SASL_SSL Access in the Public Network
Last updated:2026-01-05 15:16:58
Overview
This document uses the Java client as an example to describe how to access TDMQ for CKafka (CKafka) in the public network by using the SASL_SSL method and send and receive messages.
The core feature of SSL certificates is to protect the communication security between servers and clients. Encrypted by SSL certificates, data can be unlocked only by the intended servers, but not by any others without the private keys.
Prerequisites
Operation Steps
Step 1: Configuring the Console
1. Create an access point.
1.1 On the Instance List page, click the target instance ID to go to the instance details page.
1.2 Choose Basic Infor > Access Method, and click Add a routing policy. In the pop-up window, choose
Routing Type: Public Network Domain Name Access > Access Method: SASL_SSL.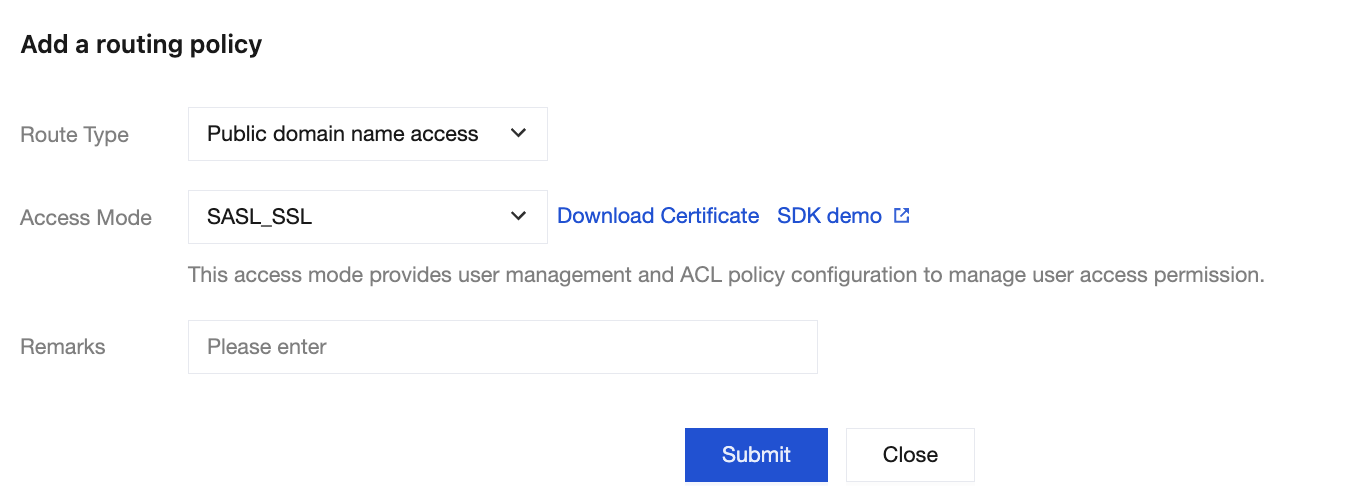
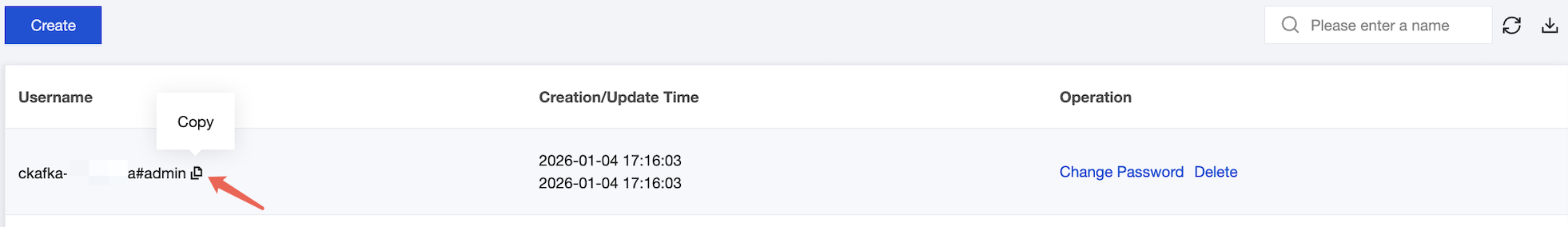
2. Create a role.
Choose ACL Policy Management > User Management. On the displayed page, create a role and set the password.
3. Create a Topic.
On the Topic List page in the console, create a topic (see Creating a Topic).
4. Configure the ACL policy.
Configure the topic read/write permissions for the created role by seeing Configuring Topic Read/Write Permissions.
Step 2: Adding the Configuration File
1. Add the following dependencies to pom.xml.
<dependencies><dependency><groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId><artifactId>kafka-clients</artifactId><version>2.1.0</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.slf4j</groupId><artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId><version>1.7.5</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.slf4j</groupId><artifactId>slf4j-simple</artifactId><version>1.6.4</version></dependency></dependencies>
2. Create the JAAS configuration file
ckafka_client_jaas.conf. Choose ACL Policy Management > User Management to create a user and modify the file as the user.KafkaClient {org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule requiredusername="yourinstance#yourusername"password="yourpassword";};
Note
Username is in the format of
instance ID + # + configured username, and password is the configured user password.3. Create the TDMQ for CKafka (CKafka) configuration file kafka.properties.
## Configure the access network and copy the network information from the Network column of the Access Method module on the instance details page in the console.bootstrap.servers=ckafka-xxxxxxx## Configure a topic and copy the topic information on the topic management page in the console.topic=XXX## Configure a consumer group. You can customize the settings.group.id=XXX## SASL configuration.java.security.auth.login.config.plain=/xxxx/ckafka_client_jaas.conf## Configure the SSL certificate, which takes effect when the access method is set to SASL_SSL.ssl.truststore.location=/xxxx/client.truststore.jksssl.truststore.password=5fi6R!M## The configuration item ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm can be left blank.ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm=
Parameter | Description |
bootstrap.servers | Access network. On the Basic Info page of the instance in the console, select the Access Mode module and copy the network information from the Network column. |
topic | Topic name. Copy the name on the Topic List page in the console. |
group.id | You can define the name and see the consumer on the Consumer Group page after successful demo running. |
java.security.auth.login.config.plain | Enter the path to the JAAS configuration file ckafka_client_jaas.conf. |
client.truststore.jks | The certificate path required when the SASL_SSL access method is used. |
ssl.truststore.password | The server certificate password is 5fi6R!M, which cannot be changed. |
ssl.endpoint.identification.algorithm | The certificate domain name verification switch. The switch is disabled if it is left empty. Keep the switch in the closed state. |
4. Create the configuration file loader CKafkaConfigurer.java.
public class CKafkaConfigurer {private static Properties properties;public static void configureSaslPlain() {//If it has been set using -D or other methods, it will not be set here.if (null == System.getProperty("java.security.auth.login.config")) {//Be sure to change XXX to your own path.System.setProperty("java.security.auth.login.config",getCKafkaProperties().getProperty("java.security.auth.login.config.plain"));}}public synchronized static Properties getCKafkaProperties() {if (null != properties) {return properties;}//Obtain the content of the configuration file kafka.properties.Properties kafkaProperties = new Properties();try {kafkaProperties.load(CKafkaProducerDemo.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("kafka.properties"));} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println("getCKafkaProperties error");}properties = kafkaProperties;return kafkaProperties;}}
Step 3: Sending Messages
1. Create a message sending program KafkaSaslProducerDemo.java.
public class KafkaSaslProducerDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {//Set the path to the JAAS configuration file.CKafkaConfigurer.configureSaslPlain();//Load kafka.properties.Properties kafkaProperties = CKafkaConfigurer.getCKafkaProperties();Properties props = new Properties();//Set the access point. You can obtain the access point of the corresponding topic in the console.props.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,kafkaProperties.getProperty("bootstrap.servers"));//// SASL_SSL access in the public network.//// Access protocol.props.put(CommonClientConfigs.SECURITY_PROTOCOL_CONFIG, "SASL_SSL");// The plaintext method of SASL authentication is used.props.put(SaslConfigs.SASL_MECHANISM, "PLAIN");// SSL encryption.props.put(SslConfigs.SSL_TRUSTSTORE_LOCATION_CONFIG, kafkaProperties.getProperty(SslConfigs.SSL_TRUSTSTORE_LOCATION_CONFIG));props.put(SslConfigs.SSL_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD_CONFIG, kafkaProperties.getProperty(SslConfigs.SSL_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD_CONFIG));props.put(SslConfigs.SSL_ENDPOINT_IDENTIFICATION_ALGORITHM_CONFIG,kafkaProperties.getProperty(SslConfigs.SSL_ENDPOINT_IDENTIFICATION_ALGORITHM_CONFIG));//Serialization method for Kafka messages.props.put(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,"org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");props.put(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,"org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");//The maximum request waiting time.props.put(ProducerConfig.MAX_BLOCK_MS_CONFIG, 30 * 1000);//Set the number of internal retries on the client.props.put(ProducerConfig.RETRIES_CONFIG, 5);//Set the interval of internal retries on the client.props.put(ProducerConfig.RECONNECT_BACKOFF_MS_CONFIG, 3000);//ack=0: The producer will not wait for acknowledgment from the broker, and the retry configuration will not take effect. Note that the connection will be closed if traffic is throttled.//ack=1: The broker leader will return an acknowledgment without waiting for acknowledgments from all broker followers.//ack=all: The broker leader will return an acknowledgment only after receiving acknowledgments from all broker followers.props.put(ProducerConfig.ACKS_CONFIG, "all");//Construct a producer object. Note that this object is thread-safe. Generally, only one producer object is required in one process.KafkaProducer<String, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<>(props);//Construct a Kafka message.String topic = kafkaProperties.getProperty(“topic”); //The topic to which the message belongs. Fill it in here after applying in the console.String value = “this is ckafka msg value”; //The content of the message.try {//Obtaining Future objects in batches can speed up the process. Be careful not to use too large a batch.List<Future<RecordMetadata>> futures = new ArrayList<>(128);for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {//Send a message and obtain a Future object.ProducerRecord<String, String> kafkaMessage = new ProducerRecord<>(topic,value + ": " + i);Future<RecordMetadata> metadataFuture = producer.send(kafkaMessage);futures.add(metadataFuture);}producer.flush();for (Future<RecordMetadata> future : futures) {//Synchronously obtain the result of the Future object.RecordMetadata recordMetadata = future.get();System.out.println("Produce ok:" + recordMetadata.toString());}} catch (Exception e) {//After the client retries internally, the sending still fails. The service needs to respond to this type of error.System.out.println("error occurred");}}}
2. Compile and run KafkaSaslProducerDemo.java to send messages.
3. The running result (output) is as follows:
Produce ok:ckafka-topic-demo-0@198Produce ok:ckafka-topic-demo-0@199
4. On the Topic List page in the CKafka console, select the target topic, and choose More > Message Query to view the message just sent.
Step 4: Consuming Messages
1. Create a consumer message subscription program
KafkaSaslConsumerDemo.java.public class KafkaSaslConsumerDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {//Set the path to the JAAS configuration file.CKafkaConfigurer.configureSaslPlain();//Load kafka.properties.Properties kafkaProperties = CKafkaConfigurer.getCKafkaProperties();Properties props = new Properties();//Set the access point. You can obtain the access point of the corresponding topic in the console.props.put(ProducerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG,kafkaProperties.getProperty("bootstrap.servers"));//// SASL_SSL access in the public network.//// Access protocol.props.put(CommonClientConfigs.SECURITY_PROTOCOL_CONFIG, "SASL_SSL");// The plaintext method of SASL authentication is used.props.put(SaslConfigs.SASL_MECHANISM, "PLAIN");// SSL encryption.props.put(SslConfigs.SSL_TRUSTSTORE_LOCATION_CONFIG, kafkaProperties.getProperty(SslConfigs.SSL_TRUSTSTORE_LOCATION_CONFIG));props.put(SslConfigs.SSL_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD_CONFIG, kafkaProperties.getProperty(SslConfigs.SSL_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD_CONFIG));props.put(SslConfigs.SSL_ENDPOINT_IDENTIFICATION_ALGORITHM_CONFIG,kafkaProperties.getProperty(SslConfigs.SSL_ENDPOINT_IDENTIFICATION_ALGORITHM_CONFIG));//Consumer timeout duration.//The default value is 30 seconds. If a consumer fails to return a heartbeat within the duration, the server determines that the consumer is not alive, removes it from the consumer group, and triggers the rebalance process.props.put(ConsumerConfig.SESSION_TIMEOUT_MS_CONFIG, 30000);//Maximum interval between two polls.//For versions earlier than 0.10.1.0, the 2 concepts are mixed and both represented by session.timeout.ms.props.put(ConsumerConfig.MAX_POLL_INTERVAL_MS_CONFIG, 30000);//Maximum number per poll.//Be careful that this value cannot be too large. If too much data is polled and cannot be consumed before the next poll, a load balancing will be triggered, resulting in delays.props.put(ConsumerConfig.MAX_POLL_RECORDS_CONFIG, 30);//Deserialization method of messages.props.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,"org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");props.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG,"org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");//The consumer group to which the current consumption instance belongs. Fill it in after applying in the console.//Consumption instances of the same group will carry consumption messages.props.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, kafkaProperties.getProperty("group.id"));//Construct a consumption object, that is, generate a consumer instance.KafkaConsumer<String, String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer<String, String>(props);//Set the topics subscribed by the consumer group. Multiple topics can be subscribed to.//If GROUP_ID_CONFIG is the same, it is recommended to set the subscribed topic as the same.List<String> subscribedTopics = new ArrayList<String>();//If multiple topics need to be subscribed to, add them here.//Create each topic in the console first.String topicStr = kafkaProperties.getProperty("topic");String[] topics = topicStr.split(",");for (String topic : topics) {subscribedTopics.add(topic.trim());}consumer.subscribe(subscribedTopics);//Consume messages in loops.while (true) {try {ConsumerRecords<String, String> records = consumer.poll(1000);//The data must be consumed before the next poll, and the total time cannot exceed the value of SESSION_TIMEOUT_MS_CONFIG.for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> record : records) {System.out.println(String.format("Consume partition:%d offset:%d", record.partition(),record.offset()));}} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println("consumer error!");}}}}
2. Compile and run KafkaSaslConsumerDemo.java to consume messages.
3. Running results.
Consume partition:0 offset:298Consume partition:0 offset:299
4. On the Consumer Group page in the CKafka console, select the target consumer group name, enter the topic name in the Topic Name area, and click View Details to view consumption details.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

