What is Clawdbot ?
Clawdbot: The Open-Source AI Assistant Redefining Autonomy and Personal Agency
Introduction: The Viral AI Phenomenon
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence, Clawdbot (often referenced as Moltbot) has emerged as a viral sensation, capturing the imagination of Silicon Valley's early adopters and tech enthusiasts. Created by developer and entrepreneur Peter Steinberger, this open-source, agentic AI assistant represents a significant leap from conversational chatbots to a proactive, autonomous digital entity. Unlike cloud-based, walled-garden assistants, Clawdbot operates on a simple but revolutionary premise: it's a smart model with "eyes and hands" that runs persistently on your own hardware, acting on your behalf across the digital tools you use every day. Its rapid ascent from a niche project to a topic of widespread discussion signals a potential paradigm shift in how humans interact with and delegate tasks to AI.
1. What is Clawdbot?
Clawdbot is an open-source, locally-hosted personal AI assistant. At its core, it is an example of agentic AI—a system designed to autonomously execute multi-step tasks and workflows rather than merely respond to queries. Its defining characteristic is persistent agency; it runs 24/7 on a user's dedicated device (commonly a Mac Mini), maintaining continuous context and memory.
A key philosophical differentiator is its architecture of user sovereignty. As noted by users, your context, memory, and the assistant's skills reside on your computer, not in a corporate-controlled cloud. This makes it a deeply personal tool that users can hack, extend, and truly own. It integrates seamlessly into existing communication workflows, primarily operating through familiar chat apps like WhatsApp, Telegram, and Discord, where you interact with it as you would a human teammate.
2. How Clawdbot Works: Architecture and Core Mechanics
Clawdbot's functionality is powered by the strategic integration of several advanced components. The table below breaks down its core operational architecture:
| Component | Function | User Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Large Language Model (LLM) Brain | Uses frontier models (e.g., Anthropic's Claude, OpenAI's GPT) via API to process language, reason, and plan. | Users must provide their own API subscriptions (Claude, ChatGPT, CoPilot), allowing for choice and control over the core intelligence. |
| Persistent Memory & Context | Maintains a rolling memory of all interactions, tasks, and user data across sessions. | The assistant remembers everything, enabling complex, long-term projects and personalized support without repetitive explanations. |
| Skill & Plugin System | A growing library of modular "skills" that grant the bot access to tools (Gmail, Calendar, code editors, browser control). | The bot can perform real-world actions: send emails, check flight status, write code, manage smart home devices, etc. |
| Communication Layer | Connects to chat app APIs (Telegram, Discord, WhatsApp), serving as the primary user interface. | Interaction is natural and happens on the user's preferred platform, lowering the barrier to delegation. |
| Local Execution Environment | Runs on a user's always-on computer with full system access (shell, files, browser). | This is the source of its powerful autonomy but also its primary security consideration, as it can execute any action a human could on that machine. |
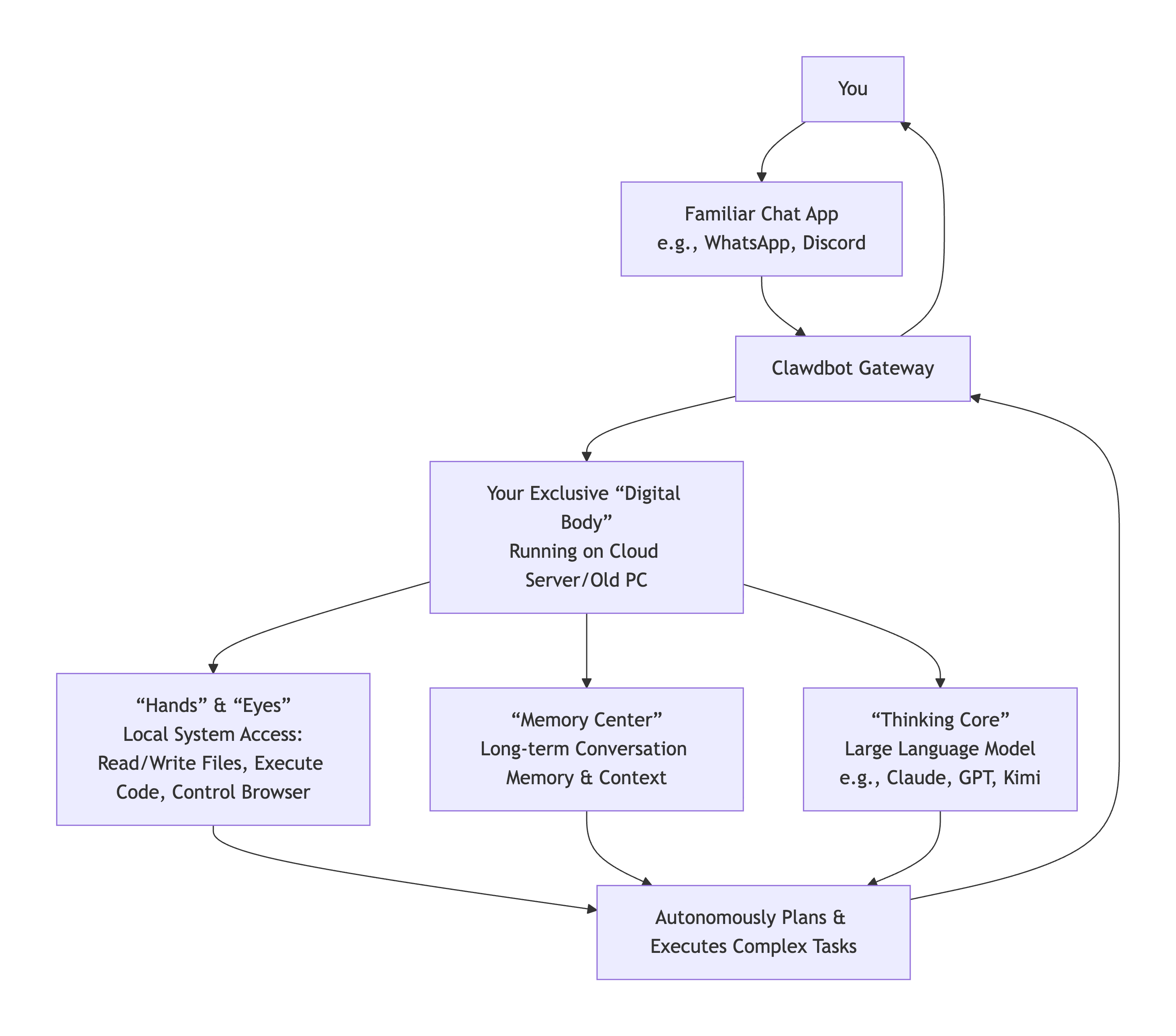
Its agentic workflow is cyclical: it receives a natural language command via chat, uses its LLM to break it down into a plan, executes steps by calling relevant skills and system tools, and reports back—all while learning and storing context for future use. Remarkably, it can even self-improve; users report it can write its own new skills or modify its configuration when it identifies a gap in its capabilities.
3. Capabilities and What Clawdbot Can Do
Clawdbot’s capabilities extend far beyond simple scheduling. User testimonials paint a picture of a versatile, proactive, and deeply integrated digital coworker:
- Life and Workflow Automation: It clears inboxes, manages calendars, checks in for flights, files health insurance reimbursements, books appointments, and monitors personal metrics (e.g., WHOOP fitness data).
- Software Development and IT Operations: It can autonomously run tests on applications, capture and resolve errors via webhooks, open pull requests, provision cloud resources (like API keys), and even control servers.
- Creative and Content Tasks: The assistant can design graphics, build websites from a phone, write content, create custom meditations with generated audio, and process video.
- Proactive and Predictive Assistance: Through "heartbeat" checks, it can proactively reach out with reminders, daily briefings, traffic alerts for appointments, or notifications about high-priority emails.
- Continuous Learning and Extension: It can ingest YouTube videos or articles to create reusable skills, connect disparate pieces of information from different conversations into a coherent summary, and continuously expand its own utility.
4. Application Scenarios
Clawdbot’s design makes it adaptable to a wide array of personal and professional contexts. The following table outlines its primary application scenarios:
| Scenario | Description | Example Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| The Personal Executive Assistant | Manages an individual's digital life and personal logistics. | Email triage, calendar management, travel coordination, personal finance tracking, habit monitoring, smart home control. |
| The Company or Team Assistant | Acts as a shared resource for a small team or business, handling operational tasks. | Automating customer support triage, managing internal documentation, coordinating project timelines, handling expense reports. |
| The Developer Co-pilot | Serves as an autonomous coding partner that can execute entire workflows. | Writing and reviewing code, debugging, running test suites, deploying applications, managing infrastructure. |
| The Family or Household Assistant | Coordinates tasks and information for a household, accessible to multiple family members. | Managing shared calendars, ordering groceries, controlling household IoT devices, organizing family photos/documents. |
| The Research and Learning Companion | Helps in synthesizing information and creating knowledge bases. | Summarizing research papers, building a "second brain" from notes (e.g., Obsidian), creating study guides from course materials. |
5. Future Prospects and Industry Impact
The explosive community response to Clawdbot suggests it is more than a fleeting trend. Its future trajectory points toward several key developments:
- Democratization of Agentic AI: By being open-source, Clawdbot lowers the barrier to creating powerful, personalized AI agents, potentially leading to a Cambrian explosion of niche, user-created assistants.
- Threat to Conventional SaaS: As one user noted, a self-hackable, on-premise assistant that can glue together workflows across multiple services poses a disruptive threat to traditional single-function SaaS products. Why subscribe to ten tools when one assistant can orchestrate actions across ten free or basic-tier services?
- The Path to "Digital Employees": The project offers a tangible glimpse into a future where individuals and small businesses can deploy multiple, affordable, 24/7 digital employees for specific roles (e.g., customer support agent, DevOps engineer, personal concierge).
- Evolution of the Personal Operating System (OS): Clawdbot is evolving into a unified layer that sits atop all apps and interfaces. As it matures, it could fundamentally collapse traditional app-centric workflows into a single, conversational OS centered around the user's intent.
6. Security, Compliance, and Critical Risks
The power of Clawdbot is inextricably linked to its most significant caveat: security.
- The Security Model: The developer, Peter Steinberger, is unequivocal: "Running an AI agent with shell access on your machine is… spicy." There is no perfectly secure setup. The threat model is real: a malicious actor could, in theory, attempt to "jailbreak" or socially engineer the AI model to perform harmful actions on your system, or a vulnerability in a skill could be exploited.
- Data Security and Privacy: From a data residency and privacy perspective, Clawdbot has a compelling advantage: all data, context, and memory remain on your local hardware. This is inherently more private than cloud-based alternatives. However, the AI's actions often involve transmitting data to third-party API services (like OpenAI or Anthropic) based on the tasks it performs, so users must be mindful of what those services' policies are.
- Compliance Considerations: Its local-first nature can aid with compliance in regulated industries where data sovereignty is paramount (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA), as sensitive data need not leave the local network. However, the responsibility for securing the environment, auditing skills, and managing access logs falls entirely on the user or their organization.
- Best Practices: Users are advised to:
- Run Clawdbot on a dedicated, isolated machine (like a Mac Mini) not used for sensitive work.
- Carefully audit and limit the skills and system permissions granted.
- Use the provided security audit tools on its GitHub repository.
- Maintain strict oversight, especially in the early stages of use.
Conclusion
Clawdbot is not merely another AI tool; it is a foundational prototype for the next era of human-computer interaction. It successfully demonstrates that effective, autonomous AI agency is possible today by combining persistent memory, tool integration, and a user-centric, open-source model. While it demands technical savvy and a serious approach to security, its promise is immense: a truly personalized, extensible, and sovereign digital entity that acts less like software and more like a competent teammate. As the project evolves, it may well be remembered as the catalyst that moved AI from being a tool we use to an agent we collaborate with and delegate to, fundamentally reshaping our digital lives.
Disclaimer: This analysis is based on publicly available documentation and user testimonials as of early 2026. The open-source project is under active development, and its features, capabilities, and security landscape are subject to rapid change.