多节点高可用
最后更新时间:2026-01-12 17:16:53
数据库高可用(High Availability, HA)旨在通过冗余设计和故障自动恢复机制,确保系统在部分节点失效时仍能持续提供服务。只读分析引擎实例通过多节点部署的方式实现高可用,通过将数据库实例分布在多个物理节点上,并结合数据同步、故障检测和流量切换等机制,保障业务连续性。本文为您介绍只读分析引擎实例实现高可用的原理以及相关操作和管理。
只读分析引擎实例高可用实现原理
冗余架构
一个只读分析引擎实例下支持部署1 - 3个节点,当节点数量为2个或3个时,可以形成对等集群(Cluster)。当只读分析引擎实例下的某一个节点发生故障时,系统可自动将 SQL 流量转发至“存活”的节点,即转发至该只读分析引擎实例下其他正常运行的节点,避免单点故障导致业务不可用。
故障检测与切换(Failover)
心跳机制:在只读分析引擎实例的节点之间,通过周期性心跳检测来探测节点的“存活”状态,若节点超时未响应(检测间隔时间为3秒),则会触发故障判定。
自动切换:当周期性心跳检测到节点故障时,系统将再次对节点进行两次无间隔时间的“存活”探测(探测时间约10秒)。如果持续探活节点失败,则系统将在1 - 5秒内将故障节点移出只读分析引擎实例,然后等待故障节点恢复或者自动重建后再加入到该只读分析引擎实例中。
负载均衡
只读分析引擎实例中的多个节点使用负载均衡的形式为您提供服务。所有节点都可以正常承载业务流量,提升业务的并发执行性能。
计费说明
调整节点数量
注意:
只读分析引擎实例目前默认采用从云数据库 MySQL 的主实例拉取数据的方式进行节点重建,故新增节点操作时,建议在业务低峰期进行。
1. 登录 MySQL 控制台。
2. 在实例列表中,找到目标只读分析引擎实例,在其操作列单击管理,进入实例详情页面。
3. 进入实例节点页面,单击节点变更。
4. 在跳转页面中,根据需要新增或删除节点,然后单击提交。
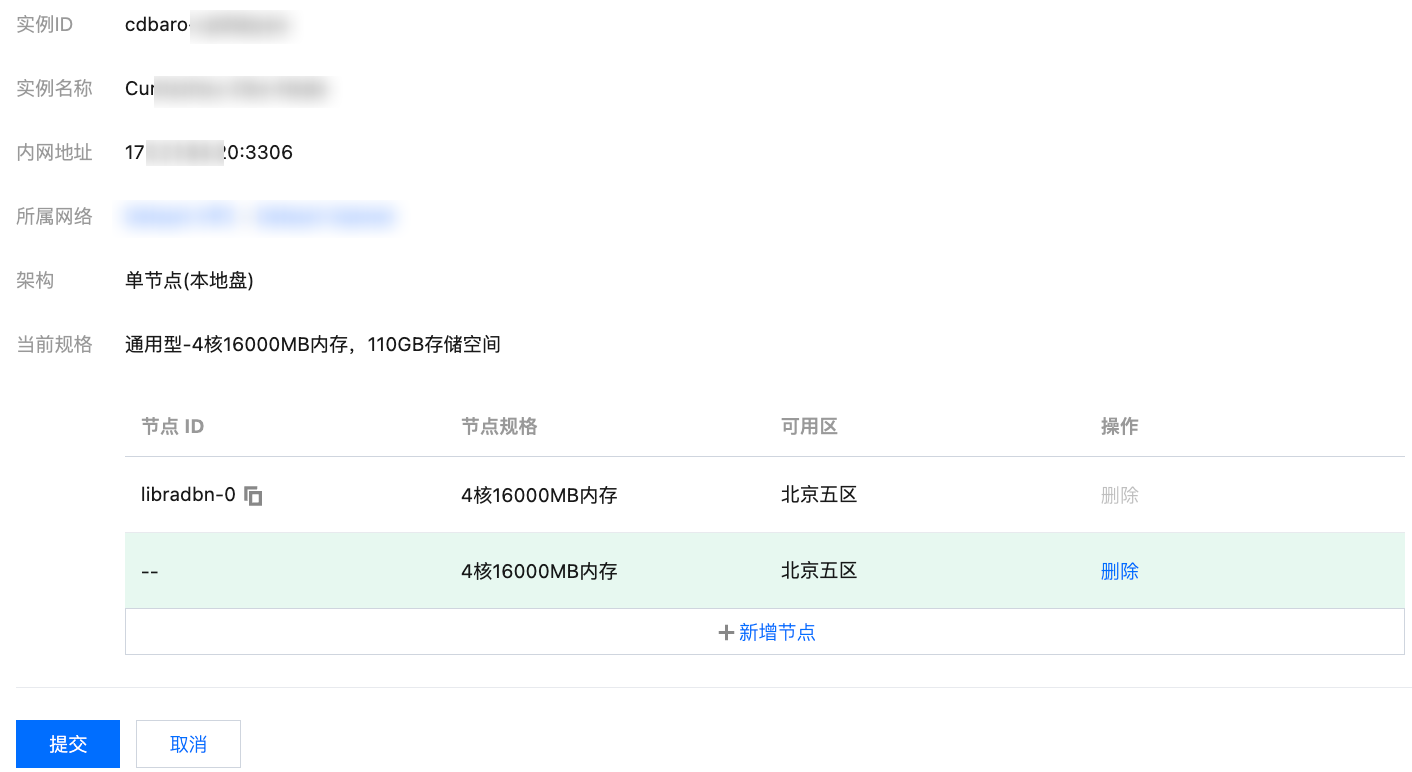
新增节点:如需增加节点,请单击新增节点,可为当前只读分析引擎实例新增1个节点,一个只读分析引擎实例下最多支持3个节点。
删除:如需删除节点,请单击删除,若操作失误删除了错误的节点,可在单击提交之前,单击恢复。
说明:
节点的规格和可用区与只读分析引擎实例一致。
一个只读分析引擎实例下至少需保留1个节点,不支持全部删除。
5. 完成操作后即可返回实例详情页面,当节点状态显示为“运行中”时,即可正常使用。
文档反馈

