Step 3: Configuring CA Certificate
Last updated:2026-01-30 14:55:28
TDMQ for MQTT supports the use of client certificates for client authentication. CA certificates can be used to issue client certificates, server certificates, and verify certificates. When a client initiates a connection request, it passes the client certificate to the server. The server will verify the validity of the client certificate based on the CA certificate associated with the client. If the verification passes, the client is allowed to connect to the server.
Restrictions and Limitations
The maximum number of CA certificates that can be registered in a single cluster is 32.
Issue CA Certificate
You can directly purchase issued CA certificates from trusted authorities or generate private CA certificates through self-signing. The following briefly describes the steps to issue a CA certificate. If you already have an issued CA certificate, you can skip the current "Issue CA Certificate" step.
Note:
If you are using a Windows system, you need to add the bin subdirectory of the OpenSSL installation directory to your system's PATH environment variable, as shown in the figure below.
2. The following example uses an RSA algorithm certificate. Generate a key pair using the following command.
openssl genrsa -out CA.key 2048
3. Use the (private key) in the key pair generated in the previous step to create a certificate signing request (csr) file.
openssl req -new -key CA.key -out CA.csr
4. The page will return the following example. Enter the corresponding parameters based on the prompts.
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:State or Province Name (full name) []:Locality Name (for example, city) []:Organization Name (for example, company) []:Organizational Unit Name (for example, section) []:Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:Email Address []:
Note:
The domain name entered in the Common Name field must match the cluster's access point domain. It is recommended to use
*.mqtt.tencenttdmq.com.To ensure that the certificate configuration takes effect only for the current cluster, you can enter the corresponding domain name based on the usage scenario (public network or VPC network). For example, for public network, enter
mqtt-xxxxxx-gz-public.mqtt.tencenttdmq.com; for private network, enter mqtt-xxxxxx-gz-vpce-xxxxxx.mqtt.tencenttdmq.com.5. To generate a self-signed CA certificate using the RSA algorithm
CA.crt.openssl x509 -req -extfile /System/Library/OpenSSL/openssl.cnf -extensions v3_ca -in CA.csr -out CA.crt -signkey CA.key -CAcreateserial -days 3650
openssl x509 -req -extfile C:\\Progra~1\\OpenSSL-Win64\\bin\\cnf\\openssl.cnf -extensions v3_ca -in CA.csr -out CA.crt -signkey CA.key -CAcreateserial -days 3650
openssl x509 -req -extfile /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf -extensions v3_ca -in CA.csr -out CA.crt -signkey CA.key -CAcreateserial -days 3650
Certificate Verification
After completing the issuance of the CA certificate locally, you can obtain the registration code in the console to generate the corresponding verification certificate. The verification certificate is used to validate the authenticity of the CA certificate itself, including whether the certificate is issued by a trusted CA authority. The process for generating a verification certificate is as follows:
1. The following example uses an RSA algorithm certificate. Generate a key pair for the verification certificate using the following command.
openssl genrsa -out VerificationCert.key 2048
2. Generate a certificate signing request (csr) file for the verification certificate using the (private key) from the key pair generated in the previous step.
openssl req -new -key VerificationCert.key -out VerificationCert.csr
3. Log in to the MQTT console, choose Resource > Cluster in the left sidebar, select a region, then click the "ID" of the cluster to configure the certificate to go to the cluster basic information page. On the CA Certificate page, click Register CA Certificate, and copy the generated registration code from the pop-up window to fill in the Common Name field in the next step.
Note:
Do not close the current pop-up window before the verification certificate is generated and uploaded locally. Closing the pop-up will cause the registration code to be regenerated, resulting in verification certificate validation failure.
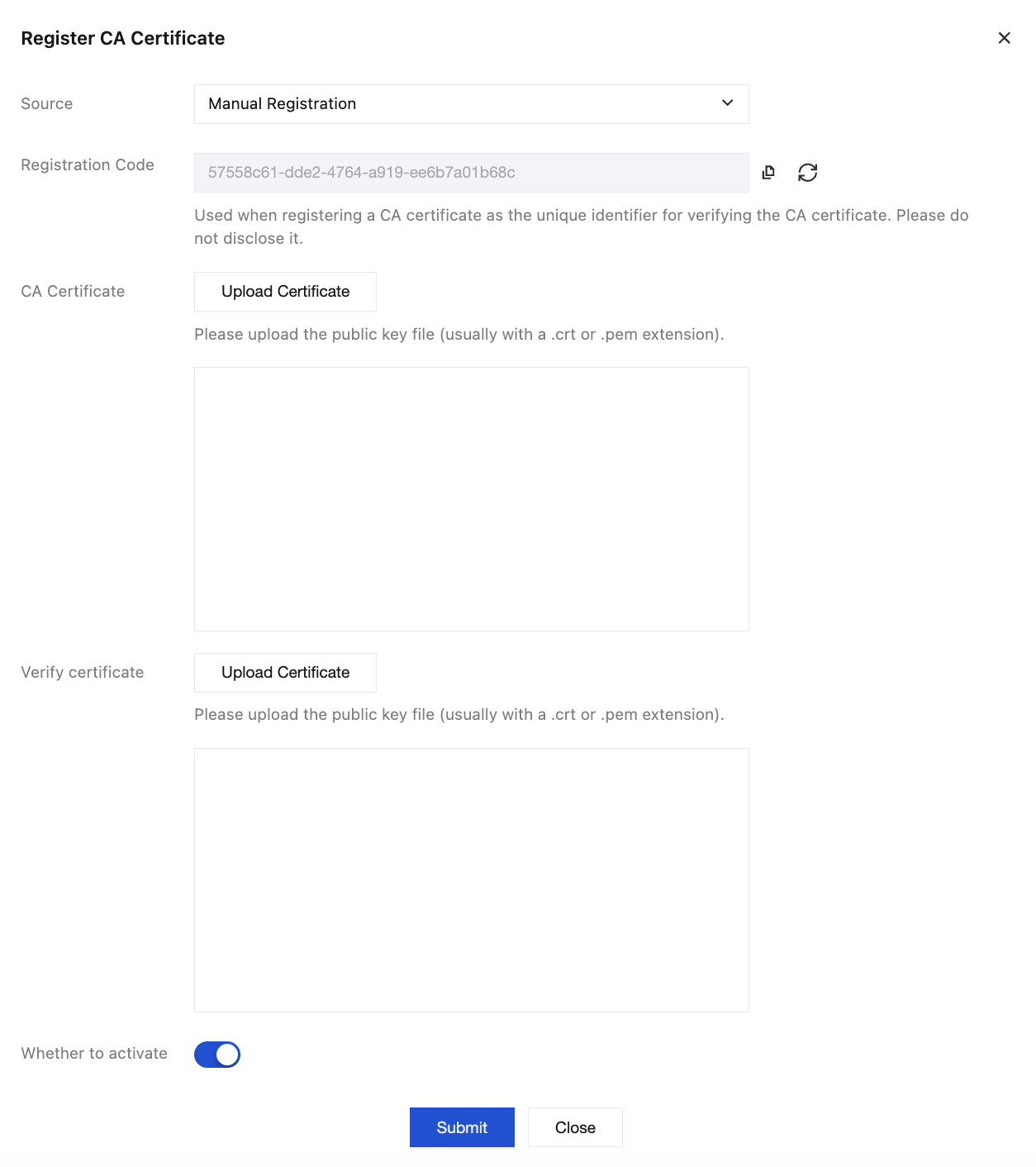
4. The page returns the following example. Enter the corresponding parameters as prompted. Enter the registration code copied in the previous step in the Common Name field. Other fields can be left blank depending on the actual situation.
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporatedinto your certificate request.What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blankFor some fields there will be a default value,If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.-----Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:State or Province Name (full name) []:Locality Name (for example, city) []:Organization Name (for example, company) []:Organizational Unit Name (for example, section) []:Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:your_registration_codeEmail Address []:Please enter the following 'extra' attributesto be sent with your certificate requestA challenge password []:An optional company name []:
5. Run the following command to generate the verification certificate VerificationCert.crt for the CA certificate.
openssl x509 -req -in VerificationCert.csr -CA CA.crt -CAkey CA.key -CAcreateserial -out VerificationCert.crt -days 600 -sha512
Uploading Certificates
Return to the console pop-up window, upload the CA Certificate and Verify Certificate, then click Submit.
After the certificate is uploaded, the server uses the public key in the verification certificate to decrypt the signature of the CA certificate and compares it with the hash value of the content in the verification certificate. If they match, the signature is valid, thereby proving that the CA certificate is trusted.
Managing CA Certificates
After the CA certificate is registered, on the CA certificate list page, you can view the status of the registered CA certificates. CA certificates have two statuses: activated and not activated. Certificates that are not activated can be deleted.
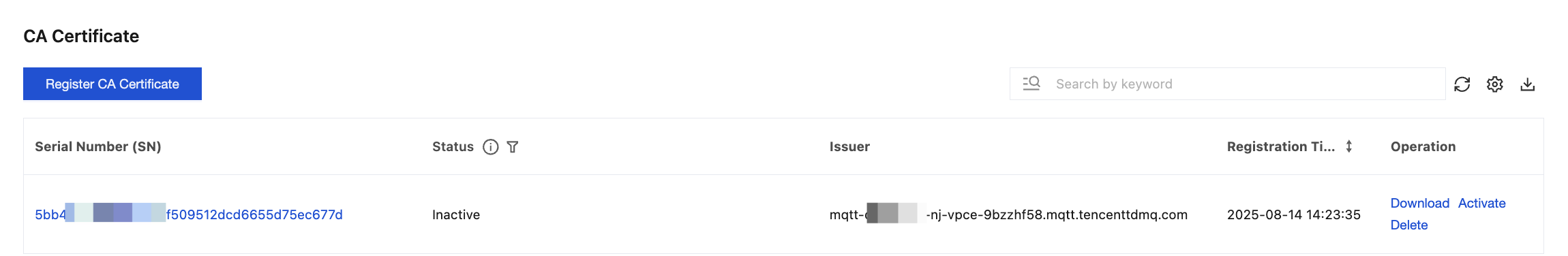
You can manage registered CA certificates on the page at any time.
Operation | Operation path | Description |
Deactivating Certificates | Click Cancel active in the operation bar. | After a CA certificate is deactivated, client certificates using this CA certificate will be rejected during connection. Therefore, special attention should be paid to the impact on client connections when changing the status of CA certificates. |
Deleting Certificates | Click Delete in the operation bar. | When a CA certificate is deleted, the system checks whether any client certificates (device certificates) under this CA certificate are in the "Activated" state. If such certificates exist, the deletion of the CA certificate is prohibited. If all client certificates (device certificates) under the CA certificate are in the "Not activated" or "Revoked" state, the CA certificate can be deleted. |
View Certificate Details | Click the serial number of the certificate. | On the certificate details page, the following information of the certificate is displayed: Basic Information: Displays the status, Common Name, Serial Number, and other details of the CA certificate. Associated Client Certificates: Displays client certificates associated with the current CA certificate. Click the serial number of a client certificate to view its details. In the operation bar, you can perform management operations such as download, activate, and revoke on the client certificate. |
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

