Integrating Data Into CKafka
Last updated:2026-01-30 14:55:30
Implementation Principles
The CKafka connector has a built-in MQTT Source Plugin that leverages the MQTT shared subscription mechanism to ingest MQTT messages in real time and forward them to CKafka clusters. This shared subscription mode supports high-concurrency configuration, effectively ensuring data transmission throughput and fully meeting the requirements for high-traffic access and processing capabilities when Kafka is integrated with the big data ecosystem.
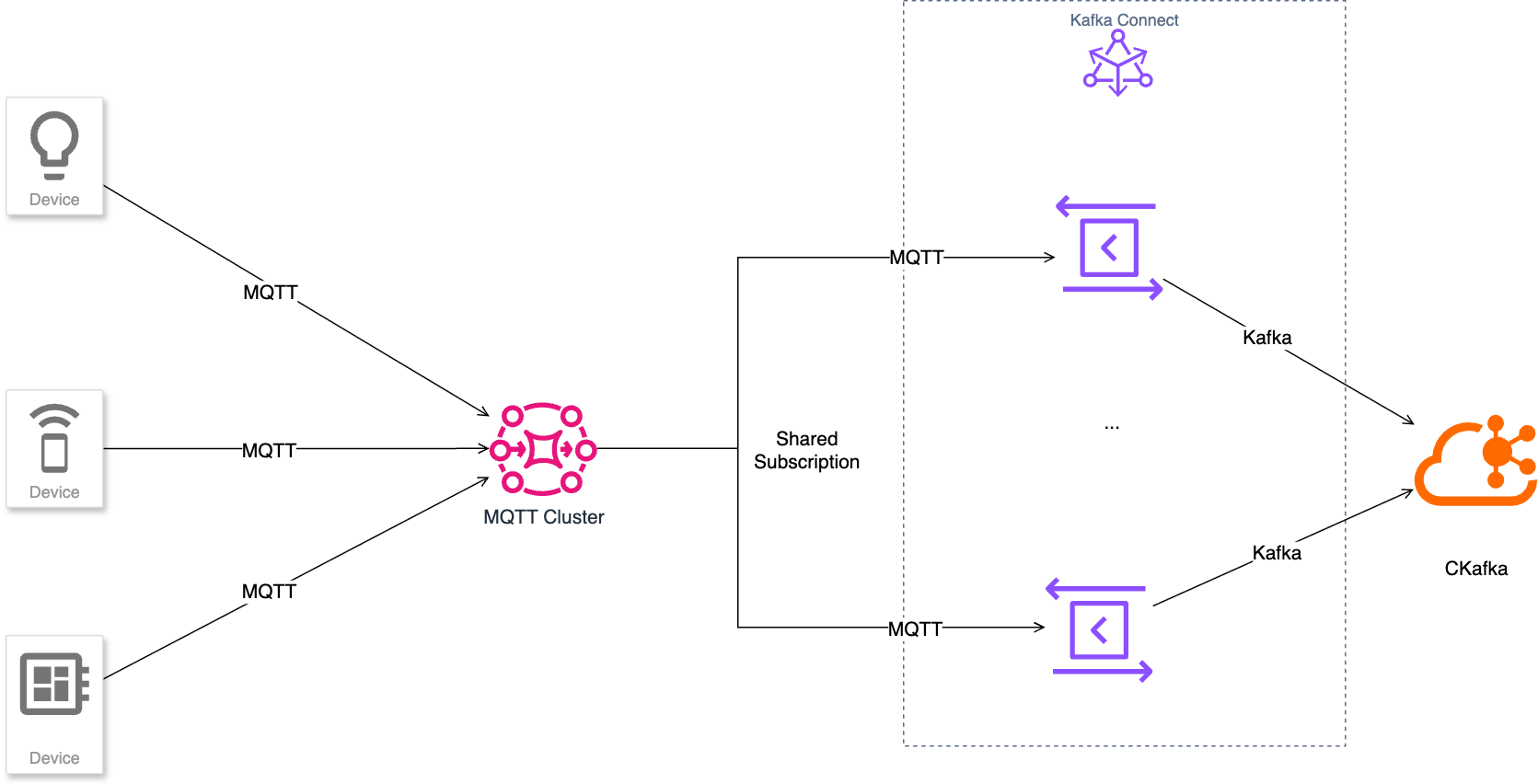
Data Mapping
When converting MQTT messages to Kafka Records, the mapping relationship is as follows:
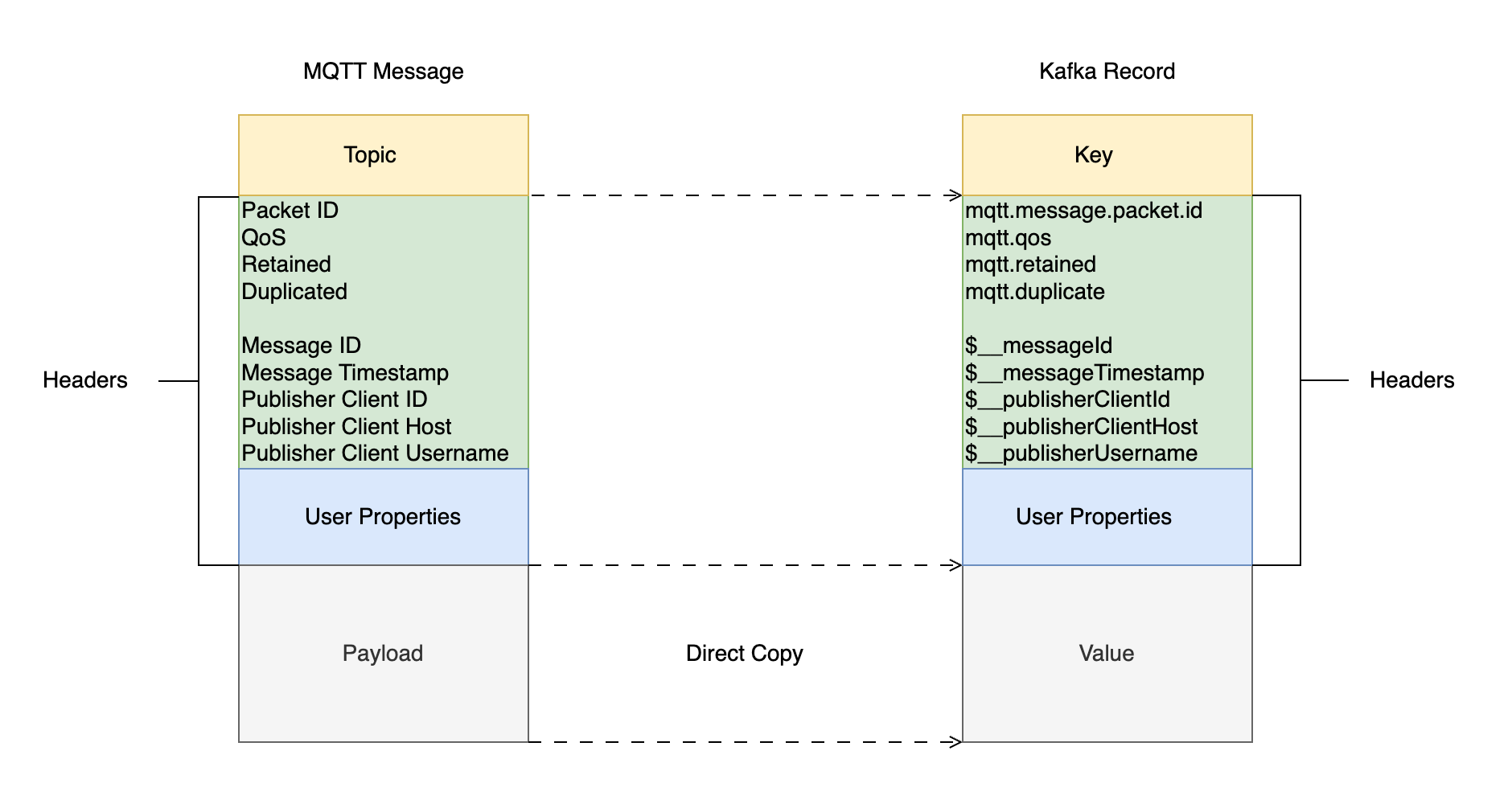
MQTT Message
An MQTT message consists of three parts: system fields, user attributes, and Payload. See MQTT Control Packet format.
System Fields
Field Name | Semantics |
Packet ID | Control command ID, not unique, for quick reuse see Spec 2.2.1 |
Duplicated | Refer to Spec 3.3.1.1 |
QoS | Refer to Spec 3.3.1.2 |
Retained | Refer to Spec 3.3.1.3 |
Message ID | Extended fields Unique message number |
Message Timestamp | Extended fields, server-side message storage time |
Publisher Client ID | Extended fields, client identifier for publishing messages |
Publisher Client Host | Extended fields, client IP for publishing messages |
Publisher Username | Extended fields, client username for publishing messages |
User Properties
Kafka Record
Field | Semantics |
Key | Key-value of the record, optional |
Headers | Key-value pairs associated with the record, often used to store metadata such as Content Type, event time, optional |
Payload | Actual data of the record, message body |
Headers Usage Scenarios
Message route
Metadata storage description
Tracing and logs
Customized service handling
authentication
Message priority
Interoperability/compatibility command
Stream processing
Use Cases
Smart City and Transportation Digital Twin
The system collects multi-source traffic data (such as vehicle license plates, speeds, and travel trajectories) from cities in real time, reports them via MQTT topics, and integrates them into the big data ecosystem through Kafka connectors.
It supports efficient search and analysis based on attributes such as license plate numbers and so on (such as vehicle trajectory restoration), providing data support for traffic monitoring, dispatching, and simulation.
Features and Advantages
CKafka is a distributed, high-throughput, and highly scalable messaging system. However, it is not inherently designed for edge IoT communication scenarios, as its clients typically require stable network environments and substantial hardware resources. In contrast, the massive volumes of data generated by devices and applications in the IoT domain are often transmitted via the lightweight MQTT protocol. The CKafka MQTT Connector enables seamless integration between the MQTT protocol and the CKafka ecosystem, allowing MQTT messages published by devices to be streamed in real time into CKafka topics. This ensures data can be processed, stored, and analyzed immediately. The integration preserves MQTT's advantages in unstable network and low-resource environments while fully utilizing CKafka's capabilities in high throughput, reliability, and ecosystem compatibility. This achieves flexible, stable, and efficient integration between IoT data and big data systems.
Operation Steps
Policy and Permissions
1. Log in to the TDMQ for MQTT console, go to the Cluster Details page, and confirm whether the authorization policy management is enabled for the current MQTT cluster.
1.1 If the permission policy is not enabled, the data plane resources have no permission management. You can use any "username + password" to connect, produce, and consume. For details, see Configure Data Plane Authorization. In this case, no additional configuration is required when data is integrated into CKafka. However, due to the lack of permission control, there are certain data security risks.
1.2 If the permission policy is already enabled, follow the steps described below.
2. Go to Authentication > Username and Password, click Create User to create a dedicated account and password for the Data Integration task, with the username
ckafka_connector. Specify in the description that this user is exclusively used for MQTT and CKafka data integration tasks, as shown in the figure.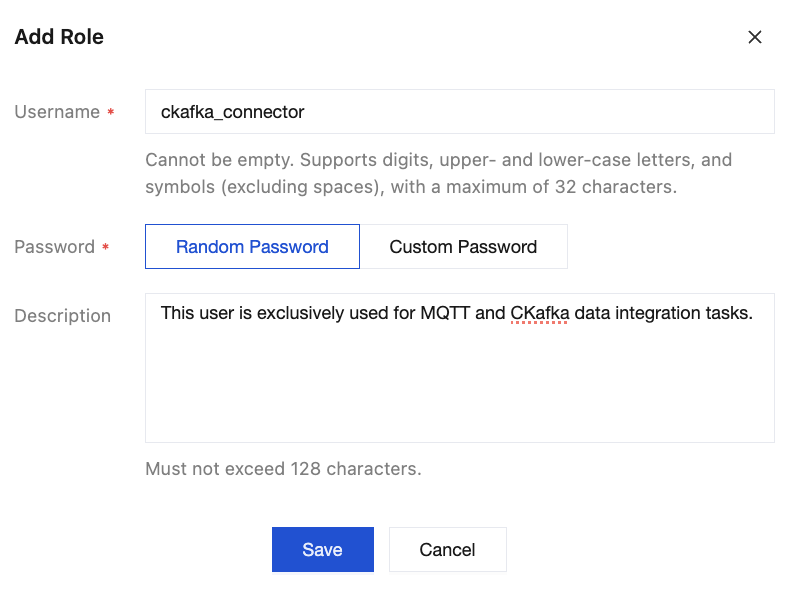
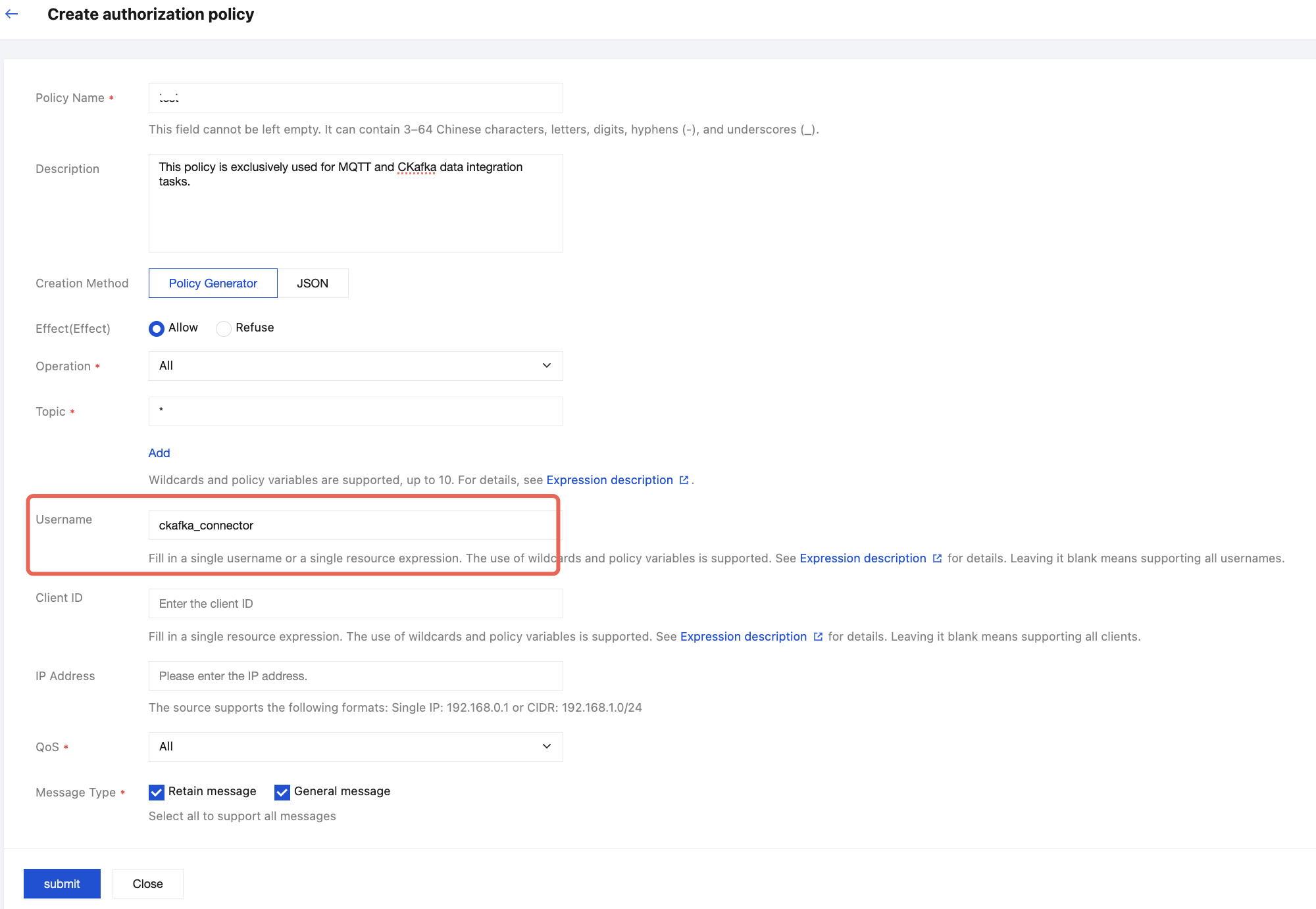
3. Go to the Authorization Policy page, click Create Policy. It is strongly recommended to explicitly authorize the CKafka Data Integration account created in the previous step within this policy to achieve granular permission control. For specific configuration methods, refer to the figure below. Fill in other fields according to actual requirements. For details, refer to Configuring Data Plane Authorization.
Configure the CKafka Connector
1. Log in to the CKafka console, go to the Connection List page, and first confirm the Region to which the connection belongs at the top of the page.
2. Click Create Connection to create the connector.
3. Follow the steps below to select connection information. Select MQTT Cluster as the connection type, then click Next to go to the connection configuration page.
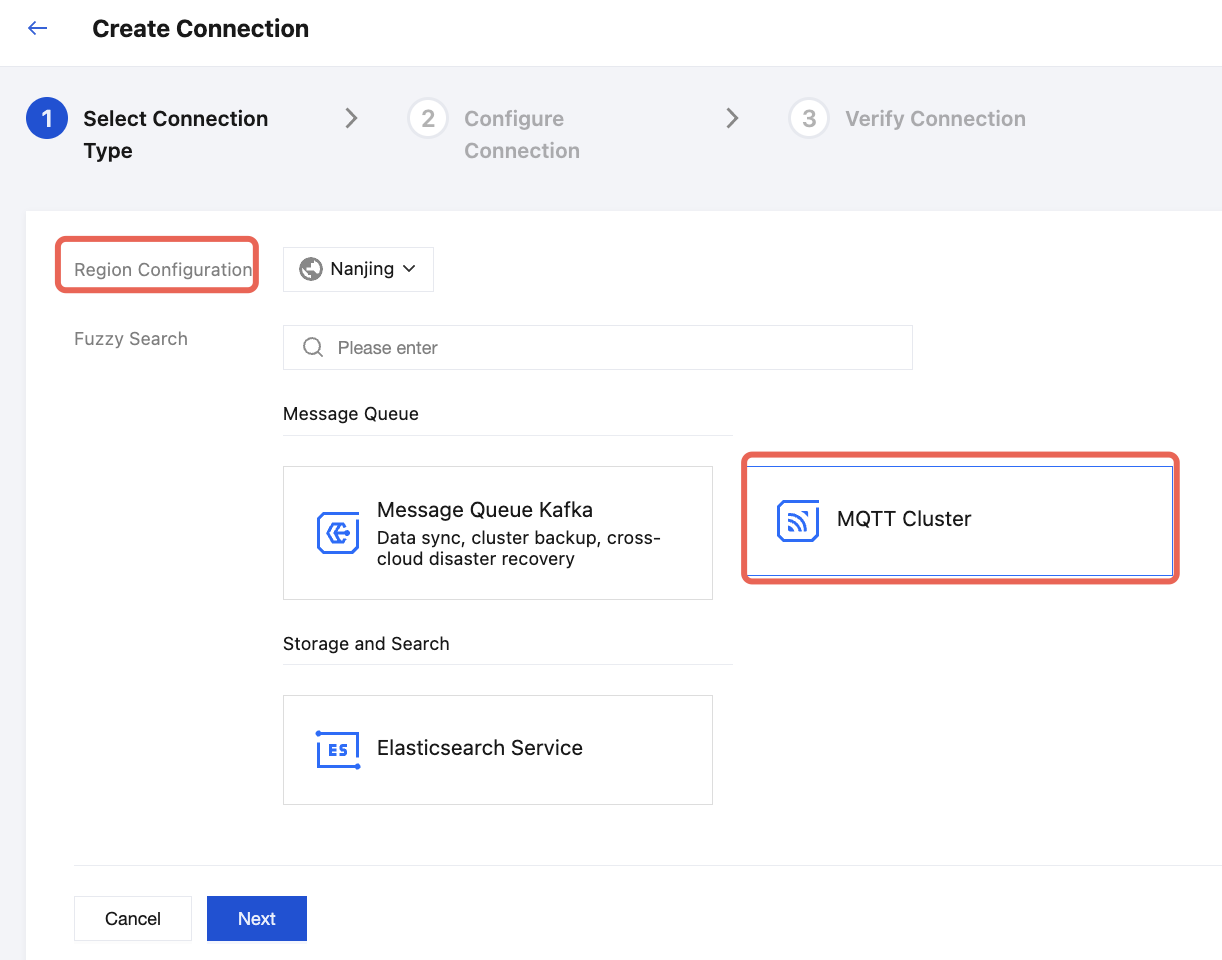
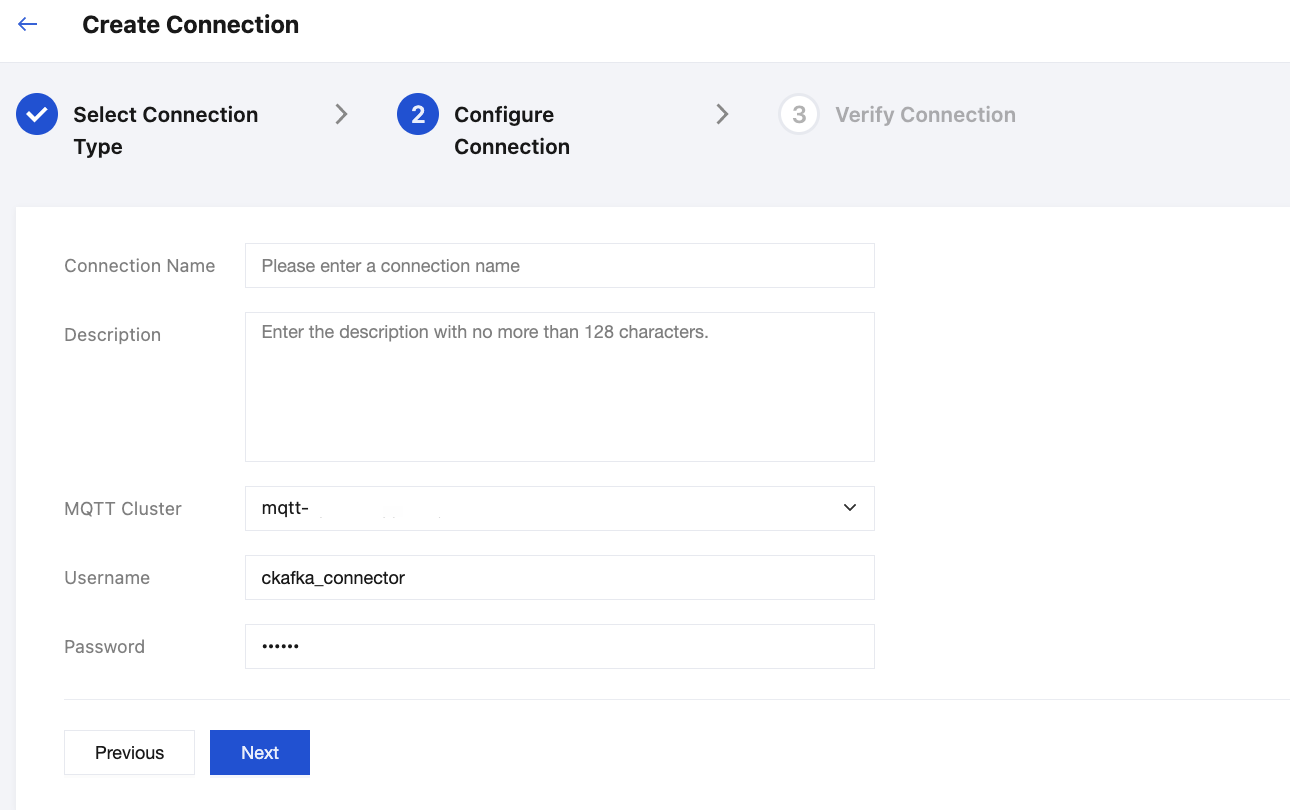
4. Enter the connection name, description, and other basic information, and select the target MQTT cluster from the dropdown. The username and password here are used for connection authentication, which are the dedicated Data Integration account credentials created in the MQTT cluster. For details, refer to the Policy and Permissions section. Click Next to enter the connection validation process.
5. After all validations pass, the connection is successfully created. You can view the newly added connection in CKafka Console > Connector > Connection List.
For created connections, the connections list displays their basic information, including ID, Name, Status, Connection Type, Bound Resources, Resource Region, Number of Associated Tasks, Creation Time, Description, and so on.
Click the Edit button in the Actions column to modify connection configurations. After the connection is updated, the system enables the "Update and restart all associated tasks" option by default. Exercise caution when performing this operation based on actual business requirements.
Click the Delete button in the Actions column to delete this connection.
Create Data Integration Task
Prerequisites
In the same region as the MQTT cluster, a CKafka instance has been created. For details, refer to CKafka Quick Start.
Task Creation
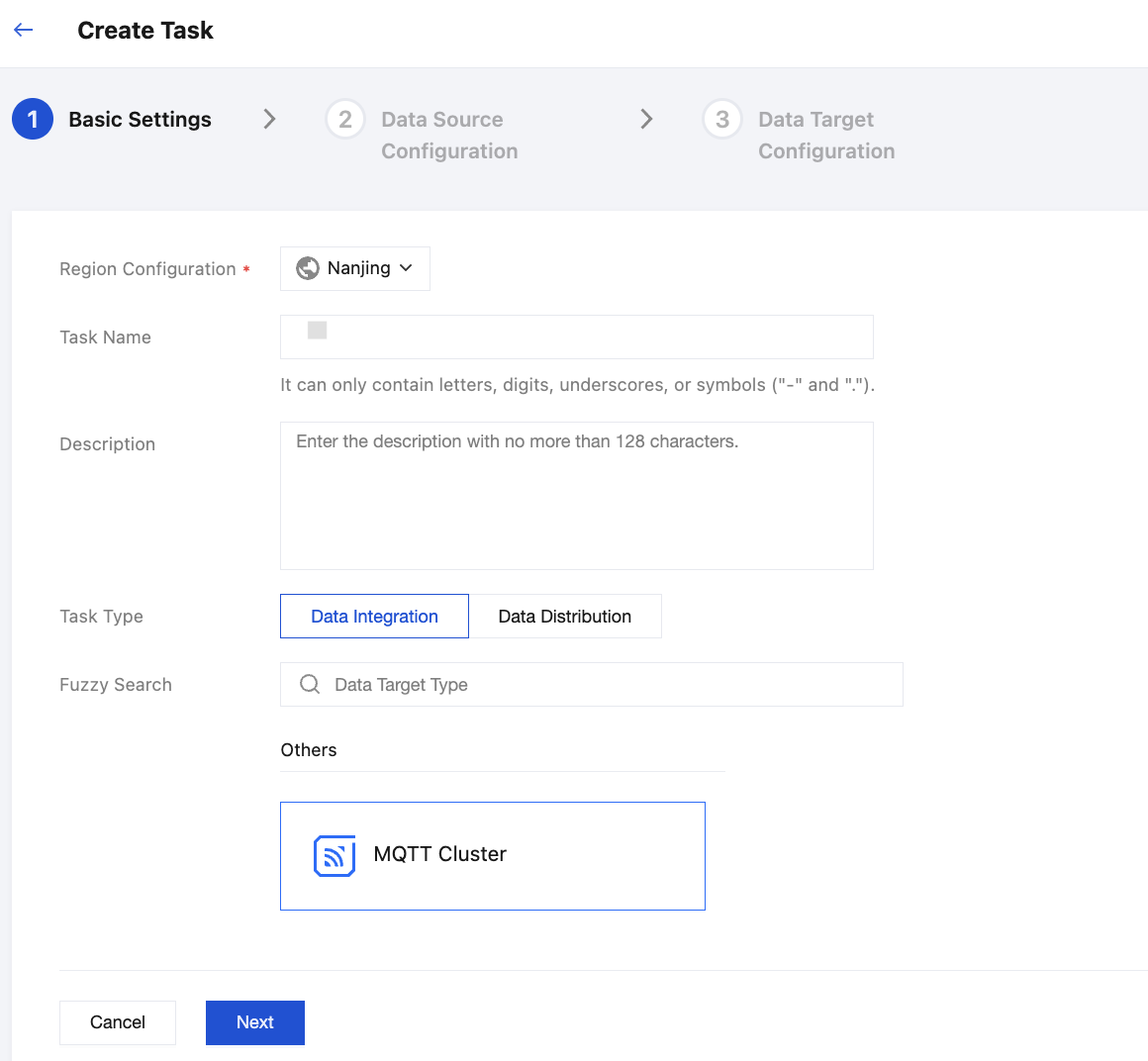
1. Go to CKafka Console > Connectors > Task List, click Create Task in the upper-left corner to fill in the task-related information. Choose Data Integration > MQTT Cluster for the task type, then click Next to go to the data source configuration.
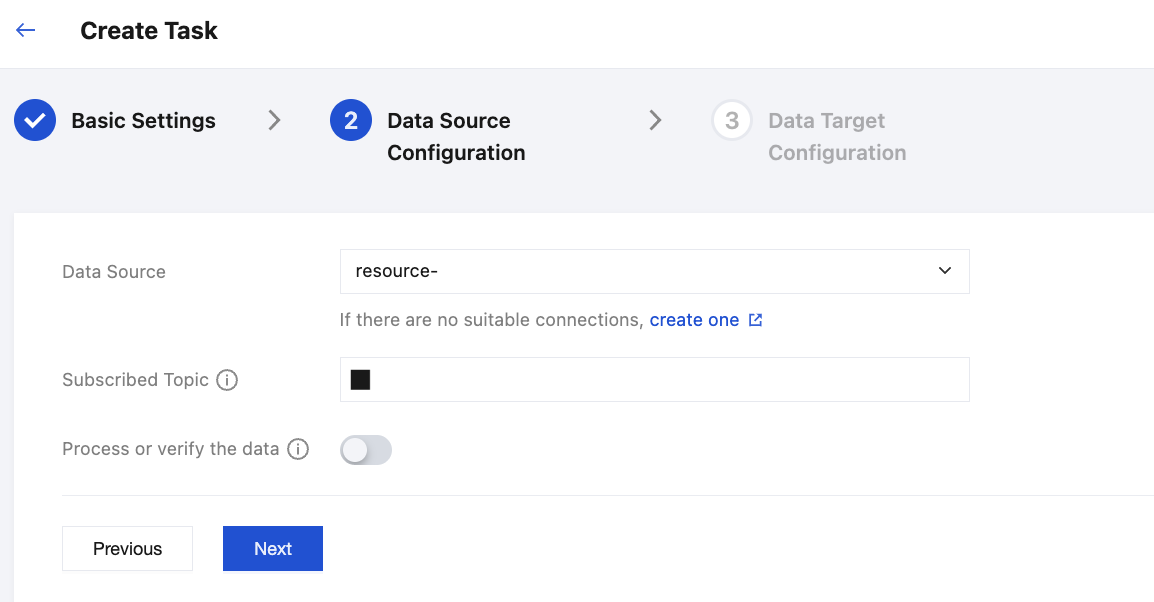
2. Select an appropriate connection from the dropdown. If no suitable option is available, click the button below to go to the New Connection step. Enter the subscribed Topic. To subscribe to multiple topics, separate them with ",".
3. Configure the data target, specify the distribution policy and target CKafka instance. Click Submit to complete task creation.
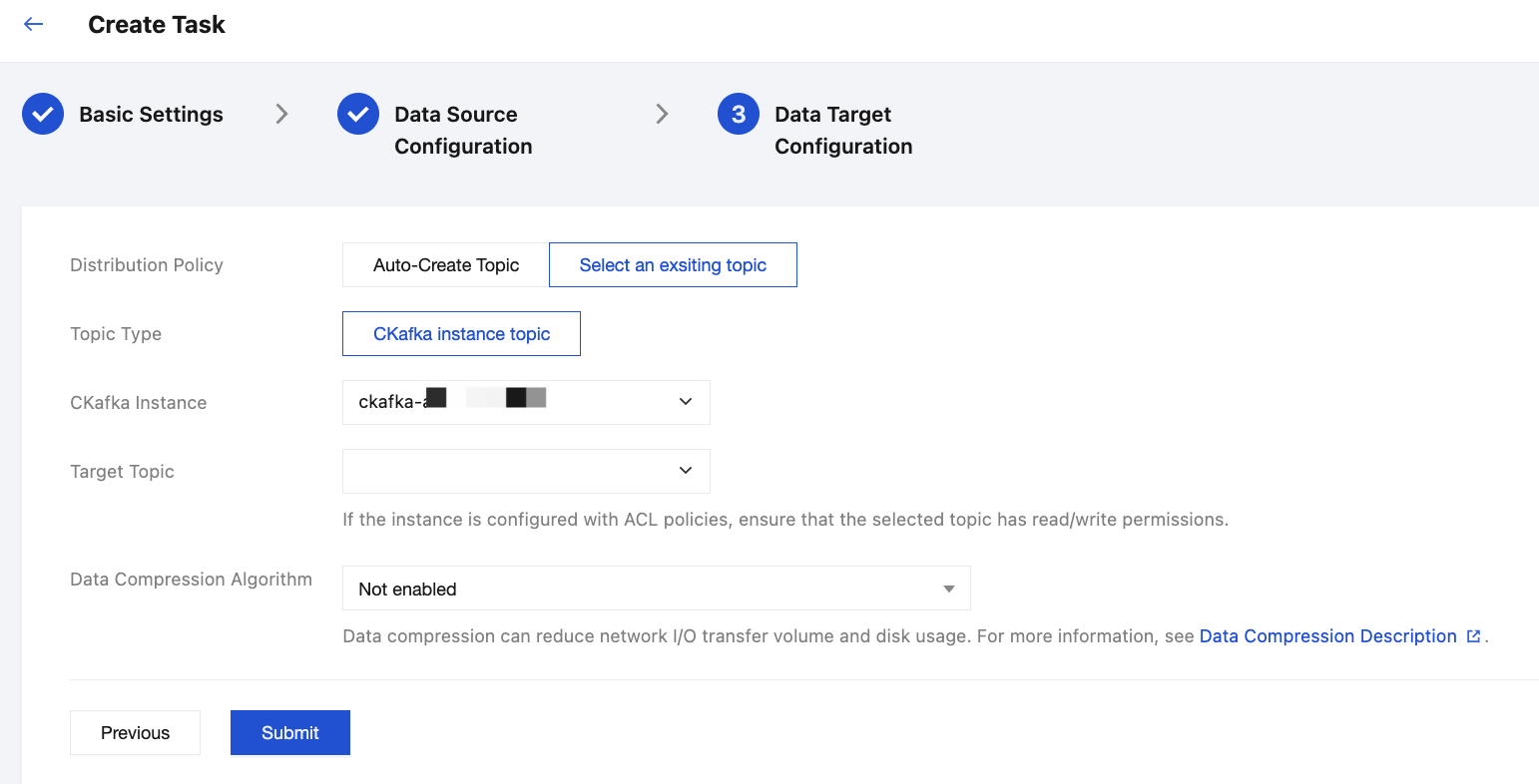
4. When the task is successfully created, a shared subscription group will be automatically created under the MQTT cluster for performing Data Integration.
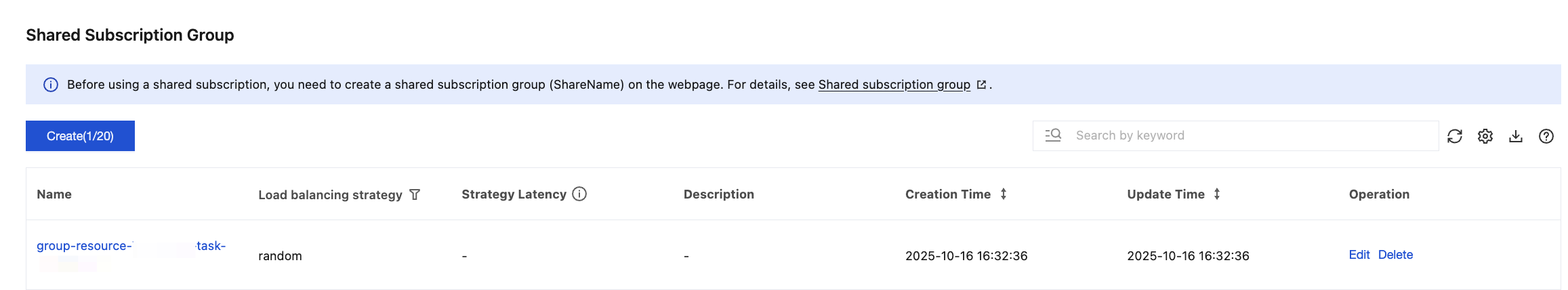
You can also go to the Client page to view details of the connector client for this task.

Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

