Network Line Acceleration
Last updated:2026-02-10 15:54:34
Introduction
This article describes how to improve the success rate and speed of COS operations such as uploads and downloads by optimizing network access routes.
Feature Overview
Tencent Cloud has deployed storage centers in many regions worldwide, and customers can selectively enable these storage centers. However, even so, it remains unavoidable that some end-users are too far from the storage centers, and some customers' business scenarios involve cross-region or even transoceanic access. Long-distance data access typically implies longer network paths and greater transmission latency. Moreover, if any intermediate node experiences network jitter, packet loss, or other issues, it will reduce the access speed and success rate of the entire link.
To address the poor network access quality caused by excessively long network paths in long-distance access scenarios, solutions like COS Global Acceleration and EdgeOne can forward user requests to the edge nodes closest to users, processing user data locally. Leveraging Tencent Cloud's acceleration network refined over years, these solutions then transmit data to storage centers via optimal paths.
Therefore, if you have high requirements for the success rate and latency of COS operations such as uploads and downloads, you can use services like COS Global Acceleration and EdgeOne to access COS.
Prerequisites
You can experience network acceleration capabilities based on COS Global Acceleration or EdgeOne. Before performing operations, you need to activate the service and configure relevant settings by following these steps:
COS Global Acceleration
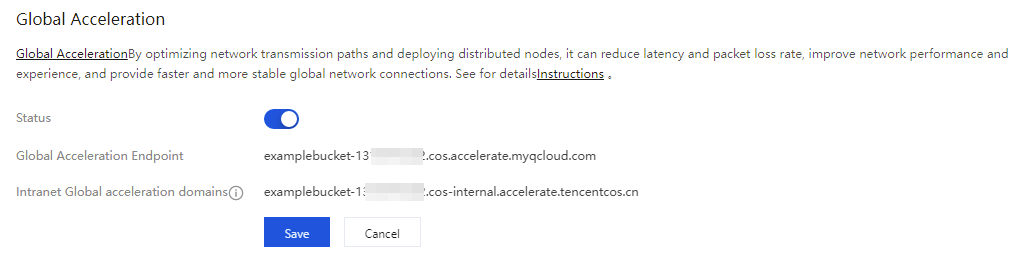
Go to the COS console to enable COS Global Acceleration. For specific operations, see enable COS Global Acceleration.
EdgeOne + COS Global Acceleration
1.1 Go to the EdgeOne console to activate. For specific operations, see activate EdgeOne.
1.2 In the EdgeOne console, click Add Site to add the acceleration domain for the business party. After going to the site, perform Domain Management. When Add Domain is performed, select COS Origin and S3 Compatible, and fill in the origin address with the COS global acceleration domain (<BucketName-APPID>.cos.accelerate.myqcloud.com).
1.3 Enable the Smart Acceleration feature in EdgeOne. For details, see Smart Acceleration.
1.4 Obtain the acceleration domain in step 1.2. This domain subsequently needs to be configured into the COS SDK.
Note:
COS Global Acceleration and EdgeOne incur certain fees. For details, see COS Global Acceleration Billing and EdgeOne Billing.
Operation Steps
Method 1: COS Global Acceleration
The request information of the COS Global Acceleration feature is accelerated via Tencent Cloud's private network dedicated line, not only enabling nearby access for requests but also enabling data upload acceleration and download acceleration.
Enable COS Global Acceleration via the CosXmlServiceConfig in the COS SDK.
String region = "ap-beijing"; // Your bucket regionCosXmlServiceConfig cosXmlServiceConfig = new CosXmlServiceConfig.Builder().setRegion(region).setAccelerate(true) // Use the COS global acceleration domain.builder();CosXmlService cosXmlService = new CosXmlService(context, cosXmlServiceConfig,credentialProvider);
Enable COS Global Acceleration via the QCloudServiceConfiguration in the COS SDK.
QCloudServiceConfiguration* configuration = [QCloudServiceConfiguration new];configuration.appID = @"appId"; // Set the APP IDconfiguration.signatureProvider = self;QCloudCOSXMLEndPoint *endpoint = [[QCloudCOSXMLEndPoint alloc]init];endpoint.suffix = @"cos.accelerate.myqcloud.com"; // Set the global acceleration domainendpoint.useHTTPS = YES; // Use httpsconfiguration.endpoint = endpoint;
In the browser, when the JavaScript SDK is instantiated, configuring UseAccelerate: true enables the use of global acceleration for upload/download.
var cos = new COS({UseAccelerate: true, // Specify true to use the global acceleration domain for requests});
Method 2: EdgeOne + COS Global Acceleration
This approach combines the advantages of EdgeOne and COS Global Acceleration: EdgeOne provides extensive coverage of edge nodes, and COS Global Acceleration enables private network acceleration for origin fetch.
Configure the acceleration domain via the CosXmlServiceConfig in the COS SDK.
String region = "ap-beijing"; // Your bucket regionString eoDomain = "exampledomain.com"; // eo acceleration domainCosXmlServiceConfig cosXmlServiceConfig = new CosXmlServiceConfig.Builder().setRegion(region).setHost(eoDomain) // Configure the acceleration domain.addNoSignHeaders("Host") // When EO forwards requests, the host may change; avoid signing the host here.builder();CosXmlService cosXmlService = new CosXmlService(context, cosXmlServiceConfig,credentialProvider);
Configure the acceleration domain through QCloudServiceConfiguration in the COS SDK.
NSString * eoDomain = @"exampledomain.com";QCloudServiceConfiguration* configuration = [QCloudServiceConfiguration new];configuration.appID = @"appId"; // Set the APP IDconfiguration.signatureProvider = self;QCloudCOSXMLEndPoint* endpoint = [[QCloudCOSXMLEndPoint alloc] initWithLiteralURL:[NSURL URLWithString:eoDomain]]; // Set the acceleration domainendpoint.useHTTPS = YES; // Use httpsconfiguration.endpoint = endpoint;
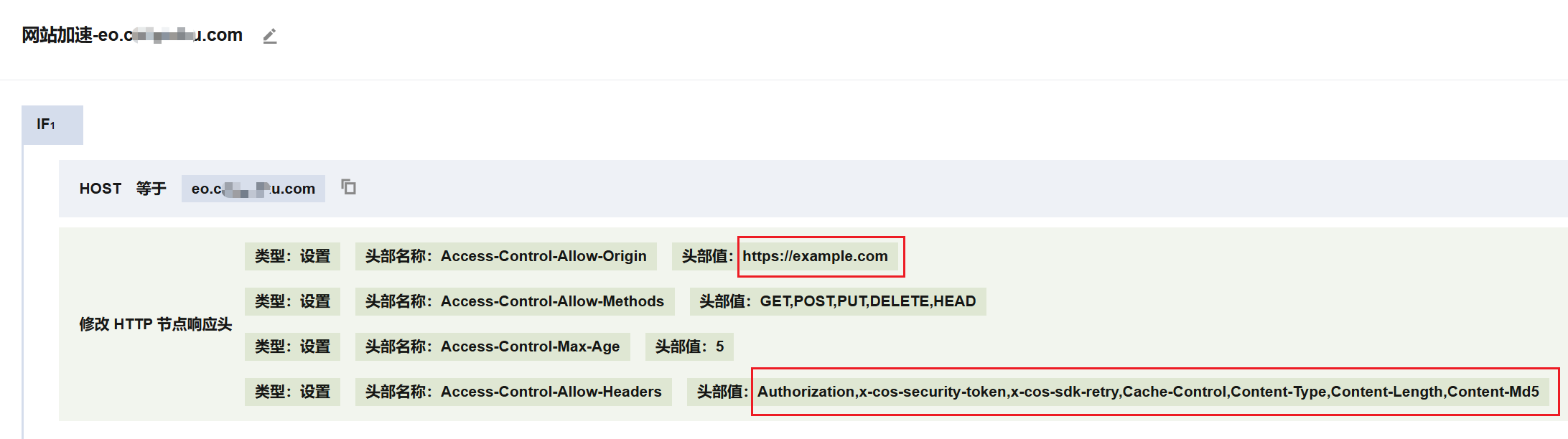
1. In the browser-side upload of the EdgeOne domain, you need to configure EdgeOne to return fixed CORS cross-origin headers in responses. Set the Access-Control-Allow-Headers header to Authorization,x-cos-security-token,x-cos-sdk-retry,Cache-Control,Content-Type,Content-Length,Content-Md5.
2. In the browser, when the JavaScript SDK is instantiated, use the Domain parameter to specify the use of the EdgeOne domain for upload/download.
var cos = new COS({Domain: 'edgeone.example.com', // Specify the request domain as the EdgeOne domain.ForceSignHost: false, // Since the actual request domain differs from the origin domain, avoid signing the Host header.Host});
Method Three: Configuring Traffic Routing Within the SDK
To improve the success rate of SDK requests and reduce costs, the SDK provides a configuration method for line switching policies:
Conservative policy: Use the COS default line for requests first, and automatically retry with the acceleration line upon network failure.
Aggressive policy: Use the acceleration line for requests first, and automatically retry with the COS default line upon network failure.
Custom policy: The SDK provides a method to configure the network line for requests, allowing the logic of request handling and switching to be flexibly controlled at the business layer (for example, automatically switching based on network quality).
If no switching policy is configured, the acceleration lines from Method 1 and Method 2 will be directly used for requests.
Configure the conservative and aggressive policies via the setNetworkSwitchStrategy method of CosXmlServiceConfig in the COS SDK.
String region = "ap-beijing"; // Your bucket regionString eoDomain = "exampledomain.com"; // eo acceleration domain// Aggressive policyCosXmlServiceConfig.RequestNetworkStrategy aggressiveStrategy = CosXmlServiceConfig.RequestNetworkStrategy.Aggressive;// Conservative policyCosXmlServiceConfig.RequestNetworkStrategy conservativeStrategy = CosXmlServiceConfig.RequestNetworkStrategy.Conservative;CosXmlServiceConfig cosXmlServiceConfig = new CosXmlServiceConfig.Builder().setRegion(region).setHost(eoDomain) // Configure the acceleration domain.addNoSignHeaders("Host") // When EO forwards requests, the host may change; avoid signing the host here.setNetworkSwitchStrategy(aggressiveStrategy) // Configure the switching policy as aggressive policy//.setNetworkSwitchStrategy(conservativeStrategy) // Configure the switching policy as conservative policy.builder();CosXmlService cosXmlService = new CosXmlService(context, cosXmlServiceConfig,credentialProvider);
Configure the custom policy via the setHost method of the request base class CosXmlRequest.
// Any CosXmlRequest supports this method, for example, uploading PutObjectRequest, downloading GetObjectRequest, deleting DeleteObjectRequest, etc.// The following uses upload as an examplePutObjectRequest putRequest = new PutObjectRequest("examplebucket-1250000000", "exampleobject.txt", "Local file path");String eoDomain = "exampledomain.com"; // eo acceleration domain// Customize the request network line for specific requests; if set to null, use the default COS domain lineputRequest.setHost(eoDomain);// Initialize TransferConfig with the default configuration. If you need to customize it, see the SDK API documentation.TransferConfig transferConfig = new TransferConfig.Builder().build();// Initialize TransferManagerTransferManager transferManager = new TransferManager(cosXmlService, transferConfig);COSXMLUploadTask uploadTask = transferManager.upload(putRequest, null);
Configure the conservative and aggressive policies via the networkStrategy method of QCloudServiceConfiguration in the COS SDK.
NSString * eoDomain = @"exampledomain.com";QCloudServiceConfiguration* configuration = [QCloudServiceConfiguration new];configuration.appID = @"appId"; // Set the APP IDconfiguration.signatureProvider = self;QCloudCOSXMLEndPoint* endpoint = [[QCloudCOSXMLEndPoint alloc] initWithLiteralURL:[NSURL URLWithString:eoDomain]]; // Set the acceleration domainendpoint.useHTTPS = YES; // Use https// Configure the acceleration domainconfiguration.endpoint = endpoint;// Configure the switch policy as the aggressive policyconfiguration.networkStrategy = QCloudRequestNetworkStrategyAggressive;// Configure the switch policy as the conservative policy// configuration.networkStrategy = QCloudRequestNetworkStrategyConservative;[QCloudCOSXMLService registerDefaultCOSXMLWithConfiguration:configuration];[QCloudCOSTransferMangerService registerDefaultCOSTransferMangerWithConfiguration:configuration];
Note:
When requests are forwarded, the host in EO changes. When generating the signature, you need to specify that the Host is excluded from the signature, as shown below:
- (void) signatureWithFields:(QCloudSignatureFields*)filedsrequest:(QCloudBizHTTPRequest*)requesturlRequest:(NSMutableURLRequest*)urlRequstcompelete:(QCloudHTTPAuthentationContinueBlock)continueBlock{// Synchronously obtain the temporary key from the backend server. It is strongly recommended to place the logic for obtaining the temporary key here to maximize the availability of the key.//...QCloudCredential* credential = [QCloudCredential new];// Temporary key SecretId// Replace sercret_id with your SecretId. Log in to the CAM console to view keys: https://console.tencentcloud.com/cam/capicredential.secretID = @"SECRETID";// Temporary key SecretKey// Replace sercret_key with your SecretKey. Log in to the CAM console to view keys: https://console.tencentcloud.com/cam/capicredential.secretKey = @"SECRETKEY";// Temporary key Token// If using a permanent key, you do not need to provide a token. If using a temporary key, you need to provide one. For instructions on generating and using temporary keys, see https://www.tencentcloud.com/document/product/436/14048?from_cn_redirect=1credential.token = @"TOKEN";/** It is strongly recommended to use the server time as the start time for the signature to avoid signature errors caused by significant deviations in the user's local device time (parameters startTime and expiredTime are in seconds).*/credential.startDate = [NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSince1970:startTime]; // Unit: secondscredential.expirationDate = [NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSince1970:expiredTime]]; // Unit: secondsQCloudAuthentationV5Creator* creator = [[QCloudAuthentationV5Creator alloc]initWithCredential:credential];// Set the headers to be included in the signature, excluding Host.creator.shouldSignedList = @[@"Cache-Control", @"Content-Disposition", @"Content-Encoding", @"Content-Length", @"Content-MD5", @"Content-Type", @"Expect", @"Expires", @"If-Match" , @"If-Modified-Since" , @"If-None-Match" , @"If-Unmodified-Since" , @"Origin" , @"Range" , @"transfer-encoding",@"Pic-Operations",@"ci-process"];// Note: Do not perform copy or mutableCopy operations on the URLRequest here.QCloudSignature *signature = [creator signatureForData:urlRequst];continueBlock(signature, nil);}
By setting the endpoint of the base class QCloudAbstractRequest, you can configure a custom domain.
QCloudPutObjectRequest* put = [QCloudPutObjectRequest new];// Set the custom domainNSString * eoDomain = @"exampledomain.com";QCloudCOSXMLEndPoint* endpoint = [[QCloudCOSXMLEndPoint alloc] initWithLiteralURL:[NSURL URLWithString:eoDomain]]; // Set the acceleration domainput.endpoint = endpoint;// Bucket name, which consists of BucketName-Appid, can be viewed in the COS console at https://console.tencentcloud.com/cos5/bucketput.bucket = @"examplebucket-1250000000";// Object key, which is the full path of the object on COS. If including a directory, the format should be "video/xxx/movie.mp4"put.object = @"exampleobject";// File content. You can pass in a variable of type NSData* or NSURL*put.body = [@"testFileContent" dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];[put setFinishBlock:^(id result, NSError *error) {// result contains the response header information// Obtain the file crc64NSString * crc64 = [[result __originHTTPURLResponse__].allHeaderFields valueForKey:@"x-cos-hash-crc64ecma"];}];[[QCloudCOSXMLService defaultCOSXML] PutObject:put];
Example Projects
Android sample Demo, see COS SDK Network Optimization Demo for CosServiceFactory.
iOS sample Demo, see COS SDK Network Optimization Demo for AppDelegate.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

