Encrypted Storage Of Keys
Last updated:2025-04-18 16:19:02
Overview
LogListener requires key authentication to access the CLS server. By default, LogListener stores the key in plaintext in its configuration file after initialization. If you do not want to save the key in plaintext, this document will guide you on how to enable encryption during the initialization of LogListener and how to modify the key storage mode afterward.
Directions
Specifying the Encrypted Storage Key During Initialization
See LogListener Installation Guideline (for Linux version). When LogListener is initialized, add the
-encryption parameter. To enable key encryption, set the input parameter to true; if encryption is not required, set the input parameter to false.Modifying the Key Storage Method After Initialization
Modified to Encrypted Storage
1. Go to the LogListener installation directory.
2. In the LogListener installation directory, run
./bin/encrypt_tool -e {Key ID} to obtain the encrypted key ID.3. In the LogListener installation directory, run
./bin/encrypt_tool -e {key} to obtain the encrypted key.4. Run
vim ./etc/loglistener.conf under the LogListener installation path to open the configuration file. Update the secret_id and secret_key fields with the encrypted key ID and key obtained in steps 2 and 3. Finally, set encryption to true.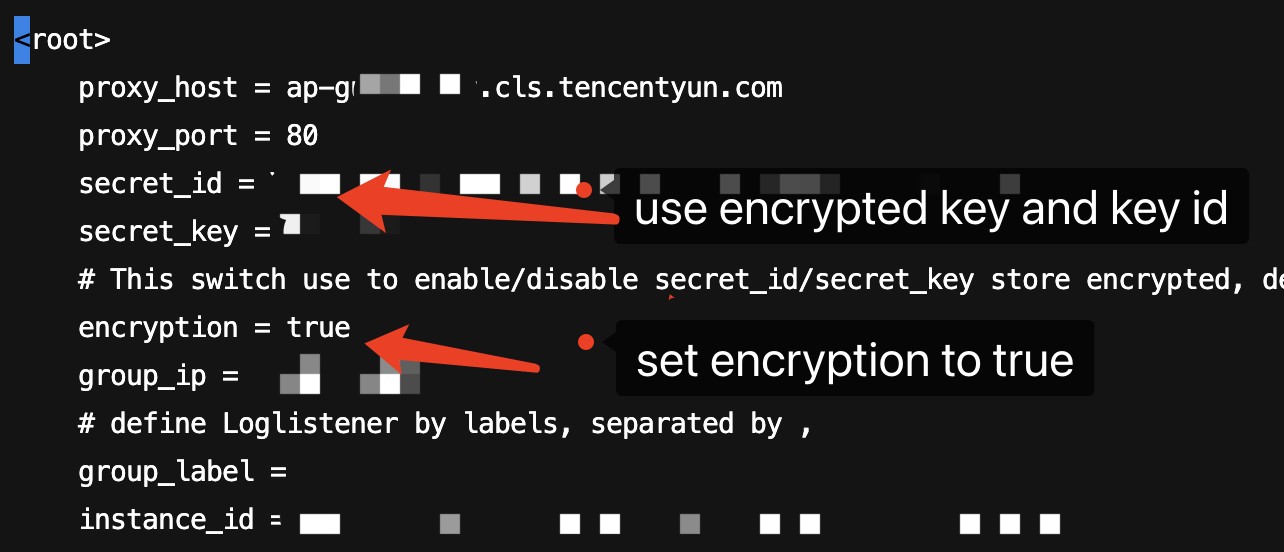
5. Run the following command to restart LogListener:
It is applicable to LogListener 2.8.3 and later versions with the operating system having a systemd.
systemctl restart loglistenerd
Applicable to LogListener 2.8.3 earlier versions or later versions with the operating system not having a systemd.
/etc/init.d/loglistenerd restart
Modified to Plaintext Storage
1. Go to the LogListener installation directory.
2. In the LogListener installation directory, run
vim ./etc/loglistener.conf to replace secret_id and secret_key in the conf file with plaintext key ID and key, and set encryption to false.3. Run the following command to restart LogListener:
It is applicable to LogListener 2.8.3 and later versions with the operating system having a systemd.
systemctl restart loglistenerd
Applicable to LogListener 2.8.3 earlier versions or later versions with the operating system not having a systemd.
/etc/init.d/loglistenerd restart
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

