Configuring Data Synchronization Between Kafka Instances
Last updated:2026-01-20 17:02:41
Configuring Data Synchronization Between Kafka Instances
Last updated: 2026-01-20 17:02:41
Feature Introduction
If your business data already resides in a message queue (such as Kafka) serving as a caching layer and requires extract, transform, load (ETL) processing before being stored to a downstream Kafka instance, you can use the Kafka-to-Kafka plugin capability provided by the TDMQ for CKafka (CKafka) connector.
This plugin supports data synchronization between Kafka instances, including both instance-level and topic-level synchronization. It enables replication and migration between instances in different regions, as well as data transfer and automatic synchronization between topics across different CKafka instances. It also provides basic data processing capabilities, such as formatting raw data, parsing specific fields, and converting data formats. The processed structured data is dumped to the downstream Kafka instance. This helps build a stable and reliable data transmission channel, enhancing your business continuity and service capability.
Data Synchronization | Instance-Level Data Synchronization | Topic-Level Data Synchronization |
Data source | Private network connection: CKafka clusters. Public network connection: CKafka clusters or self-built Kafka clusters. Cross-network connection: self-built Kafka clusters or clusters of other cloud vendors. | CKafka clusters. |
Data target | Private network connection: CKafka clusters. Public network connection: CKafka clusters or self-built Kafka clusters. | CKafka clusters. |
Operation steps | 1. Create a data source connection. 2. Create a data target connection. 3. Create a data synchronization task. 4. Configure the data source. 5. Configure the data target. 6. View the data synchronization progress. | 1. Create a data replication task. 2. Configure the data source. 3. Process data. 4. Configure the data target. 5. View the data synchronization progress. |
Use Limits
Type | Item | Limit |
Connection dimension | Number of connections per UIN | 150 |
Task dimension | Number of tasks per UIN | 150 |
| Concurrency per task | min (Total number of partitions in the data source topics, 20) |
Data Synchronization Rule Description
The Kafka-to-Kafka plugin of the CKafka connector supports synchronizing metadata, message data, and consumption offsets between instances in the console. The specific rules are as follows:
Data Type | Rule Description |
Synchronizing metadata | The process consists of two phases: initialization synchronization and scheduled synchronization. Initialization synchronization: When a task starts, it checks whether a corresponding topic of the upstream instance exists in the downstream instance. If not, it creates a topic in the downstream instance (configurations will match the upstream instance as closely as possible). If a corresponding topic already exists in the downstream instance, initialization synchronization is not triggered. Scheduled synchronization: After the task starts, it periodically (every 3 minutes) synchronizes certain metadata configurations from the upstream instance to the downstream instance. Note: Scheduled synchronization does not support synchronizing the number of replicas. During scheduled synchronization, the number of partitions can only be increased in one direction and cannot be decreased. If the number of partitions in the downstream instance is already greater than that in the upstream instance, the number of partitions will not be synchronized. For stability reasons, the retention.ms and retention.bytes metadata of the target topic will be synchronized only when their value is -1 (Note: -1 is an internal Kafka definition representing unlimited retention). In other cases, these two metadata items will not be synchronized periodically. In terms of topic-level configurations, for stability reasons, the metadata of newly added topics will be fully synchronized only once during task initialization by default. Subsequent changes to topic configurations will not be synchronized to the downstream instance. The reason is that if a user modifies the upstream topic configuration (for example, shortening the message retention period) without being aware of an active data synchronization task, synchronizing this change to the downstream instance may result in significant data loss before messages are consumed. Solution for synchronizing configuration changes: If you need to change topics within an existing task and synchronize the configuration change, it is recommended to manually modify the configurations of both the upstream and downstream topics to avoid data loss or stability issues. |
Synchronizing message data | Message data stored in the upstream Kafka instance is synchronized to the corresponding topic in the downstream Kafka instance. If synchronizing to the same partition is enabled, messages are consistently synchronized to the corresponding partition in the downstream instance. |
Synchronizing consumption offsets | When synchronizing message data stored in the upstream Kafka instance to the corresponding topic in the downstream Kafka instance, the system simultaneously synchronizes relevant consumer groups and their committed offset information for the topic. Note that this offset reflects a mapped correspondence. |
Use Limits
Note:
The default values in the following table refer to the values used when metadata is not synchronized. For example, when the configuration does not exist in the upstream instance or is invalid (non-numeric, null, or empty), these preset default values apply.
Data Synchronization Type | Parameter | Limit | Default Value |
Metadata | Number of Partitions | 1. When metadata needs to be synchronized, two parameters that do not meet the criteria will not be synchronized. If the number of partitions in the target topic is greater than that in the source topic, the number of partitions cannot be synchronized. If the number of replicas in the target topic differs from that in the source topic, the number of replicas cannot be synchronized. 2. When the length of the topic name in the source instance exceeds 128 characters, the target topic will use the first 128 characters as its name. | / |
| Number of Replicas | | / |
| retention.ms | | 604800000 (7 days) |
| cleanup.policy | | delete |
| min.insync.replicas | | 1 |
| unclean.leader.election.enable | | false |
| segment.ms | | 604800000 |
| retention.bytes | | The default value depends on the Kafka configuration. |
| max.message.bytes | | 1048588 |
| Consumer Group | If automatic creation of consumer groups is disabled for the target instance, consumer groups cannot be synchronized. | / |
Message data | / | Message data can be synchronized to the same partition. | / |
Consumption offset | / | 1. When consumption offset synchronization is required, the following situations may cause inaccurate offset alignment: The source and target instances have a topic with the same name, and the target topic has other message writers. The source and target instances have a topic with the same name, and the task is re-created. Each time a task is created, the data for the latest position read at the start of the new task is synchronized to the downstream instance without synchronizing historical data. Historical data is discarded in this case. 2. Instances of version 0.10.2.1 and earlier do not support consumption offset synchronization. If a data synchronization task involves such a version either in the upstream or downstream instance, creating a task for consumption offset synchronization is not supported. | / |
Configuring a Data Synchronization Task
Prerequisites
Data source: The source Kafka cluster is running normally.
Data target: The target Kafka cluster has been deployed and is running normally.
Creating Connections for the Data Source and Data Target Kafka Clusters
1. Log in to the CKafka console.
2. In the left sidebar, choose Connector > Connection List. Select the region and click Create Connection.
3. SelectMessage Queue Kafka as the connection type. Click Next. On the connection information setting page, enter a connection name and description to distinguish different Kafka connections.
4. Select the Kafka connection type.
Kafka Type | Description |
CKafka | If the client and the CKafka cluster are deployed in the same Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) network, the network is connected by default. You can directly select the pre-created CKafka instance from the drop-down list under the corresponding region and CKafka instance. |
Public network connection | If the client and the Kafka cluster are deployed in different network environments, you can use the public network for cross-network production and consumption. Public network connections support both self-built Kafka clusters and CKafka clusters. When you use a public network connection, it is recommended to configure security policies to ensure data transmission security. Broker Address: Enter the broker address of your Kafka cluster. If multiple brokers exist, you only need to enter the IP address and port of one broker, for example, 127.0.0.1:5664. The connector will establish network connectivity for all brokers. The entered IP address must remain accessible during data synchronization. ACL Configuration: If the source cluster has the access control list (ACL) enabled, configure the corresponding access information (ACL username and password) for this parameter. ACL configuration only supports statically configured users (PLAIN mechanism) and does not support dynamically configured users (SCRAM mechanism). |
Cross-network connection | Cross-network connection enables synchronizing data and metadata from Kafka clusters of other cloud vendors or self-built Kafka clusters to CKafka clusters. VPC Network: Select the VPC network ID of your self-built Kafka cluster or the ID of the VPC network established for cross-cloud connectivity. Subnet: Select the VPC subnet of your self-built Kafka cluster or the VPC subnet established for cross-cloud connectivity. Cloud Connect Network ID: Cross-cloud synchronization usually requires a dedicated connection established via Cloud Connect Network (CCN). Cross-Cloud Resource ID: typically the upstream instance ID of the connector, identifying a unique resource in the cross-cloud synchronization linkage. When you create a connection, the system automatically detects the node information under this resource ID, establishes network connectivity, and associates relevant routing rules. When you delete this connection, the automatically established routing rules under this resource ID are also deleted. Broker Address: Enter the broker address of your Kafka cluster. If multiple brokers exist, you only need to enter the IP address and port of one broker, for example, 127.x.x.1:5664. The connector will establish network connectivity for all brokers. The entered IP address must remain accessible during data synchronization. ACL Configuration: If the source cluster has the access control list (ACL) enabled, configure the corresponding access information (ACL username and password) for this parameter. ACL configuration only supports statically configured users (PLAIN mechanism) and does not support dynamically configured users (SCRAM mechanism). |
5. Click Next to initiate connection validation. Upon successful validation, the connection is created. You can view the created connection in the connection list.
Note:
1. The cross-network connection feature supports only one-way data synchronization, enabling data transfer from other cloud platforms to CKafka. It does not support reverse synchronization.
2. Due to different access control policies for Kafka clusters across cloud vendors, the system automatically performs permission verification during connection establishment. The connection can be created successfully only if the permission check is passed. Otherwise, a failure will be prompted.
3. Only broker addresses in IP:Port format are supported. You need to provide the broker address information. CKafka automatically completes the network connectivity configuration for each node during connection establishment.
4. Considering the functional limitations of early Kafka versions, the system does not support using Kafka instances of version 0.10.2 or earlier as the source or target instance.
6. Follow the same steps to create the data target Kafka connection.
Creating a Data Synchronization Task
1. In the left sidebar, choose Connector > Task List. Select the region and click Create Task.
2. Enter a task name. Select Data Distribution as the task type and Kafka as the data target type.
3. Click Next to go to the Data Source Configuration page.
Configuring the Data Source
1. On the Data Source Configuration page, configure the data source information.
Parameter | Description |
Task Name | Enter a task name to distinguish different data synchronization tasks. The task name must comply with the naming rule: it can contain only letters, digits, underscores (_), hyphens (-), and periods (.). |
Data Source Type | Select Full Kafka Instance. |
Connect to region | Select the region of the pre-configured data source connection from the drop-down list. |
Kafka Connection | Select the pre-configured data source connection from the drop-down list. |
Type of Synced Data | Sync metadata only: synchronizes the metadata of topic and consumer group structures within the source instance. Sync metadata and message data: synchronizes the metadata of topic and consumer group structures within the source instance, along with the message data in topics. Sync metadata, message data, and consumption offset: synchronizes the metadata of topics and consumer groups, the message data in topics, and the consumption offsets of consumer groups in the source instance. Updates to the consumption offsets of the source instance's consumer groups will be synchronized to the consumer groups with the same name in the target instance. |
Start Offset | If you select Sync metadata and message data or Sync metadata, message Data, and consumption offset, you need to configure the topic offset to set the processing policy for historical messages during the dump. Two methods are supported: Start consumption from the latest offset: the maximum offset. Consumption starts from the latest data (skipping historical messages). Start consumption from the start offset: the minimum offset. Consumption starts from the earliest data (synchronizing all historical messages). |
Topic sync range | If you select Sync metadata and message data or Sync metadata, message data, and consumption offset, you need to configure the topic scope for data synchronization. Sync metadata and message data: You can select All Topics or specify certain topics. If you choose to specify certain topics, you need to match topics using a regular expression. After the expression passes validation, you can proceed to the next step. Note: When you use a regular expression to synchronize certain topics, the consumer groups corresponding to these topics will not be synchronized. Sync metadata, message data, and consumption offset: You can select All Topics only. |
2. Confirm that the information is correct, and click Next to configure the data target information.
Configuring the Data Target
1. On the data target configuration page, select the connection for the data target.
2. Click Submit to complete task creation. On the task list page, you can view the created data synchronization task. After the task is successfully created, the task will automatically start data synchronization according to the task settings, replicating data in real time.
Viewing the Data Synchronization Progress
1. On the task list page, click the ID of the created task to go to the basic task information page.
2. At the top of the page, select the Synchronization Progress tab to view the progress and details of data synchronization.
Prerequisites
You have created a CKafka instance and topic, and the cluster status is Healthy.
The data source and data target topics are in the same region.
Creating a Data Replication Task
1. Log in to the CKafka console.
2. In the left sidebar, choose Connector > Task List. Select the region and click Create Task.
3. Select the region of the data target. Enter a task name. Select Data Distribution as the task type and Kafka as the data target type. Click Next.
4. On the Data Source Configuration page, configure the data source information.
Parameter | Description |
Task Name | Enter a task name to distinguish different data synchronization tasks. The task name must comply with the naming rule: it can contain only letters, digits, underscores (_), hyphens (-), and periods (.). |
Data Source Type | Select Topic in the CKafka Instance. |
Data Source Region | Select the region where the data source instance resides from the drop-down list. |
CKafka Instance | Select the pre-configured data source CKafka instance from the drop-down list. |
Source Topic | Select the pre-configured data source topic from the drop-down list. If an ACL policy is configured for the data source instance, ensure that you have read/write permissions on the selected source topic. |
Start Offset | Configure the topic offset to set the processing policy for historical messages during the dump. Three methods are supported: Start consumption from the latest offset: the maximum offset. Consumption starts from the latest data (skipping historical messages). Start consumption from the start offset: the minimum offset. Consumption starts from the earliest data (processing all historical messages). Start consumption from the specified time point: Consumption starts from a user-defined point in time. |
5. After you set the preceding information, click Next to go to the Data Processing Rules page.
Configuring Data Processing Rules
1. On the Data Processing Rules page, click Preview Topic Messages in the source data section. The first message from the source topic will be selected for parsing.
Note
The messages to be parsed must meet the following conditions: the messages must be in JSON string format, and the source data must be in a single-layer JSON format. Nested JSON formats can be converted using data processing for basic message format conversion.
2. If you need to cleanse the source data, enable Processing Source Data and proceed to Step 3. If no data cleansing is needed and you only require data synchronization, you can skip the subsequent steps and proceed directly to configure the data target.
3. (Optional) The data processing rule configuration supports importing templates from a local computer. If you have prepared a rule template, import it directly. If not, proceed to Step 4 to configure data processing rules. After completing the configuration, you can also export and save the rules as a template for reuse in other tasks.
4. In the Raw Data section, select the data source. You can select Pulled from source topic or Custom. In this example, Custom is selected.
5. In the Parsing Mode section, select the corresponding data parsing mode and click OK to view the data parsing result. In this example, JSON is selected. Click the parsing result on the left to generate a structured preview on the right.
Parsing Mode | Description |
JSON | Parse data in standard JSON format, support nested fields, and output in key-value pairs. |
Separator | Parse unstructured text based on specified delimiters. Supported delimiters include Space, Tab, ,, ;, |, :, and Custom. |
Regex | It is suitable for extracting specific fields from long array-type messages. You can manually enter a regular expression or use the regular expression auto-generation feature. For more information, see Regular Expression Extraction. Note: When the input regular expression contains capture groups such as (?<name>expr) or (?P<name>expr), it is treated as a pattern string for matching. When a message successfully matches the pattern string, the capture group content is parsed. Otherwise, the entire input regular expression is treated as a capture group, extracting all matching content from the message. |
JSON object array - single-row output | Each object in the array has a consistent format. Only the first object is parsed, and the output is a single JSON object of map type. |
JSON object array - multi-row output | Each object in the array has a consistent format. Only the first object is parsed, and the output is an array type. |
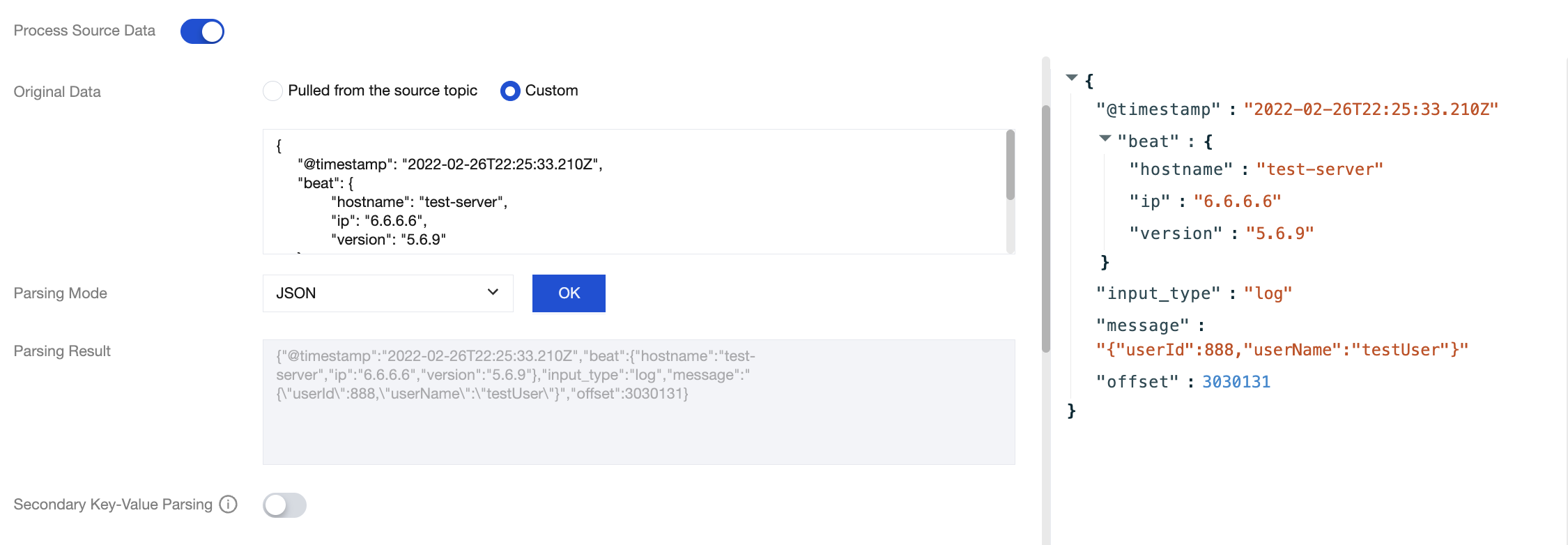
6. If Secondary Key-Value Parsing is enabled, the data in the value will be parsed again as key-value.
7. In the Data Processing section, set data processing rules. You can edit and delete fields, adjust timestamp formats, add a field for the current system time, and so on. Click Process Value to add a processing chain for further processing of individual data entries.
Operation | Description |
Mapping | You can select an existing key, and the final output value is mapped from the specified key. |
JSONPATH | Parse multi-layer nested JSON data, starting with the $ symbol and using the . symbol to locate specific fields in multi-layer JSON. For more information, see JSONPath. |
Current system time | You can select a system-preset value. DATE (timestamp) is supported. |
Custom | You can enter a custom value. |
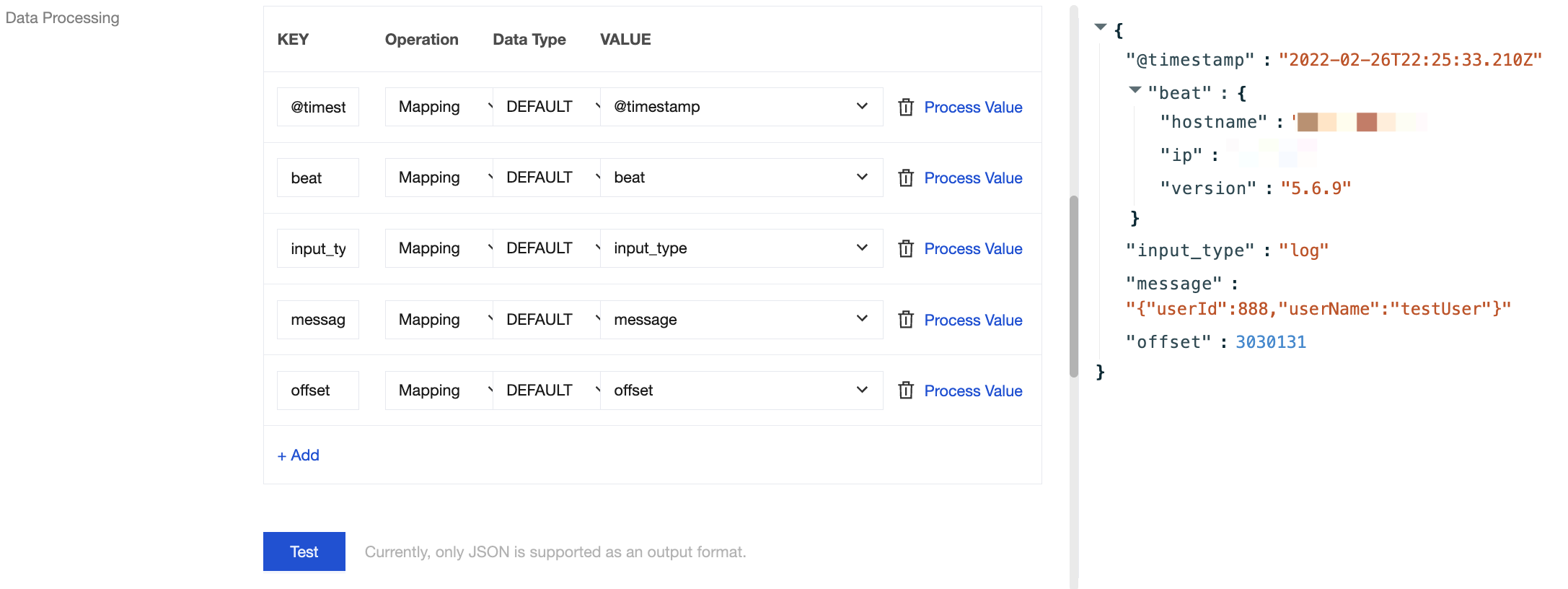
8. Click Test to view the test results of data processing. At this point, you can add a processing chain based on your actual business requirements to reprocess the above data processing results.
9. In the Filter section, choose whether to enable a filter. If enabled, only data matching the filter rules will be output. Filter matching modes include prefix match, suffix match, contains match, except match, numeric match, and IP match. For more information, see Filter Rule Description.
10. In the Retain Source Topic Metadata section, choose whether to retain the source topic data.
11. In the Output Format section, set the data output content. The default is JSON. The ROW format is also supported. If the ROW format is selected, you need to select the output row content.
Output Row Content | Description |
VALUE | Only output the values in the above test results, separated by delimiters. The delimiter between values defaults to the None option. |
KEY&VALUE | Output the key and value in the above test results. Neither the delimiter between the key and value nor the delimiter between values can be None. |
12. In the Handle Failed Message section, set the rules for handling delivery-failed messages. Three methods are supported: Discard, Retain, and Put to dead letter queue.
Handling Method | Description |
Discard | It is suitable for production environments. When a task fails to run, the current failed message will be ignored. It is recommended to use the Retain mode for testing until no errors are detected, and then edit the task in Discard mode for production. |
Retain | It is suitable for test environments. When a task fails to run, it will be terminated, no retries will be performed, and the failure reasons will be recorded in Event Center. |
Put to dead letter queue | You need to specify a topic for the dead letter queue. It is suitable for strict production environments. When a task fails to run, the failed messages along with metadata and failure reasons will be delivered to the specified CKafka topic. |
13. After configuring the data rules, you can directly click Export as Template at the top to reuse them in your subsequent data tasks, reducing the operating cost of repeating the configuration.
14. Click Next to configure the data target.
Configuring the Data Target
1. On the data target configuration page, select the target topic for data transfer and set the message replication multiplier. If the message replication multiplier is set to N, writing one message to the source will result in N messages written to the target.
2. Click Submit to complete task creation. On the task list page, you can view the created data synchronization task. After the task is successfully created, the task will automatically start data synchronization according to the task settings, replicating data in real time.
Viewing the Data Synchronization Progress
1. On the task list page, click the ID of the created task to go to the basic task information page.
2. At the top of the page, select the Synchronization Progress tab to view the progress and details of data synchronization.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

