Authentication Method Overview
Last updated:2026-01-30 14:55:28
TDMQ for MQTT provides multiple authentication methods to ensure communication security between the server and clients. During client access, the configured authentication method verifies the client's identity. Only after successful authentication is access permitted, ensuring legitimate device integration.
Authentication Method
Transport layer: The underlying communication foundation of the MQTT protocol system, responsible for providing end-to-end reliable or unreliable data transfer channels between MQTT clients and servers. This layer is not part of the protocol itself but depends on existing network transport protocols to achieve its functionality.
Application layer: A core security component in the MQTT application protocol, acting on the connection establishment stage. It is responsible for verifying the identity of clients attempting to connect to the server, ensuring only authorized clients can access the service and system resources.
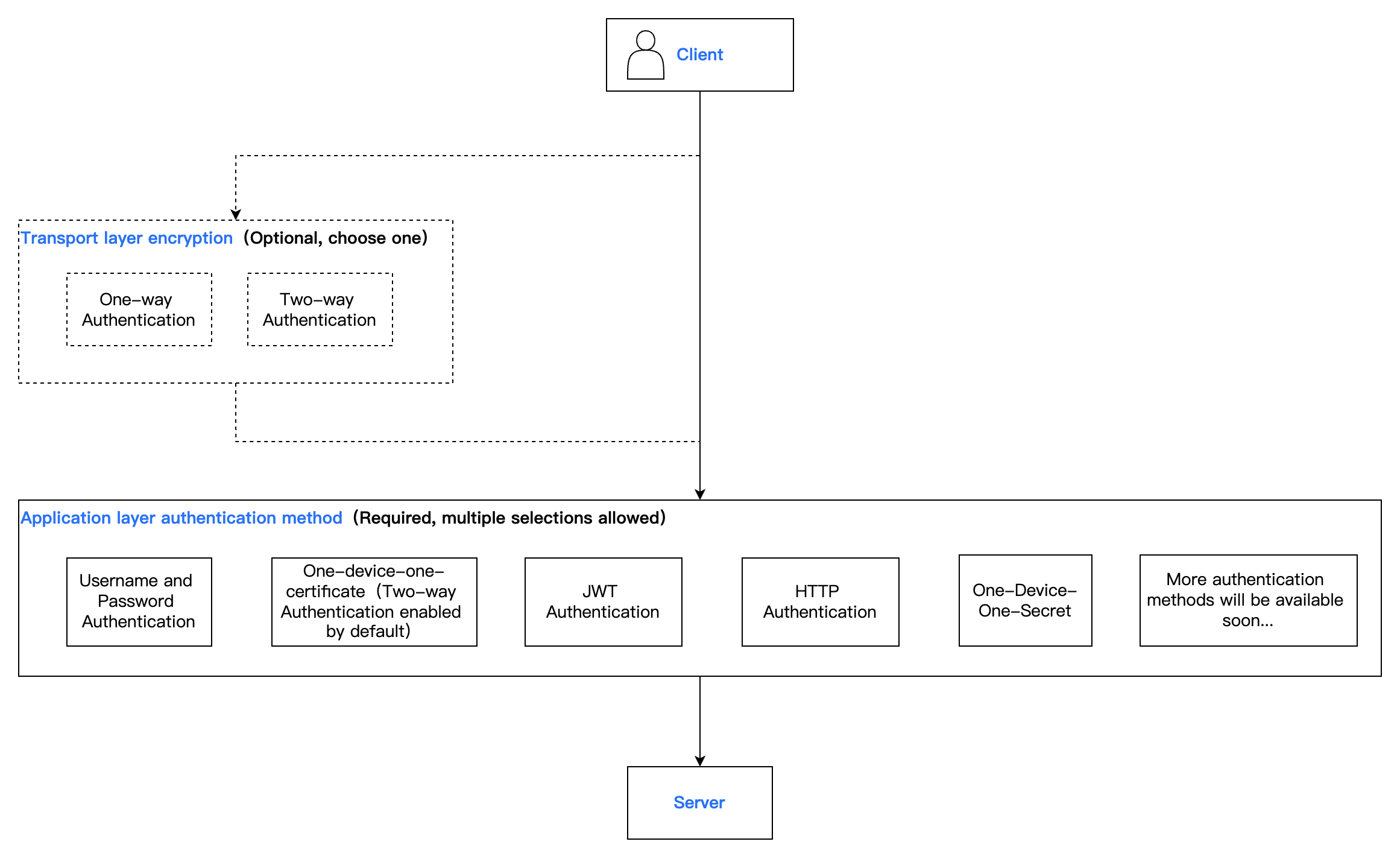
Applicable Scenarios
Authentication Method | Note | Basic Version (Sold Out) | Professional Edition | Platinum Version | Use Cases |
Username + Password Authentication | The most basic authentication method requires the client to provide Username and Password when connecting. MQTT matches them with credentials in internal storage and accepts the client request if the match passes. | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Common scenarios with not high security requirements. |
X.509 Certificate Authentication | One-way Authentication: The client authenticates the server, and the authentication of the server by the client is completed through the server certificate. The server will use the selected certificate to establish a connection with the client. | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Normal security requirements, or testing scenario. |
| Two-way Authentication: The client and server authenticate with each other. The client authenticates the server through the server certificate, and the server authenticates the client through the CA certificate. If verification passed, the client is allowed to connect to server. | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | The device is relatively high in value and has high security requirements. |
| One Device One Certificate: A unique mutual authentication where each client (each device) uses a self-issued CA certificate and different client certificates (device certificates) issued by the CA certificate for authentication. | × | ✓ | ✓ | The device is extremely high in value and has extremely high security requirements. |
JWT Authentication | JWT Authentication is a Token-based authentication mechanism, independent of server retention of client authentication information or session information. The client submits JWT in the password field or a separate field. MQTT verifies the JWT signature and claims. After verification passes, the server accepts the client connection request. | × | ✓ | ✓ | Implement flexible, time-sensitive dynamic authentication with custom permissions for end users or temporary sessions. |
HTTP Authentication | When a client connects, MQTT will use client info to construct an HTTP request and judge the authentication result based on the request return content. If authentication passes, the client is allowed to connect to server. | × | ✓ | ✓ | Authentication scenarios requiring integration with the existing unified identity authentication system. |
One device, one secret | Each device uses an independent key to connect to server for authentication. This key is the unique proof of device identity, used for authentication when connecting to server. | × | ✓ | ✓ | There is a relatively high demand for security, but the device itself has finite computing power and is unable to support the use of PKI certificate-based "one device, one certificate." |
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

