DNS 防火墙最佳实践
最后更新时间:2023-12-11 16:40:39
NAT 防火墙 DNS 开关开启后,系统会修改所接入 VPC 的 DNS 解析地址,将 DNS 流量牵引至 NAT 边界防火墙,从而获取全流量域名。
说明
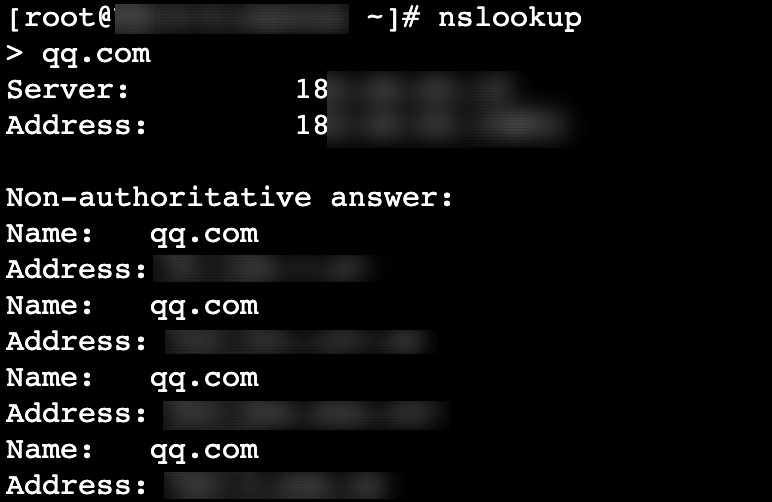
腾讯云默认 DNS 为:183.60.83.19,183.60.82.98。
可以按照如下流程,配置 DNS 防护:
创建相关地区 NAT 防火墙接入 VPC 网络。
开启 NAT 防火墙开关,流量都从 NAT 防火墙经过。(涉及到路由变更网络会抖动1-2秒)
开启 DNS 开关进行验证 DNS 地址。
使用 NAT 防火墙访问控制限制 DNS 解析(验证)。
如下图示例:腾讯云 CVM 公网资源为默认的 DNS 服务器。
步骤1:创建 NAT 防火墙
1. 登录 云防火墙控制台,在左侧导航中,单击防火墙开关 > NAT 边界开关 > 网络拓扑。
2. 在网络拓扑页面,单击创建实例,选择所需地域。
3. 在新建 NAT 边界防火墙弹窗中,配置相关参数,单击下一步。
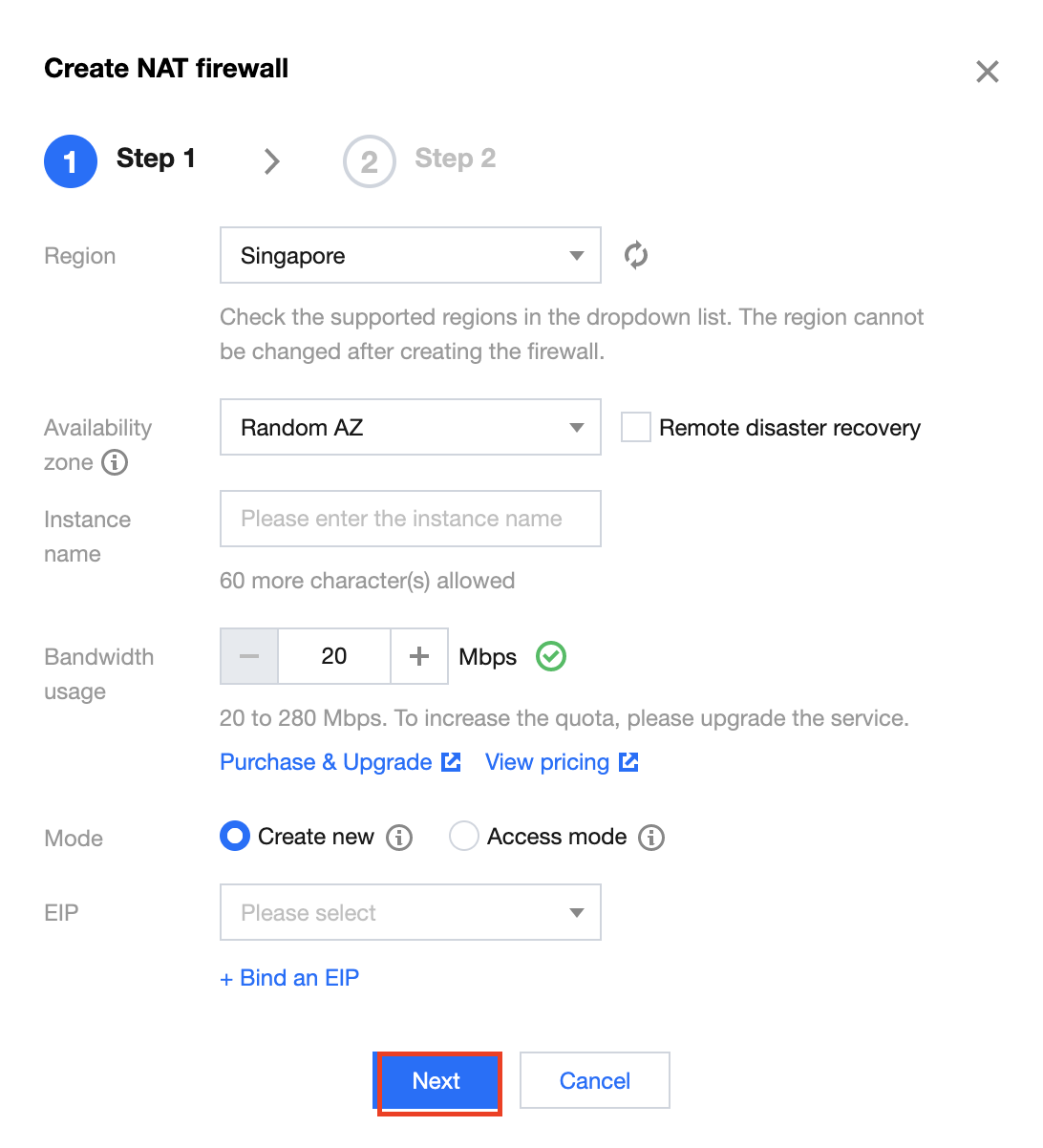

地域:选择创建地域,支持国内所有地域,创建实例后不可更改。
说明:
用户可在拥有 VPC 的所有国内地域(支持中国香港地域)中进行地域选择,同地域下可创建多个防火墙实例,但总带宽不能超过限定规格。
可选区:根据需求选择合适的可用区。
实例名称:输入实例名称。
带宽规格:根据需求选择带宽规格,最小20Mbps,如需更多带宽请 升级扩容。
说明:
互联网带宽保持一致,如果分了多个 NAT 防火墙,那么多个 NAT 防火墙的带宽之和,要小于等于互联网边界的带宽。
模式:分为新增模式和接入模式。
新增模式:若当前地域没有 NAT 网关,新增模式可以通过 NAT 边界防火墙内置的 NAT 功能,实现指定实例通过防火墙访问互联网。
接入模式:若当前地域已有 NAT 网关,或者希望公网对外的出口 IP 保持不变,接入模式可以将 NAT 边界防火墙平滑接入到 NAT 网关与 CVM 实例之间。
弹性 IP:若选择新建弹性 IP,系统会自动为用户申请一个弹性 IP,用户也可从所有闲置的弹性 IP 中选择一个进行绑定。
4. 选择需要接入的 VPC,单击创建,等待若干分钟后,即可在防火墙实例列表中,查看刚刚创建的实例。
步骤2:开启防火墙开关

步骤3:开启和验证 DNS
1. 在 NAT 边界开关页面,单击防火墙实例 ,选择 步骤1 创建的防火墙实例,单击实例配置。


2. 在接入 VPC 与公网 IP 页面,选择所需 ID,单击

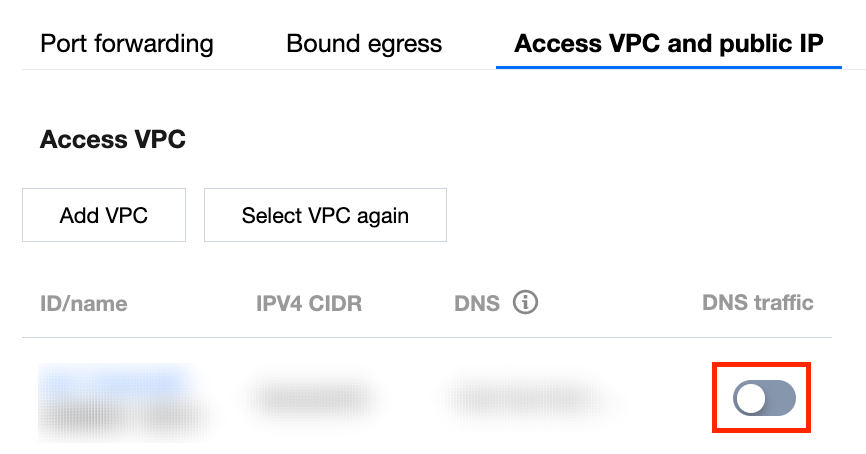
3. 通过
ipconfig /release Ipconfig /renew 刷新 DNS 获取地址。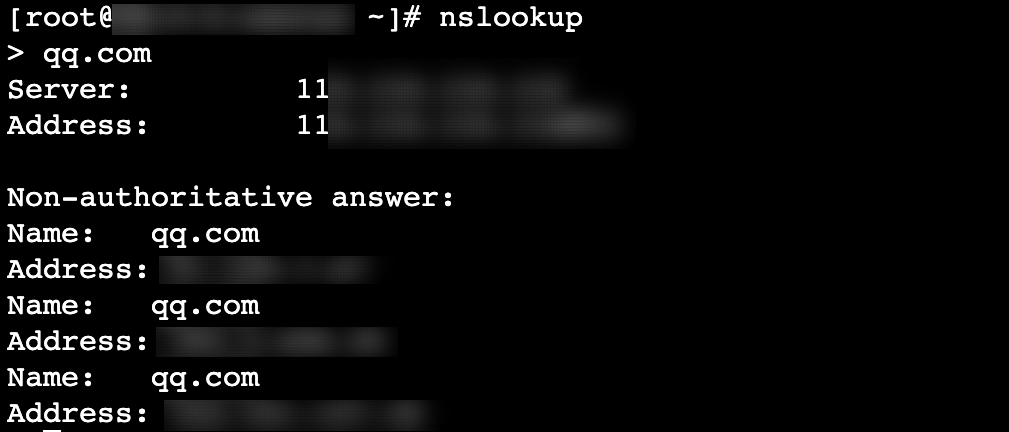
步骤4:限制 DNS 解析
1. 在 NAT 边界规则页面,选择所需地域,单击出向规则 > 添加规则。
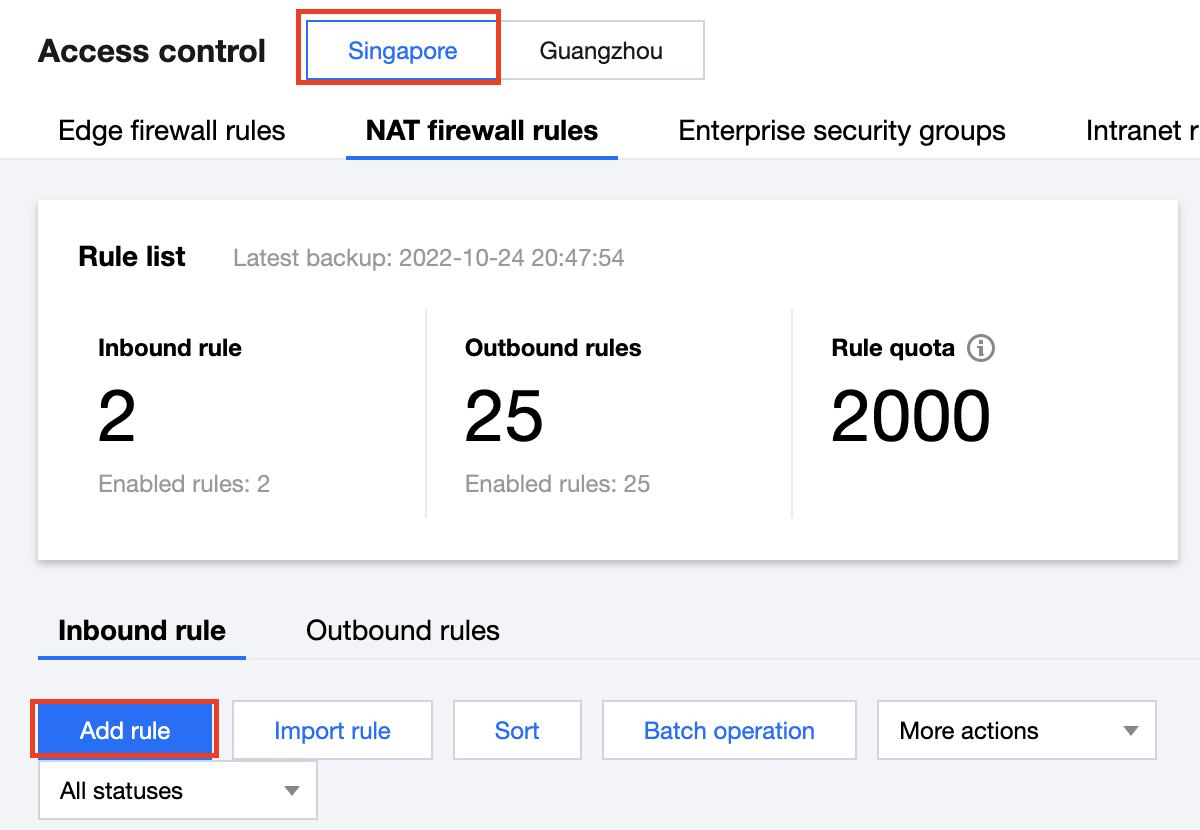
2. 在添加出向规则弹窗中,配置相关参数,单击确定。
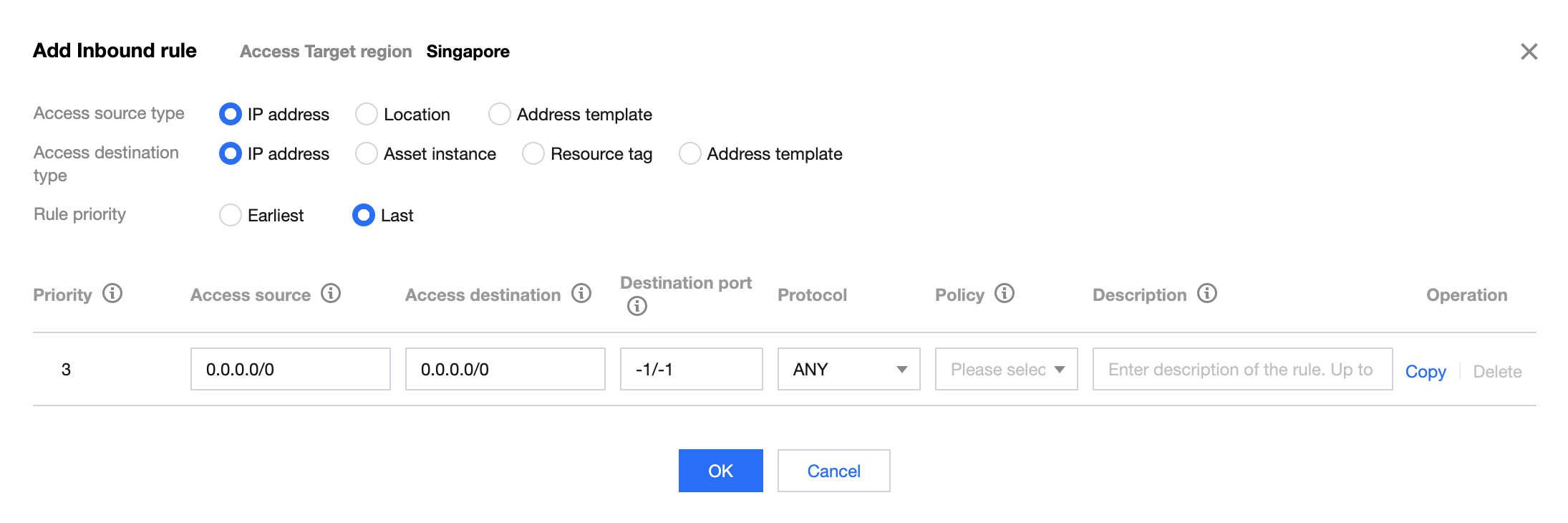

字段说明:
执行顺序:访问控制规则的执行顺序,出站规则和入站规则的执行顺序互不影响,执行顺序较高的规则被优先匹配,命中某条规则后,不再匹配后序规则。当您修改某条规则的执行顺序时,原本该位置的规则的执行顺序+1,以此类推。当您删除某条规则时,后序所有规则的执行顺序-1。
访问源:出向规则访问源仅对当前地域内的所有内网资产生效,支持 IP 和 CIDR。
访问目的:出向规则访问目的对所有公网 IP/域名生效,支持 IP、CIDR、域名和地理位置。
目的端口:
TCP/UDP/ANY 规则支持单端口号、基于'/'的端口段以及英文逗号分隔的离散端口值,例如“80”、“80/80”、“-1/-1”、“1/65535”或“80,443,3380/3389”。
HTTP/HTTPS/SMTP/SMTPS/FTP 规则仅支持配置单端口值,且 SMTP/FTP 协议间端口不可重复。
ICMP 规则不需要配置端口。
协议:当前版本的出向规则支持 ANY、TCP、UDP 和 ICMP 协议。
策略说明:
放行:放通命中规则的流量,记录命中次数但不记录访问控制日志,且记录流量日志。
观察:放通命中规则的流量,记录命中次数并记录访问控制日志与流量日志。
阻断:拦截命中规则的流量,记录命中次数并记录访问控制日志,但不记录流量日志。
描述:用于描述规则,最多支持50个字符。
3. 配置完成后验证 DNS 是否连通。


文档反馈


