High Availability
Last updated:2026-01-30 14:40:38
Cluster-Level High Availability (Multi-AZ Deployment)
TDMQ for MQTT provides cluster-level high availability capability. Multi-AZ deployment effectively improves service stability and disaster recovery capability. When purchasing an MQTT instance, you only need to select the region where the MQTT cluster is located. The server will deploy across multiple AZs by default when creating the cluster.
Deployment Architecture
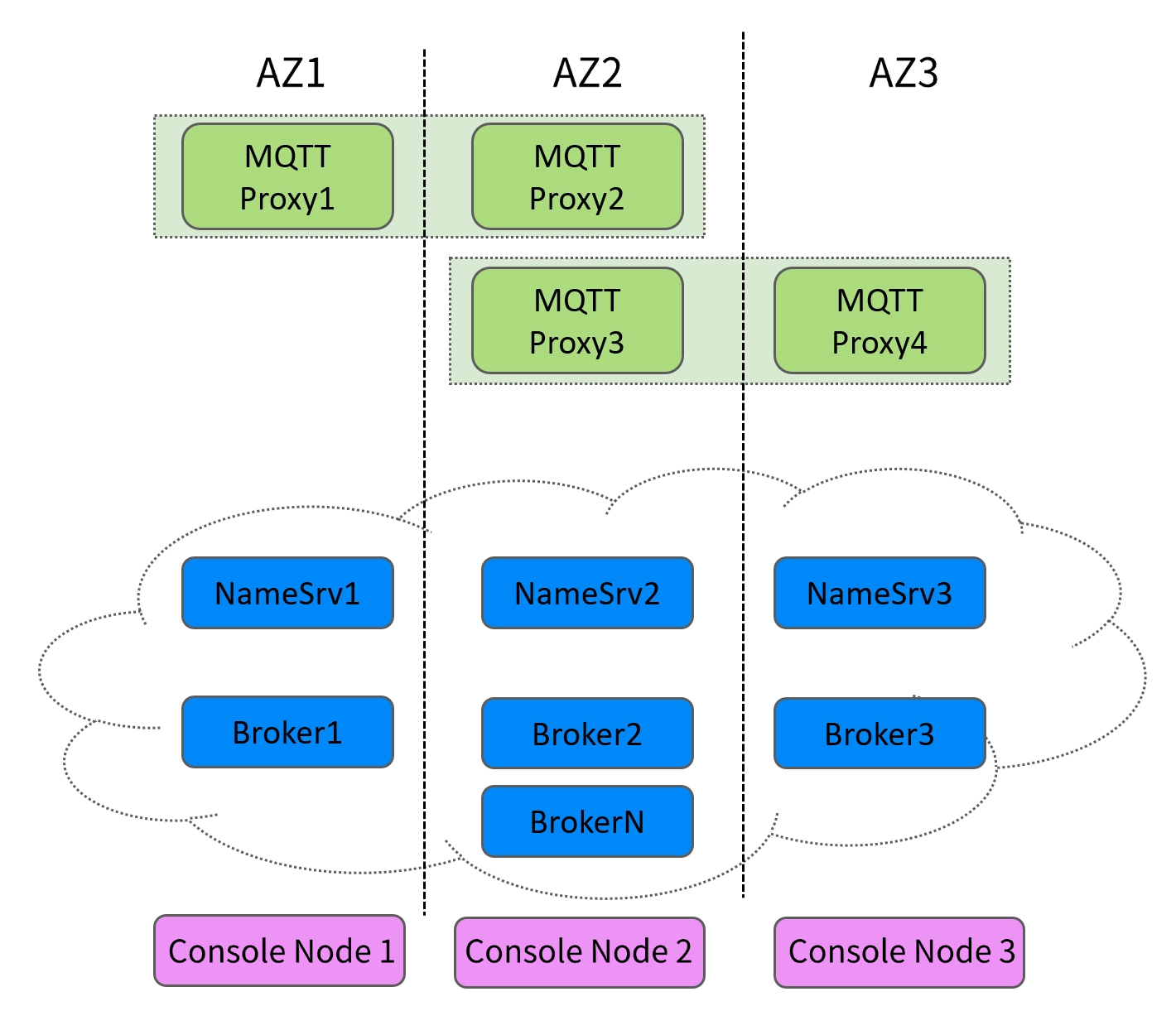
The cross-AZ deployment architecture of MQTT is divided into the network layer, data layer, and control layer.
Network Layer
MQTT exposes multiple cluster access addresses to clients in the form of domain names. After connecting to a cluster access address, clients communicate with the MQTT data layer. This domain name supports failover to other availability zones at any time. When a certain AZ is unavailable, the backend service switches to available nodes in the same region, thereby achieving cross-AZ disaster recovery.
Data Layer
The MQTT data plane adopts a distributed deployment method, where multiple components are deployed across AZs.
The proxy component is stateless. When a certain AZ (such as AZ1) or the entire AZ fails, the server automatically removes it from the backend server pool and attempts to establish a new Proxy Node. ALL new client connections and requests are seamlessly forwarded to Proxy Nodes in other available AZs (such as AZ2 and AZ3).
For the client, it always communicates with a uniform domain name (the cluster access address mentioned above) and is unaware of any backend Proxy switchover, requiring no modification or application restart. It may only observe a very brief (seconds-level) network jitter or timeout, then automatically recover. After AZ1 is restored, the server's health check will detect that its Proxy instance is healthy again and gradually add it back to the server pool to resume receiving traffic.
The Broker is responsible for message storage because the client does not support communication with Broker nodes and cannot directly sense the health status of the Broker. When a certain AZ (such as AZ1) or the entire AZ fails, the routing information in the NameServer cluster will be updated, indicating that the queue for all topics is now served by new Broker nodes (e.g., in AZ2). ALL Proxy Nodes will pull the latest routing information from the NameServer and route new client requests to Broker nodes in AZ2.
Control layer
Likewise, MQTT console deployment also meets cross-AZ requirements. The control node does not sustain data stream, with one set of management and control services deployed per region.
Data-Level High Availability (Message Durability)
One of the advantages of TDMQ for MQTT is persistent storage of messages.
After the client receives PUBACK (QoS=0 or 1) or PUBCOMP (QoS=2) from the server, it means the message was sent successfully and the server has received the message. Upon receiving the message, the server will persistently store it on the cloud disk of the Broker node. The Broker node itself supports cross-AZ disaster recovery. Additionally, with the aid of cloud disk backup points and replica storage, message persistence and data high availability are doubly secured. Even if all regional Broker nodes go down, stored messages will still be saved.
After messages are persistently stored, you can view message details and trace information via the query ordinary messages feature. By default, messages are retained on the server for three days. If this does not meet your requirements, you may purchase a Platinum Edition cluster and contact Tencent Cloud via after-sales tickets to adjust the retention period.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

