Query Cache
最后更新时间:2025-06-12 14:47:32
功能介绍
查询缓存(Query Cache)是 MySQL 为了提升数据库查询性能而设计的功能。在数据库中执行查询语句时,该功能会把查询文本及其对应结果集存入查询缓存。若之后收到相同查询请求,数据库会先查看查询缓存,若有对应结果,便直接返回,无需再次解析、优化和执行查询,从而大幅缩短查询响应时间。由于 MySQL 的原生查询缓存功能存在性能相关问题,因此 TDSQL-C MySQL 版针对 MySQL 原生查询缓存的不足进行了重新设计,推出 TDSQL-C MySQL 版的查询缓存功能,能够有效提高数据库的查询性能。

MySQL 原生查询缓存功能存在的问题
查询缓存的命中率和 Hash 查询性能有限。
查询缓存会浪费缓存空间。
查询缓存的参数配置困难。
TDSQL-C MySQL 版针对以上问题进行的优化和说明
优化场景 | 说明 | 价值 |
查询缓存分区优化 | 对 Query Cache/Meta Hash 进行分区处理,将不同类型或范围的查询精准映射至特定分区,降低 Hash 冲突概率,加速查询缓存的定位与检索流程。 | 提升查询缓存的 Hash 性能与命中率,在高并发查询场景中显著减少 CPU 资源消耗,更高效地响应大量查询请求。 |
只读节点开表优化 | 针对只读节点查询缓存有效性验证环节中的开表操作进行深度优化,减少因表操作引发的不必要的缓存失效情形,确保查询缓存在更多场景中维持有效状态。 | 提升缓存的实际利用率与系统整体查询性能。 |
基于命中率的智能缓存控制 | 当查询缓存命中率处于较低水平时,自动启动智能缓存控制机制,限制并发查询数量,合理设置采样频率,让绝大多数查询绕过查询缓存,仅用专用线程负责采样与命中率估算工作,命中率回升后重新启用查询缓存功能。 | 避免在低命中率状况下大量查询涌入缓存系统导致的资源浪费与性能下滑问题,减少无效查询缓存占用的空间资源,维持系统在不同命中率场景下的稳定高效运行。 |
缓存换入换出开销优化 | 优化缓存替换算法与内存管理策略,降低缓存换入换出操作的频率与资源消耗,依据科学合理策略进行缓存替换,优先保留高频次及重要的查询缓存结果。 | 减少因频繁换入换出导致的系统性能波动,让查询缓存在有限内存资源下发挥最大效能,提供持续稳定的查询加速支持。 |
LRU 缓存策略优化 | 依据查询的大小与 Hit 数对 Query Cache LRU 缓存策略进行精细化调整,优先存储高频次及标量查询结果,避免缓存低效查询造成的空间浪费。 | 提升缓存空间的利用效率与系统在特定负载下的查询响应性能,确保缓存资源分配至最具价值的查询任务上。 |
动态缓存开关控制 | 在系统面临写负载压力时及时动态关闭查询缓存,读写负载停止后秒级恢复启用状态。 | 防止因频繁更新数据导致的查询缓存失效及性能退化问题,提高查询缓存的适应性与灵活性,使系统在复杂读写负载环境中维持良好性能表现。 |
动态缓存容量调整 | 支持动态 resize query cache size,且调整过程不阻塞当前正在进行的读写请求,根据实时负载需求与资源状况灵活调整缓存大小。 | 解决固定缓存大小设置不合理的性能瓶颈问题,避免因缓存容量调整引发的性能急剧下降或中断现象,为系统持续稳定高效提供查询加速服务。 |
支持版本
内核版本 TXSQL 8.0 3.1.15.004及以上。
适用场景
查询缓存(Query Cache)作为一种读缓存系统,适用于有局部热点读或存在较长时间只读的业务负载场景。
说明:
如果您的业务负载场景不存在热点读负载,或者数据库中每个表都在频繁进行更新,使用查询缓存功能可能存在一定的性能损耗。
功能使用建议
当存在热点读负载时,可以通过状态 Qcache_free_memory(缓存剩余空间) 和 Qcache_hit_rate(近期查询命中率) 来确定是否需要调整 query_cache_size 以提高读性能。
当缓存剩余空间较少,近期查询命中率相对较低时,可以通过适当增大 query_cache_size 来提高缓存系统命中率,从而提高读性能。
如果增大 query_cache_size 无法明显提升缓存命中率,则说明当前负载访问范围较大,没有明显热点。也可以通过状态 Qcache_queries_in_cache(缓存查询数量)观察当前系统中缓存的查询数量来确定能否覆盖业务热点读。
不建议将 query_cache_size 设置超过实例内存的10%,这是由于较大的 query_cache_size 会带来 OOM 风险。
使用限制
注意:
当前版本的查询缓存(Query Cache)和数据库审计不兼容。若已开启查询缓存功能,则无法开启数据库审计,需要先关闭查询缓存功能才能开启数据库审计;若已开启数据库审计,则无法开启查询缓存功能,需要先关闭数据库审计才能开启查询缓存功能。
使用说明
参数名 | 是否重启 | 是否全局 | 默认值 | 取值范围 | 支持配置的节点 | 说明 |
query_cache_limit | no | 否 | 1048576 | 0 - ulong_max* | 读写实例 只读实例 | 超过该值的 Query 结果集不会被缓存,单位:Bytes。 |
query_cache_size | no | 否 | 1048576 | 1048576 - ulong_max* | 读写实例 只读实例 | 系统中可以用于 Query Cache 内存的大小(实际使用时才会占用内存空间),单位:Bytes,取值必须为1024的倍数。 说明: Sysbench Poc 场景建议设置表大小的20%以上作为 query_cache_size。正常场景建议为 Buffer Pool 的5%左右,如果业务没有只读表或者热点不明显,建议降低 query_cache_size大小。 |
query_cache_type | 详见说明列 | 否 | OFF | OFF/ON/DEMAND | 读写实例 只读实例 | 取值 OFF:表示功能关闭。 取值 ON:表示缓存所有结果,除非 SELECT 语句使用 sql_no_cache 禁用查询缓存。 取值 DEMAND:表示只缓存 SELECT 语句中通过 sql_cache 指定需要缓存的查询。 注意: 如果查询缓存最初是关闭的(配置文件中 query_cache_type=0),则无法再动态开启,需要配置 my.cnf 重启才能开启查询缓存。但是关闭查询缓存始终都可以动态执行。 |
query_cache_wlock_invalidate | no | 否 | OFF | ON/OFF | 读写实例 只读实例 | 当写锁发生在表上时,是否先失效该表相关的查询缓存。 ON:是 OFF:否 |
*ulong_max = 18446744073709551615
以下是查询缓存新增的 Status,可以通过命令查询 Query Cache 相关 Status,语法如下。
SHOW STATUS LIKE 'Qcache%';
Status | 描述 |
Qcache_hits | 查询缓存命中次数。 |
Qcache_hit_rate | 近期查询命中率,值为最近10000次查询缓存(Qcache_search_times 每增加10000)中,命中查询缓存的比例。 |
Qcache_search_times | Query 查询 Cache 的次数(被限流以及不满足走 Query Cache 的查询不会计数)。 |
Qcache_total_times | Query 走 Query Cache 的总次数(限流等情况也会被记录)。 |
Qcache_free_memory | Query Cache 剩余空间。 |
Qcache_inserts | 成功缓存结果集的次数。 |
Qcache_not_cached | 未能缓存结果集的次数。 |
Qcache_queries_in_cache | 在 Query Cache 中缓存的 Query 数量。 |
Qcache_lowmem_prunes | 被 LRU 驱逐的 Query Cache 数量。 |
性能测试
测试环境
备节点数量:1个读写实例和1个只读实例。
集群配置:8核16GB。
测试工具:Sysbench 1.0.20。
数据库内核版本:TXSQL 8.0 3.1.15.004。
数据量:
全缓存场景:Sysbench 的数据量约为1.4GB,共25000*250张表。
大 IO 场景:Sysbench 的数据量约为54GB,共800000*300张表。
测试目标、场景、步骤、结果
测试目标 | 测试场景 | 测试步骤及结果 |
查询缓存对读场景性能的提升。 | 不同数据量下,Query Cache 带来的性能提升。 | |
查询缓存大小(query_cache_size)对性能的影响。 | 不同 query_cache_size 及数据量下,Query Cache 带来的性能提升。 |
测试场景一:查询缓存对读场景的性能提升
测试步骤
1. 开启查询缓存功能(设置参数 query_cache_type 为 ON),设置 query_cache_size 的值为1073741824(即1024MB)。
2. 在全缓存的场景下,在不同并发度下,记录集群的 QPS。Sysbench 的数据量约为1.4GB,共25000*250张表。
3. 在大 IO 场景下,在不同并发度下,记录集群的 QPS。Sysbench 的数据量约为54GB,共800000*300张表。
测试结果
1. 全缓存场景下,机器内存为16GB,数据量大小为1.4GB。开启 Query Cache 后,点查可提升了171%左右的性能,范围查可提升了36%左右的性能。
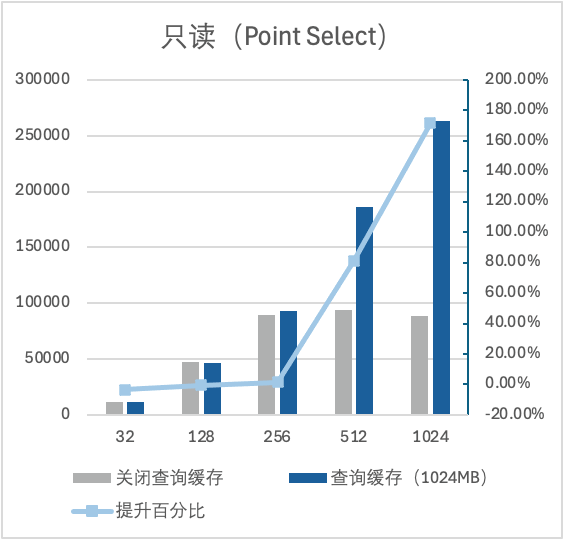
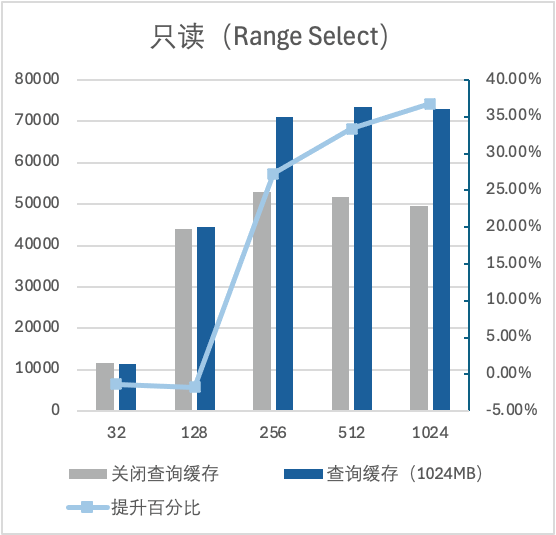
2. 大 IO 场景下,机器内存为16GB,数据量大小为54GB。开启 Query Cache 后,点查可提升了36%左右的性能,范围查可提升了10%左右的性能。
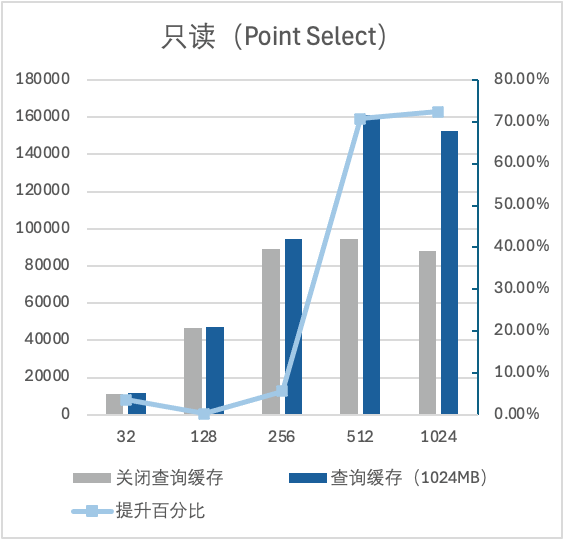
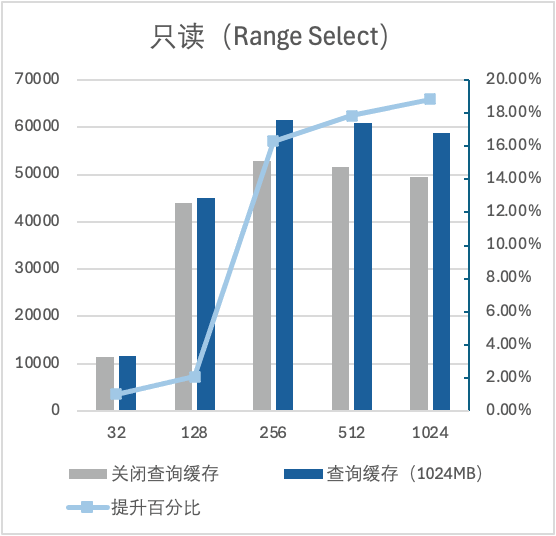
测试场景二:查询缓存大小对性能的影响
测试步骤
1. 设置并发度为1024,开启查询缓存(设置参数 query_cache_type 为 ON)。
2. 在全缓存场景下,调整不同查询缓存大小 query_cache_size,进行性能测试,记录集群的 QPS。
3. 在大 IO 场景下,调整不同查询缓存大小 query_cache_size,进行性能测试,记录集群的 QPS。
测试结果
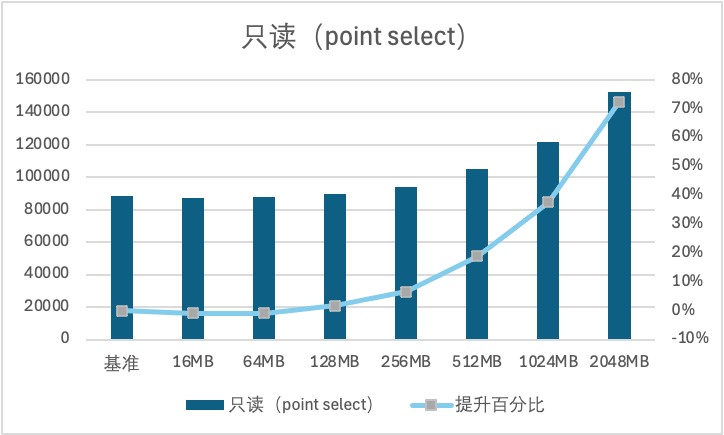
1. 全缓存场景下,随着查询缓存大小提升,性能逐渐上升。在查询缓存为2048MB时,对点查 Point Select 带来的提升约为194%,对范围查 Range Select 带来的提升为74%。

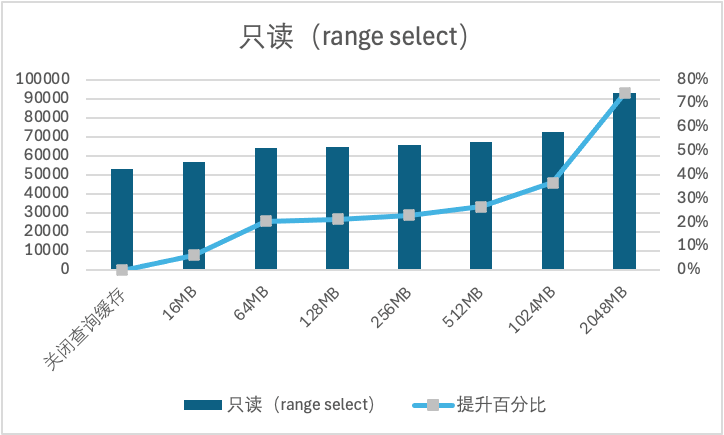
2. 大 IO 场景下,随着查询缓存大小提升,性能逐渐上升。在查询缓存为2048MB时,对点查 Point Select 带来的提升约为72%,对范围查 Range Select 带来的提升为19%。
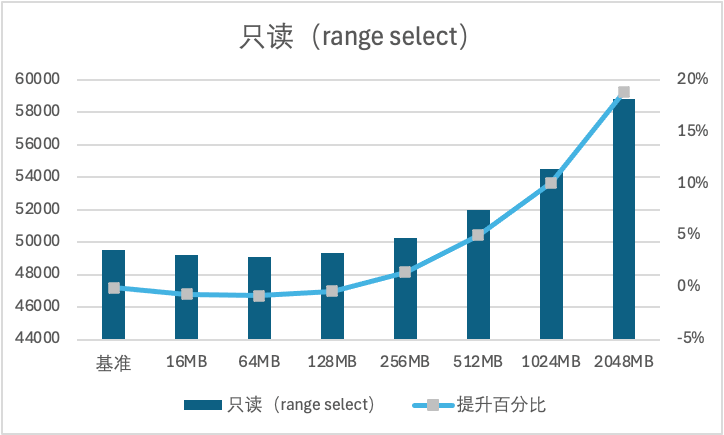
文档反馈

