Step 4: Configuring Client Certificate
Last updated:2026-01-30 14:55:29
A client certificate is a digital certificate issued by a CA certificate to a client device. When a connection is established with the server, the server performs security verification on the client's identity based on the client certificate. After successful verification, both parties can achieve secure communication using the built-in encryption key in the certificate. If verification fails, the server will reject the client's connection request.
Restrictions and Limitations
The maximum number of client certificate signups per second is 15, and any requests exceeding this limit will be rejected.
Prerequisites
Register client certificate
Client certificates support two registration methods: Manual Registration and Automatic Registration. The registration method is specified when one-device-one-certificate is enabled. For specific steps, see Step 1: Enable One-Device-One-Certificate.
Automatic Client Certificate Registration
If automatic client registration is selected, when the client connects to the server, the server will check whether the CA certificate associated with the client certificate has been registered. If the corresponding CA certificate is not registered, authentication fails and the client connection will be rejected.
If the corresponding CA certificate is registered, authentication is passed, and the client certificate will be automatically registered and appear on the Client Certificate Management page.
Manual Client Certificate Registration
Step 1: Use CA Certificate to Generate Client Certificate
The following uses the RSA algorithm as an example to briefly describe how to generate server or client certificates using a CA certificate.
If you use a self-signed CA certificate to generate client certificates, you can follow the instructions below to generate them.
1. Create a file named
client.csr.cfg, and modify the file content according to the actual situation.[req]default_bits = 2048prompt = nodefault_md = sha256distinguished_name = dn[dn]C=CNST=SHXXXL=SHO=TXOU=MQTTemailAddress=xxx@xxxCN=client-test
2. Create a file named
client.crt.cfg with the following content:authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuerbasicConstraints=CA:FALSEkeyUsage = digitalSignature, nonRepudiation, keyEncipherment, dataEncipherment, keyCertSign
3. Generate the client certificate private key and the Certificate Signing Request (CSR) file for the verification certificate.
openssl req -new -sha256 -nodes -out client.csr -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout client.key -config <(cat client.csr.cfg)
openssl req -new -sha256 -nodes -out client.csr -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout client.key -config client.csr.cfg
4. Generate a client certificate.
openssl x509 -req -in client.csr -CA CA.crt -CAkey CA.key -CAcreateserial -out client.crt -days 500 -sha256 -extfile client.crt.cfg
Step 2: Register Client Certificate
1. Log in to the MQTT Console.
2. Click Resource > Cluster in the left sidebar. After selecting a region, click the "ID" of the cluster for which you want to configure a certificate, and enter the basic information page of the cluster.
3. Go to the Client Certificate page, click Register Client Certificate. Fill in the client certificate information in the following pop-up window:
Source: Manually registered.
CA Certificate: Select a registered CA certificate.
Client Certificate: Upload the issued client certificate according to the file format requirements.
Client ID: A supplementary field in the "one-device-one-certificate" scenario, which is optional. You can fill it according to your actual scenario. If the client id passed during client connection is empty, this field will be considered as the client id. If both the client id and this field are empty, the server will use the Common Name field of the client certificate. Therefore, if the client does not pass a client id, please ensure this field does not have duplicate values.
Whether to activate: Indicates the activation status of the client certificate after registration. It is enabled by default. You can also manually enable it in the console after registration is completed.
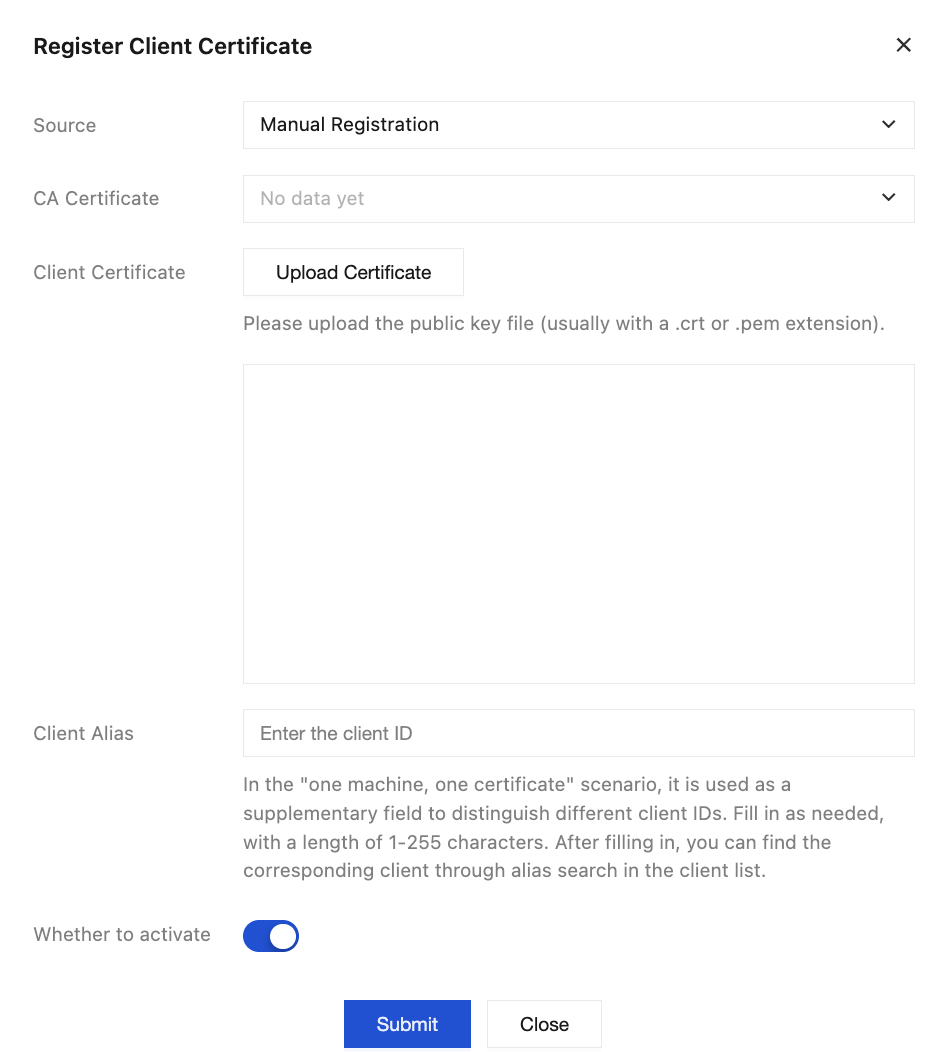
4. Click Submit to complete the client certificate registration.
Manage Client Certificate
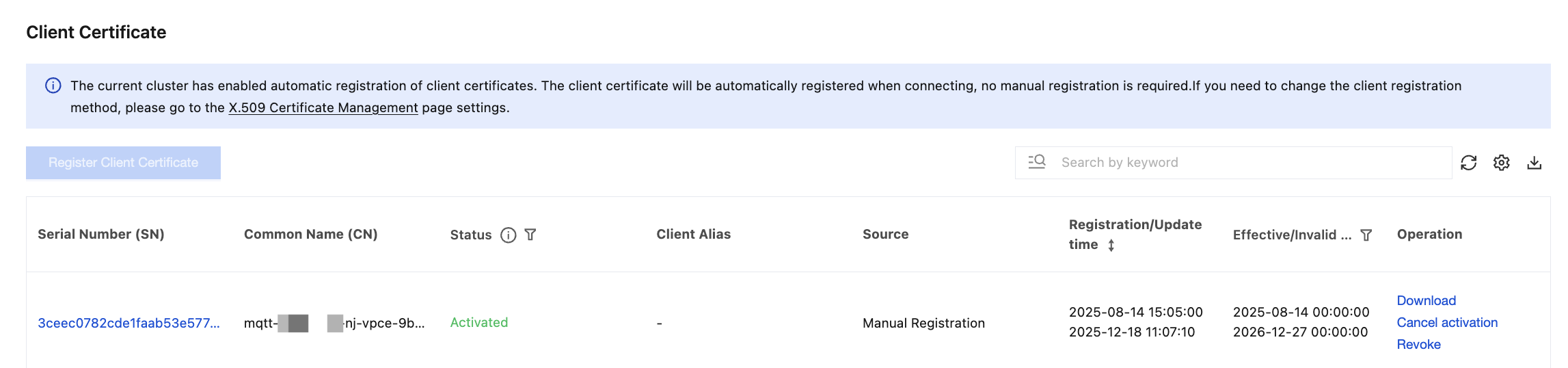
After the client certificate is registered, you can view the status of registered certificates on the client certificate list page. Client certificates have four statuses: Activated, Not activated, Registered but not activated, and Revoked.
Operation | Operation path | Description |
Filter by Effective/Expiration Time | Click the  | Filter expired and expiring client certificates (expiring within 30 days). |
Deactivating Certificates | Click Cancel activation in the operation bar. | After a certificate is deactivated, clients using that certificate will be rejected during connection. Therefore, special attention is required regarding the impact on client connections when the certificate status is changed. |
Deleting Certificates | Click More > Delete in the operation bar. | Certificates in the "Activated" state cannot be deleted. Only certificates in the "Not activated" or "Revoked" state can be deleted. |
Revoking Certificates | Click More > Revoke in the operation bar. | Once a client certificate is revoked, it cannot be reactivated. After the certificate status changes, there is a minute-level delay before the new status takes actual effect. |
View Certificate Details | Click the serial number of the certificate. | On the certificate details page, the following information of the certificate is displayed: Basic Information: Displays the status, Common Name, Serial Number, and other details of the certificate. Associated Clients: Displays the list of clients associated with the current certificate. |
The search box on the client certificate list page supports filtering by multiple resource attributes and combinations of attributes, including: Certificate Serial Number (SN), Certificate Organizational Unit (OU), Certificate Common Name (CN), Certificate Status, and Effective/Expiration Time.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

