Product Management
Last updated:2025-08-07 15:47:32
Overview
An artifact repository can be used to store, manage, and distribute artifacts generated during the software build process.
Cloud Native Build supports the following types of artifacts:
Docker
Helm
Maven
npm
ohpm
PyPI
Composer
NuGet
Among them, Docker and Helm container type artifacts can be directly published to the source code repository for storage, management, and distribution.
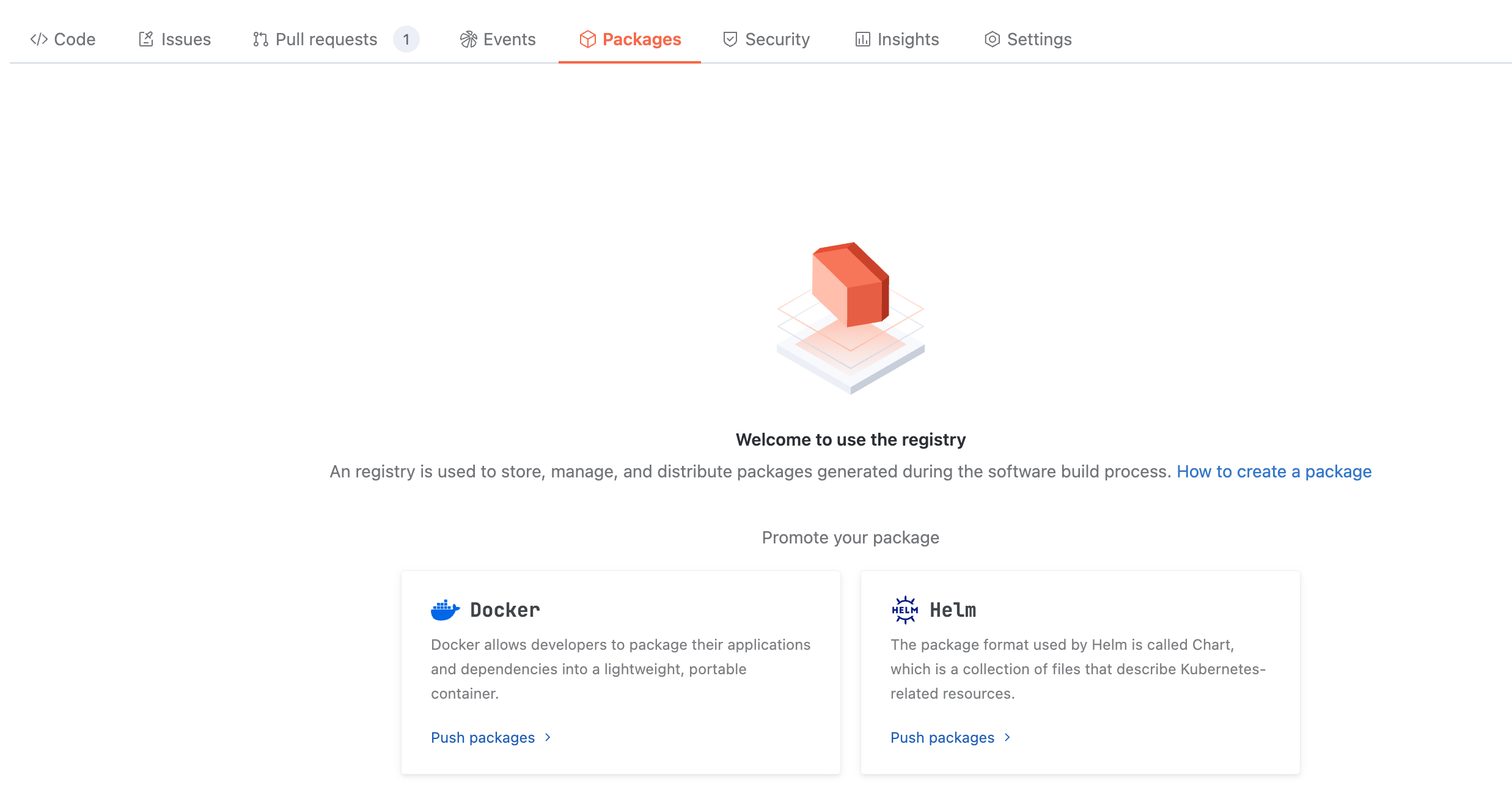
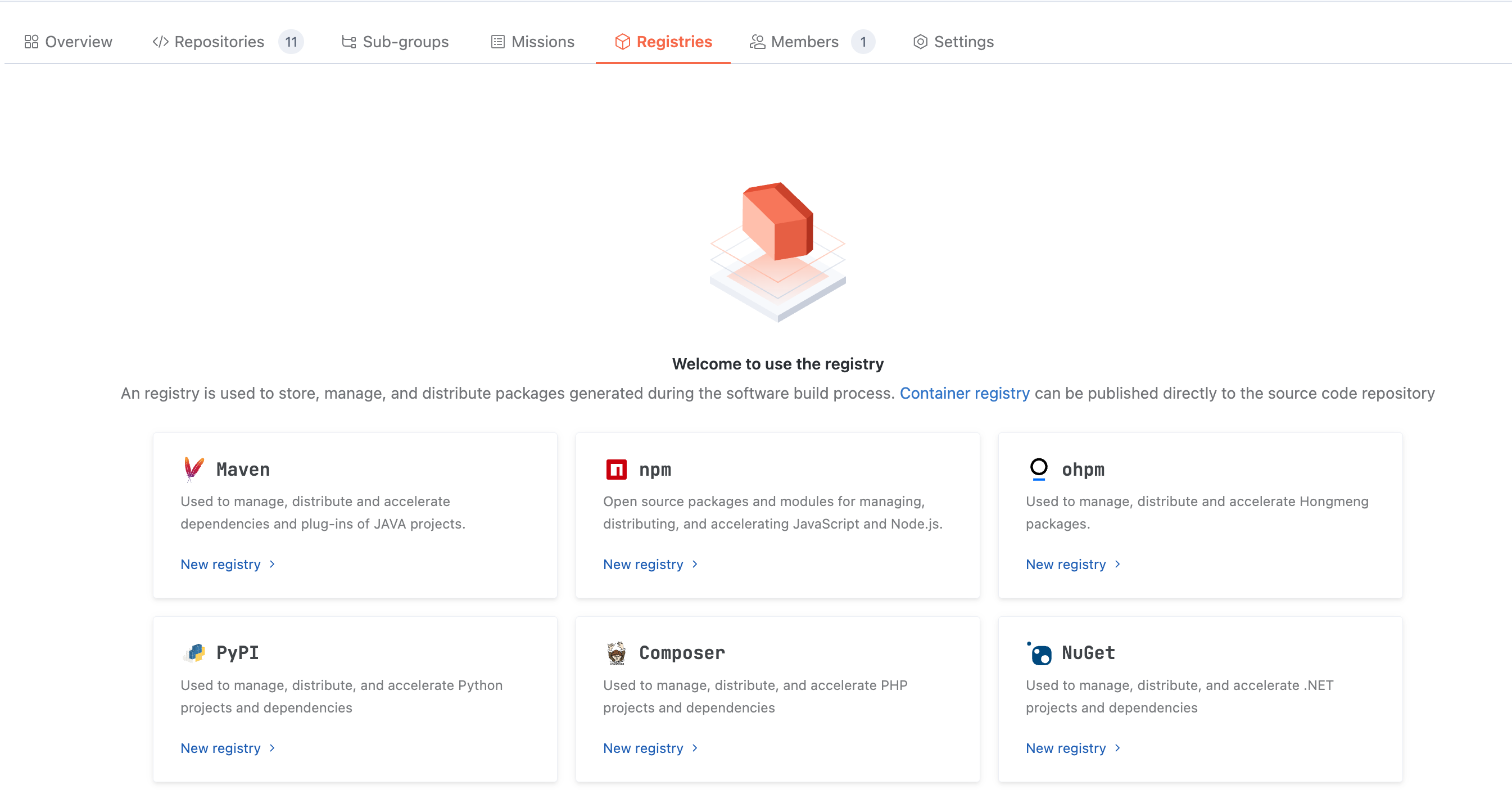
Since Maven, npm, ohpm, PyPI, Composer, and NuGet involve unified management of second-party and third-party dependencies, separate artifact repositories must be created to store, manage, and distribute them.
Docker
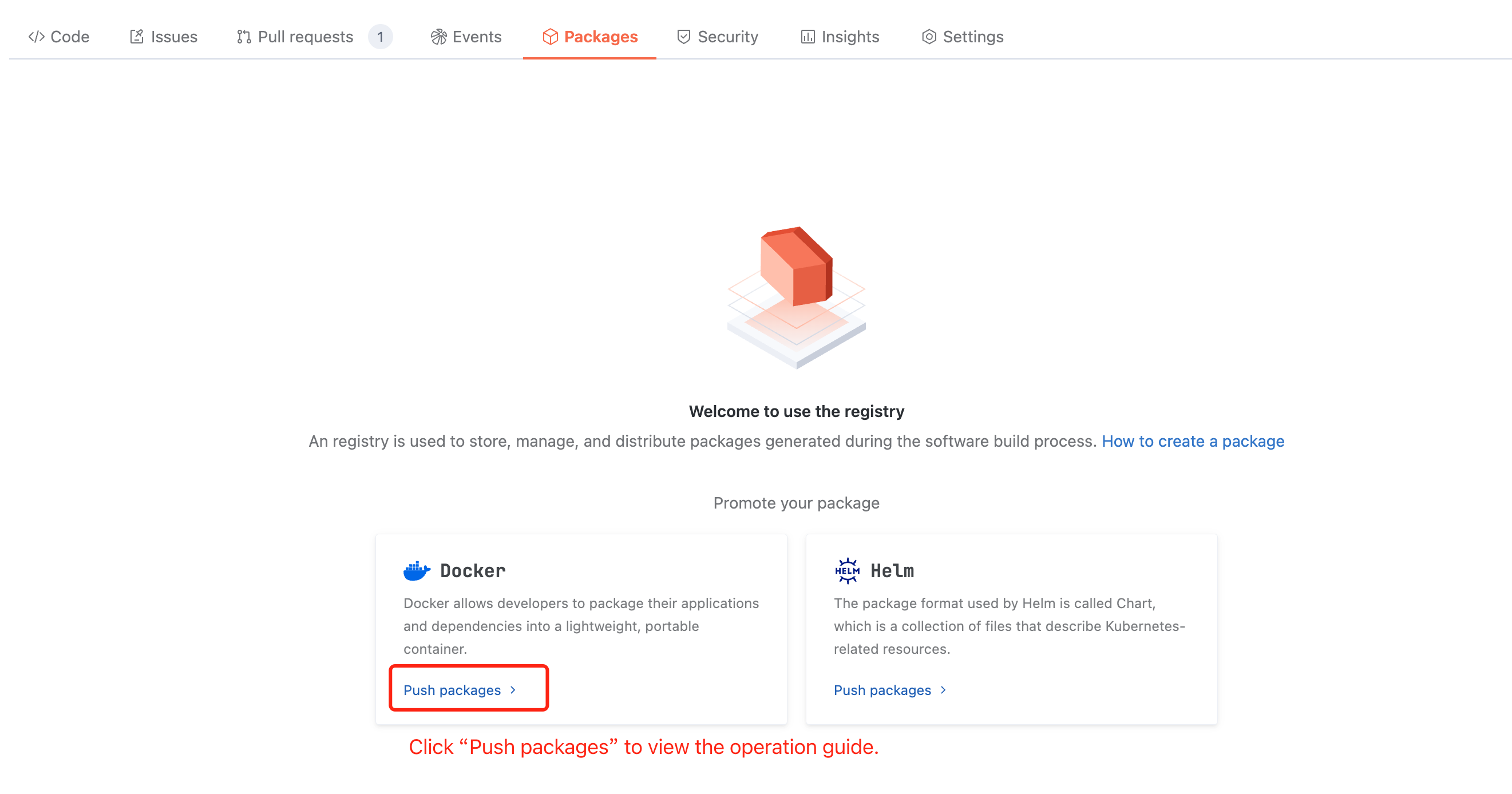
Pushing Artifacts
Docker artifacts can be published directly to the source code repository without creating a product library, just push them according to the specified naming rules:
Artifacts with the same name: The artifact path matches the repository path, for example:
docker.cnb.build/{repository-path}.Non-identical artifacts: The repository path serves as the namespace of the artifact, and the artifact path is exactly repository-path/artifact-name, for example:
docker.cnb.build/{repository-path}/{artifact-name}.After entering the target repository, select Product, then click Pushing Artifacts to view the specific push method. The interface is as follows:
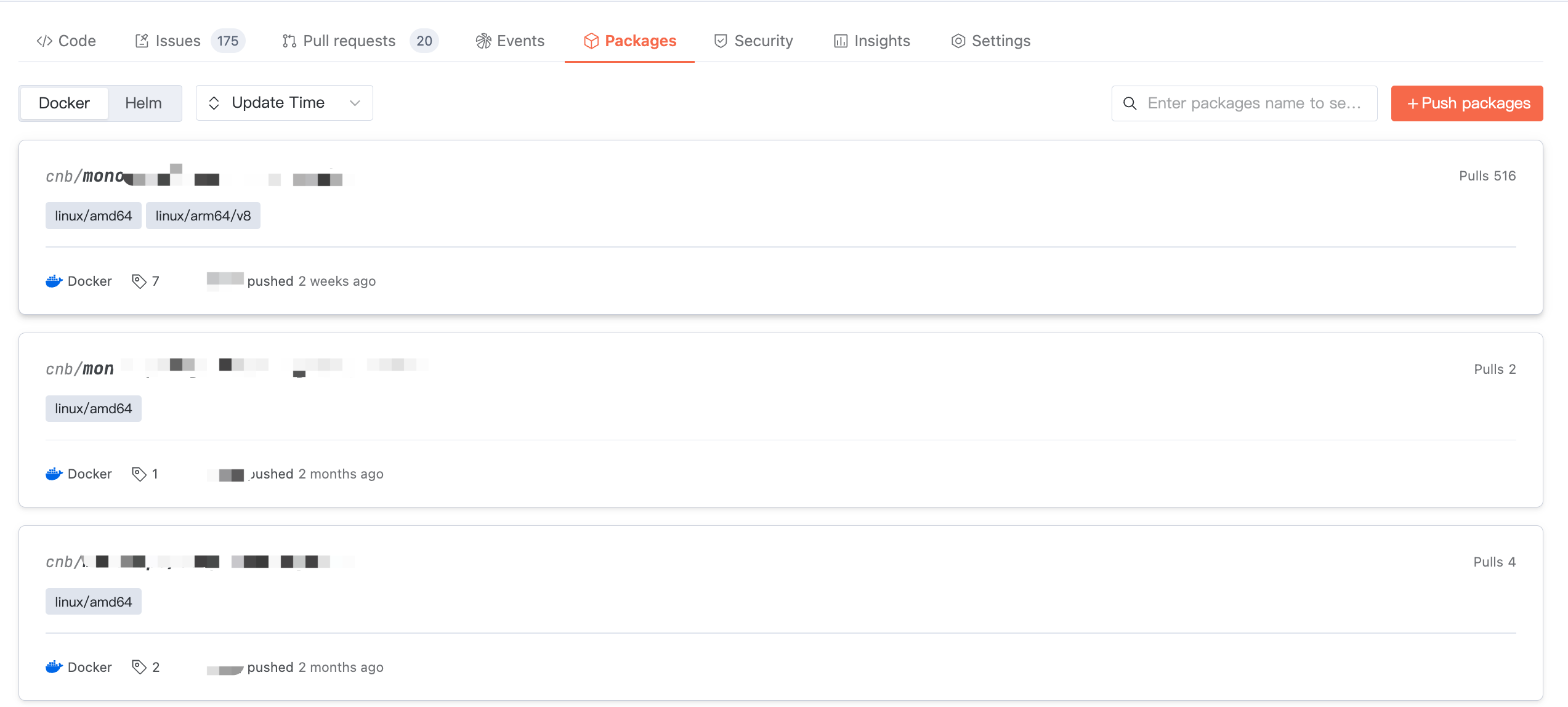
Artifact List
In the source code repository > Product Library, you can view artifacts released to the current source code repository. You can freely switch selection between Docker or Helm artifact types to check corresponding artifacts.
Artifact Details
Docker pull artifact address to fetch the Docker artifact with the latest tag by default.Click the artifact name to enter the artifact details, where you can view basic information such as the user guide, artifact address, name, description, push time, and download volume.
In addition, you can view recent artifacts and the tag list.
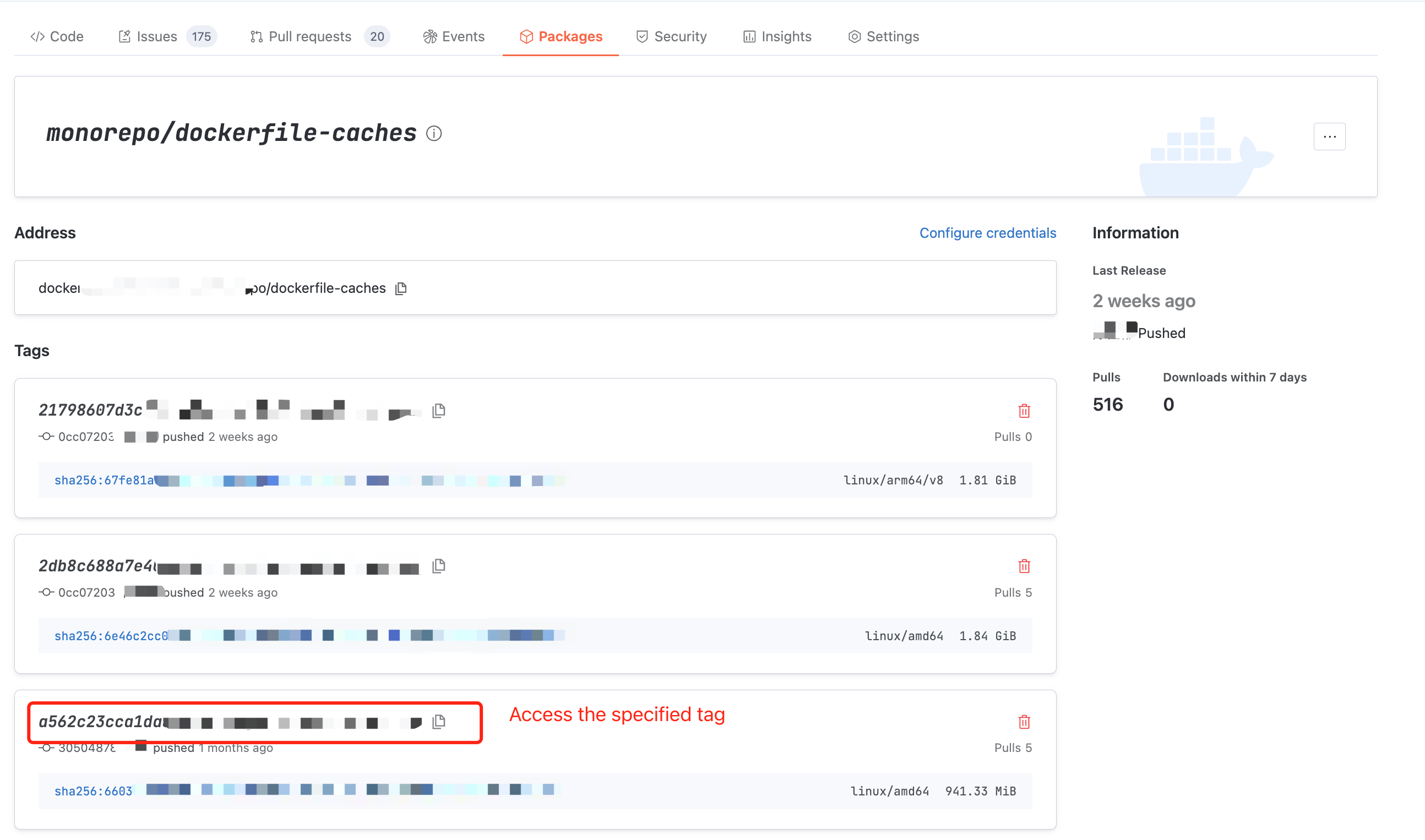
Tag Detail
Access the specified tag of the artifact to view the tag's usage guide, basic information, and usage data. layers info is also viewable at the bottom of the page.
At this moment
docker pull artifact address to fetch the specified tag.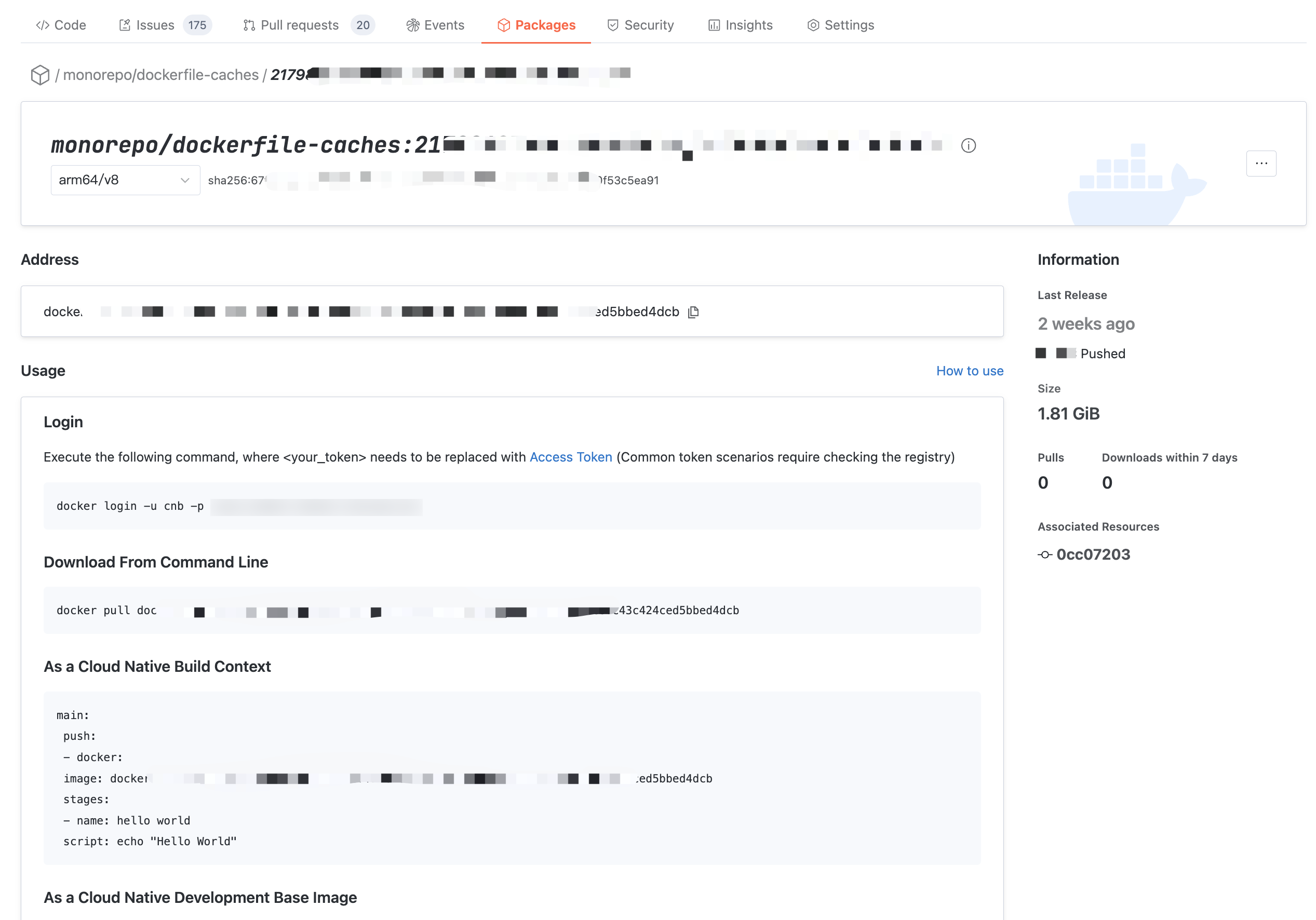
Learn More
Helm
Pushing Artifacts
Helm artifacts support two naming rules when published to a repository.
1. Artifacts with the same name: The artifact path matches the repository path, for example:
helm.cnb.build/{repository-path}.2. Non-identical artifacts: The repository path serves as the namespace of the artifact, and the artifact path is exactly repository-path/artifact-name, for example:
helm.cnb.build/{repository-path}/{artifact-name}.Note:
When pushing a helm chart to a remote, the chart name is not included in the remote-url but is instead read from the chart. Therefore, the remote-url for artifacts with the same name is
helm.cnb.build/{group-path}, while for non-identical artifacts, it is helm.cnb.build/{repository-path}.Viewing Artifacts
After entering the target repository, select Artifact Repository, switch to the Helm artifact type to check corresponding artifacts.
Artifact Details
helm pull artifact address to fetch the Helm artifact with the latest tag by default.Click the artifact name to enter the artifact details, where you can read basic information such as the usage guide, artifact address, name, description, push time, and download volume.
In addition, you can view recent artifacts and the tag list.
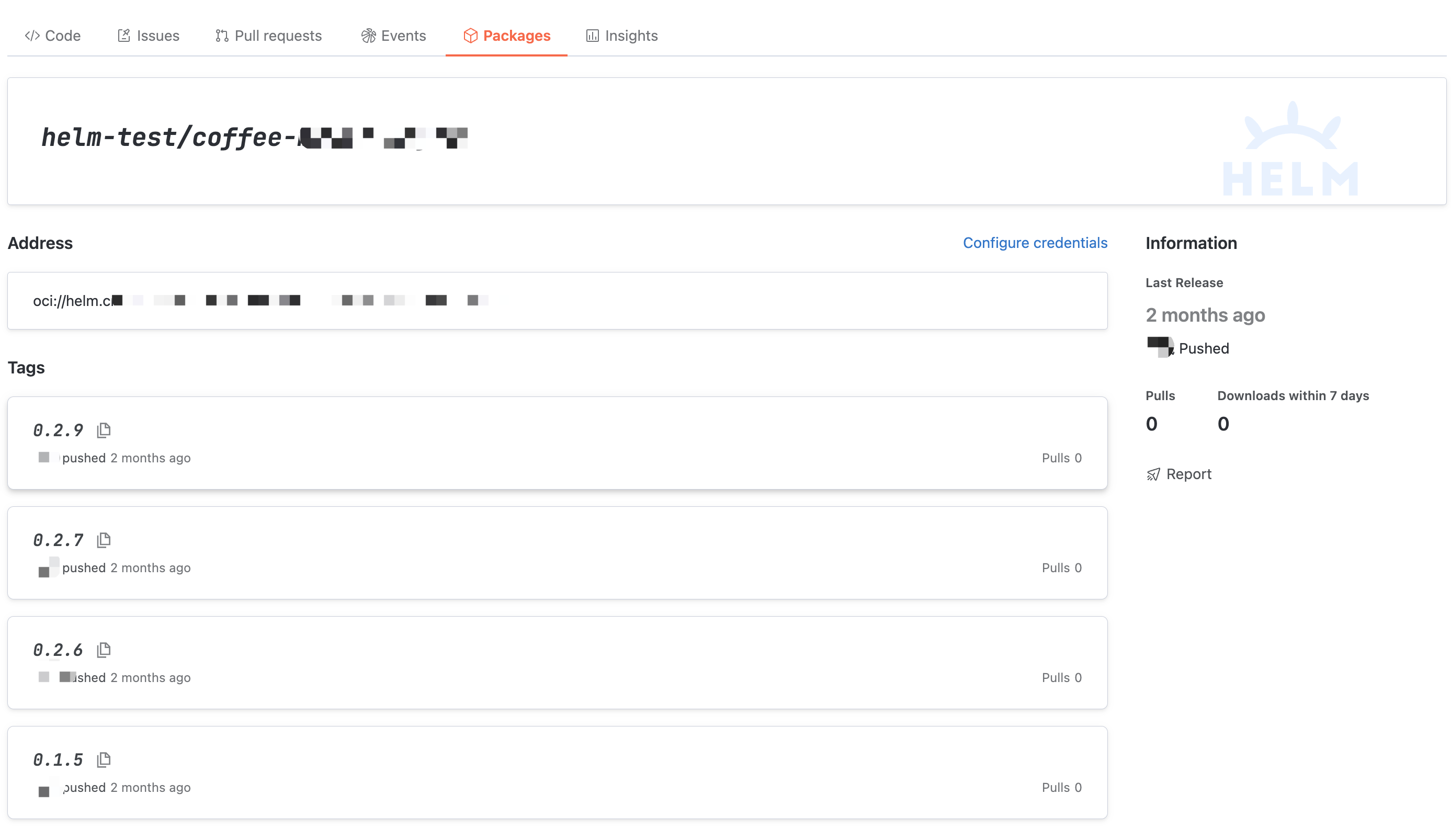
Tag Detail
Access the specified tag of the artifact to view the tag's usage guide, basic information, and usage data.
At this point,
helm pull artifact address to fetch the specified tag.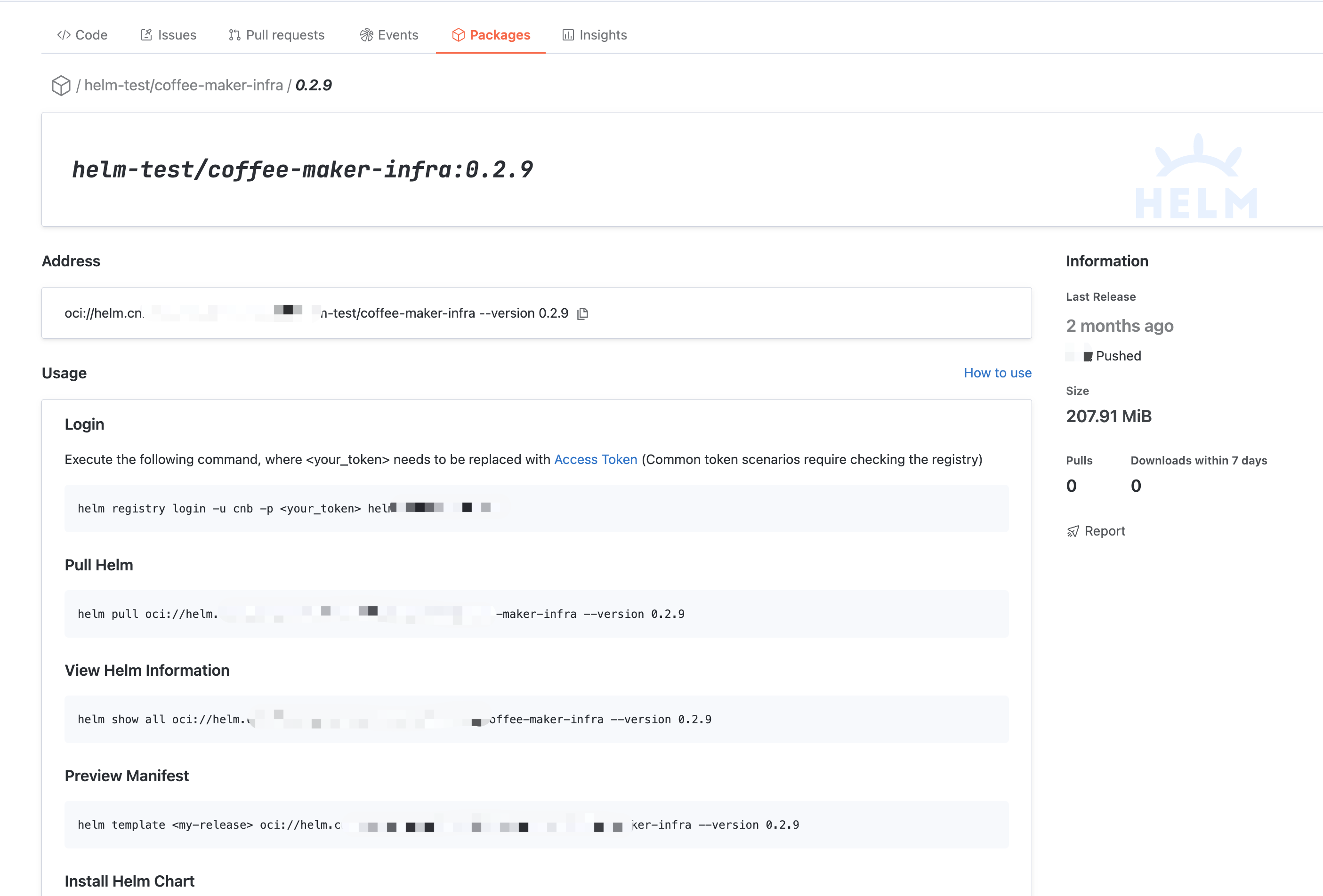
Learn More
Maven
Creating Product Library
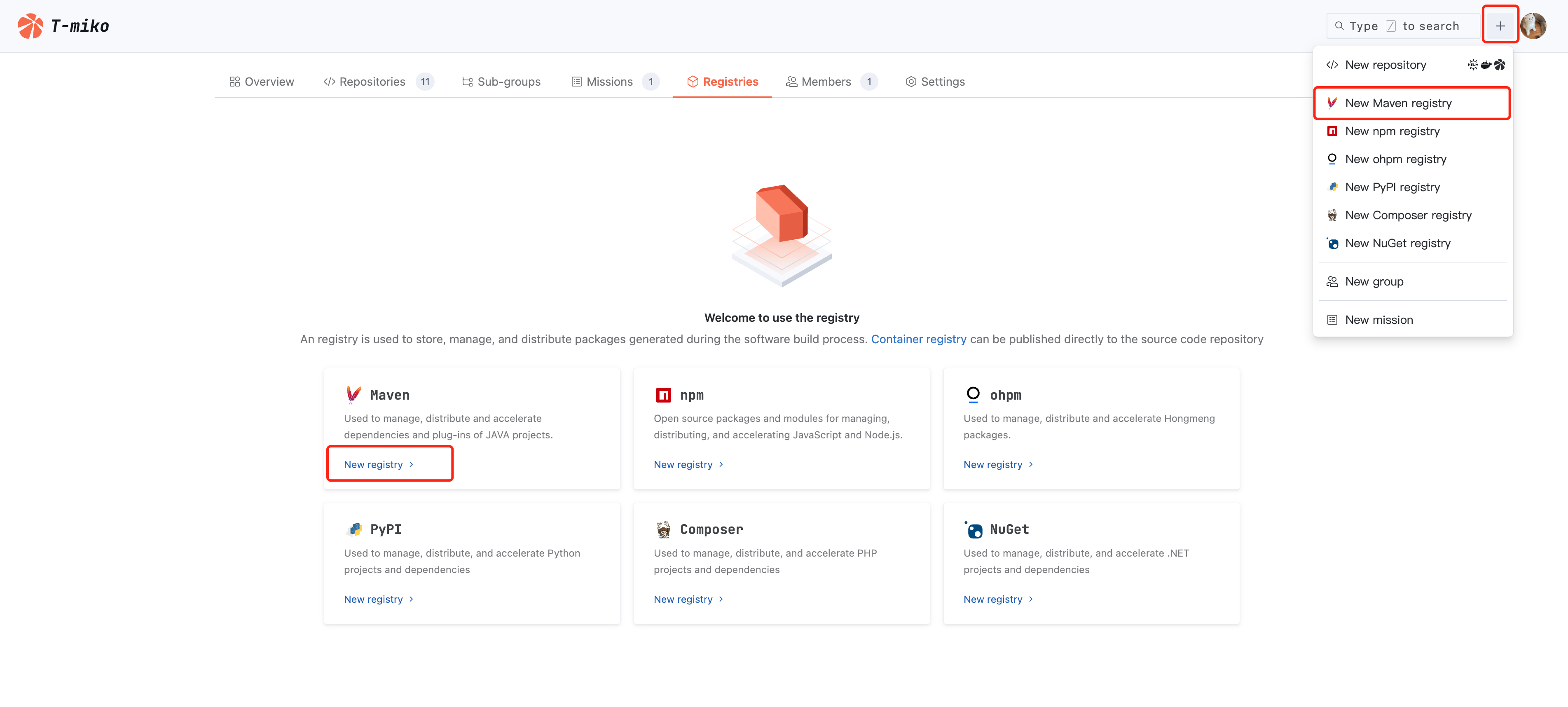
1. Click + > Create Maven Repository in the top right corner of page navigation to quickly initiate creation, or enter a certain organization and click Create Artifact Repository in the Artifact Repository section.
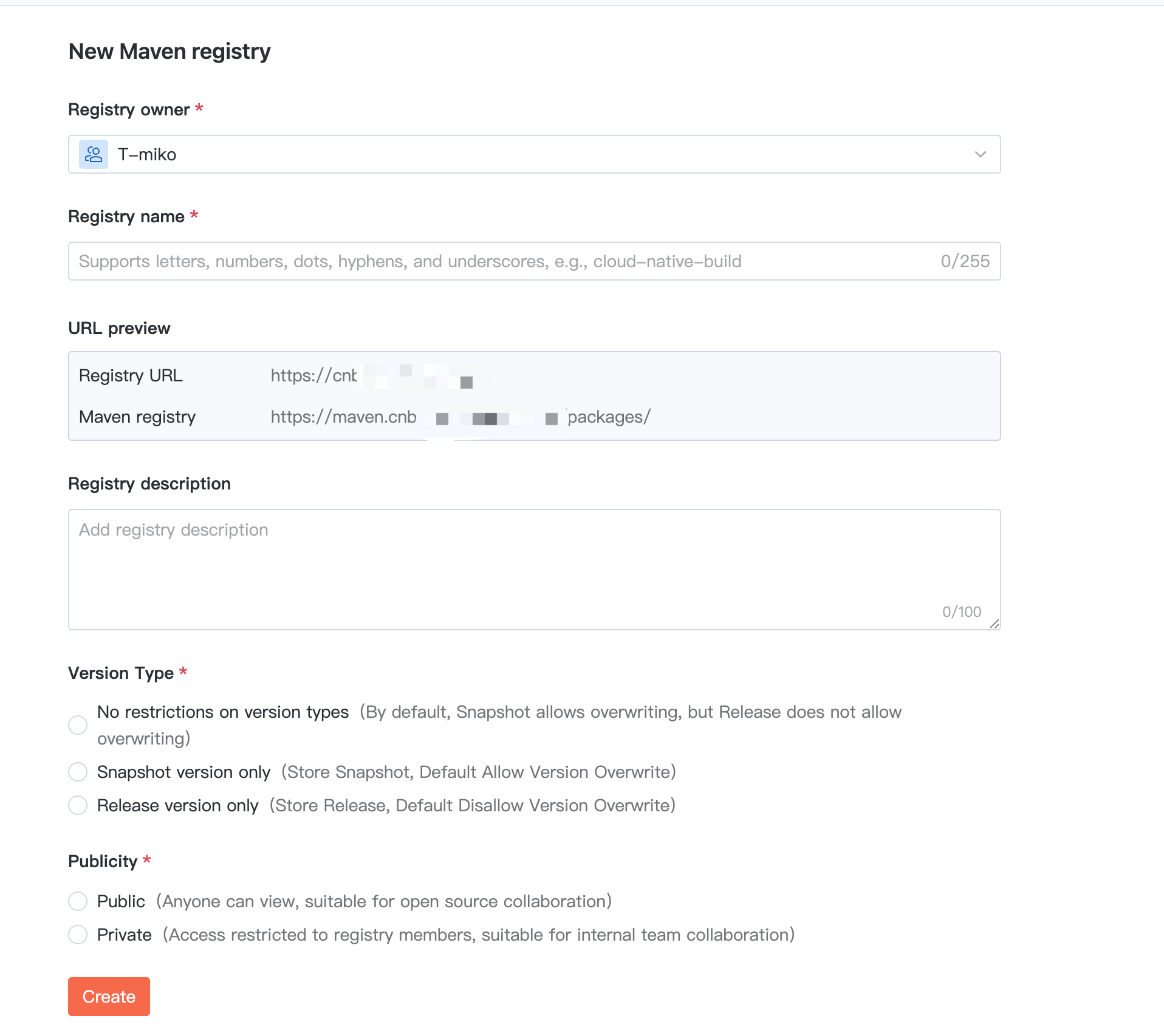
2. When creating a Maven repository, in addition to basic information such as name, description, and visibility, you can configure version types to manage the version strategy of storage products.
Note:
Note: The version policy cannot be modified after creation.
Viewing Artifacts
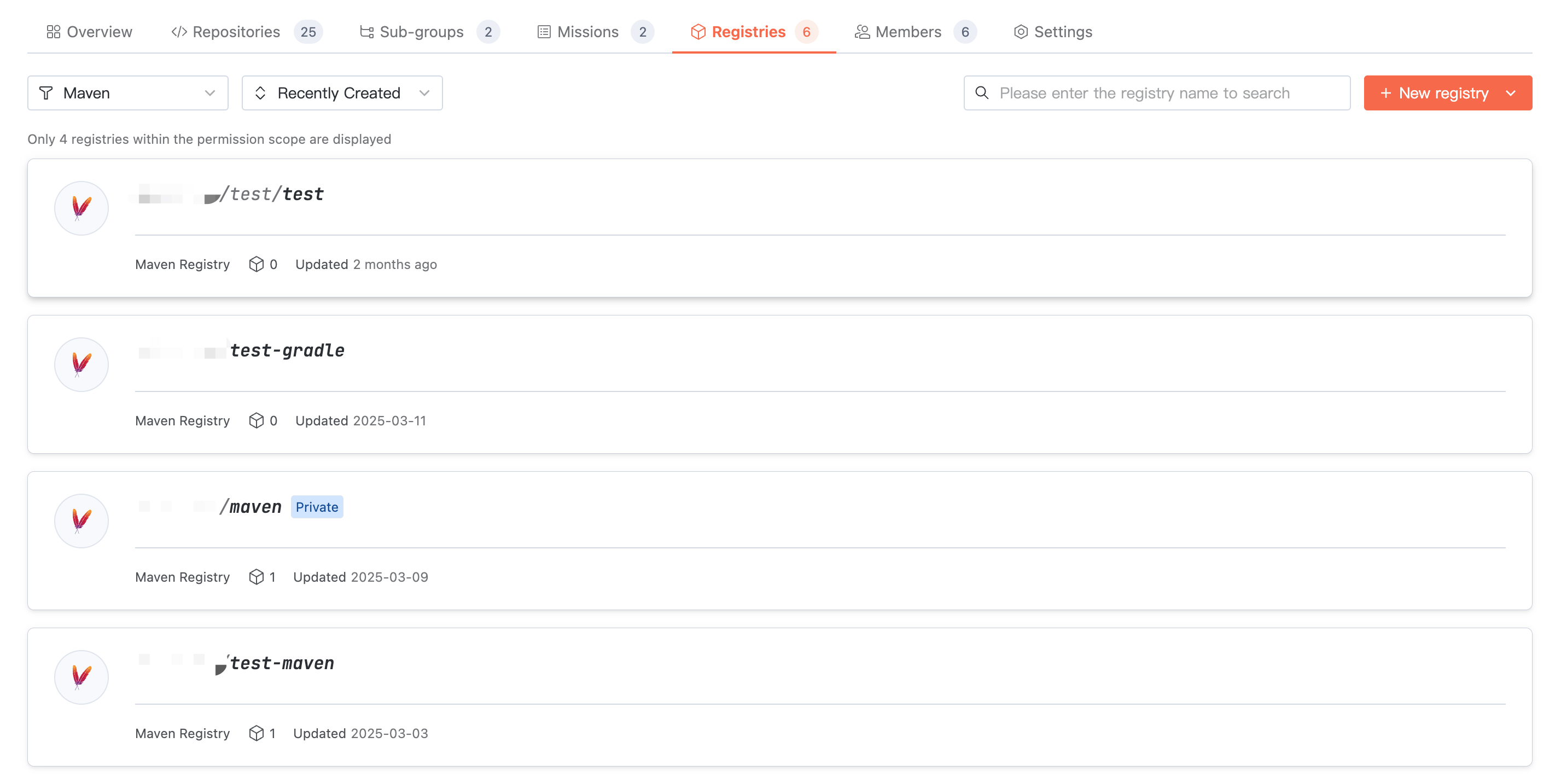
Access target organization > Artifact Repository, where you can view the repository list under the organization. Switch the artifact type to view repositories of the corresponding type.
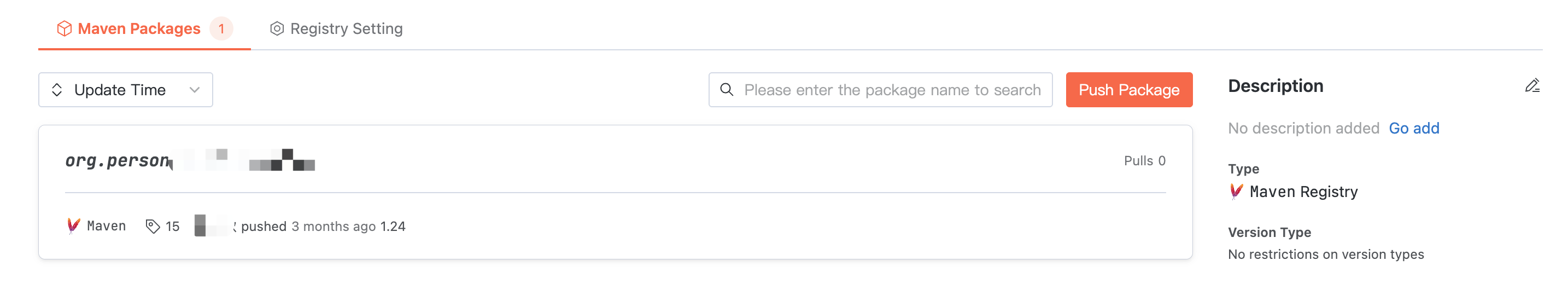
Artifact Package List
Click an artifact repository, and the homepage displays the package list in the repository. The artifact name in the Maven package list consists of the basic information of the Maven package, following the format:
group-id:artifact-id.Click User Guide on the right of the interface to read reference commands for configuring credentials, pulling artifacts, and pushing artifacts.
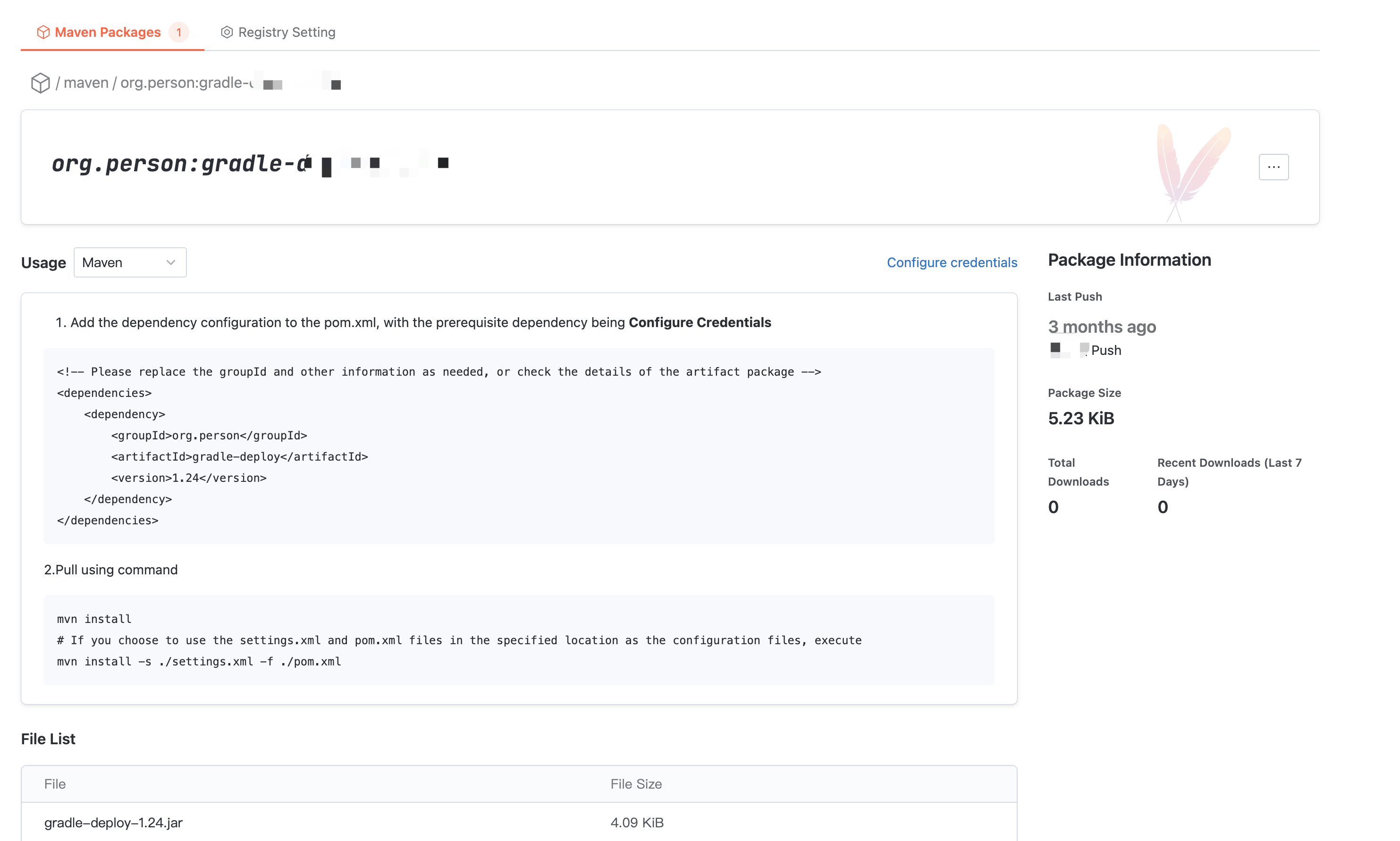
Artifact Package Details
In Artifact Package Details, you can view basic information such as usage guide, name, description, push time, and download volume. Switch usage methods to check the usage guides for different package managers like maven and gradle.
Note:
Note: The version information is not specified in the package detail usage guide. Please replace it.
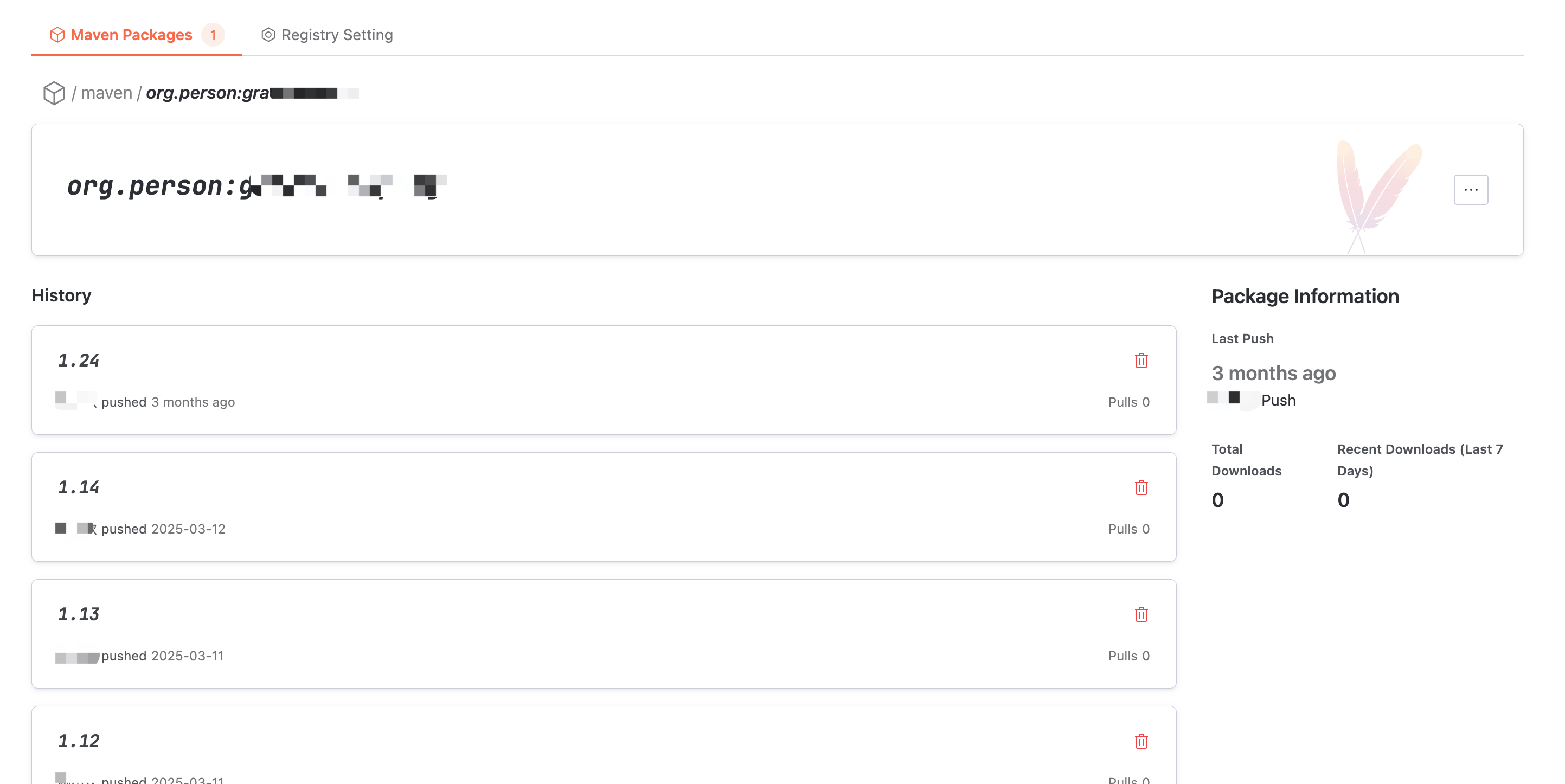
Artifact Package Version Detail
In Artifact Package Details, click the earlier version at the bottom of the interface to enter this version detail. In the file list, you can read the files in the Artifact Package version and check the individual file size.
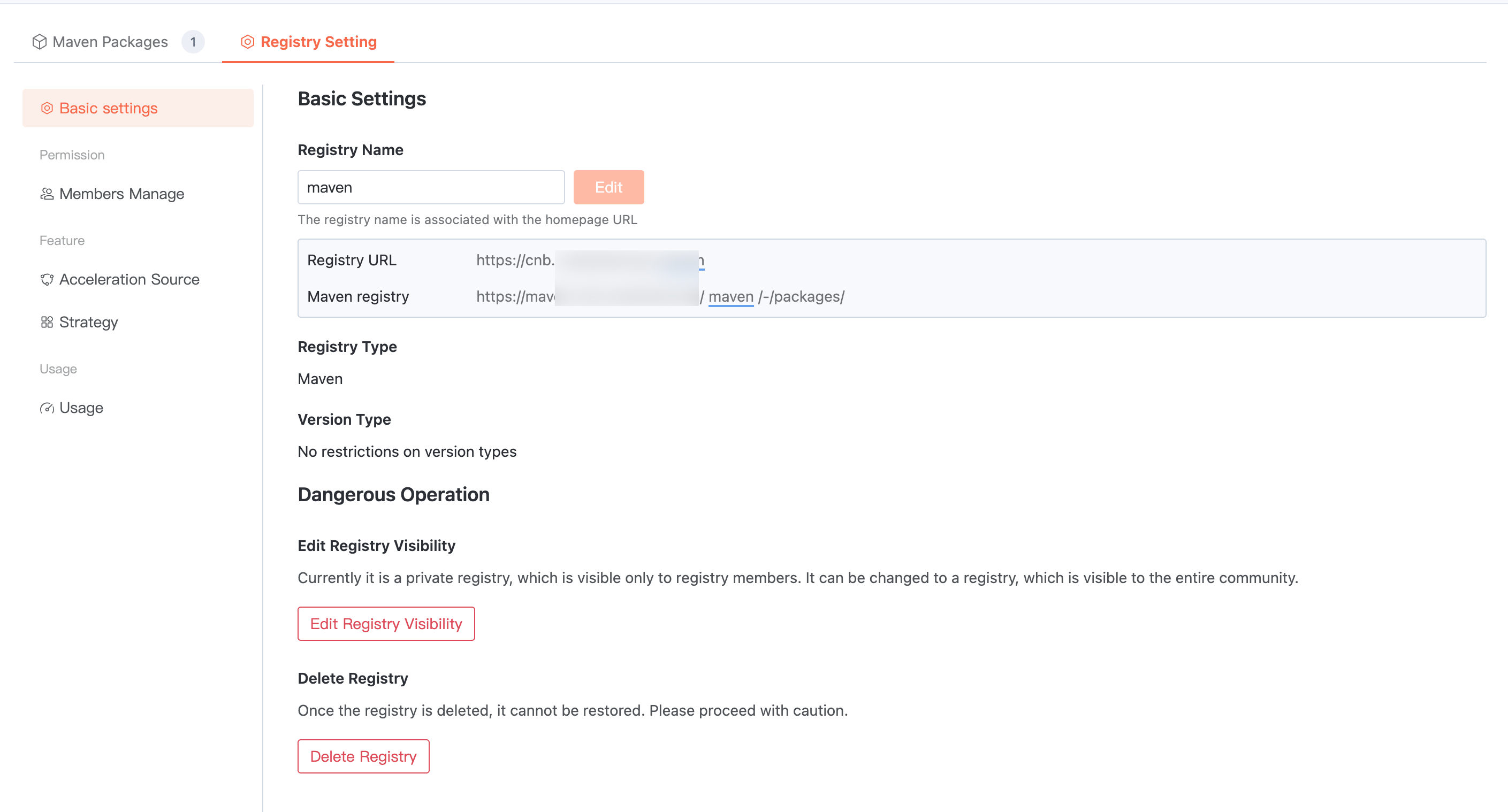
Artifact Repository Settings
Basic Settings
Enter the target artifact repository > Artifact Repository Settings > Basic Settings. The artifact repository name can be modified, visibility can be changed, and the repository can be deleted.
Member Management
Permissions are inherited by default from the parent organization for all members. In addition, you can invite Member directly to join the current artifact repository as "artifact repository members" or "external Collaborators". Among them, external Collaborators are suitable for users temporarily participating in collaboration.
Proxy Settings
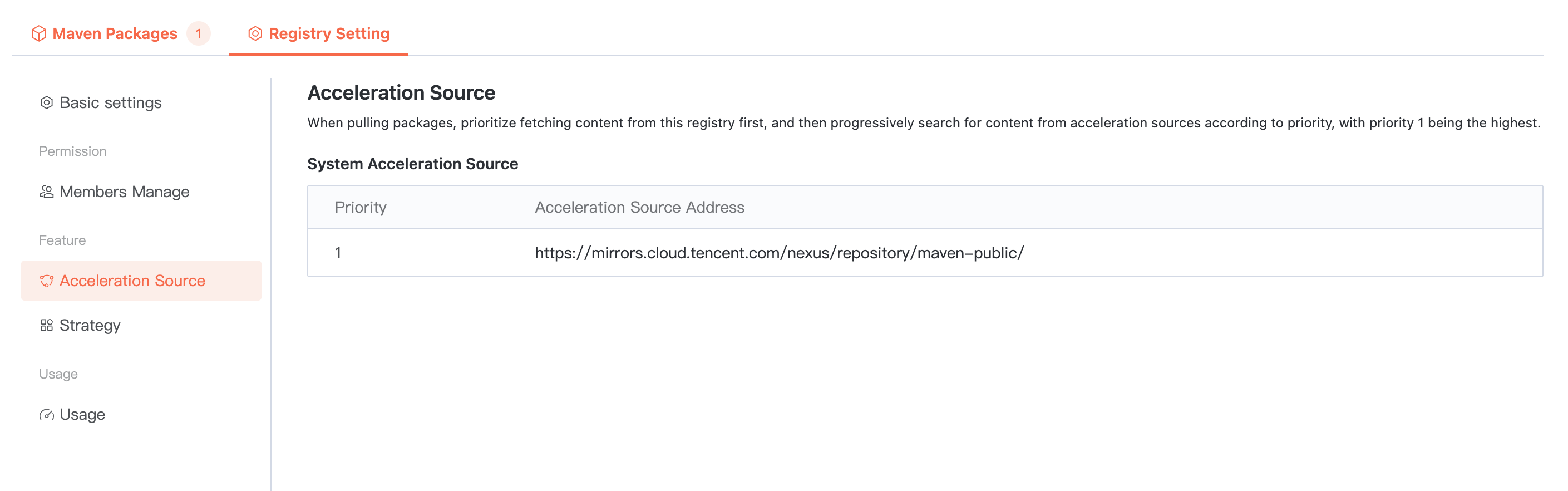
To enhance the pull efficiency of public artifacts, the Cloud Native Build artifact repository is configured with a built-in acceleration source. When using the artifact repository, you can directly speed up based on the built-in source address.
Policy Management
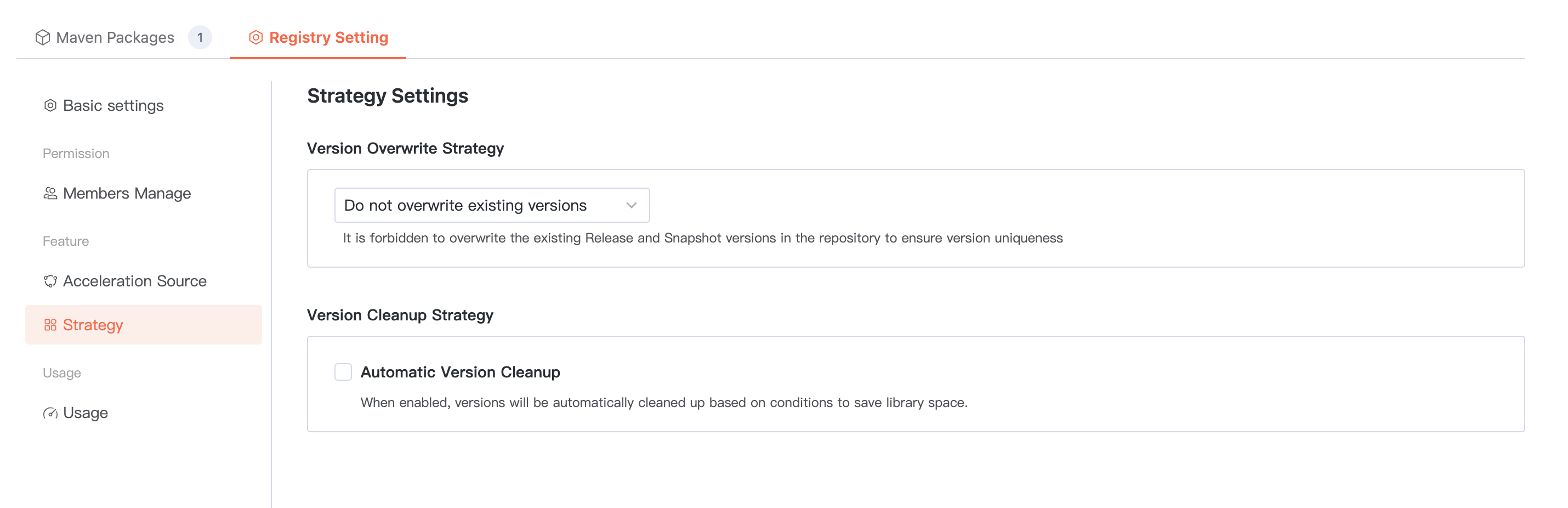
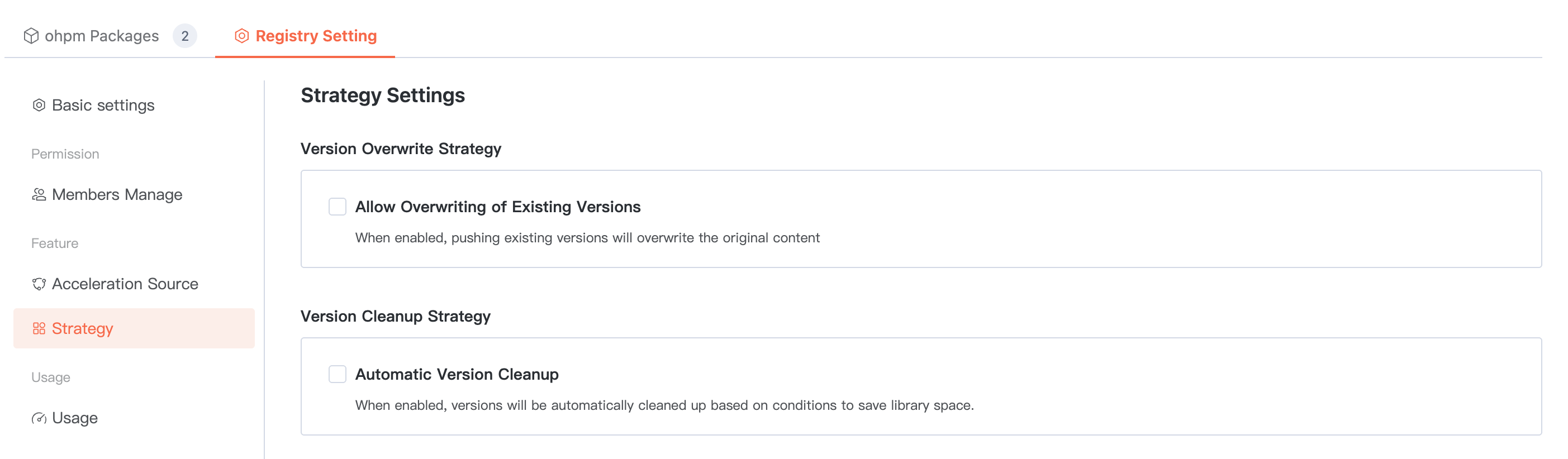
Configurable artifact package overwrite policy and cleanup policy.
When configuring the cleanup policy, you can set the maximum number of versions to reserve. If it exceeds this limit, the system will automatically clean up earlier push time/earlier usage time based on configuration to save database space.
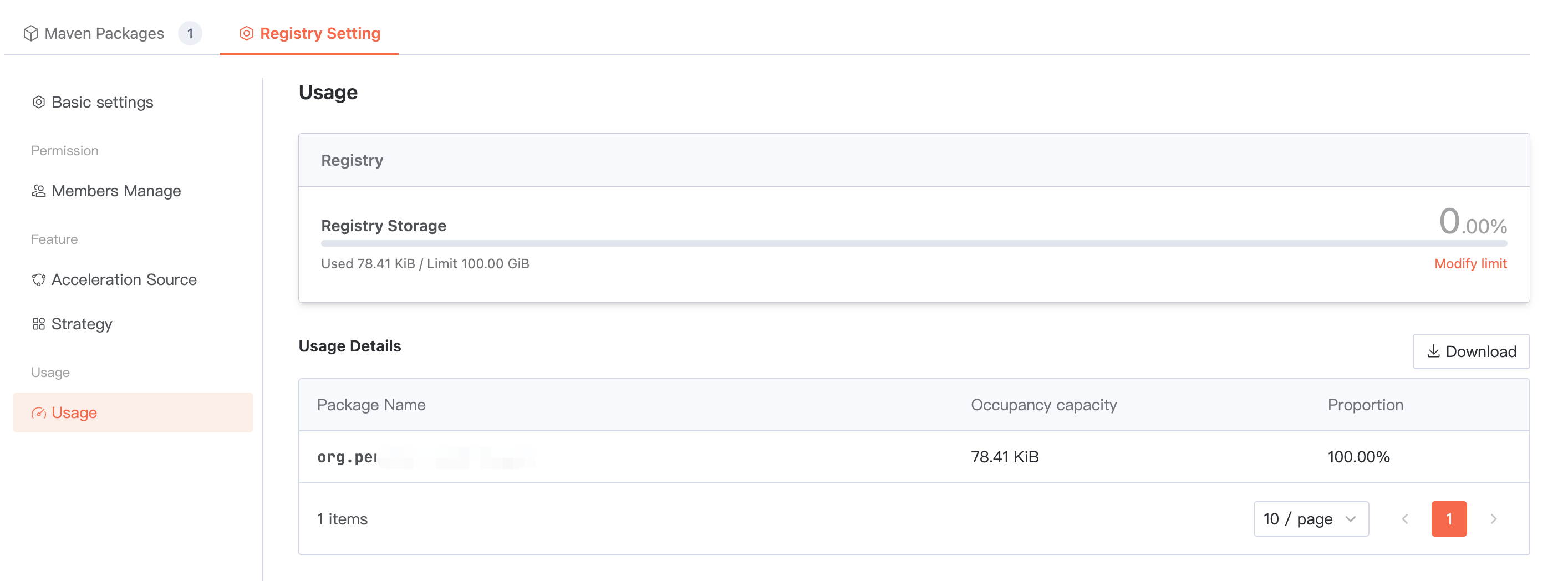
Usage statistics
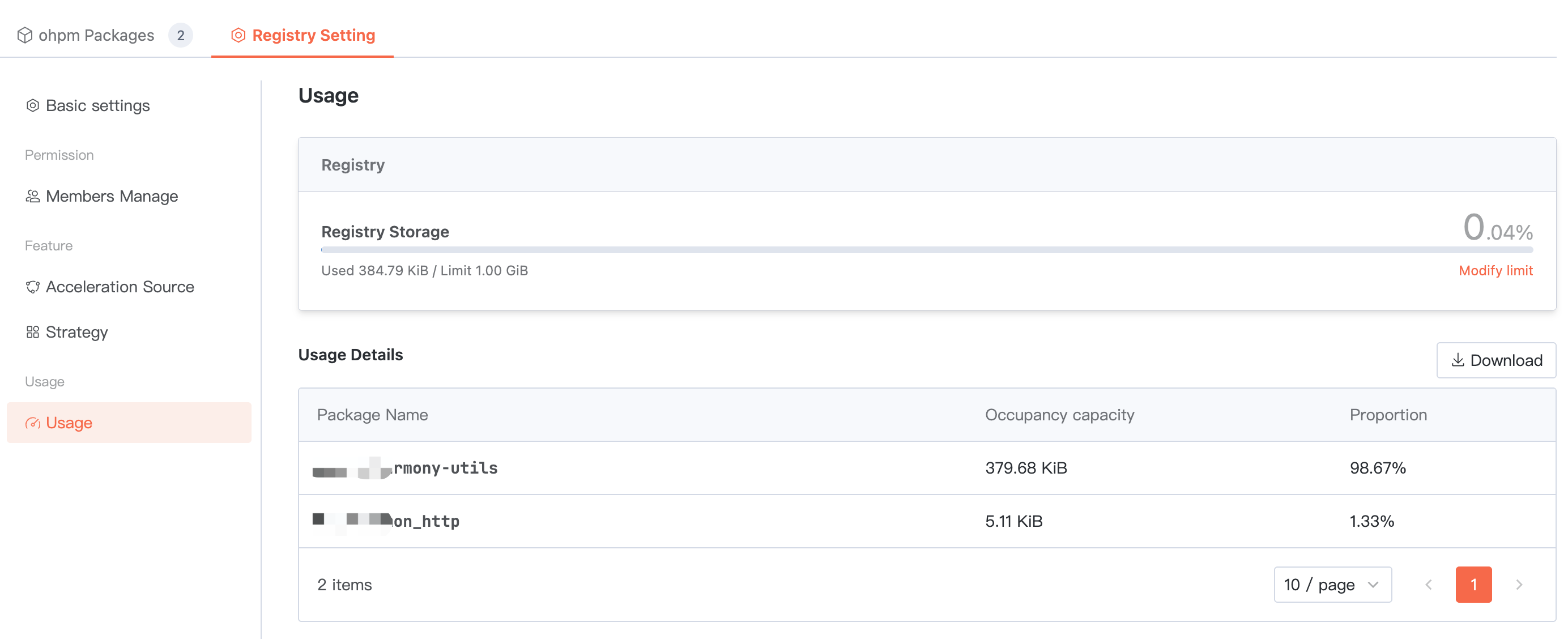
Summarize the total storage space occupied by ALL packages in the current artifact repository. Below, you can view the usage of each package and support downloading the detailed list.
npm
Creating Product Library
1. Click + > Create npm Repository in the upper-right corner of cnb.build to quickly initiate creation, or enter a certain organization and click Create Artifact Repository in the Artifact Repository section.
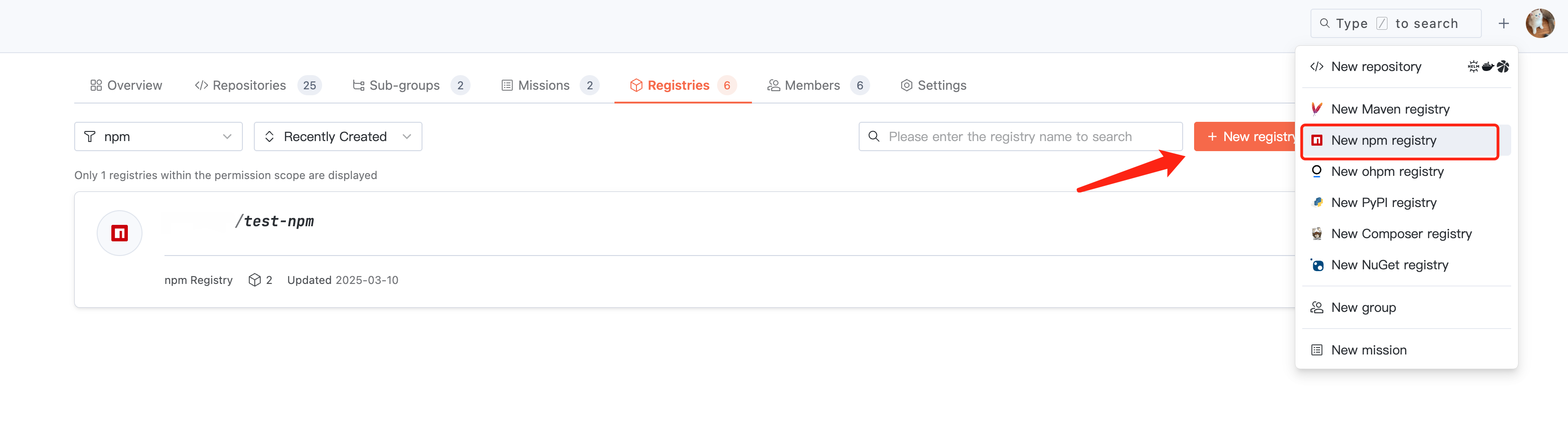
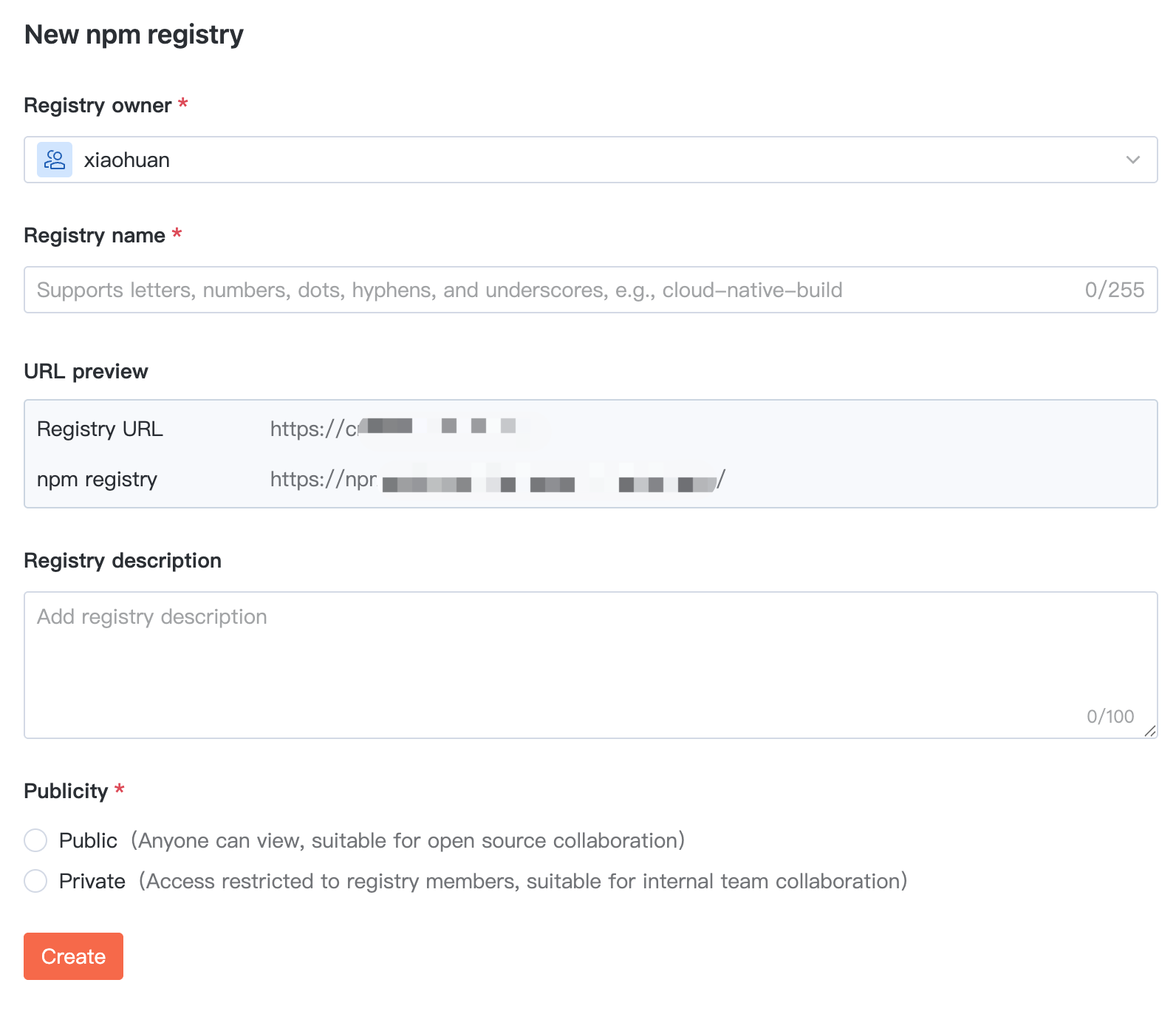
2. To create an npm artifact repository, configure the name, description, and visibility in basic information.
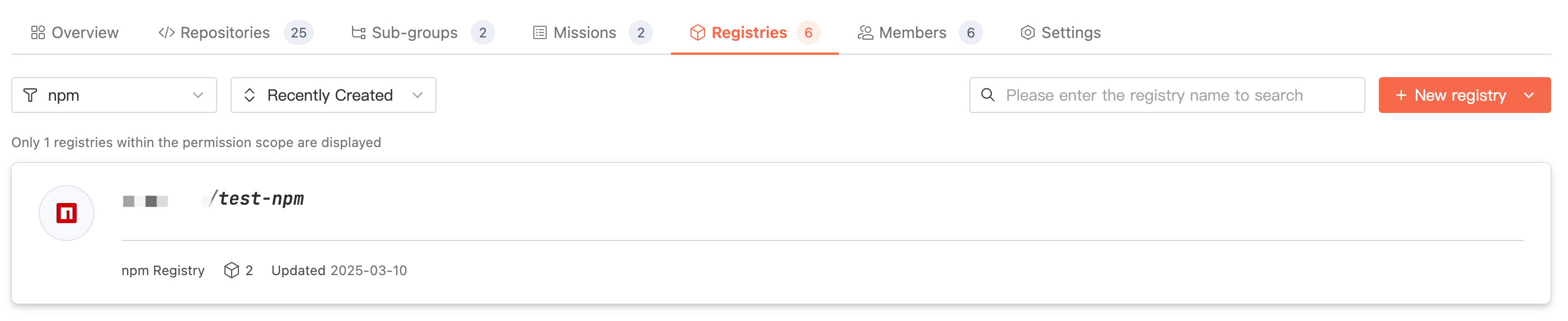
Viewing Artifacts
Access target organization > Artifact Repository, where you can view the repository list under the organization. Switch the artifact type to view repositories of the corresponding type.
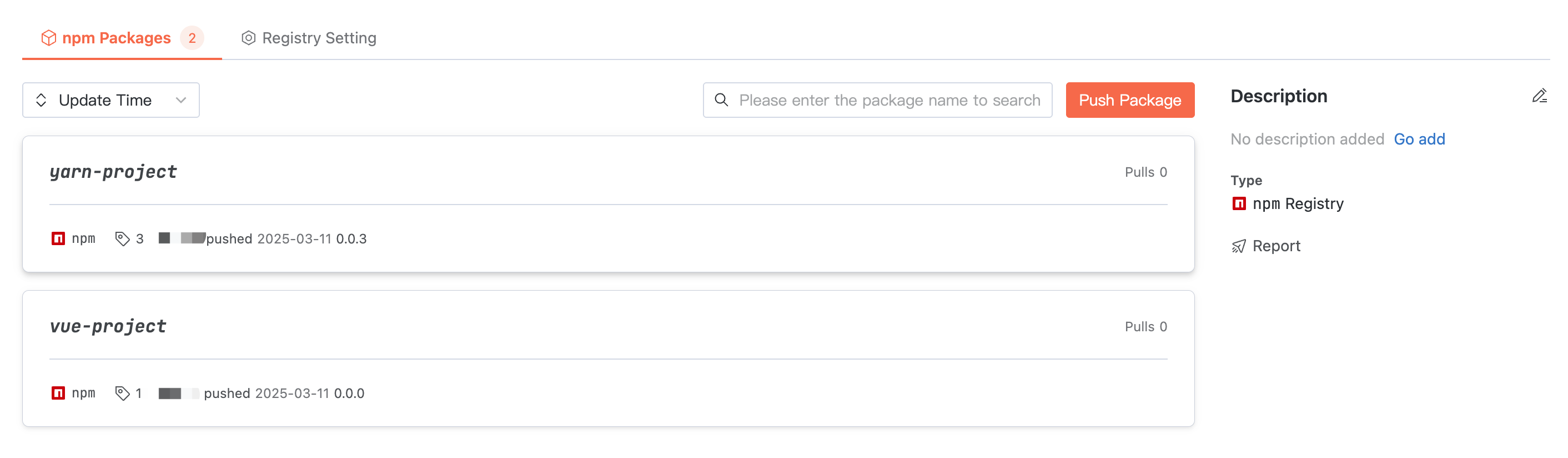
Artifact Package List
Click an artifact repository, and the homepage displays the package list in the repository. The artifact name in the npm package list is specified by
package.json with name.Click User Guide on the right of the interface to read reference commands for configuring credentials, pulling artifacts, and pushing artifacts.
Artifact Package Details
In Artifact Package Details, you can view basic information such as usage guide, name, description, push time, and download volume. Switch usage methods to check the command guides for different ways to use npm and yarn.
Note:
When npm pulls a package with no version specified, it will fetch the version tagged as
latest.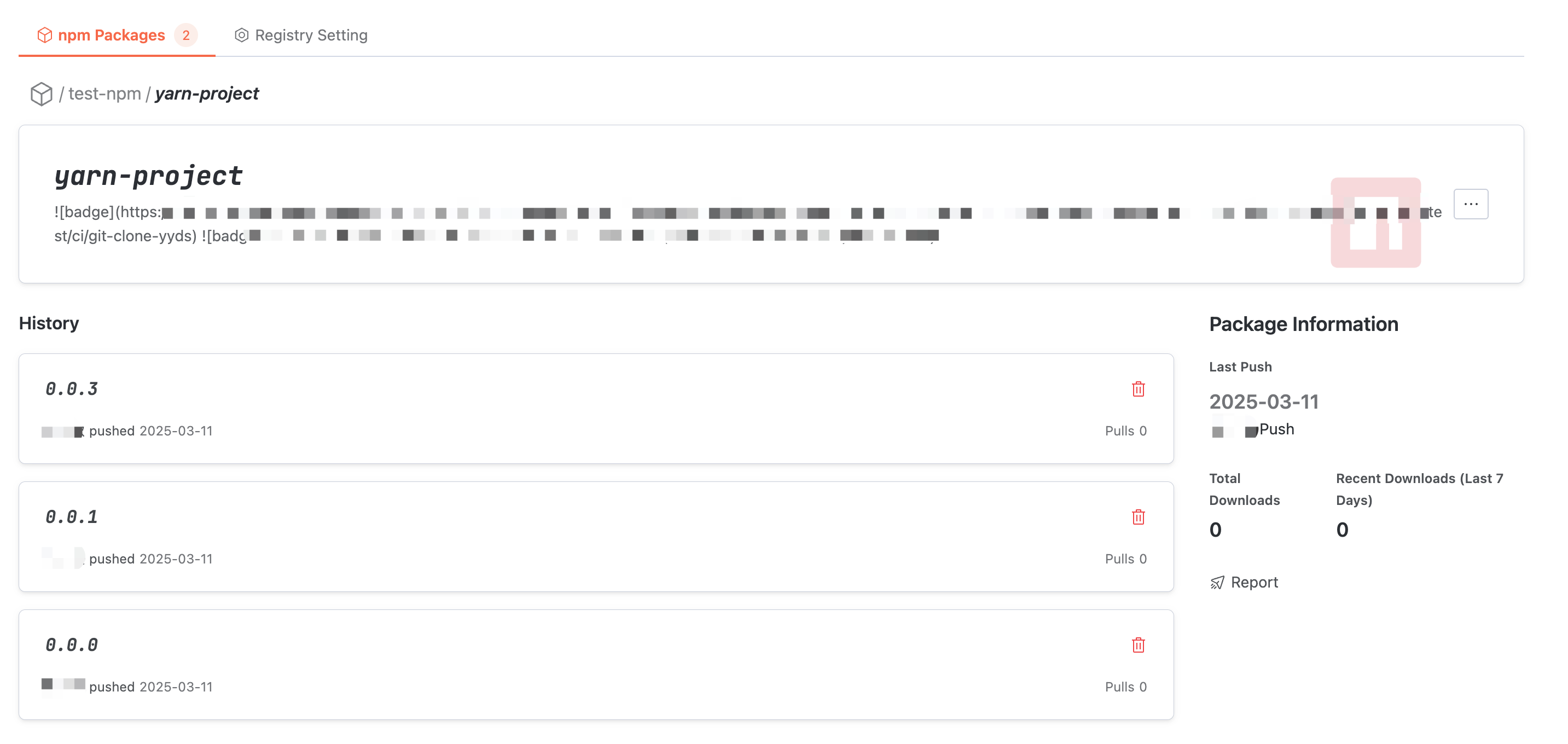
Artifact Package Version Detail
In Artifact Package Details, click the earlier version at the bottom of the interface to enter this version detail.
In the file list, you can read the files in the Artifact Package version and check the individual file size.
In the dependency list, you can check the other packages and versions that the artifact package version depends on, taken from
package.json dependencies.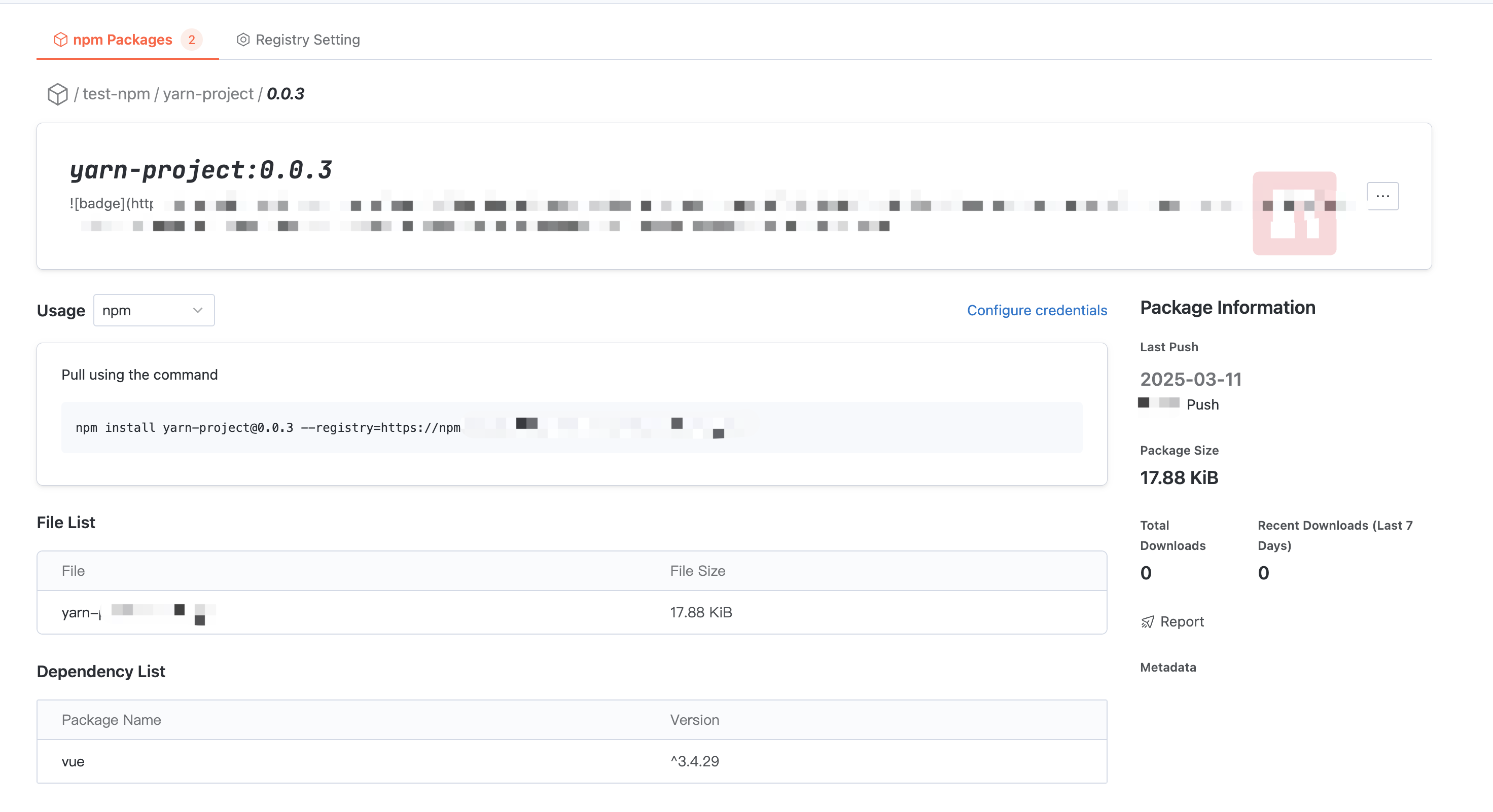
Artifact Repository Settings
Basic Settings
Enter the target artifact repository > Artifact Repository Settings > Basic Settings. The artifact repository name can be modified, visibility can be changed, and the repository can be deleted.
Member Management
Permissions are inherited by default from the parent organization for all members. In addition, you can invite members directly to join the current artifact repository as "artifact repository members" or "external Collaborators". Among them, external Collaborators are suitable for users temporarily participating in collaboration.
Proxy Settings
To enhance the pull efficiency of public artifacts, the Cloud Native Build artifact repository is configured with a built-in acceleration source. When using the artifact repository, you can directly speed up based on the built-in source address.
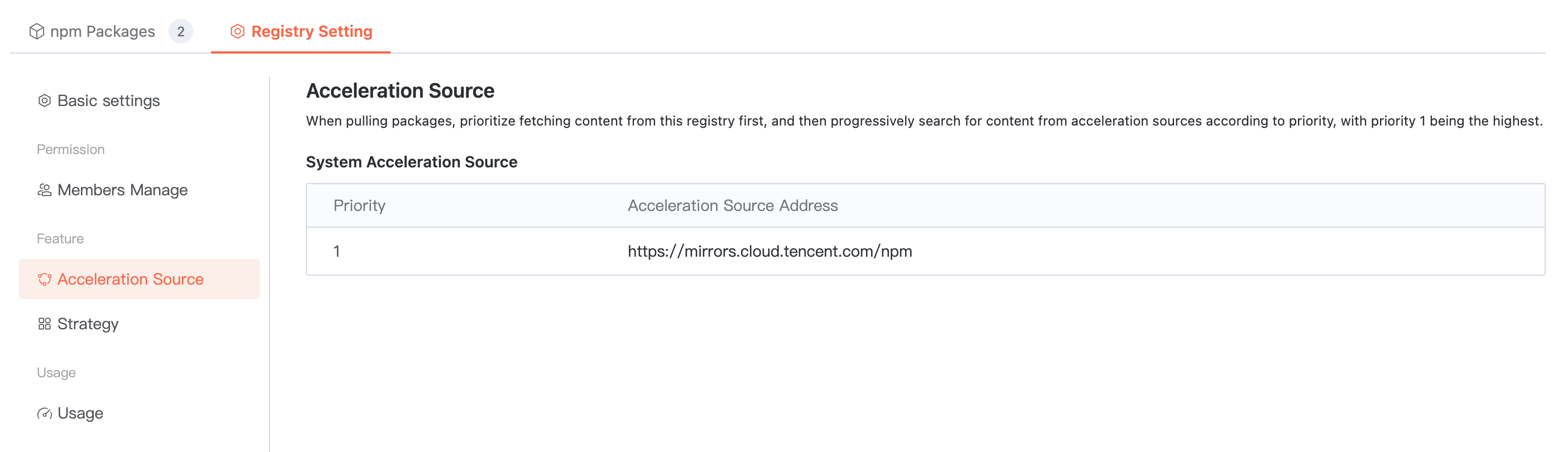
Policy Management
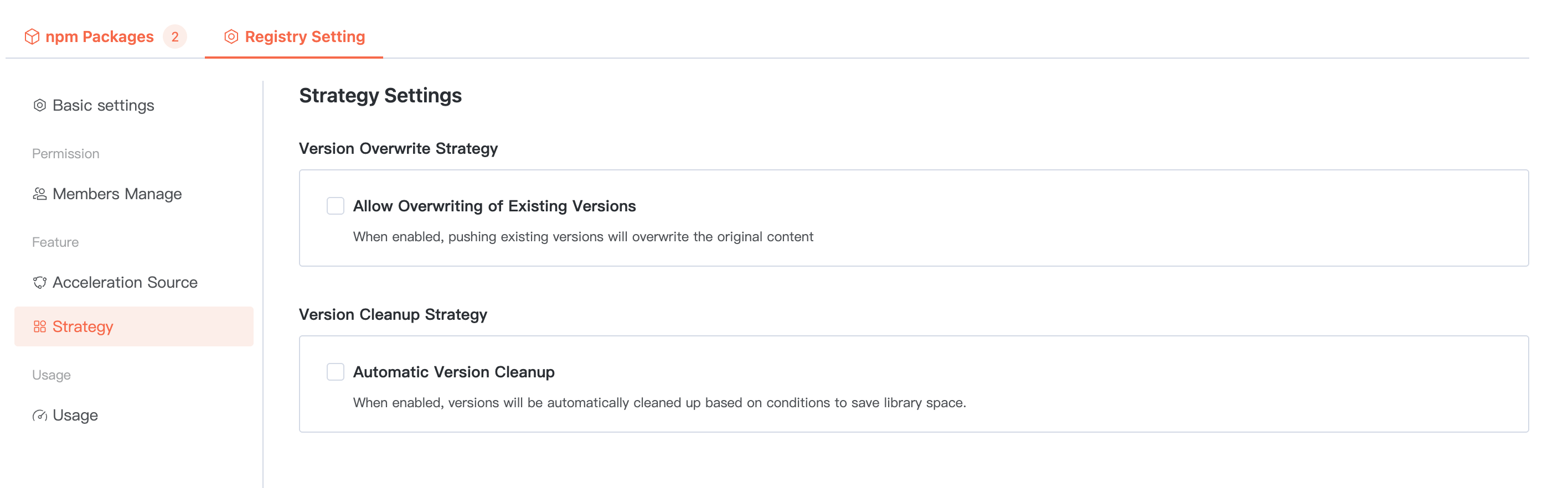
Configurable artifact package overwrite policy and cleanup policy.
When configuring the cleanup policy, you can set the maximum number of versions to reserve. If it exceeds this limit, the system will automatically clean up earlier push time/earlier usage time based on configuration to save database space.
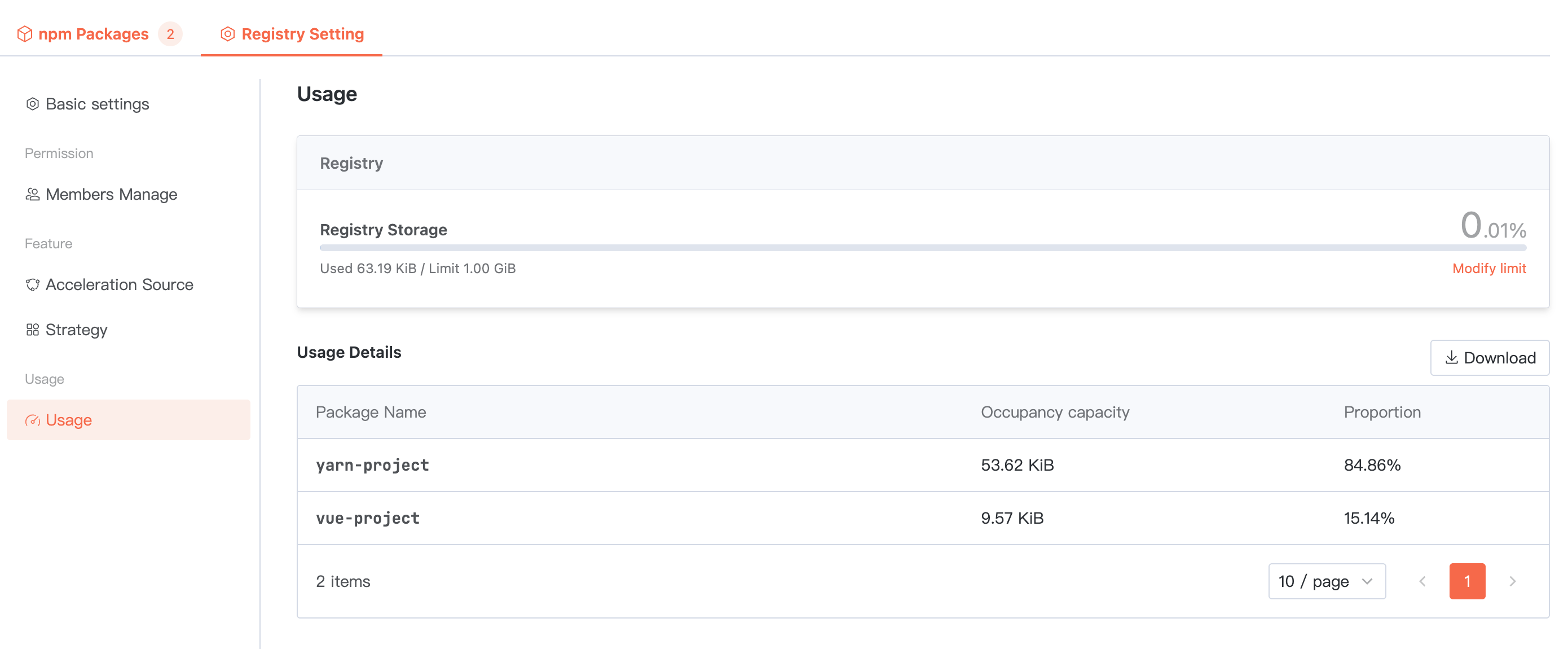
Usage statistics
Summarize the total storage space occupied by ALL packages in the current artifact repository. Below, you can view the usage of each package and support downloading the detailed list.
ohpm
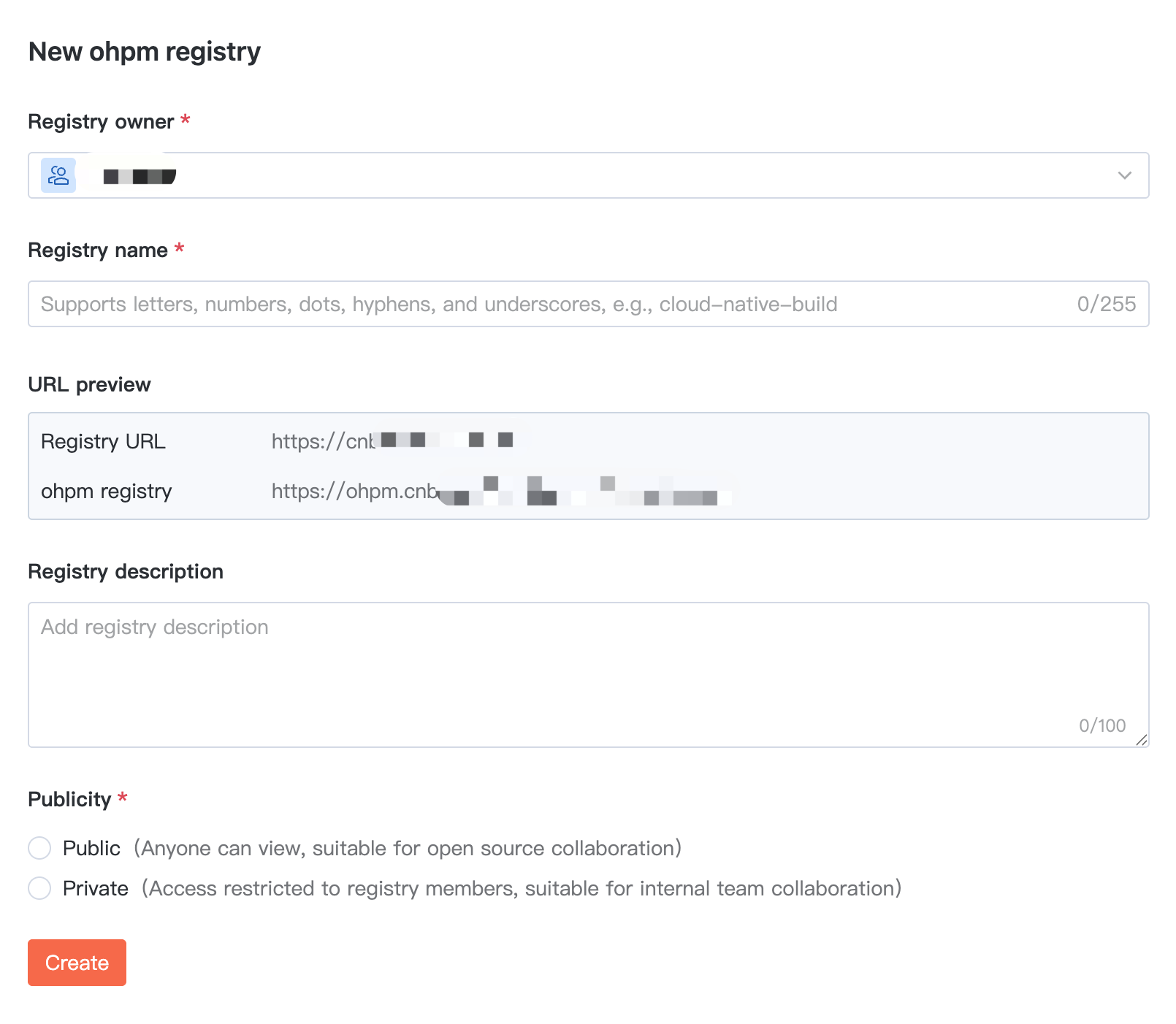
Creating Product Library
1. Click + > Create ohpm Repository in the top right corner of the page navigation to quickly initiate creation, or enter a certain organization and click Create Artifact Repository in the Artifact Repository section.
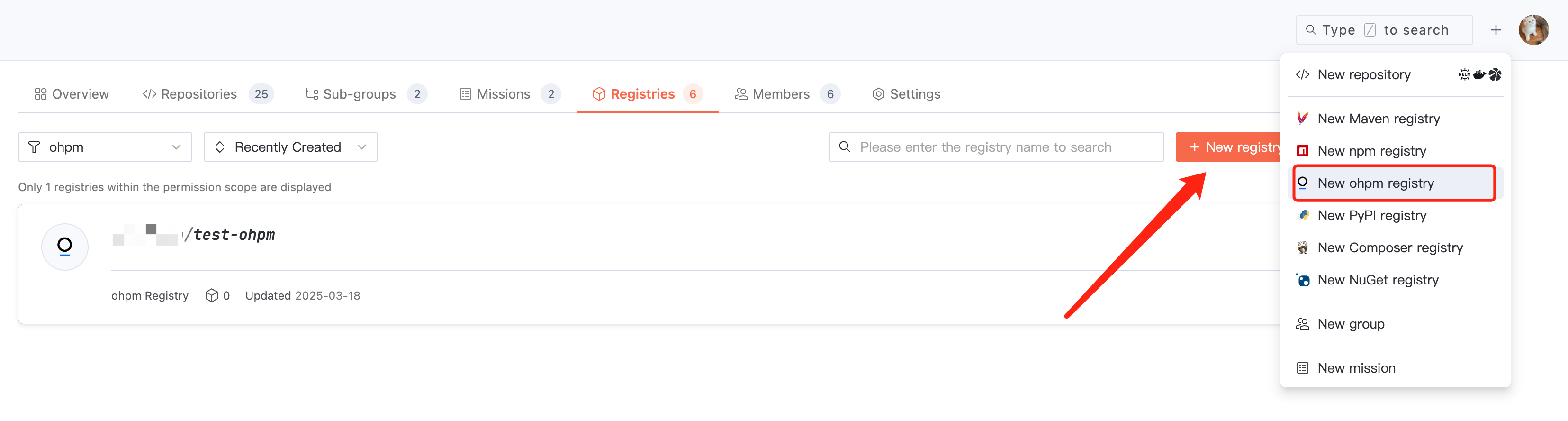
2. To create an ohpm artifact repository, configure the name, description, and visibility in basic information.
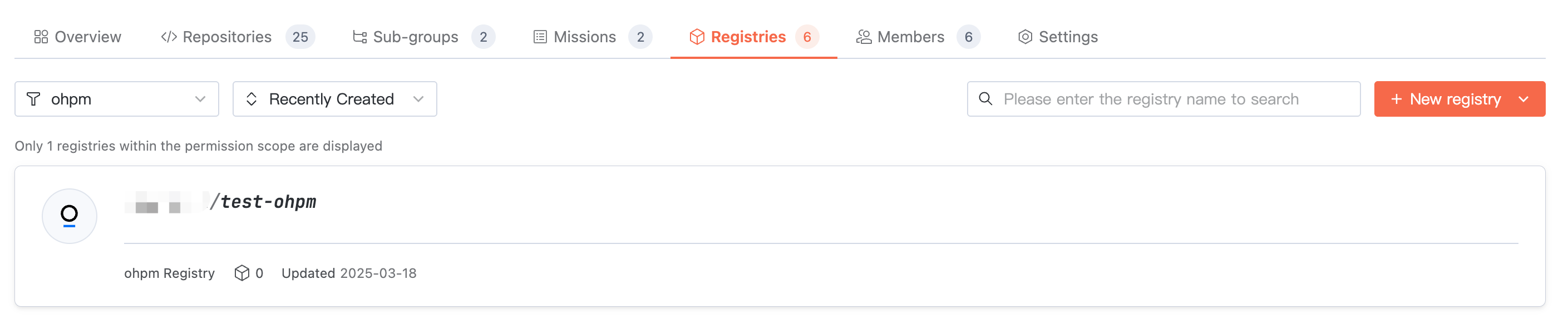
Viewing Artifacts
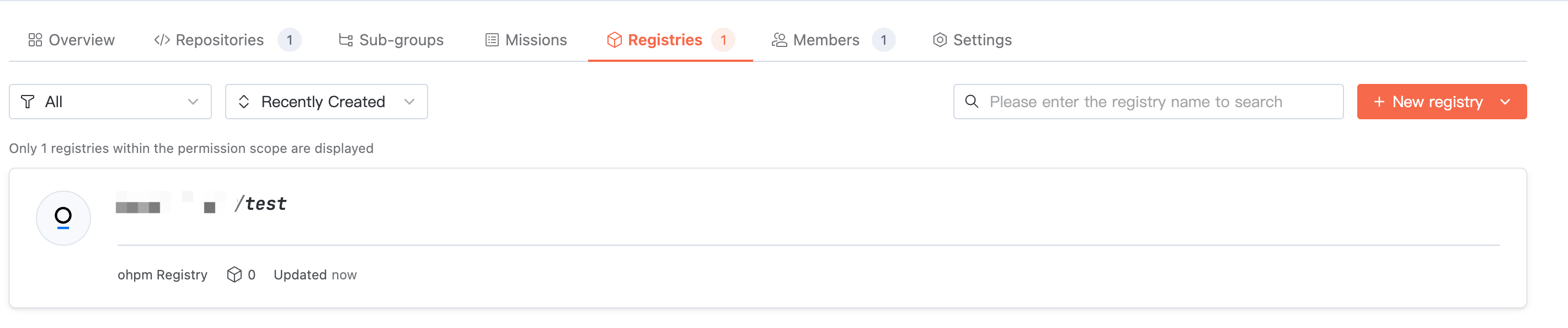
Access target organization > Artifact Repository, where you can view the repository list under the organization. Switch the artifact type to view repositories of the corresponding type.
Artifact Package List
Click an artifact repository, and the homepage displays the package list in the repository. The artifact name in the ohpm package list is specified by
oh-package.json5 with name.Click User Guide on the right of the interface to read reference commands for configuring credentials, pulling artifacts, and pushing artifacts.
Artifact Package Details
In the artifact package details, you can read basic information such as the usage guide, name, description, push time, and download volume.
Note:
Note: When ohpm pulls a package with no version specified, it will fetch the version tagged as
latest.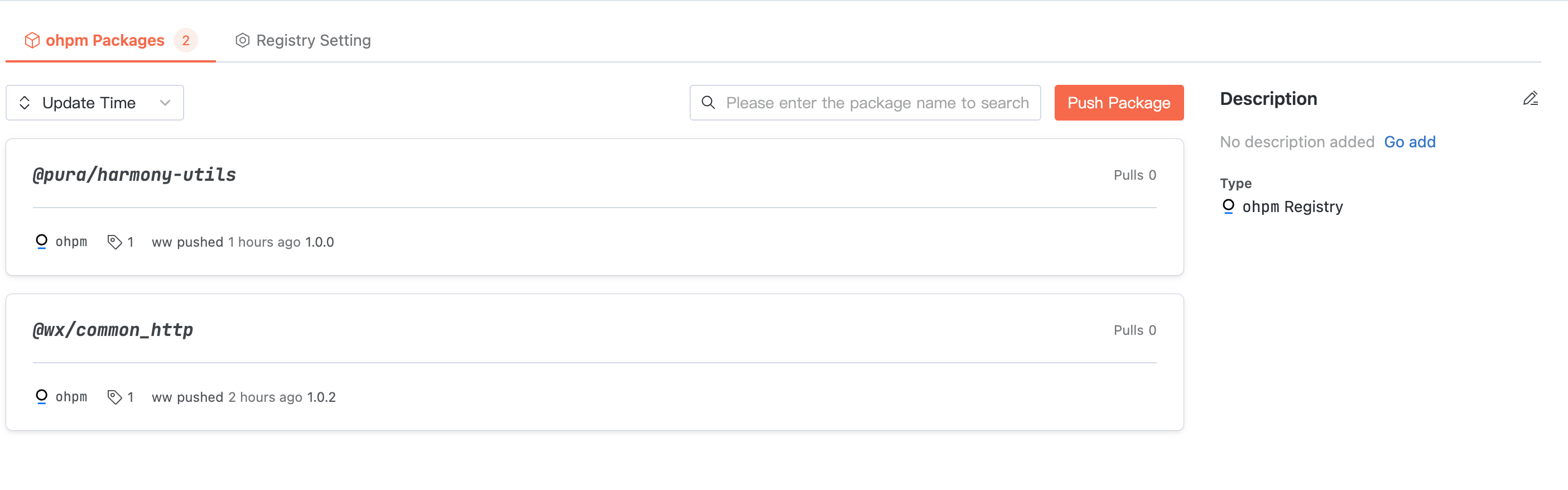
Artifact Package Version Detail
In Artifact Package Details, click the earlier version at the bottom of the interface to enter this version detail.
In the file list, you can read the files in the Artifact Package version and check their size.
In the dependency list, you can check the other packages and versions that the artifact package version depends on, taken from
oh-package.json5 dependencies.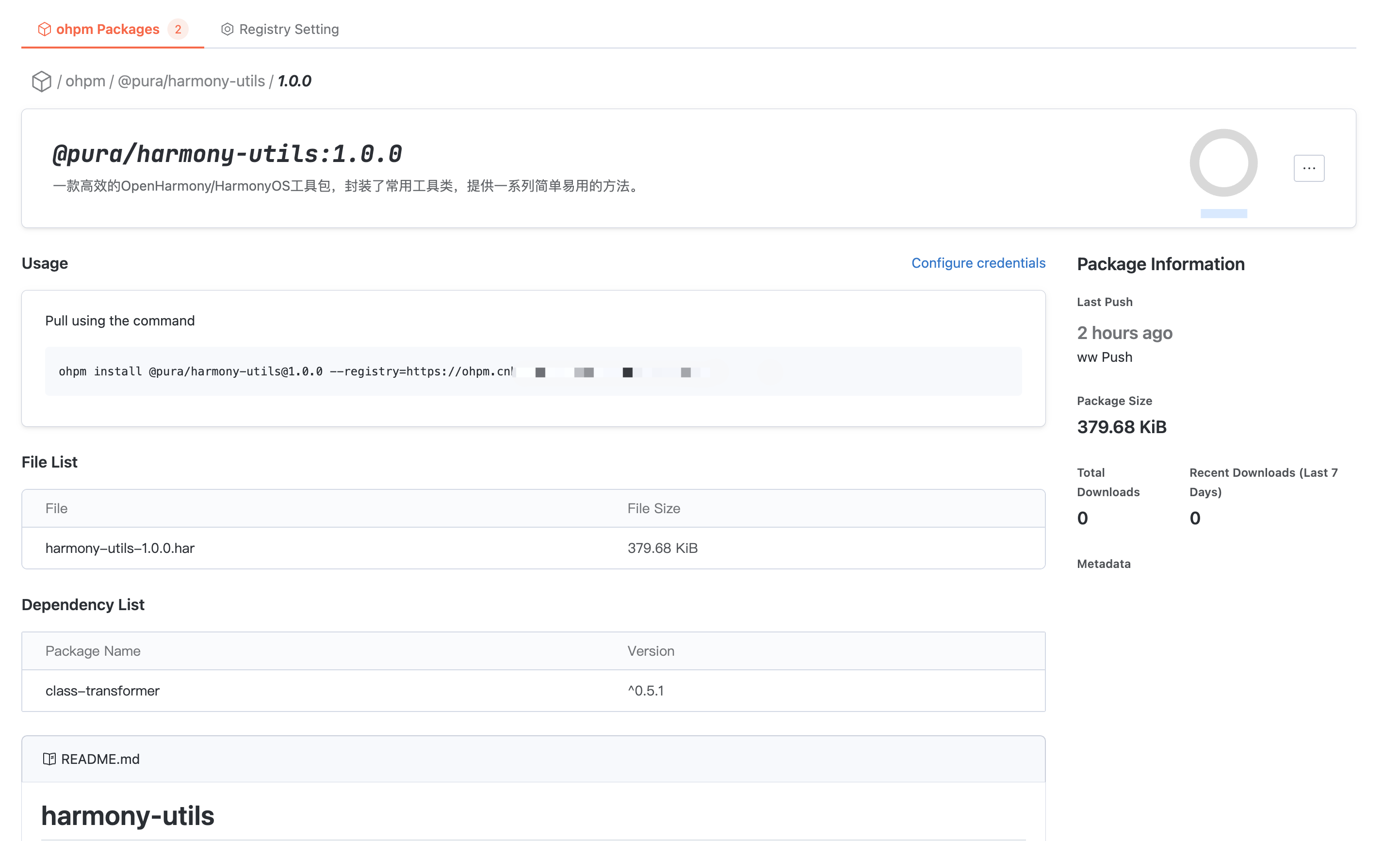
Artifact Repository Settings
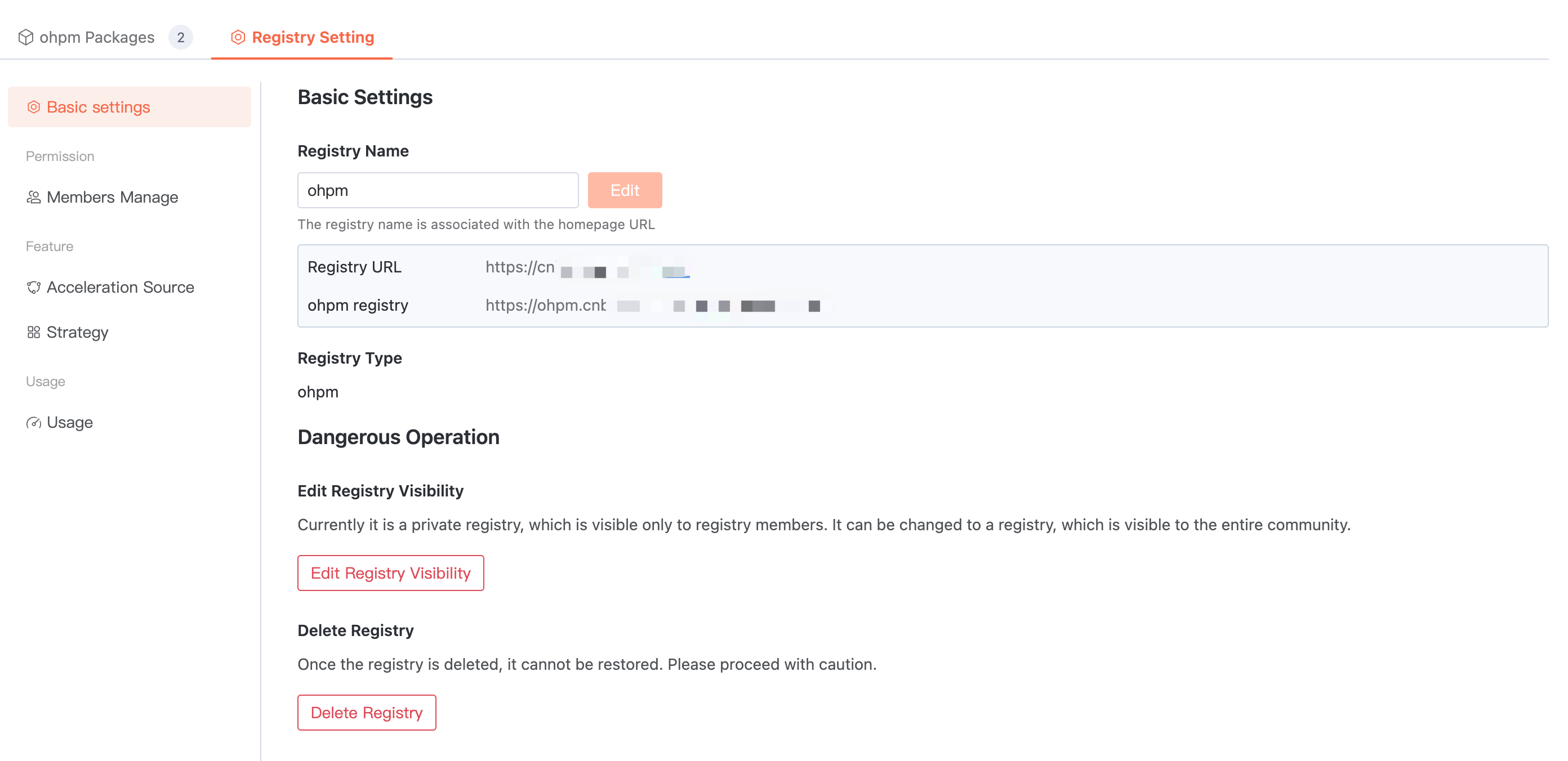
Basic Settings
Enter the target artifact repository > Artifact Repository Settings > Basic Settings. The artifact repository name can be modified, visibility can be changed, and the repository can be deleted.
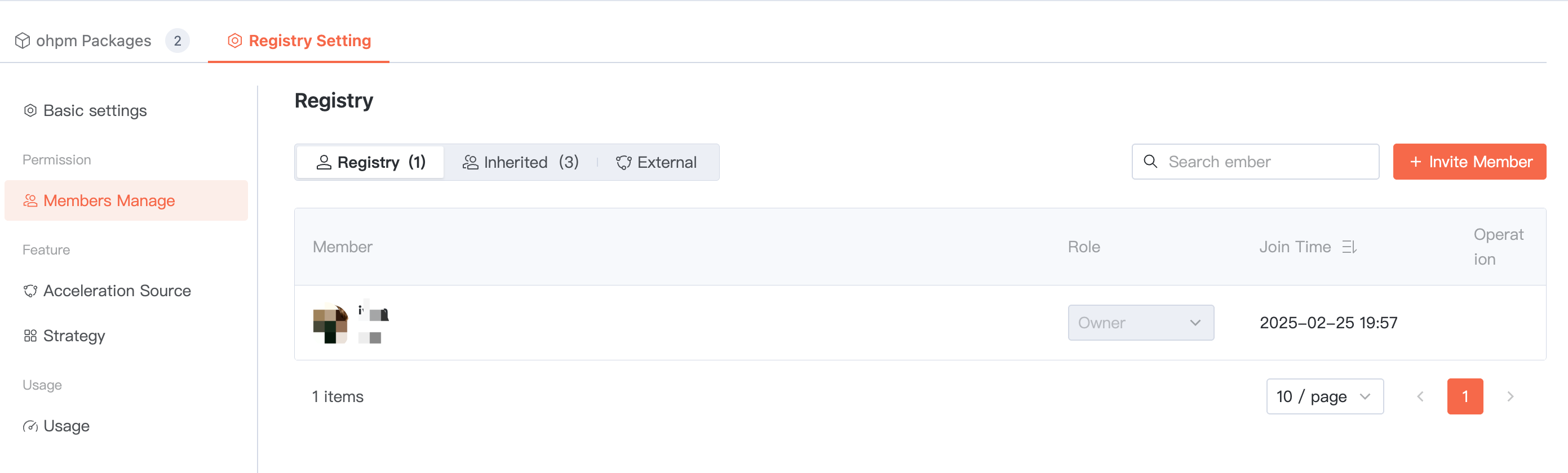
Member Management
Permissions are inherited by default from the parent organization for all members. In addition, you can Invite Member directly to join the current artifact repository as "artifact repository members" or "external Collaborators". Among them, external Collaborators are suitable for users temporarily participating in collaboration.
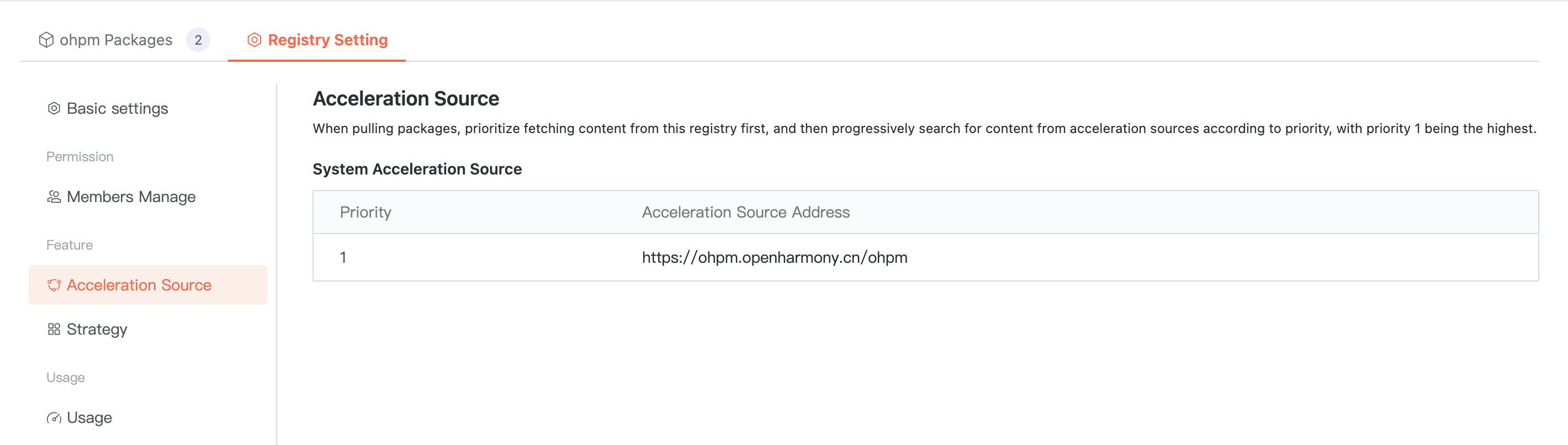
Proxy Settings
To enhance the pull efficiency of public artifacts, the Cloud Native Build artifact repository is configured with a built-in acceleration source. When using the artifact repository, you can directly speed up based on the built-in source address.
Policy Management
Configurable artifact package overwrite policy and cleanup policy.
When configuring the cleanup policy, you can set the maximum number of versions to reserve. If it exceeds this limit, the system will automatically clean up earlier push time/earlier usage time based on configuration to save database space.
Usage statistics
Summarize the total storage space occupied by ALL packages in the current artifact repository. Below, you can view the usage of each package and support downloading the detailed list.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

