SASL_PLAINTEXT Access in the Public Network
Last updated:2026-01-05 15:16:59
Scenarios
This document uses the PHP client as an example to describe how to use the SASL_PLAINTEXT method to access TDMQ for CKafka (CKafka) in the public network and send and receive messages.
Prerequisites
Operation Steps
Step 1: Preparations
1. Create an access point.
1.1 On the Instance List page, click the target instance ID to go to the instance details page.
1.2 Choose Basic Info > Access Mode, and click Add a routing policy. In the pop-up window, choose
Routing Type: Public Network Domain Name Access > Access Method: SASL_PLAINTEXT.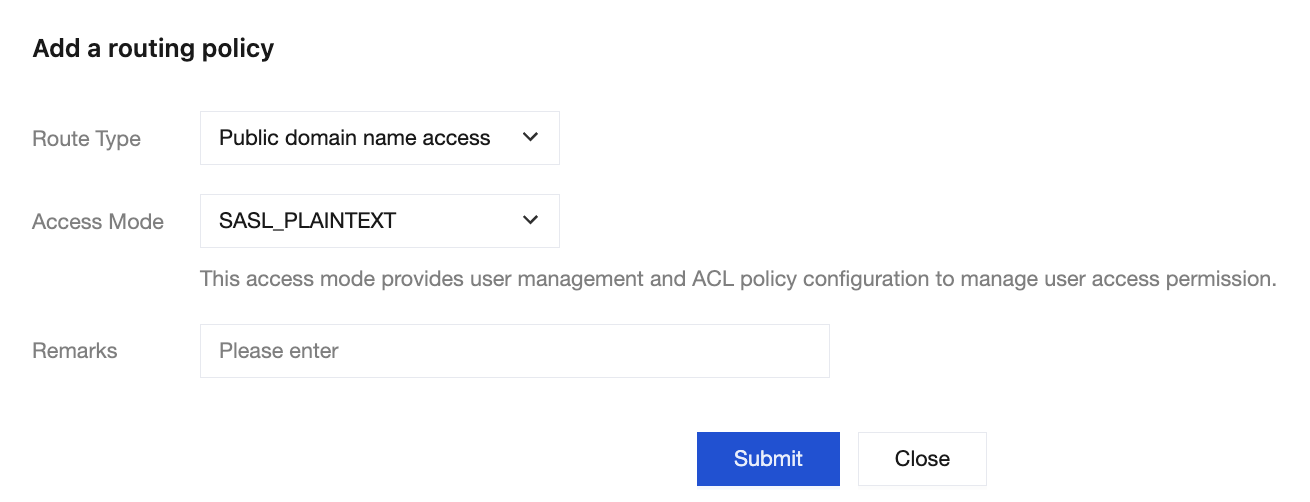
2. Create a role.
Select ACL Policy Management to go to the User Management page. On the displayed page, create a role and set the password.
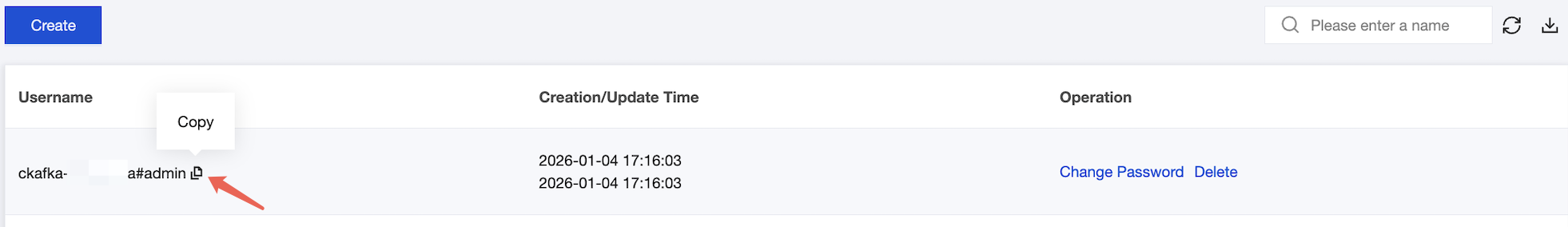
3. Create a topic.
4. Configure the ACL policy.
Configure the topic read/write permissions for the created role by seeing Configuring Topic Read/Write Permissions.
Step 2: Adding the Rdkafka Extension
1. Find the latest rdkafka PHP extension package on the rdkafka official website.
Note
Different package versions require different PHP versions. The following uses version 4.1.2 as an example.
2. Install the rdkafka extension.
wget --no-check-certificate https://pecl.php.net/get/rdkafka-4.1.2.tgzpear install rdkafka-4.1.2.tgz# If the installation is successful, the messages "install ok" and "You should add extension=rdkafka.so to php.ini" will be displayed.# If the message "could not extract the package.xml file from rdkafka-4.1.2.tgz" is displayed, indicating that the installation fails, please manually unzip the package, copy the package.xml file into the rdkafka directory, and run pear install package.xml to install the extension package.# If other errors occur, follow the prompts to resolve them.# After successful installation, add extension=rdkafka.so to php.ini.# After php --ini is run, the Loaded Configuration File: shows the location of php.ini.echo 'extension=rdkafka.so' >> /etc/php.ini
Step 3: Preparing for Configurations
Create the configuration file CKafkaSetting.php.
<?phpreturn ['bootstrap_servers' => 'bootstrap_servers1:port,bootstrap_servers2:port','topic_name' => 'topic_name','group_id' => 'php-demo','ckafka_instance_id' => 'ckafka_instance_id','sasl_username' => 'username','sasl_password' => 'password'];
Parameter | Description |
bootstrap_servers | Access network. On the Basic Info page of the instance in the console, select the Access Mode module and copy the network information from the Network column. |
topic_name | Topic name. Copy the name on the Topic List page in the console. |
group_id | Consumer group ID. Define the ID according to business requirements and see the consumer on the Consumer Group page after successful demo running. |
ckafka_instance_id | Instance ID. Obtain the ID from the basic information of the instance in the CKafka console. |
sasl_username | Username. Choose ACL Policy Management > User Management in the console to create a user and set the username. |
sasl_password | User password. Choose ACL Policy Management > User Management in the console to create a user and set the password. |
Step 3: Sending Messages
1. Write the message production program Producer.php.
<?php$setting = require __DIR__ . '/CKafkaSetting.php';$conf = new RdKafka\\Conf();// Set the entry service. Obtain the corresponding service address in the console.$conf->set('bootstrap.servers', $setting['bootstrap_servers']);// ---------- It is required to enable SASL authentication. ----------// The default SASL authentication mechanism type is PLAIN.$conf->set('sasl.mechanism', 'PLAIN');// Set the username in the format of instance ID + # + username configured in **User Management**.$conf->set('sasl.username', $setting['ckafka_instance_id'] . '#' . $setting['sasl_username']);// Set the password: Use the password configured in **User Management**.$conf->set('sasl.password', $setting['sasl_password']);// Configure the ACL policy locally.$conf->set('security.protocol', 'SASL_PLAINTEXT');// ---------- It is required to enable SASL authentication. ----------// 3 acknowledgment mechanisms are available for the Kafka producer, as described below:// -1 or all: The broker responds to the producer to continue sending the next (batch of) message(s) only after the leader receives the data and synchronizes it to the follower in all ISRs.// This configuration ensures high data reliability. As long as there is a synchronized replica alive, no message will be lost. Note: This configuration does not ensure all replicas are written before the data is returned.// Can be used in conjunction with the topic level parameter min.insync.replicas.// 0: The producer continues to send the next (batch of) message(s) without waiting for the broker acknowledgment that the synchronization is completed. This configuration provides high production performance but low data reliability.//(Data may be lost if the broker server where the leader replica is stored fails, because the server will not receive any message if the producer is unaware of the failure.)// 1: The producer sends the next (batch of) message(s) after the leader has successfully received the data as acknowledged. This configuration balances the production throughput and data reliability.//(Messages may be lost if the broker server where the leader replica is stored fails, but the replica is not copied.)// The default value 1 is used if the configuration is not displayed. You can set it based on your business requirements.$conf->set('acks', '1');// The number of retries when a request error occurs. It is recommended to set this value to greater than 0 to ensure that the message is not lost to the maximum extent during failed retries.$conf->set('retries', '0');// The time between the failed request transmission and the next retry request.$conf->set('retry.backoff.ms', 100);// The timeout period for producer network requests.$conf->set('socket.timeout.ms', 6000);$conf->set('reconnect.backoff.max.ms', 3000);// Register a callback for message sending.$conf->setDrMsgCb(function ($kafka, $message) {echo '**Producer**Send messages: message=' . var_export($message, true) . "\\n";});// Register a callback for message sending errors.$conf->setErrorCb(function ($kafka, $err, $reason) {echo "**Producer** Message sending errors: err=$err reason=$reason \\n";});$producer = new RdKafka\\Producer($conf);// Set it to LOG_DEBUG if debugging is enabled.//$producer->setLogLevel(LOG_DEBUG);$topicConf = new RdKafka\\TopicConf();$topic = $producer->newTopic($setting['topic_name'], $topicConf);// Produce and send messages.for ($i = 0; $i < 5; $i++) {// RD_KAFKA_PARTITION_UA allows Kafka to choose the partition freely.$topic->produce(RD_KAFKA_PARTITION_UA, 0, "Message $i");$producer->poll(0);}while ($producer->getOutQLen() > 0) {$producer->poll(50);}echo "**Producer** Message sent successfully.\\n";
2. Run Producer.php to send messages.
php Producer.php
3. View the running results.
>**Producer**Send message: message=RdKafka\\Message::__set_state(array(> 'err' => 0,> 'topic_name' => 'topic_name',> 'timestamp' => 1618800895159,> 'partition' => 0,> 'payload' => 'Message 0',> 'len' => 9,> 'key' => NULL,> 'offset' => 0,> 'headers' => NULL,>))>**Producer**Send message: message=RdKafka\\Message::__set_state(array(> 'err' => 0,> 'topic_name' => 'topic_name',> 'timestamp' => 1618800895159,> 'partition' => 0,> 'payload' => 'Message 1',> 'len' => 9,> 'key' => NULL,> 'offset' => 1,> 'headers' => NULL,>))...>**Producer**Message sent successfully.
4. On the Topic List page in the CKafka console, select the target topic, and choose More > Message Query to view the message just sent.
Step 4: Consuming Messages
1. Write the message subscription and consumption program Consumer.php.
<?php$setting = require __DIR__ . '/CKafkaSetting.php';$conf = new RdKafka\\Conf();$conf->set('group.id', $setting['group_id']);// Set the entry service. Obtain the corresponding service address in the console.$conf->set('bootstrap.servers', $setting['bootstrap_servers']);// ---------- It is required to enable SASL authentication. ----------// The default SASL authentication mechanism type is PLAIN.$conf->set('sasl.mechanism', 'PLAIN');// Set the username in the format of instance ID + # + username configured in **User Management**.$conf->set('sasl.username', $setting['ckafka_instance_id'] . '#' . $setting['sasl_username']);// Set the password: Use the password configured in **User Management**.$conf->set('sasl.password', $setting['sasl_password']);// Configure the ACL policy locally.$conf->set('security.protocol', 'SASL_PLAINTEXT');// ---------- It is required to enable SASL authentication. ----------// Consumer timeout interval when the Kafka consumer group mechanism is used. If the broker does not receive the heartbeat from the consumer within this interval,// the consumer is considered to be failed, and the broker initiates the rebalancing process again.$conf->set('session.timeout.ms', 10000);// Client request timeout period. If no response is received after this period, the request times out and fails.$conf->set('request.timeout.ms', 305000);// Set the interval of internal retries on the client.$conf->set('reconnect.backoff.max.ms', 3000);$topicConf = new RdKafka\\TopicConf();#$topicConf->set('auto.commit.interval.ms', 100);// Offset reset policy, which is set based on the actual business scenario. Improper settings may result in the loss of consumed data.$topicConf->set('auto.offset.reset', 'earliest');$conf->setDefaultTopicConf($topicConf);$consumer = new RdKafka\\KafkaConsumer($conf);// Set it to LOG_DEBUG if debugging is enabled.//$consumer->setLogLevel(LOG_DEBUG);$consumer->subscribe([$setting['topic_name']]);$isConsuming = true;while ($isConsuming) {$message = $consumer->consume(10 * 1000);switch ($message->err) {case RD_KAFKA_RESP_ERR_NO_ERROR:echo "**Consumer** received the message: " . var_export($message, true) . "\\n";break;case RD_KAFKA_RESP_ERR__PARTITION_EOF:echo "**Consumer** waiting for messages\\n";break;case RD_KAFKA_RESP_ERR__TIMED_OUT:echo "**Consumer** waiting timeout\\n";$isConsuming = false;break;default:throw new \\Exception($message->errstr(), $message->err);break;}}
2. Run Consumer.php to consume messages.
php Consumer.php
3. View the running results.
>**Consumer** received the message: RdKafka\\Message::__set_state(array(> 'err' => 0,> 'topic_name' => 'topic_name',> 'timestamp' => 1618800895159,> 'partition' => 0,> 'payload' => 'Message 0',> 'len' => 9,> 'key' => NULL,> 'offset' => 0,> 'headers' => NULL,>))>**Consumer** received the message: RdKafka\\Message::__set_state(array(> 'err' => 0,> 'topic_name' => 'topic_name',> 'timestamp' => 1618800895159,> 'partition' => 0,> 'payload' => 'Message 1',> 'len' => 9,> 'key' => NULL,> 'offset' => 1,> 'headers' => NULL,>))...
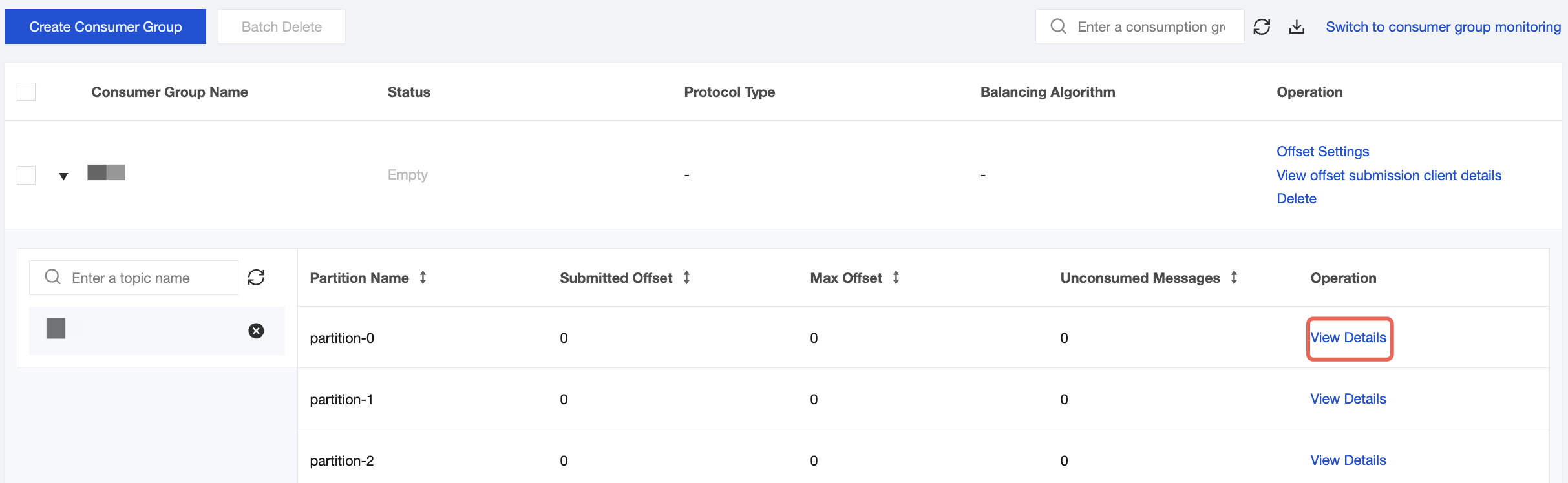
4. On the Consumer Group page in the CKafka console, select the target consumer group, enter the topic name in the Topic Name area, and click View Details to view consumption details.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

