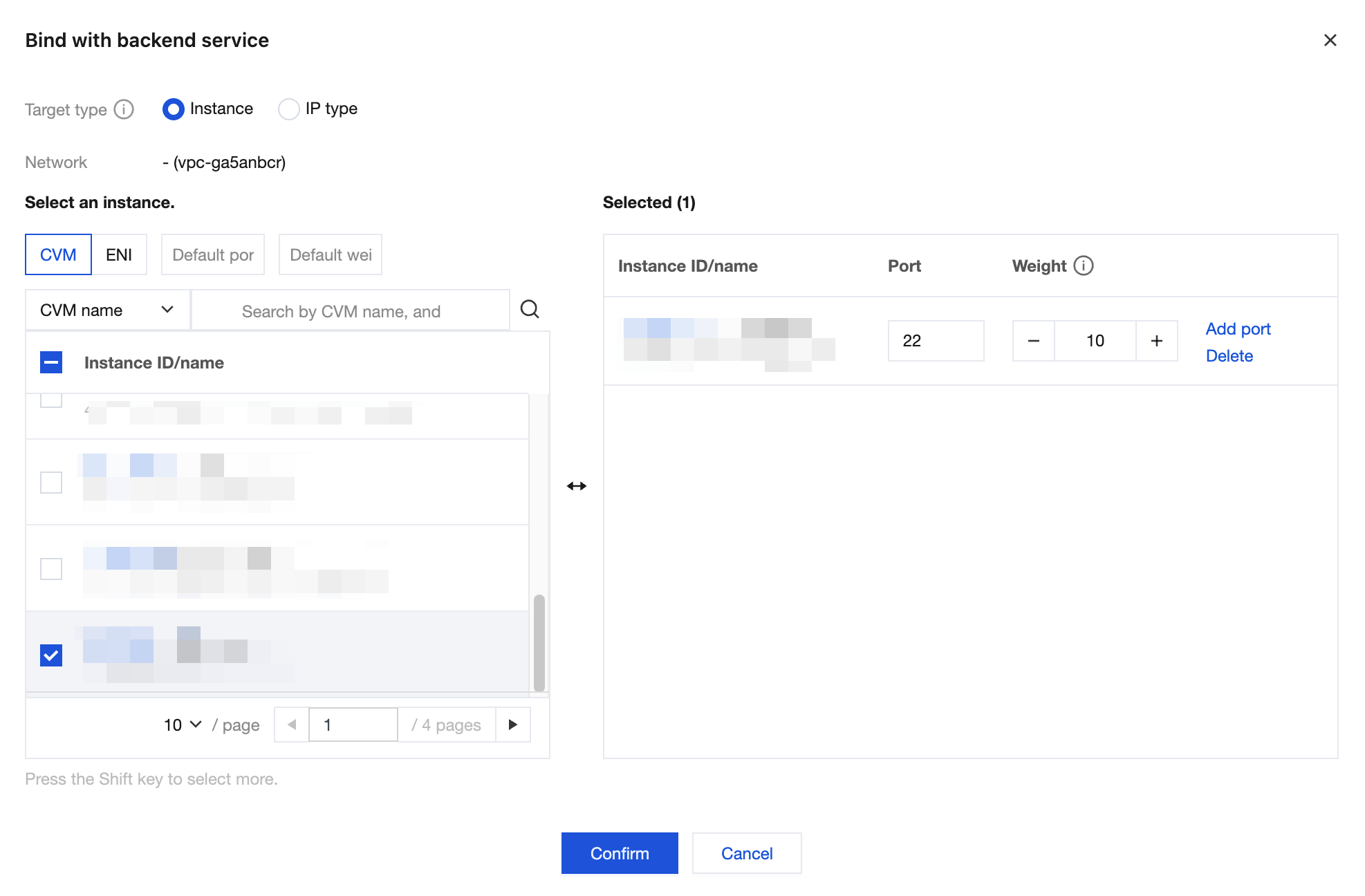
Check the port health status to confirm that it is Healthy.
4. Test connectivity: Use the nc (Netcat) command to test connectivity, or log in to the CVM instance in the console and use the ping command to test public network connectivity.
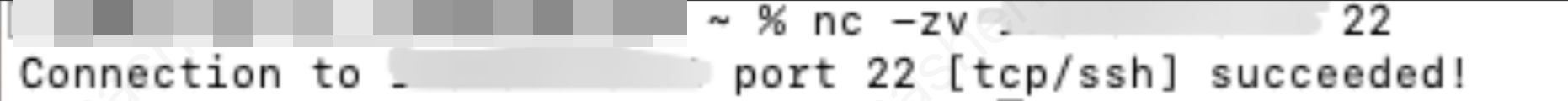
Scenarios
This sub-solution is suitable for enterprises that already have a regional private network CLB architecture and wish to extend public network access capability to CVM instances within a CDZ. This sub-solution requires creating a private network CLB instance in the region and binding an EIP to it, then using the CLB instance to forward traffic to backend servers in the CDZ.
Operation Process
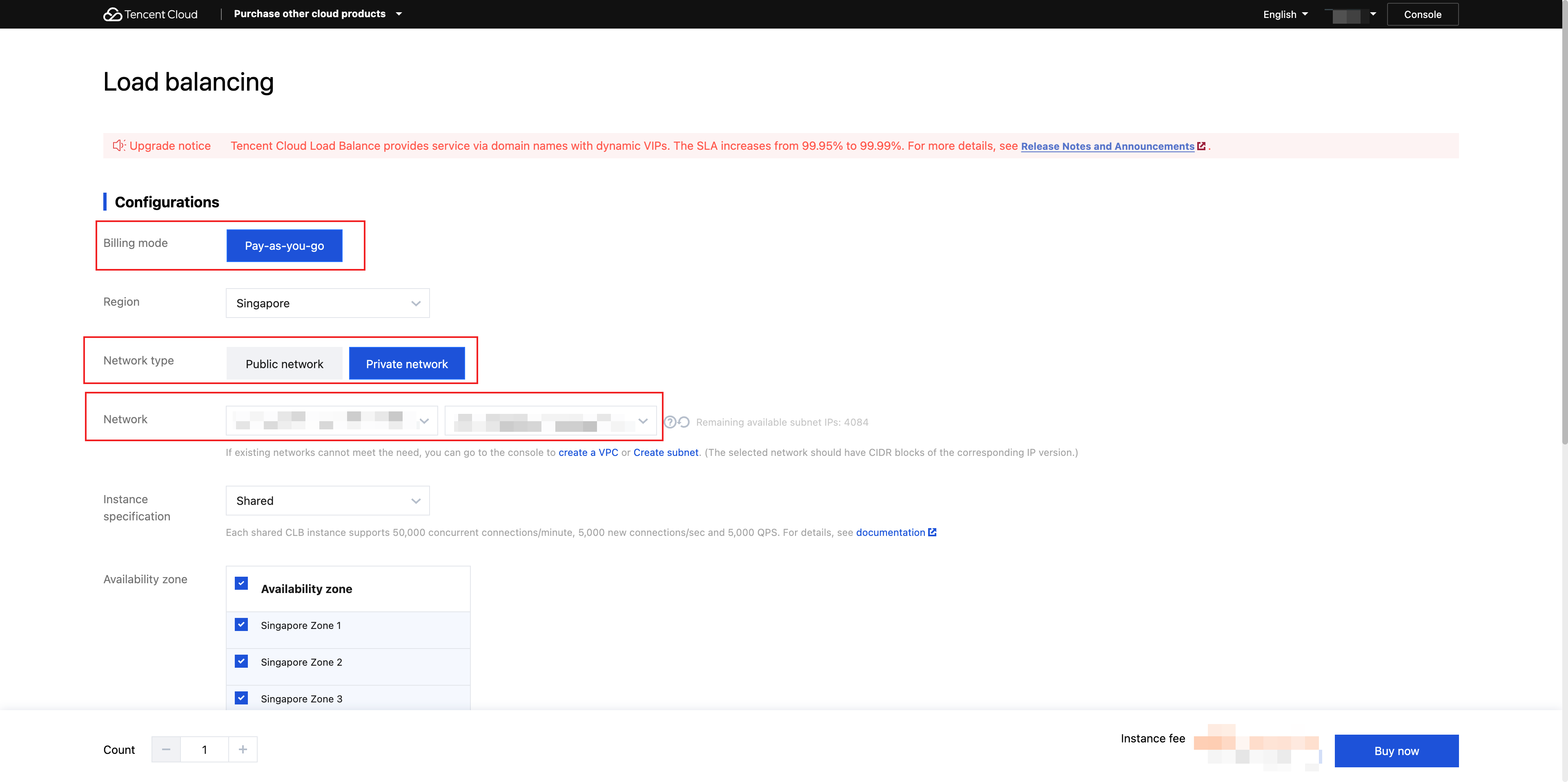
1. Create a private network CLB instance: Log in to the CLB console, create a public network CLB instance in the CDZ primary region. On the CLB console page, click Create and configure the CLB instance as follows:
Billing Mode: Select Pay-as-You-Go Billing.
Region: Select the region where the CDZ is located.
Network Type: Select Private Network.
Availability Zone: Select an AZ in the region.
Network:
VPC selection: Select a VPC that includes the CDZ subnet.
Subnet: Select a non-CDZ subnet to support EIP binding and realize public network access.
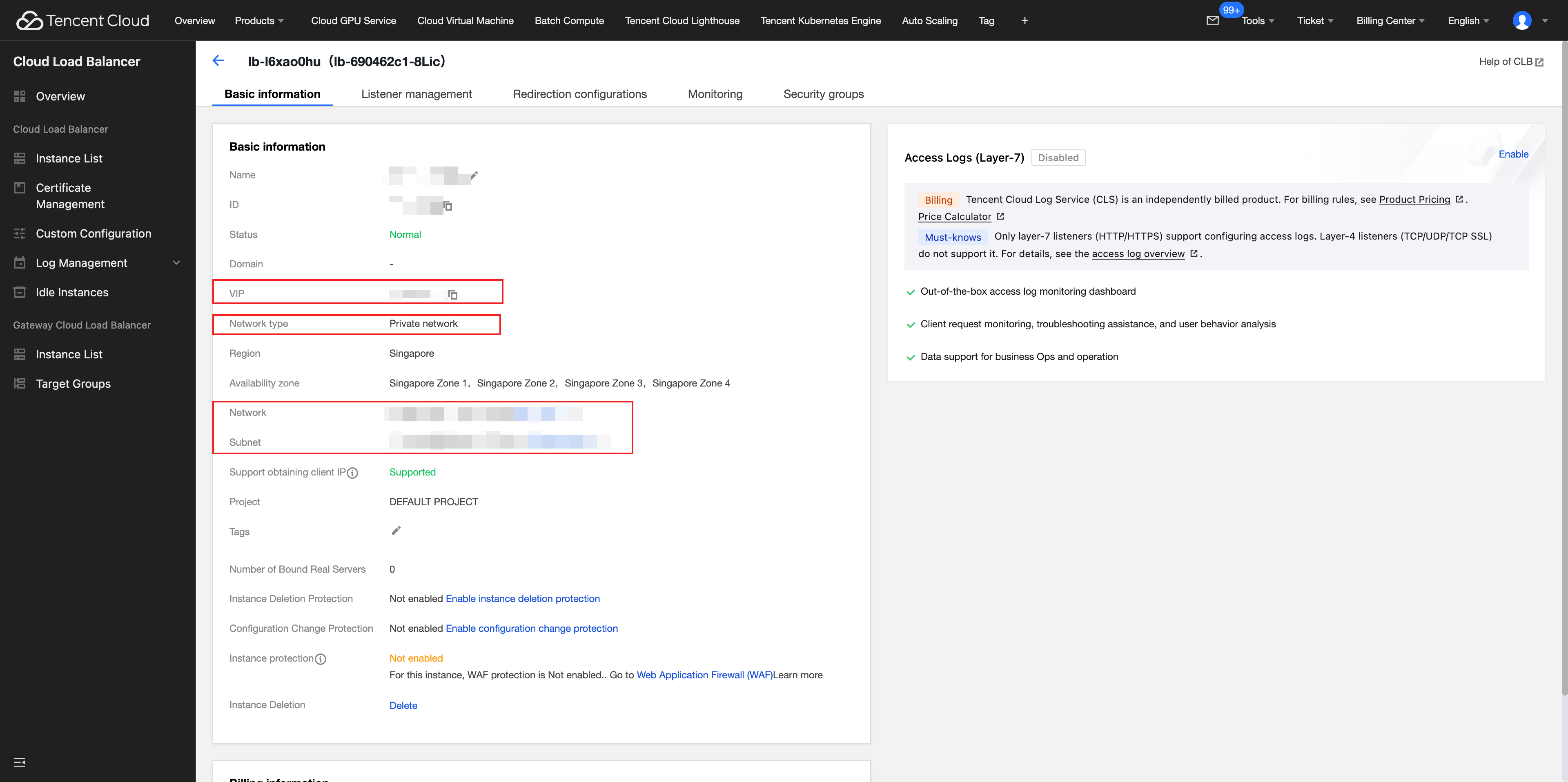
2. Configure listeners and backend services: Configure listeners and backend services on the private network CLB instance.
3. Apply for an EIP: In the EIP console, apply for an EIP.
4. Bind an EIP:
4.1 Go to the CLB Instance Management page.
4.2 In the operation column, choose More > Bind Elastic IP.
4.3 Select the applied EIP to complete the binding.
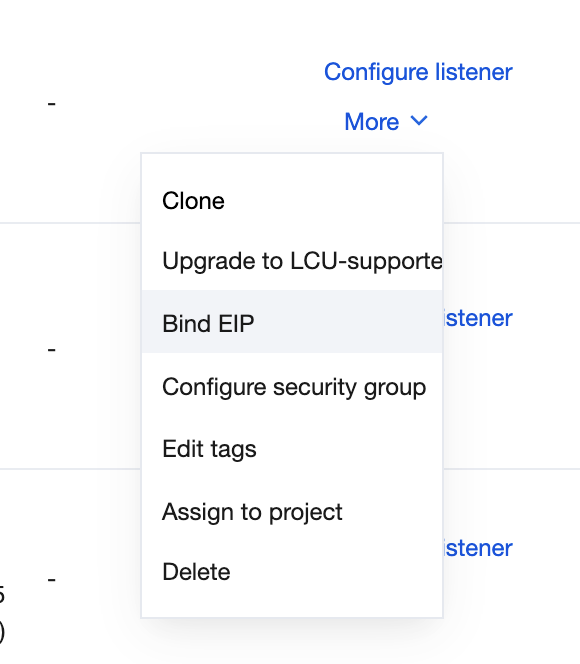
After binding, you can view the bound EIP on the Instance Management page in the CLB console.

5. Test connectivity: Use the nc (Netcat) command to test connectivity, or log in to the CVM instance in the console and use the ping command to test public network connectivity.

FAQs
Q: Can the private network CLB instance in CDZ be bound to a regional EIP?
A: The private network CLB instance in CDZ cannot be directly bound to a regional EIP. The private network CLB instance in CDZ is a load balancing service designed for internal traffic scenarios in a VPC. It provides only private IP addresses and does not have public network access capability itself, nor does it support binding to a regional EIP or exposing public IP addresses. Therefore:
If you select CDZ subnet when creating a CLB instance, the system will use the CLB cluster in CDZ by default. This CLB instance does not support EIP binding, and no CLB instance fee is charged. An error will occur if you bind an EIP to a CLB cluster in CDZ subnet:
If you select a non-CDZ subnet when creating a CLB instance, it supports binding to a regional EIP, and a CLB instance fee is charged.
Therefore, we recommend that you create the CLB in a different subnet of the same VPC as CDZ to obtain complete public network access capability.
Subnet | CLB Cluster Used | Support for EIP Binding | Billing |
CDZ subnet | CLB cluster built in CDZ (cdz-clb) | ❌ EIP binding is not supported. | No CLB instance fee is charged. |
Non-CDZ subnet | Primary region CLB cluster (region-clb) | ✅ EIP binding is supported. | The CLB instance fee is charged. |
Solution 2: Accessing the Public Network Through the Self-Owned IDC
Scenarios
This solution is suitable for enterprises that have built a complete self-owned IDC network and hope that public network traffic will be transmitted back to the enterprise IDC through a connection, and then access the Internet through the public network egress of the IDC. Applicable scenarios include:
Reuse of existing infrastructure: Enterprises have a mature IDC network architecture and security system, and wish to make full use of existing investments.
Compliance and regulatory requirements: Due to data sovereignty, industry regulation, or internal compliance requirements, all public network traffic must pass through the self-owned egress.
Unified hybrid cloud management: In hybrid cloud scenarios, unified network policies, security protection, and access control should be implemented.
Fully autonomous and controllable egress: Enterprises want to perform fully independent management and audit on the public network egress.
Prerequisite Dependencies
Connection:
Establishing a connection between Tencent Cloud CDZ and your self-owned IDC is a prerequisite and should be completed first.
Dependency | Detailed Explanation and Requirement |
Connection readiness | Application and activation: You have applied for a connection in the Tencent Cloud console and completed the survey and implementation. The connection status is activated. Access point: The access point of the connection should be within a reasonable distance from your IDC location to ensure transmission quality and low latency. Bandwidth specification: The connection bandwidth should meet the peak egress traffic demand of your cloud business accessing the public network, with a certain amount of redundancy reserved. |
Dedicated tunnel configuration | Network connectivity: Create a dedicated tunnel on the Tencent Cloud side and complete the Layer-3 network interconnection configuration with the boundary router on your IDC side. BGP session: A BGP session must be successfully configured and established on the dedicated tunnel to exchange routing information dynamically. This is the key to achieving route reachability. Redundancy design (optional but recommended): To ensure high service availability, it is strongly recommended to deploy two or more connections to form a primary-secondary or load-sharing architecture. |
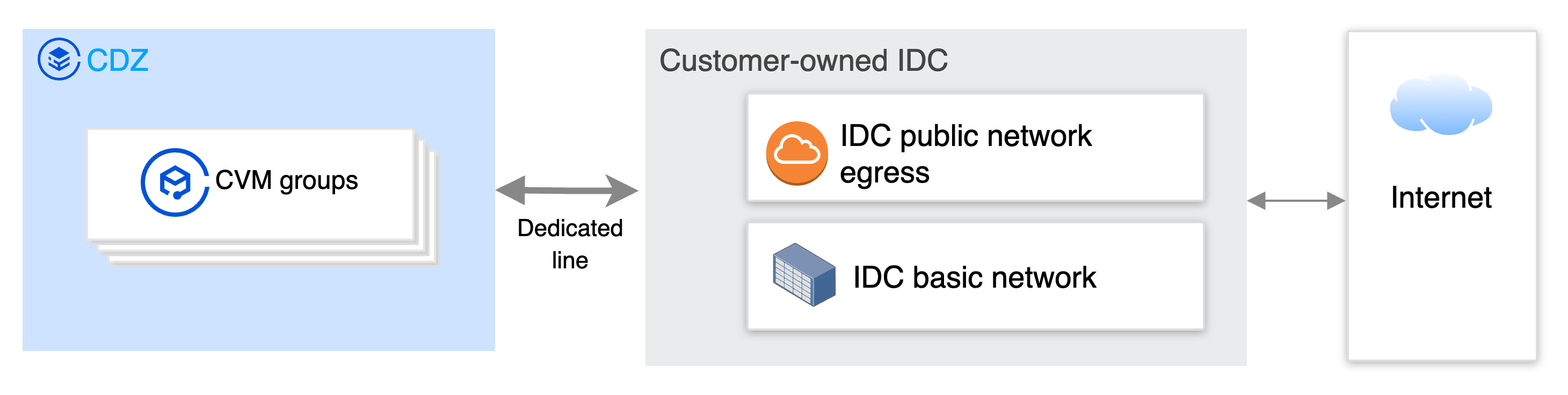
Self-owned IDC network and public network egress
Note:
Tencent Cloud is only responsible for delivering traffic to your IDC boundary through a connection. The design and configuration of egress from IDC to the public network should be done manually.
This is the final egress for traffic and the policy execution point, which requires corresponding processing capabilities.
Dependency | Detailed Explanation and Requirement |
Boundary router configuration | Route advertisement: The router on your IDC side must be able to advertise a default route (0.0.0.0/0) or specific public network IP ranges you want to access from the cloud to the Tencent Cloud DC gateway through a BGP session. Routing reception: It should be correctly configured to receive and learn the private IP range routes of CDZ from Tencent Cloud. |
Public network egress device | Egress capability: Equipment with public network egress capability (such as firewalls, routers, or dedicated NAT gateways) should be deployed in the IDC, and public network lines (such as fiber cable or metropolitan area networks) from the internet service provider (ISP) have been applied for. Public IP addresses: Ensure that the egress equipment has one or more available public IP addresses. |
IDC private network planning | Routing guide: The private network of your IDC can correctly route traffic received from DC (with the public network as the destination) to the public network egress equipment. Bandwidth and performance: The throughput performance of internal IDC equipment (such as core switches and firewalls) should be able to bear the additional public network traffic pressure brought by cloud services. |
Network Architecture
Operation Process
Complete the operation process for DC access in the Tencent Cloud console. For details, see Operation Process.
Solution 3: Accessing the Public Network Through Local Public Network Clusters in CDZ
Scenarios
This solution provides public network egress capability for cloud resources deployed in CDZ through a local public network cluster within CDZ. Public network traffic is forwarded within CDZ without passing through Tencent Cloud center regions or your self-owned IDC, thereby achieving minimal network latency and maximum bandwidth performance. It is suitable for the following scenarios:
Ultra-low latency business: Businesses highly sensitive to network latency, such as high-frequency trading systems, Tencent Real-Time Communication (TRTC), and Massively Multiplayer Online (MMO) games.
High-traffic public network service: Scenarios with massive inbound and outbound public network traffic, such as CDN edge nodes, and big data file distribution and download centers.
Compliance and sovereignty requirements: Industries with compliance requirements for independent public network egress, such as finance and government service, must meet regulatory requirements for data localization.
Simplified Ops: Enterprises want public network capabilities to be uniformly provided and maintained by cloud vendors locally, simplifying their own network management.
Prerequisite Dependencies
Local public network cluster: The deployment of a local public network cluster has been confirmed and completed during CDZ activation planning.
Public IP address resource
IP source: Generally, the Bring Your Own IP (BYOIP) method is used, or you can apply for IP addresses from a local ISP. Tencent Cloud will assist in importing and managing the IP range into the public network cluster of CDZ.
IP authorization: Ensure that the provided IP range has been authorized by the corresponding Internet registration authority and can be broadcast normally.
Network Architecture
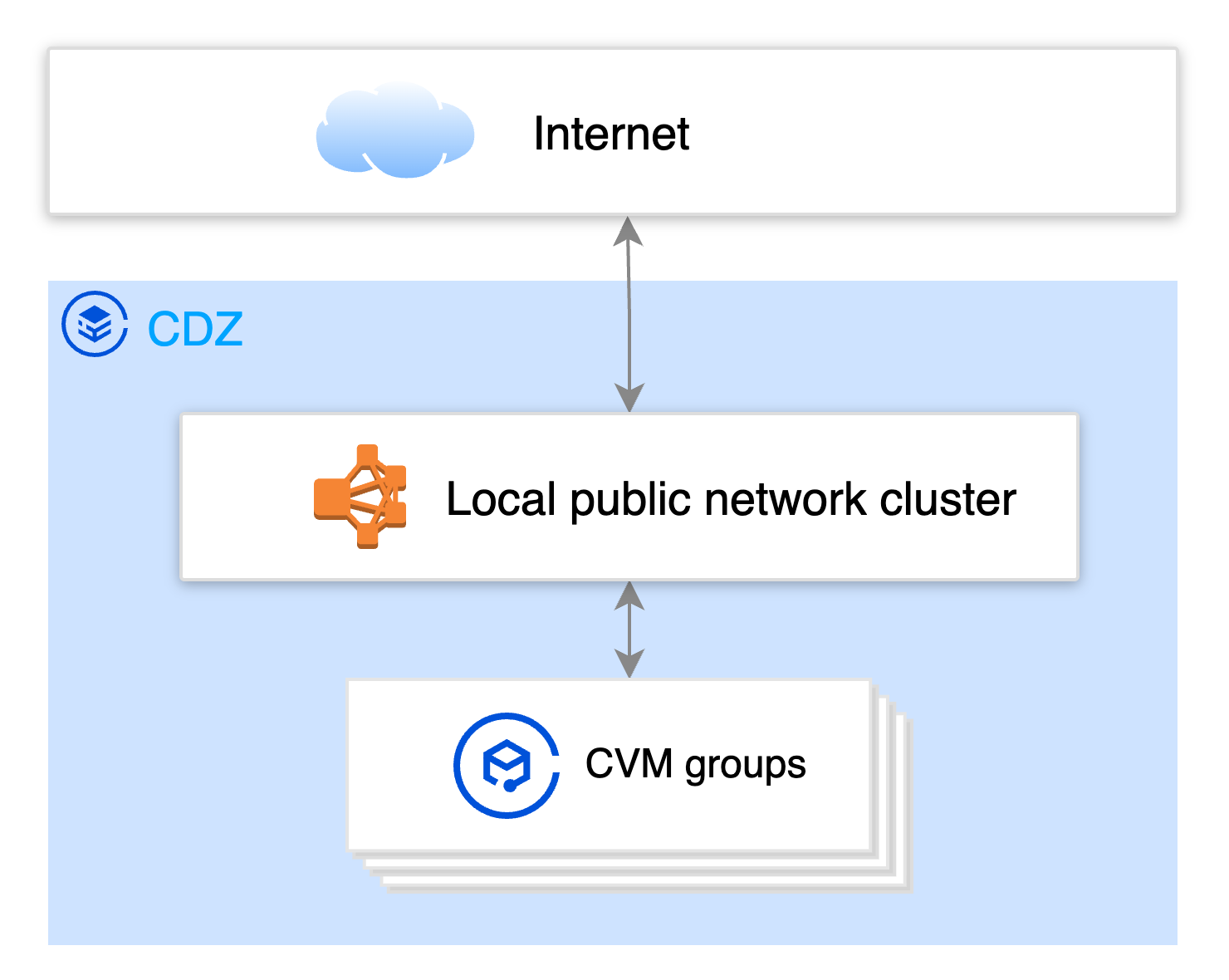
Operation Process
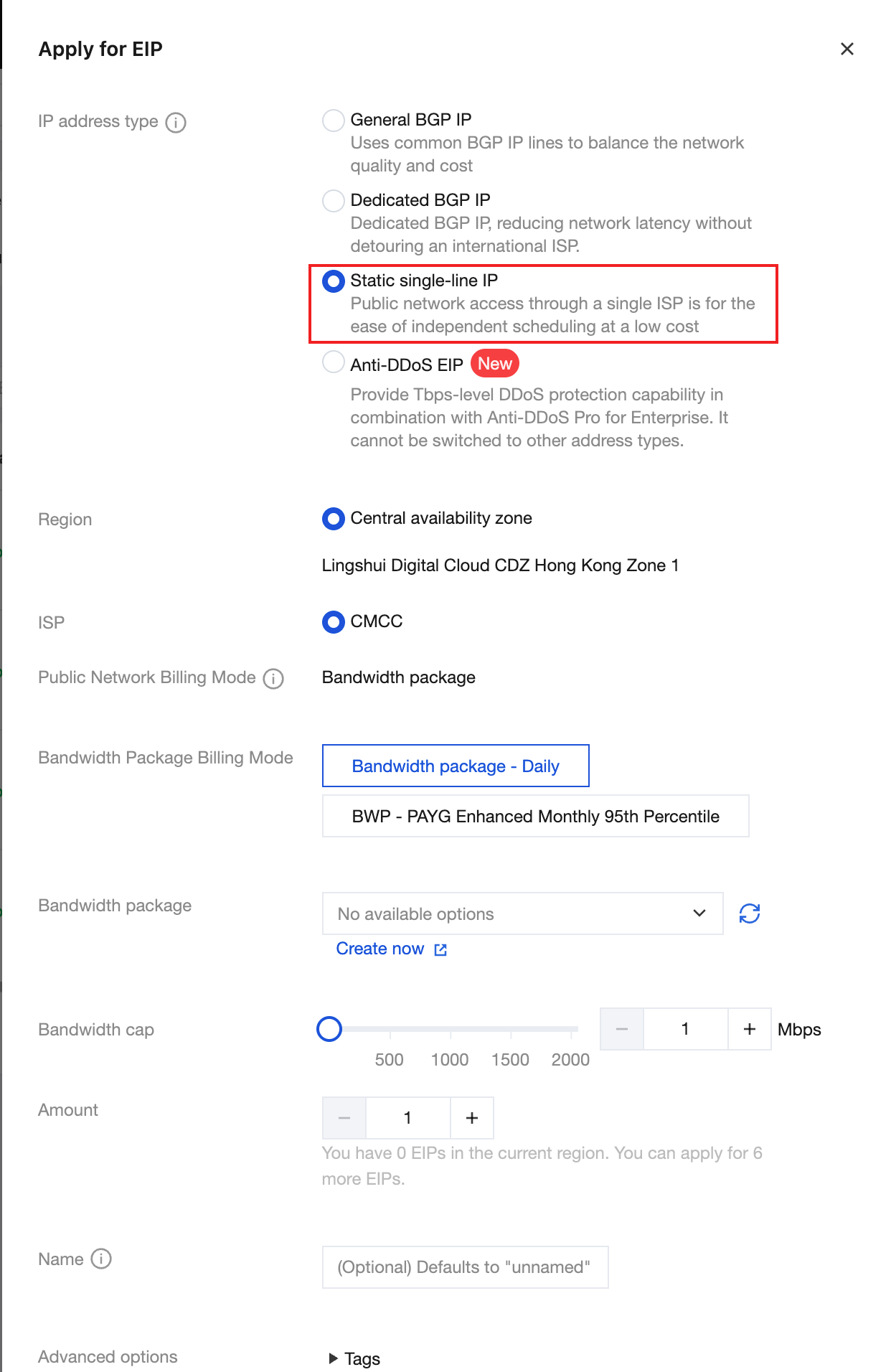
1. Create an EIP: Log in to the EIP console and click Apply.
IP Address Type: Select Static Single-Line IP.
Region: Select the region where your CDZ is located.
Click Apply Now to complete the creation. In this case, the EIP has been allocated from the local public network cluster in CDZ.
2. Bind the EIP to a CVM instance: In the EIP list, locate the applied EIP, choose More > Bind in the Operation column. In the Bind Resource pop-up window:
Resource Type: Select CVM Instance.
Binding an Instance: Select the CVM instance in your CDZ that needs to access the public network.
3. Complete the verification: After successful binding, you can access the Internet through the private IP plus EIP of the CVM instance. You can log in to the CVM instance and run the
ping or tracert command to test public network connectivity. The traffic will directly pass through the local egress of CDZ.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

