Uploading Log over Kafka
Terakhir diperbarui:2025-12-16 21:38:01
Uploading Log over Kafka
Terakhir diperbarui: 2025-12-16 21:38:01
The Cloud Log Service (CLS) currently supports uploading logs to the CLS using Kafka Producer SDK and other Kafka-related agents.
Use Cases
Using Kafka as a message pipeline is common in log applications. First, the open source collection client or the producer on the machine directly writes logs to be collected, and then provides them to the downstream, such as Spark and Flink, for consumption through the Kafka message pipeline. CLS has complete upstream and downstream capabilities of the Kafka message pipeline. The following describes the scenarios suitable for you to upload logs using the Kafka protocol. For more Kafka protocol consumption scenarios, see Kafka Protocol real-time consumption.
Scenario 1: You have a self-built system based on open source collection, and do not want complex secondary transformation. You can upload logs to CLS by modifying the configuration file.
For example, your previous clients who used ELK to build logging systems now simply need to modify the configuration file of Filebeat or Logstash and configure Output (please see Filebeat configuration for details) to CLS to upload logs very easily and concisely.
Scenario 2: You want to collect logs and upload them via Kafka producer SDK without installing a collection Agent.
CLS supports collecting logs using various Kafka producer SDKs and uploading them to CLS by using the Kafka protocol. For details, please refer to the SDK invocation example provided in this document.
Use Limits
Support Kafka protocol versions: 0.11.0.X, 1.0.X, 1.1.X, 2.0.X, 2.1.X, 2.2.X, 2.3.X, 2.4.X, 2.5.X, 2.6.X, 2.7.X, 2.8.X, 3.X.X.
Supported compression modes: gzip, snappy, lz4.
SASL_PLAINTEXT authentication is currently used.
To upload using Kafka protocol, configure the RealtimeProducer permission. For details, see CLS Access Policy Template.
Configuration Method
When using the Kafka protocol to upload logs to the CLS Kafka producer side, you need to configure the CLS Kafka access information.
Parameter | Description |
Authentication Mechanism | Currently support SASL_PLAINTEXT. |
hosts | The CLS Kafka address is configured according to the region of the target write log topic. See CLS Kafka address. |
topic | CLS Kafka topic name, configured as the log topic ID. Example: 76c63473-c496-466b-XXXX-XXXXXXXXXXXX. |
username | CLS Kafka access user name, configured as the logset ID. Example: 0f8e4b82-8adb-47b1-XXXX-XXXXXXXXXXXX. |
password | CLS Kafka access password, format ${secret_id}#${secret_key}, such as: XXXXXXXXXXXXXX#YYYYYYYY. For key information acquisition, visit key acquisition. Please ensure the associated account has appropriate Kafka Protocol Log Upload Permission.To upload anonymously, the format is topic_id#${log topic ID}, for example: topic_id#76c63473-c496-466b-XXXX-XXXX. Note: The target log topic must enable Anonymous upload, and select Log upload via Kafka under Anonymous operation. For details, see Log Topic. 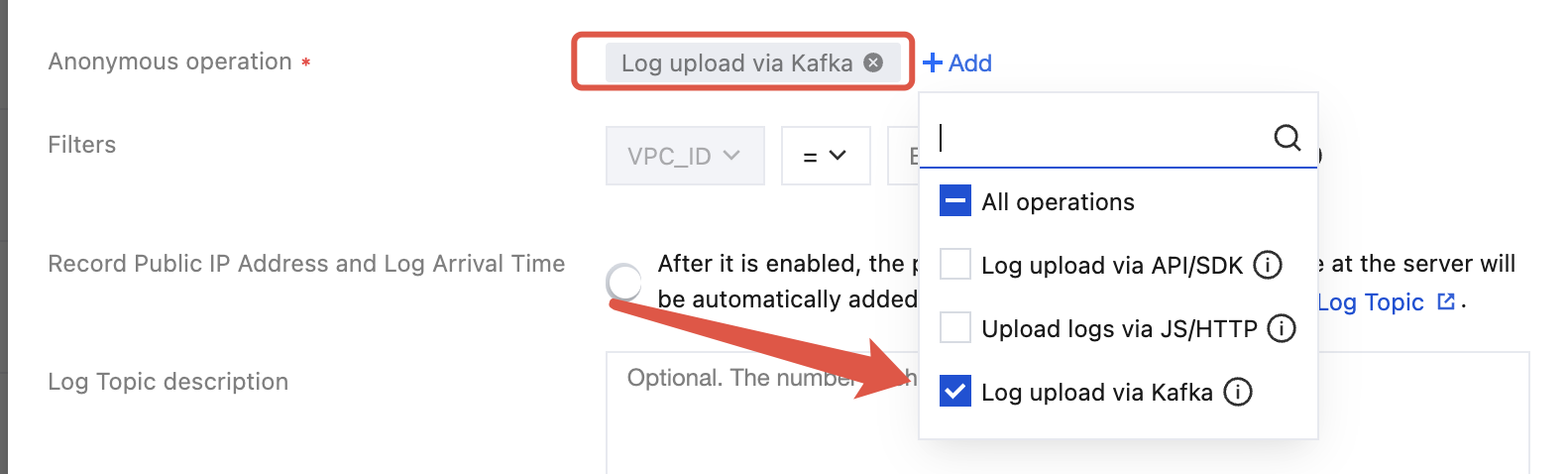 |
header | Define the parsing behavior when uploading worklogs by using Kafka protocol. json_remove_escape: whether to perform JSON parsing with escape removal, value is true or false, default to false if not specified. time_key: the specified time field in logs, means select the specified field as log collection time. time_format: when time_key is configured, additional configuration is required for the time parsing format of the specified field. For details, see configure time format. |
CLS Kafka Address
When uploading logs by using the Kafka protocol, the CLS Kafka address is configured as follows based on the access method (private network/public network) and the region where the target log topic is located.
Note:
region format, see Available domain - Kafka log upload.
Access method:
Private network access: The data initiator is a Tencent Cloud server and the server region matches the target log topic.
Public network access: The data initiator is a non-Tencent Cloud server or the server region differs from the target log topic.
Access Method | CLS Kafka Address |
Private Network | ${region}-producer.cls.tencentyun.com:9095 |
Public Network | ${region}-producer.cls.tencentcs.com:9096 |
Examples
Example of Beat
Filebeat/Winlogbeat Configuration
Note:
Different filebeat versions require different configuration content.
output.kafka:enabled: truehosts: ["${region}-producer.cls.tencentyun.com:9095"] # TODO service address; public network port 9096, private network port 9095topic: "${ClsTopicID}" # TODO log topic IDversion: "1.0.0"compression: "${compress}" # TODO configure compression mode, support gzip, snappy, lz4, such as "lz4"username: "${ClslogsetID}" # TODO logset ID# For anonymous upload, password: "topic_id#${log topic ID}"password: "${secret_id}#${secret_key}"
output.kafka:enabled: truehosts: ["${region}-producer.cls.tencentyun.com:9095"] # TODO service address; public network port 9096, private network port 9095topic: "${ClsTopicID}" # TODO log topic IDversion: "0.11.0.2"compression: "${compress}" # TODO configure compression mode, support gzip, snappy, lz4, such as "lz4"username: "${ClslogsetID}" # TODO logset ID# For anonymous upload, password: "topic_id#${log topic ID}"password: "${secret_id}#${secret_key}"
If an error occurs
kafka: client has run out of available brokers to talk to, it is recommended to upgrade the version to 1.0.0.Example of Logstash
Logstash Configuration
output {kafka {topic_id => "${ClstopicID}"bootstrap_servers => "${region}-producer.cls.tencentyun.com:${port}"sasl_mechanism => "PLAIN"security_protocol => "SASL_PLAINTEXT"compression_type => "${compress}"# For anonymous upload, password='topic_id#${log topic ID}'sasl_jaas_config => "org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username='${ClslogsetID}' password='${secret_id}#${secret_key}';"codec => json}}
Example of FluentTD
Note:
This demo is verified based on fluentd-1.15.3 and depends on ruby version ruby=2.7.6.
FluentTD Configuration
<match *>@type rdkafka2# brokers setting# For TODO domain name, refer to https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/614/18940. Pay attention to the private network port 9095 and public network port 9096.brokers "${domain}:${port}" # e.g. gz-producer.cls.tencentyun.com:9095# topic settings# TODO replace log topic IDtopic "${topic_id}"# saslrdkafka_options {"sasl.mechanism": "PLAIN","security.protocol": "sasl_plaintext",# TODO logset ID of the topic"sasl.username": "${logset_id}",# TODO key of the topic's owner uin, format ${secret_id}#${secret_key}; for anonymous upload, format topic_id#${log topic ID}"sasl.password": "${secret_id}#${secret_key}"}required_acks 1compression_codec gzip<format>@type json</format><buffer tag>flush_at_shutdown trueflush_mode intervalflush_interval 1schunk_limit_size 3MBchunk_full_threshold 1total_limit_size 1024MBoverflow_action block</buffer></match>
Example of FluentBit
FluentBit Configuration
[OUTPUT]Name kafkaMatch *# For TODO domain name, refer to https://cloud.tencent.com/document/product/614/18940. Pay attention to the private network port 9095 and public network port 9096.Brokers ${domain}:${port} # e.g. gz-producer.cls.tencentyun.com:9095# TODO replace log topic IDTopics ${topic_id}# The maximum size of TODO request message, not more than 5M.rdkafka.message.max.bytes 5242880rdkafka.sasl.mechanisms PLAINrdkafka.security.protocol sasl_plaintext# TODO Select the value of acks based on the usage scenariordkafka.acks 1# TODO configuration compression moderdkafka.compression.codec lz4# TODO logset ID of the topicrdkafka.sasl.username ${logset_id}# TODO key of the topic's owner uin, format ${secret_id}#${secret_key}; for anonymous upload, format topic_id#${log topic ID}rdkafka.sasl.password ${secret_id}#${secret_key}
Example of SDK
Example of Golang SDK
The following figure takes sarama.V1_1_0_0 as an example, and other versions are configured according to similar rules:
import ("fmt""github.com/Shopify/sarama")func main() {config := sarama.NewConfig()config.Net.SASL.Mechanism = "PLAIN"config.Net.SASL.Version = int16(1)config.Net.SASL.Enable = true// TODO logset IDconfig.Net.SASL.User = "${logsetID}"// TODO format: ${secret_id}#${secret_key}. For anonymous upload, format: topic_id#${log topic ID}config.Net.SASL.Password = "${secret_id}#${secret_key}"config.Producer.Return.Successes = true# TODO Select the value of acks based on the usage scenarioconfig.Producer.RequiredAcks = ${acks}config.Version = sarama.V1_1_0_0// TODO configuration compression modeconfig.Producer.Compression = ${compress}// TODO service address: public network port 9096, private network port 9095producer, err := sarama.NewSyncProducer([]string{"${region}-producer.cls.tencentyun.com:9095"}, config)if err != nil {panic(err)}msg := &sarama.ProducerMessage{Topic: "${topicID}", // TODO log topic IDValue: sarama.StringEncoder("goland sdk sender demo"),}// Send the message.for i := 0; i <= 5; i++ {partition, offset, err := producer.SendMessage(msg)if err != nil {panic(err)}fmt.Printf("send response; partition:%d, offset:%d\\n", partition, offset)}_ = producer.Close()}
Example of Python SDK
from kafka import KafkaProducerif __name__ == '__main__':produce = KafkaProducer(# TODO service address: public network port 9096, private network port 9095bootstrap_servers=["${region}-producer.cls.tencentyun.com:9095"],security_protocol='SASL_PLAINTEXT',sasl_mechanism='PLAIN',# TODO logset IDsasl_plain_username='${logsetID}',# TODO format: ${secret_id}#${secret_key}. For anonymous upload, format: topic_id#${log topic ID}sasl_plain_password='${secret_id}#${secret_key}',api_version=(0, 11, 0),# TODO configuration compression modecompression_type="${compress_type}",)for i in range(0, 5):# sendMessage TODO log topic IDfuture = produce.send(topic="${topicID}", value=b'python sdk sender demo')result = future.get(timeout=10)print(result)
Example of Java SDK
Maven dependency:
<dependencies><!--https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.kafka/kafka-clients--><dependency><groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId><artifactId>kafka-clients</artifactId><version>0.11.0.2</version></dependency></dependencies>
Sample code:
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.*;import java.util.Properties;import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;import java.util.concurrent.Future;import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;public class ProducerDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {// 0. Configure a series of parameters.Properties props = new Properties();// TODO when usingprops.put("bootstrap.servers", "${region}-producer.cls.tencentyun.com:9095");// TODO The following values are set according to the business scene.props.put("acks", ${acks});props.put("retries", ${retries});props.put("batch.size", ${batch.size});props.put("linger.ms", ${linger.ms});props.put("buffer.memory", ${buffer.memory});props.put(ProducerConfig.COMPRESSION_TYPE_CONFIG, "${compress_type}"); // TODO configuration compression modeprops.put("key.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");props.put("value.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");props.put("security.protocol", "SASL_PLAINTEXT");props.put("sasl.mechanism", "PLAIN");// TODO username logsetID; password is combination of secret_id and secret_key, format ${secret_id}#${secret_key},// For anonymous upload, password is topic_id#${log topic ID}props.put("sasl.jaas.config","org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username='${logsetID}' password='${secret_id}#${secret_key}';");// 1. Create a producer objectProducer<String, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<String, String>(props);// 2. Call the send method TODO log topic IDFuture<RecordMetadata> meta = producer.send(new ProducerRecord<String, String>("${topicID}", ${message}));RecordMetadata recordMetadata = meta.get(${timeout}, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);System.out.println("offset = " + recordMetadata.offset());// 3. Close the producer.producer.close();}}
Example of C SDK
// https://github.com/edenhill/librdkafka - master#include <iostream>#include <librdkafka/rdkafka.h>#include <string>#include <unistd.h>#define BOOTSTRAP_SERVER "${region}-producer.cls.tencentyun.com:${port}"// USERNAME is the logset ID.#define USERNAME "${logsetID}"// PASSWORD format: ${secret_id}#${secret_key}. For anonymous upload, format: topic_id#${log topic ID}#define PASSWORD "${secret_id}#${secret_key}"// log topic ID#define TOPIC "${topicID}"#define ACKS "${acks}"// Configuration Compression Mode#define COMPRESS_TYPE "${compress_type}"static void dr_msg_cb(rd_kafka_t *rk, const rd_kafka_message_t *rkmessage, void *opaque) {if (rkmessage->err) {fprintf(stdout, "%% Message delivery failed : %s\\n", rd_kafka_err2str(rkmessage->err));} else {fprintf(stdout, "%% Message delivery successful %zu:%d\\n", rkmessage->len, rkmessage->partition);}}int main(int argc, char **argv) {// 1. Initialize the configuration.rd_kafka_conf_t *conf = rd_kafka_conf_new();rd_kafka_conf_set_dr_msg_cb(conf, dr_msg_cb);char errstr[512];if (rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "bootstrap.servers", BOOTSTRAP_SERVER, errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK) {rd_kafka_conf_destroy(conf);fprintf(stdout, "%s\\n", errstr);return -1;}if (rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "acks", ACKS, errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK) {rd_kafka_conf_destroy(conf);fprintf(stdout, "%s\\n", errstr);return -1;}if (rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "compression.codec", COMPRESS_TYPE, errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK) {rd_kafka_conf_destroy(conf);fprintf(stdout, "%s\\n", errstr);return -1;}// Set the authentication method.if (rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "security.protocol", "sasl_plaintext", errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK) {rd_kafka_conf_destroy(conf);fprintf(stdout, "%s\\n", errstr);return -1;}if (rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "sasl.mechanisms", "PLAIN", errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK) {rd_kafka_conf_destroy(conf);fprintf(stdout, "%s\\n", errstr);return -1;}if (rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "sasl.username", USERNAME, errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK) {rd_kafka_conf_destroy(conf);fprintf(stdout, "%s\\n", errstr);return -1;}if (rd_kafka_conf_set(conf, "sasl.password", PASSWORD, errstr, sizeof(errstr)) != RD_KAFKA_CONF_OK) {rd_kafka_conf_destroy(conf);fprintf(stdout, "%s\\n", errstr);return -1;}// 2. Create handler.rd_kafka_t *rk = rd_kafka_new(RD_KAFKA_PRODUCER, conf, errstr, sizeof(errstr));if (!rk) {rd_kafka_conf_destroy(conf);fprintf(stdout, "create produce handler failed: %s\\n", errstr);return -1;}// 3. Send data.std::string value = "test lib kafka ---- ";for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i) {retry:rd_kafka_resp_err_t err = rd_kafka_producev(rk, RD_KAFKA_V_TOPIC(TOPIC),RD_KAFKA_V_MSGFLAGS(RD_KAFKA_MSG_F_COPY),RD_KAFKA_V_VALUE((void *) value.c_str(), value.size()),RD_KAFKA_V_OPAQUE(nullptr), RD_KAFKA_V_END);if (err) {fprintf(stdout, "Failed to produce to topic : %s, error : %s", TOPIC, rd_kafka_err2str(err));if (err == RD_KAFKA_RESP_ERR__QUEUE_FULL) {rd_kafka_poll(rk, 1000);goto retry;}} else {fprintf(stdout, "send message to topic successful : %s\\n", TOPIC);}rd_kafka_poll(rk, 0);}std::cout << "message flush final" << std::endl;rd_kafka_flush(rk, 10 * 1000);if (rd_kafka_outq_len(rk) > 0) {fprintf(stdout, "%d message were not deliverer\\n", rd_kafka_outq_len(rk));}rd_kafka_destroy(rk);return 0;}
Example of C# SDK
/** The demo only provides the simplest method of use, specific production can be achieved by combine calls* During use, the todo items in the Demo need to be replaced** Notes:* 1. The Demo is verified based on Confluent.Kafka/1.8.2* 2. MessageMaxBytes must not exceed 5M* 3. The Demo uses synchronous production and can be changed to asynchronous based on business scenario when using* 4. Other parameters can be adjusted themselves according to the business reference document during use: https://docs.confluent.io/platform/current/clients/confluent-kafka-dotnet/_site/api/Confluent.Kafka.ProducerConfig.html** Confluent.Kafka reference document: https://docs.confluent.io/platform/current/clients/confluent-kafka-dotnet/_site/api/Confluent.Kafka.html*/using Confluent.Kafka;namespace Producer{class Producer{private static void Main(string[] args){var config = new ProducerConfig{// TODO domain name, refer to https://www.tencentcloud.com/document/product/614/18940?from_cn_redirect=1.// Fill in Kafka. Pay attention to the private network port 9095 and public network port 9096.BootstrapServers = "${domain}:${port}",SaslMechanism = SaslMechanism.Plain,// TODO logset ID of the topicSaslUsername = "${logsetID}",// TODO key for the uin the topic belongs to, format: ${secret_id}#${secret_key}// For anonymous upload, format is topic_id#${log topic ID}SaslPassword = "${secret_id}#${secret_key}",SecurityProtocol = SecurityProtocol.SaslPlaintext,// TODO assign according to the actual use scene. Available values: Acks.None, Acks.Leader, and Acks.AllAcks = Acks.None,// The maximum size of TODO request message, not more than 5M.MessageMaxBytes = 5242880};// deliveryHandlerAction<DeliveryReport<Null, string>> handler =r => Console.WriteLine(!r.Error.IsError ? $"Delivered message to {r.TopicPartitionOffset}" : $"Delivery Error: {r.Error.Reason}");using (var produce = new ProducerBuilder<Null, string>(config).Build()){try{// TODO Test Verification Codefor (var i = 0; i < 100; i++){// TODO replace log topic IDproduce.Produce("${topicID}", new Message<Null, string> { Value = "C# demo value" }, handler);}produce.Flush(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10));}catch (ProduceException<Null, string> pe){Console.WriteLine($"send message receiver error : {pe.Error.Reason}");}}}}}
Apakah halaman ini membantu?
Anda juga dapat Menghubungi Penjualan atau Mengirimkan Tiket untuk meminta bantuan.
Ya
Tidak
masukan