Creating a Data Consistency Check Task
Last updated:2025-12-03 10:43:50
Scenarios
Data consistency check involves comparing table data between the source and target databases through Data Transfer Service (DTS) during data synchronization, providing comparison results and inconsistency details to help users quickly verify synchronization results before switch. The data consistency check task is run independently and does not affect the normal business of the source database or the DTS tasks.
Note:
Consistency check serves only as an auxiliary data verification method. Users are required to perform experiment operations by themselves to ensure that the results meet the migration requirements before the formal migration.
Currently, data consistency check is only supported for the full synchronization scenario, and it is not supported for the incremental synchronization scenario. Therefore, before creating a data consistency check task, stop data write operations.
The currently supported data consistency check link is SQL Server > SQL Server.
Must-Knows and Constraints
The data consistency check task may increase the load on the source database instance. Therefore, it is recommended to perform these operations during off-peak hours.
When the check type is sampling check, the tables to be checked must have a primary key or a unique key; otherwise, they will be skipped. When the check type is row number check, a primary key or unique key is not required. However, if a table lacks a primary key or a unique key and contains more than 10,000 data entries, a full check cannot be performed.
If the user chooses to complete or terminate the DTS task before the data consistency check task is finished, the data consistency check task will fail.
Creating a Data Consistency Check Task
Note:
When a separate data consistency check task is created, only the independent check is supported, and the built-in check is not supported.
The independent check operates independently from the DTS task and selects the same data blocks from both the source and target for comparison. Check tasks cannot be initiated once the DTS task stops running.
Independent check tasks can only be initiated when the task is running. Once the task is completed, check tasks cannot be initiated. Based on different migration stages, you can initiate check tasks using different check methods multiple times and in batches.
1. Log in to the DTS console, choose Data Synchronization in the left sidebar, find the target task in the task list, and choose More > Create Data Consistency Check Task in the operation column.

Note:
You can also click View in the Operation column of the task list, or directly click the task ID to go to the task details page. Then click the Consistency Check tab and click Create Data Consistency Check.
2. In the pop-up window, complete the following configuration and click Create and Start Consistency Check Task.
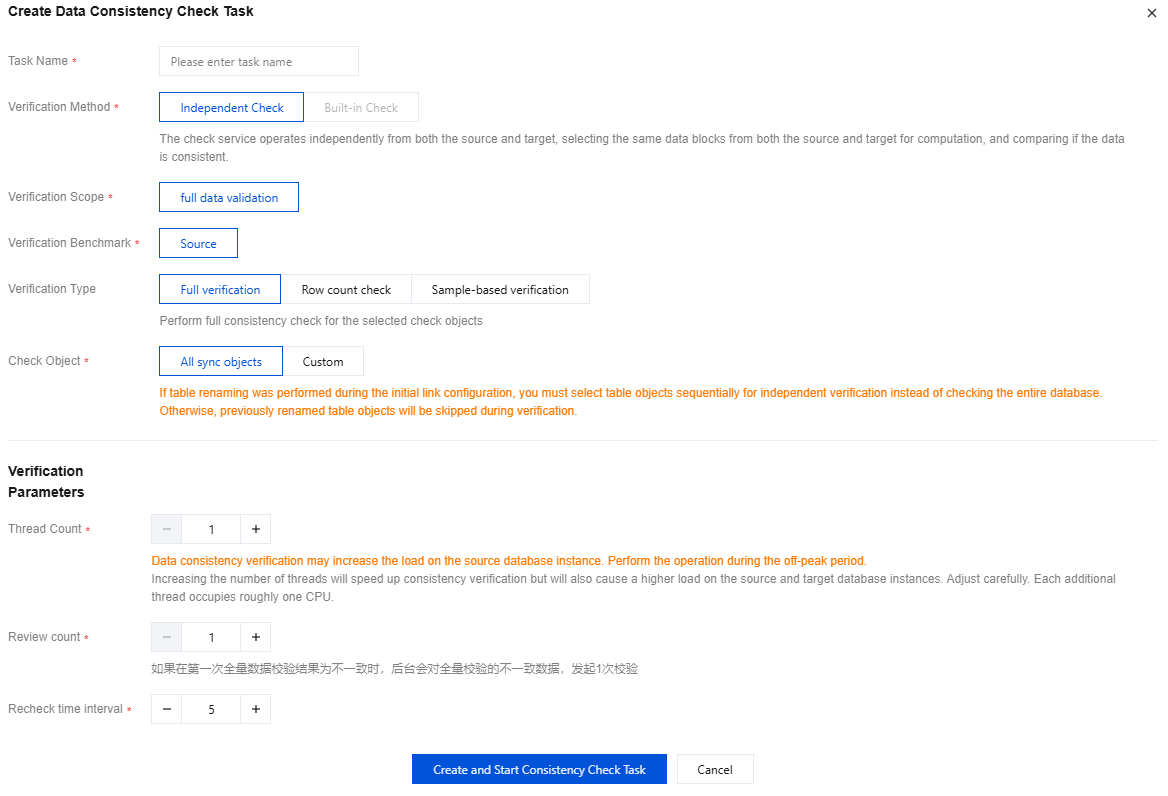
Parameter | Description |
Task Name | Enter the name of the check task. |
Check Method | Independent check: The check service operates independently from both the source and target, selecting the same data blocks from both the source and target for computation, and comparing if the data is consistent. |
Check Content | The default option is full check, which indicates that all data in the source and target databases is compared when a check task is initiated. |
Check Benchmark | The default option is the source, which indicates that data from the source is used as the check benchmark. |
Check Type | Full check: Perform a complete consistency check on the selected check objects. Row number check: Compare only the number of rows in the selected check objects. It is not required that the table objects have a primary key during row number comparison, and this check can be performed on tables without primary keys. Sampling check: Perform a data consistency check on a selected proportion of the check objects. The sampling ratio can be 10%, 20%, 30% ... 90%. |
Check Object | All synchronization objects: The check scope includes all objects selected for the synchronization task. Custom selection: Select specific objects from the selected synchronization objects for checking. |
Thread Number Selection | The value range is 1–8. Select an appropriate value according to the actual situation. Increasing the number of threads can accelerate the consistency check speed, but it will also increase the load on the source and target databases. Please adjust the number with caution. Each additional thread approximately increases CPU usage by one core. The data consistency check may increase the load on the source database instance. It is recommended to perform operations during off-peak hours. |
Number of Rechecks | Set the number of rechecks. If the first full data check result is inconsistent, the background will recheck the inconsistent data in the full check. The value range is 1–2. |
Recheck Interval | Set the recheck interval in the unit of minutes. The value range is 1–10. |
Viewing the Data Consistency Check Results
1. Log in to the DTS console, choose Data Synchronization in the left sidebar, and click View in the Operation column of the task list, or directly click the task ID to go to the task details page.
2. Click Consistency Check to enter the task list of the data consistency check, under which you can view the check result (consistent or inconsistent) of the created data consistency check task.

3. Click View to go to the check details page.
Summary of Data Check Results
The summary of data check results is shown in the table below:
Project | Details |
Overview | Comparison type: Currently, all are independent checks. Comparison method: Available methods include full check, sampling check, and row number check. Status: status of the current check task, which can be created, waiting to run, running, or completed. Comparison conclusion: result of running the current check task, which can be inconsistent or consistent. Thread number: number of threads configured for the current task. Start time: start time of the current task. End time: end time of the current task. |
Estimated total number of tables | Total number of all tables that need to be checked, which is estimated by the system. |
Number of checked tables | Current number of tables that have completed the check for the task. |
Number of inconsistent tables | Number of tables with inconsistencies between the source and target among the tables that have completed the check. Go to the inconsistency details page to view the tables that are inconsistent. |
Number of skipped tables | Number of skipped tables in the check. |
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

