LogListener New Architecture Installation and Upgrade Guide
Last updated:2025-11-13 16:49:51
LogListener New Architecture Installation and Upgrade Guide
Last updated: 2025-11-13 16:49:51
This documentation introduction covers the installation and upgrade method of LogListener new architecture (version≥3.4.0). All operations are uniformly passed through the loglistener_operator script. Currently only support Linux version.
Preparations
Download the loglistener_operator script first.
private network download address:
wget https://mirrors.tencentyun.com/install/cls/script/loglistener/loglistener_operator && chmod u+x loglistener_operator
public network download address:
wget https://mirrors.tencent.com/install/cls/script/loglistener/loglistener_operator && chmod u+x loglistener_operator
Operation Steps
Step 1: Install LogListener
Execute the script as the root user. The command is as follows:
./loglistener_operator install -s ${secret_id} -k ${secret_key} -r ${region}
./loglistener_operator install -s ${secret_id} -k ${secret_key} -r ${region} --version ${version}
Note:
The script supports only packages of version 3.4.0 or later.
./loglistener_operator install -s ${secret_id} -k ${secret_key} -r ${region} --package_path ${package_path}
./loglistener_operator install -s ${secret_id} -k ${secret_key} -r ${region} --url https://xxx.tar.gz
Note:
In the installation command, -secret_id, -secret_key, and -region are required parameters. For more other parameters, see the following parameter description.
If the root account has granted read/write permissions for the CLS to the collaborator, it is recommended to use the collaborator's key.
-Note: The --region parameter specifies the location of your CLS, not the location of your business machine. When the CLS region is inconsistent with your business machine's region, configure the additional parameter -network as internet to represent public network access.
When the Cloud Virtual Machine (CVM) and the logset are in the same region, it is recommended to access the service domain name via the private network. Conversely, if they are located in different regions, it is recommended to access the service domain name via the public network.
For details on log collection permissions, see LogListener Log Collection Permissions.
After installation, the results are shown below.
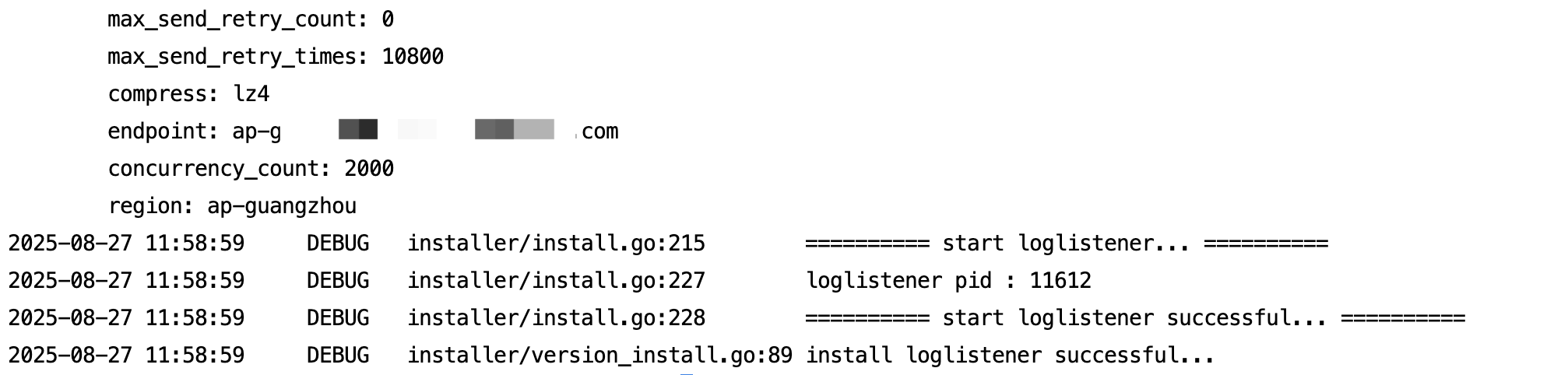
Parameter Description
Parameter Name | Required or Not | Description |
-s | Yes | Part of the Cloud API Key, which is used to identify the API caller. Ensure that the account associated with the Cloud API key has the appropriate LogListener log collection permission. |
-k | Yes | Part of the Cloud API Key, which is used to encrypt signature strings and the server-side verification key for signature strings. Please ensure the associated account of the cloud API key has appropriate LogListener Log Collection Permissions. |
-n | No | Indicates the method LogListener uses to access the service domain. Valid values: internal (private network access, default), internet (public network access). Private network access: Applicable to Tencent Cloud servers located in the same region as the machine group. Public network access: Applicable to non-Tencent Cloud servers or to servers located in regions that do not match those of the machine group. |
-r | Yes | region indicates the region where the CLS is deployed. Enter the appropriate domain name abbreviation, such as ap-beijing or ap-guangzhou. Note: Note: When the CLS region is inconsistent with your business machine's region, configure the parameter network as internet to represent public network access. |
-d | No | The domain name representing the CLS region. For example, ap-beijing.cls.tencentyun.com, ap-guangzhou.cls.tencentyun.com. Note: When the CLS service area is inconsistent with your business machine region, configure the public network domain name. For example, ap-beijing.cls.tencentcs.com. |
-i | No | The IP address of the machine. The machine group can be associated with the machine using the configured IP address. For details, see Machine Group. If not specified, LogListener will automatically obtain the local IP address. |
-l | No | Machine ID. Once entered, the machine will be associated with the machine group also having the filled machine identification. For details, see Machine Group. Multiple identifiers separated by commas. Note: If a machine label is configured, the machine can only be associated with the machine group using the machine label instead of the IP address; if not configured, the machine group can only be associated with the machine using the IP address. |
-p | No | Port, default 80. |
-u | No | Do not upload machine identification to CLS by default. |
--base_dir | No | LogListener installation path, default installation under the /opt directory. |
--package_path | No | Specify the local package path when installing with a local package. |
--url | No | Specify URL during installation, specify mirrors domain names or IP addresses. |
--version | No | Install specified version number, default to latest version. |
Note:
More details are available with
./loglistener_operator install --help.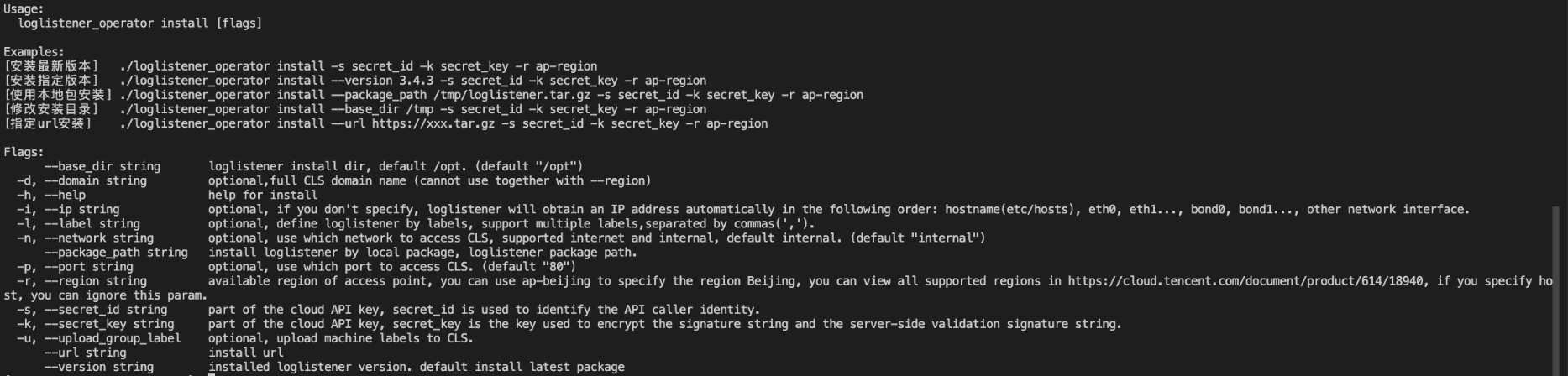
Step 2: Start LogListener
systemctl start loglistener
Run
systemctl check loglistener to check if startup is successful.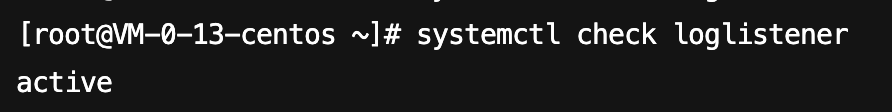
Step 3: Adding to Machine Group
After completing LogListener installation and startup, you need to create or select an existing machine group in the CLS console and add the server to the machine group. You can add the server to the machine group in the following two ways:
Step 4: Collect Logs
After the server is added to the machine group, you can configure text log collection on the server.
Common LogListener Operations
Note:
This document example's operating command description is applicable only to LogListener-3.4.0 and above versions.
Viewing LogListener Versions
In the LogListener installation directory (default installation directory
/opt/loglistener), run the following command to view the version../loglistener -v
View LogListener help document
In the LogListener installation directory (default installation directory
/opt/loglistener), run the following command to view help../loglistener -h
Stopping LogListener
systemctl stop loglistener
Restarting LogListener
systemctl restart loglistener
Run
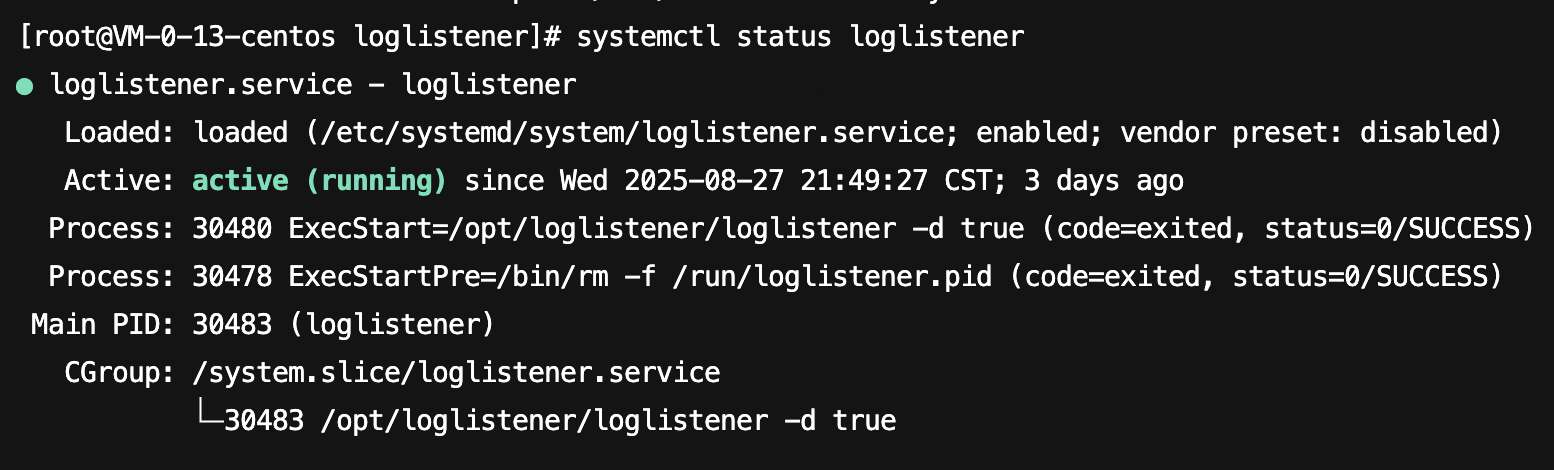
systemctl check loglistener to check whether the restart is successful.Check the process status of LogListener
systemctl status loglistener
Checking the Heartbeat and Configuration Of LogListener
systemctl check loglistener
Uninstalling LogListener
1. Use the stop command
systemctl stop loglistener to stop running the previous version of LogListener.systemctl stop loglistene
2. In the LogListener installation directory (default installation directory
/opt/loglistener), run the uninstallation command with administrator privileges in the path /opt/loglistener/tools:./loglistener_operator uninstall
Manually Upgrading LogListener
Reusing Breakpoint File (No Log Collection Duplication)
1. Use the stop command
systemctl stop loglistener to stop running the previous version of LogListener.2. Take the installation directory
/opt/loglistener as an example, go to the installation directory and backup the checkpoint file directory ./data in the old version. For example, backup the old version of checkpoint file to /tmp/loglistener-backup.cp -r ./data /tmp/loglistener-backup/
3. Use the uninstall command
./loglistener_operator uninstall to uninstall the old version of LogListener.4. Download and install the latest version of LogListener again.
5. Take the installation directory
/opt/loglistener, copy the backup checkpoint file directory (procedure 2) to the new version of LogListener directory.cp -r /tmp/loglistener-backup/data ./
6. Use the start command
systemctl start loglistener to start running the new version of LogListener.Not Reusing Checkpoint Files (Possibly Duplicate Acquisition Logs)
1. Use the stop command
systemctl stop loglistener to stop running the previous version of LogListener.2. Use
./loglistener_operator uninstall to uninstall the old version of LogListener.3. Download and install the latest version of LogListener again.
4. Use the start command
systemctl start loglistener to start running the new version of LogListener.Upgrade to the New Architecture LogListener
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

