Overview
Last updated:2025-12-29 11:50:23
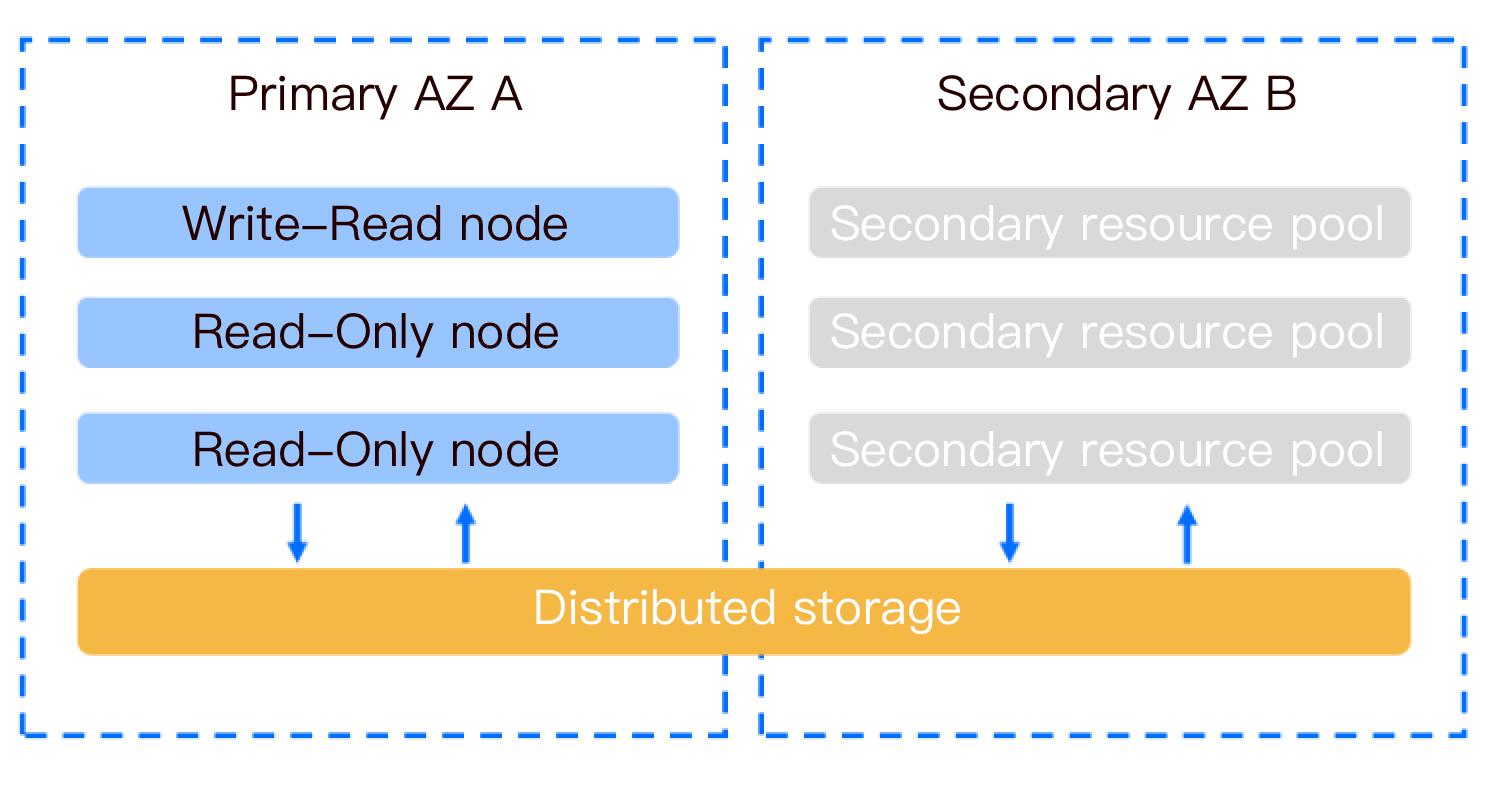
TDSQL-C for MySQL clusters come in either pre-configured resources or Serverless forms, both supporting multi-AZ deployments. Compared to single-AZ deployment, multi-AZ deployment offers higher disaster recovery capabilities to protect the database against instance failures or AZ interruptions, capable of withstanding data center-level failures. Multi-AZ deployment provides database instances with High Availability and failover support. A multi-AZ structure combines several single-AZs within the same region into a physical zone at a level above single-AZ. This article introduces multi-AZ deployment for clusters with pre-configured resources. For details on multi-AZ deployment for Serverless instance types, see Multi-AZ deployment.
Note:
The secondary AZ of TDSQL-C for MySQL is used for disaster recovery and does not provide external access.
Prerequisites
The cluster region has at least two AZs.
The target AZ has sufficient computing resources.
Database version requirements:
Database version 5.7 with kernel minor version 2.0.15 or above.
Database version 8.0 with kernel minor version 3.0.1 or above.
Multi-AZ Deployment Architecture
Supported Regions and AZs
Currently, this feature is in beta test and only supports the following regions and AZs.
This feature will gradually support more regions and AZs.
If required by your business, you can submit a ticket to apply for deployment in other regions and AZs.
Supported Regions | Supports primary availability zone | Supports secondary availability zone |
Beijing | Beijing Zone 3 | Beijing Zone 5 |
| Beijing Zone 5 | Beijing Zone 7 |
| Beijing Zone 6 | Beijing Zone 7 |
| | Beijing Zone 8 |
| Beijing Zone 7 | Beijing Zone 5 |
Guangzhou | Guangzhou Zone 3 | Guangzhou Zone 4 |
| Guangzhou Zone 4 | Guangzhou Zone 6 |
| Guangzhou Zone 6 | Guangzhou Zone 4 |
| | Guangzhou Zone 7 |
| Guangzhou Zone 7 | Guangzhou Zone 4 |
Shanghai | Shanghai Zone 2 | Shanghai Zone 4 |
| Shanghai Zone 4 | Shanghai Zone 2 |
| Shanghai Zone 5 | Shanghai Zone 4 |
Hong Kong (China) | Hong Kong (China) Zone 1 | Hong Kong (China) Zone 3 |
| Hong Kong (China) Zone 2 | Hong Kong (China) Zone 3 |
Singapore | Singapore Zone 2 | Singapore Zone 4 |
| Singapore Zone 3 | Singapore Zone 4 |
| Singapore Zone 4 | Singapore Zone 3 |
Silicon Valley | Silicon Valley Zone 2 | Silicon Valley Zone 1 |
Frankfurt | Frankfurt Zone 1 | Frankfurt Zone 2 |
| Frankfurt Zone 2 | Frankfurt Zone 1 |
Virginia | Virginia Zone 1 | Virginia Zone 2 |
| Virginia Zone 2 | Virginia Zone 1 |
Tokyo | Tokyo Zone 1 | Tokyo Zone 2 |
| Tokyo Zone 2 | Tokyo Zone 1 |
Jakarta | Jakarta Zone 2 | Jakarta Zone 1 |
How to Implement Multi-AZ Architecture
Regarding the multi-AZ architecture, it can be achieved by creating a new cluster via the console. Existing single-AZ clusters will also be upgraded to multi-AZ clusters. This upgrade is automatically completed through online data migration, with no impact on your business. For more details, see Setting Multi-AZ Deployment.
Multi-AZ Billing Description
There are no additional fees for the multi-AZ feature for the time being.
Note:
Currently, single-AZ clusters can also be upgraded to multi-AZ clusters for free.
Multi-AZ Information Display
On the cluster list page, display according to the view mode actually used:
1. Click the cluster in the left side of the Cluster List page to enter the cluster management page.
2. On the cluster management page, under Deployment Mode, and in the Architecture section of the cluster details, you can see the deployment mode and primary and secondary availability zones of the cluster.
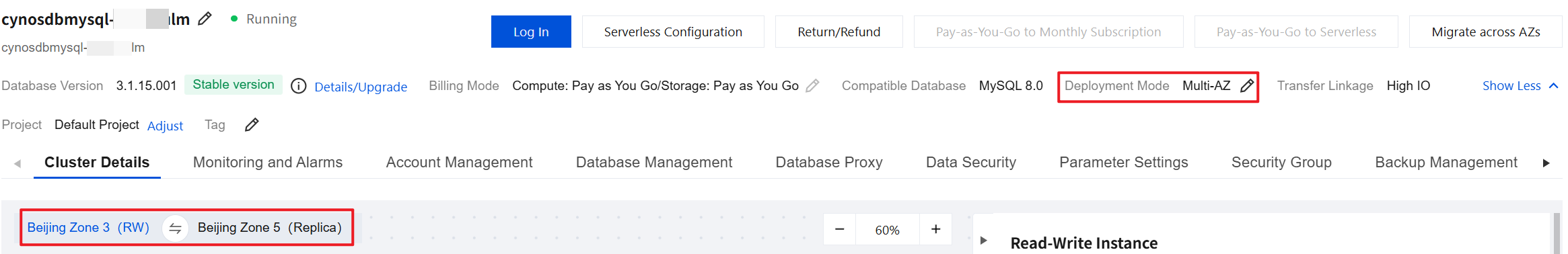
1. The Cluster List page displays the information of the cluster's primary AZ.

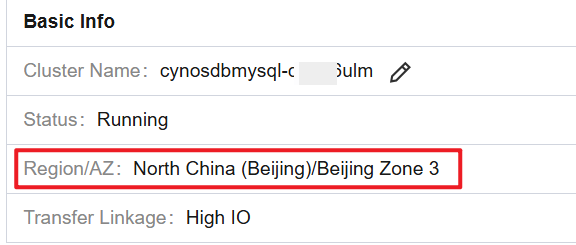
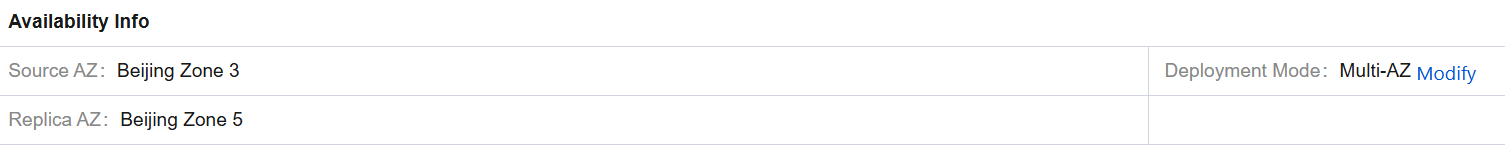
2. On the cluster details page, you can view the availability zones where the cluster deployment is distributed in Basic Info and Availability Info sections.
Data Replication Modes Supported by TDSQL-C for MySQL
Asynchronous Replication
The application initiates a data update request (including insertion, update, and deletion). After completing the update operation, the source node immediately sends a response to the application, and then the data is replicated from the source node to replica nodes. During the data update process, the source node does not need to wait for the response from replica nodes. Therefore, database instances with asynchronous replication usually offer high performance, and the unavailability of replica nodes does not affect the services provided by the source node. However, the data is not synchronously updated to replica nodes in real time. As a result, data inconsistency might occur due to source node faults caused by replica node delay.
Semi-Synchronous Replication
The application initiates a data update request (including insertion, update, and deletion). After completing the update operation, the source node immediately replicates data to replica nodes. Then, replica nodes receive the data, write it to the relay log (relay execution not required), and return a success message to the source node. The source node sends a response to the application after receiving the success message from replica nodes.
The source node will stop sending a response to the application (10 seconds by default) only when a data replication error occurs (caused by replica node unavailability or a data replication network error). In this case, the replication mode changes to asynchronous replication. When data replication becomes normal again, the replication mode changes back to semi-synchronous replication.
Strong Synchronous Replication
The application initiates a data update request (including insertion, update, and deletion). After completing the update operation, the source node immediately replicates data to replica nodes. Then, replica nodes receive the data, write it to the relay log (relay execution required), and return a success message to the source node. The source node sends a response to the application after receiving the success message from replica nodes.
To ensure data consistency, the replication mode will not change when a data replication error occurs (caused by replica node unavailability or a data replication network error). In this case, the source node will stop sending a response to the application until the error is fixed.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

