Configuring Shared Subscription
Last updated:2026-01-30 14:55:29
Shared subscription is a load-balancing consumption method. Multiple clients belonging to the same shared subscription group distribute and receive subscribed messages in a round-robin manner. Therefore, it is commonly referred to as consumer load balancing.
As shown in the figure below, the publisher has published 4 messages: M1, M2, M3, M4. Clients Client-0 and Client-1 consume the subscribed topic messages in a shared subscription manner. This is different from the default MQTT Pub/Sub. Client-0 only consumed M1 and M3; Client-1 only consumed M2 and M4.
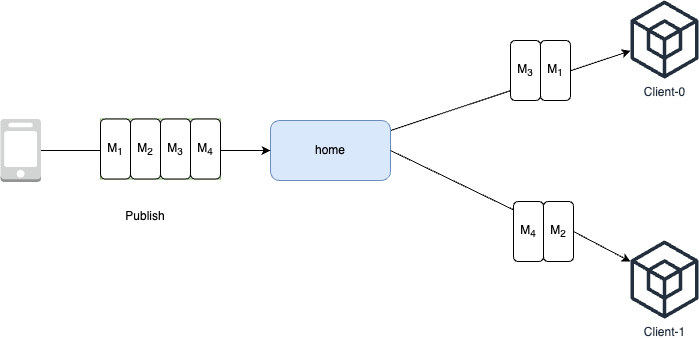
In the standard MQTT protocol, Shared Subscription (Shared Subscription) is a new feature added in MQTT 5.0. However, Tencent Cloud Message Queue MQTT Edition has enhanced this feature on the server-side. In addition to clients of version 5.0, it also supports clients of versions 3.1 and 3.1.1. Clients of versions 3.1 and 3.1.1 can directly subscribe according to the usage specifications of Shared Subscription.
Before using shared subscription, you need to first create a shared subscription group on the page (ShareName); otherwise, the client will fail to subscribe.
Restrictions and Limitations
A single cluster supports a maximum of 20 shared subscription groups. Each shared subscription group allows up to 10 subscription expressions. The aggregate TPS limit for subscription and unsubscription requests per shared subscription group is 10. A single shared subscription group can accommodate up to 1,024 clients. When these limits are reached, client subscription requests (SUBSCRIBE) will return errors. For Platinum Edition clusters requiring special quota adjustments, you may submit a ticket to contact us for assistance.
Prerequisites
Using Shared Subscription to Subscribe to Messages
Step 1: Create a Shared Subscription Group
1. Log in to the MQTT Console.
2. Click Resource > Cluster in the left sidebar. After selecting a region, click the "ID" of the target cluster to enter the cluster basic information page.
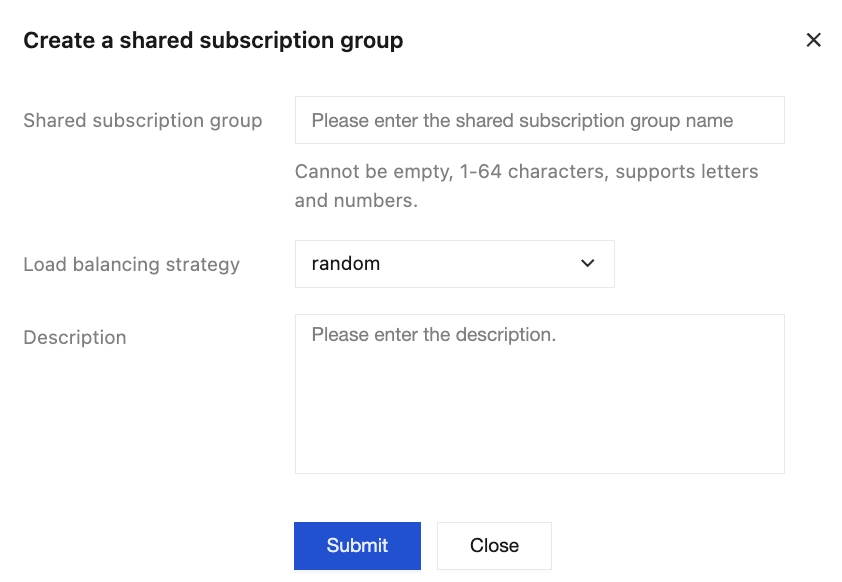
3. Select the Shared Subscription Group tab, click Create to create a shared subscription group, and fill in the following fields in the pop-up window as required:
Parameter Items | Description | Example Value |
Shared subscription group | The shared subscription group name must comply with the naming rules: it cannot be empty, must be 1-64 characters long, and support letters and numbers. | order_processing_group |
Load balancing strategy | ○ Random (default policy, that is, random): Distributes the load randomly among subscribed clients. ○ Partition hash: To some extent, it ensures message order during message distribution. When this mode is selected, you need to additionally specify the time for load balancing to take effect. That is, after a new consumer client joins, it will be added to the load balancing policy only after the specified delay. (The current default implementation is Topic-hash, which prioritizes message order under the same Topic in shared subscriptions. If you require ClientID-hash, please submit a ticket to contact us.) | Random |
Description | Enter the description for the shared subscription group (optional). | Order processing for multiple client loads |
4. Click Submit to complete the creation.
Step 2: Configure Shared Subscription in the Client
Usage Method
When you want to subscribe to messages in shared subscription mode, configure the topic-filter as follows:
$share/{ShareName}/{TopicFilter}
Parameter | Description |
$share | The token specified by the protocol for shared subscription usage, which is a fixed string. |
{ShareName} | The name of a shared subscription group created in the console must not contain " / ", " + ", " # ". |
{TopicFilter} | The Topic Filter used by clients for normal subscriptions has the same requirements and semantics as MQTT TopicFilter requirements. |
Sample Code
package org.apache.rocketmq.mqtt.example.quickstart;import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.IMqttDeliveryToken;import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttCallback;import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttClient;import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttConnectOptions;import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttException;import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.MqttMessage;import org.eclipse.paho.client.mqttv3.persist.MemoryPersistence;public class SharedSubscriptionQuickStart {public static void main(String[] args) throws MqttException, InterruptedException {String serverUri = "tcp://127.0.0.1:1883";String clientId = "shared-sub-0";try (MqttClient client = new MqttClient(serverUri, clientId, new MemoryPersistence())) {client.setTimeToWait(3000);MqttConnectOptions options = new MqttConnectOptions();options.setUserName("YOUR-USERNAME");options.setPassword("YOUR-PASSWORD".toCharArray());options.setCleanSession(true);options.setAutomaticReconnect(true);client.connect(options);int total = 1;CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(total);client.setCallback(new MqttCallback() {public void messageArrived(String topic, MqttMessage message) {System.out.printf("Message arrived, topic=%s, QoS=%d content=[%s]%n", topic, message.getQos(),new String(message.getPayload()));latch.countDown();}public void connectionLost(Throwable cause) {System.out.println("connectionLost: " + cause.getMessage());}public void deliveryComplete(IMqttDeliveryToken token) {System.out.println("deliveryComplete: " + token.isComplete());}});// Shared subscription expression// {ShareName} here is Group0// {topic-filter} is home/#String topic = "$share/Group0/home/#";// Subscribeclient.subscribe(topic, 1);TimeUnit.HOURS.sleep(1);client.disconnect();}}}
Shared Subscription Offline Message Retention Policy
If there is an active Session subscription ${TopicFilter} under ${ShareName}, offline messages matching ${TopicFilter} will be retained. When subscribers reconnect, they will resume consumption from the last position.
Session Validity Period
MQTT 3.1 and 3.1.1 define the Session lifecycle through clean-Session. When clean-Session = true, the Session lifecycle aligns with the transport layer lifecycle. When clean-Session = false, the Session is independent of the transport layer lifecycle. To avoid resource wastage, the product defines that after transport layer disconnection, the maximum Session retention period is 3 days.
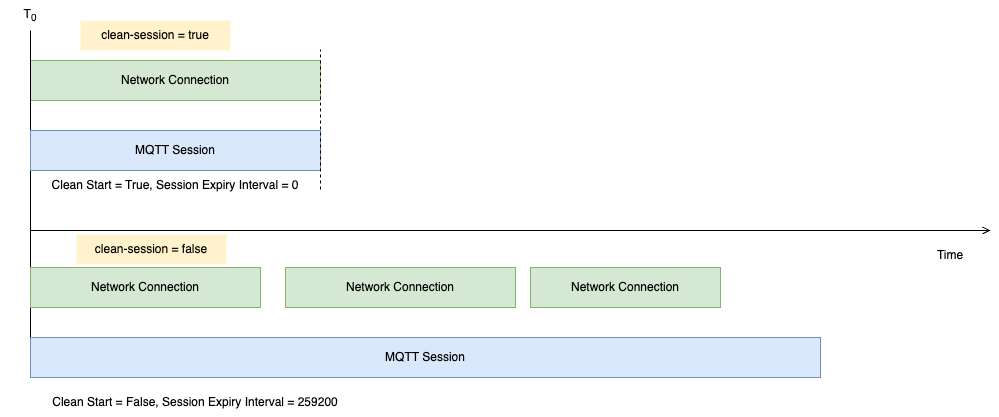
As defined by the MQTT 5.0 protocol, the following semantics are equivalent:
MQTT 3.1,3.1.1 | MQTT 5 | |
clean-session = true | clean-start = true | session-expiry-interval = 0 |
clean-session = false | clean-start = false | session-expiry-interval = 259200 |
View Shared Subscription Group
1. Log in to the MQTT Console.
2. Click Resource > Cluster in the left sidebar. After selecting a region, click the "ID" of the target cluster to enter the cluster basic information page.
3. Select the Shared Subscription Management tab to view and manage the list of shared subscription groups (ShareName) in the current cluster.
Note:
To facilitate customer usage, the list page automatically displays existing shared subscription groups in the current cluster. If a client uses
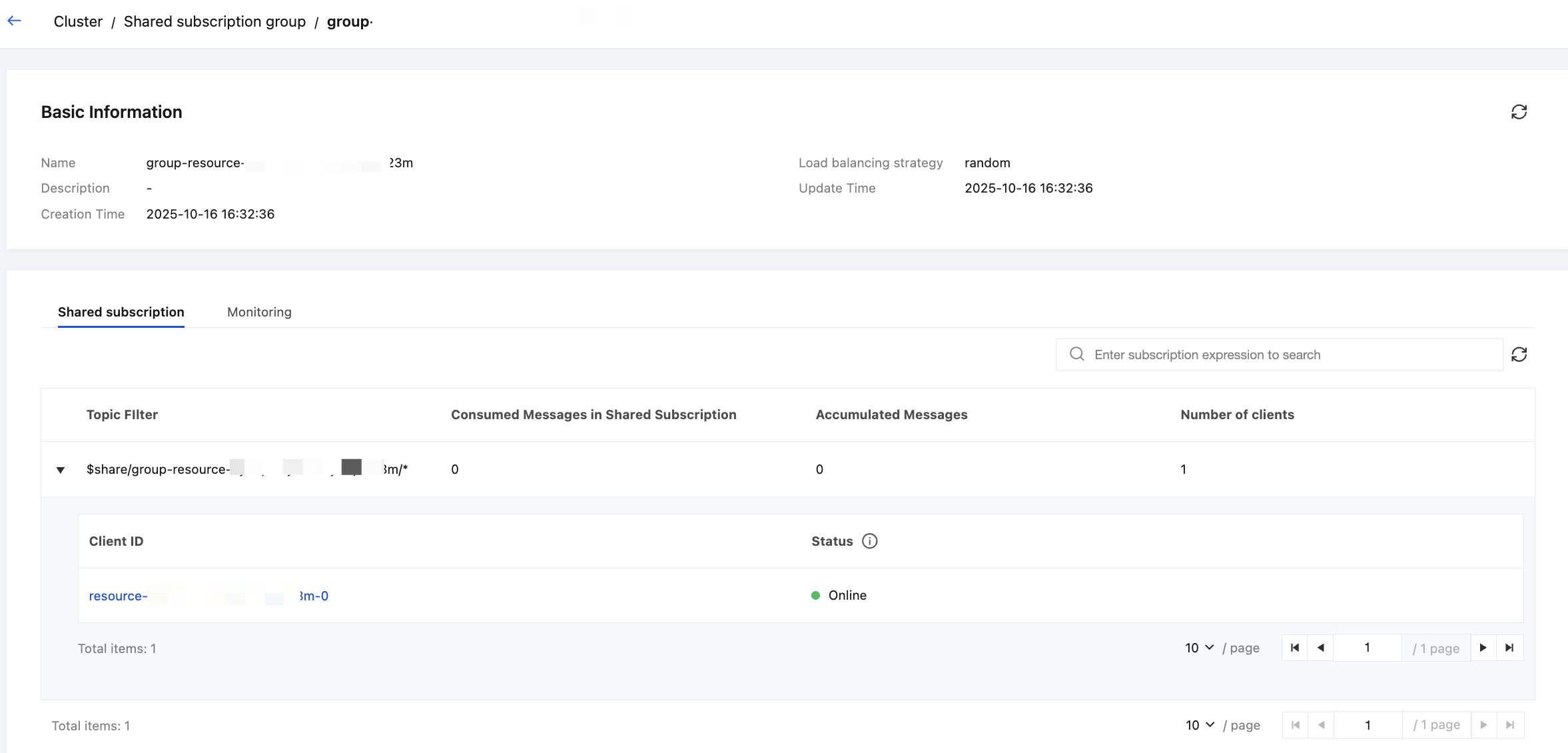
$share/{ShareName}/{topicfilter} for shared subscription, the ShareName will automatically appear in the shared subscription group list, with the default load balancing policy set to random policy.4. Click the specific subscription group name to enter and view the details of the shared subscription group, as shown below. The details page shows the current subscription details, the subscription expression (filter) under the current subscription group (ShareName), and the corresponding clients and client status under the filter when expanded.
Note:
When ensuring is performed for the sequentiality of shared subscription message loads, that is, when the load balancing mode is set to "partitioned hash", the online status of clients will be affected by load balancing delays. If the client session no longer exists, it will still be displayed as "online" as long as it is within the load balancing effective period. Once the client disconnection time exceeds the load balancing effective delay, it will be displayed as "offline".
Edit Shared Subscription
To avoid issues such as message duplication or loss of sequentiality during policy transitions, the shared subscription group name and load balancing policy cannot be modified after creation. If you need to change the load balancing policy for a shared subscription group, pause client operations, delete the existing group, and recreate a new shared subscription group with a different load balancing policy.
1. Log in to the MQTT Console.
2. Click Resource > Cluster in the left sidebar. After selecting a region, click the "ID" of the target cluster to enter the cluster basic information page.
3. Select the Shared Subscription Management tab to view and manage the list of shared subscription groups (ShareName) in the current cluster.
4. In the Operation column of the shared subscription group list, click Edit to modify the shared subscription group information.
If the load balancing policy is "random", you can only modify the description part.
If the load balancing policy is "hash partitioning", you can modify the description and effective time.
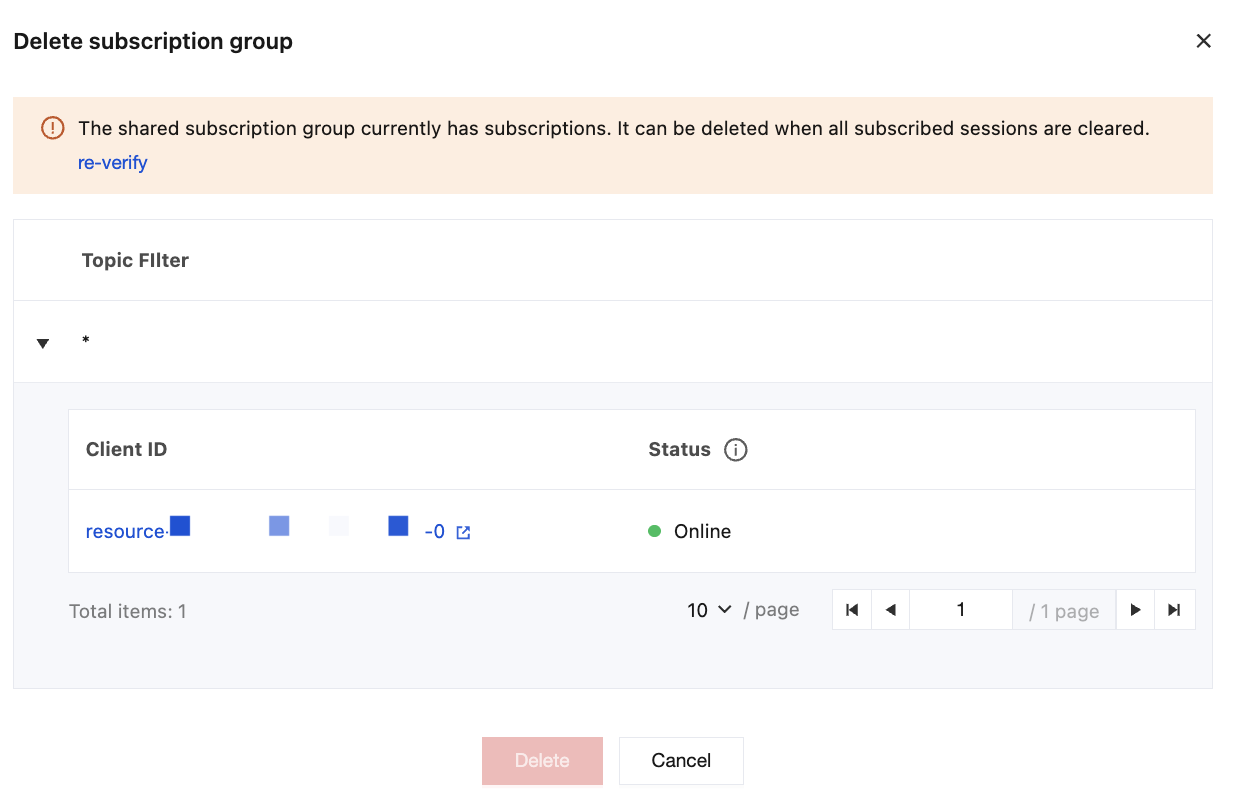
Delete Shared Subscription Group
When a shared subscription group is deleted, carefully evaluate its impact on online services. MQTT verifies whether active subscriptions exist in the shared subscription group. To avoid unexpected service interruption, it is recommended to ensure all relevant client sessions are disconnected before the deletion is performed.
1. Log in to the MQTT Console.
2. Click Resource > Cluster in the left sidebar. After selecting a region, click the "ID" of the target cluster to enter the cluster basic information page.
3. Select the Shared Subscription Management tab to view and manage the list of shared subscription groups (ShareName) in the current cluster.
4. In the operation column of the shared subscription group list, click Delete, then confirm the deletion in the pop-up window to complete the deletion.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

