采集 Windows 事件日志
最后更新时间:2025-04-18 16:21:04
Windows 事件日志记录为应用程序和操作系统记录重要软件和硬件事件提供了一种标准的集中式方法。当软件、硬件或操作系统发生异常错误时,您可以通过 Windows 事件日志来检查错误发生的原因。本文将介绍如何通过 LogListener(Windows 版)采集 Windows 事件日志至 CLS 日志服务。
前提条件
操作条件
步骤1:选择日志主题
支持创建新的日志主题和使用现有的日志主题,您可按需选择。
如果您想选择新的日志主题,可执行如下操作:
1. 登录 日志服务控制台。
2. 在左侧导航栏中,选择概览,进入概览页面。
3. 在快速接入中,找到并单击 Windows 事件日志,进入采集配置流程。
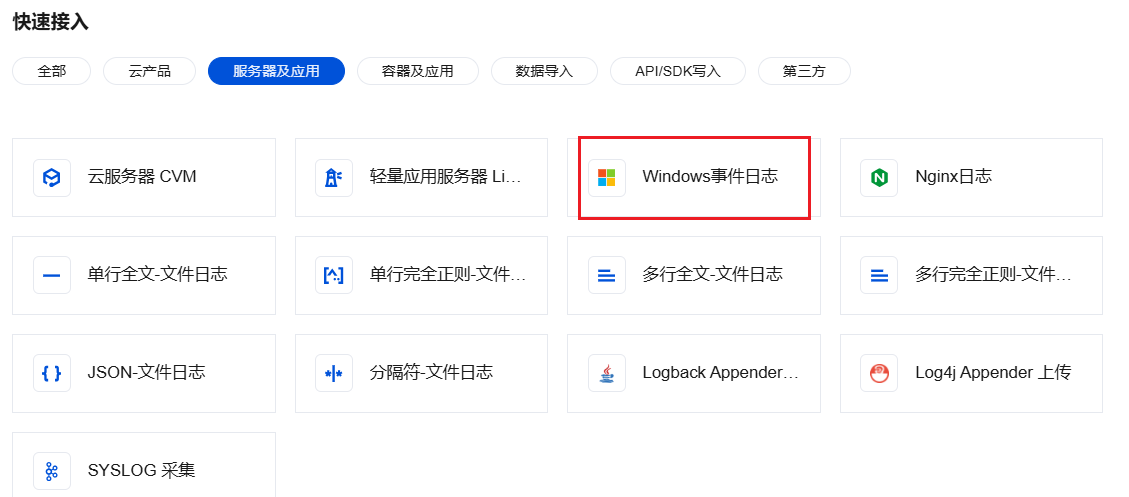
4. 在创建日志主题页面,根据实际需求,输入日志主题名称,配置日志保存时间等信息,单击下一步 。
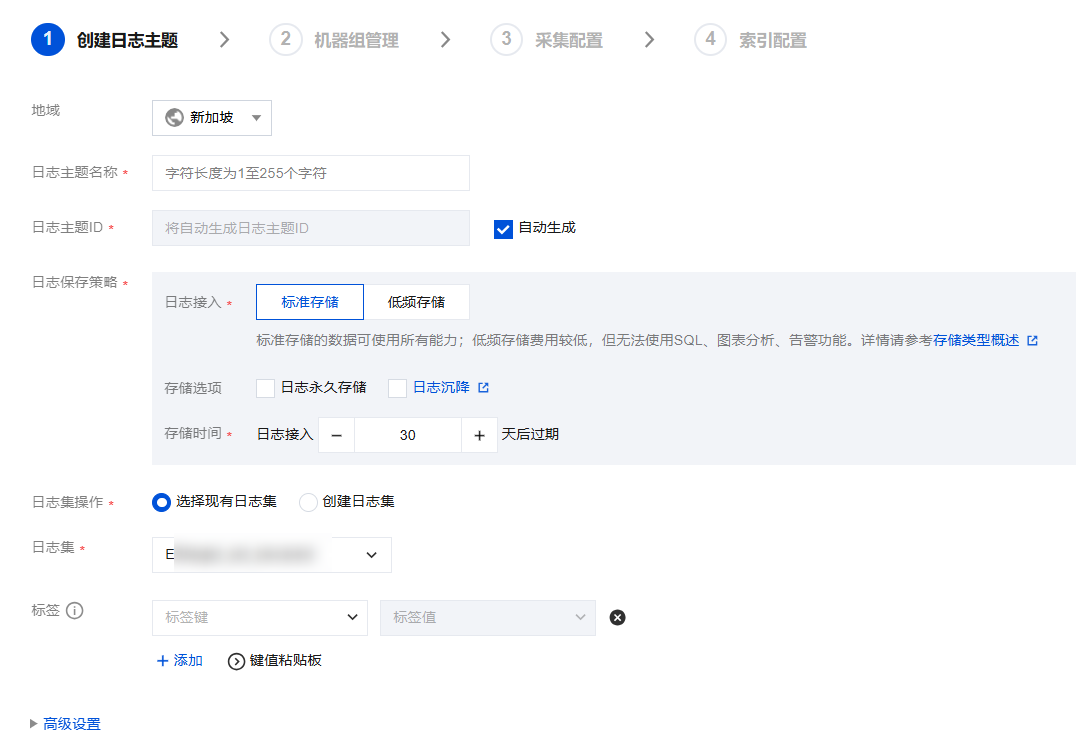
如果您想选择现有的日志主题,可执行如下操作:
1. 登录 日志服务控制台。
2. 在左侧导航栏中,选择日志主题,选择需要投递的日志主题,单击日志主题名称,进入日志主题管理页面。
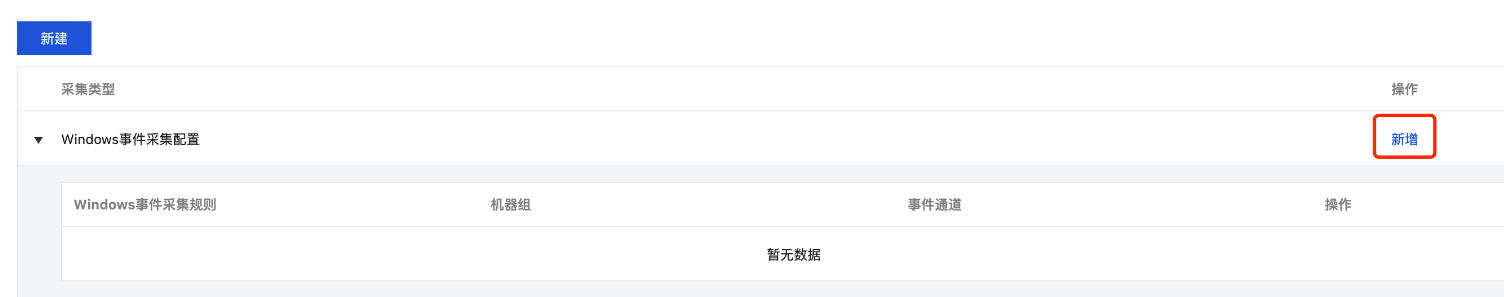
3. 选择采集配置页签,在 Windows 事件采集配置栏单击新增。
步骤2:管理机器组
1. 完成日志主题新建或选择之后,进入机器组管理配置。
2. 在机器组列表中选择需要采集的 Windows 机器组。
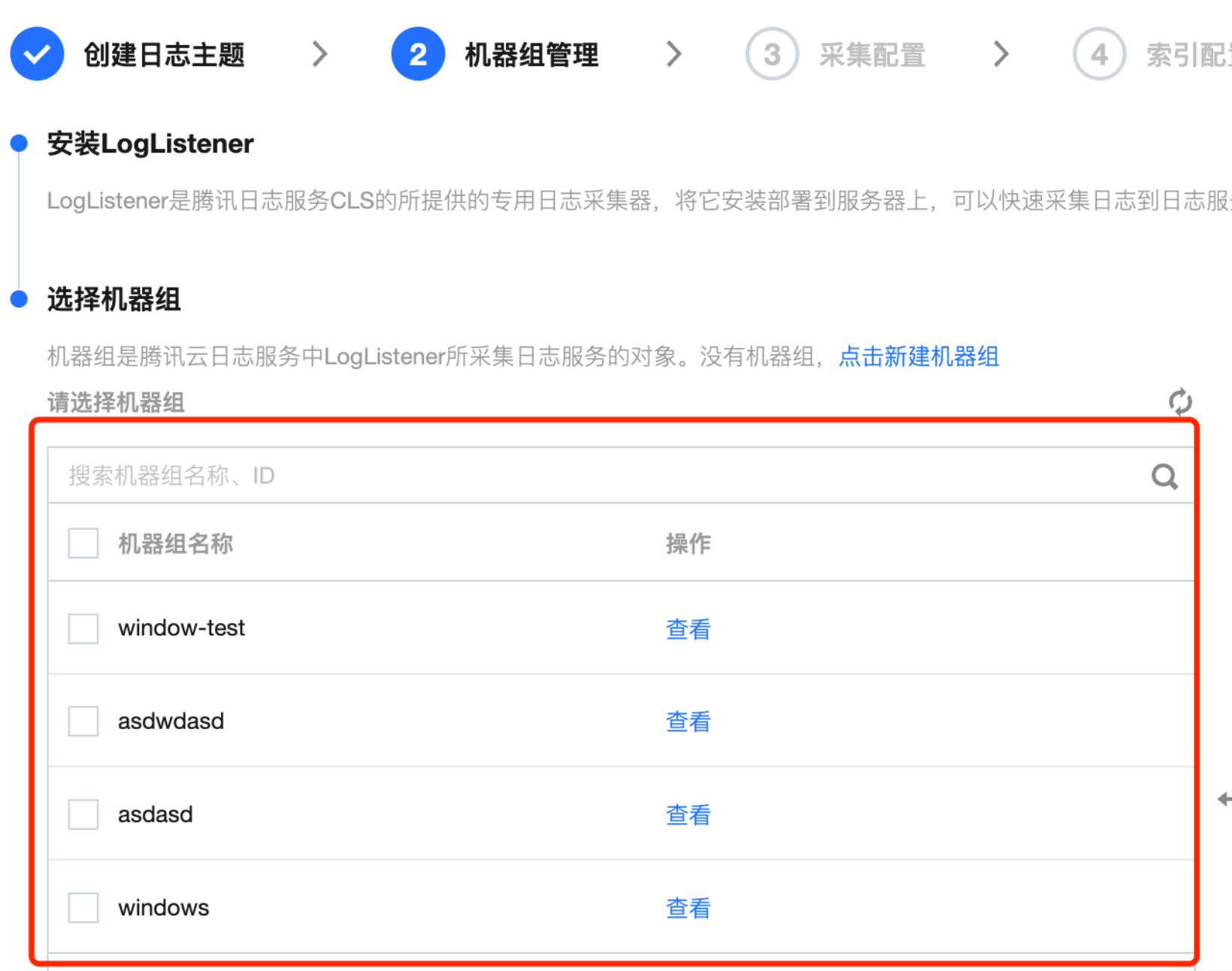
如果您想选择新的机器组,可单击新建机器组,系统环境选择 Windows,并选择通过 IP 或者机器标识的方式关联目标 Windows 服务器。详情请参见 机器组。完成创建后,在机器组列表中选中新建的机器组。
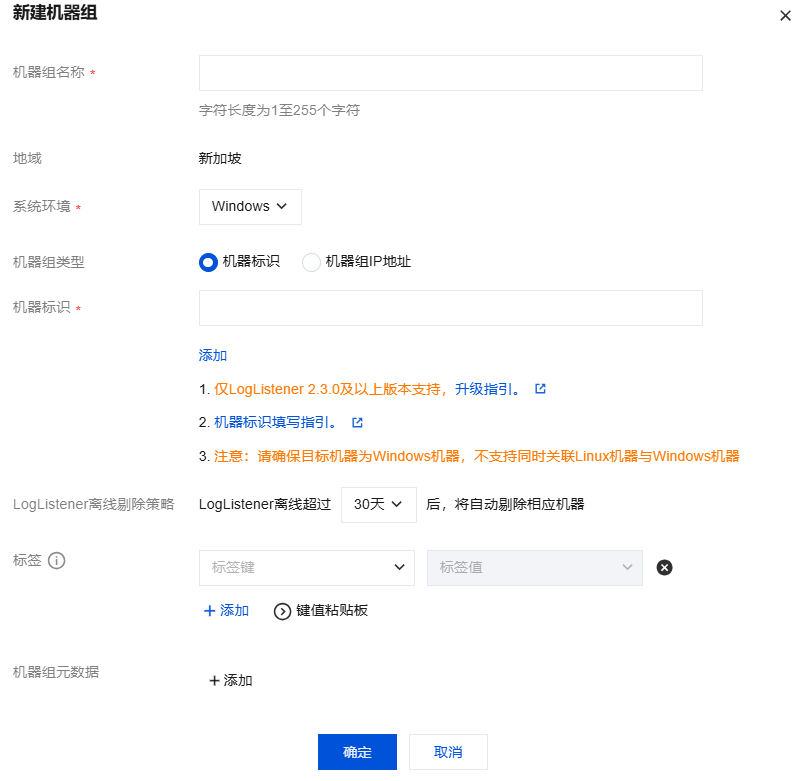
3. 选择完成后,单击下一步,进入采集配置流程。
步骤3:采集配置
在采集配置页面, 配置 Windows 事件采集规则。完成采集配置后,单击下一步。
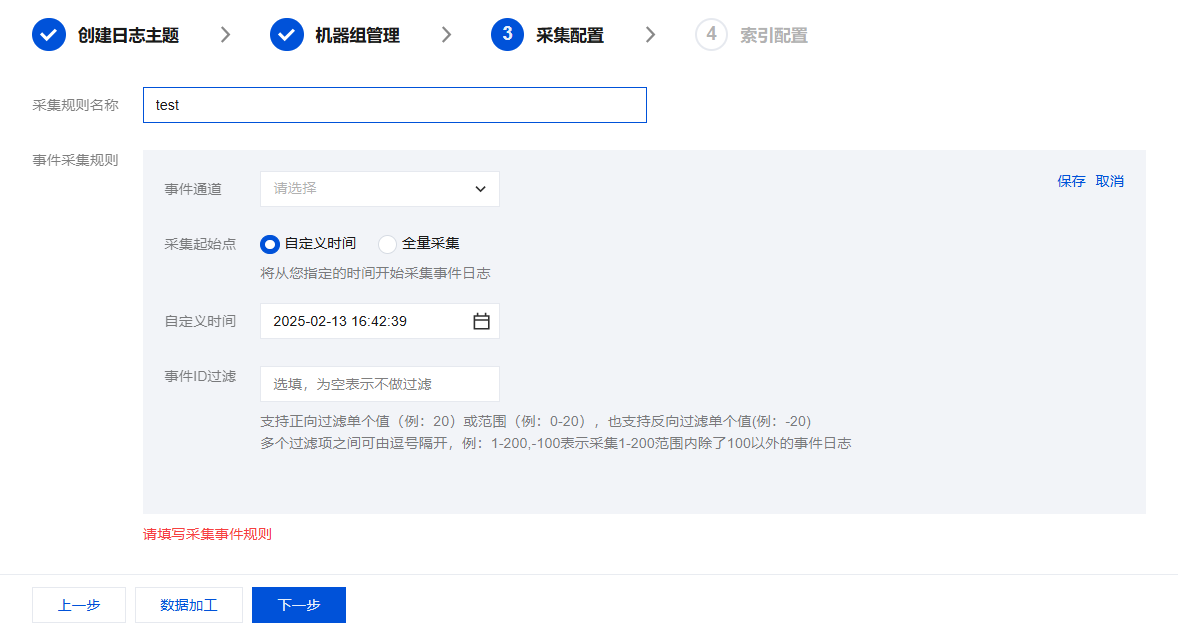
配置事件采集规则
一个采集配置支持配置多个事件采集规则,一个事件采集规则包含以下配置项。
配置项 | 是否必填 | 说明 |
事件通道 | 是 | 目标采集的事件通道,支持选择: Application(应用事件):记录由应用程序生成的事件,例如软件崩溃、配置更改、错误消息等 System(系统事件):记录操作系统组件的事件,例如驱动程序、系统服务、硬件问题等 Security(安全性事件):记录与安全相关的事件,例如用户登录/注销、权限更改、审核策略更改等 Setup(配置事件):记录系统设置和配置更改的事件 ALL(所有事件) 注意: 推荐一个服务器中的一种事件通道仅被一个采集配置采集。 若配置多个采集配置采集同一事件通道, 可能导致重复采集。 |
采集起始点 | 是 | 支持以下两种采集起始点: 自定义时间:将从您指定的时间开始采集事件日志。 全量采集:将采集服务器上所有的事件日志。注意:若事件超出了 Windows 系统保留时长,其日志将不会采集。 |
自定义时间 | 是 | 当采集起始点选择为“自定义起始点”时, 需指定开始采集事件日志的时间。 |
事件 ID 过滤 | 否 | 支持正向过滤单个值(例:20)或范围(例:0-20),也支持反向过滤单个值(例:-20)。多个过滤项之间可由逗号隔开,例:1-200。-100表示采集1-200范围内除了100以外的事件日志。 |
步骤4:索引配置
在索引配置流程,设置如下信息。
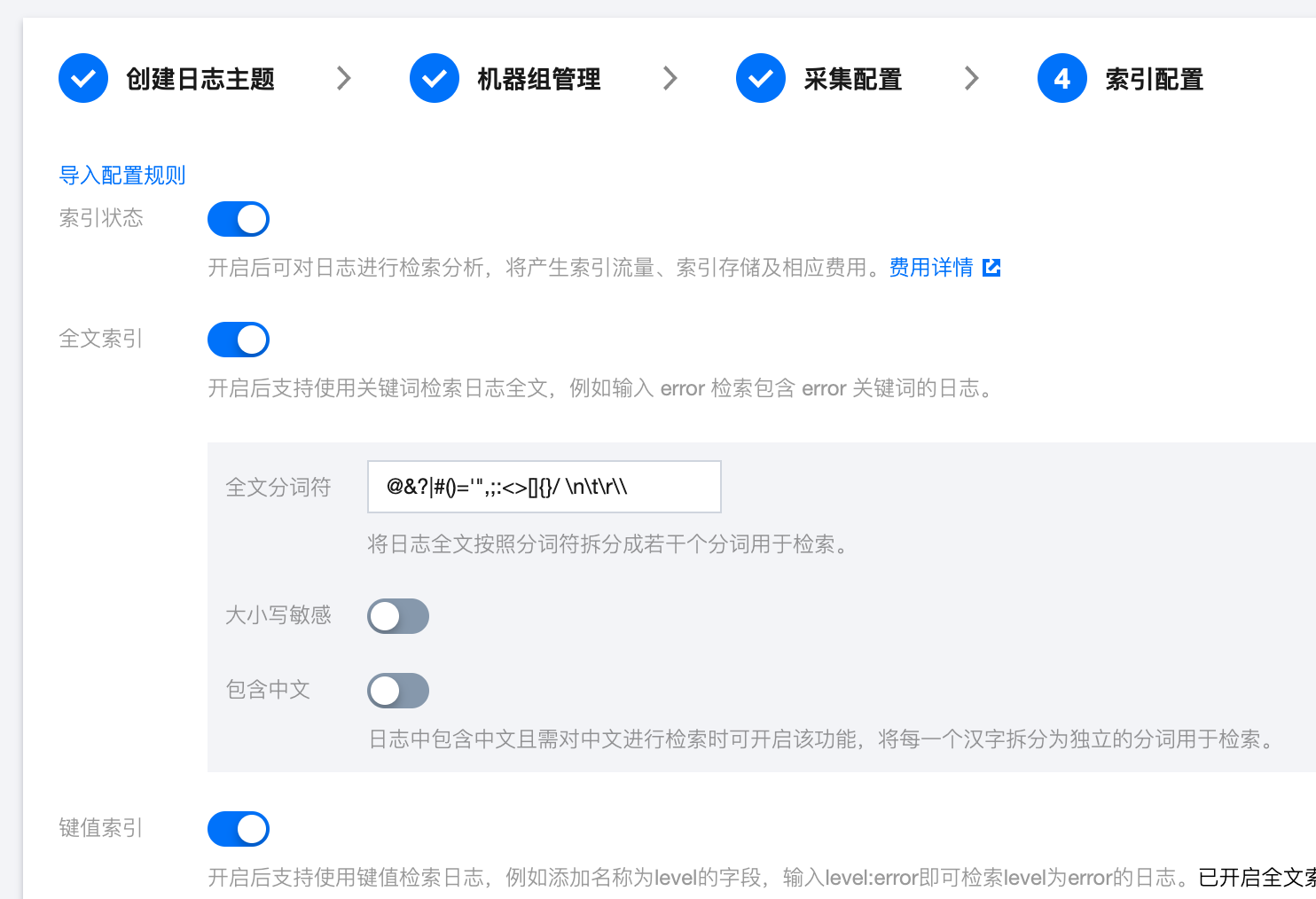

索引状态:确认是否开启。
注意:
检索必须开启索引配置,否则无法检索。
全文索引:确认是否需要设置大小写敏感。
全文分词符:默认为“@&()='",;:<>[]{}/ \\n\\t\\r”,确认是否需要修改。
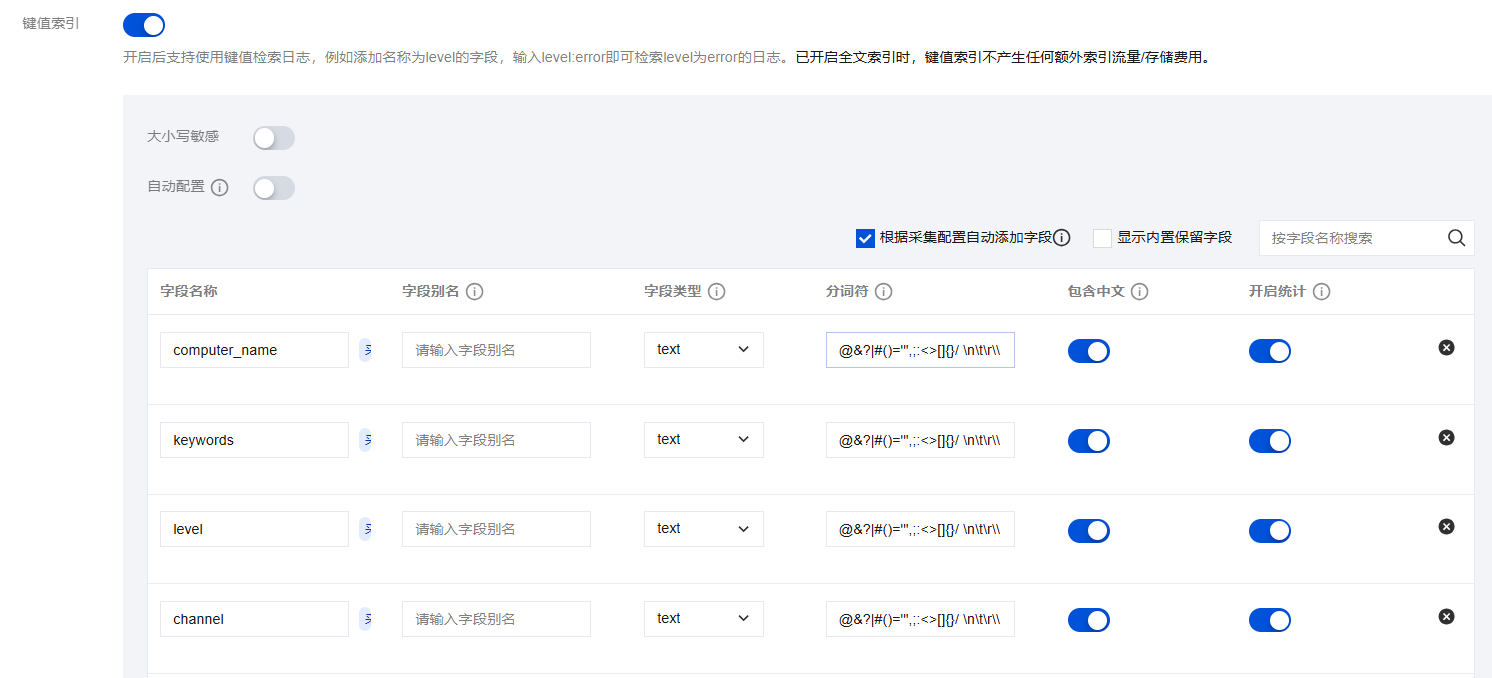
键值索引:默认开启,并基于 Windows 事件日志字段 填充键值。若您不需要开启键值索引,可将 



说明:
开启全文索引的同时, 开启键值索引不收取额外费用。
步骤5:检索分析
日志字段解释
字段名 | 描述 |
computer_name | 产生当前事件的节点名。 |
keywords | 当前事件关联的关键字,用于事件分类。 |
level | 当前事件的等级。 |
channel | 当前事件的通道名。 |
event_data | 和当前事件相关的数据。 |
message | 当前事件关联的消息。 |
opcode | 当前事件关联的操作码。 |
process.pid | 当前事件的进程 ID。 |
type | 获取当前事件使用的 API。 |
version | 当前事件的版本号。 |
record_id | 当前事件关联的记录编号。 |
event_id | 当前事件的 ID。 |
task | 当前事件关联的任务。 |
provider_guid | 当前事件来源的全局事务 ID。 |
activity_id | 当前事件所属活动的全局事务 ID,同一个活动的事件具有相同的全局事务 ID。 |
process.thread.id | 当前事件的线程 ID。 |
provider_name | 当前事件的来源。 |
raw_data | 当前事件最原始的信息,XML 格式。 |
文档反馈

