Integrating Data into RocketMQ
Last updated:2026-01-30 14:55:30
Note: The feature is currently in gradual rollout. If you need to use it, please contact us by submitting a ticket.
Implementation Principles
TDMQ for MQTT supports message routing and forwarding between Message Queue MQTT and TDMQ for RocketMQ: MQTT messages are forwarded to the corresponding topics in RocketMQ via the cross-cluster replication capability provided by RocketMQ, according to pre-configured routing rules; similarly, messages from RocketMQ can also be delivered to MQTT and then further delivered to device endpoints.
RocketMQ, as a distributed message queue, is responsible for persisting and distributing messages for consumption and processing by multiple downstream business services, thus forming a closed-loop mechanism from IoT terminal state perception to cloud business response. The entire process achieves transparent conversion between the MQTT protocol and the RocketMQ protocol, as well as reliable message synchronization, ensuring that device status changes can reach the backend business system in real time and accurately.
Use Cases
Intelligent Ops and Status Management for EV Charging Stations
Device Connection and Will Message Configuration: When an EV charging station device connects to the cloud server via the MQTT protocol, it pre-configures a will message in its connection request and designates the MQTT topic to which the message will be published.
Abnormal Offline and Will Triggering: When an EV charging station abnormally disconnects due to sudden power outages, network interruptions, or device failures, the MQTT server will immediately publish the device's preset will message to the designated topic, indicating to the cloud that the device has gone offline abnormally.
Cross-protocol Message Routing: Through the message routing rules pre-configured in the TDMQ console, the will messages on the specified topics of the MQTT server will be automatically and reliably forwarded to a specific topic in TDMQ RocketMQ.
Ops Service Consumption and Status Awareness: The backend cloud maintenance service continuously subscribes to the RocketMQ topic. Once a new will message (that is, failure notification) arrives, the service immediately consumes and parses the message to accurately obtain the faulty device's identity ID, location information, and potential error codes. Upon detecting the device's abnormal status, it automatically triggers subsequent business processes.
Features and Advantages
High Reliability and Automation: Reliably batch and send MQTT messages to RocketMQ to achieve integration between IoT devices and RocketMQ and application systems.
Flexible Topic Mapping: Data Integration supports flexibly mapping MQTT topics to RocketMQ topics.
Business Scalability: As a message middleware, RocketMQ allows multiple business services to consume device status messages simultaneously, supporting smooth system scaling and flexible business iteration.
Operation Steps
Create Cross-Cluster Replication Task
1. Log in to the TDMQ for RocketMQ console and go to the Cross-Cluster Replication page.
2. Click Create Task to create a task.
3. Select the Notification Source and Message Replication Target, then fill in the fields as required:
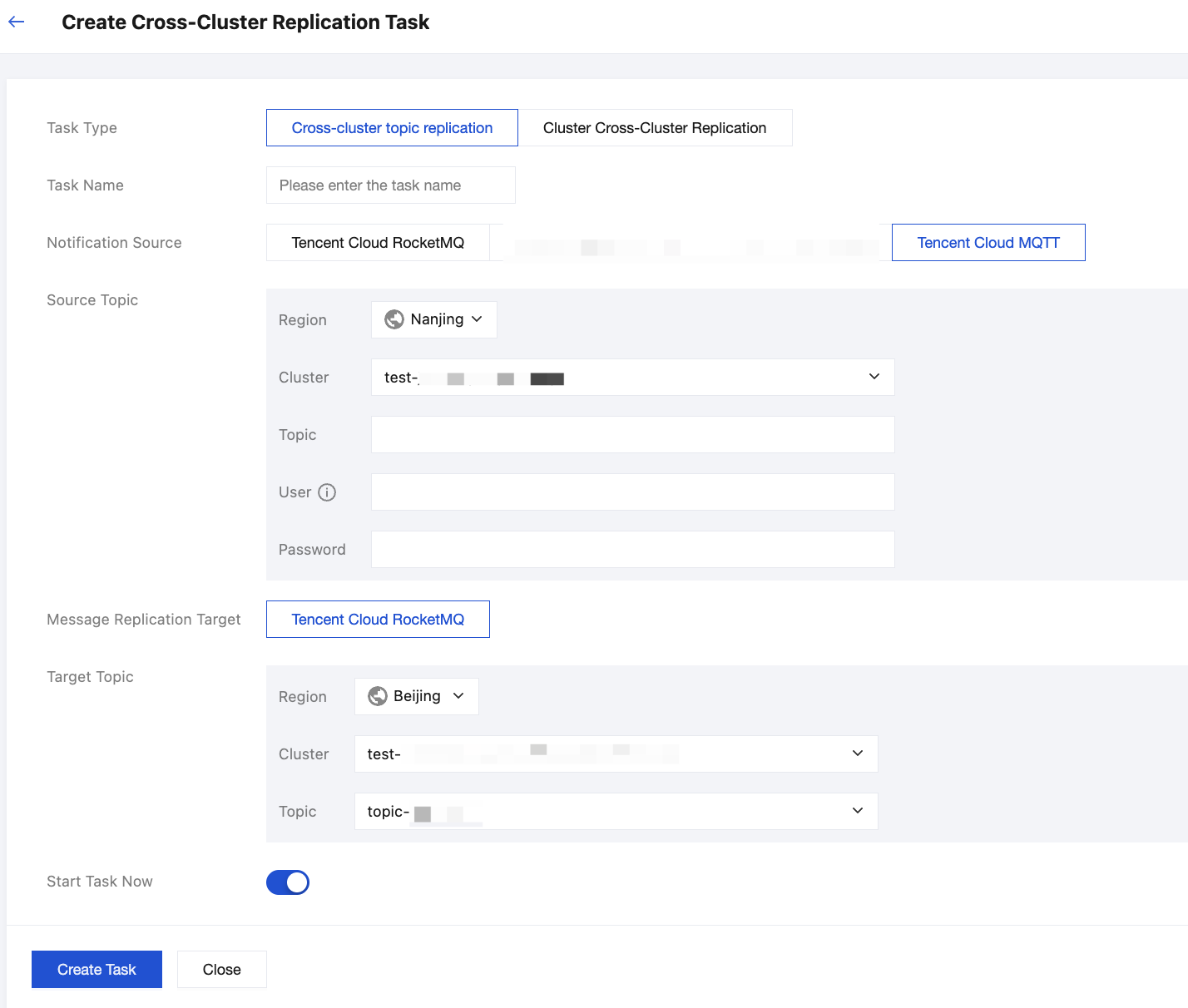
Task Name: contains no more than 200 characters. It can only contain English words, digits, letters, hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
Source Topic: Select the region, cluster, and Topic sequentially from the dropdown. If no suitable cluster or Topic is available, a new one can be created on the cluster list page.
Target Topic: Select the region, cluster, and Topic sequentially from the dropdown. If no suitable cluster or Topic is available, a new one can be created on the cluster list page.
Start Task Now: If the switch is enabled, the task will be replicated according to the configuration of the current task after it is created.
3.1 After you click Create Task, the Task List page will be displayed. After the task is initialized, it indicates that it has been created.
Viewing Task Details
1. After the task is created, you can view the newly added replication task on the task list page and quickly check its status. Click Start/Pause in the Operation column to start or pause the task with one click.
2. You can click the task name to go to the task details page and view the detailed configuration of the task. Running tasks cannot be modified. To adjust the replication task configuration, pause the task first, then click Edit in the Operation column. Alternatively, go to the task details page and click Edit in the upper-right corner of "Basic Information" to modify the task details.
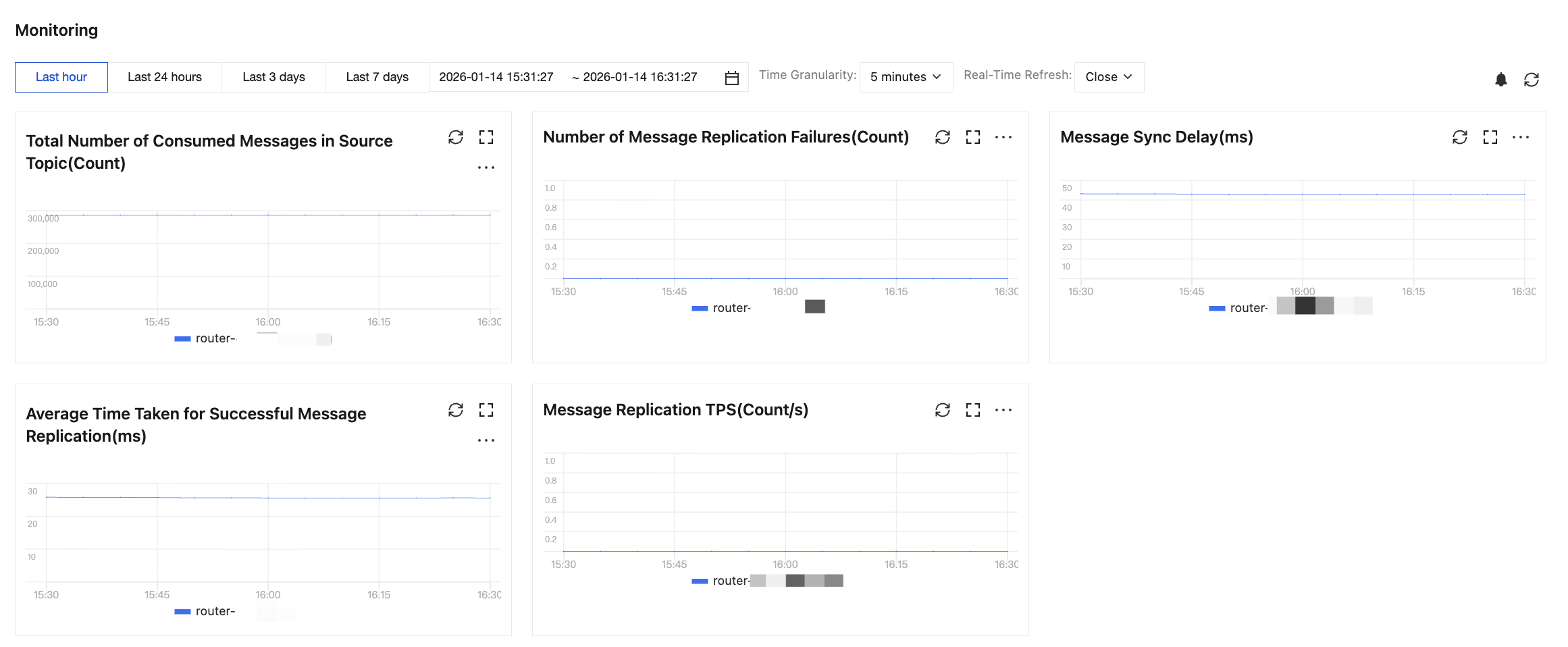
3. In the monitoring section, you can view real-time metrics of the current message replication task, such as the total number of source messages consumed, the number of failed message replications, and message synchronization latency.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

