Overview
Last updated:2025-12-23 11:04:31
TencentDB for MySQL supports setting automatic and custom CPU scale-out for instances, which effectively alleviates performance pressure caused by sudden requests, adapts to peak business traffic, and ensures the stability of online businesses. It also supports CPU scale-in during periods of decreased traffic to avoid resource waste. This section provides a brief overview of the CPU Elastic Expansion feature.
Background
In many business scenarios, peak traffic periods or sudden traffic surges can impose tremendous pressure on server loads. The CPU utilization of the application can skyrocket, and if CPU resources are not scaled in a timely manner, it could lead to system performance degradation, increased request response time, and other issues, severely affecting user experience and satisfaction. Beyond burst traffic scenarios, situations such as low cache hit rate in the database, ineffective indexes, database deadlocks, complex database query statements, a high volume of concurrent updates, coupled with insufficient hardware configurations, can also lead to CPU overloads.
Traditional Solutions
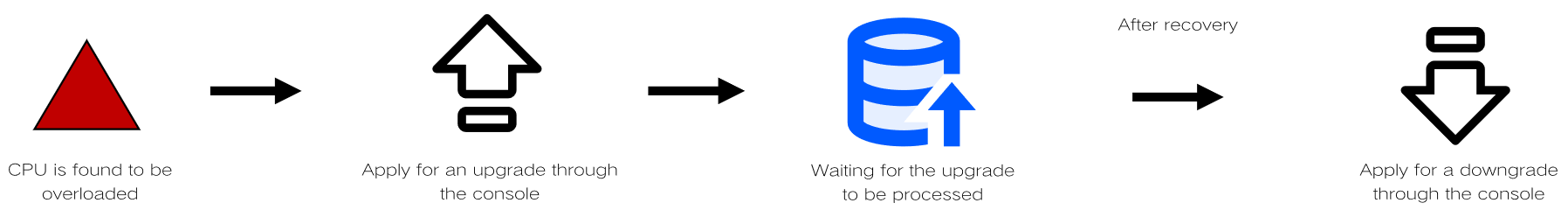
Upon detecting a CPU overload, users typically manually upgrade it through the console and wait for the upgrade to be completed. The upgrade duration, influenced by the amount of data, is uncertain. Moreover, the upgrade process may result in transient disruptions, affecting regular operations. After the business traffic become normal after the upgrade, users need to manually apply for a downgrade through the console. Thus, the traditional solution poses challenges such as the necessity for rapid response, unpredicted time frames, risk of transient disruptions, and an extensive follow-up workload.
CPU Elastic Scaling
Scenario 1: Daily enabling for uncertain/unknown traffic

Scenario 2: Specific activity time with traffic peaks
The CPU Elastic Scaling feature, underpinned by the advantages of the cloud environment, allows for the dynamic assignment of CPU resources. As the database traffic increases or CPU resource usage escalates, it can automatically allocate more CPU resources, then scale in after peak periods. Users can choose whether to enable the CPU Elastic Scaling feature via the console, and dynamically configure the database's CPU resources based on the business needs and traffic volume. Consequently, elastic scaling can be achieved to handle peak pressure, ensuring superior performance, high availability, and stability of the database instance.
Feature Type
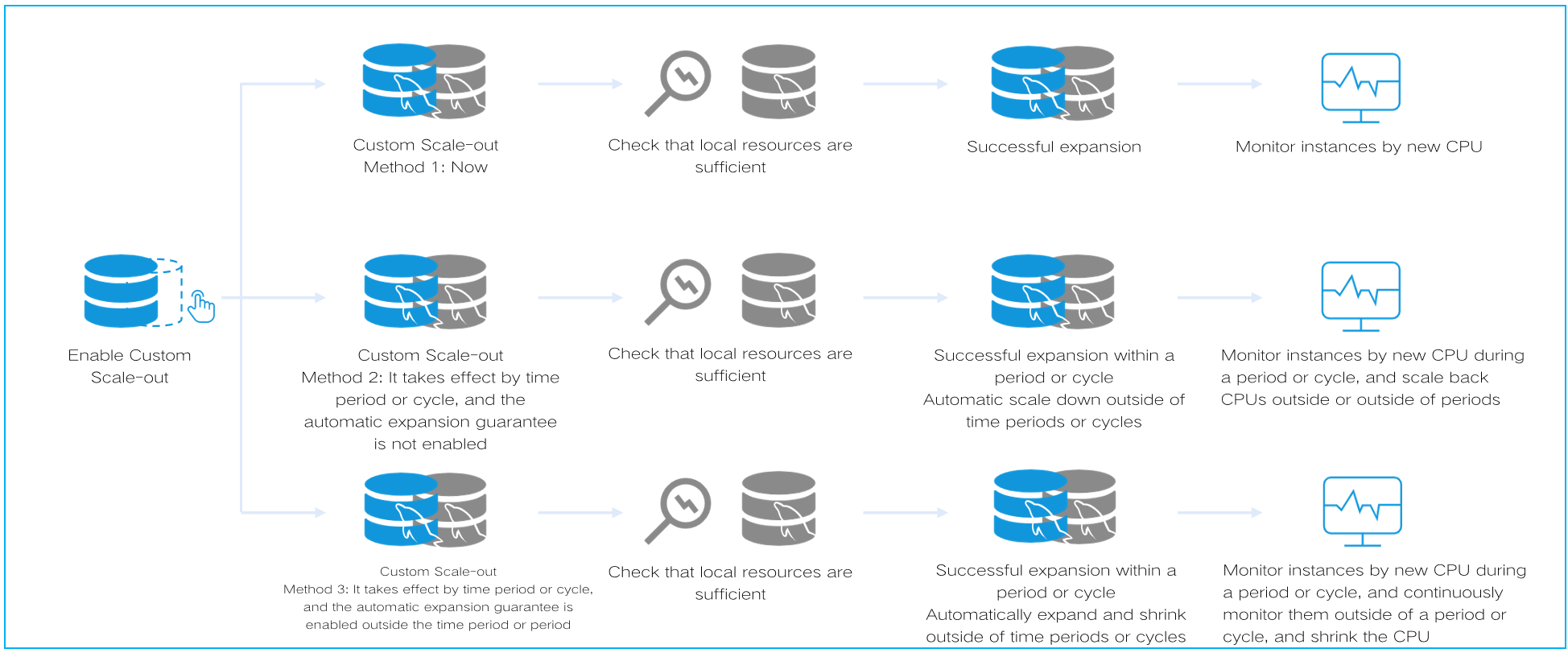
The CPU elastic scale-out feature includes automatic scale-out and custom scale-out. When automatic scale-out is enabled, you need to set scale-out and scale-in rules. When custom scale-out is enabled, you need to first select the number of cores for scale-out and then select the scale-out time. For scale-out time, you can select Now, which means the CPU will be scaled out immediately; however, it will not automatically scale in after scale-out, and the feature needs to be disabled manually. In addition, you can choose to scale out By Period or By Cycle, which will allow the CPU to be scaled out within the selected period or cycle, and scale-in will be automatically performed within other periods or cycles. You can also enable automatic scale-out within other periods or cycles, allowing for a more precise setup of the CPU elastic scale-out policy for instances to better align with actual business fluctuations.
Automatic scale-out
Automatic scale-out description
After Auto scaling under CPU Elastic Scaling is enabled, the system will double the number of CPU cores based on the original computing specification, when the average CPU utilization of the database instance within the observation window reaches the set threshold. For example, if the original computing specification has 4 CPU cores, it will be upgraded to 8 cores. Simultaneously, the IOPS of the instance will also increase; specifically, when the number of CPU cores increases by 1, IOPS increases by 1,000 accordingly. If the user's Tencent Cloud account balance is insufficient or there are not enough CPU resources available on the host (which is a rare occurrence), the scale-out operation will not be performed, and a scale-out failure event will be sent.
Note:
Only supports doubling the number of CPU cores based on the original computing specification, and no further increase is supported. For instance, after the original CPU cores are doubled to 8, it cannot be increased to 16.
Automatic scale-in description
After Auto Scaling under CPU Elastic Scaling is enabled, within the observation window set for the scale-in rules, if CPU utilization falls below the set threshold, the system will automatically scale in the number of CPU cores and IOPS back to the original computing specification.
Note:
After enabling CPU Elastic Scaling -> Auto Scaling, the system will monitor the database instance based on the most recent configuration parameters. When the instance meets the conditions for automatic scale-in, the system will automatically scale in the instance.
To learn how to enable or disable automatic scale-out and set scaling rules, see Configuring Automatic Scale-out.
Custom Scale-out
Custom scale-out description
After Custom Scaling under CPU Elastic Scaling is enabled, if the scale-out time is set to now, the instance will run with the scaled-out CPU cores right away. If the scale-out time is set by period or cycle, the instance will run with the scaled-out CPU cores within the selected period or cycle, and it is automatically scaled in in other periods or cycles. If the scale-out time is set by period or cycle with automatic scaling enabled, the instance will automatically scale in other periods or cycles based on the configured scaling rules.
Note:
In the CPU elastic scale-out feature, enabling automatic scale-out can avoid sudden CPU traffic in other periods or cycles.
Manual disabling description
After Custom Scale-out is enabled under CPU Elastic Scaling, if the scale-out time is set to Now, users need to manually disable the CPU elastic scale-out feature. When the business no longer requires more CPU resources. Otherwise, charges will be continually incurred.
Description of Scale-Out Rules
In scenarios involving automatic expansion and enabling automatic scale-up, the system determines whether the scale-up conditions you set have been met by independently collecting 1-second CPU monitoring data and calculating the p90 value. For example, if the rule is that automatic scale-up is triggered when CPU utilization reaches 80%, the system will mark points for the independently collected CPU monitoring data, and automatic scale-up is triggered only when the CPU utilization of at least 90% of the data points meet or exceed the 80% threshold.
In scenarios involving automatic expansion and enabling automatic scale-up, the system maintains the scale-out for at least 10 minutes before scale-in, regardless of whether CPU utilization falls below the set scale-in threshold during this period.
Description of the Number of Cores for Automatic Scale-out and Custom Scale-out
The default number of CPU cores for automatic scale-out is set to be double the original number of CPU cores for the instance and cannot be modified. For example, if the original number of CPU cores for the instance is 4 cores, 4 cores will be added for scale-out, resulting in a total number of 8 cores after scaling.
CPU cores for the custom scale-out feature support scale-out units of 1 core, with a maximum limit set at double the original number of CPU cores for the instance. For example, if the original instance specification has 4 CPU cores, the cores for scale-out can be set to 5, 6, 7, or 8 cores.
Regardless of automatic scale-out or custom scale-out, the original number of CPU cores of an instance should not exceed 32. For example, if the original instance specification is 48 cores and 488,000 MB of memory, enabling the CPU elastic scale-out feature is not supported.
Billing Instructions
Event Alarm Explanation
For automatic scale-out and custom scale-out, related event alarms are supported to be set, and alarm notifications can be configured. The following are the event metrics and descriptions related to the CPU Elastic Scaling feature.
Scaling Type | Event Metrics | Description |
Auto Scaling | CPUExpansion | Automatic CPU scale-out is successful. |
| CPUExpansionFailed | Automatic CPU scale-out failed. |
| CPUConstraction | Automatic CPU scale-in is successful. |
Custom scale-out | CPUExpansion | Custom CPU scale-out succeeded |
| CPUExpansionFailed | Custom CPU scale-out failed |
| CPUConstraction | Disabling Custom CPU Scale-out |
There are two causes for failures of automatic scale-out and custom scale-out: insufficient balance in the Tencent Cloud account of the user or inadequate CPU resources on the host (rarely occurs).If insufficient account balance leads to a scaling failure, users can recharge their account and retry. For other causes, please submit a ticket for assistance.
Feature Impact Overview
The CPU elastic scale-out feature for two-node and three-node instances takes effect on both the source node and the replica node simultaneously. If an HA switch for two-node and three-node instances occurs after the feature takes effect, the switched node will also inherit the scaled-out CPU specifications. After automatic scale-in is enabled or custom scale-out is disabled, the node will automatically scale in to the original CPU specification.
The feature should be separately enabled for read-only instances and disaster recovery instances, which will not simultaneously scale out. In other words, the read-only instances and disaster recovery instances attached to the primary instance will not simultaneously expand their CPU resources even after the CPU Elastic Scaling feature of the primary instance is triggered. The CPU Elastic Scaling feature must be enabled for these two types of instances separately.
If an instance with the CPU elastic scale-out feature enabled needs to adjust configuration, note that the feature will be disabled after the adjustment is completed. Promptly monitor whether the CPU meets business needs after adjustment. If you want to use the feature again, re-enable it.
If an instance with the CPU elastic scale-out feature enabled is migrated, including user-initiated migration or synchronous migration during processes (such as primary instance upgrade migration along with read-only instance upgrade migration scenarios), note that the feature will be disabled after the migration is completed. Promptly monitor whether the CPU meets business needs after adjustment. If you want to use the feature again, re-enable it.
Related Operations
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

