SASL_SSL Access in the Public Network
Last updated:2026-01-05 15:16:59
Scenarios
This document describes how the Go client accesses TDMQ for CKafka (CKafka) in the public network environment by using the SASL_SSL method to send and receive messages.
Prerequisites
Operation Steps
Step 1: Preparing Go Dependency Libraries
1. Upload gokafkademo in the downloaded demo to the Linux server. You need to install the Go environment and librdkafka in advance.
2. Log in to the Linux server, go to the gokafkademo directory, and run the following command to add dependency libraries.
go get -v gopkg.in/confluentinc/confluent-kafka-go.v1/kafka
Step 2: Configuring Parameters
Parameter | Description |
topic | Topic name. Copy the name on the Topic List page in the console. 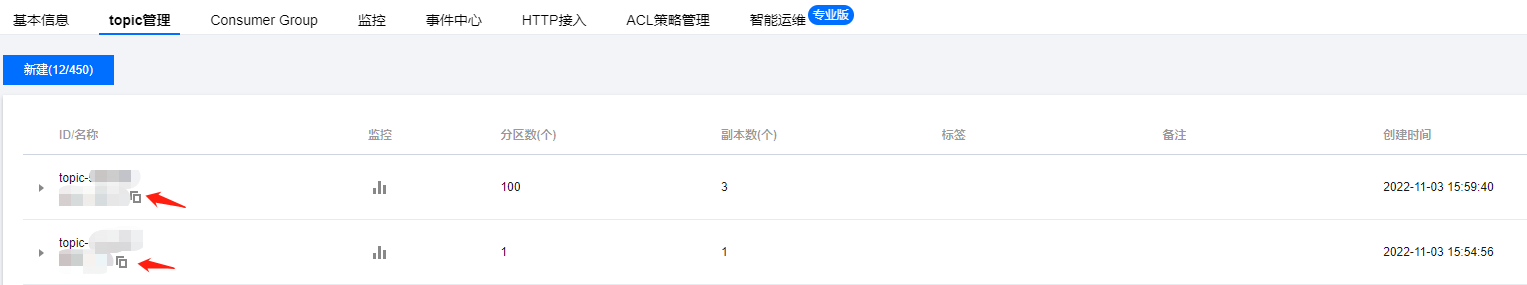 |
sasl.username | Username. In the console, choose ACL Policy Management > User Management to create a user and set the username. |
sasl.password | User password. In the console, choose ACL Policy Management > User Management to create a user and set the password. |
bootstrapServers | Access network. On the instance details page in the console, select the Access Mode module to copy the network information in the Network column. |
consumerGroupId | You can define the name and see the consumer on the Consumer Group page after successful demo running. |
Step 3: Sending Messages
1. Write a message production program.
// main.gopackage mainimport ("fmt""github.com/confluentinc/confluent-kafka-go/kafka")func main() {// ======== Replace with your actual configuration. ========brokers := "$bootstrapServers" // Kafka address.topic := "$topic" // Topic name.saslUsername := "$sasl.username" // SASL username.saslPassword := "$sasl.password" // SASL password.caFile := "./CARoot.pem" // CA certificate path. Download it in the console.retries := 5 // Number of retries.message := "Hello from Go with SASL+SSL"// =====================================config := &kafka.ConfigMap{"bootstrap.servers": brokers,"security.protocol": "sasl_ssl", // Enable SASL over SSL."ssl.ca.location": caFile, // Specify the CA certificate."sasl.mechanisms": "PLAIN", // Authentication mechanism."sasl.username": saslUsername,"sasl.password": saslPassword,"acks": "1", // Wait only for the leader acknowledgment."message.send.max.retries": retries,"retry.backoff.ms": 1000,"socket.timeout.ms": 30000,"session.timeout.ms": 30000,"enable.idempotence": false, // Disable idempotence to avoid compulsory acks=all."max.in.flight.requests.per.connection": 5,}// Create a producer.p, err := kafka.NewProducer(config)if err != nil {fmt.Printf("Failed to create a producer: %v\\n", err)return}defer p.Close()fmt.Printf("Producer enabled and connected to %s\\n", brokers)// Send messages.err = p.Produce(&kafka.Message{TopicPartition: kafka.TopicPartition{Topic: &topic,Partition: kafka.PartitionAny,},Value: []byte(message),}, nil)if err != nil {fmt.Printf("Message sending failed: %v\\n", err)} else {fmt.Printf("Message sent: %s\\n", message)}p.Flush(3*1000)}
2. Compile and run the program to send messages.
go run main.go
3. View the running results. An example is as follows.

4. On the Topic List page in the CKafka console, select the target topic, and choose More > Message Query to view the message just sent.
Step 4: Consuming Messages
1. Write a message consumption program.
// main.gopackage mainimport ("fmt""github.com/confluentinc/confluent-kafka-go/kafka")func main() {// ======== Replace with your configuration. ========brokers := "$bootstrapServers" // Kafka address.groupID := "$consumerGroupId" // Name of the consumer group.topic := "$topic" // Topic name.saslUsername := "$sasl.username" // SASL username.saslPassword := "$sasl.password" // SASL password.caFile := "./CARoot.pem" // CA certificate path. Download it in the console.// ==============================// Configure the consumer.config := &kafka.ConfigMap{"bootstrap.servers": brokers,"security.protocol": "sasl_ssl","ssl.ca.location": caFile,"sasl.mechanisms": "PLAIN","sasl.username": saslUsername,"sasl.password": saslPassword,"group.id": groupID,"auto.offset.reset": "earliest","enable.auto.commit": true, // Enable autocommit."auto.commit.interval.ms": 5000, // Commit every 5 seconds.}// Create a consumer.c, err := kafka.NewConsumer(config)if err != nil {panic(err)}defer c.Close()// Subscribe to a topic.c.SubscribeTopics([]string{topic}, nil)// Keep pulling messages.for {ev := c.Poll(1000)if ev == nil {continue}// Type assertion.if msg, ok := ev.(*kafka.Message); ok {if msg.Value != nil {fmt.Printf("Received: %s\\n", string(msg.Value))}}}}
2. Compile and run the program to consume messages.
go run main.go
3. View the running results. An example is as follows.

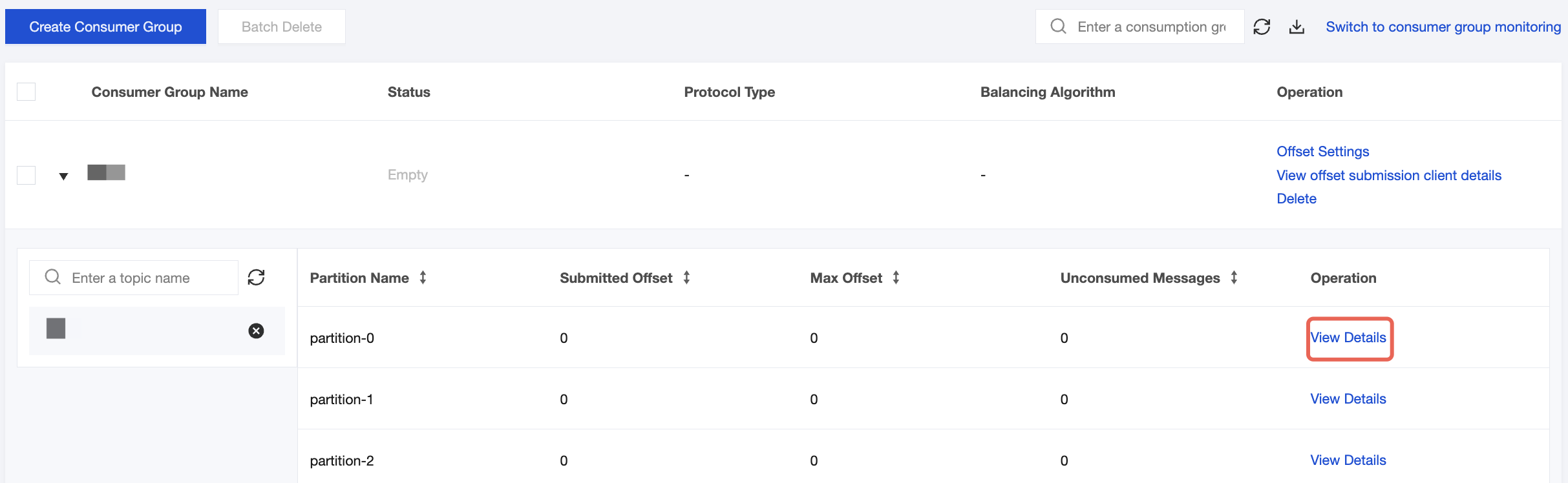
4. On the Consumer Group page in the CKafka console, select the target consumer group name, enter the topic name in the Topic Name area, and click View Details to view consumption details.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

