Configuring Custom SSL Certificates
Last updated:2026-01-20 16:52:40
When the security protocol of CKafka is set to SASL_SSL, SSL certificates will be used to encrypt data during transmission between the client and the CKafka instance, preventing data from being intercepted or eavesdropped on during network transmission and thereby enhancing data security.
By default, SSL certificates are provided by the server. You can also use custom certificates. This document describes how to configure custom certificates.
Constraints and Limitations
1. Only Pro Edition instances support using SASL_SSL access points and configuring custom SSL certificates.
2. Encryption algorithm of custom certificates.
Currently, only certificates with the following encryption algorithms are supported.
RSA | | ECC | |
2048 | 4096 | prime256v1 | secp384r1 |
3. Only one-way authentication certificates are supported.
Only one-way authentication certificates are supported, and two-way authentication certificates are not supported.
4. Replacement of expiring custom certificates.
It is recommended that you select certificates with a long validity period. Currently, replacing custom certificates through a productized approach is not supported. If needed, contact us through after-sales channels.
5. Domain name verification.
Domain name verification for custom certificates is not supported. Clients are required to disable domain name verification.
Step 1: Preparing an SSL Certificate
CKafka supports loading certificates managed in SSL Certificates. First, complete the management of a self-signed certificate or purchase a certificate in the SSL Certificates console. For specific steps, see Getting Started with SSL Certificates.
Step 2: Configuring a Custom SSL Certificate
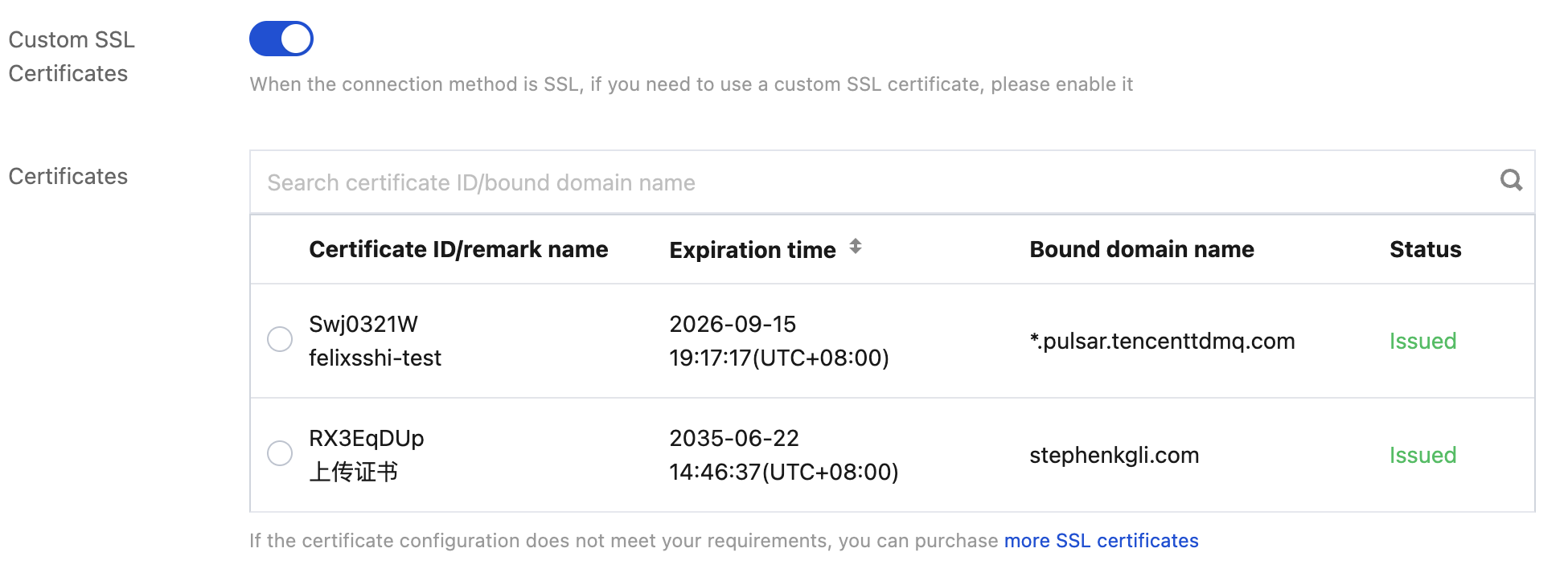
When purchasing a Pro Edition instance, enable Custom SSL Certificate Customization and select the appropriate certificate. You can only select certificates in the Issued status. For specific steps on purchasing a cluster, see Creating an Instance.
Step 3: Enabling an SASL_SSL Access Point
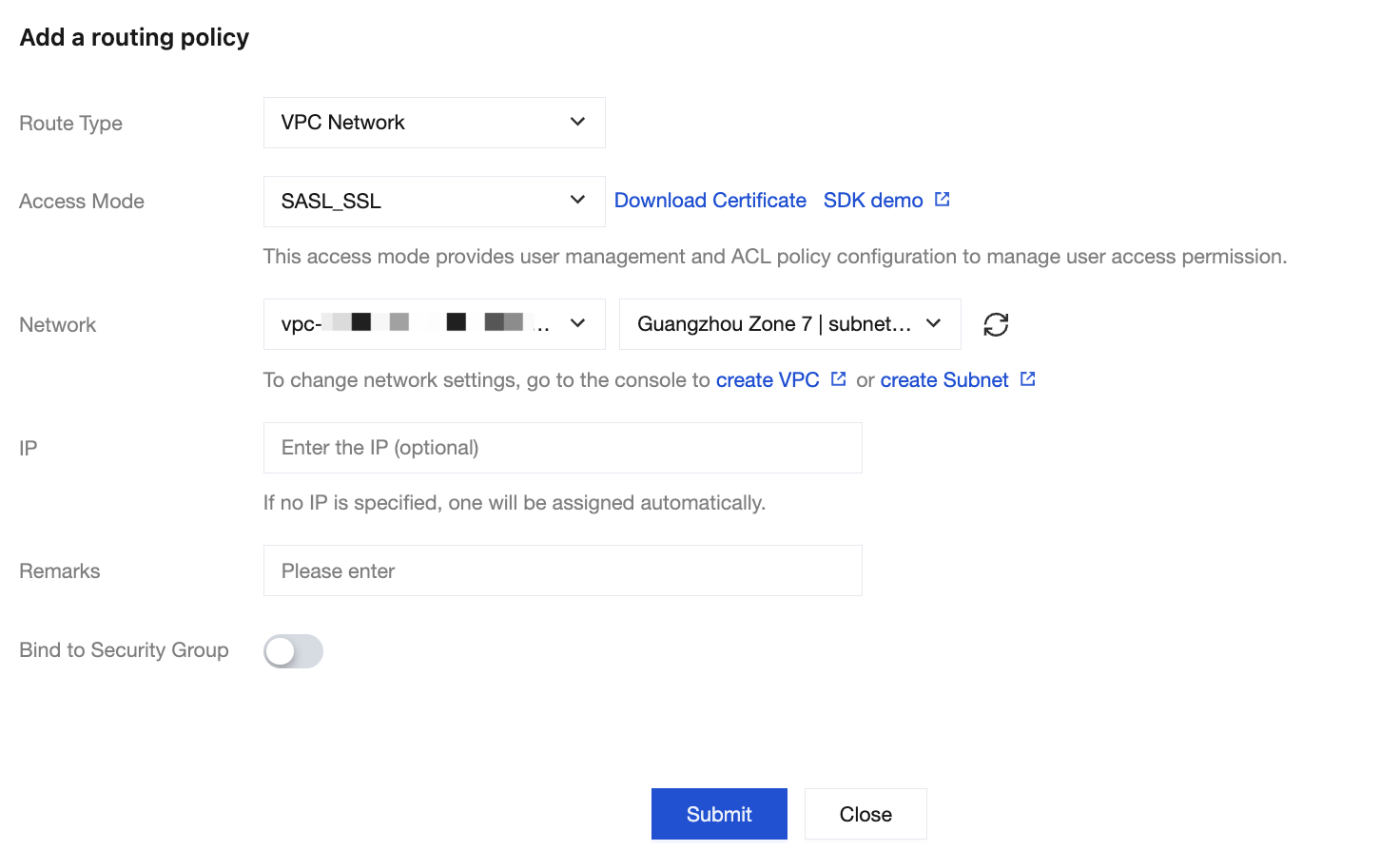
When adding a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) network or public network routing policy, set the access method to SASL_SSL. For specific steps, see Configuring VPC and Configuring Public Network Access.
Step 4: Using a Client to Send and Receive Messages
The way in which a client loads certificates remains unchanged. For specific usage, see Access Through SASL_SSL.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

