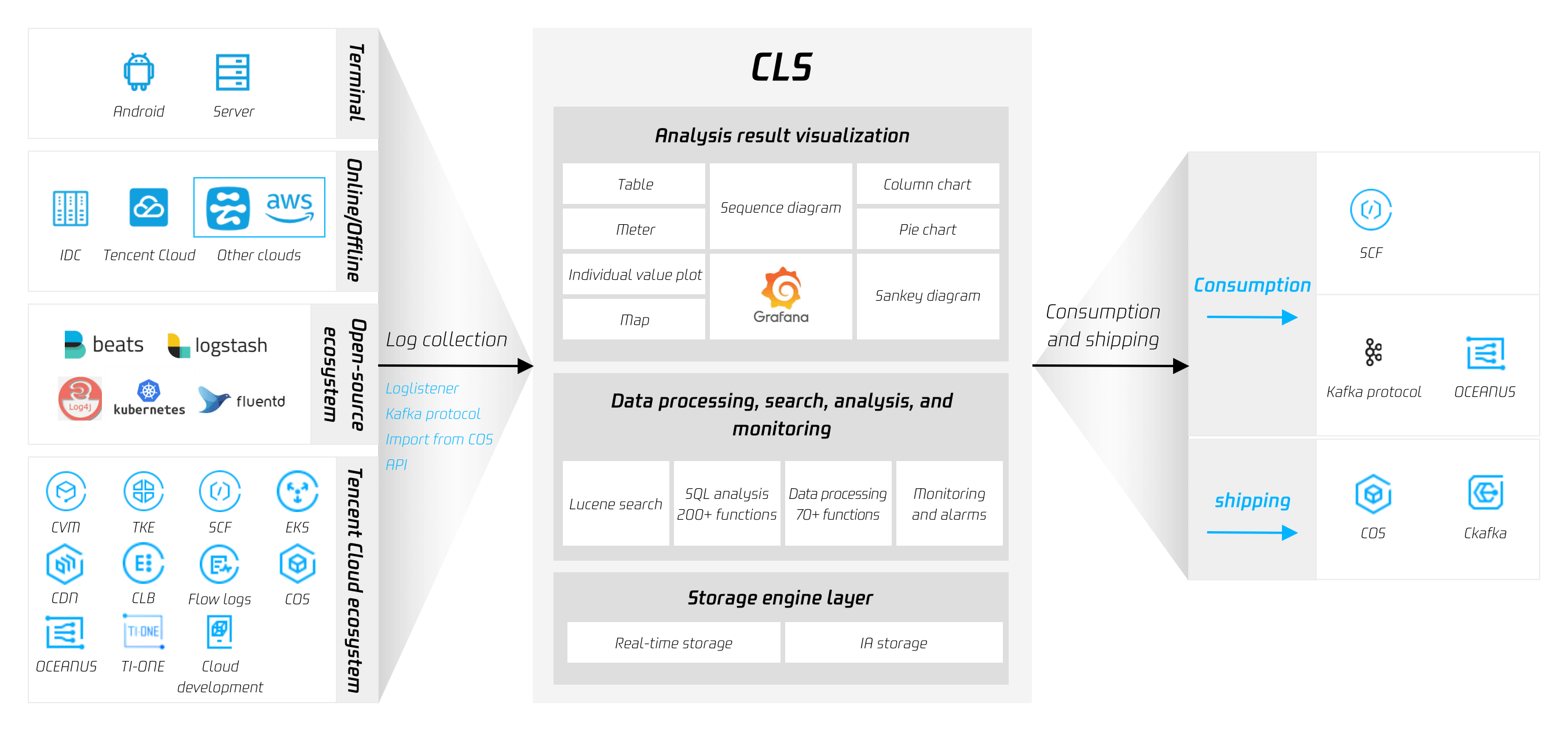
Overview

Copyright Notice
©2013-2025 Tencent Cloud. All rights reserved.
Copyright in this document is exclusively owned by Tencent Cloud. You must not reproduce, modify, copy or distribute in any way, in whole or in part, the contents of this document without Tencent Cloud's the prior written consent.
Trademark Notice

All trademarks associated with Tencent Cloud and its services are owned by the Tencent corporate group, including its parent, subsidiaries and affiliated companies, as the case may be. Trademarks of third parties referred to in this document are owned by their respective proprietors.
Service Statement
This document is intended to provide users with general information about Tencent Cloud's products and services only and does not form part of Tencent Cloud's terms and conditions. Tencent Cloud's products or services are subject to change. Specific products and services and the standards applicable to them are exclusively provided for in Tencent Cloud's applicable terms and conditions.
Last updated:2024-01-20 16:29:01

Last updated:2025-11-25 09:11:39
Last updated:2025-12-05 11:14:51
Region | Code |
Beijing | ap-beijing |
Guangzhou | ap-guangzhou |
Shanghai | ap-shanghai |
Chengdu | ap-chengdu |
Nanjing | ap-nanjing |
Chongqing | ap-chongqing |
Hong Kong (China) | ap-hongkong |
Silicon Valley | na-siliconvalley |
Virginia | na-ashburn |
Singapore | ap-singapore |
Bangkok | ap-bangkok |
Frankfurt | eu-frankfurt |
Tokyo | ap-tokyo |
Seoul | ap-seoul |
Jakarta | ap-jakarta |
São Paulo | sa-saopaulo |
Region | Code | Private Network Domain Name | Public Network Domain Name |
Beijing | ap-beijing | ap-beijing.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-beijing.cls.tencentcs.com |
Guangzhou | ap-guangzhou | ap-guangzhou.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-guangzhou.cls.tencentcs.com |
Shanghai | ap-shanghai | ap-shanghai.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-shanghai.cls.tencentcs.com |
Chengdu | ap-chengdu | ap-chengdu.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-chengdu.cls.tencentcs.com |
Nanjing | ap-nanjing | ap-nanjing.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-nanjing.cls.tencentcs.com |
Chongqing | ap-chongqing | ap-chongqing.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-chongqing.cls.tencentcs.com |
Hong Kong (China) | ap-hongkong | ap-hongkong.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-hongkong.cls.tencentcs.com |
Silicon Valley | na-siliconvalley | na-siliconvalley.cls.tencentyun.com | na-siliconvalley.cls.tencentcs.com |
Virginia | na-ashburn | na-ashburn.cls.tencentyun.com | na-ashburn.cls.tencentcs.com |
Singapore | ap-singapore | ap-singapore.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-singapore.cls.tencentcs.com |
Bangkok | ap-bangkok | ap-bangkok.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-bangkok.cls.tencentcs.com |
Frankfurt | eu-frankfurt | eu-frankfurt.cls.tencentyun.com | eu-frankfurt.cls.tencentcs.com |
Tokyo | ap-tokyo | ap-tokyo.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-tokyo.cls.tencentcs.com |
Seoul | ap-seoul | ap-seoul.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-seoul.cls.tencentcs.com |
Jakarta | ap-jakarta | ap-jakarta.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-jakarta.cls.tencentcs.com |
São Paulo | sa-saopaulo | sa-saopaulo.cls.tencentyun.com | sa-saopaulo.cls.tencentcs.com |
Region | Code | Private Network Domain Name | Public Network Domain Name |
Beijing | ap-beijing | bj-producer.cls.tencentyun.com | bj-producer.cls.tencentcs.com |
Guangzhou | ap-guangzhou | gz-producer.cls.tencentyun.com | gz-producer.cls.tencentcs.com |
Shanghai | ap-shanghai | sh-producer.cls.tencentyun.com | sh-producer.cls.tencentcs.com |
Chengdu | ap-chengdu | cd-producer.cls.tencentyun.com | cd-producer.cls.tencentcs.com |
Nanjing | ap-nanjing | nj-producer.cls.tencentyun.com | nj-producer.cls.tencentcs.com |
Chongqing | ap-chongqing | cq-producer.cls.tencentyun.com | cq-producer.cls.tencentcs.com |
Hong Kong (China) | ap-hongkong | hk-producer.cls.tencentyun.com | hk-producer.cls.tencentcs.com |
Silicon Valley | na-siliconvalley | usw-producer.cls.tencentyun.com | usw-producer.cls.tencentcs.com |
Virginia | na-ashburn | use-producer.cls.tencentyun.com | use-producer.cls.tencentcs.com |
Singapore | ap-singapore | sg-producer.cls.tencentyun.com | sg-producer.cls.tencentcs.com |
Bangkok | ap-bangkok | th-producer.cls.tencentyun.com | th-producer.cls.tencentcs.com |
Frankfurt | eu-frankfurt | de-producer.cls.tencentyun.com | de-producer.cls.tencentcs.com |
Tokyo | ap-tokyo | jp-producer.cls.tencentyun.com | jp-producer.cls.tencentcs.com |
Seoul | ap-seoul | kr-producer.cls.tencentyun.com | kr-producer.cls.tencentcs.com |
Jakarta | ap-jakarta | jkt-producer.cls.tencentyun.com | jkt-producer.cls.tencentcs.com |
Region | Code | Private Network Domain Name | Public Network Domain Name |
Beijing | ap-beijing | kafkaconsumer-ap-beijing.cls.tencentyun.com | kafkaconsumer-ap-beijing.cls.tencentcs.com |
Guangzhou | ap-guangzhou | kafkaconsumer-ap-guangzhou.cls.tencentyun.com | kafkaconsumer-ap-guangzhou.cls.tencentcs.com |
Shanghai | ap-shanghai | kafkaconsumer-ap-shanghai.cls.tencentyun.com | kafkaconsumer-ap-shanghai.cls.tencentcs.com |
Chengdu | ap-chengdu | kafkaconsumer-ap-chengdu.cls.tencentyun.com | kafkaconsumer-ap-chengdu.cls.tencentcs.com |
Nanjing | ap-nanjing | kafkaconsumer-ap-nanjing.cls.tencentyun.com | kafkaconsumer-ap-nanjing.cls.tencentcs.com |
Chongqing | ap-chongqing | kafkaconsumer-ap-chongqing.cls.tencentyun.com | kafkaconsumer-ap-chongqing.cls.tencentcs.com |
Hong Kong (China) | ap-hongkong | kafkaconsumer-ap-hongkong.cls.tencentyun.com | kafkaconsumer-ap-hongkong.cls.tencentcs.com |
Silicon Valley | na-siliconvalley | kafkaconsumer-na-siliconvalley.cls.tencentyun.com | kafkaconsumer-na-siliconvalley.cls.tencentcs.com |
Virginia | na-ashburn | kafkaconsumer-na-ashburn.cls.tencentyun.com | kafkaconsumer-na-ashburn.cls.tencentcs.com |
Singapore | ap-singapore | kafkaconsumer-ap-singapore.cls.tencentyun.com | kafkaconsumer-ap-singapore.cls.tencentcs.com |
Bangkok | ap-bangkok | kafkaconsumer-ap-bangkok.cls.tencentyun.com | kafkaconsumer-ap-bangkok.cls.tencentcs.com |
Frankfurt | eu-frankfurt | kafkaconsumer-eu-frankfurt.cls.tencentyun.com | kafkaconsumer-eu-frankfurt.cls.tencentcs.com |
Tokyo | ap-tokyo | kafkaconsumer-ap-tokyo.cls.tencentyun.com | kafkaconsumer-ap-tokyo.cls.tencentcs.com |
Seoul | ap-seoul | kafkaconsumer-ap-seoul.cls.tencentyun.com | kafkaconsumer-ap-seoul.cls.tencentcs.com |
Jakarta | ap-jakarta | kafkaconsumer-ap-jakarta.cls.tencentyun.com | kafkaconsumer-ap-jakarta.cls.tencentcs.com |
Region | Code | Private Network Domain Name | Public Network Domain Name |
Beijing | ap-beijing | ap-beijing.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-beijing.cls.tencentcs.com |
Guangzhou | ap-guangzhou | ap-guangzhou.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-guangzhou.cls.tencentcs.com |
Shanghai | ap-shanghai | ap-shanghai.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-shanghai.cls.tencentcs.com |
Chengdu | ap-chengdu | ap-chengdu.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-chengdu.cls.tencentcs.com |
Nanjing | ap-nanjing | ap-nanjing.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-nanjing.cls.tencentcs.com |
Chongqing | ap-chongqing | ap-chongqing.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-chongqing.cls.tencentcs.com |
Hong Kong (China) | ap-hongkong | ap-hongkong.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-hongkong.cls.tencentcs.com |
Silicon Valley | na-siliconvalley | na-siliconvalley.cls.tencentyun.com | na-siliconvalley.cls.tencentcs.com |
Virginia | na-ashburn | na-ashburn.cls.tencentyun.com | na-ashburn.cls.tencentcs.com |
Singapore | ap-singapore | ap-singapore.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-singapore.cls.tencentcs.com |
Bangkok | ap-bangkok | ap-bangkok.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-bangkok.cls.tencentcs.com |
Frankfurt | eu-frankfurt | eu-frankfurt.cls.tencentyun.com | eu-frankfurt.cls.tencentcs.com |
Tokyo | ap-tokyo | ap-tokyo.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-tokyo.cls.tencentcs.com |
Seoul | ap-seoul | ap-seoul.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-seoul.cls.tencentcs.com |
Jakarta | ap-jakarta | ap-jakarta.cls.tencentyun.com | ap-jakarta.cls.tencentcs.com |
São Paulo | sa-saopaulo | sa-saopaulo.cls.tencentyun.com | sa-saopaulo.cls.tencentcs.com |
cls.tencentcloudapi.com (Only supported in non-financial zones). Your API request will be automatically resolved to a server nearest to the client. For latency-sensitive businesses, we recommend you specify the domain name in a region.Region | Code | Private Network Domain Name | Public Network Domain Name |
Beijing | ap-beijing | cls.internal.tencentcloudapi.com | cls.ap-beijing.tencentcloudapi.com |
Guangzhou | ap-guangzhou | cls.internal.tencentcloudapi.com | cls.ap-guangzhou.tencentcloudapi.com |
Shanghai | ap-shanghai | cls.internal.tencentcloudapi.com | cls.ap-shanghai.tencentcloudapi.com |
Chengdu | ap-chengdu | cls.internal.tencentcloudapi.com | cls.ap-chengdu.tencentcloudapi.com |
Nanjing | ap-nanjing | cls.internal.tencentcloudapi.com | cls.ap-nanjing.tencentcloudapi.com |
Chongqing | ap-chongqing | cls.internal.tencentcloudapi.com | cls.ap-chongqing.tencentcloudapi.com |
Hong Kong (China) | ap-hongkong | cls.internal.tencentcloudapi.com | cls.ap-hongkong.tencentcloudapi.com |
Silicon Valley | na-siliconvalley | cls.internal.tencentcloudapi.com | cls.na-siliconvalley.tencentcloudapi.com |
Virginia | na-ashburn | cls.internal.tencentcloudapi.com | cls.na-ashburn.tencentcloudapi.com |
Singapore | ap-singapore | cls.internal.tencentcloudapi.com | cls.ap-singapore.tencentcloudapi.com |
Bangkok | ap-bangkok | cls.internal.tencentcloudapi.com | cls.ap-bangkok.tencentcloudapi.com |
Frankfurt | eu-frankfurt | cls.internal.tencentcloudapi.com | cls.eu-frankfurt.tencentcloudapi.com |
Tokyo | ap-tokyo | cls.internal.tencentcloudapi.com | cls.ap-tokyo.tencentcloudapi.com |
Seoul | ap-seoul | cls.internal.tencentcloudapi.com | cls.ap-seoul.tencentcloudapi.com |
Jakarta | ap-jakarta | cls.internal.tencentcloudapi.com | cls.ap-jakarta.tencentcloudapi.com |
São Paulo | sa-saopaulo | cls.internal.tencentcloudapi.com | cls.sa-saopaulo.tencentcloudapi.com |
Last updated:2024-12-16 14:56:26
Related Words | Description |
Logset | Up to 100 logsets can be created for each account in each region. |
| Up to 500 log topics and metric topics can be created for each logset. |
| The name can contain 1 to 255 characters. Supported characters: uppercase letters, lowercase letters, digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-). |
Log Topic | The length of topic names ranges from 1 to 255 characters, allowing characters a-z, A-Z, 0-9, _, and -. |
| Up to 50 partitions can be created under each log topic, and up to 10 partitions can be created when a new log topic is added. |
| Each topic can be bound with up to 100 machine groups. |
| Log topics of standard storage can be stored for 1-3600 days or permanently. |
| Log topics of infrequent access storage can be stored for 7-3600 days or permanently. |
| The log settlement function can be enabled only when the log topic of standard storage type is stored for more than 7 days. |
Metric Topic | The length of topic names ranges from 1 to 255 characters, allowing characters a-z, A-Z, 0-9, _, and -. |
Machine Group | Each account can create up to 200 machine groups in different regions. |
| Each IP machine group can be bound with up to 200 machine IPs. |
| Each label machine group can be bound with up to 50 Labels. |
Dashboard | Each account can create up to 100 dashboard subscription tasks. |
Last updated:2025-09-25 20:20:00
Limit | Description |
Kafka Data Subscription Task | A single log topic can create up to 100 Kafka data subscription tasks. |
Limit | Description |
Kafka Topic | A single Kafka data subscription task can consume up to 100 Kafka topics. |
Size of a Single Log | A single log cannot exceed 1 MB. When the size of a single log exceeds the limit, this log will be discarded. |
Single Kafka Message | A single Kafka message can contain a maximum of one log. If it exceeds this limit, the entire message will be treated as a parsing-failed log. |
Starting Position | Only the earliest and latest positions can be specified. Importing from a position at the specified time is not supported. |
Limit | Description |
Maximum Throughput per Task | The maximum throughput for a single task is limited to 240 MB/s. |
Last updated:2024-01-20 16:34:39
Item | Capability and Limit |
File encoding | Supports UTF8 and GBK codec. Note: only LogListener v2.6.2 and above support GBK codec. |
Soft link | Supported. |
Size of a single log | The size of a single-line log is limited to 512 KB. If the size of a single-line log exceeds 512 KB, the log will be truncated and only the first 512 KB is retained. For a multi-line log, after it is divided according to the first-line regular expression, the maximum limit for a single log is 1 MB. |
Regular expression | Perl-compatible regular expressions are supported. |
First log collection behavior | LogListener supports full/incremental collection policies: Full collection: after LogListener is started for the first time after installation, all logs that meet requirements are collected, including files that have not been written. Incremental collection: after LogListener is started for the first time after installation, existing files will be collected from the latest position. Note: Full/Incremental collection policies are available starting from LogListener v2.6.2. |
Log file rotation | Supported. (It is recommended that the file name after rotation not be matched by the wildcard collection path.) |
Collection behavior when log parsing fails | We recommend you enable the feature of uploading parsing-failure logs. If the feature is enabled, parsing-failure logs will be uploaded to the preset index in the format of full text in a single line. Otherwise, the logs will be discarded. |
File opening | LogListener opens files when reading files for log collection and closes the files when the reading is completed. |
Item | Capability and Limit |
Checkpoint storage location | The default save path is the data directory in the LogListener installation directory. You can customize a save path in the loglistener.conf file. |
Checkpoint storage policy | LogListener stores two copies of checkpoint metadata: One copy records the information only of checkpoints where upload is completed, and the information is persisted to a disk in real time. The other copy records the information of checkpoints where upload is completed and checkpoints where upload is not completed, and the information is periodically persisted to a disk. Persistence takes precedence when the program exits. |
Item | Capability and Limit |
Default CPU resource limits | LogListener does not limit CPU resources by default. You can configure CPU resource limits in the configuration file. Without CPU resource limits, the current implementation architecture of LogListener can achieve a maximum CPU usage of 110% (up to 100% for a single business thread and about 10% for a control thread). |
Default memory resource limits | LogListener's default memory threshold is 2 GB. You can change the threshold to 300 MB or higher as needed. |
Default bandwidth resource limits | LogListener does not limit bandwidth resources by default. You can configure bandwidth resource limits in the loglistener.conf file. |
Resource overrun handling policy | If LogListener overruns CPU and memory resources for more than 5 minutes, LogListener will be forced to restart automatically. |
Log compression | Collected logs are shipped as compact logs by default. You can modify log compression configuration in the loglistener.conf file. |
Number of monitored directories | The recommended maximum number of monitored directories is 5,000. If this limit is exceeded, log collection may fail. |
Number of monitored files | The recommended maximum number of monitored files is 10,000. If this limit is exceeded, log collection may fail. |
Item | Capability and Limit |
Network error handling | Except exceptions requiring special handling (such as log topic deletion), all other errors (such as network exceptions, timeout, frequency control, and overdue payment) will be retried. |
Maximum retry timeout duration | If data fails to be sent after retrying for more than 1 hour, the system discards the data. The default behavior is to retry at an interval, and the retry interval becomes longer and longer until the maximum retry timeout duration is exceeded. |
Maximum number of retries | The maximum number of retries can be set in the loglistener.conf configuration file and is not set by default. By default, the system retries until the maximum retry duration is exceeded, and then discards the data.If the maximum number of retries is set, the system retries until the maximum number of retries is exceeded, and then discards the data. |
Item | Capability and Limit |
Log upload policy | LogListener automatically aggregates and uploads logs of the same file when any of the following aggregation conditions is met: 10,000 logs, the total logset size reaching 1 MB, or the log collection time exceeding 3 seconds. |
File collection handling policy | A single target file (a file that can be matched by the collection path) can be uploaded to only one log topic. The same file cannot be matched by the collection paths of multiple topics. If you need to upload a file to multiple topics, use soft links. You can create different soft links for the same target file so that it can be collected to different topics via different soft links. |
Log collection delay | In the case of real-time collection, data collection, transmission, and storage to disks will be completed within 1 minute, and the logs are retrievable in the console. If the log volume is large, or LogListener can use only a limited amount of resources, there will be some collection delay. |
Item | Capability and Limit |
Machine group logic | At present, machine groups are divided into the following two categories, and their usage methods are independent of and incompatible with each other. If the two usage methods are used together, LogListener will not be able to pull the correct collection configuration, resulting in no collection. IP machine group: a machine IP must be manually added to the machine group in the console, and the group_label field in loglistener.conf on the corresponding machine must be empty.Label machine group: the machine group label is set in the console, and the group_label field in loglistener.conf on the corresponding machine must be set to the same label. |
Relationships between machine groups and log topics | A single log topic can be bound to multiple machine groups. A single machine group can be bound to multiple log topics. |
Relationships between machine groups and machines | A single machine can be added to multiple machine groups. For an IP machine group, there is no limit to the number of machine groups that a machine can join. For a label machine group, the maximum number of machine groups that a machine can join is 20. |
Limits on the labels of label machine groups | Currently, the label of a label machine group can contain up to 32 characters. Up to 20 labels can be configured for a single label machine group. |
Item | Capability and Limit |
Collection blocklist | This feature is used to specify the content to ignore in the collection path. Currently, collection blocklists support two modes: FILE mode: specify the files to ignore in the collection path. PATH mode: specify the subdirectories to ignore in the collection path. Wildcard filtering is supported. Notes: The FILE and PATH modes can be used together. A collection blocklist is to exclude content from the collection path, and for both the FILE and PATH modes, the specified path to exclude must be a subset of the collection path. |
Last updated:2024-12-16 14:58:40
Restriction Item | Description |
Metric name | Supports English letters, numbers, underscores, and colons. It should conform to the regular expression [a-zA-Z_:][a-zA-Z0-9_:]*. |
Label name | Supports English letters, numbers, and underscores. It should conform to the regular expression [a-zA-Z_][a-zA-Z0-9_]*. |
Label value | No special restrictions, supporting all types of Unicode characters. |
Sample value | A float64 type value |
Sample timestamp | Millisecond precision |
Metric upload frequency control | Related to the number of partitions. The maximum number of partitions is 50, and the partition write request limit for individual topics is 500 QPS. It is recommended to enable partition auto-split during metric topic creation. |
Metric upload flow control | Related to the number of partitions. The maximum number of partitions is 50, and the partition write traffic limit for individual topics is 5 MB/s. It is recommended to enable partition auto-split during metric topic creation. |
Last updated:2024-12-16 14:59:44
Type | Restriction Item | Description |
Index | Number of Fields | Up to 300 fields can be added for a single log topic key-value index. |
| Field Name | Letters, digits, and special characters (except for *\",) are supported. The name cannot start with _ (except for the __CONTENT__ field).It is not allowed to contain JSON parent-child fields at the same time, such as a and a.b. |
| Field Hierarchy | When the key-value index for multi-level JSON is configured, there shall be no more than 10 levels for the Key, such as a.b.c.d.e.f.g.h.j.k. |
| Delimiter | Only English symbols, \n\t\r and escape characters\ are supported. |
| Field Length | After the field is enabled for statistics, only the first 32,766 bytes are involved in SQL operation. The excess part cannot execute SQL, but the log will still be completely stored. |
| Token Length | After the field is tokenized, only the first 10,000 characters of a single word are involved in search. The excess part cannot be searched, but the log will still be completely stored. |
| Numeric Field Precision and Range | The data range supported by the long type field is -1E15 ~ 1E15. Data outside of this range may lose accuracy or do not support search. The data range supported by the double type field is -1.79E+308 ~ +1.79E+308. If the number of floating-point coding bits exceeds 64, precision will be lost. Suggestions on index configuration of ultra-long numerical field: If the field does not need to be searched by value range comparison, it can be stored as text type. If the field needs to be searched by value range comparison, it can be stored as double type and some precision may be lost. |
| Activation Mechanism | Index configuration is effective only for newly collected data. The index rules after editing are effective only for newly written logs and existing data will not be updated. To update existing data, rebuild the index. |
| Modifying index configuration | When the index configurations are created, modified and deleted, a single user has a maximum of 10 tasks being executed at the same time. If the number is exceeded, other tasks need to wait for the previous ones to completed and a single task usually takes no more than 1 minute. |
| Reindexing | A single log topic allows to run only one index rebuilding task at a time. A single log topic can have 10 index rebuilding task records at most. An index task can only be created after the task records that are no longer needed are deleted. For logs within the same time range, the index can only be rebuilt once. You need to delete previous task records before rebuilding. The write traffic of logs corresponding to the selected time range cannot exceed 5 TB. The index rebuilding time range is subject to the log time. When there is a deviation of more than 1 hour between the log uploading time and the index rebuilding time range (for example, a 02:00 log is uploaded to CLS at 16:00, and the log index from 00:00 to 12:00 is rebuilt), it will not be rebuilt and cannot be retrieved subsequently. When a new log is submitted to the time range for which the index has been rebuilt, the index will not be rebuilt and the log will not be searched later. |
Query | Sentence Length | Search and analysis statements support up to 12,000 characters. |
| Query Concurrency | A single log topic supports 15 concurrent queries, including search and analysis queries. |
| Fuzzy search | Fuzzy prefix search is not supported, e.g. search for error by *rror. |
| Phrase search | Wildcards in phrase search can only match with 128 words that meet the conditions, and all logs containing these 128 words will be returned. The more accurate the specified word is, the more accurate the query result will be. |
| Logical group nesting depth | When parentheses are used for logical grouping of search conditions under CQL syntax rules, up to 10 layers can be nested. This limitation is not applicable to Lucene syntax rules. For example, (level:ERROR AND pid:1234) AND service:test is 2-layer nesting and can perform search normally. The statement below is 11-layer nesting, and an error will be reported when the search is performed. status:"499" AND ("0.000" AND (request_length:"528" AND ("https" AND (url:"/api" AND (version:"HTTP/1.1" AND ("2021" AND ("0" AND (upstream_addr:"169.254.128.14" AND (method:"GET" AND (remote_addr:"114.86.92.100")))))))))) |
| Memory usage (analysis) | The server memory occupied by statistical analysis each time cannot exceed 3 GB. Generally, this limitation may be triggered when group by, distinct() and count(distinct()) are used, because there are too many values in the statistical field after deduplication through group by or distinct(). It is recommended to optimize the query statement and use fields with fewer values to perform grouping statistics on data, or use approx_distinct() to replace count(distinct()). |
| Query Result | If raw logs are queried, a maximum of 1,000 raw logs can be returned for each query. |
| | If statistical analysis results are queried, a maximum of 100 results can be returned for each query by default. If a LIMIT clause is used, a maximum of 1 million results can be returned for each query. |
| | The maximum data packet returned for the query cannot be greater than 49 MB. GZIP compression (Header Accept-Encoding:gzip) can be enabled if the corresponding API is used. |
| Timeout Time | The timeout time for a single query is 55 seconds, including search and analysis. |
| Query Latency | The delay from log reporting to being available for search and analysis is less than 1 minute. |
Download | Log Count | The maximum number of logs downloaded at a time is 50 million. |
| Task Quantity | For a single log topic, a maximum of 2 tasks can be in the File Generating status, and other unfinished tasks are in the Waiting status and queuing for execution. A single log topic can have up to 1,000 tasks at the same time, including completed tasks in the status of File Generated. |
| File Retention Duration | The generated log files will be retained for only 3 days. |
Related external data | Quantity Limit | A single log topic can be associated with up to 20 external data. |
| Query Timeout | When an external database is queried, the timeout period is 50 seconds. |
| MySQL Version | It is compatible with MySQL 5.7, 8.0 and later versions. MySQL 5.6 has not received a complete compatibility test. It is necessary to actually test whether the SQL statements are executed properly. |
| CSV file size | The file shall not exceed 50 MB and compression is not supported. |
Restriction Item | Description |
Query Concurrency | A single metric topic supports up to 15 concurrent queries. |
Query data volume | A single query can involve up to 200,000 time series, with a maximum of 11,000 data points per time series in the query results. |
Timeout Time | The timeout time for a single query is 55 seconds, including search and analysis. |
Last updated:2024-12-16 15:01:53
Type | Restriction Item | Description |
Alarm Policy | Monitoring Object | A maximum of 20 log topics can be selected for a single alarm policy, and cross-region alarm is not supported. |
| Query Statement | The limitations are the same as Search and Analysis, including statement length and concurrent limitations. |
| Number of Query Statement | When each execution statement uses the same log topic, up to 3 execution statements can be added for a single alarm policy. When each execution statement selects log topics separately, up to 10 execution statements can be added for a single alarm policy. |
| Execution statement query time range | The maximum time range is the last 24 hours. |
| Execution Cycle | The minimum execution cycle is 1 minute and the maximum execution cycle is 1,440 minutes. |
| Trigger by group | The execution statement results can be divided into 1,000 groups at most. The 1,000 groups will be judged separately to determine whether they meet the triggering conditions, and no judgment will be performed for the groups beyond the range. Note: Triggering by group is an optional function, and this limitation is not involved if it is not enabled. |
| Trigger condition judgment times | When the result of the execution statement is multiple values (after grouping), the results will be judged to determine whether the triggering conditions are met, and the judgment will stop when the triggering conditions are met or more than 1,000 times of judgement have been performed. |
Alarm Type | Phone | The same phone number can receive up to 1 phone call alarm within 30 seconds, up to 3 phone call alarms within 10 minutes, and up to 50 phone call alarms within 1 day. The same phone number can receive a maximum of 3 phone call alarms from 22:00 to 08:00 the next day. To eliminate this restriction, go to the Message Center to enable receiving alarms at night. The above limitations are not limited to phone call alarms generated by the Cloud Log Service. Phone notifications generated by the Cloud Observability Platform and Message Center are also subject to these limitations. To receive alarms through phone calls, it is recommended to add the following phone numbers to the allowlist of your phone. Otherwise, the calls will be blocked.
|
| WeCom, DingTalk, and Lark | Each Chatbot cannot send more than 20 messages per minute. |
| Custom webhooks | Public network access should be supported. Private network addresses are not supported. When the status code returned by the interface is 200, it indicates that callback is successful. |
Alarm Records | Storage Period | 30 days |
Alarm Notification | Alarm Notification Variables | The following alarm notification variables are subject to data entry count or data size restrictions. The data will be automatically truncated if the upper limits are exceeded. {{.Message}}: The maximum size is 10 KB. {{.QueryResult}}: Each execution statement can contain up to 1,000 data entries, and the maximum data size is 10 KB. The maximum number of statements is 10, with a total maximum data size of 100 KB. {{.TriggerResult}}: Each execution statement can contain up to 1,000 data entries, and the maximum data size is 10 KB. The maximum number of statements is 10, with a total maximum data size of 100 KB. {{.QueryLog}}: Each execution statement can contain up to 10 data entries, and the maximum data size is 10 KB. The maximum number of statements is 10, with a total maximum data size of 100 KB. {{.AnalysisResult}}: The maximum data size of each multidimensional analysis result is 10 KB. The maximum number of multidimensional analysis results is 5, with a total maximum data size of 50 KB. Related raw logs: Each statement can contain up to 10 data entries, depending on the user configuration. Top 5 fields and their proportions: Each statement can contain up to 5 data entries. Custom search and analysis (SQL): Each statement can contain up to 1,000 data entries. Custom search and analysis (search): Each statement can contain up to 10 data entries. |
Last updated:2024-12-17 17:55:46
Type | Restriction Item | Description |
Data Processing | Number of Data Processing Tasks | One log topic can create 50 data processing tasks. |
| Number of Target Topics | One data processing task can have up to 1000 target topics. |
| The number of debugging data | By default,100 pieces of logs are loaded from the source topic for you to debug the DSL function. |
| Processing Capability | 10 ~ 20 MB/s/partition (uncompressed data), with partition referring to the that of the source log topic. |
| Processing Task Latency | Up to 99.9% of the data will be processed in the data processing module within 1 second. |
| Impact of starting and stopping processing tasks on data | When the processing task is restarted within 12 hours after it is suspended, processing will be started from the data when it was suspended. When the processing task is restarted after 12 hours, processing will be started from the latest data. |
| Cross-region/Cross-account | Not supported. |
| Processing History Data | Not supported. |
Scheduled SQL analysis | Number of scheduled SQL tasks | One log topic can be associated with 10 scheduled SQL tasks. (The log topic can be the source log topic of the task or the target log topic.) |
| Query Concurrency | A single log topic supports 15 concurrent queries (Scheduled SQL、 search and analysis、Alarms、Dashboards). |
| Viewing the query result | When the query results are statistical analysis results, 100 results will be returned at a time by default. When SQL LIMIT syntax is used, a maximum of 1 million results will be returned at a time. |
| | The maximum size of the returned data packet of query results is 49 MB, and gzip compression can be enabled when API is used. |
| Query Timeout Duration | The timeout period for a single query is 55 seconds. |
| SQL time window | 1 minute to 7 days. |
| Scheduling cycle | 1 minute to 24 hours. |
| Custom timestamp | The minimum custom timestamp interval is 15 seconds. For example, 15:00:00, 15:00:15, and 15:00:30. |
| SQL execution delayed | The default value is 60 seconds and the maximum value is 120 seconds. It takes about 5 seconds to generate 99.9% of the log indexes, and 60 seconds in extreme cases. Therefore, set a delay for execution to ensure that the query can successfully obtain index data. |
| Cross-region/Cross-account | Not supported. |
Last updated:2024-12-17 17:57:09
Type | Restriction Item | Description |
Ship to COS | Number of Tasks Submitted | For each log topic, a maximum of 10 shipping to COS tasks can be configured. |
| Deliverable Data Scope | Data (including historical and real-time data) of log topics in the lifecycle. |
| Task Submission Delay | The latency of shipping to COS is about 60 seconds. Note: If you set the shipping interval to be 5 minutes, logs from 12:00 to 12:05, meeting the interval of 5 minutes, will be shipped as a whole to COS in a batch. With a latency of 60 seconds, this batch of logs will arrive at COS around 12:06. |
| Trigger Delivery | One shipping will be triggered when a partition meets any of the following conditions: Size of logs to be shipped (accumulated log data). Range: 5 to 256 MB (uncompressed). Shipping interval. Range: 5 to 15 minutes. |
| Cross-account/Cross-region | Cross-account: supported Cross-region: not supported |
Ship to CKafka | Number of Tasks Submitted | For each log topic, one shipping to CKafka task can be configured. |
| Deliverable Data Scope | At present, only real-time log data can be shipped, and historical data is not supported. |
| Task Submission Delay | The latency of shipping 99.9% of logs to the CKafka are within 5 seconds. (The target CKafka functions properly, has a throughput capacity sufficient to process messages from the CLS and the disk is not full or throttled). Note: If the timestamp (value of _TIMESTAMP_) of a log collected to CLS is 12:00:00, the log will arrive at CKafka before 12:00:05. |
| Cross-account/Cross-region | Cross-account: supported Cross-region: not supported |
Consumption over Kafka | Versions | Kafka protocol version supported: 1.1.1 and earlier. |
| Number of consumer groups | Each log topic can be configured with 20 consumer groups. |
| Authentication Method | Only SASL_PLAINTEXT is supported. |
| Consumable data range | Once this feature is enabled, consumption will start from the latest data. Data will be retained for 2 hours. If data is not consumed within 2 hours, it will not be saved. Note: For example, if you enable consumption over Kafka protocol at 12:00, you will consume data from 12:00. Until 15:00, you can consume data from 13:00 to 15:00. Data before 13:00 cannot be consumed. |
| Consumption latency | The consumption latency of 99.9% log data is within 5 seconds. Note: If the timestamp (value of _TIMESTAMP_) of a log collected to CLS is 12:00:00, the log will arrive at the consumer before 12:00:05. |
| Cross-account/Cross-region | Cross-account: Account A can be a collaborator of account B to consume the log topics of account B. Permissions need to be set for the collaborator. For details, see the permission configuration. Cross-region: Cross-region consumption can be implemented through public network. |
Last updated:2024-01-20 16:31:37
59.x.x.x - - [06/Aug/2019:12:12:19 +0800] "GET /nginx-logo.png HTTP/1.1" 200 368 "http://119.x.x.x/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_14_5) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/75.0.3770.142 Safari/537.36" "-"
java.net.SocketTimeoutException:Receive timed outat j.n.PlainDatagramSocketImpl.receive0(Native Method)[na:1.8.0_151]at j.n.AbstractPlainDatagramSocketImpl.receive(AbstractPlainDatagramSocketImpl.java:143)[^]at j.n.DatagramSocket.receive(DatagramSocket.java:812)[^]at o.s.n.SntpClient.requestTime(SntpClient.java:213)[classes/]at o.s.n.SntpClient$1.call(^:145)[^]at ^.call(^:134)[^]at o.s.f.SyncRetryExecutor.call(SyncRetryExecutor.java:124)[^]at o.s.f.RetryPolicy.call(RetryPolicy.java:105)[^]at o.s.f.SyncRetryExecutor.call(SyncRetryExecutor.java:59)[^]at o.s.n.SntpClient.requestTimeHA(SntpClient.java:134)[^]at ^.requestTimeHA(^:122)[^]at o.s.n.SntpClientTest.test2h(SntpClientTest.java:89)[test-classes/]at s.r.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)[na:1.8.0_151]
Component | Description | Example |
__TIMESTAMP__ | Log time, in the format of a UNIX timestamp in milliseconds | 1640005601188 |
__FILENAME__ | Log source file | /data/log/nginx/access.log |
__SOURCE__ | Log source IP | 10.0.1.2 |
Log body | Log body content, in key:value format (key is the field name, and value is the field value.)If the log extraction mode is full text in a single line or full text in multi lines (the entire raw log is reported without splitting), the entire log is stored in the __CONTENT__ field. If the log extraction mode is any other mode (such as splitting with a separator), each part of the raw log corresponds to a key:value pair. | Full text in a single line or full text in multi lines: 10.20.20.10;[2018-07-16 13:12:57];GET /online/sample HTTP/1.1;200 Other modes: IP: 10.20.20.10 request: GET /online/sample HTTP/1.1 status: 200 time: [2018-07-16 13:12:57] |
Metadata | Simple description or categorization of logs. For example, the cluster or container of a TKE log is stored in the key:value format, where key starts with __TAG__. | __TAG__.clusterId:1skzv59c |
Last updated:2024-01-20 16:32:37
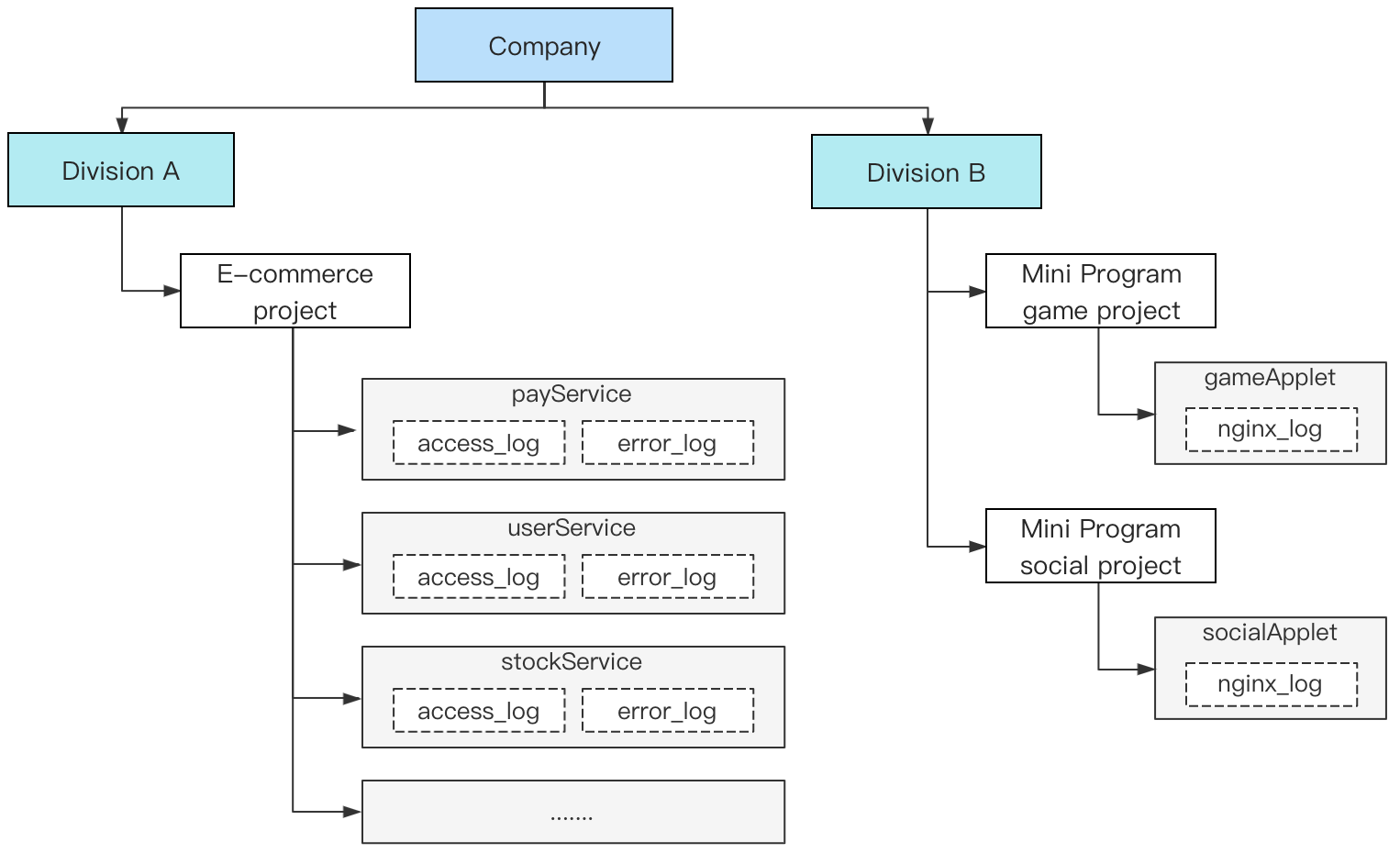
Logset | Log Topic | Label |
e_commerce_logset | payService_access_log_topic | Department: Department A |
e_commerce_logset | payService_error_log_topic | Department: Department A |
e_commerce_logset | userService_access_log_topic | Department: Department A |
e_commerce_logset | userService_error_log_topic | Department: Department A |
e_commerce_logset | stockService_access_log_topic | Department: Department A |
e_commerce_logset | stockService_error_log_topic | Department: Department A |
e_commerce_logset | ...... | Department: Department A |
gameApplet_logset | gameApplet_nginx_log_topic | Department: Department B |
socialApplet_logset | socialApplet_nginx_log_topic | Department: Department B |
Last updated:2024-01-20 16:33:07
Machine | Service Deployed | Log File Path |
192.168.1.1 | payService | /data/log/payService/access_log.log /data/log/payService/error_log.log |
192.168.1.2 | payService | /data/log/payService/access_log.log /data/log/payService/error_log.log |
192.168.1.3 | userService,stockService | /data/log/userService/access_log.log /data/log/userService/error_log.log /data/log/stockService/access_log.log /data/log/stockService/error_log.log |
192.168.1.4 | userService,stockService | /data/log/userService/access_log.log /data/log/userService/error_log.log /data/log/stockService/access_log.log /data/log/stockService/error_log.log |
192.168.1.5 | userService,stockService | /data/log/userService/access_log.log /data/log/userService/error_log.log /data/log/stockService/access_log.log /data/log/stockService/error_log.log |
192.168.1.6 | userService,stockService | /data/log/userService/access_log.log /data/log/userService/error_log.log /data/log/stockService/access_log.log /data/log/stockService/error_log.log |
Machine | Service Deployed | Label |
192.168.1.1 | payService | payService |
192.168.1.2 | payService | payService |
192.168.1.3 | userService,stockService | userService,stockService |
192.168.1.4 | userService,stockService | userService,stockService |
192.168.1.5 | userService,stockService | userService,stockService |
192.168.1.6 | userService,stockService | userService,stockService |
Log Topic | Associated Machine Group | Collection Path |
payService_access_log_topic | payService | /data/log/payService/access_log.log |
payService_error_log_topic | payService | /data/log/payService/error_log.log |
userService_access_log_topic | userService | /data/log/userService/access_log.log |
userService_error_log_topic | userService | /data/log/userService/error_log.log |
stockService_access_log_topic | stockService | /data/log/stockService/access_log.log |
stockService_error_log_topic | stockService | /data/log/stockService/error_log.log |
Last updated:2024-01-20 16:33:38
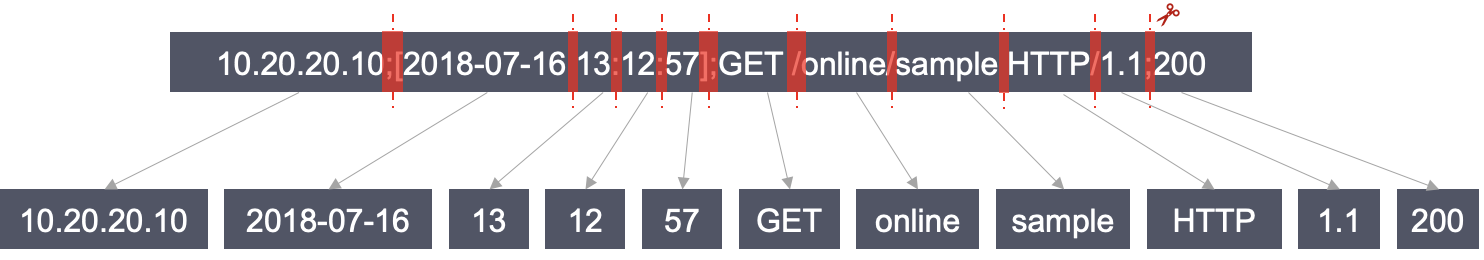
sample:10.20.20.10;[2018-07-16 13:12:57];GET /online/sample HTTP/1.1;200
sample. The complete log and the search condition are not identical. Therefore, sample cannot be used as the search condition to search for the log. To meet this search requirement, the full text of the log needs to be divided into multiple fragments, and each fragment is called a word, and this process is called "segmentation".@&()='",;:<>[]{}/ \n\t\r, that is, wherever the symbols occur, segmentation is executed. The segmentation result is as follows:
sample, the preceding log after segmentation contains sample and therefore is considered to meet the search condition.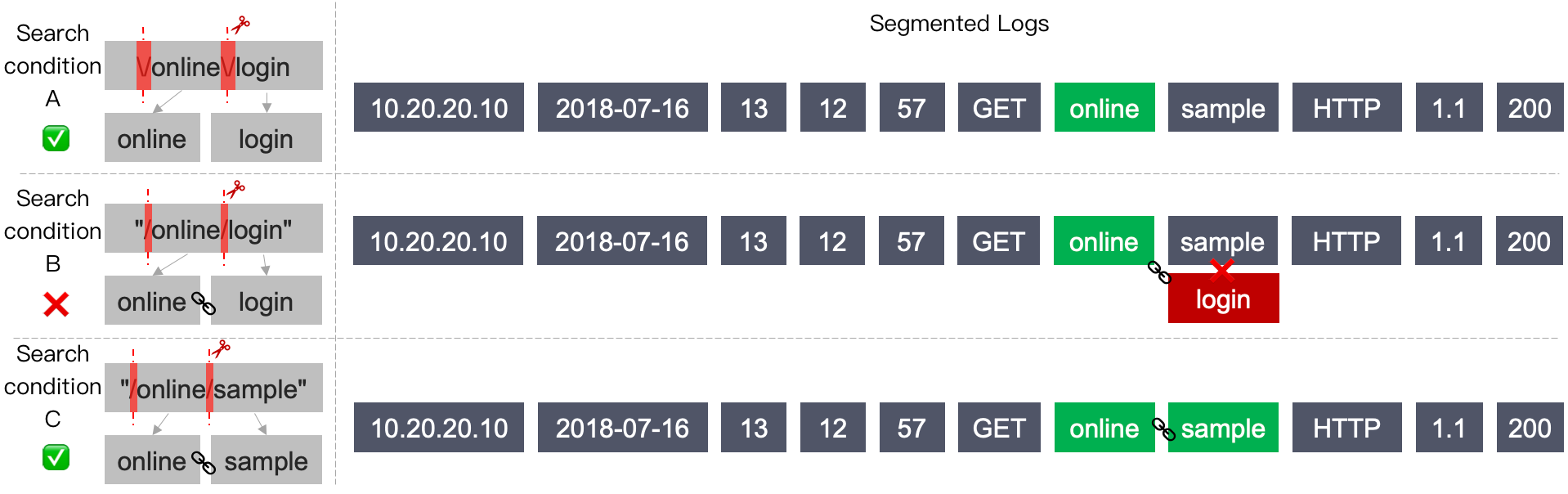
\/online\/login\ is used to escape the / symbol (this symbol is a reserved symbol of the search syntax and therefore needs to be escaped)./ symbol is a delimiter, so the actual search condition is online OR login. A log containing onlineorlogin is considered to meet the search condition."/online/login"/ symbol does not need to be escaped.login and therefore does not meet the search condition."/online/sample"online and sample in the exact order as that in the search condition and therefore is considered to meet the search condition.@&()='",;:<>[]{}/ \n\t\r are delimiters.

Last updated:2024-01-20 16:34:10
[00000000000000000000000000000000,ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff). All read-write partitions segment the entire value range of a log topic and each occupies a left-closed and right-open interval to ensure that every log record collected is written to the corresponding partition.Partition No. | Status | Partition Range |
1 | Read-write | [00000000000000000000000000000000,7fffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff) |
2 | Read-write | [7fffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff,a0000000000000000000000000000000) |
3 | Read-write | [a0000000000000000000000000000000,ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff) |
2fffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff is written to partition 1 and log data with the Key value of 9f000000000000000000000000000000 is written to partition 2.Feature | Item | Description |
Frequency control | Write requests | Every partition supports a maximum of 500 QPS of write operations. It will reject requests and return the status code 429 with an error message of "SpeedQuotaExceed" when the limit is exceeded. |
| Read requests | Every partition supports a maximum of 200 QPS of read operations. It will reject requests and return the status code 429 with an error message of "SpeedQuotaExceed" when the limit is exceeded. |
Traffic throttling | Write traffic | Every partition supports the write traffic of up to 5 MB/sec. It will truncate data and return the status code 429 with an error message of "SpeedQuotaExceed" when the limit is exceeded. |
Last updated:2025-12-16 21:28:42