Single-Node Instances (Formerly Basic Edition and Cloud Disk Edition)
Last updated:2025-11-14 10:54:44
Single-Node Instances (Formerly Basic Edition and Cloud Disk Edition)
Last updated: 2025-11-14 10:54:44
TencentDB for MySQL supports four types of architectures: single-node, two-node, three-node,and Cluster Edition. This document describes the single-node architecture.
A single-node architecture can be divided into basic (formerly Basic Edition) and basic (cloud disk) based on different isolation policies. See Isolation Policy. The architecture adopts single-node deployment, so read-only instances also belong to the single-node architecture.
Single-Node - Basic (Cloud Disk Edition)
This architecture is displayed in the console as Single-node (Cloud Disk).
Use cases
The single-node architecture has only one database node, so it is very cost-effective and suitable for business scenarios that don't require a high availability, such as testing, development, and learning.
Features
The underlying storage uses Cloud SSD, Premium Disk, and Enhanced SSD.
SSD cloud disk: It is an all-flash cloud disk storage type with NVMe SSD as the storage media. It provides low-latency and high-throughput I/O capabilities with a high random IOPS and 99.9999999% (nine nines) data security. It is suitable for scenarios that require a high I/O performance.
Enhanced SSD cloud disk: It is based on Tencent Cloud's latest storage engine, NVMe SSD storage media and the latest network infrastructure. It provides high-performance storage with low latency, high random IOPS, high throughput I/O, and data security up to 99.9999999% (nine nines), making it suitable for I/O-intensive applications with high requirements for latency. Uniquely, the performance and capacity of Enhanced SSD cloud disks can be independently adjusted to meet your requirements.
Random IOPS formula for SSD cloud disk: Random IOPS = min{1800 + capacity (GiB) * 30, 26000}.
Throughput formula for SSD cloud disk (MB/s): Throughput = min{120 + capacity (GiB) * 0.2, 260}.
Calculation formula for random IOPS performance of Premium Disk: Random IOPS = min{1800 + capacity (GiB) x 8, 6000}.
Calculation formula for throughput performance (MB/s) of Premium Disk: Throughput = min{100 + capacity (GiB) x 0.15, 150}.
Random IOPS formula for Enhanced SSD cloud disk: Random IOPS = min{1800 + capacity (GiB) * 50, 50000}.
Throughput formula for Enhanced SSD cloud disk (MB/s): Throughput = min{120 + capacity (GiB) * 0.5, 350}.
Note:
Single-node (cloud disk) instances do not provide SLA, leading to longer fault recovery times. It is recommended to use two-node or three-node architecture instances in production environments, which can guarantee up to 99.99% availability.
In order to ensure the data availability and recoverability of the database instance, a small part (5%) of the disk space is used as the system protection space, which protects the data in the instance but cannot store data.
When a single-node (cloud disk) instance is created, approximately 2 GB of redo log files will be generated (comprising four 512 MB ib_logfile files), which are inherent files of TencentDB for MySQL.
Enhanced SSD is only supported in certain regions. For details, see the cloud disk options available during the purchase of single-node (cloud disk) instances.
Basic framework diagram
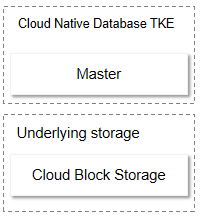
Single-Node - Basic (Formerly Basic Edition)
This architecture is referred to as single-node (formerly Basic Edition) architecture in this product document and is currently offline. If you need to use a single-node instance, purchase a single-node (cloud disk) instance.
Use cases
It is not recommended for official business environments; the single-node (formerly Basic Edition) architecture is suitable for personal learning, micro-websites, non-core small systems for enterprises, as well as development and testing environments for medium and large enterprises.
Features
Supports computation-storage separation. If a compute node fails, fast recovery can be achieved by switching to another node. Underlying data is stored in three copies on cloud disks, which ensures a certain level of data reliability and enables quick data restoration from disk snapshots in case of disk failures.
The single-node (formerly Basic Edition) architecture offers over 20 monitoring metrics across multiple dimensions, such as database connections, access, and resource, and corresponding alarm policies can be configured, making it easier to manage compared to self-built cloud servers. Additionally, it features significant cost strengths, saving up to 40% compared to cloud servers. This architecture is deployed on cloud servers, offering better database performance than systems built by users.
The single-node (formerly Basic Edition) architecture uses Premium Disk as the underlying storage medium, which is suitable for 90% of I/O scenarios, providing excellent quality at a low price, with stable performance. The specific IOPS range calculation formula is: {min 1,500 + 8 x hard disk capacity, max 4,500}. For example, if the disk capacity is 50 GB, the IOPS range is {min 1,900, max 4,500}.
Basic framework diagram
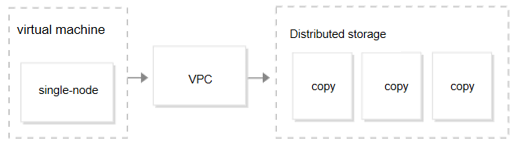
Note:
Due to the single-node (formerly Basic Edition) architecture, when a fault occurs on the node, the recovery time is longer than that of cloud server fault recovery (involving instance startup and data recovery). It is recommended that you use MySQL two-node or three-node instances for businesses with high availability requirements.
Single-Node - Read-Only Instance
A read-only instance adopts the single-node deployment. It is mounted under two-node or three-node instances and cannot be created independently without a primary instance. This architecture is displayed in the console as Single-node (Local Disk).
Note:
The Cluster Edition architecture instances support adding read-only nodes to improve the read load capability of the instance. Read-only nodes can only be displayed under the primary instances of the corresponding Cluster Edition architecture. Additionally, the Cluster Edition architecture instances also support adding independent read-only instances, which are displayed in the console as Cluster Edition (Cloud Disk), with the underlying storage using cloud disks.
Use cases
Currently, it is ideal only for read-only instances in various industries with read/write separation requirements.
Features
It uses local NVMe SSD disks for underlying storage with excellent IO performance and is ideal for read-only instances to share business read load.
Basic framework diagram
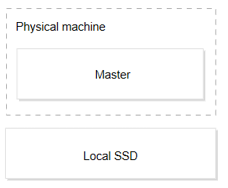
Note:
Single-node deployment is susceptible to single points of failure. If only one read-only instance is purchased, it is impossible to ensure high availability for your business, because a failure of the single read-only instance will lead to business disruption.
As the time taken to recover a single read-only instance depends on the business data volume, the recovery time cannot be guaranteed. As a result, if your business requires high availability, we recommend that you purchase at least two read-only instances for the read-only group as instructed in Managing the RO Group of Read-Only Instance.
Relevant operations
You can create one or more read-only instances, which can be applied to read/write separation and one-source-multiple-replica application scenarios. For more information, see Creating Read-Only Instance.
You can create one or more read-only instances and put them in an RO group to ensure availability. For more information, see Managing the RO Group of Read-Only Instance.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

