Configuring VPC
Last updated:2026-01-20 16:52:40
Scenarios
When purchasing a cluster, if you select Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and specify a particular VPC (such as VPC A) network, only resources within that VPC network can access the TDMQ for CKafka (CKafka) service (including producing/consuming data, and more) by default. If other VPC networks (such as VPC B) need to access the CKafka service later, you can enable this by configuring VPC network routing policies for the CKafka cluster to bind VPC B to the CKafka service.
To ensure secure access, two permission control methods, namely security groups and access control list (ACL) policy configuration, are supported in CKafka. This provides dual protection for user access control during private network transmission, enhancing control over production and consumption permissions of such resources as topics.
Security group binding: It is used to configure network access control for instances, managing inbound and outbound traffic at the instance level. For specific operations, see Binding a Security Group for VPC Access.
ACL policy configuration: It manages user access permissions via the native ACL mechanism of Kafka. For specific operations, see Configuring Topic Read/Write Permissions.
Constraints and Limitations
Up to 5 routes can be created for one instance, among which there is one and can only be one public network route.
There is one and can only be one route for using the SASL_PLAINTEXT access method. For example, if the SASL_PLAINTEXT access method is selected for public domain name access, you cannot select the SASL_PLAINTEXT access method again when creating a VPC route.
Only in the Pro Edition instances, it is supported to specify IP addresses when adding VPC routing policies.
Prerequisites
The available VPC network and subnet have been prepared in advance. For specific steps to create a VPC network and a subnet, see Creating a VPC Network and Subnet.
Adding a VPC Routing Policy
1. Log in to the CKafka console.
2. In the left sidebar, click Instance List, and click ID/Name of the target instance to go to the basic information page.
3. On the basic instance information page, click Add a routing policy in the Access Method module.
4. In the pop-up window, select VPC Network as the route type, and then select the access method, network, and whether to bind a security group.
Parameter | Required | Description |
Routing Type | Yes | Select a VPC network. |
Access Mode | Yes | Multiple security authentication mechanisms are provided. You can select an appropriate authentication method based on your actual business requirements. For specific feature differences and use limits, see Network Connection Instructions. If the access method is set to PLAINTEXT, clients are allowed to connect to the CKafka instance without authentication. If the access method is set to SASL_XXX, authentication is performed using SASL, and clients are allowed to connect to the CKafka instance only after passing authentication. |
Network | Yes | Select the pre-configured VPC network and subnet in the same region from the drop-down list. |
IP | No | When selecting VPC network access, you can specify an IP address to keep it unchanged when changing the access method. If no IP address is specified, the system will assign one automatically. IP addresses ending with ".1" or ".255" are not allowed, as they are typically the subnet's default gateway and broadcast address, respectively. |
Bind to Security Group | No | A security group is a virtual firewall that can filter the stateful data packets and set network access control for instances to control inbound and outbound traffic at the instance level. Currently, only the Pro Edition CKafka instances support binding security groups. |
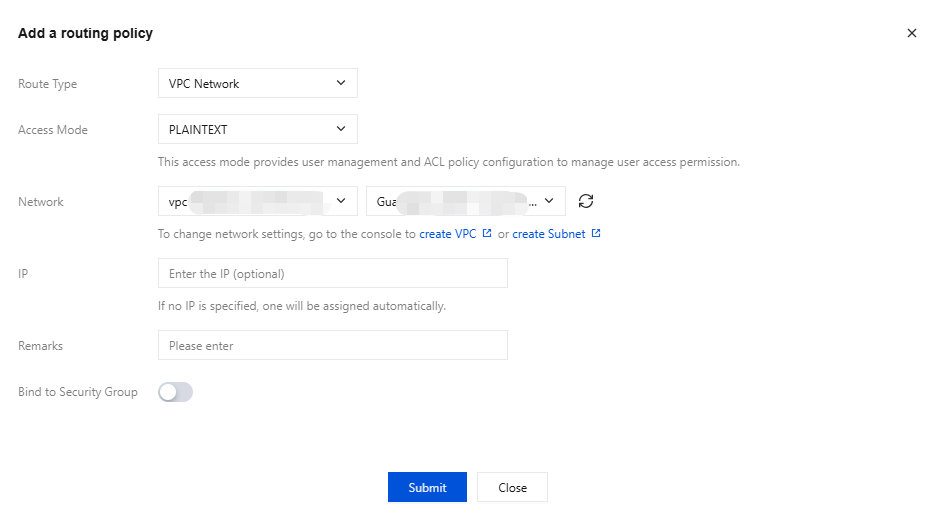
5. Click Submit to complete the addition of the VPC network. In the Network column, you can view information about the access point for connecting to a cluster for message production and consumption.
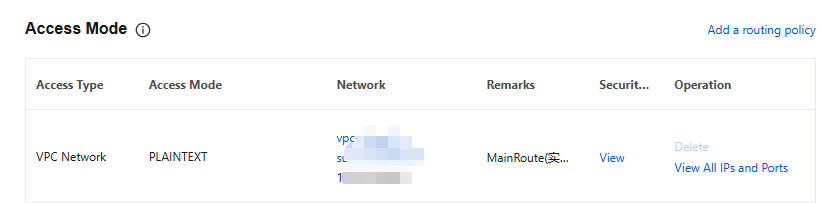
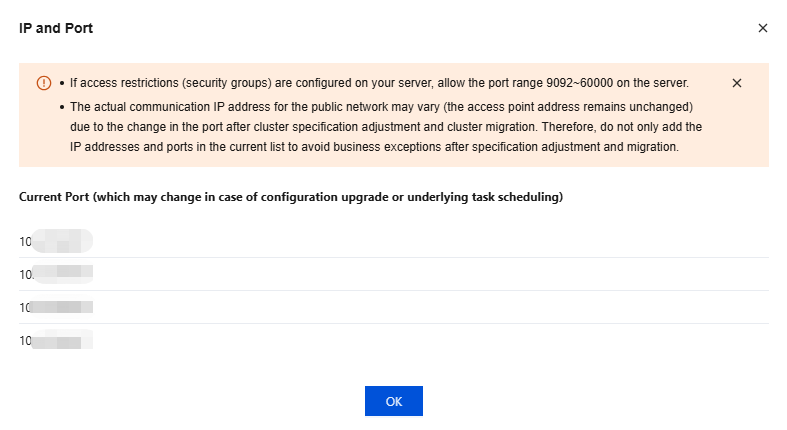
6. In the Operation column, click View All IPs and Ports to view the list of IP addresses and ports that need to be allowed.
Note:
If your server has access restrictions (security group) configured, allow a port range of 50000–53000 on the server. Since ports may change after cluster configuration changes or migrations, do not only add the current list of IP addresses and ports to avoid service exceptions after configuration changes or migrations.
Binding a Security Group for VPC Access
A security group is a virtual firewall that can filter the stateful data packets and set network access control for instances to control inbound and outbound traffic at the instance level. They serve as an important means of network security isolation. Currently, only the Pro Edition CKafka instances support binding security groups.
Security Group Features
A security group is a logical grouping. You can add instances such as CKafka, Cloud Virtual Machine (CVM), and TencentDB that require the same network security isolation within the same region to the same security group.
By binding security groups to instances and configuring ACL policies, CKafka provides dual protection for user access control during private network transmission, enhancing control over production and consumption permissions of such resources as topics.
Binding Instructions
You can add instances with the same protection requirements to a single security group, without needing to configure a separate security group for each instance.
It is not recommended to bind an excessive number of security groups to a single instance, as conflicting rules across different security groups may cause network disconnection.
Binding Method
1. After an instance is created, you can configure VPC route access in the console. When adding a routing policy, you can enable the Binding Security Group button to bind a security group.
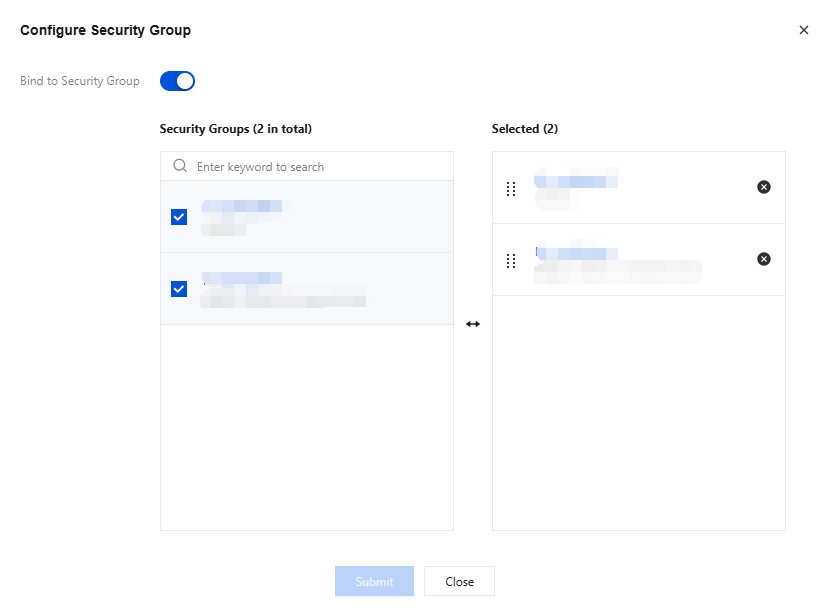
2. After clicking Submit, in access methods of the console, you can click View in the Security Group column to view the security groups bound to the corresponding VPC access point.
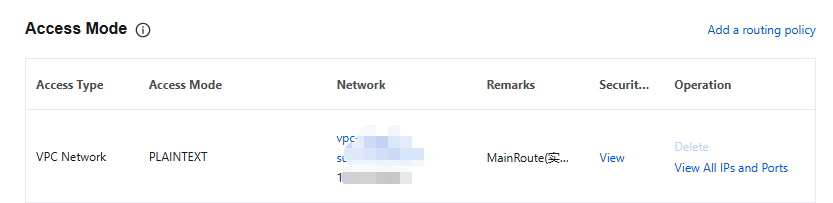
3. Click Configure Security Group in the upper-right corner to modify the bound security groups.
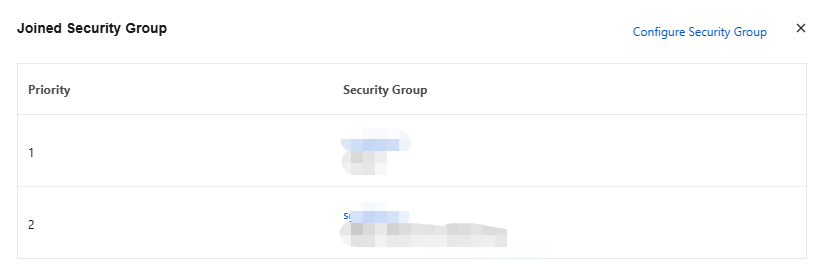
Rule Priority
Rules within a security group have priorities. Rule priority decreases sequentially from top to bottom in a list, meaning the rule at the top of the list has the highest priority and is matched first, while the rule at the bottom has the lowest priority and is matched last.
If a rule conflict occurs, the rule positioned higher is matched by default.
When inbound/outbound traffic passes through an instance bound to a security group, the system will match rules from the top to the bottom of the rule list for the security group. If a rule is matched successfully and allows the traffic to pass, no subsequent rules will be matched.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

