High Latency in Client Message Production
Last updated:2026-01-20 17:19:22
Issue Symptom
The client symptom manifests as increased latency in the producer sending messages.
The message writing speed slows down, and the sending latency increases.
CPU utilization is too high.
Troubleshooting Steps
Step 1: Traffic Throttling Check
Check whether the traffic of a single topic is throttled: If a traffic throttling value is set, it restricts the message sending rate.
Optimization suggestion: Increase the traffic throttling value for the topic (based on actual business requirements).
Check whether the traffic of the instance is throttled. If traffic throttling occurs, the bandwidth needs to be increased.
Step 2: Cluster Performance Check
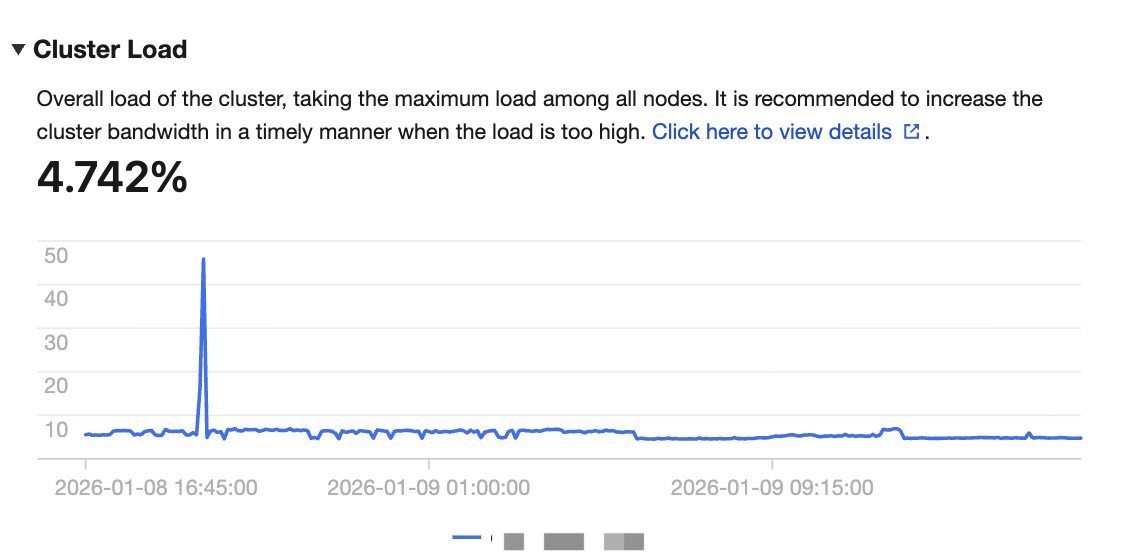
Check the cluster CPU load. If the overall cluster load is high, it directly causes increased sending latency.
Optimization solution: Scale out.
Step 3: Client Parameter Optimization
Set reasonable batch parameters to reduce fragmented requests and improve sending performance. Small batches cause clients to initiate requests frequently, which increases server queuing pressure and leads to higher latency and CPU consumption.
Optimization suggestion:
Set acks \\batch.size and linger.ms appropriately and adjust the parameters based on business requirements. Recommended values:
acks=1batch.size=16384linger.ms=1000
Detailed explanation is as follows:
1. Adjusting the ack parameter
The acks parameter controls the acknowledgment mechanism that the producer waits after sending messages:
acks=0: No server acknowledgment is required. Performance is high, but the risk of data loss is significant.
acks=1: The primary node returns an acknowledgment upon successful write. Performance is medium. This configuration is suitable for most scenarios.
acks=all or -1: The primary node and all replicas return an acknowledgment after a successful write. Data reliability is high, but performance is poor.
Optimization suggestion:
To improve sending performance, it is recommended to set
acks to 1.2. Adjusting the batch sending parameter
Batch sending can reduce the number of requests and improve network throughput:
batch.size: Total size of messages cached per partition (in bytes). When the set value is reached, batch sending is triggered.
linger.ms: Maximum time a message stays in the cache. After the value is exceeded, the message will be sent immediately, even if
batch.size is not reached.Recommended configuration:
batch.size=16384 (default value: 16 KB).linger.ms=1000 (default value: 0, meaning that messages are sent immediately without waiting).3. Adjusting the cache size
buffer.memory: Controls the overall size of cached messages. When the cache exceeds the limit, it forces a send, regardless of
batch.size and linger.ms.The default value is 32 MB, which can ensure sufficient performance for a single producer.
Recommended configuration:
buffer.memory ≧ batch.size * number of partitions * 2.Note:
If multiple producers are started within the same JVM, set
buffer.memory with caution to avoid OOM issues.Key Issues
1. Causes for high CPU load
The high CPU load of Kafka typically results from the following aspects:
Production and consumption request processing:
High-throughput producers and consumers consume significant CPU resources.
Data replication:
The replica synchronization process requires performing data replication operations.
High-frequency control requests:
For example, high-frequency operations such as offset management and metadata queries consume the CPU resources of brokers.
2. How to handle high cluster load
Common symptoms of high cluster load include:
Message sending latency increases.
Request queue depth is excessively and persistently large.
The CPU or disk I/O of the broker is persistently under high load.
Solution:
2.1 Scale-out:
Increase the number of broker nodes to distribute partition load and reduce pressure on individual servers.
Optimize partition distribution to ensure partitions are evenly distributed across all brokers.
2.2 Traffic throttling:
Set reasonable production traffic throttling values to prevent producer traffic surges from overloading brokers.
3. How to optimize the client implementation for low latency under high cluster load
When the Kafka cluster cannot be scaled out or the load cannot be effectively reduced, you can optimize client configurations to reduce latency as much as possible.
See Client Parameter Optimization.
Set
acks \\batch.size and linger.ms appropriately and adjust the parameters based on business requirements. Recommended values:acks=1batch.size=16384linger.ms=1000
Summary
Through the above troubleshooting steps and parameter optimization methods, you can effectively address high load on Kafka clusters and high latency in message production.
For high cluster load, scale-out is the most direct solution.
For client parameter optimization, adjusting batch sending and cache size can significantly improve performance.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

