- Release Notes
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Getting Started
- Operation Guide
- Troubleshooting
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- Cluster Security APIs
- SetCheckMode
- DescribeUserCluster
- DescribeUnfinishRefreshTask
- DescribeTaskResultSummary
- DescribeRiskList
- DescribeRefreshTask
- DescribeClusterSummary
- DescribeClusterDetail
- DescribeCheckItemList
- DescribeAffectedWorkloadList
- DescribeAffectedNodeList
- DescribeAffectedClusterCount
- CreateRefreshTask
- CreateClusterCheckTask
- CreateCheckComponent
- Network Security APIs
- UpdateNetworkFirewallPolicyYamlDetail
- UpdateNetworkFirewallPolicyDetail
- UpdateAndPublishNetworkFirewallPolicyYamlDetail
- UpdateAndPublishNetworkFirewallPolicyDetail
- DescribeNetworkFirewallPolicyYamlDetail
- DescribeNetworkFirewallPolicyStatus
- DescribeNetworkFirewallPolicyList
- DescribeNetworkFirewallPolicyDiscover
- DescribeNetworkFirewallPolicyDetail
- DescribeNetworkFirewallPodLabelsList
- DescribeNetworkFirewallNamespaceLabelList
- DescribeNetworkFirewallClusterRefreshStatus
- DescribeNetworkFirewallClusterList
- DescribeNetworkFirewallAuditRecord
- DeleteNetworkFirewallPolicyDetail
- CreateNetworkFirewallUndoPublish
- CreateNetworkFirewallPublish
- CreateNetworkFirewallPolicyDiscover
- CreateNetworkFirewallClusterRefresh
- ConfirmNetworkFirewallPolicy
- CheckNetworkFirewallPolicyYaml
- AddNetworkFirewallPolicyYamlDetail
- AddNetworkFirewallPolicyDetail
- AddAndPublishNetworkFirewallPolicyYamlDetail
- AddAndPublishNetworkFirewallPolicyDetail
- Security Compliance APIs
- ScanComplianceScanFailedAssets
- ScanCompliancePolicyItems
- ScanComplianceAssetsByPolicyItem
- ScanComplianceAssets
- ModifyCompliancePeriodTask
- InitializeUserComplianceEnvironment
- DescribeComplianceWhitelistItemList
- DescribeComplianceTaskPolicyItemSummaryList
- DescribeComplianceTaskAssetSummary
- DescribeComplianceScanFailedAssetList
- DescribeCompliancePolicyItemAffectedSummary
- DescribeCompliancePolicyItemAffectedAssetList
- DescribeCompliancePeriodTaskList
- DescribeComplianceAssetPolicyItemList
- DescribeComplianceAssetList
- DescribeComplianceAssetDetailInfo
- DeleteCompliancePolicyItemFromWhitelist
- DeleteCompliancePolicyAssetSetFromWhitelist
- DeleteComplianceAssetPolicySetFromWhitelist
- CreateExportComplianceStatusListJob
- CreateComplianceTask
- AddCompliancePolicyItemToWhitelist
- AddCompliancePolicyAssetSetToWhitelist
- AddComplianceAssetPolicySetToWhitelist
- Runtime security - High-risk syscalls
- Runtime Security - Reverse Shell APIs
- Runtime Security - Container Escape APIs
- ModifyEscapeWhiteList
- ModifyEscapeRule
- ModifyEscapeEventStatus
- DescribeEscapeWhiteList
- DescribeEscapeSafeState
- DescribeEscapeRuleInfo
- DescribeEscapeEventsExport
- DescribeEscapeEventTypeSummary
- DescribeEscapeEventTendency
- DescribeEscapeEventInfo
- DescribeEscapeEventDetail
- DeleteEscapeWhiteList
- CreateEscapeWhiteListExportJob
- CreateEscapeEventsExportJob
- AddEscapeWhiteList
- Runtime Security APIs
- StopVulScanTask
- OpenTcssTrial
- ModifyAccessControlStatus
- ModifyAccessControlRuleStatus
- ModifyAbnormalProcessStatus
- ModifyAbnormalProcessRuleStatus
- DescribeWebVulList
- DescribeVulScanLocalImageList
- DescribeVulScanInfo
- DescribeVulImageList
- DescribeVulDetail
- DescribeVulContainerList
- DescribeSupportDefenceVul
- DescribeRiskSyscallDetail
- DescribeEmergencyVulList
- DescribeAssetImageBindRuleInfo
- DescribeAccessControlRulesExport
- DescribeAccessControlRules
- DescribeAccessControlRuleDetail
- DescribeAccessControlEventsExport
- DescribeAccessControlEvents
- DescribeAccessControlDetail
- DescribeAbnormalProcessRulesExport
- DescribeAbnormalProcessRules
- DescribeAbnormalProcessRuleDetail
- DescribeAbnormalProcessLevelSummary
- DescribeAbnormalProcessEventsExport
- DescribeAbnormalProcessEvents
- DescribeAbnormalProcessEventTendency
- DescribeAbnormalProcessDetail
- DeleteAccessControlRules
- DeleteAbnormalProcessRules
- CreateWebVulExportJob
- CreateVulScanTask
- CreateVulImageExportJob
- CreateVulContainerExportJob
- CreateSystemVulExportJob
- CreateRiskDnsEventExportJob
- CreateProcessEventsExportJob
- CreateEmergencyVulExportJob
- CreateDefenceVulExportJob
- AddEditRiskSyscallWhiteList
- AddEditAccessControlRule
- AddEditAbnormalProcessRule
- Image Security APIs
- DescribeVulRegistryImageList
- UpdateImageRegistryTimingScanTask
- UpdateAssetImageRegistryRegistryDetail
- SyncAssetImageRegistryAsset
- SwitchImageAutoAuthorizedRule
- RenewImageAuthorizeState
- RemoveAssetImageRegistryRegistryDetail
- ModifyVulDefenceSetting
- ModifyVulDefenceEventStatus
- ModifyImageAuthorized
- ModifyAssetImageScanStop
- ModifyAssetImageRegistryScanStopOneKey
- ModifyAssetImageRegistryScanStop
- ModifyAsset
- DescribeVulTopRanking
- DescribeVulTendency
- DescribeVulSummary
- DescribeVulScanAuthorizedImageSummary
- DescribeVulLevelSummary
- DescribeVulLevelImageSummary
- DescribeVulImageSummary
- DescribeVulIgnoreRegistryImageList
- DescribeVulIgnoreLocalImageList
- DescribeVulDefenceSetting
- DescribeVulDefencePlugin
- DescribeVulDefenceHost
- DescribeVulDefenceEventTendency
- DescribeVulDefenceEventDetail
- DescribeVulDefenceEvent
- DescribeValueAddedSrvInfo
- DescribeSystemVulList
- DescribeSecEventsTendency
- DescribeScanIgnoreVulList
- DescribePostPayDetail
- DescribeNewestVul
- DescribeImageSimpleList
- DescribeImageRiskTendency
- DescribeImageRiskSummary
- DescribeImageRegistryTimingScanTask
- DescribeImageRegistryNamespaceList
- DescribeImageComponentList
- DescribeImageAutoAuthorizedTaskList
- DescribeImageAutoAuthorizedRule
- DescribeImageAutoAuthorizedLogList
- DescribeContainerSecEventSummary
- DescribeContainerAssetSummary
- DescribeAutoAuthorizedRuleHost
- DescribeAssetWebServiceList
- DescribeAssetSummary
- DescribeAssetProcessList
- DescribeAssetPortList
- DescribeAssetImageVulListExport
- DescribeAssetImageVulList
- DescribeAssetImageVirusListExport
- DescribeAssetImageVirusList
- DescribeAssetImageSimpleList
- DescribeAssetImageScanTask
- DescribeAssetImageScanStatus
- DescribeAssetImageScanSetting
- DescribeAssetImageRiskListExport
- DescribeAssetImageRiskList
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryVulListExport
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryVulList
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryVirusListExport
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryVirusList
- DescribeAssetImageRegistrySummary
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryScanStatusOneKey
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryRiskListExport
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryRiskInfoList
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryRegistryList
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryRegistryDetail
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryListExport
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryList
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryDetail
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryAssetStatus
- DescribeAssetImageListExport
- DescribeAssetImageList
- DescribeAssetImageHostList
- DescribeAssetImageDetail
- DescribeAssetHostList
- DescribeAssetHostDetail
- DescribeAssetDBServiceList
- DescribeAssetContainerList
- DescribeAssetContainerDetail
- DescribeAssetComponentList
- DescribeAssetAppServiceList
- DeleteIgnoreVul
- CreateVulExportJob
- CreateVulDefenceHostExportJob
- CreateVulDefenceEventExportJob
- CreateOrModifyPostPayCores
- CreateImageExportJob
- CreateComponentExportJob
- CreateAssetImageScanTask
- CreateAssetImageRegistryScanTaskOneKey
- CreateAssetImageRegistryScanTask
- CheckRepeatAssetImageRegistry
- AddIgnoreVul
- AddEditImageAutoAuthorizedRule
- AddAssetImageRegistryRegistryDetail
- Runtime Security - Trojan Call APIs
- DescribeExportJobResult
- StopVirusScanTask
- ModifyVirusScanTimeoutSetting
- ModifyVirusScanSetting
- ModifyVirusMonitorSetting
- ModifyVirusFileStatus
- ModifyVirusAutoIsolateSetting
- ModifyVirusAutoIsolateExampleSwitch
- ExportVirusList
- DescribeVirusTaskList
- DescribeVirusSummary
- DescribeVirusScanTimeoutSetting
- DescribeVirusScanTaskStatus
- DescribeVirusScanSetting
- DescribeVirusSampleDownloadUrl
- DescribeVirusMonitorSetting
- DescribeVirusManualScanEstimateTimeout
- DescribeVirusList
- DescribeVirusEventTendency
- DescribeVirusDetail
- DescribeVirusAutoIsolateSetting
- DescribeVirusAutoIsolateSampleList
- DescribeVirusAutoIsolateSampleDownloadURL
- DescribeVirusAutoIsolateSampleDetail
- CreateVirusScanTask
- CreateVirusScanAgain
- Asset Management APIs
- ModifyContainerNetStatus
- DescribeUnauthorizedCoresTendency
- DescribeTcssSummary
- DescribePromotionActivity
- DescribeInspectionReport
- DescribeExportJobManageList
- DescribeExportJobDownloadURL
- DescribeAssetSyncLastTime
- DescribeAgentInstallCommand
- DescribeAgentDaemonSetCmd
- DescribeABTestConfig
- DeleteMachine
- CreateHostExportJob
- CreateAssetImageVirusExportJob
- CreateAssetImageScanSetting
- Security Operations - Log Analysis APIs
- ResetSecLogTopicConfig
- ModifySecLogKafkaUIN
- ModifySecLogJoinState
- ModifySecLogJoinObjects
- ModifySecLogDeliveryKafkaSetting
- ModifySecLogDeliveryClsSetting
- ModifySecLogCleanSettingInfo
- DescribeSecLogKafkaUIN
- DescribeSecLogJoinTypeList
- DescribeSecLogJoinObjectList
- DescribeSecLogDeliveryKafkaSetting
- DescribeSecLogDeliveryKafkaOptions
- DescribeSecLogDeliveryClsSetting
- DescribeSecLogDeliveryClsOptions
- DescribeSecLogCleanSettingInfo
- DescribeSecLogAlertMsg
- DescribeSearchTemplates
- DescribeSearchLogs
- DescribeSearchExportList
- DescribePublicKey
- DescribeLogStorageStatistic
- DescribeIndexList
- DescribeESHits
- DescribeESAggregations
- DeleteSearchTemplate
- CreateSearchTemplate
- Alert Settings APIs
- Advanced prevention - K8s API abnormal requests
- ModifyK8sApiAbnormalRuleStatus
- ModifyK8sApiAbnormalRuleInfo
- ModifyK8sApiAbnormalEventStatus
- DescribeK8sApiAbnormalTendency
- DescribeK8sApiAbnormalSummary
- DescribeK8sApiAbnormalRuleScopeList
- DescribeK8sApiAbnormalRuleList
- DescribeK8sApiAbnormalRuleInfo
- DescribeK8sApiAbnormalEventList
- DescribeK8sApiAbnormalEventInfo
- DescribeAssetClusterList
- DeleteK8sApiAbnormalRule
- CreateK8sApiAbnormalRuleInfo
- CreateK8sApiAbnormalRuleExportJob
- CreateK8sApiAbnormalEventExportJob
- CreateAccessControlsRuleExportJob
- Billing APIs
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- FAQs
- TCSS Policy
- Contact Us
- Glossary
- Release Notes
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Getting Started
- Operation Guide
- Troubleshooting
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- Cluster Security APIs
- SetCheckMode
- DescribeUserCluster
- DescribeUnfinishRefreshTask
- DescribeTaskResultSummary
- DescribeRiskList
- DescribeRefreshTask
- DescribeClusterSummary
- DescribeClusterDetail
- DescribeCheckItemList
- DescribeAffectedWorkloadList
- DescribeAffectedNodeList
- DescribeAffectedClusterCount
- CreateRefreshTask
- CreateClusterCheckTask
- CreateCheckComponent
- Network Security APIs
- UpdateNetworkFirewallPolicyYamlDetail
- UpdateNetworkFirewallPolicyDetail
- UpdateAndPublishNetworkFirewallPolicyYamlDetail
- UpdateAndPublishNetworkFirewallPolicyDetail
- DescribeNetworkFirewallPolicyYamlDetail
- DescribeNetworkFirewallPolicyStatus
- DescribeNetworkFirewallPolicyList
- DescribeNetworkFirewallPolicyDiscover
- DescribeNetworkFirewallPolicyDetail
- DescribeNetworkFirewallPodLabelsList
- DescribeNetworkFirewallNamespaceLabelList
- DescribeNetworkFirewallClusterRefreshStatus
- DescribeNetworkFirewallClusterList
- DescribeNetworkFirewallAuditRecord
- DeleteNetworkFirewallPolicyDetail
- CreateNetworkFirewallUndoPublish
- CreateNetworkFirewallPublish
- CreateNetworkFirewallPolicyDiscover
- CreateNetworkFirewallClusterRefresh
- ConfirmNetworkFirewallPolicy
- CheckNetworkFirewallPolicyYaml
- AddNetworkFirewallPolicyYamlDetail
- AddNetworkFirewallPolicyDetail
- AddAndPublishNetworkFirewallPolicyYamlDetail
- AddAndPublishNetworkFirewallPolicyDetail
- Security Compliance APIs
- ScanComplianceScanFailedAssets
- ScanCompliancePolicyItems
- ScanComplianceAssetsByPolicyItem
- ScanComplianceAssets
- ModifyCompliancePeriodTask
- InitializeUserComplianceEnvironment
- DescribeComplianceWhitelistItemList
- DescribeComplianceTaskPolicyItemSummaryList
- DescribeComplianceTaskAssetSummary
- DescribeComplianceScanFailedAssetList
- DescribeCompliancePolicyItemAffectedSummary
- DescribeCompliancePolicyItemAffectedAssetList
- DescribeCompliancePeriodTaskList
- DescribeComplianceAssetPolicyItemList
- DescribeComplianceAssetList
- DescribeComplianceAssetDetailInfo
- DeleteCompliancePolicyItemFromWhitelist
- DeleteCompliancePolicyAssetSetFromWhitelist
- DeleteComplianceAssetPolicySetFromWhitelist
- CreateExportComplianceStatusListJob
- CreateComplianceTask
- AddCompliancePolicyItemToWhitelist
- AddCompliancePolicyAssetSetToWhitelist
- AddComplianceAssetPolicySetToWhitelist
- Runtime security - High-risk syscalls
- Runtime Security - Reverse Shell APIs
- Runtime Security - Container Escape APIs
- ModifyEscapeWhiteList
- ModifyEscapeRule
- ModifyEscapeEventStatus
- DescribeEscapeWhiteList
- DescribeEscapeSafeState
- DescribeEscapeRuleInfo
- DescribeEscapeEventsExport
- DescribeEscapeEventTypeSummary
- DescribeEscapeEventTendency
- DescribeEscapeEventInfo
- DescribeEscapeEventDetail
- DeleteEscapeWhiteList
- CreateEscapeWhiteListExportJob
- CreateEscapeEventsExportJob
- AddEscapeWhiteList
- Runtime Security APIs
- StopVulScanTask
- OpenTcssTrial
- ModifyAccessControlStatus
- ModifyAccessControlRuleStatus
- ModifyAbnormalProcessStatus
- ModifyAbnormalProcessRuleStatus
- DescribeWebVulList
- DescribeVulScanLocalImageList
- DescribeVulScanInfo
- DescribeVulImageList
- DescribeVulDetail
- DescribeVulContainerList
- DescribeSupportDefenceVul
- DescribeRiskSyscallDetail
- DescribeEmergencyVulList
- DescribeAssetImageBindRuleInfo
- DescribeAccessControlRulesExport
- DescribeAccessControlRules
- DescribeAccessControlRuleDetail
- DescribeAccessControlEventsExport
- DescribeAccessControlEvents
- DescribeAccessControlDetail
- DescribeAbnormalProcessRulesExport
- DescribeAbnormalProcessRules
- DescribeAbnormalProcessRuleDetail
- DescribeAbnormalProcessLevelSummary
- DescribeAbnormalProcessEventsExport
- DescribeAbnormalProcessEvents
- DescribeAbnormalProcessEventTendency
- DescribeAbnormalProcessDetail
- DeleteAccessControlRules
- DeleteAbnormalProcessRules
- CreateWebVulExportJob
- CreateVulScanTask
- CreateVulImageExportJob
- CreateVulContainerExportJob
- CreateSystemVulExportJob
- CreateRiskDnsEventExportJob
- CreateProcessEventsExportJob
- CreateEmergencyVulExportJob
- CreateDefenceVulExportJob
- AddEditRiskSyscallWhiteList
- AddEditAccessControlRule
- AddEditAbnormalProcessRule
- Image Security APIs
- DescribeVulRegistryImageList
- UpdateImageRegistryTimingScanTask
- UpdateAssetImageRegistryRegistryDetail
- SyncAssetImageRegistryAsset
- SwitchImageAutoAuthorizedRule
- RenewImageAuthorizeState
- RemoveAssetImageRegistryRegistryDetail
- ModifyVulDefenceSetting
- ModifyVulDefenceEventStatus
- ModifyImageAuthorized
- ModifyAssetImageScanStop
- ModifyAssetImageRegistryScanStopOneKey
- ModifyAssetImageRegistryScanStop
- ModifyAsset
- DescribeVulTopRanking
- DescribeVulTendency
- DescribeVulSummary
- DescribeVulScanAuthorizedImageSummary
- DescribeVulLevelSummary
- DescribeVulLevelImageSummary
- DescribeVulImageSummary
- DescribeVulIgnoreRegistryImageList
- DescribeVulIgnoreLocalImageList
- DescribeVulDefenceSetting
- DescribeVulDefencePlugin
- DescribeVulDefenceHost
- DescribeVulDefenceEventTendency
- DescribeVulDefenceEventDetail
- DescribeVulDefenceEvent
- DescribeValueAddedSrvInfo
- DescribeSystemVulList
- DescribeSecEventsTendency
- DescribeScanIgnoreVulList
- DescribePostPayDetail
- DescribeNewestVul
- DescribeImageSimpleList
- DescribeImageRiskTendency
- DescribeImageRiskSummary
- DescribeImageRegistryTimingScanTask
- DescribeImageRegistryNamespaceList
- DescribeImageComponentList
- DescribeImageAutoAuthorizedTaskList
- DescribeImageAutoAuthorizedRule
- DescribeImageAutoAuthorizedLogList
- DescribeContainerSecEventSummary
- DescribeContainerAssetSummary
- DescribeAutoAuthorizedRuleHost
- DescribeAssetWebServiceList
- DescribeAssetSummary
- DescribeAssetProcessList
- DescribeAssetPortList
- DescribeAssetImageVulListExport
- DescribeAssetImageVulList
- DescribeAssetImageVirusListExport
- DescribeAssetImageVirusList
- DescribeAssetImageSimpleList
- DescribeAssetImageScanTask
- DescribeAssetImageScanStatus
- DescribeAssetImageScanSetting
- DescribeAssetImageRiskListExport
- DescribeAssetImageRiskList
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryVulListExport
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryVulList
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryVirusListExport
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryVirusList
- DescribeAssetImageRegistrySummary
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryScanStatusOneKey
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryRiskListExport
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryRiskInfoList
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryRegistryList
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryRegistryDetail
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryListExport
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryList
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryDetail
- DescribeAssetImageRegistryAssetStatus
- DescribeAssetImageListExport
- DescribeAssetImageList
- DescribeAssetImageHostList
- DescribeAssetImageDetail
- DescribeAssetHostList
- DescribeAssetHostDetail
- DescribeAssetDBServiceList
- DescribeAssetContainerList
- DescribeAssetContainerDetail
- DescribeAssetComponentList
- DescribeAssetAppServiceList
- DeleteIgnoreVul
- CreateVulExportJob
- CreateVulDefenceHostExportJob
- CreateVulDefenceEventExportJob
- CreateOrModifyPostPayCores
- CreateImageExportJob
- CreateComponentExportJob
- CreateAssetImageScanTask
- CreateAssetImageRegistryScanTaskOneKey
- CreateAssetImageRegistryScanTask
- CheckRepeatAssetImageRegistry
- AddIgnoreVul
- AddEditImageAutoAuthorizedRule
- AddAssetImageRegistryRegistryDetail
- Runtime Security - Trojan Call APIs
- DescribeExportJobResult
- StopVirusScanTask
- ModifyVirusScanTimeoutSetting
- ModifyVirusScanSetting
- ModifyVirusMonitorSetting
- ModifyVirusFileStatus
- ModifyVirusAutoIsolateSetting
- ModifyVirusAutoIsolateExampleSwitch
- ExportVirusList
- DescribeVirusTaskList
- DescribeVirusSummary
- DescribeVirusScanTimeoutSetting
- DescribeVirusScanTaskStatus
- DescribeVirusScanSetting
- DescribeVirusSampleDownloadUrl
- DescribeVirusMonitorSetting
- DescribeVirusManualScanEstimateTimeout
- DescribeVirusList
- DescribeVirusEventTendency
- DescribeVirusDetail
- DescribeVirusAutoIsolateSetting
- DescribeVirusAutoIsolateSampleList
- DescribeVirusAutoIsolateSampleDownloadURL
- DescribeVirusAutoIsolateSampleDetail
- CreateVirusScanTask
- CreateVirusScanAgain
- Asset Management APIs
- ModifyContainerNetStatus
- DescribeUnauthorizedCoresTendency
- DescribeTcssSummary
- DescribePromotionActivity
- DescribeInspectionReport
- DescribeExportJobManageList
- DescribeExportJobDownloadURL
- DescribeAssetSyncLastTime
- DescribeAgentInstallCommand
- DescribeAgentDaemonSetCmd
- DescribeABTestConfig
- DeleteMachine
- CreateHostExportJob
- CreateAssetImageVirusExportJob
- CreateAssetImageScanSetting
- Security Operations - Log Analysis APIs
- ResetSecLogTopicConfig
- ModifySecLogKafkaUIN
- ModifySecLogJoinState
- ModifySecLogJoinObjects
- ModifySecLogDeliveryKafkaSetting
- ModifySecLogDeliveryClsSetting
- ModifySecLogCleanSettingInfo
- DescribeSecLogKafkaUIN
- DescribeSecLogJoinTypeList
- DescribeSecLogJoinObjectList
- DescribeSecLogDeliveryKafkaSetting
- DescribeSecLogDeliveryKafkaOptions
- DescribeSecLogDeliveryClsSetting
- DescribeSecLogDeliveryClsOptions
- DescribeSecLogCleanSettingInfo
- DescribeSecLogAlertMsg
- DescribeSearchTemplates
- DescribeSearchLogs
- DescribeSearchExportList
- DescribePublicKey
- DescribeLogStorageStatistic
- DescribeIndexList
- DescribeESHits
- DescribeESAggregations
- DeleteSearchTemplate
- CreateSearchTemplate
- Alert Settings APIs
- Advanced prevention - K8s API abnormal requests
- ModifyK8sApiAbnormalRuleStatus
- ModifyK8sApiAbnormalRuleInfo
- ModifyK8sApiAbnormalEventStatus
- DescribeK8sApiAbnormalTendency
- DescribeK8sApiAbnormalSummary
- DescribeK8sApiAbnormalRuleScopeList
- DescribeK8sApiAbnormalRuleList
- DescribeK8sApiAbnormalRuleInfo
- DescribeK8sApiAbnormalEventList
- DescribeK8sApiAbnormalEventInfo
- DescribeAssetClusterList
- DeleteK8sApiAbnormalRule
- CreateK8sApiAbnormalRuleInfo
- CreateK8sApiAbnormalRuleExportJob
- CreateK8sApiAbnormalEventExportJob
- CreateAccessControlsRuleExportJob
- Billing APIs
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- FAQs
- TCSS Policy
- Contact Us
- Glossary
Accessing an External Cluster
This document describes how to access an external cluster for unified management and risk check.
Limits
You can access an external cluster with up to 500 nodes.
Directions
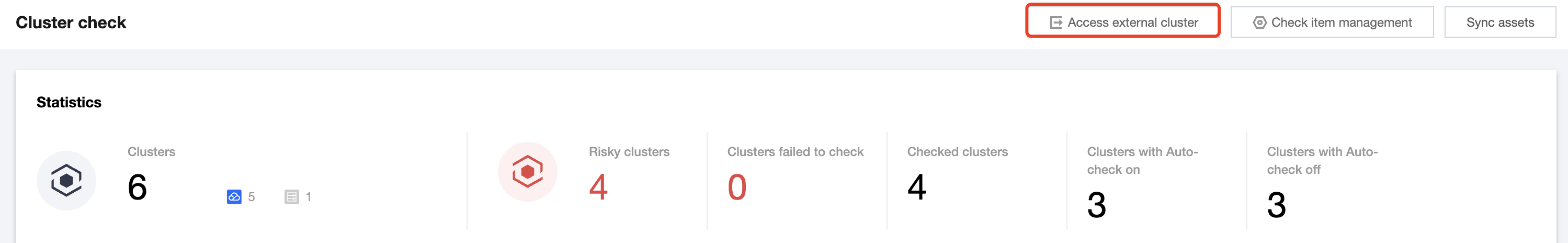
1. Log in to the TCSS console and click Cluster Risk Management > Security Check on the left sidebar.
2. On the Security Check page, click Access external cluster.

3. On the Configure cluster information page, configure parameters and click Next.
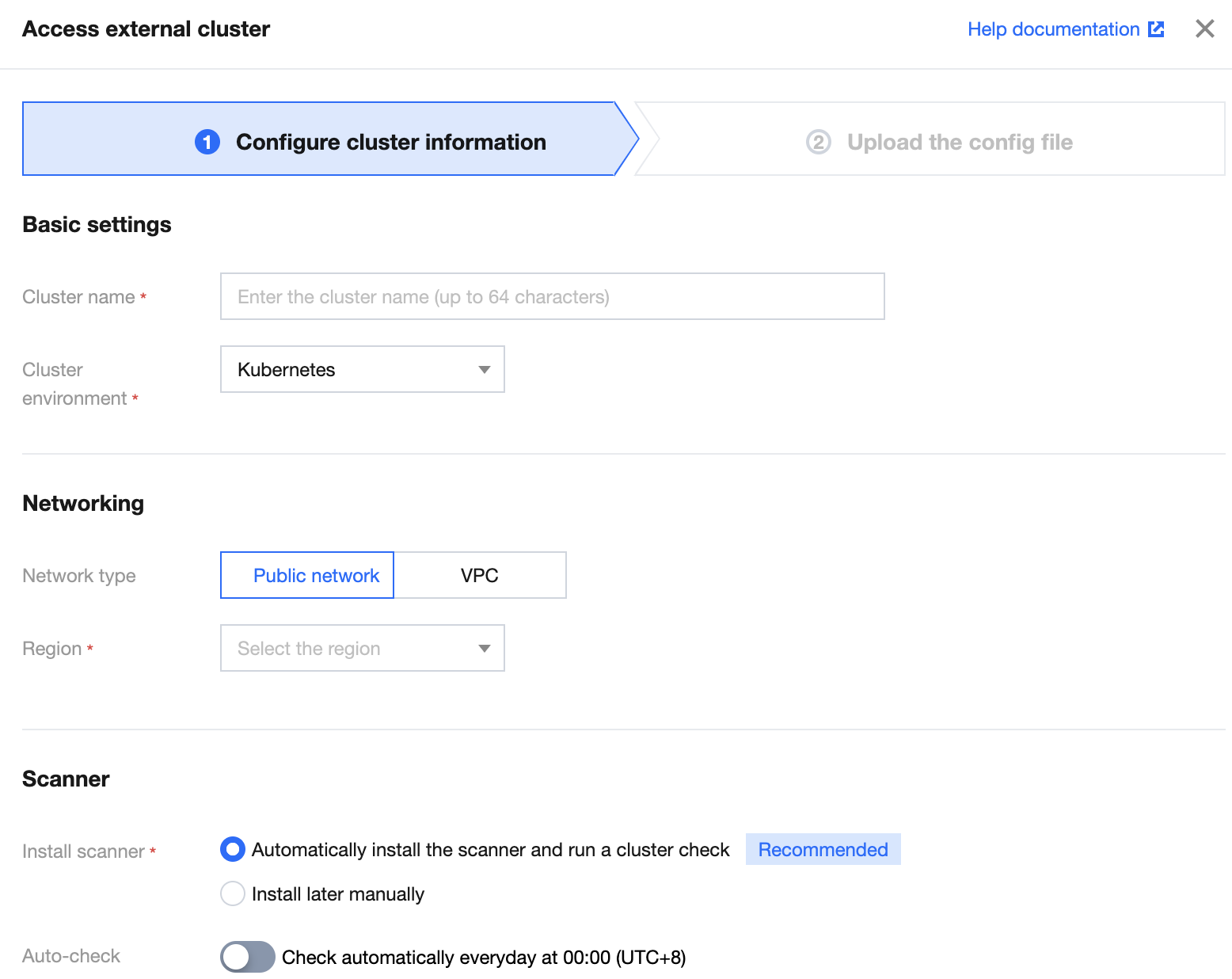

Parameter description:
Parameter Group | Parameter | Description | Option |
Basic settings | Cluster name | Enter the name of the external cluster, which can contain up to 64 characters. | - |
| Cluster environment | Select the type of the external cluster. | Kubernetes or OpenShift |
| Cluster version | Select the cluster version of the cluster environment. | 1.13 or later for Kubernetes clusters |
Networking | Network type | Select the public network or VPC for accessing the external cluster. | Public network or VPC |
| Region | Select the region of the external cluster. There is no limit on the region for the public network. | - |
| VPC ID | Select the VPC information of the cluster when you set the network type to VPC. | - |
| API server address | Select the backend service type of the cluster API server when you set the network type to VPC. | Server or load balancer |
Scanner | Scanner installation | Select the automatic or manual installation of the scanner. | Select the automatic installation and perform a security check. Select the manual installation and deliver and install the component in the cluster manually after the connection. |
| Automatic check | Set whether to enable the automatic check feature of the cluster. | Enable Disable |
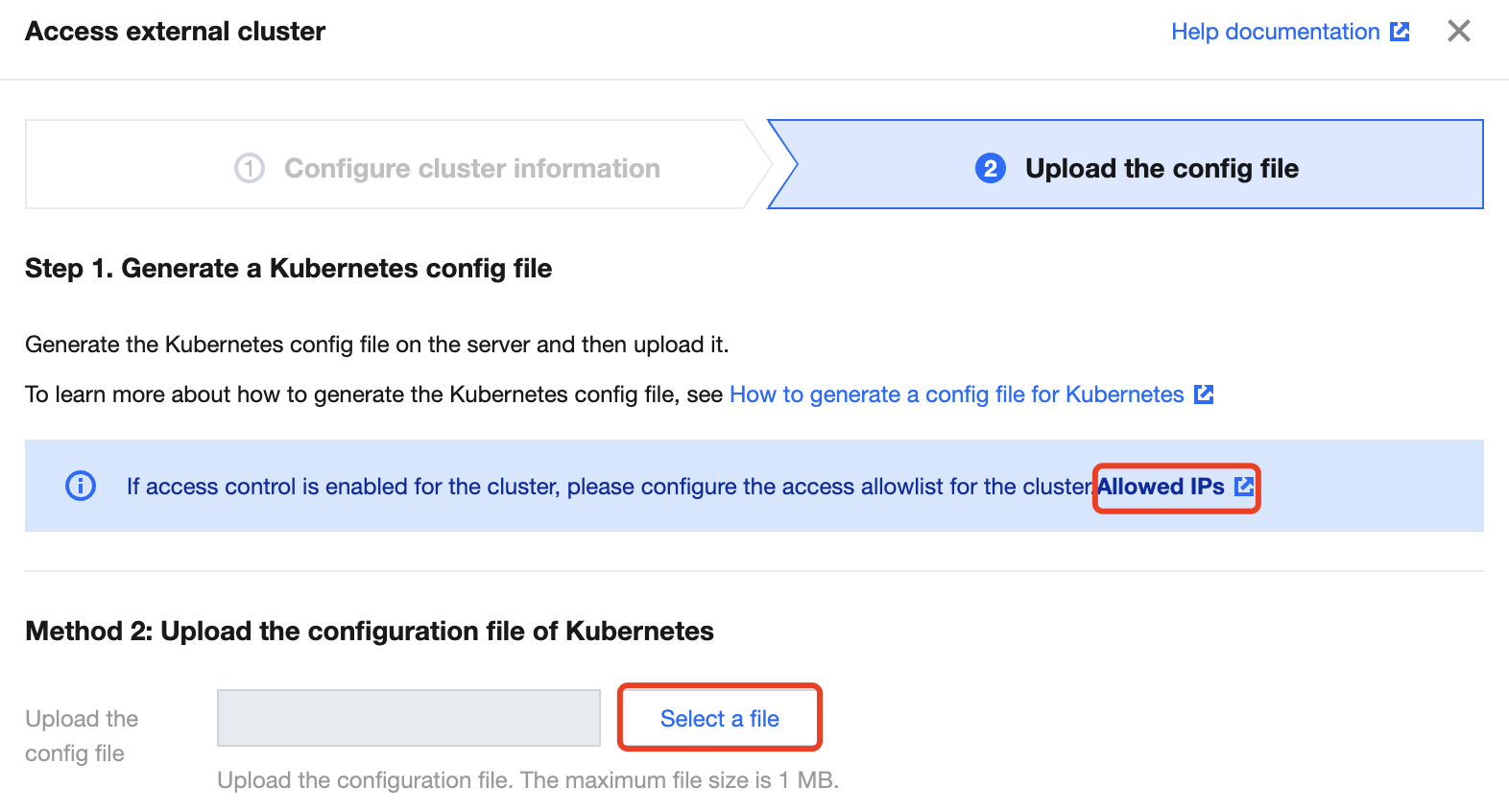
4. Click Select a file, upload a local configuration file, and click Complete.
Note:
If the self-built cluster is accessed over the public network and the access control policy is set, you need to click Allowed IPs to add the IP on the page.
You need to generate a Kubernetes configuration file on the server before you can upload it. For detailed directions, see Generating a Kubernetes Configuration File.
You can upload a configuration file of up to 1 MB.

Generating a Kubernetes Configuration File
This section describes how to generate a Kubernetes configuration file of the least privilege required by TCSS.
Prerequisites
You have set up a Kubernetes cluster on the server as instructed in Getting started.
You have installed the Docker service.
Directions
1. Log in to the server of the master node of the Kubernetes cluster as the root user.
2. Enter the following command to create a namespace and bind the permission.
# 1. Create the `tcss` namespace# 2. Create the `tcss-admin` admin role under the `tcss` namespace# 3. Bind the `tcss-admin` role to the `tcss` user# 4. Create the `tcss-agent-secret` key and bind it to the `tcss-agent` service account# 5. Create the `security-clusterrole` read-only cluster role# 6. Bind the `security-clusterrole` role to the `tcss-agent` service account---apiVersion: v1kind: Namespacemetadata:name: tcss---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: Rolemetadata:namespace: tcssname: tcss-adminrules:- apiGroups: ["extensions", "apps", ""]resources: ["*"]verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: RoleBindingmetadata:name: tcss-admin-rbnamespace: tcsssubjects:- kind: Username: tcssapiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.ioroleRef:kind: Rolename: tcss-adminapiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io---apiVersion: v1kind: Secretmetadata:name: tcss-agent-secretnamespace: tcssannotations:kubernetes.io/service-account.name: tcss-agenttype: kubernetes.io/service-account-token---apiVersion: v1kind: ServiceAccountmetadata:name: tcss-agentnamespace: tcsssecrets:- name: tcss-agent-secretnamespace: tcss---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: ClusterRolemetadata:name: security-clusterrolerules:- apiGroups: ["", "v1"]resources: ["namespaces", "pods", "nodes"]verbs: ["get", "list"]- apiGroups: ["apps"]resources: ["replicasets", "daemonsets", "deployments", "statefulsets"]verbs: ["get", "list"]- apiGroups: ["batch"]resources: ["jobs", "cronjobs"]verbs: ["get", "list"]- apiGroups: ["rbac.authorization.k8s.io"]resources: ["clusterroles", "clusterrolebindings"]verbs: ["get"]---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: ClusterRoleBindingmetadata:name: security-clusterrolebindingroleRef:apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.iokind: ClusterRolename: security-clusterrolesubjects:- kind: ServiceAccountname: tcss-agentnamespace: tcss- kind: Username: tcssapiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
3. Go to the Kubernetes configuration directory (/etc/kubernetes/) and enter the following command to create a certificate.
# Create the `tcss.key` key for `User`openssl genrsa -out tcss.key 2048# Create the `tcss.csr` certificate signing requestopenssl req -new -key tcss.key -out tcss.csr -subj "/O=K8s/CN=tcss"# Sign the certificate and generate `tcss.crt`openssl x509 -req -in tcss.csr -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -CAcreateserial -out tcss.crt -days 365
4. Enter the following command to create a cluster configuration file.
# Create and set the cluster configuration. Here, the API server address must be a public network address that is accessible.kubectl config set-cluster tcss --server=https://xx.xx.xx.xx:60002 --certificate-authority=/etc/kubernetes/ca.crt --embed-certs=true --kubeconfig=/root/tcss.conf# Create and set the user configurationkubectl config set-credentials tcss --client-certificate=tcss.crt --client-key=tcss.key --embed-certs=true --kubeconfig=/root/tcss.conf# Set the `context` configurationkubectl config set-context tcss@tcss --cluster=tcss --user=tcss --kubeconfig=/root/tcss.conf# Switch the `context` configurationkubectl config use-context tcss@tcss --kubeconfig=/root/tcss.conf
5. Verify and upload the cluster configuration file.
KUBECONFIG=/root/tcss.conf kubectl -n tcss get pod
Note:
Run the above command. If the returned result displays a Pod or indicates that there are no relevant resources in the current namespace, the cluster configuration is available, and you just need to upload the file to
/root/tcss.conf.Quick script
On the master node, you can use the following script code to quickly generate a cluster configuration file.
Note:
You need to install OpenSSL in the environment in advance.
#!/bin/bashset -e;# You need to set `API_SERVER` as the accessible address and port of the public network.# API_SERVER=https://xx.xx.xx.xx:xxxx# Set the following paths as neededKUBECONFIG_TARGET=/root/tcss.confCA_FILE=/etc/kubernetes/ca.crtCAKEY_FILE=/etc/kubernetes/ca.keyTCSS_TMPDIR=/tmp/tcss# In the OpenShift environment, replace it with `oc`KUBECTL_CMD=kubectlif [ ! $API_SERVER ]; thenecho "API_SERVER does not set.";exit 1;fiif ! which kubectl ; thenecho "kubectl does not exist.";exit 1;fiif [ ! -f "$CA_FILE" ]; thenecho "$CA_FILE does not exist.";exit 1;fiif [ ! -f "$CAKEY_FILE" ]; thenecho "$CAKEY_FILE does not exist.";exit 1;fiif [ ! -d $TCSS_TMPDIR ]; thenmkdir -p $TCSS_TMPDIR;ficat <<EOF > $TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss_res.yaml---apiVersion: v1kind: Namespacemetadata:name: tcss---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: Rolemetadata:namespace: tcssname: tcss-adminrules:- apiGroups: ["extensions", "apps", ""]resources: ["*"]verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: RoleBindingmetadata:name: tcss-admin-rbnamespace: tcsssubjects:- kind: Username: tcssapiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.ioroleRef:kind: Rolename: tcss-adminapiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io---apiVersion: v1kind: Secretmetadata:name: tcss-agent-secretnamespace: tcssannotations:kubernetes.io/service-account.name: tcss-agenttype: kubernetes.io/service-account-token---apiVersion: v1kind: ServiceAccountmetadata:name: tcss-agentnamespace: tcsssecrets:- name: tcss-agent-secretnamespace: tcss---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: ClusterRolemetadata:name: security-clusterrolerules:- apiGroups: ["", "v1"]resources: ["namespaces", "pods", "nodes"]verbs: ["get", "list"]- apiGroups: ["apps"]resources: ["replicasets", "daemonsets", "deployments", "statefulsets"]verbs: ["get", "list"]- apiGroups: ["batch"]resources: ["jobs", "cronjobs"]verbs: ["get", "list"]- apiGroups: ["rbac.authorization.k8s.io"]resources: ["clusterroles", "clusterrolebindings"]verbs: ["get"]---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: ClusterRoleBindingmetadata:name: security-clusterrolebindingroleRef:apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.iokind: ClusterRolename: security-clusterrolesubjects:- kind: ServiceAccountname: tcss-agentnamespace: tcss- kind: Username: tcssapiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.ioEOF# echo "generate tcss resource file ($TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss_res.yaml) success."$KUBECTL_CMD apply -f $TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss_res.yaml;# Create the `tcss.key` key for `User`openssl genrsa -out $TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss.key 2048# Create the `tcss.csr` certificate signing requestopenssl req -new -key $TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss.key -out $TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss.csr -subj "/O=K8s/CN=tcss"# Sign the certificate and generate `tcss.crt`openssl x509 -req -in $TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss.csr -CA $CA_FILE -CAkey $CAKEY_FILE -CAcreateserial -out $TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss.crt -days 365# Create and set the cluster configuration$KUBECTL_CMD config set-cluster tcss --server=$API_SERVER --certificate-authority=$CA_FILE --embed-certs=true --kubeconfig=$KUBECONFIG_TARGET# Create and set the user configuration$KUBECTL_CMD config set-credentials tcss --client-certificate=$TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss.crt --client-key=$TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss.key --embed-certs=true --kubeconfig=$KUBECONFIG_TARGET# Set the `context` configuration$KUBECTL_CMD config set-context tcss@tcss --cluster=tcss --user=tcss --kubeconfig=$KUBECONFIG_TARGET# Switch the `context` configuration$KUBECTL_CMD config use-context tcss@tcss --kubeconfig=$KUBECONFIG_TARGETecho "generate KUBECONFIG file success. $KUBECONFIG_TARGET"
Generating an OpenShift Configuration File
This section describes how to generate an OpenShift configuration file of the least privilege required by TCSS.
Prerequisites
1. You have set up a Kubernetes cluster on the server as instructed in Getting started.
2. You have installed the Docker service.
3. Currently, only OpenShift 3.0 and later are supported. Earlier versions may involve uncertain issues.
Directions
Note:
The overall idea is similar to that described in the previous section. The only difference lies in the path and command line tool. If kubectl has been installed on the master node in the cluster, the directions are the same as those described in the previous section.
1. Log in to the server of the master node in the OpenShift cluster as the root user.
2. Enter the following command to create a namespace and bind the permission.
# 1. Create the `tcss` namespace# 2. Create the `tcss-admin` admin role under the `tcss` namespace# 3. Bind the `tcss-admin` role to the `tcss` user# 4. Create the `tcss-agent-secret` key and bind it to the `tcss-agent` service account# 5. Create the `security-clusterrole` read-only cluster role# 6. Bind the `security-clusterrole` role to the `tcss-agent` service account---apiVersion: v1kind: Namespacemetadata:name: tcss---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: Rolemetadata:namespace: tcssname: tcss-adminrules:- apiGroups: ["extensions", "apps", ""]resources: ["*"]verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: RoleBindingmetadata:name: tcss-admin-rbnamespace: tcsssubjects:- kind: Username: tcssapiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.ioroleRef:kind: Rolename: tcss-adminapiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io---apiVersion: v1kind: Secretmetadata:name: tcss-agent-secretnamespace: tcssannotations:kubernetes.io/service-account.name: tcss-agenttype: kubernetes.io/service-account-token---apiVersion: v1kind: ServiceAccountmetadata:name: tcss-agentnamespace: tcsssecrets:- name: tcss-agent-secretnamespace: tcss---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: ClusterRolemetadata:name: security-clusterrolerules:- apiGroups: ["", "v1"]resources: ["namespaces", "pods", "nodes"]verbs: ["get", "list"]- apiGroups: ["apps"]resources: ["replicasets", "daemonsets", "deployments", "statefulsets"]verbs: ["get", "list"]- apiGroups: ["batch"]resources: ["jobs", "cronjobs"]verbs: ["get", "list"]- apiGroups: ["rbac.authorization.k8s.io"]resources: ["clusterroles", "clusterrolebindings"]verbs: ["get"]---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: ClusterRoleBindingmetadata:name: security-clusterrolebindingroleRef:apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.iokind: ClusterRolename: security-clusterrolesubjects:- kind: ServiceAccountname: tcss-agentnamespace: tcss- kind: Username: tcssapiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
3. Go to the configuration directory (/etc/origin/master/) and enter the following command to create a certificate.
# Create the `tcss.key` key for `User`openssl genrsa -out tcss.key 2048# Create the `tcss.csr` certificate signing requestopenssl req -new -key tcss.key -out tcss.csr -subj "/O=K8s/CN=tcss"# Sign the certificate and generate `tcss.crt`openssl x509 -req -in tcss.csr -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -CAcreateserial -out tcss.crt -days 365
4. Enter the following command to create a cluster configuration file.
# Create and set the cluster configuration. Here, the main server address must be a public network address that is accessible.KUBECONFIG=/root/tcss.conf oc config set-cluster tcss --server=https://xx.xx.xx.xx:60002 --certificate-authority=/etc/origin/master/ca.crt --embed-certs=true --kubeconfig=/root/tcss.conf# Create and set the user configurationKUBECONFIG=/root/tcss.conf oc config set-credentials tcss --client-certificate=tcss.crt --client-key=tcss.key --embed-certs=true --kubeconfig=/root/tcss.conf# Set the `context` configurationKUBECONFIG=/root/tcss.conf oc config set-context tcss@tcss --cluster=tcss --user=tcss --kubeconfig=/root/tcss.conf# Switch the `context` configurationKUBECONFIG=/root/tcss.conf oc config use-context tcss@tcss --kubeconfig=/root/tcss.conf
5. Enter the following command to verify and upload the cluster configuration file.
KUBECONFIG=/root/tcss.conf oc -n tcss get pod
Note:
Run the above command. If the returned result displays a Pod or indicates that there are no relevant resources in the current namespace, the cluster configuration is available, and you just need to upload the file to
/root/tcss.conf.Quick script
On the master node, you can use the following script code to quickly generate a cluster configuration file.
Note:
You need to install OpenSSL in the environment in advance.
#!/bin/bashset -e;# You need to set `API_SERVER` as the accessible address and port of the public network.# API_SERVER=https://xx.xx.xx.xx:xxxx# Set the following paths as neededKUBECONFIG_TARGET=/root/tcss.confCA_FILE=/etc/kubernetes/ca.crtCAKEY_FILE=/etc/kubernetes/ca.keyTCSS_TMPDIR=/tmp/tcssKUBECTL_CMD=ocif [ ! $API_SERVER ]; thenecho "API_SERVER does not set.";exit 1;fiif ! which $KUBECTL_CMD ; thenecho "$KUBECTL_CMD does not exist.";exit 1;fiif [ ! -f "$CA_FILE" ]; thenecho "$CA_FILE does not exist.";exit 1;fiif [ ! -f "$CAKEY_FILE" ]; thenecho "$CAKEY_FILE does not exist.";exit 1;fiif [ ! -d $TCSS_TMPDIR ]; thenmkdir -p $TCSS_TMPDIR;ficat <<EOF > $TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss_res.yaml---apiVersion: v1kind: Namespacemetadata:name: tcss---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: Rolemetadata:namespace: tcssname: tcss-adminrules:- apiGroups: ["extensions", "apps", ""]resources: ["*"]verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "patch", "delete"]---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: RoleBindingmetadata:name: tcss-admin-rbnamespace: tcsssubjects:- kind: Username: tcssapiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.ioroleRef:kind: Rolename: tcss-adminapiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io---apiVersion: v1kind: Secretmetadata:name: tcss-agent-secretnamespace: tcssannotations:kubernetes.io/service-account.name: tcss-agenttype: kubernetes.io/service-account-token---apiVersion: v1kind: ServiceAccountmetadata:name: tcss-agentnamespace: tcsssecrets:- name: tcss-agent-secretnamespace: tcss---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: ClusterRolemetadata:name: security-clusterrolerules:- apiGroups: ["", "v1"]resources: ["namespaces", "pods", "nodes"]verbs: ["get", "list"]- apiGroups: ["apps"]resources: ["replicasets", "daemonsets", "deployments", "statefulsets"]verbs: ["get", "list"]- apiGroups: ["batch"]resources: ["jobs", "cronjobs"]verbs: ["get", "list"]- apiGroups: ["rbac.authorization.k8s.io"]resources: ["clusterroles", "clusterrolebindings"]verbs: ["get"]---apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1kind: ClusterRoleBindingmetadata:name: security-clusterrolebindingroleRef:apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.iokind: ClusterRolename: security-clusterrolesubjects:- kind: ServiceAccountname: tcss-agentnamespace: tcss- kind: Username: tcssapiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.ioEOF# echo "generate tcss resource file ($TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss_res.yaml) success."$KUBECTL_CMD apply -f $TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss_res.yaml;$KUBECTL_CMD adm policy add-scc-to-user privileged -n tcss -z tcss-agent;$KUBECTL_CMD adm policy add-scc-to-user hostaccess -n tcss -z tcss-agent;$KUBECTL_CMD adm policy add-scc-to-user privileged tcss;$KUBECTL_CMD adm policy add-scc-to-user hostaccess tcss;oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-reader tcss;# Create the `tcss.key` key for `User`openssl genrsa -out $TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss.key 2048# Create the `tcss.csr` certificate signing requestopenssl req -new -key $TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss.key -out $TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss.csr -subj "/O=K8s/CN=tcss"# Sign the certificate and generate `tcss.crt`openssl x509 -req -in $TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss.csr -CA $CA_FILE -CAkey $CAKEY_FILE -CAcreateserial -out $TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss.crt -days 365# Create and set the cluster configurationKUBECONFIG=$KUBECONFIG_TARGET $KUBECTL_CMD config set-cluster tcss --server=$API_SERVER --certificate-authority=$CA_FILE --embed-certs=true --kubeconfig=$KUBECONFIG_TARGET# Create and set the user configurationKUBECONFIG=$KUBECONFIG_TARGET $KUBECTL_CMD config set-credentials tcss --client-certificate=$TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss.crt --client-key=$TCSS_TMPDIR/tcss.key --embed-certs=true --kubeconfig=$KUBECONFIG_TARGET# Set the `context` configurationKUBECONFIG=$KUBECONFIG_TARGET $KUBECTL_CMD config set-context tcss@tcss --cluster=tcss --user=tcss --kubeconfig=$KUBECONFIG_TARGET# Switch the `context` configurationKUBECONFIG=$KUBECONFIG_TARGET $KUBECTL_CMD config use-context tcss@tcss --kubeconfig=$KUBECONFIG_TARGETecho "generate KUBECONFIG file success. $KUBECONFIG_TARGET"

 Yes
Yes
 No
No
Was this page helpful?