Environment Variable and Secret
Last updated:2025-10-20 15:02:13
Overview
Environment Variables or Secret are key-value pairs set in the runtime environment of edge functions, which can be accessed as global Variables or Secret in edge function scripts without the need for explicit importing or initialization. By using environment Variables or Secret, function code can be decoupled from configuration. Their common uses are as follows:
Configuration decoupling: Environment Variables or Secret allow developers to configure edge functions without modifying the function's code, meaning developers can set different variable values for different environments (such as development, testing, and production) to control function behavior.
Security: By storing sensitive information (like API keys) in environment Variables or Secret instead of hardcoding them into the code, application security is enhanced. This approach reduces the risk of leakage of sensitive information in the code repository and simplifies key management.
Flexibility: Environment Variables or Secret provide great flexibility for edge functions, allowing developers to adjust the behavior of edge functions as needed. For example, developers can use environment Variables or Secret to achieve grayscale release by controlling different user groups to access different versions of code or configuration.
Directions
1. Log in to the Tencent Cloud EdgeOne console, enter Service Overview in the left menu bar, and click the site to be configured under Website Security Acceleration.
2. On the site details page, click Edge Functions > Function Management.
3. On the Function Management page, click the specific function name. At the bottom of the page, find the Environment Variables or Secret module. If the function has not been created, follow the Creating and Deploying a Function guide to complete the function creation first.
Creating and Deploying Environment Variables or Secret
1. In the Environment Variables or Secret module, click Quick add and configure the relevant parameters.
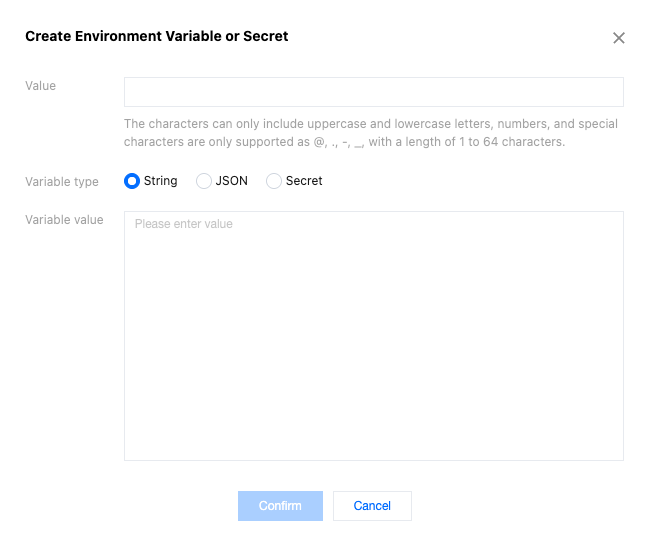
Parameter Name | Description |
Variable name | Required. It can only include uppercase and lowercase letters, digits, and special characters limited to @, ., -, ,. The length is restricted to 1 to 64 characters. The variable name cannot be duplicated and cannot be modified after creation. For example, keytest. |
Variable type | Required. It supports String, JSON and Secret types. String: After this option is selected, the input variable value content will be saved as a string. For specific usage, refer to the Edge Functions Referencing Environment Variables or Secret section for the variable type String. JSON: After this option is selected, the input variable value content will be saved as a JSON array. The edge functions will automatically parse the variable value into a JavaScript object without the need to manually call JSON.parse(). For specific usage, refer to the Edge Functions Referencing Environment Variables or Secret section for the variable type JSON. Secret: When this option is selected, the variable can be saved as either a JSON array or a string. Once saved, the variable value will no longer be visible—please keep it secure. For details, see the Edge Functions Referencing Environment Variables or Secret section, under the "Secret" variable type. |
Value | Required. It supports a maximum of 5 KB. For example, if the type is String, enter valuetest as the variable value. If the type is JSON, the variable value will be validated to check if the input content follows the JSON data structure. If it does not, there will be an exception prompt. |
2. Click OK to complete the creation of the environment variable. A single edge function supports creating up to 64 environment Variables or Secret.
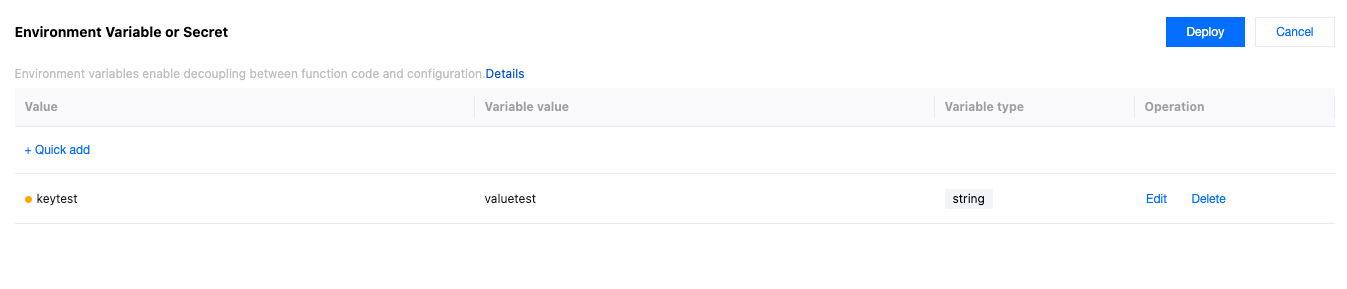
3. Click Deploy to make it effective.
Edge Functions Referencing Environment Variables or Secret
If the environment Variables or Secret referenced by the function do not contain special characters
@, ., -, ,, they can be referenced in the form of env.envname. For example, if the environment variable envname is keytest, the way to reference it in edge function code is env.keytest. For specific usage, refer to the section for the variable type String.If the name of the environment variable referenced by the function contains special characters
@, ., -, ,, it can be referenced in the form of env['envname']. For example, if the environment variable envname is test-@.-a, the way to reference it in edge function code is env['test-@.-a'].Below are sample codes for edge functions referencing environment Variables or Secret of types String, JSON and Secret. Developers can adjust them according to actual situations.
Variable Type: String
Through the above steps to create and deploy environment Variables or Secret, create an environment variable named
testString with the value valuetest. The edge function reference is as follows:
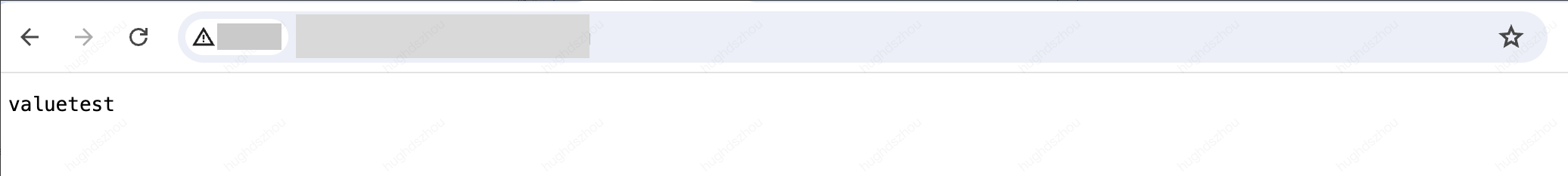
// Entry functionaddEventListener('fetch', event => {event.respondWith(handleRequest(event.request));});// Function to handle requestsasync function handleRequest(request) {// Obtain a value from an environment variable, and this environment variable needs to be created and deployed in edge function environment Variables or Secret.const valueFromEnv = env.testString;// Create response.const response = new Response(valueFromEnv, {headers: {'Content-Type': 'text/plain' // Set the response Content-Type.}});// Return the response.return response;}
The semantic summary of the above code is to obtain the environment variable that the function has created and deployed, and respond it to the client as text.
Deploy the code, and you can view the result by accessing the trigger rules or default access of the function.
Variable Type: JSON
Repeat the steps to create and deploy environment Variables or Secret, and create and deploy an environment variable of type JSON named
testJSON, as shown below: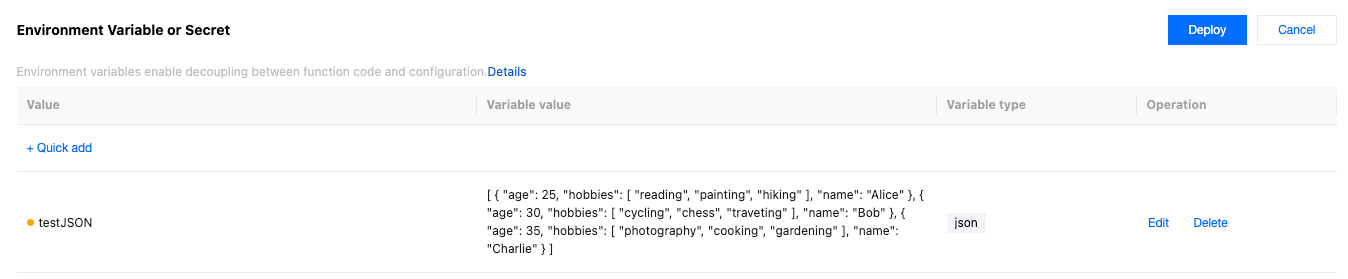
// Entry functionaddEventListener('fetch', event => {event.respondWith(handleRequest(event.request));});async function handleRequest(request) {// Obtain a value from an environment variable, and this environment variable needs to be created and deployed in edge function environment Variables or Secret.const myJsonData = env.testJSON;// Create response body.const response = new Response(JSON.stringify(myJsonData), {headers: {'Content-Type': 'application/json'}});// Return the response.return response;}
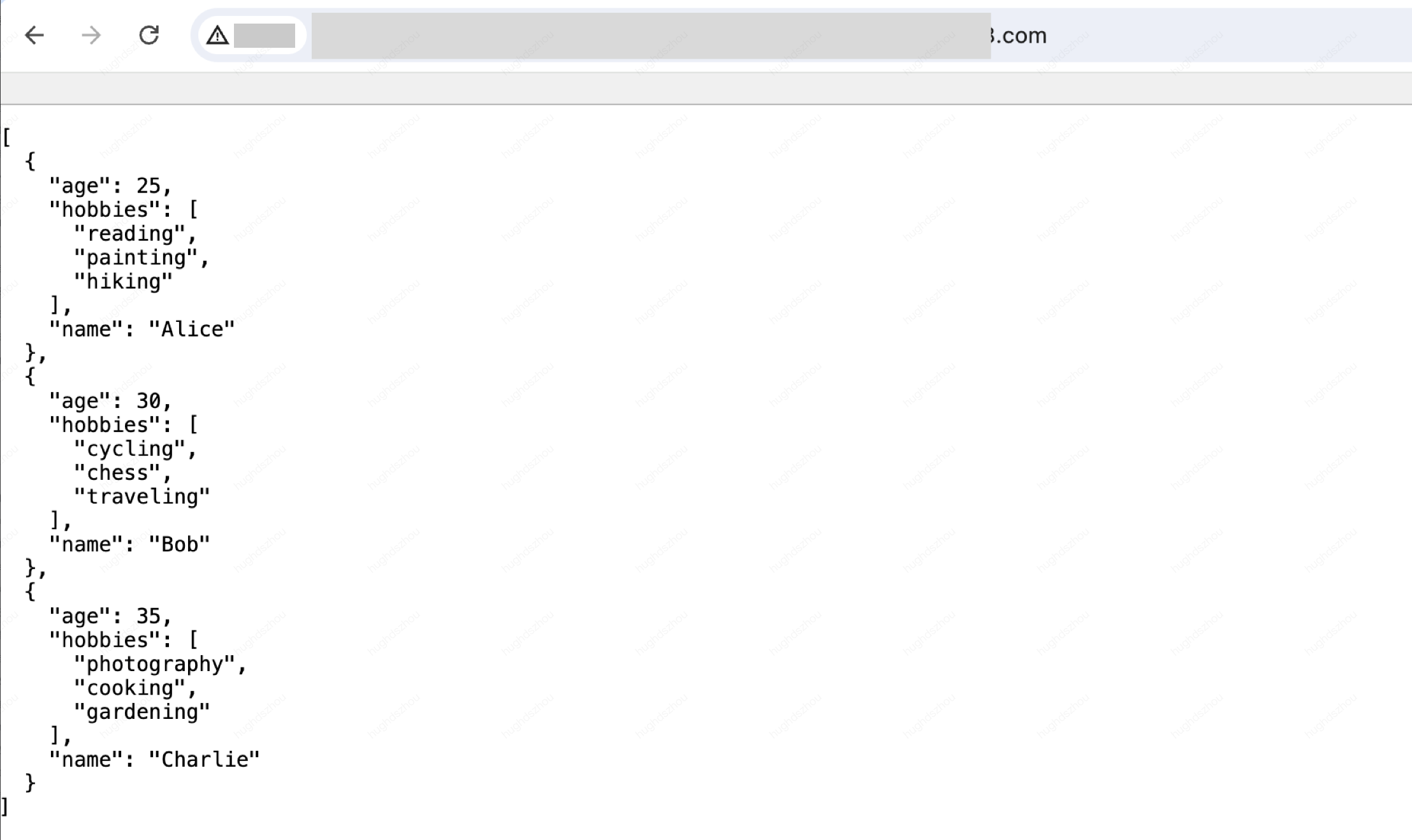
The semantic summary of the above code is to obtain the environment variable that the function has created and deployed, and respond it to the client as JSON data.
Deploy the code, and you can view the result by accessing the trigger rules or default access of the function.
Variable Type: Secret
Repeat the steps to create and deploy environment Variables or Secret,and create and deploy an environment variable of type Secret named
testSecret, Note: The variable value will no longer be visible after saving, please keep it safe. As shown below: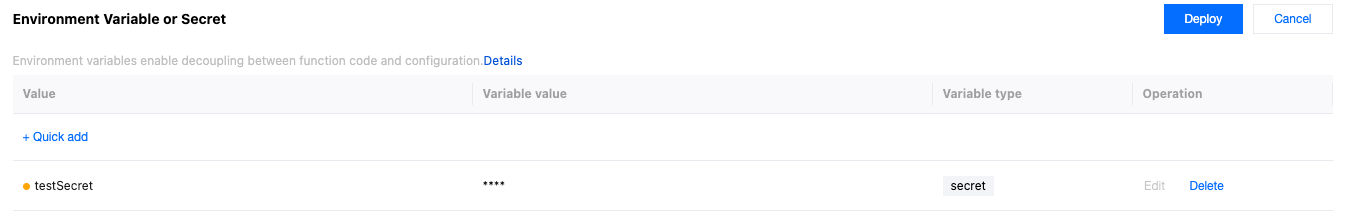
// Entry functionaddEventListener('fetch', event => {event.respondWith(handleRequest(event.request));});async function handleRequest(request) {// Obtain a value from an environment variable, and this environment variable needs to be created and deployed in edge function environment Variables or Secret.const secretData = env.testSecret;// Create response body.const response = new Response(secretData, {headers: {'Content-Type': 'application/json'}});// Return the response.return response;}
The semantic summary of the above code is to obtain the environment variable that the function has created and deployed, and respond it to the client as Body "Secret".
Deploy the code, and you can view the result by accessing the trigger rules or default access of the function.
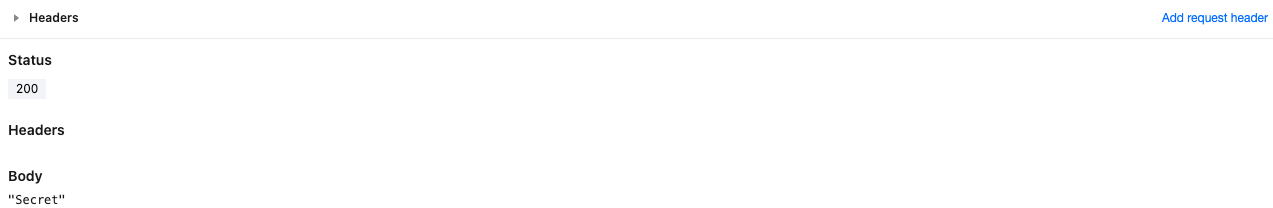
Editing Environment Variables or Secret
1. In the Environment Variables or Secret module, click Edit for a specific environment variable. In the pop-up window, you can change the variable type and the variable value. Click OK to save the edited content.
2. In the Environment Variables or Secret module, click Deploy. The pop-up window will display the specific updates for this operation. Click OK to complete the deployment.
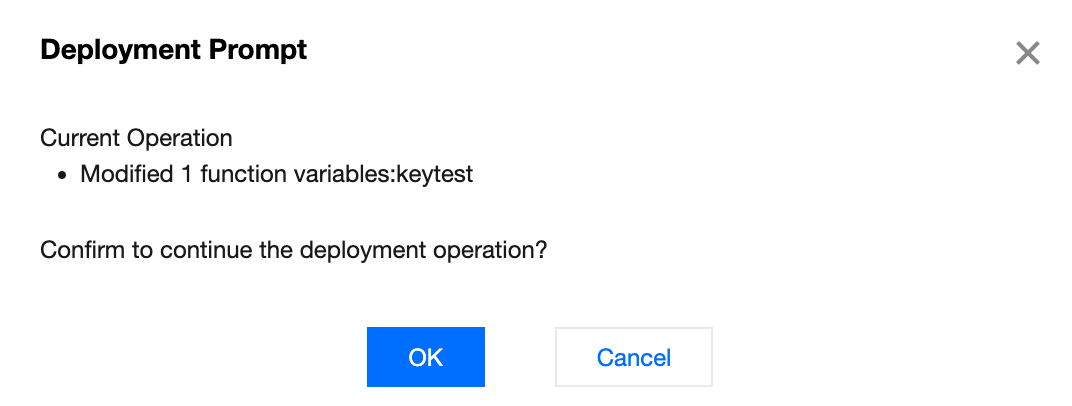
Deleting Environment Variables or Secret
In the Environment Variables or Secret module, click Delete for a specific environment variable, and then click Deploy. The pop-up window will display the specific environment variable being deleted in this operation. Click OK to complete the deployment.
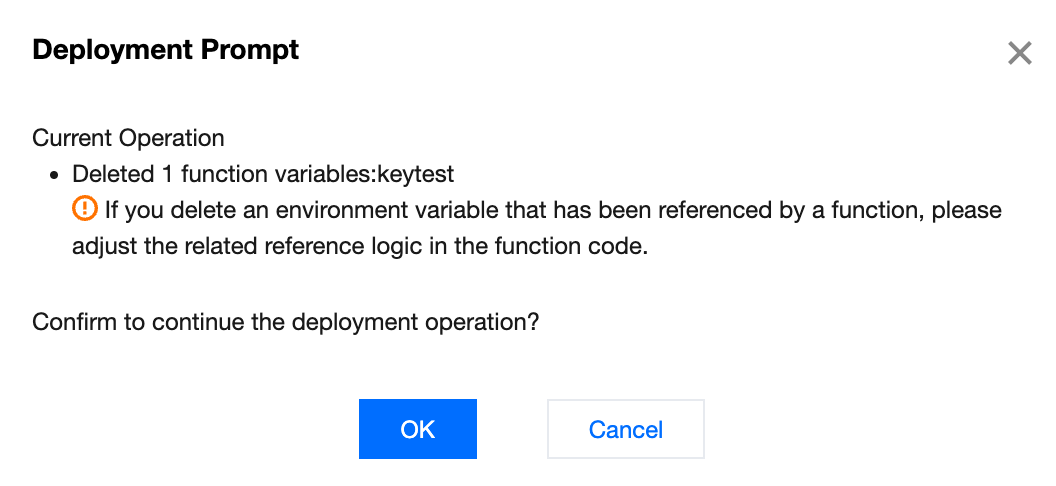
Note:
If the environment Variables or Secret referenced by the function are deleted through the above operations, adjust the logic of related references in the function code.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

