TencentDB for PostgreSQL
User Guide
Product Documentation


Copyright Notice
©2013-2026 Tencent Cloud. All rights reserved.
Copyright in this document is exclusively owned by Tencent Cloud. You must not reproduce, modify, copy or distribute in any way, in whole or in part, the contents of this document without Tencent Cloud's the prior written consent.
Trademark Notice

All trademarks associated with Tencent Cloud and its services are owned by the Tencent corporate group, including its parent, subsidiaries and affiliated companies, as the case may be. Trademarks of third parties referred to in this document are owned by their respective proprietors.
Service Statement
This document is intended to provide users with general information about Tencent Cloud's products and services only and does not form part of Tencent Cloud's terms and conditions. Tencent Cloud's products or services are subject to change. Specific products and services and the standards applicable to them are exclusively provided for in Tencent Cloud's applicable terms and conditions.
Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51

Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51
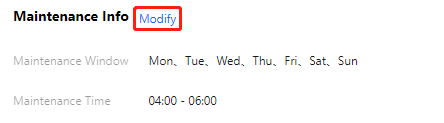
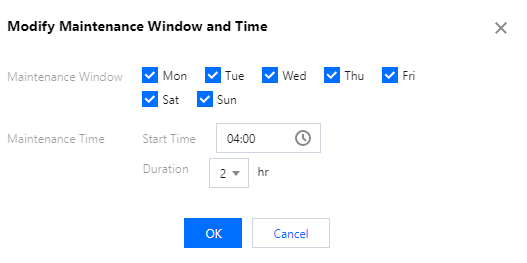
Last updated:2025-07-22 20:25:30
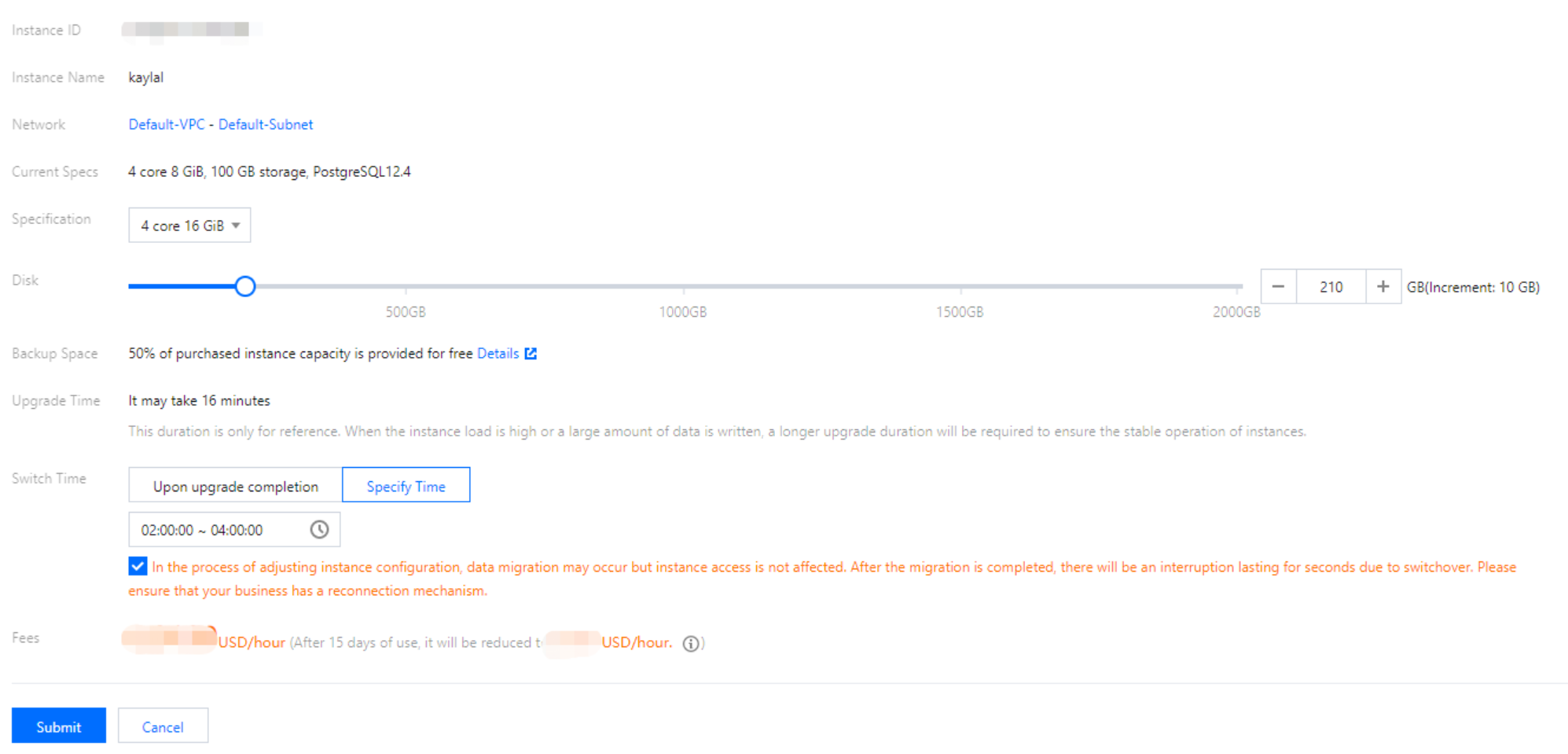
Last updated:2025-08-14 16:25:52

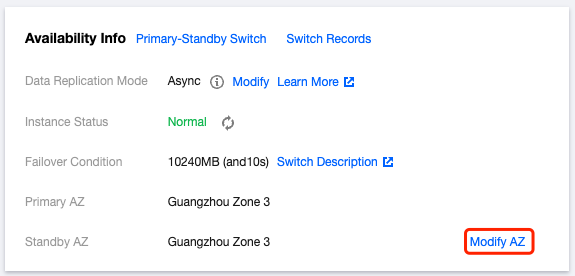

Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51


Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51
Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51
Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51
Last updated:2025-08-05 11:22:59
Last updated:2025-05-21 15:53:27
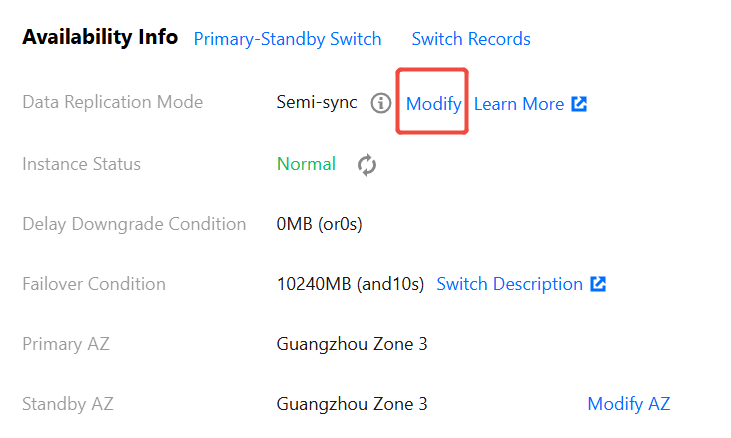
Information | Description |
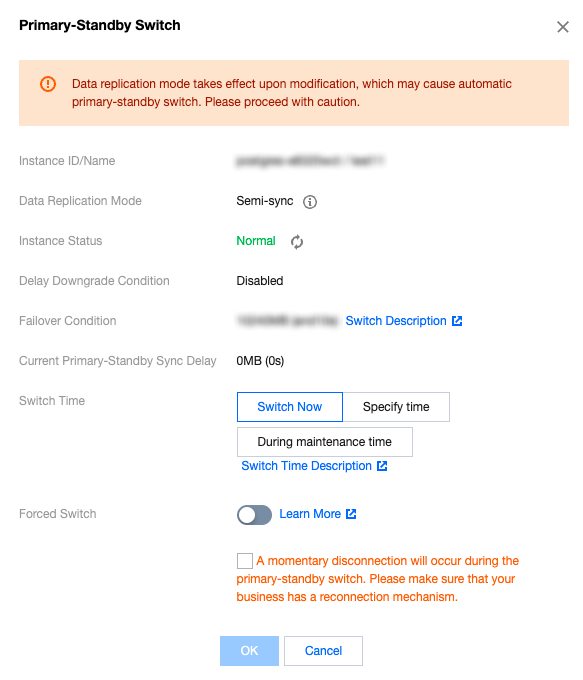
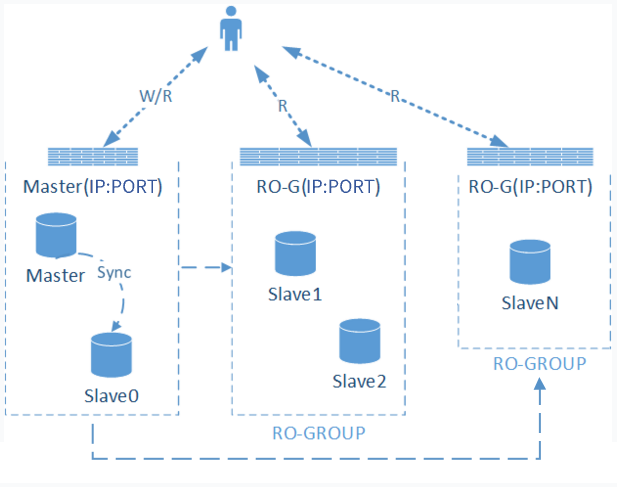
Data Replication Mode | For the data synchronization mode between the master and the slave, the current two-machine high availability (one master and one slave) architecture supports Async ( Asynchronous replication )and Semi-Sync ( Semi-synchronous replication ). |
Instance Status | Display the current accessibility status of the instance. When the status is normal, normally receive user requests. If an abnormal display occurs, it indicates that the instance currently cannot receive application requests. |
| |
Failover Condition | When the Master node fails and cannot be recovered, automatic failover is required, with the Slave providing services. At this point, the system defines the failover conditions, which are the size and time of primary-backup latency. The default system conditions are less than or equal to 10240 MB and 10 seconds. For specific switch conditions, refer to Failover Description. |
Primary AZ | It refers to the availability zone of the master node. |
Standby AZ | It refers to the availability zone of the slave node. |
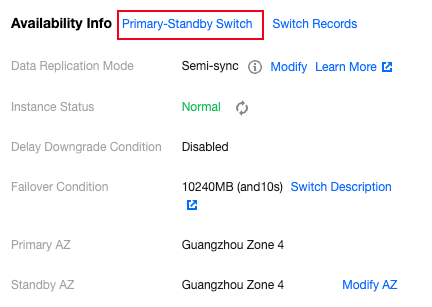
Information | Description |
Data Replication Mode | For the data synchronization mode between the master and the slave, the current two-machine high availability (one master and one slave) architecture supports Async ( Asynchronous replication )and Semi-Sync ( Semi-synchronous replication ). |
Instance Status | It displays the current accessibility status of the instance. When the status is normal, user requests are normally received. If the status is abnormal, the instance currently cannot accept application requests. |
Delay Downgrade Condition | When the data replication mode of the instance is semi-synchronous replication, the system will automatically degrade the master and slave replication method to asynchronous to ensure system availability outside the range of user-set conditions. This degradation condition is the master and standby latency size or latency time. Among them, PostgreSQL instances with a large version number of 9 only support the condition of master and standby latency size. For details, see Degradation Description. |
Failover Condition | When the master node fails and cannot be recovered, an automatic failover is required, to switch to the slave to provide service. At this time, the system has defined the failover conditions, which are the size or time of master-slave latency. Applications can modify the switch conditions based on special needs. For details, see Failover Description. |
Primary AZ | It refers to the availability zone of the master node. |
Standby AZ | It refers to the availability zone of the slave node. |
Last updated:2025-05-21 15:53:27
Metric Name | Metric Description |
Slave Log Write-to-Disk Latency (Bytes) | It refers to the difference in size between the slave log write-to-disk LSN and the current LSN of the master instance. For the master instance, this metric reflects the data loss size in the event of a failover. |
Slave Log Write-to-Disk Time Latency (Seconds) | The time difference between the transmission of logs from the primary database to the secondary database and the reception and persistence of these logs on the secondary database reflects the potential data loss during failover for the primary instance. This metric is available only for instance versions 10.x and above. |
Master-Slave Data Synchronization Latency (Bytes) | It refers to the difference in size between the slave replay LSN and the current LSN of the master instance. For the master instance, this metric reflects the RTO in the event of a failover. For read-only instances, this metric reflects the data latency size. |
Master-Slave Data Synchronization Latency Time (Seconds) | The time difference between the transmission of logs from the primary database to the secondary database and the reception and replay of these logs by the secondary database. This metric is available only for instance versions 10.x and above. |
Slave Log Send and Replay Position Difference (Bytes) | It refers to the size difference between the master instance sending the log to the slave instance and the completion of slave log replication. It reflects the speed of slave log application. You can mainly check the performance of the slave instance and the speed of network transmission through this metric. This metric is not available for read-only instances. |
Last updated:2025-06-09 10:26:09
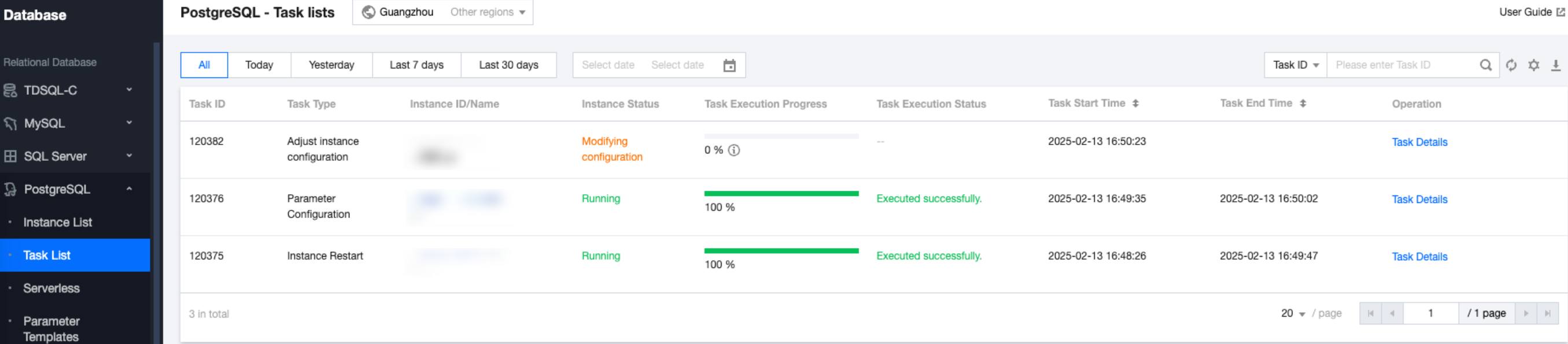

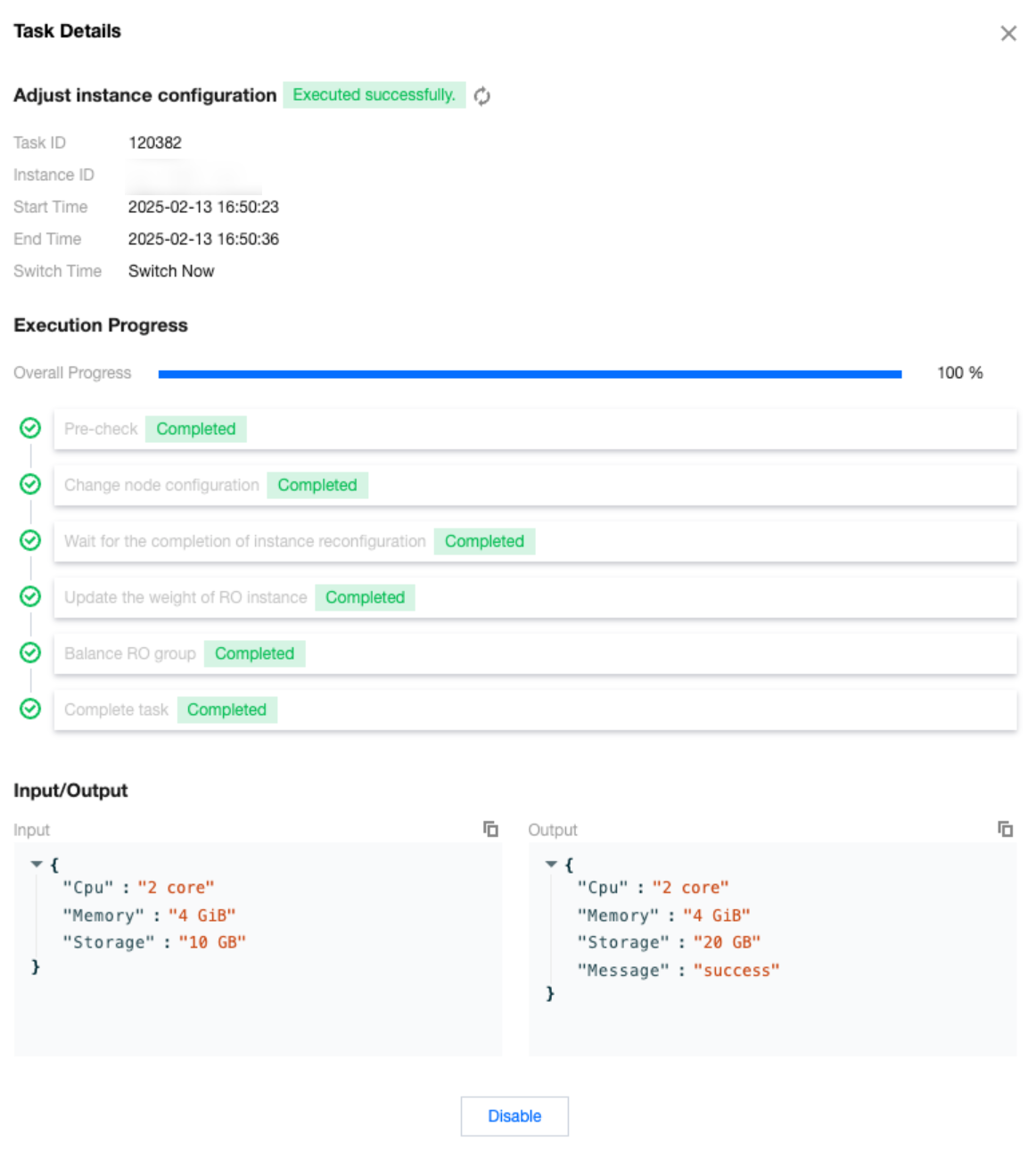
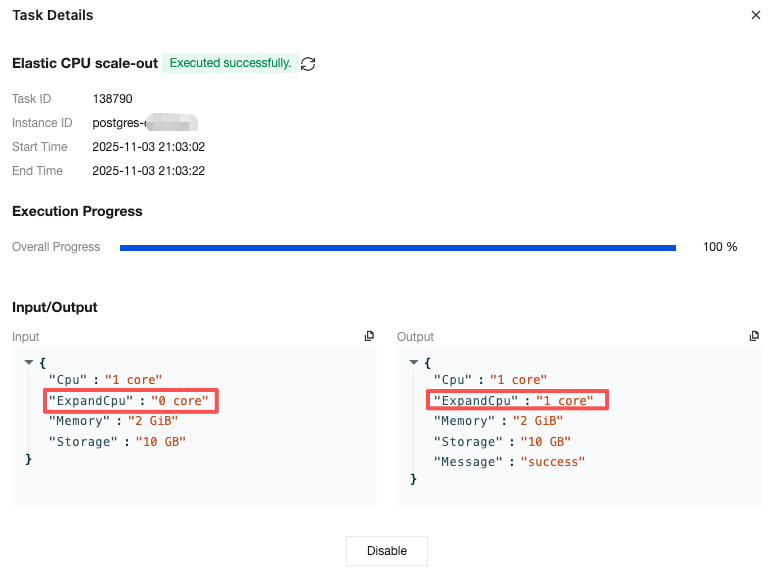
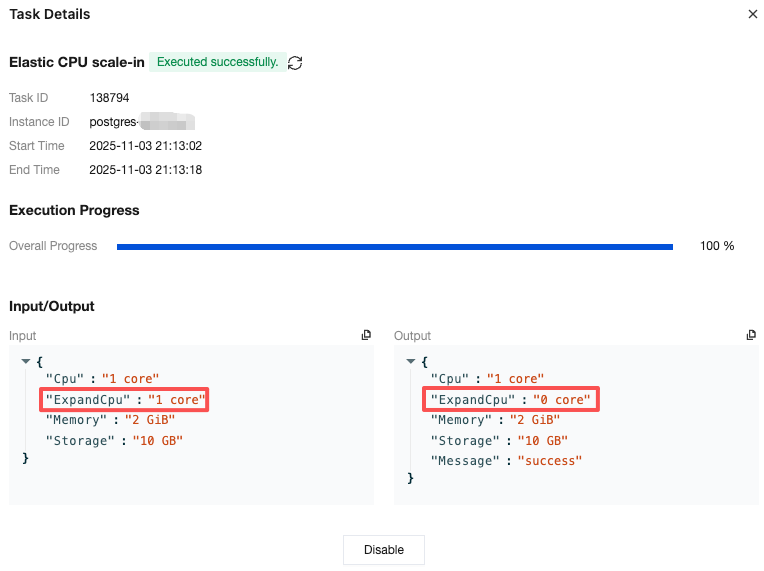
Task Type | Input | Output |
Adjusting instance configuration | { "Cpu":"2 core"//CPU configuration before instance adjustment. "Memory":"4 GiB"//Memory configuration before instance adjustment. "Storage":"10 GB"//Storage space configuration before instance adjustment. } | { "Cpu":"2 core"//CPU configuration after instance adjustment. "Memory":"4 GiB"//Memory configuration after instance adjustment. "Storage":"20 GB"//Storage space configuration after instance adjustment. "Message":"success"//Specific returned result of the task. Success indicates success. For other statuses, see the specific information. } |
Changing the read-only group for a read-only instance | { "NewROGroupId":"pgrogrp-3p21ssox"//Target read-only group ID. "OldROGroupId":"pgrogrp-dct9wsml"//Source read-only group ID. "ROInstanceId":"pgro-a9qea3c9"//Read-only instance ID. } | { "NewROGroup":{//Target read-only group details. "ROGroupId":"pgrogrp-3p21ssox" "ROGroupIp":"10.0.0.2" "ROGroupName":"1" "ROGroupPort":5432 } "OldROGroup":{//Source read-only group details. "ROGroupId":"pgrogrp-dct9wsml" "ROGroupIp":"10.0.0.6" "ROGroupName":"2" "ROGroupPort":5432 } "ROInstance":{//Read-only instance details. "ROInstanceId":"pgro-a9qea3c9" "ROInstanceIp":[ 0:"10.0.0.17" ] "ROInstanceName":"Unnamed" "ROInstancePort":5432 } } |
Adding a read-only instance to a read-only group | { "ReadOnlyGroupId":"pgrogrp-3p21ssox"//Target read-only group ID. "ReadOnlyInstanceId":"pgro-82nkylkb"//Read-only instance ID. } | { "ROGroup":{//Target read-only group details. "ROGroupId":"pgrogrp-3p21ssox" "ROGroupIp":"10.0.0.2" "ROGroupName":"1" "ROGroupPort":5432 } "ROInstance":{//Read-only instance details. "ROInstanceId":"pgro-82nkylkb" "ROInstanceIp":[ 0:"10.0.0.10" ] "ROInstanceName":"Unnamed" "ROInstancePort":5432 } } |
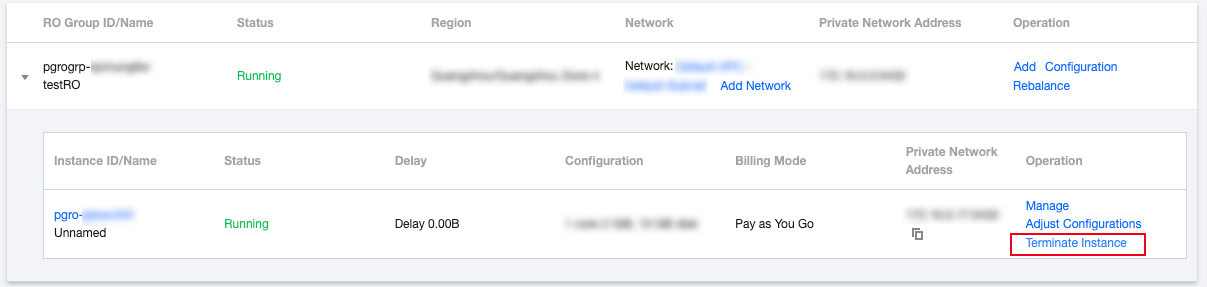
Removing a read-only instance from a read-only group | { "ROGroupId":"pgrogrp-3p21ssox"//Source read-only group details. "ROInstanceId":"pgro-a9qea3c9"//Read-only instance ID. } | { "ROGroup":{//Source read-only group details. "ROGroupId":"pgrogrp-3p21ssox" "ROGroupIp":"10.0.0.2" "ROGroupName":"1" "ROGroupPort":5432 } "ROInstance":{//Read-only instance details. "ROInstanceId":"pgro-a9qea3c9" "ROInstanceIp":[ 0:"10.0.0.17" ] "ROInstanceName":"Unnamed" "ROInstancePort":5432 } } |
Adding a network | { "DBInstanceId":"postgres-6s1kuw28"//Instance ID. "IsAssignVip":false//Whether the assigned VIP is registered. All are false here. "SubnetId":"subnet-piadji8r"//Subnet ID. "Vip":""//The VIP that is about to be assigned. All are empty here. "VpcId":"vpc-fz41fhgo"//Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) ID. } | { "DBInstanceId":"postgres-6s1kuw28"//Instance ID. "DBInstanceNetInfo":{//Details of the newly added network. "Address":"" "Ip":"10.0.10.15" "Port":5432 "Status":"opened" "NetType":"private" "VpcId":"vpc-fz41fhgo" "SubnetId":"subnet-piadji8r" "ProtocolType":"postgresql" } } |
Deleting a network | { "DBInstanceId":"postgres-6s1kuw28"//Instance ID. "SubnetId":"subnet-piadji8r"//Subnet ID. "Vip":"10.0.10.15"//VIP to be deleted. "VpcId":"vpc-fz41fhgo"//Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) ID. } | { "DBInstanceId":"postgres-6s1kuw28"//Instance ID. "DBInstanceNetInfo":{//Details of the deleted network. "Address":"" "Ip":"10.0.10.15" "Port":5432 "Status":"closed" "NetType":"private" "VpcId":"vpc-fz41fhgo" "SubnetId":"subnet-piadji8r" "ProtocolType":"postgresql" } } |
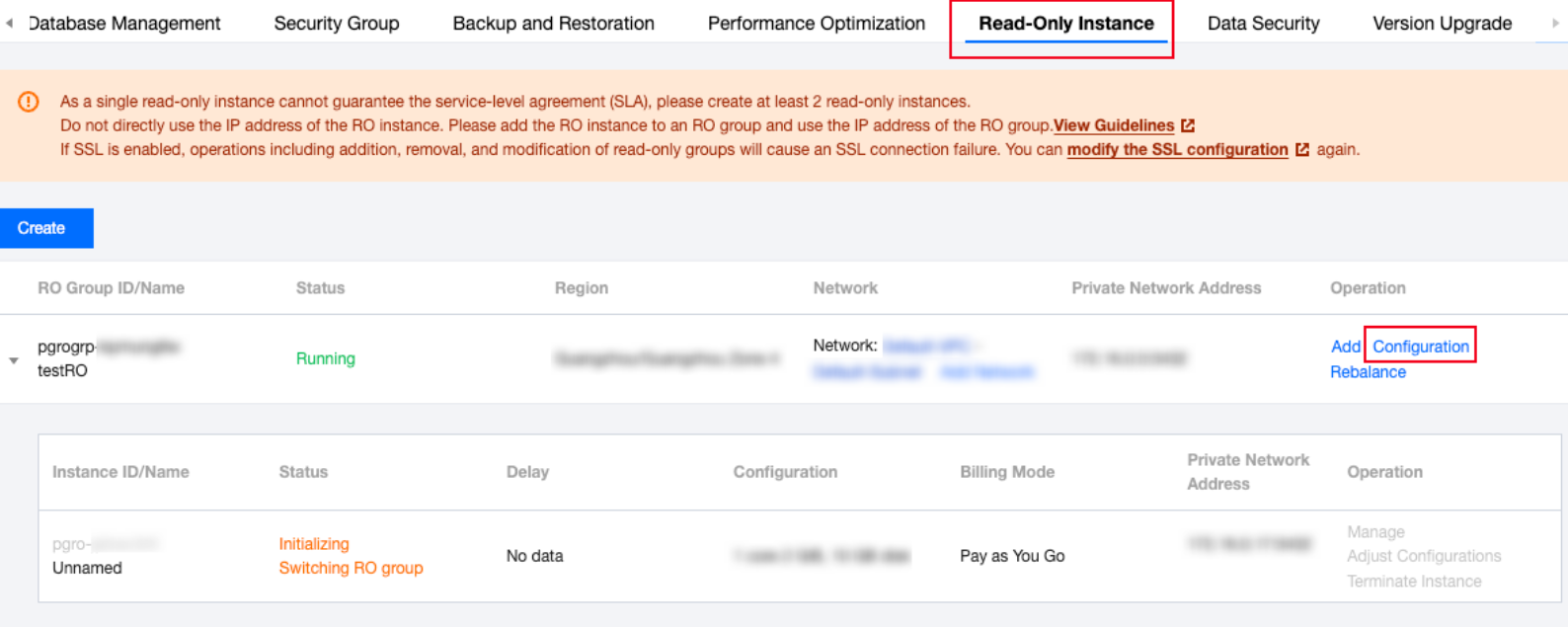
Parameter configuration | { "Name":"max_connections"//Modify the parameter name. "ExpectedValue":"2040"//Modify the parameter target value. } | { "max_connections":{//Parameter name. "message":"this parameter must be modified on the master node first and reboot"//Prompt information for reference. "modify_after_value":"2040"//Target value of the parameter. "modify_before_value":"2048"//Original value of the parameter. "status":"success"//Modification status. } } |
Last updated:2024-11-04 09:36:12
Last updated:2025-07-22 20:25:30
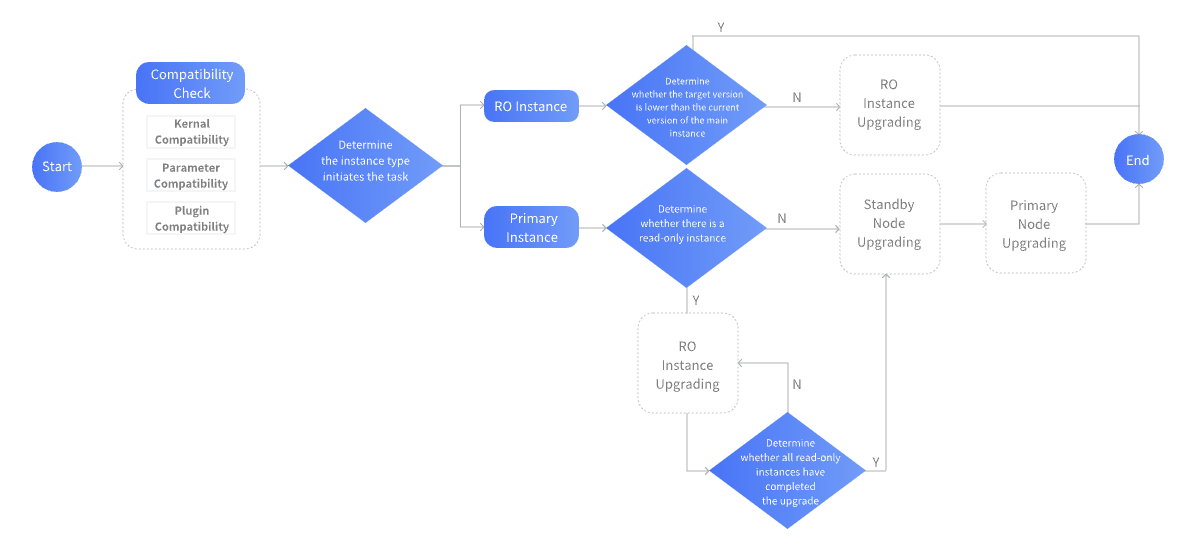
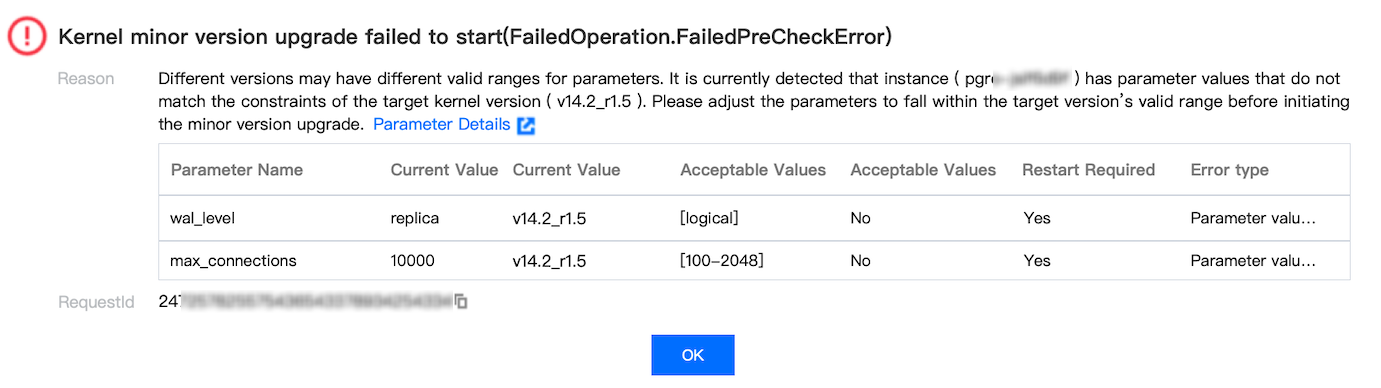
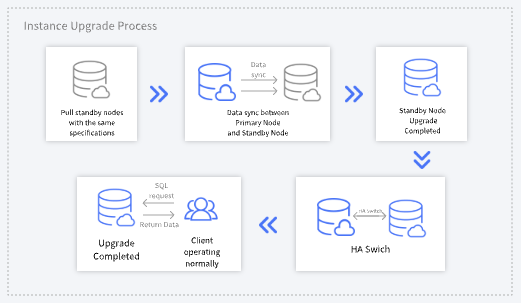
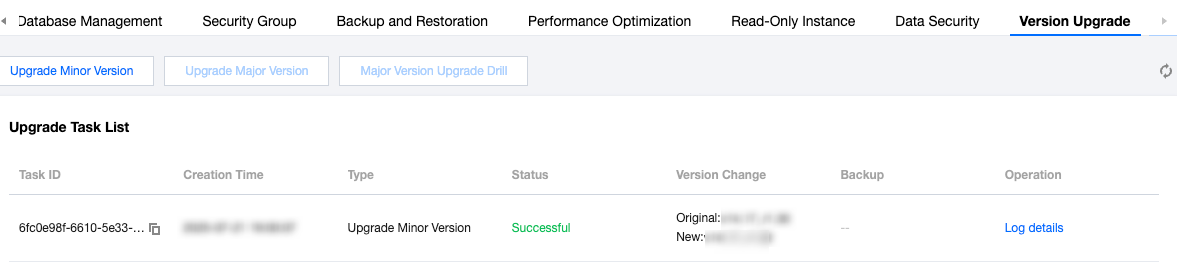
Last updated:2025-05-21 15:53:27
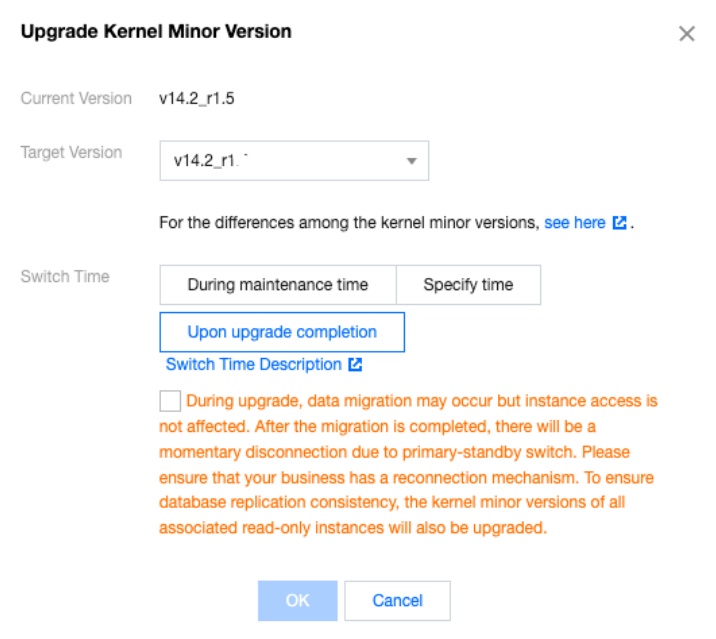
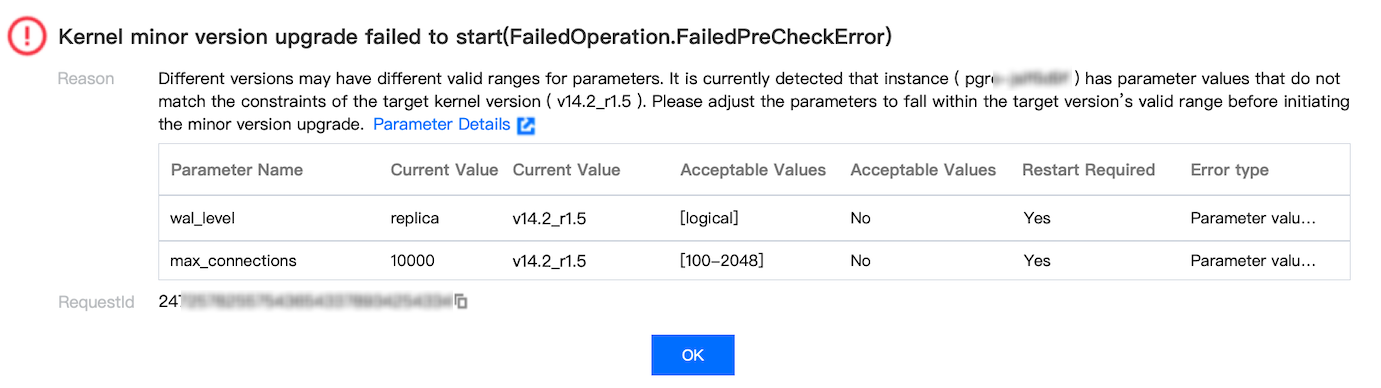
Last updated:2025-07-22 20:25:30
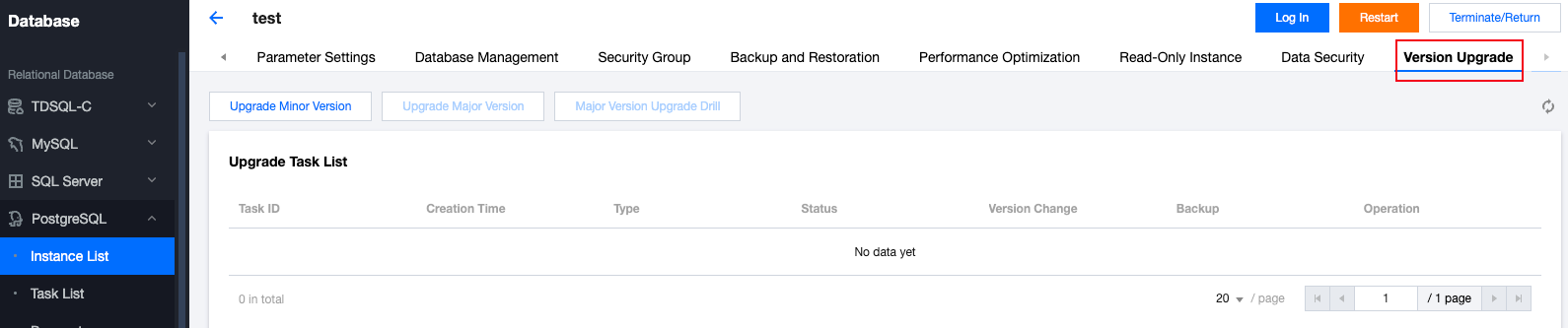
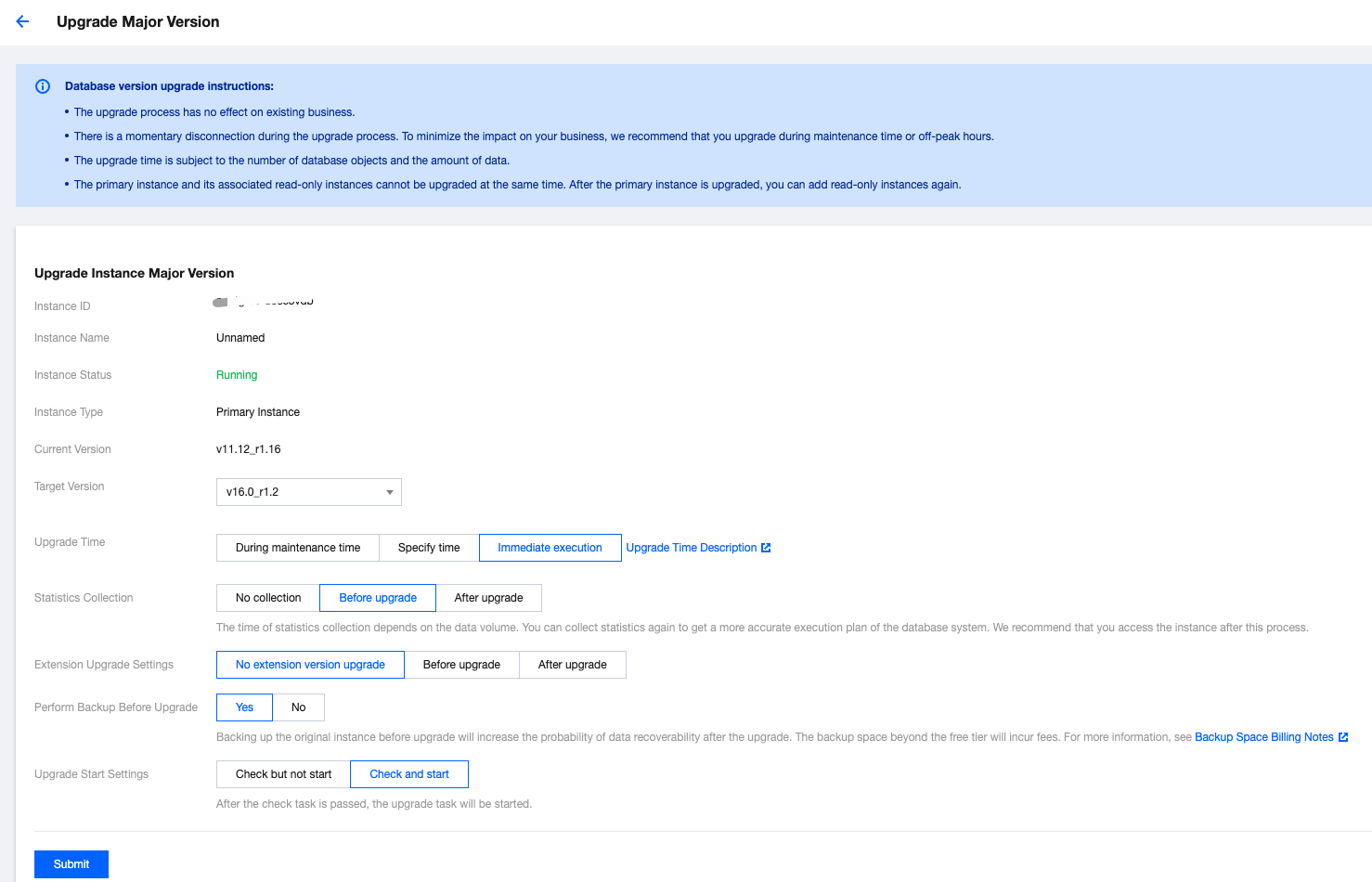
Upgrade Time | Description |
Upgrade plugins before completing the major version upgrade. | Under this method, you need to check the plugin list of all databases and upgrade the plugins to the corresponding versions. The execution time is positively correlated with the number of databases and the number of plugins, which will extend the execution time of the entire major version upgrade. Please assess and then select. |
Upgrade plugins after completing the major version upgrade. | Under this method, the database will promptly resume read and write operations upon the completion of the major version upgrade, during which the plugins will undergo updates. However, during the plugin update period, the plugin features may become unavailable. When selecting this upgrade time, you need to evaluate whether your business will be affected. |
Do not upgrade the plugin version | Under this method, the database will promptly resume read and write operations upon completion of the major version upgrade, without automatically upgrading plugins. If needed, you can manually upgrade the plugins. When selecting this upgrade time, you need to evaluate whether your business will be affected. |
Option | Description |
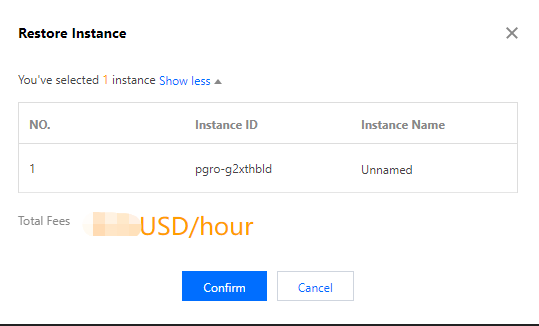
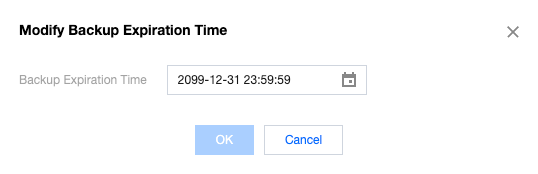
Yes | Default option. Backup will incur fees. For details, reference Backup Space Billing. Users can choose to delete it after upgrade verification is completed. The deletion policy for this backup file is also managed by the user-configured backup retention rules. If you want to extend the backup set retention time, enter the backup recovery interface and click  |
No | Select this option when the instance has backups that can be restored to the pre-upgrade state. Otherwise, it is not recommended. |
Option | Description |
Check without initiating task | Only perform pre-upgrade checks, including instance running status, legitimacy of instance parameter settings, database connection check, etc., but do not initiate the task. Users can use this operation to pre-check the feasibility of the upgrade. |
Check and initiate task | Perform pre-upgrade checks, including instance running status, legitimacy of instance parameter settings, and database connection check. If the check passes, directly initiate the task. |
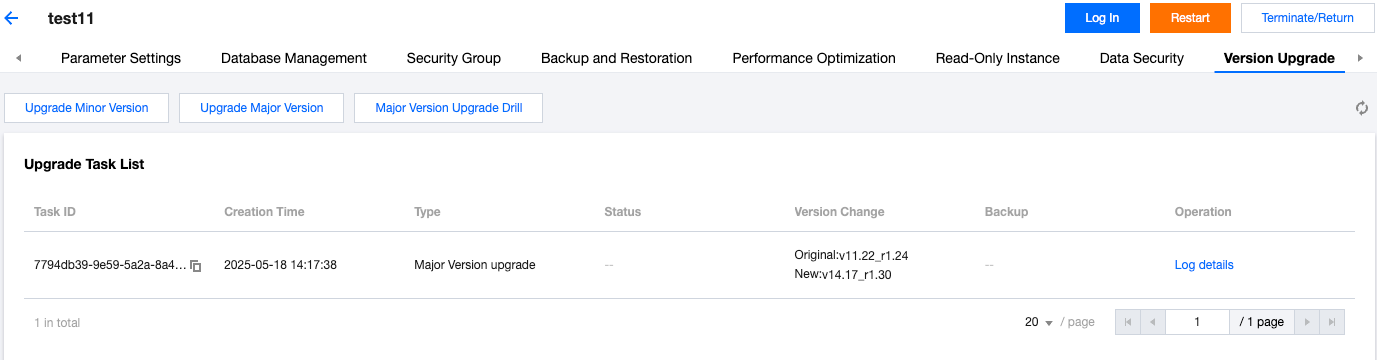

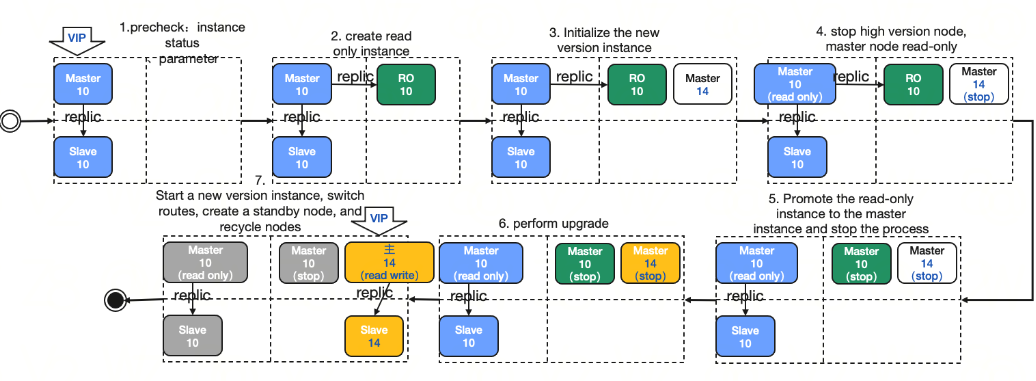
Last updated:2025-11-20 09:44:41
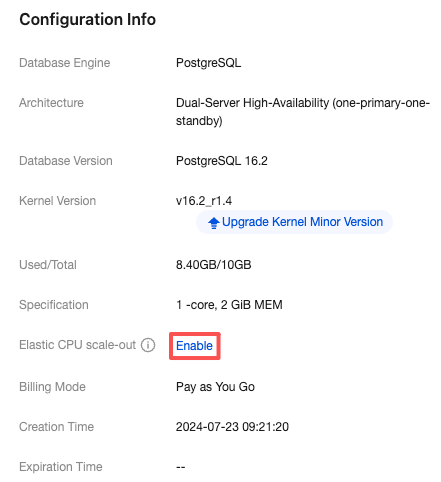
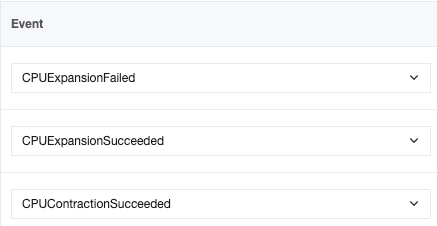
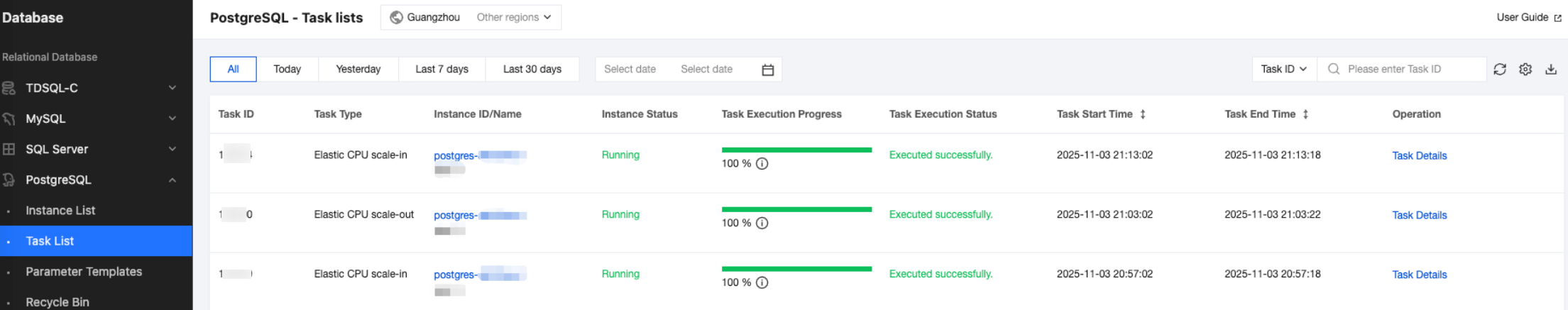
Scaling Type | Event Metric | Description |
Automatic scaling | ExpandCpuSucceeded | CPU elastic scale-out succeeded. |
| ExpandCpuFailed | CPU elastic scale-out failed. |
| ContractCpuSucceeded | CPU elastic scale-in succeeded. |
Custom scaling | ExpandCpuSucceeded | CPU elastic scale-out succeeded. |
| ExpandCpuFailed | CPU elastic scale-out failed. |
| ContractCpuSucceeded | CPU elastic scale-in succeeded. |
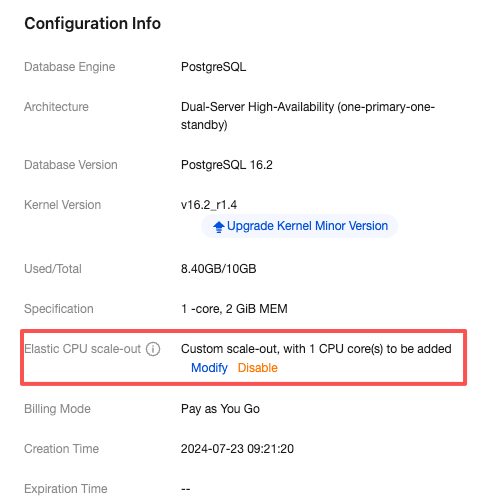
Last updated:2025-11-20 09:44:41
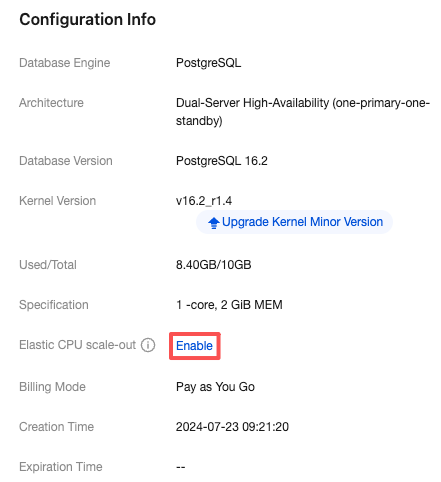
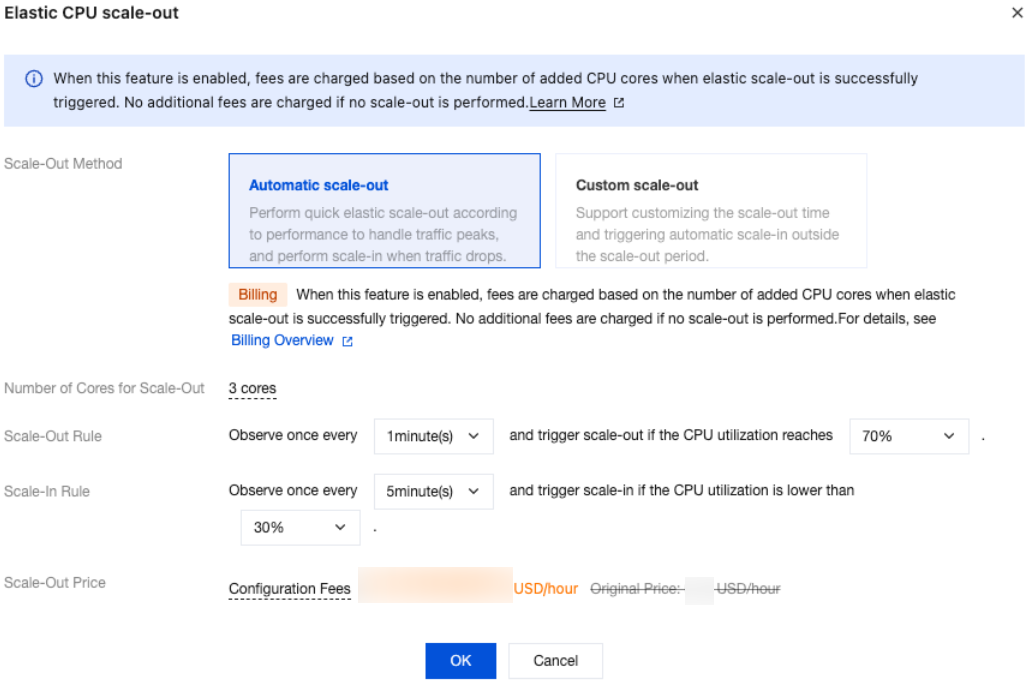
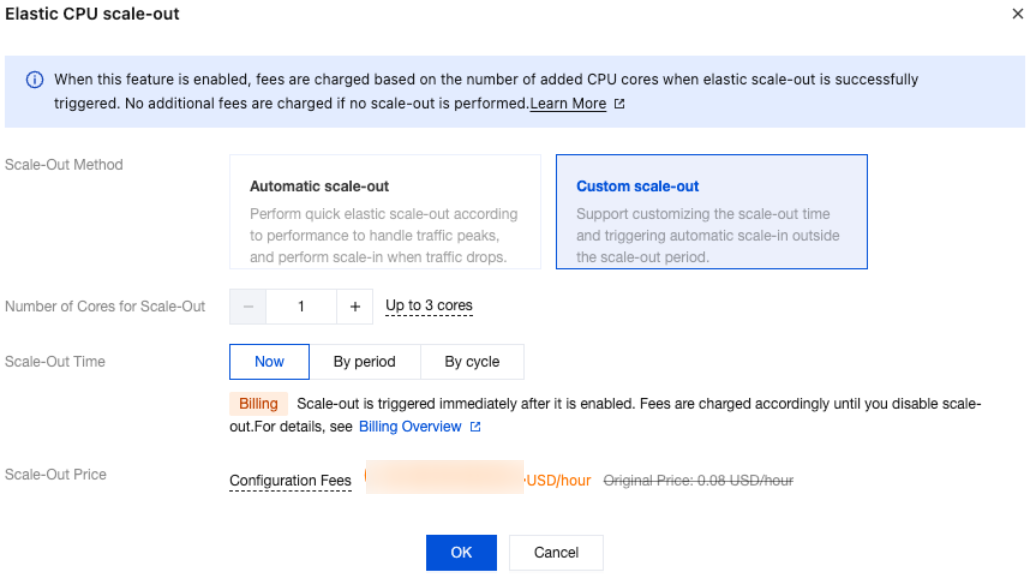
Parameter | Description |
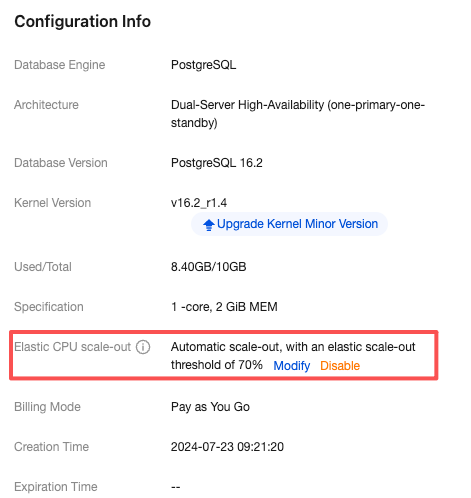
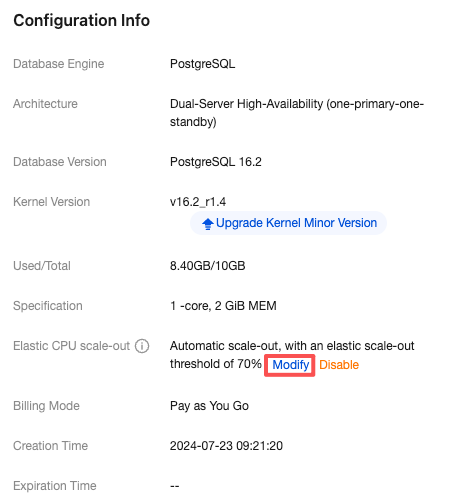
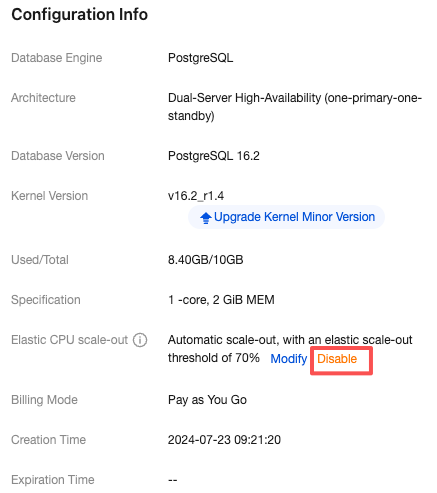
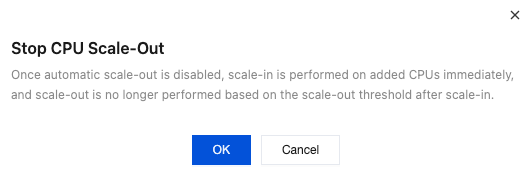
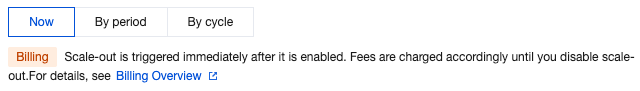
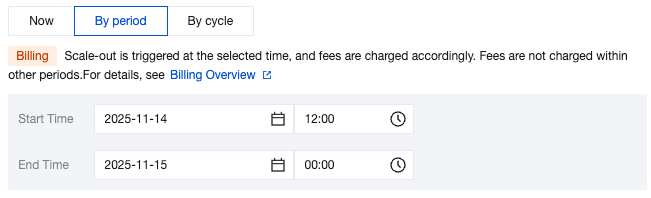
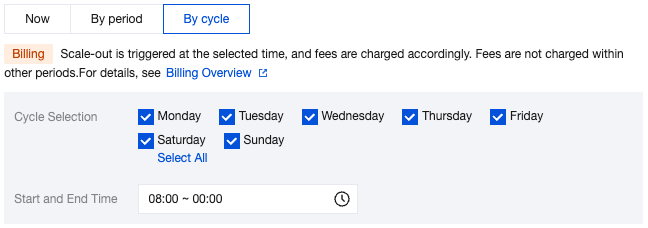
Scale-Out Method | Automatic scale-out and custom scale-out are supported. Select automatic scale-out here. Automatic scale-out: Perform a quick elastic scale-out operation based on performance to adapt to traffic peaks, and perform scale-in when traffic drops. Custom scale-out: Perform scale-out during a custom time period or cycle, and automatically perform CPU scale-in during other periods. |
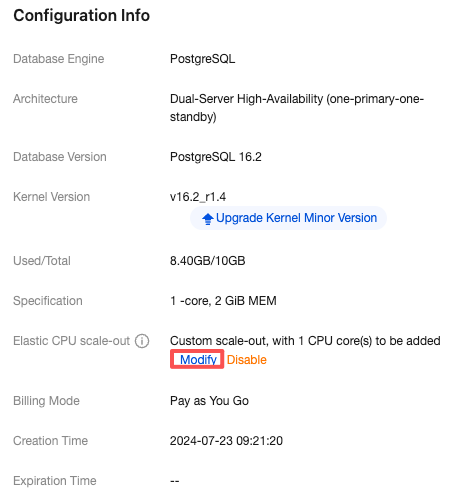
Number of cores for Scale-Out | The default value is consistent with the number of CPU cores of the current instance specification. For example, if the current instance specification is 2 cores and 4 GiB of memory, the number of cores for scale-out will also be 2 cores. After scale-out is successfully triggered, the CPU of the instance will be 4 cores. |
Scale-Out Rule | Set the observation period and threshold for triggering scale-out. Observation period: Supported options are 1 minute, 3 minutes, 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 15 minutes, and 30 minutes. Threshold: Supported options include 40%, 50%, 60%, 70%, 80%, and 90%. The system will automatically monitor the CPU utilization metrics during the observation period. When the set threshold is reached, a CPU scale-out operation will be initiated. |
Scale-In Rule | Set the observation period and threshold for triggering scale-in. Observation period: Supported options include 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 15 minutes, and 30 minutes. Threshold: Supported options include 10%, 20%, and 30%. The system will automatically monitor the CPU utilization metrics during the observation period. When the set threshold is reached, a CPU scale-in operation will be initiated. |
Last updated:2025-11-20 09:44:42
Last updated:2025-11-20 09:44:42
Last updated:2025-11-20 09:44:42
Last updated:2025-11-20 09:44:42


Last updated:2025-09-11 15:27:47
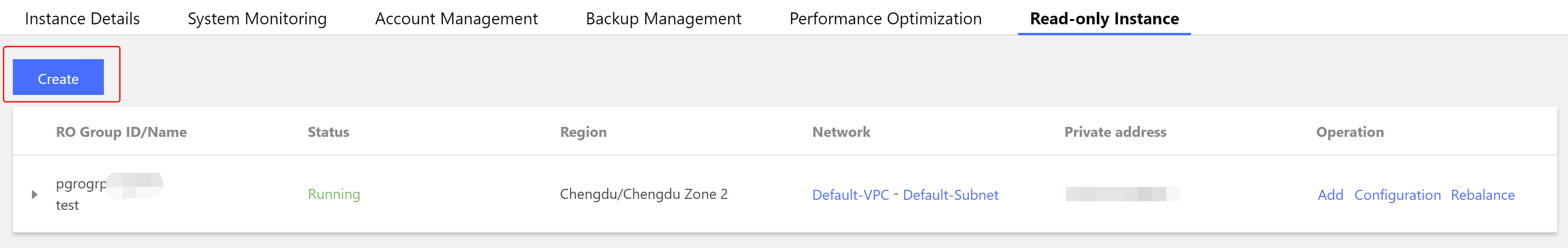
Last updated:2025-09-10 22:02:23
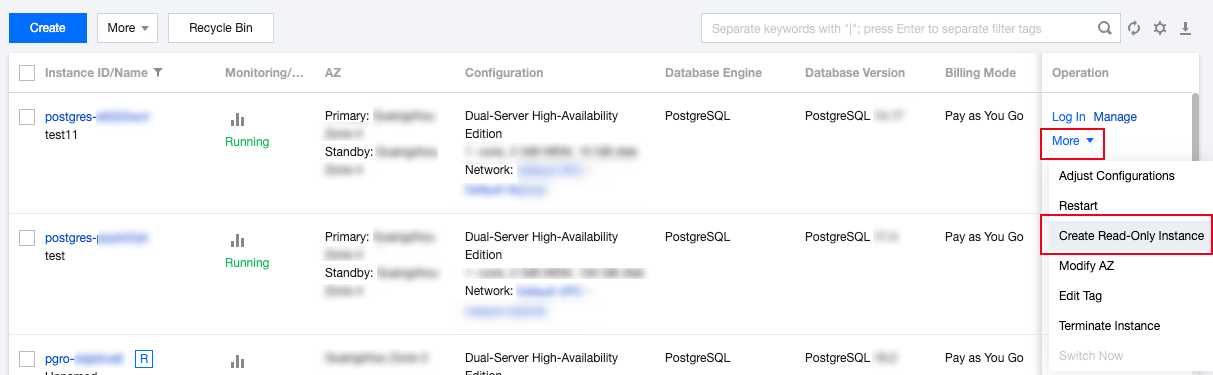
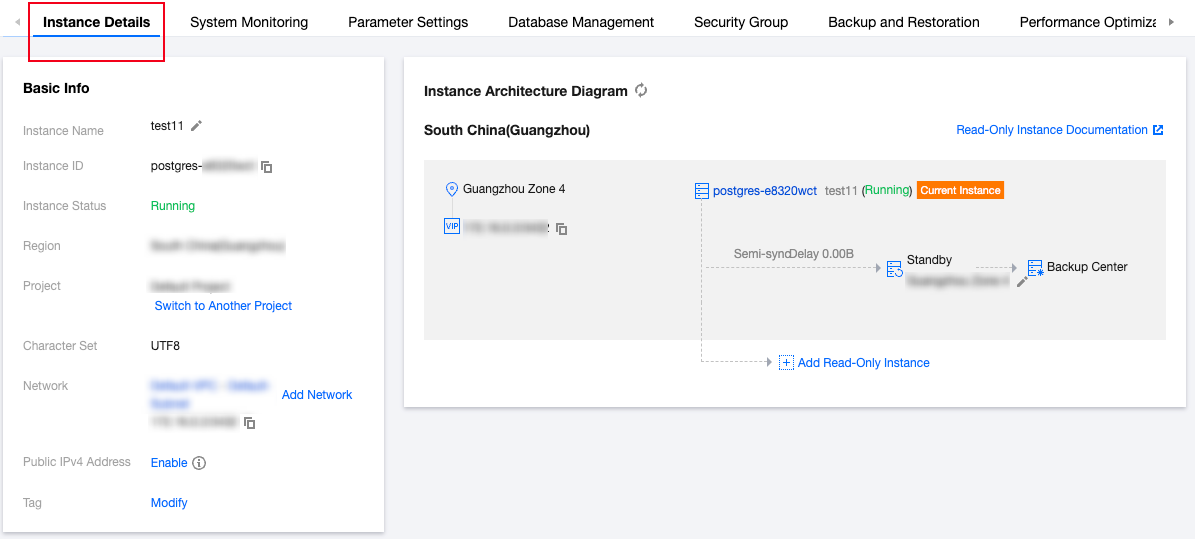
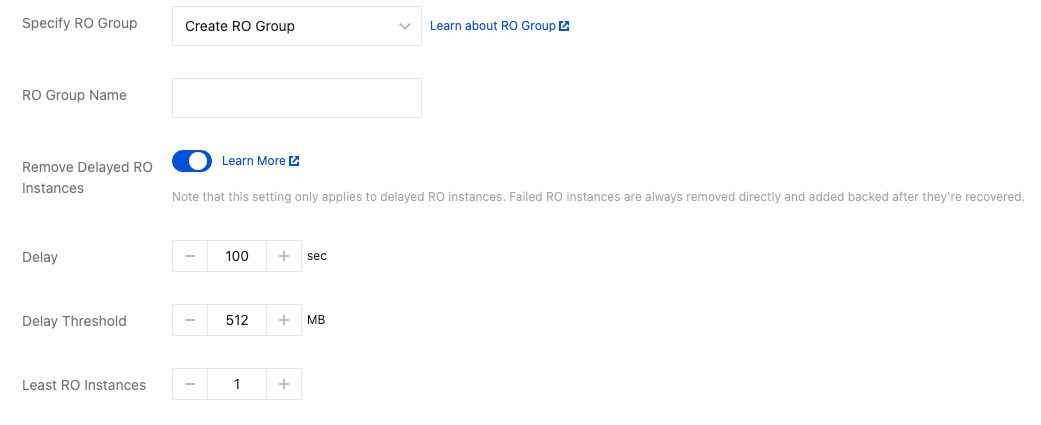
Specification | Weight |
2 GB memory | 1 |
4 GB memory | 2 |
8 GB memory | 2 |
12 GB memory | 4 |
16 GB memory | 4 |
24 GB memory | 8 |
32 GB memory | 8 |
48 GB memory | 10 |
64 GB memory | 12 |
96 GB memory | 14 |
128 GB memory | 16 |
240 GB memory | 26 |
480 GB memory | 50 |
Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51
Specification | Weight |
2 GB memory | 1 |
4 GB memory | 2 |
8 GB memory | 2 |
12 GB memory | 4 |
16 GB memory | 4 |
24 GB memory | 8 |
32 GB memory | 8 |
48 GB memory | 10 |
64 GB memory | 12 |
96 GB memory | 14 |
128 GB memory | 16 |
240 GB memory | 26 |
480 GB memory | 50 |
Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51
CREATE ROLE name [ [ WITH ] option [ ... ] ]where option can be:SUPERUSER | NOSUPERUSER| CREATEDB | NOCREATEDB| CREATEROLE | NOCREATEROLE| INHERIT | NOINHERIT| LOGIN | NOLOGIN| REPLICATION | NOREPLICATION| BYPASSRLS | NOBYPASSRLS| CONNECTION LIMIT connlimit| [ ENCRYPTED ] PASSWORD 'password' | PASSWORD NULL| VALID UNTIL 'timestamp'| IN ROLE role_name [, ...]| IN GROUP role_name [, ...]| ROLE role_name [, ...]| ADMIN role_name [, ...]| USER role_name [, ...]| SYSID uid
Role | Allowed Access |
pg_execute_server_program | Allow executing programs on the database server as the user the database runs as with COPY and other functions which allow executing a server-side program. |
pg_monitor | Read/Execute various monitoring views and functions. This role is a member of pg_read_all_settings, pg_read_all_stats, and pg_stat_scan_tables. |
pg_read_all_settings | Read all configuration variables, even those normally visible only to superusers. |
pg_read_all_stats | Read all pg_stat_* views and use various statistics related extensions, even those normally visible only to superusers. |
pg_read_server_files | Allow reading files from any location the database can access on the server with COPY and other file-access functions. |
pg_signal_backend | Signal another backend to cancel a query or terminate its session. |
pg_stat_scan_tables | Execute monitoring functions that may take ACCESS SHARE locks on tables, potentially for a long time. |
pg_write_server_files | Allow writing to files in any location the database can access on the server with COPY and other file-access functions. |
public | An implicitly defined group that always includes all roles. Any particular role will have the sum of permissions granted directly to public. PostgreSQL grants default permissions on some types of objects to public. |
Permissions | Abbreviation | Supported Object |
SELECT | r ("read") | LARGE OBJECT, SEQUENCE, TABLE (and table-like objects), table column |
INSERT | a ("append") | TABLE, table column |
UPDATE | w ("write") | LARGE OBJECT, SEQUENCE, TABLE, table column |
DELETE | d | TABLE |
TRUNCATE | D | TABLE |
REFERENCES | x | TABLE, table column |
TRIGGER | t | TABLE |
CREATE | C | DATABASE, SCHEMA, TABLESPACE |
CONNECT | c | DATABASE |
TEMPORARY | T | DATABASE |
EXECUTE | X | FUNCTION, PROCEDURE |
USAGE | U | DOMAIN, FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER, FOREIGN SERVER, LANGUAGE, SCHEMA, SEQUENCE, TYPE |
Object Type | Permissions | Permissions of Default Role (public) | psql Command to Query Permissions |
DATABASE | CTc | Tc | \l |
DOMAIN | U | U | \dD+ |
FUNCTION or PROCEDURE | X | X | \df+ |
FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER | U | none | \dew+ |
FOREIGN SERVER | U | none | \des+ |
LANGUAGE | U | U | \dL+ |
LARGE OBJECT | rw | none | - |
SCHEMA | UC | none | \dn+ |
SEQUENCE | rwU | none | \dp |
TABLE (and table-like objects) | arwdDxt | none | \dp |
Table column | arwx | none | \dp |
TABLESPACE | C | none | \db+ |
TYPE | U | U | \dT+ |
postgres=# \dpAccess privilegesSchema | Name | Type | Access privileges | Column privileges | Policies--------+------+-------+-------------------+-------------------+----------public | t1 | table | test1=arwdDxt/test1 | |(1 rows)postgres=# grant select on t1 to normal_user;GRANTpostgres=# grant insert on t1 to normal_user with grant option;GRANTpostgres=# grant update on t1 to public;GRANTpostgres=# grant select (a) on t1 to test2;GRANTpostgres=# \dpAccess privilegesSchema | Name | Type | Access privileges | Column privileges | Policies--------+------+-------+-----------------------+-------------------+----------public | t1 | table | test1=arwdDxt/test1 +| a: +|| | | normal_user=a*r/test1+| test2=r/test1 || | | =w/test1 | |(1 rows)-- Where, "=w/test1" specifies that test1 grants public the UPDATE privilege.
Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51
superuser role attribute and the pg_execute_server_program, pg_read_server_files, and pg_write_server_files roles for you to use. However, as some operations require the superuser role, TencentDB for PostgreSQL provides the pg_tencentdb_superuser to replace superuser.Permission | Description |
CREATEDB | Create a database. |
BYPASSRLS | Bypass all row-level security policy checks. |
REPLICATION | Have the REPLICATION permission by default, and allow granting the REPLICATION permission to other users. |
CREATEROLE | Have the same CREATEROLE permission as the community edition, except that the role cannot create the pg_read_server_files, pg_write_server_files, and pg_execute_server_program roles. |
Object | Description |
database | By default, have the permissions of all databases not owned by a a superuser. |
schema | By default, have the permissions of all schemas not owned by a superuser. |
table/sequence | By default, have the permissions of all tables/sequences not owned by a a superuser. |
function | By default, have the permissions of all functions not owned by a superuser. |
language | No permissions. |
tablespace | No permissions. |
FDW/foreign server | By default, have the permissions of all FDWs/foreign servers not owned by a a superuser. |
TYPE | By default, have the permissions of all TYPEs not owned by a superuser. |
pg_tencentdb_superuser is temporarily escalated to superuser and passes all permission checks. pgstat_get_backend_current_activity function to view deadlock details, so that users can easily troubleshoot deadlocks themselves.pg_signal_backend function is restricted, and processes of the pg_tencentdb_superuser role can only be killed by itself.CREATE USER name [ [ WITH ] option [ ... ] ]where option can be:SUPERUSER | NOSUPERUSER| CREATEDB | NOCREATEDB| CREATEROLE | NOCREATEROLE| INHERIT | NOINHERIT| LOGIN | NOLOGIN| REPLICATION | NOREPLICATION| BYPASSRLS | NOBYPASSRLS| CONNECTION LIMIT connlimit| [ ENCRYPTED ] PASSWORD 'password' | PASSWORD NULL| VALID UNTIL 'timestamp'| IN ROLE role_name [, ...]| IN GROUP role_name [, ...]| ROLE role_name [, ...]| ADMIN role_name [, ...]| USER role_name [, ...]| SYSID uid
CREATE ROLE name [ [ WITH ] option [ ... ] ]where option can be:SUPERUSER | NOSUPERUSER| CREATEDB | NOCREATEDB| CREATEROLE | NOCREATEROLE| INHERIT | NOINHERIT| LOGIN | NOLOGIN| REPLICATION | NOREPLICATION| BYPASSRLS | NOBYPASSRLS| CONNECTION LIMIT connlimit| [ ENCRYPTED ] PASSWORD 'password' | PASSWORD NULL| VALID UNTIL 'timestamp'| IN ROLE role_name [, ...]| IN GROUP role_name [, ...]| ROLE role_name [, ...]| ADMIN role_name [, ...]| USER role_name [, ...]| SYSID uid
ALTER ROLE role_specification [ WITH ] option [ ... ]where option can be:SUPERUSER | NOSUPERUSER| CREATEDB | NOCREATEDB| CREATEROLE | NOCREATEROLE| INHERIT | NOINHERIT| LOGIN | NOLOGIN| REPLICATION | NOREPLICATION| BYPASSRLS | NOBYPASSRLS| CONNECTION LIMIT connlimit| [ ENCRYPTED ] PASSWORD 'password' | PASSWORD NULL| VALID UNTIL 'timestamp'
# Syntax exampleGRANT <privilege> on <object> to <role>;
# Syntax exampleREVOKE <privilege> ON <object> FROM <role>;
# Syntax exampleGRANT <role name> to <another role>;
Last updated:2025-07-22 20:25:30
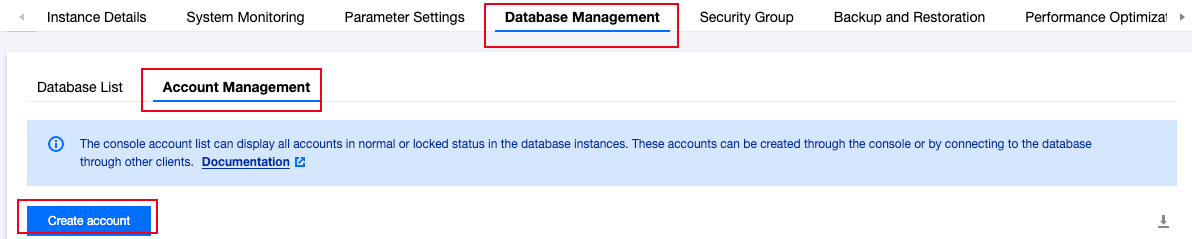
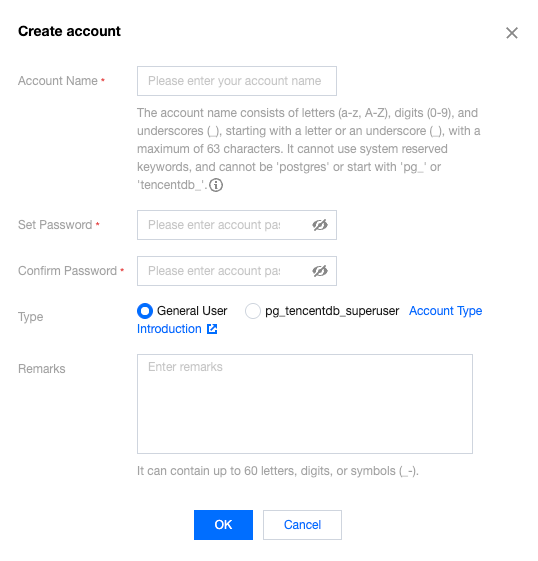
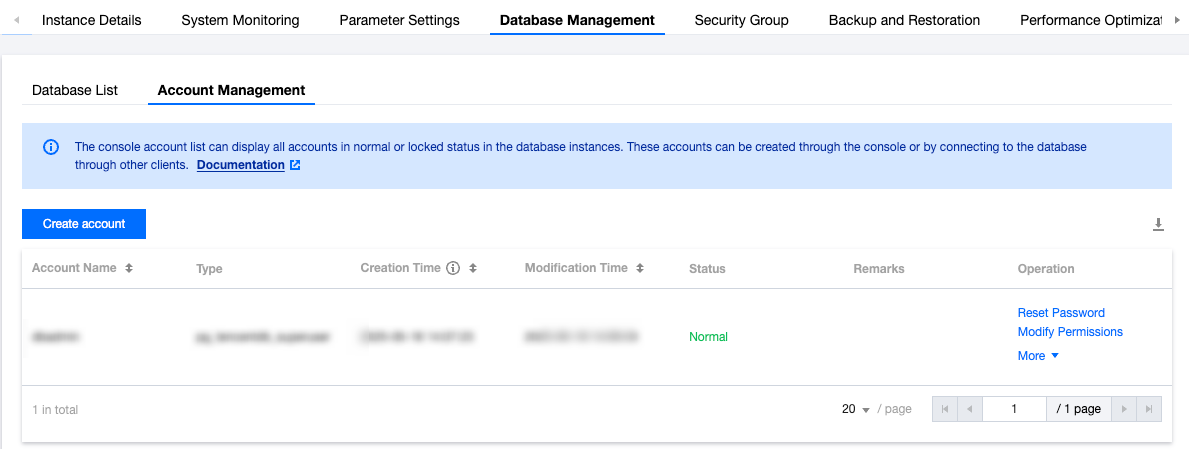
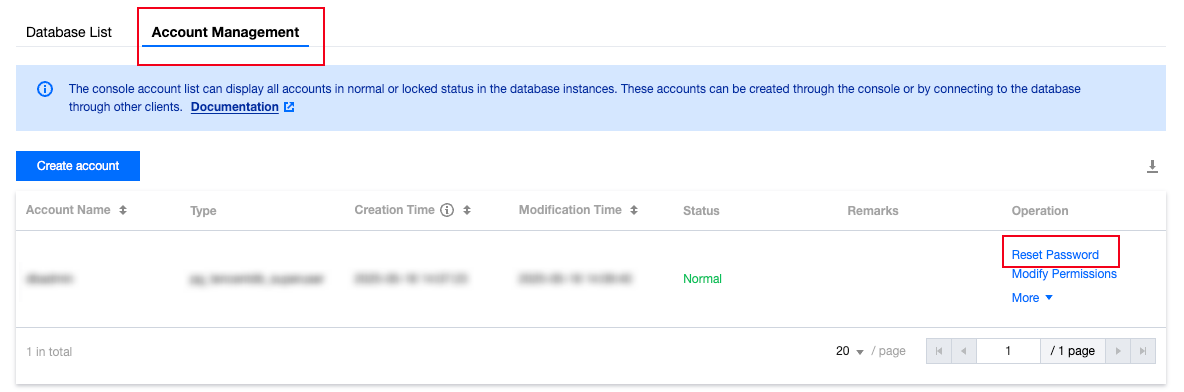
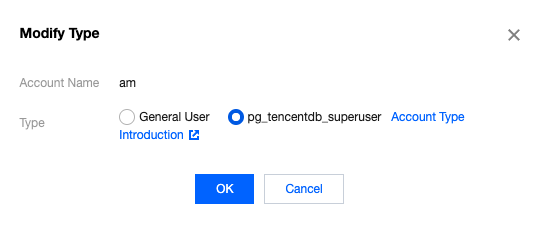
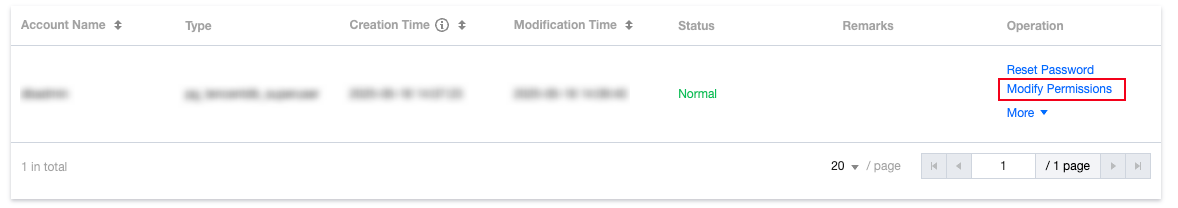
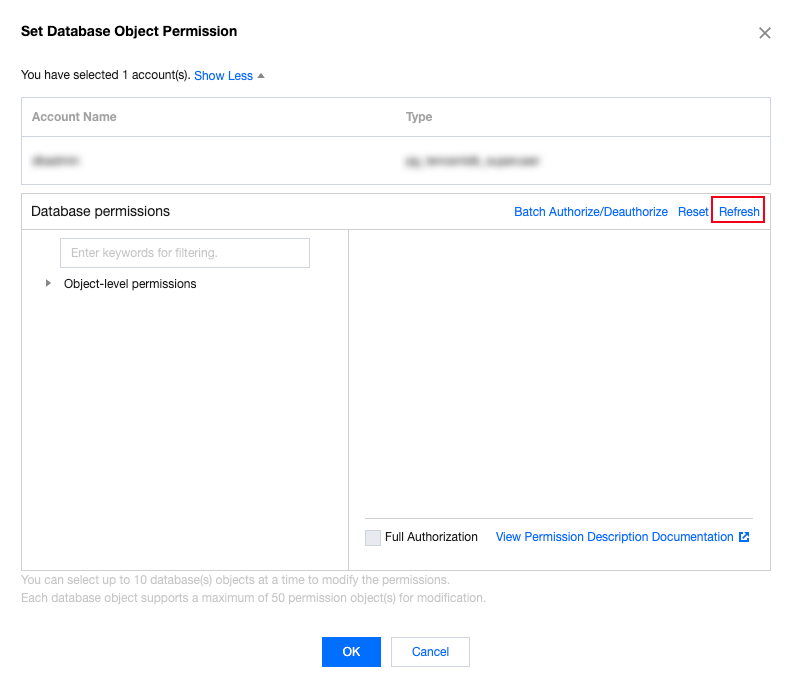
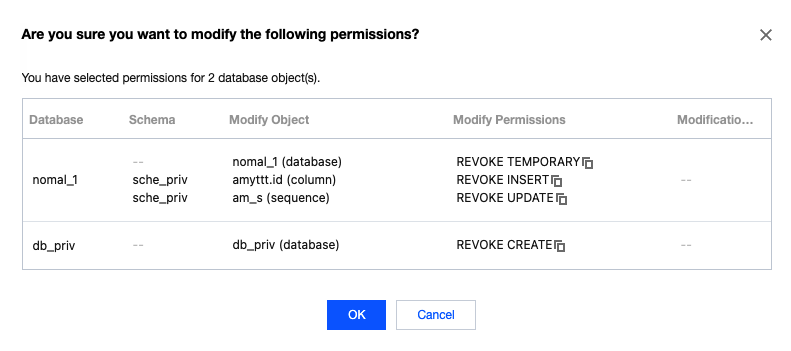
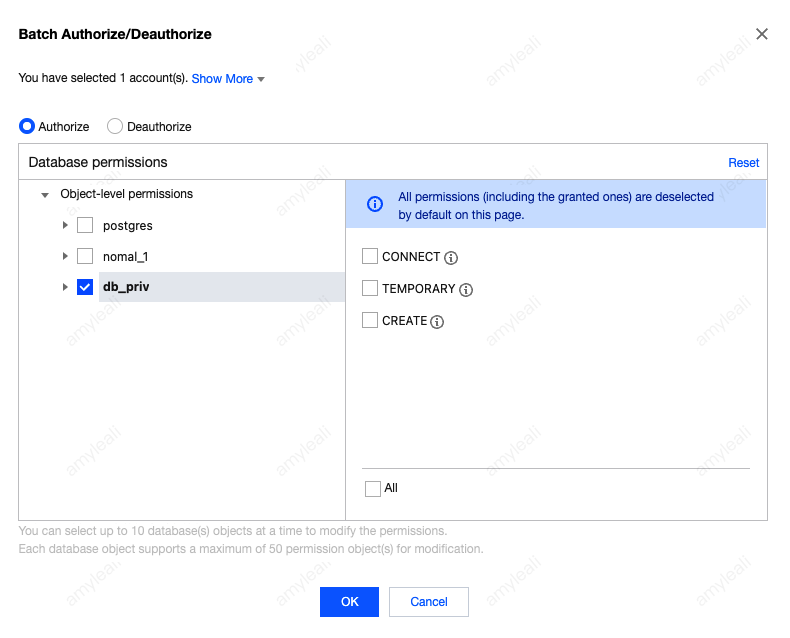
nomal_1=> select datname,datacl from pg_database;datname | datacl-----------+------------------------------------------------------------------------template1 | {=c/postgres,postgres=CTc/postgres}template0 | {=c/postgres,postgres=CTc/postgres}postgres | {=Tc/postgres,postgres=CTc/postgres,pg_tencentdb_superuser=C/postgres}nomal_1 | {=Tc/nomal_usr1,nomal_usr1=CTc/nomal_usr1}db_priv | {=Tc/dbadmin,dbadmin=Tc/dbadmin}(5 rows)
nomal_1=> select nspname,nspacl from pg_namespace;nspname | nspacl--------------------+----------------------------------------------------------pg_toast |pg_temp_1 |pg_toast_temp_1 |pg_catalog | {postgres=UC/postgres,=U/postgres}public | {postgres=UC/postgres,=UC/postgres}information_schema | {postgres=UC/postgres,=U/postgres,nomal_usr1=C/postgres}sche_priv | {dbadmin=UC/dbadmin}(7 rows)
nomal_1=> select relname,a.typname as reltype ,relacl from pg_class join pg_type a on pg_class.reltype=a.oid ;
nomal_1=> SELECT r.rolname,d.datdba,datname AS database_name FROM pg_database d left JOIN pg_catalog.pg_roles r on d.datdba=r.oid WHERE d.datdba in (SELECT usesysid FROM pg_user WHERE usename in('dbadmin','nomal_usr1','nomal_usr2'));rolname | datdba | database_name------------+--------+---------------dbadmin | 16398 | db_privnomal_usr1 | 16401 | nomal_1
nomal_1=> SELECT n.nspname as schema_name, pg_catalog.pg_get_userbyid(n.nspowner) as schema_owner FROM pg_catalog.pg_namespace n ORDER BY schema_name;schema_name | schema_owner--------------------+--------------information_schema | postgrespg_catalog | postgrespg_temp_1 | postgrespg_toast | postgrespg_toast_temp_1 | postgrespublic | postgressche_priv | dbadmin
nomal_1=> select * from (select relname,relnamespace as schema_name ,a.typname as reltype,pg_catalog.pg_get_userbyid(relowner )as owner from pg_class join pg_type a on pg_class.reltype=a.oid ) d where owner in('dbadmin','nomal_1');relname | schema_name | reltype | owner----------------+-------------+----------------+---------pg_toast_16488 | 99 | pg_toast_16488 | dbadminamyttt | 16480 | amyttt | dbadminam | 2200 | am | dbadminam_s | 16480 | am_s | dbadminbug_id_seq | 2200 | bug_id_seq | dbadminbug | 2200 | bug | dbadminpg_toast_16507 | 99 | pg_toast_16507 | dbadmin
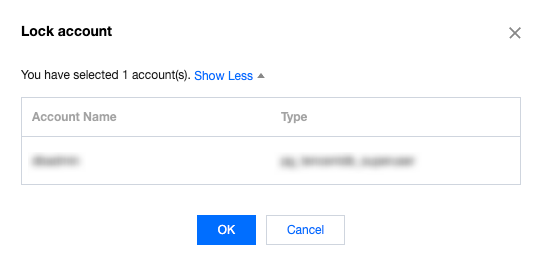
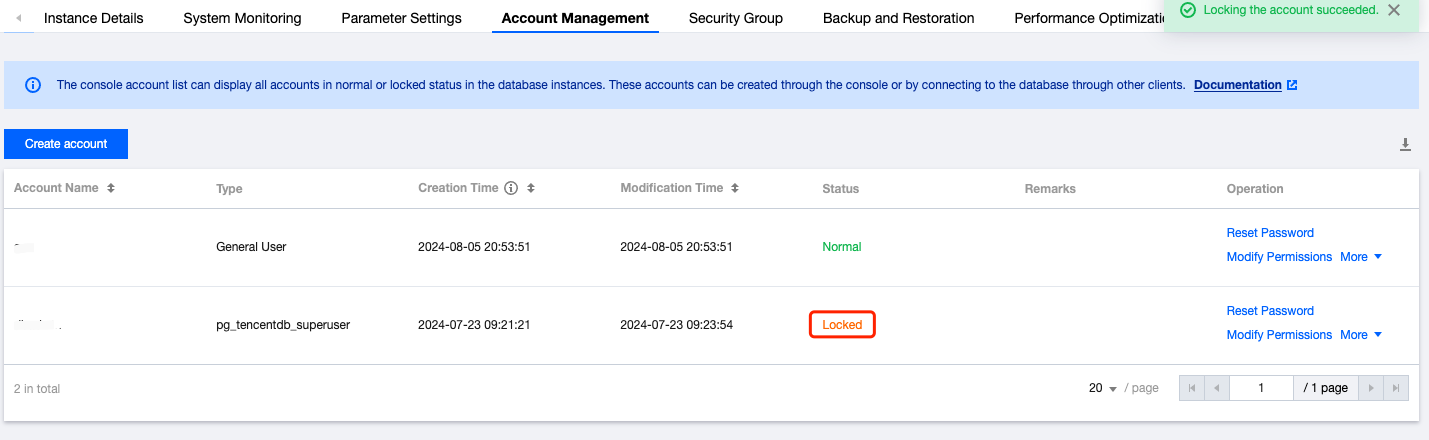
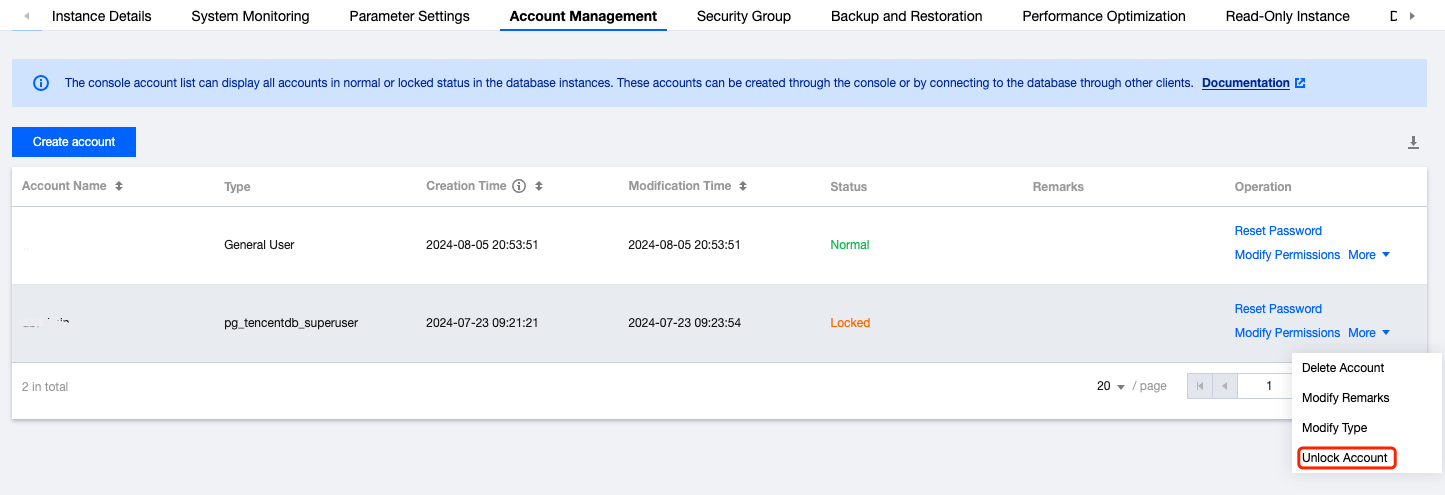
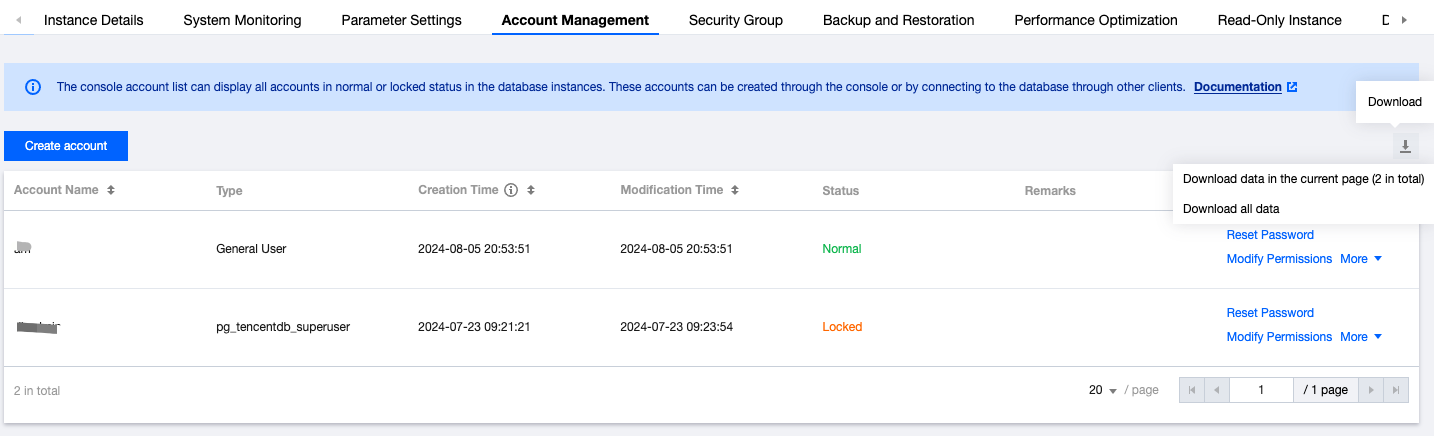
Last updated:2025-11-03 14:21:06
Object Type | Default PUBLIC Permission |
Databases | CONNECT,TEMPORARY |
Functions/Procedures | EXECUTE |
Languages | USAGE |
Data Types | USAGE |
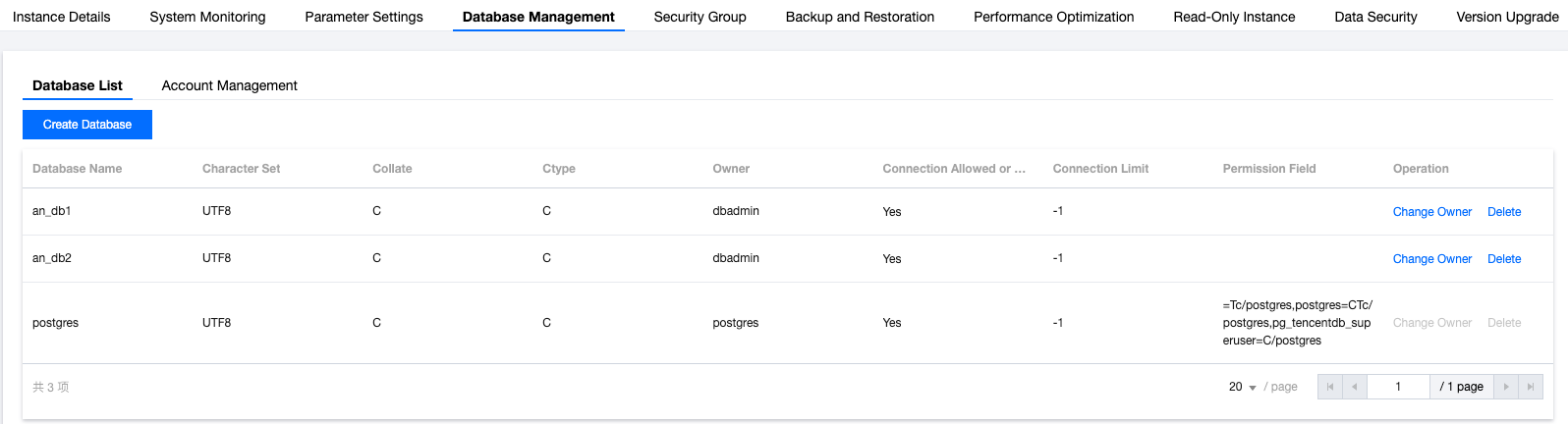
drop extension tencentdb_superuser; in the corresponding database, then execute create extension tencentdb_superuser; before using this capacity after upgrading the kernel minor version.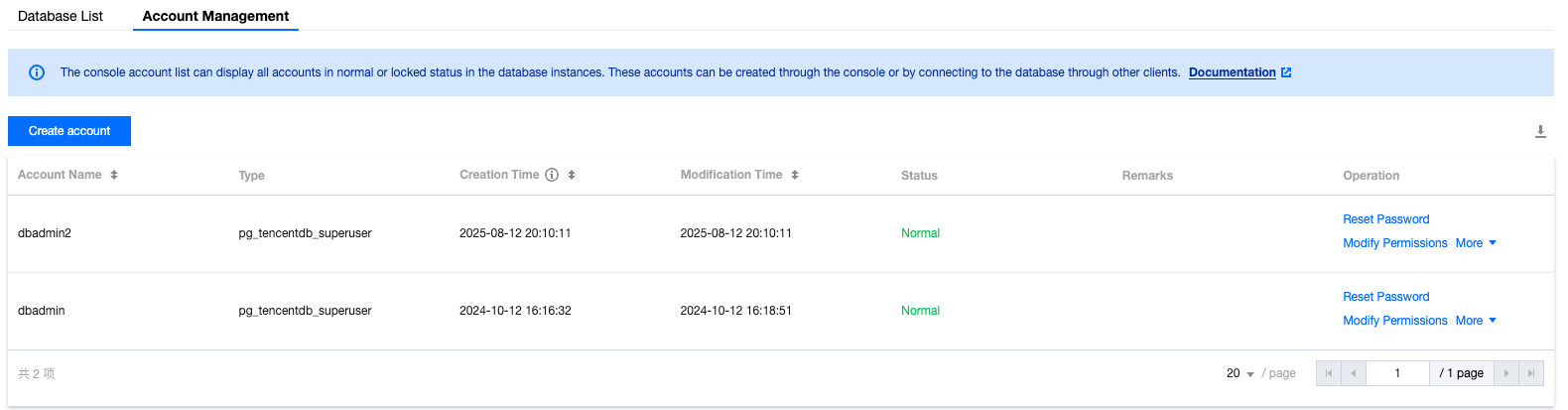
[am@VM-91-60-centos ~]$psql -h10.*.*.* -p5432 -Udbadmin -dtest_dbPassword for user dbadmin:psql (16.0, server 16.10)Type "help" for help.
test_db=> \c - am_apsql (16.0, server 16.10)You are now connected to database "test_db" as user "am_a".test_db=> select oid FROM pg_class LIMIT 1;oid------2619(1 row)
test_db=> \c - dbadminPassword for user dbadmin:psql (16.0, server 16.10)You are now connected to database "test_db" as user "dbadmin".test_db=> REVOKE SELECT ON pg_class FROM PUBLIC;REVOKEtest_db=> \c - am_aPassword for user am_a:psql (16.0, server 16.10)You are now connected to database "test_db" as user "am_a".test_db=> select oid FROM pg_class LIMIT 1;ERROR: permission denied for table pg_class
test_db=> \c - dbadminPassword for user dbadmin:psql (16.0, server 16.10)You are now connected to database "test_db" as user "dbadmin".test_db=> REVOKE CONNECT ON DATABASE test_db FROM PUBLIC;REVOKEtest_db=> \c - am_aPassword for user am_a:connection to server at "10.*.*.*", port 5432 failed: FATAL: permission denied for database "test_db"DETAIL: User does not have CONNECT privilege.Previous connection kept
test_db=> \c - dbadminpsql (16.0, server 16.10)You are now connected to database "test_db" as user "dbadmin".test_db=> GRANT CONNECT ON DATABASE test_db TO am_a;GRANTtest_db=> GRANT SELECT ON pg_class TO am_a;GRANTtest_db=> \c - am_aPassword for user am_a:psql (16.0, server 16.10)You are now connected to database "test_db" as user "am_a".test_db=> select oid FROM pg_class LIMIT 1;oid------2619(1 row)
Last updated:2025-07-22 20:25:30
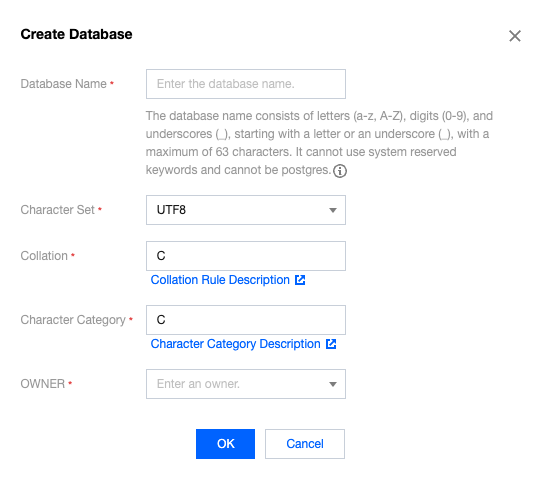
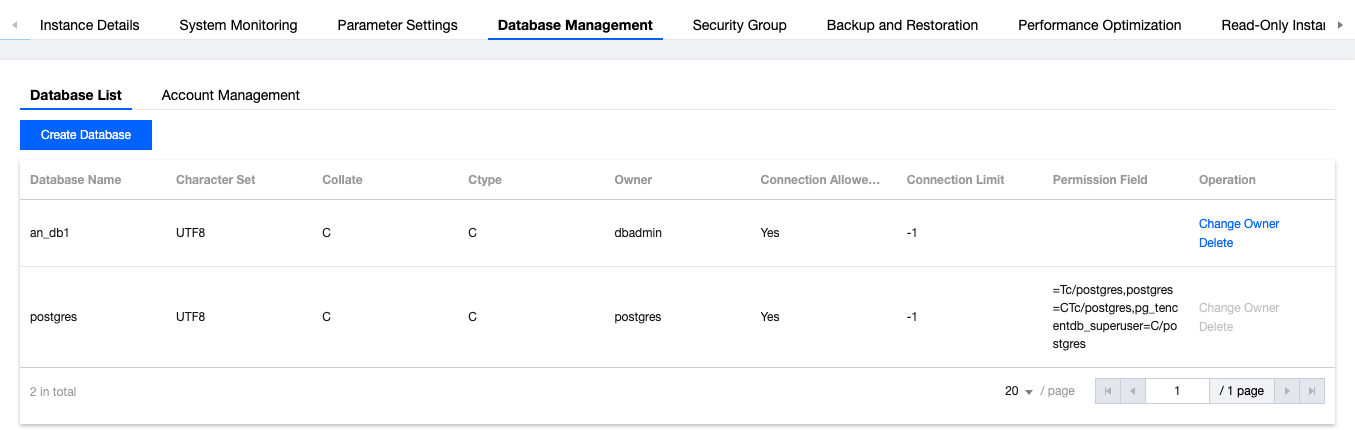
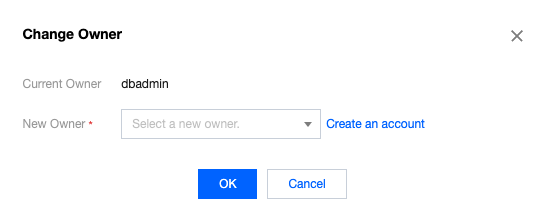
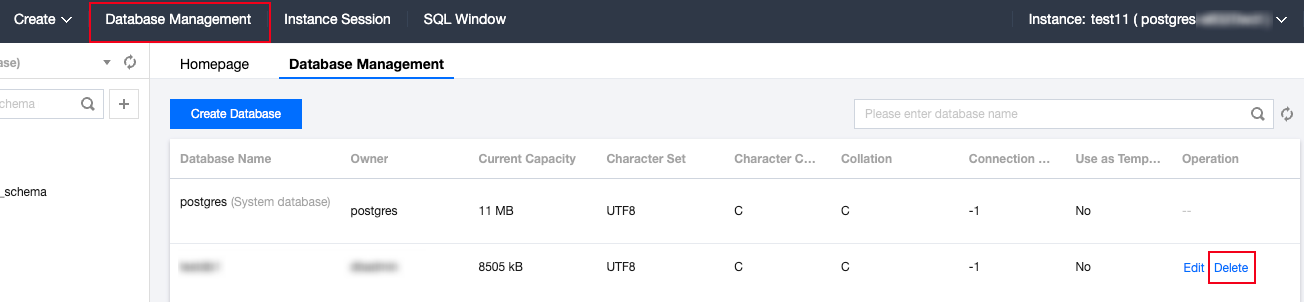
Last updated:2025-08-14 16:29:50

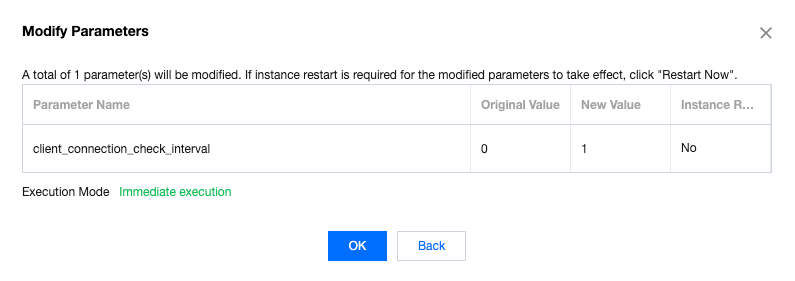

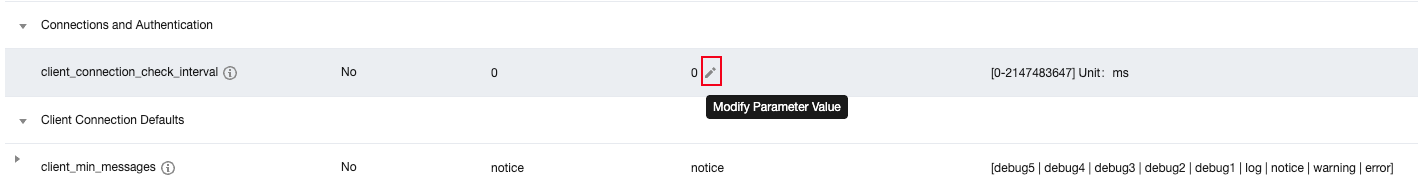


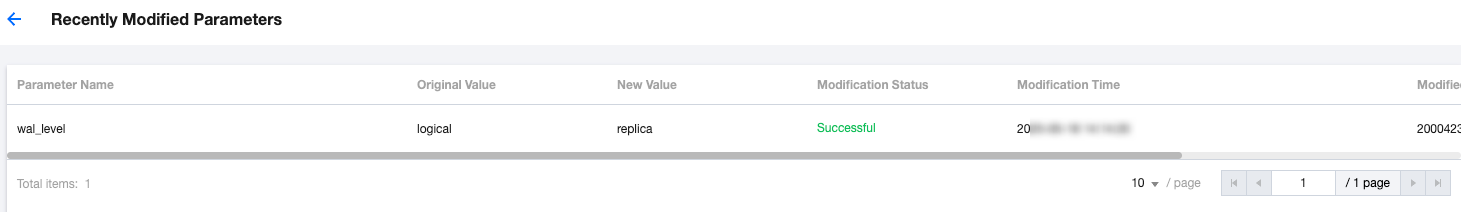
Last updated:2025-06-16 17:32:07
Specification\Parameter | max_replication_slots | max_wal_senders | max_worker_processes | max_logical_replication_workers | max_parallel_workers | max_connections |
1C2GiB | [10-100] | [27-150] | [4-300] | [4-150] | [8-8] | [100-2048] |
2C4GiB | [10-100] | [27-150] | [4-300] | [4-150] | [8-8] | [100-2048] |
2C6GiB | [10-150] | [27-200] | [4-400] | [4-200] | [8-8] | [100-2048] |
4C8GiB | [10-150] | [27-200] | [4-400] | [4-200] | [8-8] | [100-2048] |
4C16GiB | [10-150] | [27-200] | [4-400] | [4-200] | [8-8] | [100-2048] |
6C24GiB | [10-200] | [27-250] | [4-500] | [4-250] | [8-12] | [100-2048] |
8C16GiB | [10-150] | [27-200] | [4-400] | [4-200] | [8-8] | [100-2048] |
8C32GiB | [10-200] | [27-250] | [4-500] | [4-250] | [8-16] | [100-4000] |
8C48GiB | [10-200] | [27-250] | [4-500] | [4-250] | [8-16] | [100-4500] |
8C64GiB | [10-400] | [27-450] | [4-900] | [4-450] | [8-24] | [100-5500] |
12C24GiB | [10-200] | [27-250] | [4-500] | [4-250] | [8-12] | [100-2048] |
12C64GiB | [10-400] | [27-450] | [4-900] | [4-450] | [8-24] | [100-5500] |
16C32GiB | [10-200] | [27-250] | [4-500] | [4-250] | [8-16] | [100-4000] |
16C96GiB | [10-400] | [27-450] | [4-900] | [4-450] | [8-32] | [100-8000] |
20C128GiB | [10-500] | [27-450] | [4-900] | [4-450] | [8-40] | [100-10000] |
24C48GiB | [10-200] | [27-250] | [4-500] | [4-250] | [8-16] | [100-4500] |
24C192GiB | [10-500] | [27-550] | [4-1200] | [4-550] | [8-50] | [100-12000] |
28C240GiB | [10-600] | [27-650] | [4-1300] | [4-650] | [8-60] | [100-13000] |
32C64GiB | [10-400] | [27-450] | [4-900] | [4-450] | [8-24] | [100-5500] |
48C480GiB | [10-600] | [27-650] | [4-1300] | [4-650] | [8-60] | [100-22000] |
64C256GiB | [10-600] | [27-650] | [4-1300] | [4-650] | [8-60] | [100-13000] |
64C384GiB | [10-600] | [27-650] | [4-1300] | [4-650] | [8-60] | [100-20000] |
64C512GiB | [10-600] | [27-650] | [4-1300] | [4-650] | [8-60] | [100-22000] |
90C720GiB | [10-600] | [27-650] | [4-1300] | [4-650] | [8-60] | [100-36000] |
Last updated:2025-06-09 10:25:33
**.conf to import and create a template.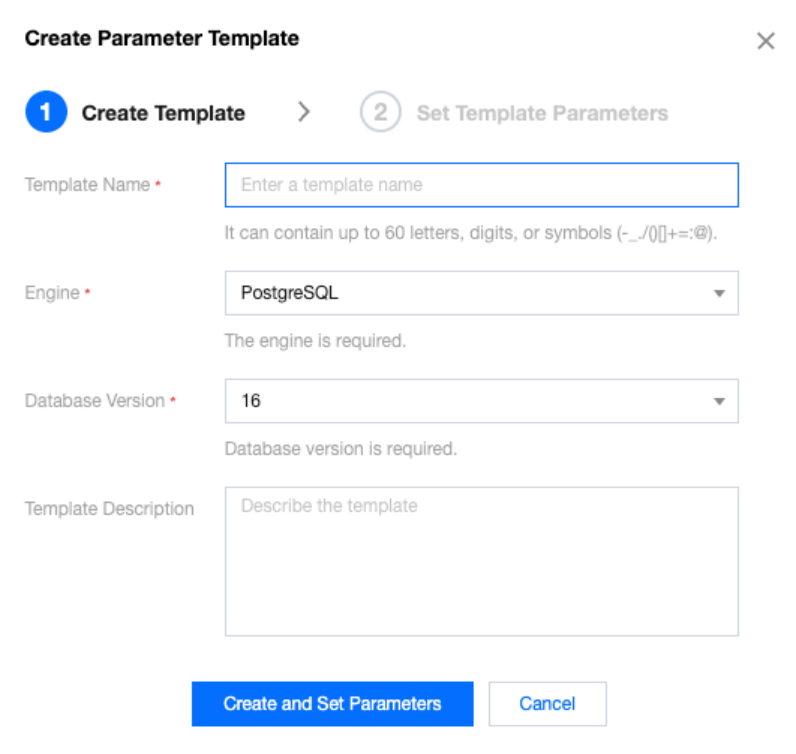

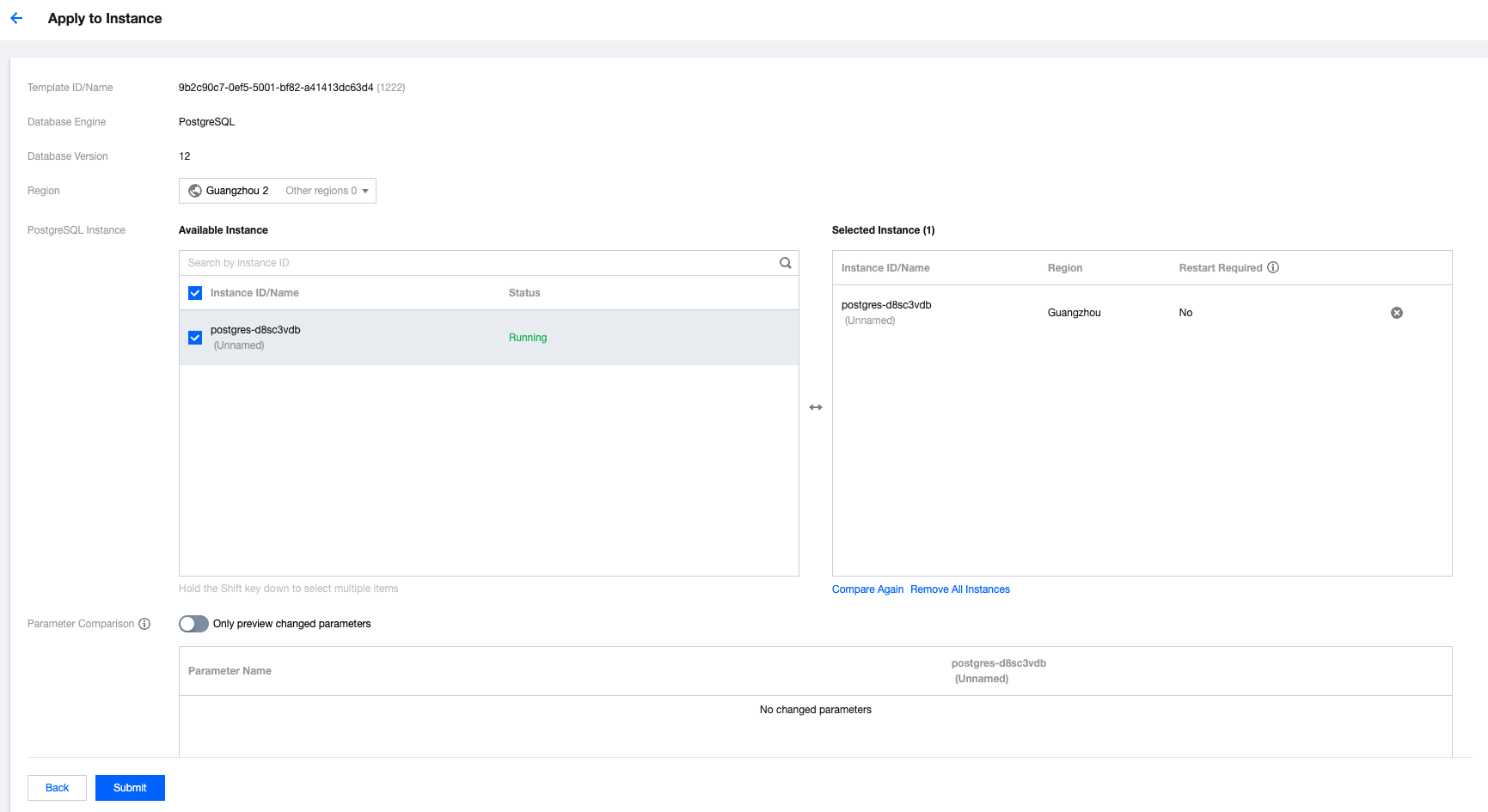
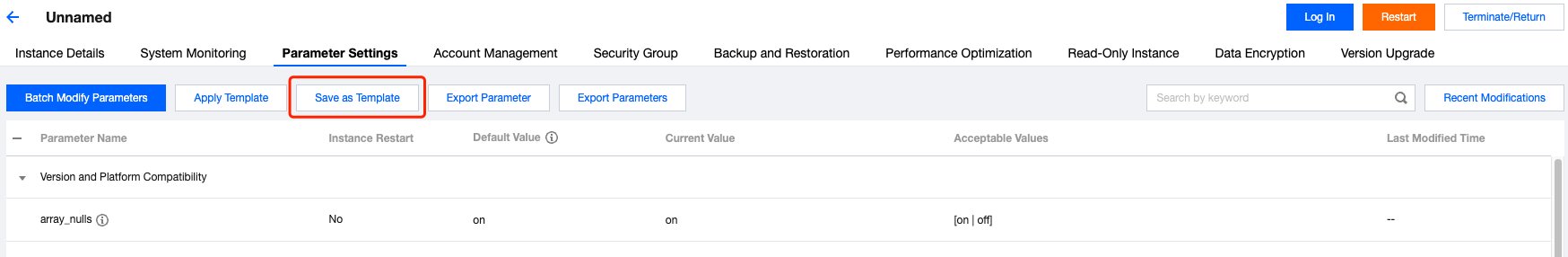
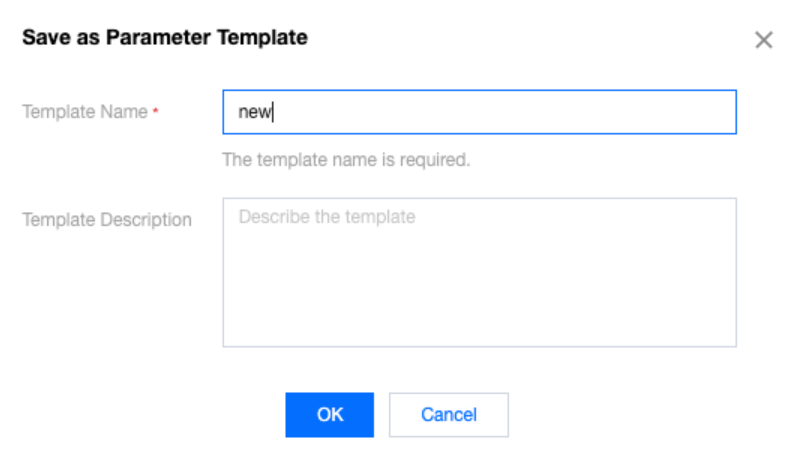
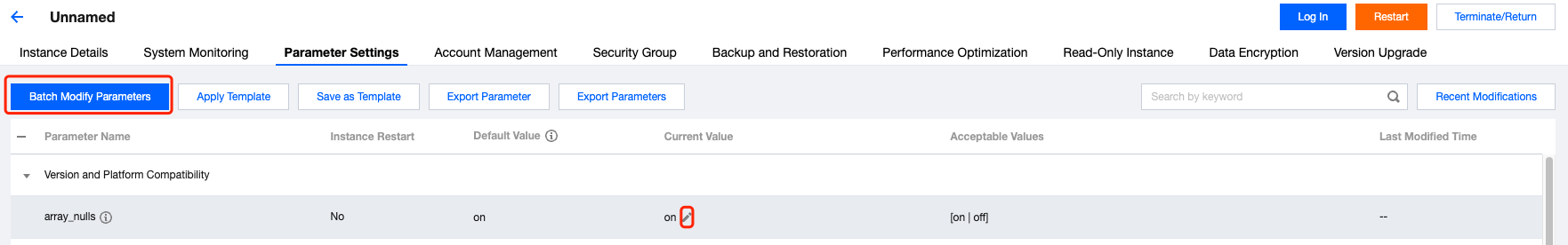
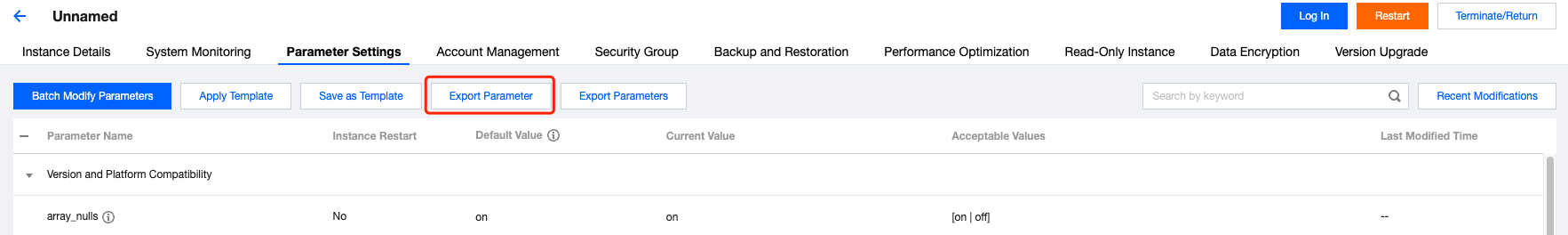
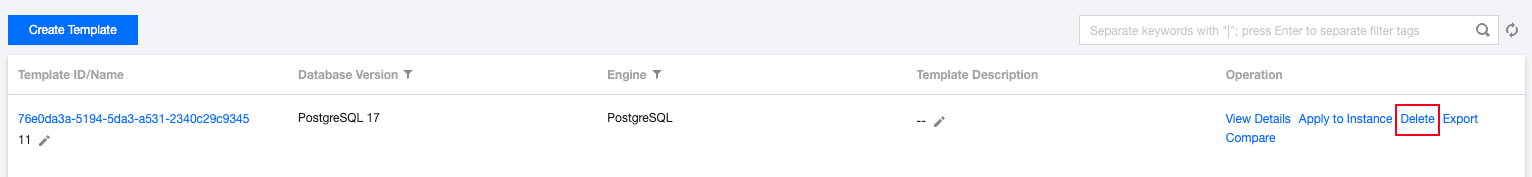
Last updated:2024-10-28 15:03:30
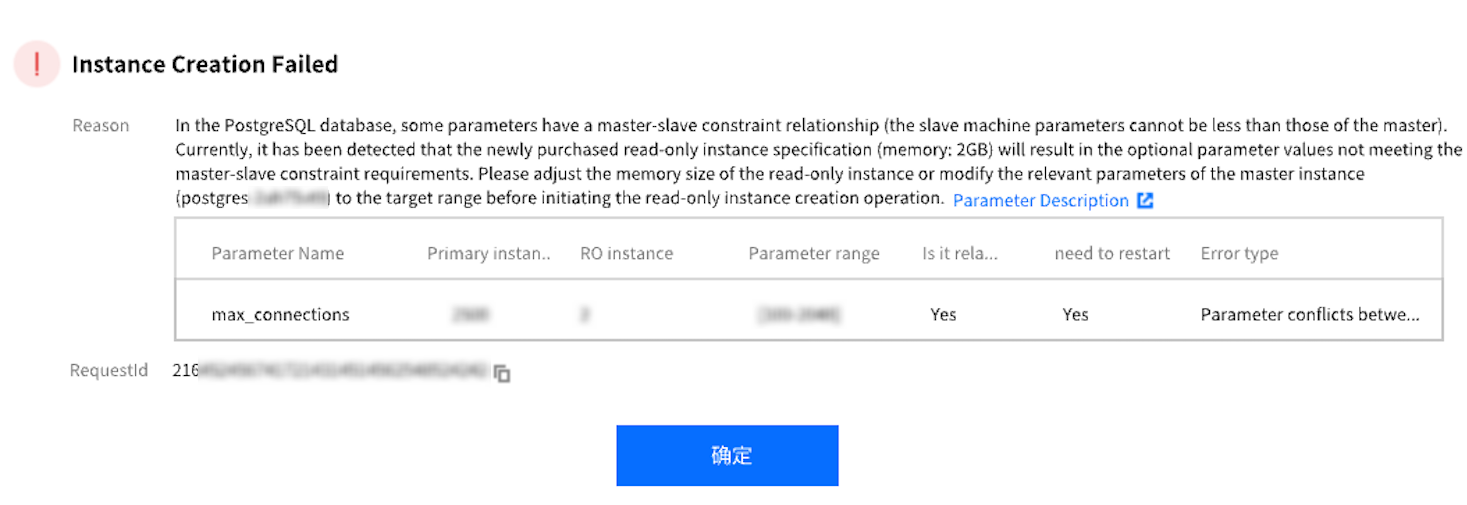
Instance Type | Instance Configuration | Maximum max_connections Value |
Primary instance | 8 CPU cores and 48 GB memory with 100 GB disk | 4500 |
Read-only instance | 1 CPU core and 2 GB memory with 100 GB disk | 2048 |
Read-only instance | 1 CPU core and 2 GB memory with 100 GB disk | 2048 |
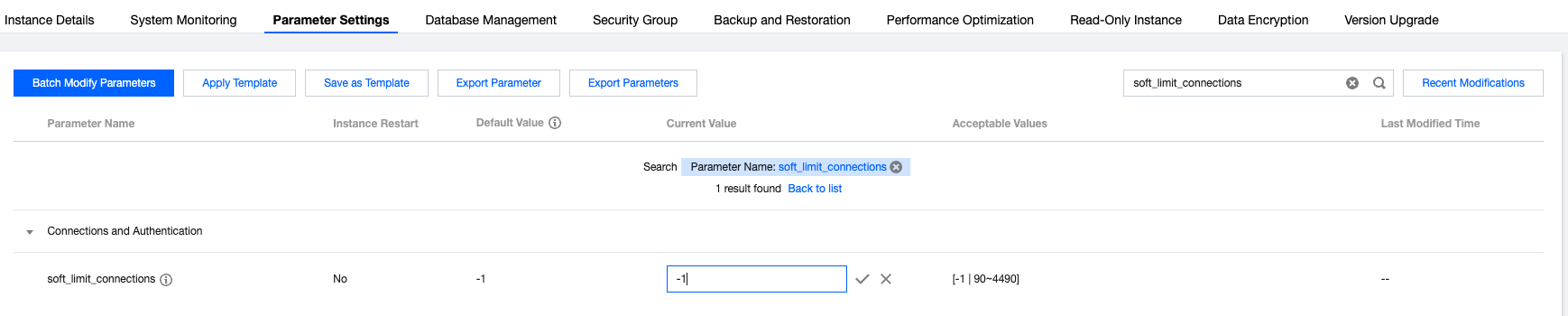
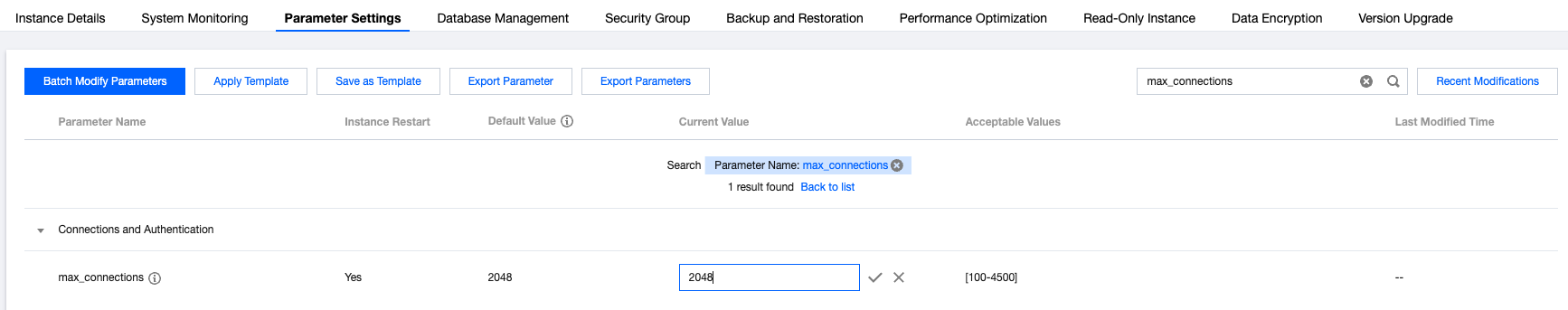
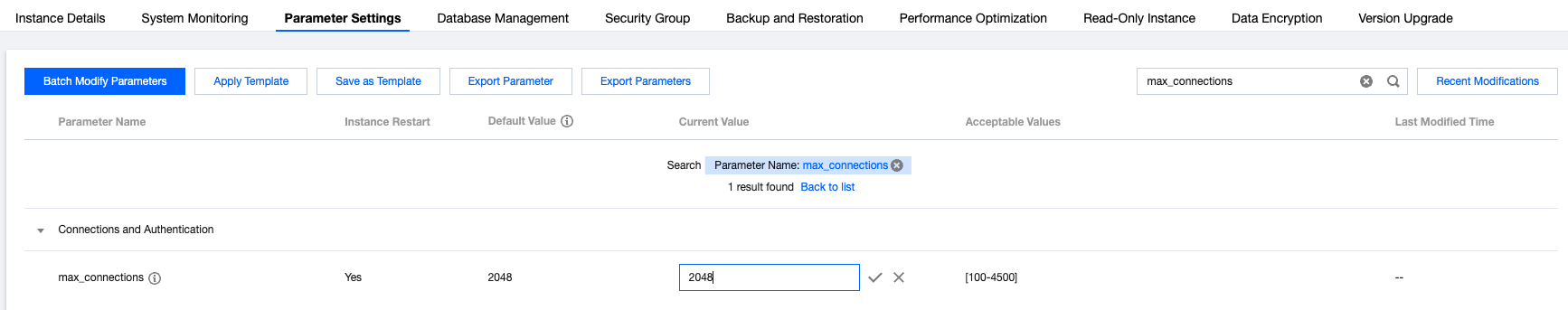
Last updated:2026-01-26 14:15:59
-- View table typeSELECTschemaname,tablename,CASEWHEN relpersistence = 'u' THEN 'UNLOGGED'WHEN relpersistence = 'p' THEN 'PERMANENT'ELSE 'OTHER'END as table_typeFROM pg_tables tJOIN pg_class c ON c.relname = t.tablenameWHERE schemaname = 'public';
-- Convert UNLOGGED tables to regular tables, where unlogged_table_name is the table nameALTER TABLE unlogged_table_name SET LOGGED;-- Lock status monitoring: the mode field indicates the lock type, AccessExclusiveLock is the most restrictive lock, and unlogged_table_name is the table nameSELECTl.locktype,l.mode,l.granted,l.pid,a.state,a.query_start,now() - a.query_start as duration,CASEWHEN l.granted THEN 'GRANTED'ELSE 'WAITING'END as lock_status,substring(a.query, 1, 80) as query_snippetFROM pg_locks lLEFT JOIN pg_stat_activity a ON l.pid = a.pidWHERE l.relation IS NOT NULLAND EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM pg_class cWHERE c.oid = l.relationAND c.relname = 'unlogged_table_name')ORDER BY l.granted, a.query_start;
-- For large tables, it is recommended to convert them in batches-- 1. Create a new LOGGED tableCREATE TABLE user_cache_new (LIKE user_cache);-- 2. Migrate data in batchesINSERT INTO user_cache_newSELECT * FROM user_cacheWHERE created_at >= '2024-01-01' AND created_at < '2024-01-02';-- 3. Rename the tableBEGIN;DROP TABLE user_cache;ALTER TABLE user_cache_new RENAME TO user_cache;COMMIT;
tencentdb_log_unlogged_table parameter, while maintaining PostgreSQL's native functionality, to provide users with enhanced data security. For modifying parameters, see Setting Instance Parameters.-- Create UNLOGGED tableamy=> CREATE UNLOGGED TABLE test_table (id INT, data TEXT);-- System WARNING:WARNING: change unlogged table to logged table, If you want to use unlogged tables, please set tencentdb_log_unlogged_table to false.CREATE TABLE-- Verify table type, returns: 'p' (PERMANENT/LOGGED)am=> SELECT relpersistence FROM pg_class WHERE relname = 'test_table';relpersistence----------------p(1 row
tencentdb_log_unlogged_table Parameter Require Rebooting the Instance?ALTER TABLE SET LOGGED conversion.Last updated:2026-02-11 20:33:56
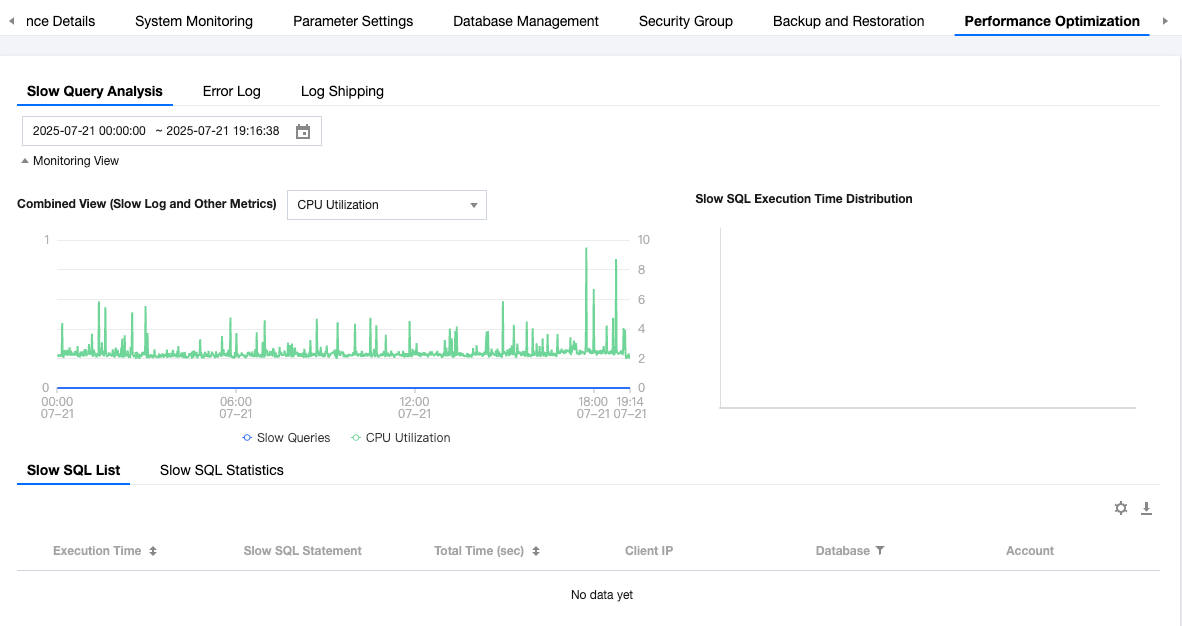


Last updated:2025-07-22 20:25:30
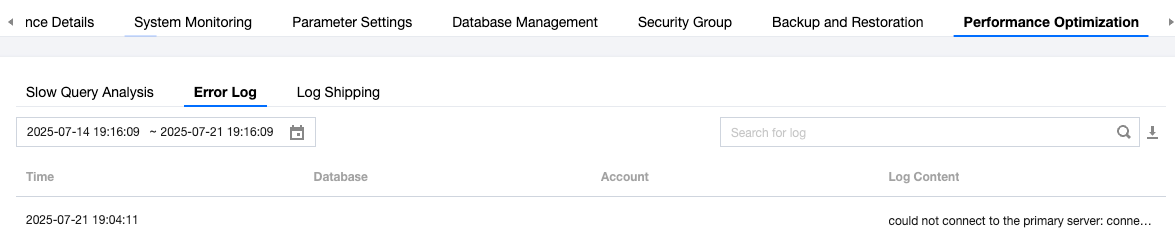
Last updated:2025-11-03 14:26:13
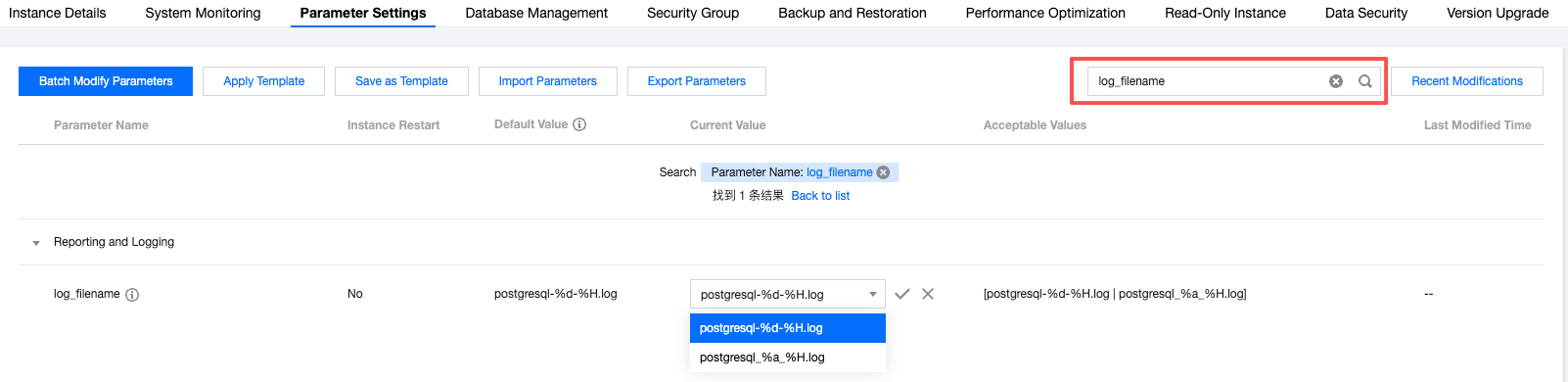
Parameter Value | Description |
postgresql_%a_%H.log | Selecting this value will keep logs for 7 days. |
postgresql_%d_%H.log | Selecting this value allows logs to be retained for 30 days, which is the system default. |
SELECT pg_rotate_logfile();
Last updated:2025-10-15 20:18:39
Field value. | Type | Description |
Timestamp | - | A reserved field for CLS, which represents the log generation time. |
InstanceId | String | Database instance ID, such as postgres-xxx. |
Database | Long | The database used by the client to connect to the database instance. |
UserName | String | The username used by the client to connect to the database instance. |
ErrMsg | String | Original SQL error logs. |
ErrTime | String | Error occurrence time. |
Field value. | Type | Description |
Timestamp | - | A reserved field for CLS, which represents the log generation time. |
InstanceId | String | Database instance ID, such as postgres-xxx. |
DatabaseName | String | The database to which the client connects. |
UserName | String | User of client connection. |
RawQuery | String | Slow log content. |
Duration | String | Duration. |
ClientAddr | String | Client address. |
SessionStartTime | Unix timestamp | Session start time. |
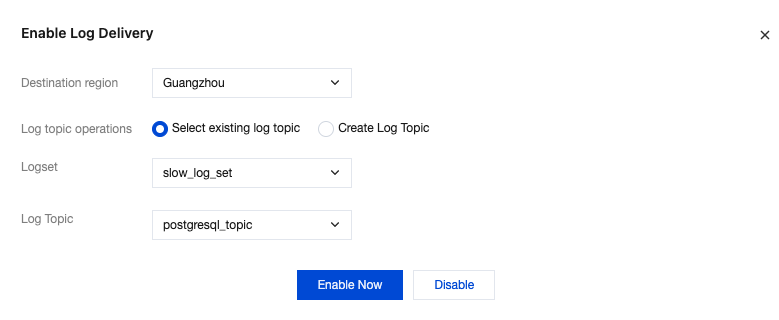
Parameter | Description |
Destination region | Select the region for log shipping, supporting offsite shipping. |
Log topic operations | Log topics serve as the fundamental units for collecting, storing, retrieving, and analyzing log data. You can either select an existing log topic or create a new one. |
Logset | Logsets serve as a classification mechanism for log topics, enabling efficient management of log topics. You can either select existing log topics or create new ones as needed. Select an existing logset: You can filter existing logsets in the search box to categorize slow log shipping. Create a logset: You can create a new logset to categorize slow log shipping. Only English letters, digits, and underscores are supported, and the length cannot exceed 20. |
Log Topic | Select an existing log topic: This option is available only when an existing logset is selected. You can filter log topics under the selected logset in the search box. Create a log topic: Create a new log topic under the selected logset. Only English letters, digits, and underscores are supported, and the length cannot exceed 20. Note: |
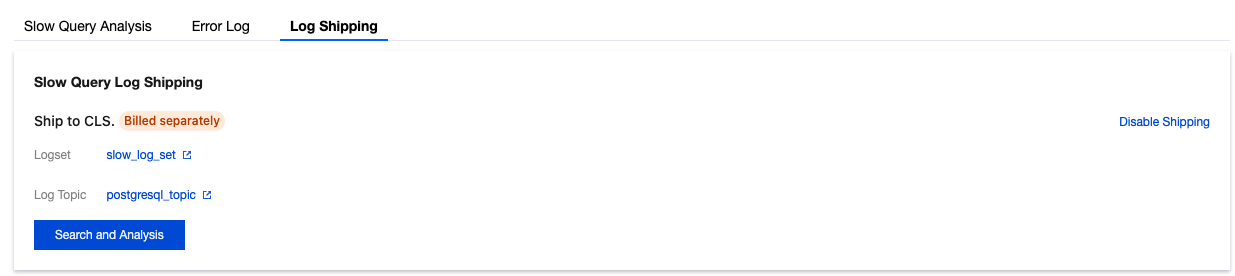
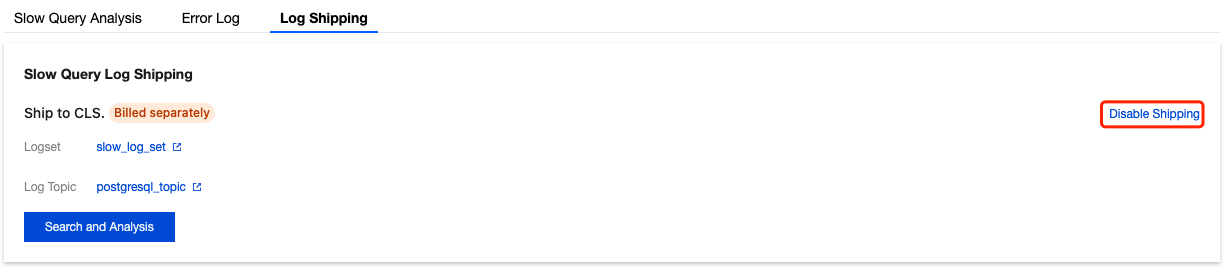
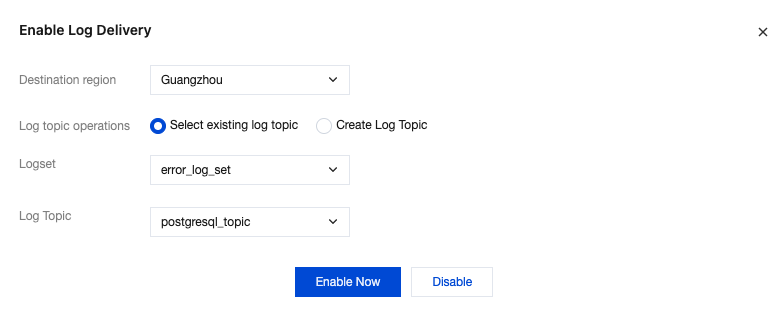
Parameter | Description |
Destination region | Select the region for log shipping, supporting offsite shipping. |
Logset Operation | A logset categorizes log topics to facilitate your management of log topics. You can select an existing logset or create a logset. |
Logset | Select an existing logset: You can filter existing logsets in the search box to categorize error log shipping. Create a logset: You can create a new logset to categorize error log shipping. The naming format for creating a logset is custom_logset, where the custom part supports only English letters, digits, and underscores, with a length not exceeding 20. |
Log Topic | Select an existing log topic: This option is available only when an existing logset is selected. You can filter log topics under the selected logset in the search box. Create a log topic: You can create a new log topic under the selected logset. The naming format for creating a log topic is custom_topic, where the custom part supports only English letters, digits, and underscores, with a length not exceeding 20. Note: |
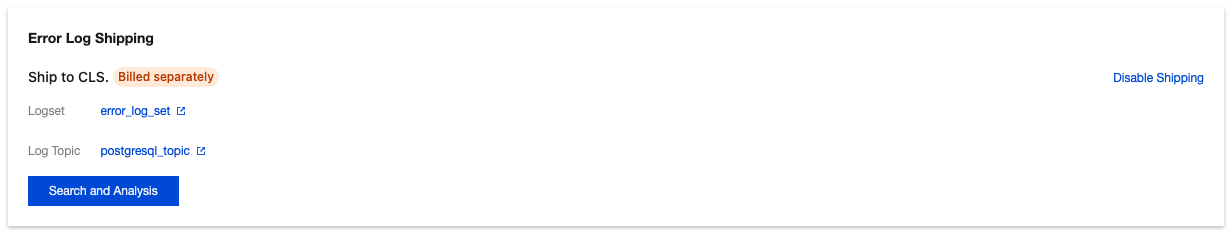
Last updated:2024-03-20 14:30:33
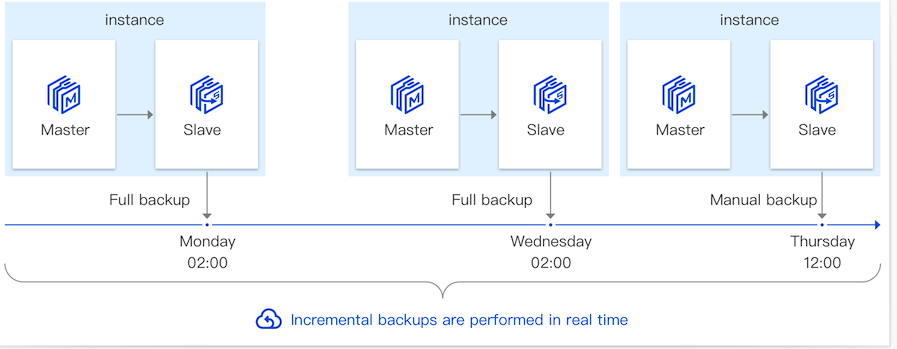
Operation Type | Backup Type | Operation Details |
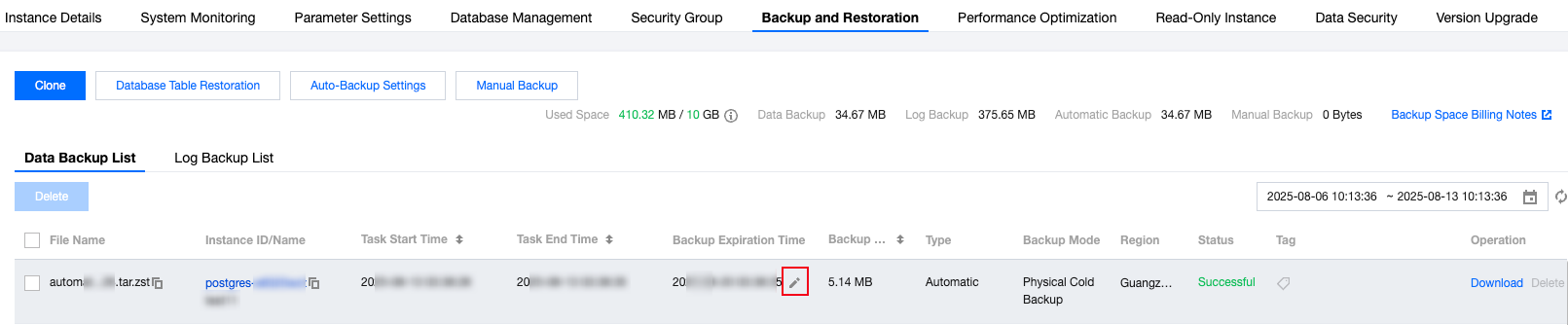
Data Backup | Data Backup | The system will trigger a full data backup according to your automatic backup setting within the specified time. The backup method is physical backup, which offers fast backup speed and higher recovery efficiency. The generated full automatic backup data is retained based on the data backup retention time you set. The backup data will not be deleted when the instance is terminated. It will be automatically deleted when it expires. This can meet your need to extend the retention of backup data to prevent serious impact due to accidental deletion of instances. Since full backup uses backup storage space, you can delete it promptly if necessary. The automatic backup data within one week cannot be deleted, while data older than one week can be flexibly deleted according to your needs. Please be cautious when deleting backup data as it cannot be recovered after deletion. |
| Manual Backup | You can manually initiate a full instance backup based on application needs through the console. After the manual backup task is initiated, the system will perform a full instance backup using the physical backup method within 1 minute. The expiration time of manual backups is one week after they are initiated. Since manual backups occupy backup storage space, you can delete manual backups promptly if necessary. |
| Incremental Backup | Incremental backup is WAL log backup, which is automatically enabled by default and cannot be disabled. The incremental backup is stored based on the data backup retention time you set. The system will perform real-time backup based on the WAL log generated by the database. Since incremental backup occupies backup storage space, you can delete it promptly if necessary. Incremental backup data within a week is not allowed to be deleted, while data older than one week can be flexibly deleted according to your needs. After the incremental backup data is deleted, point-in-time recovery cannot be performed, so exercise caution when deleting incremental backup data. |
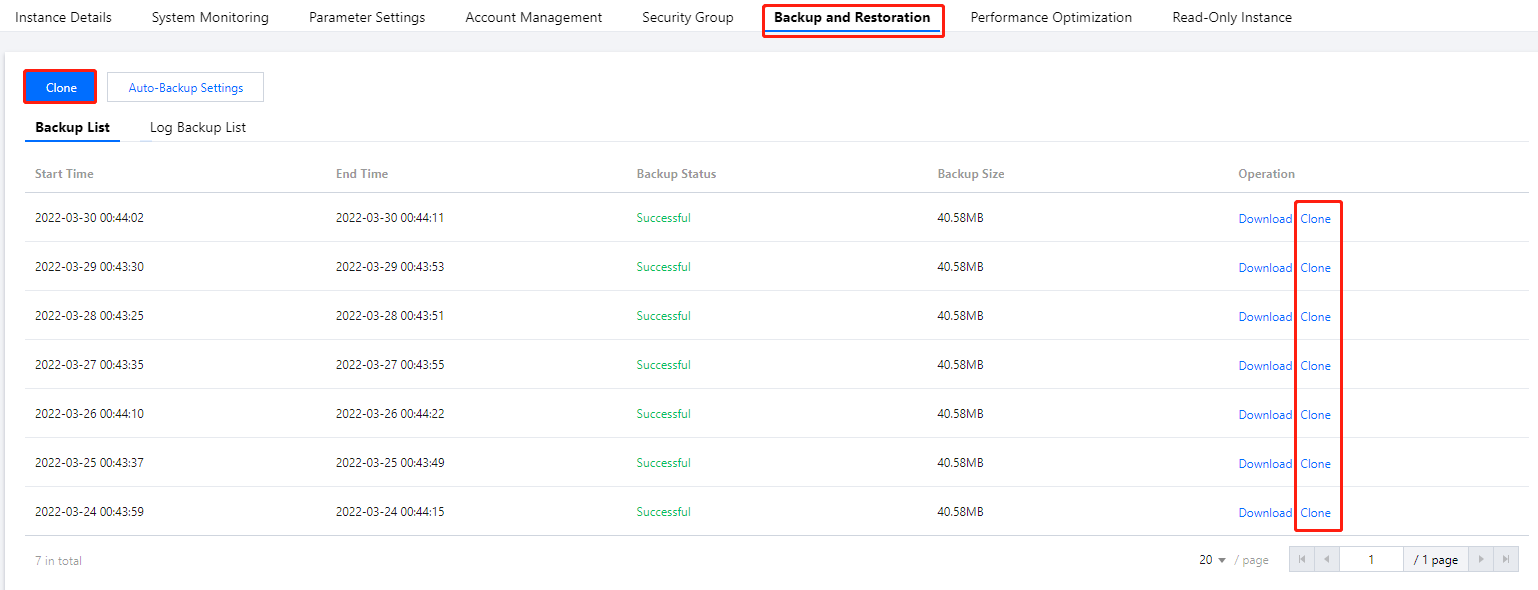
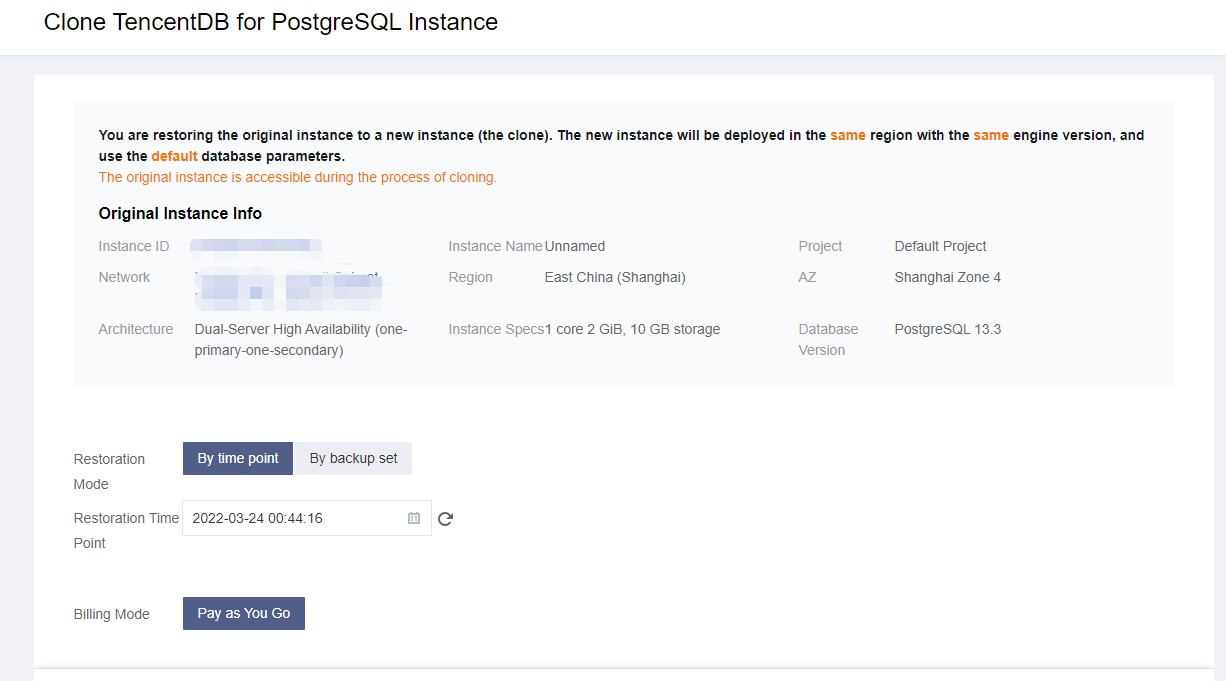
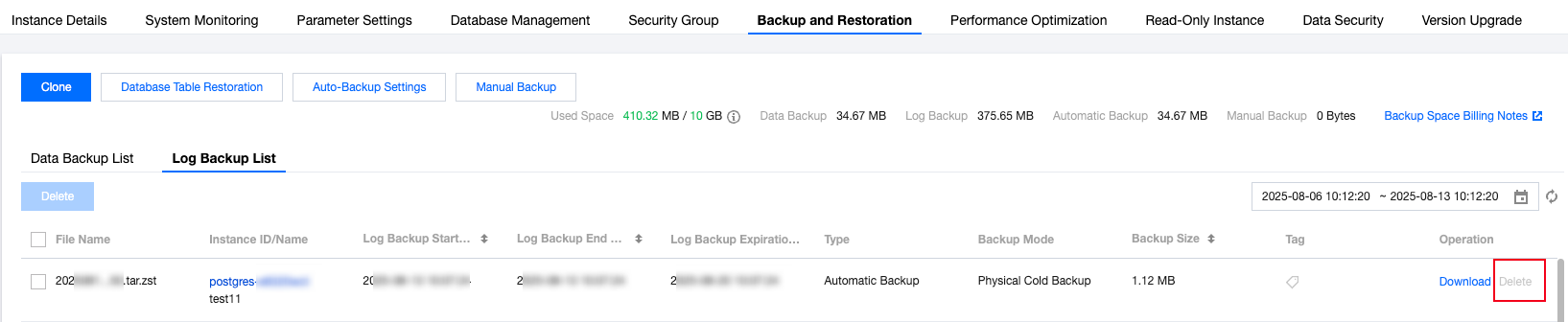
Backup Files Download | Download Full Backup | Supports local browser download and download by address. |
| Download Incremental Backup | Supports local browser download and download by address. |
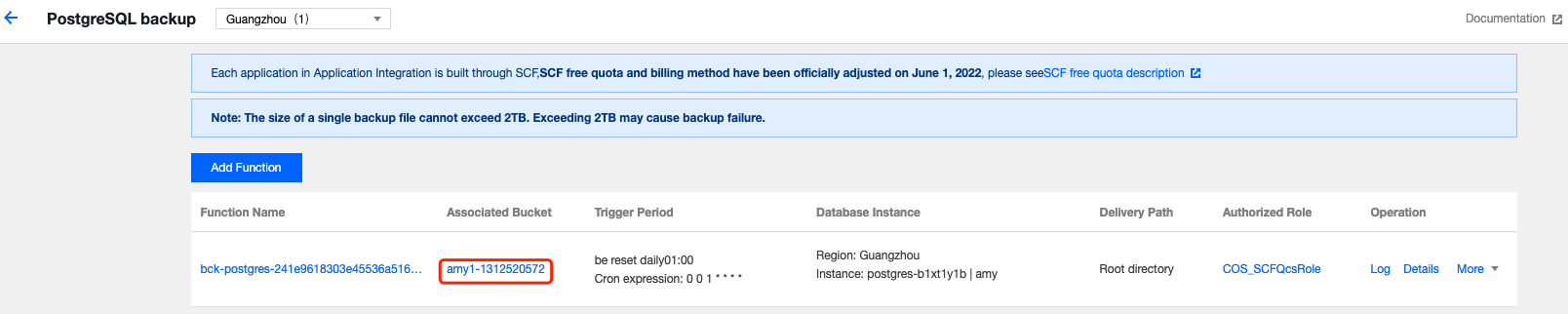
Transfer Historical Backup Through Serverless Cloud Function | Transfer through Serverless Cloud Function | You can transfer historical backup data using the Serverless Cloud Function. For more information, please see Use Serverless Cloud Function to transfer historical PostgreSQL backup. |
Last updated:2025-08-14 16:35:08
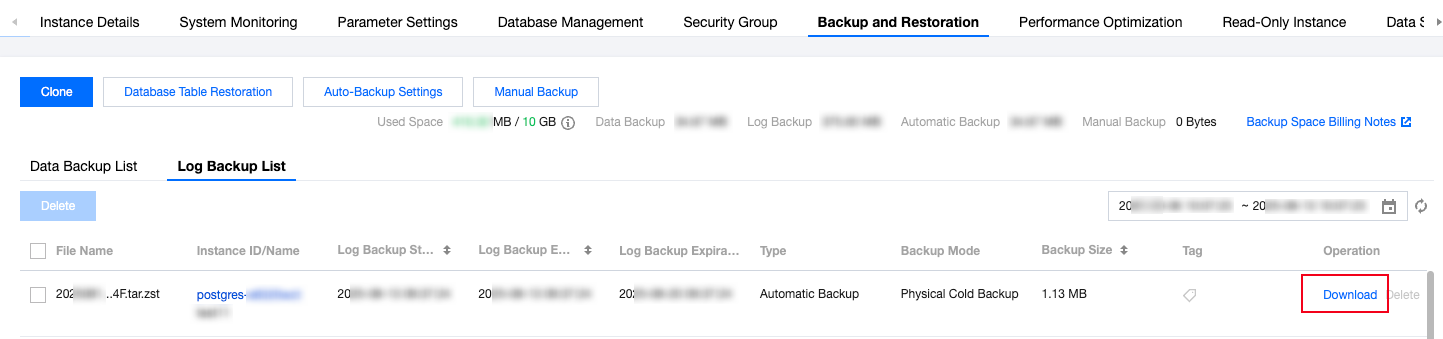
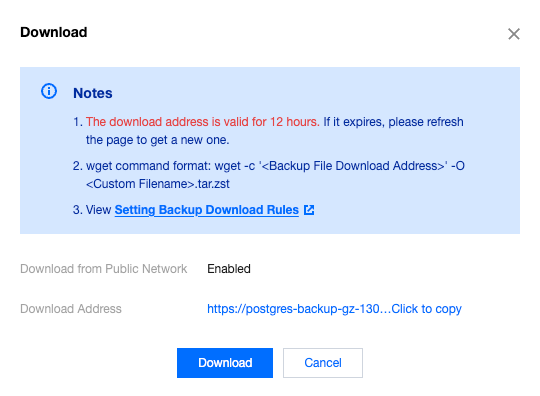
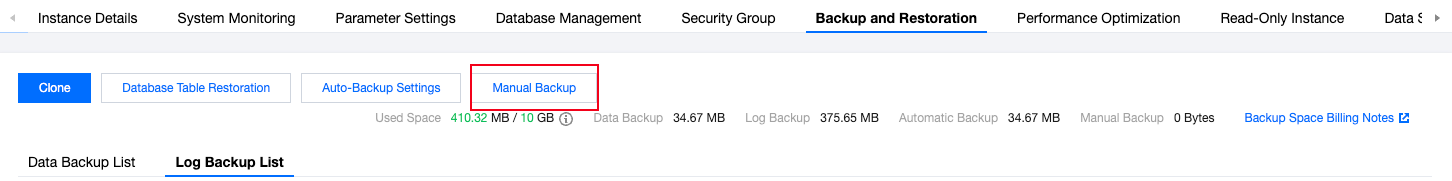
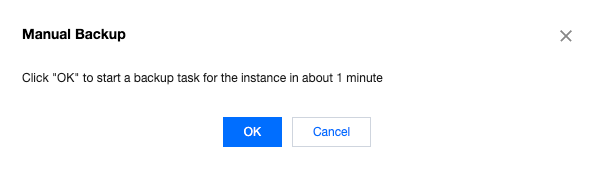
Last updated:2025-08-14 16:38:17
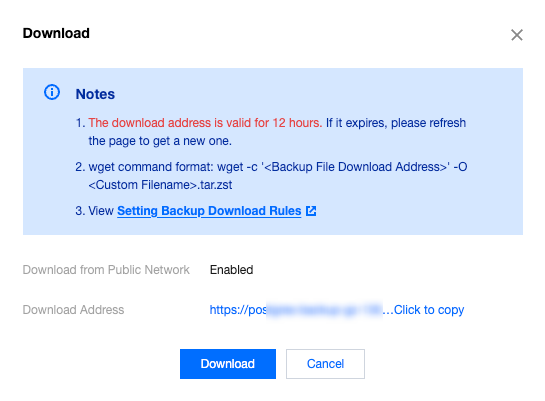
wget command is used to download.
wget command for fast download over the private network. For more information, see Customizing Linux CVM Configurations.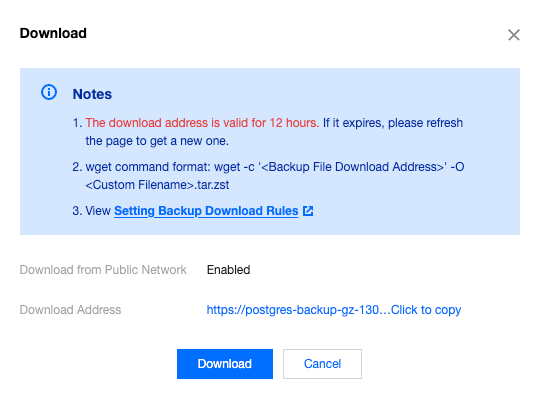
Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51
Last updated:2025-05-19 12:01:32
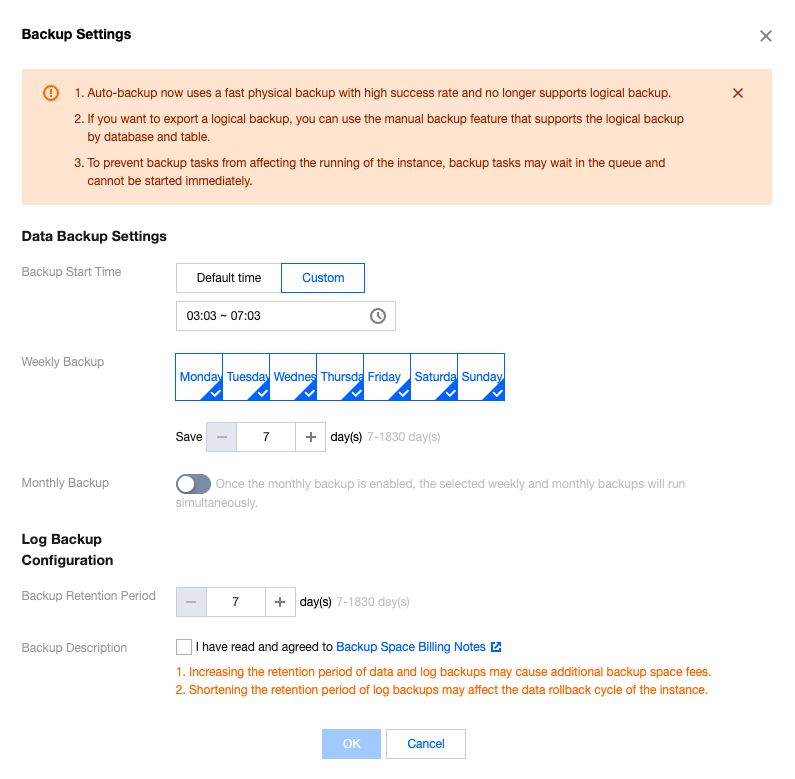
Parameter | Description |
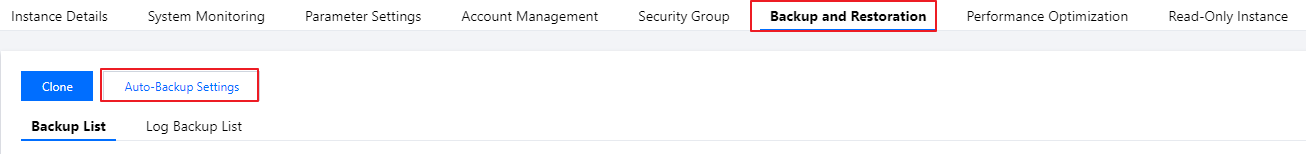
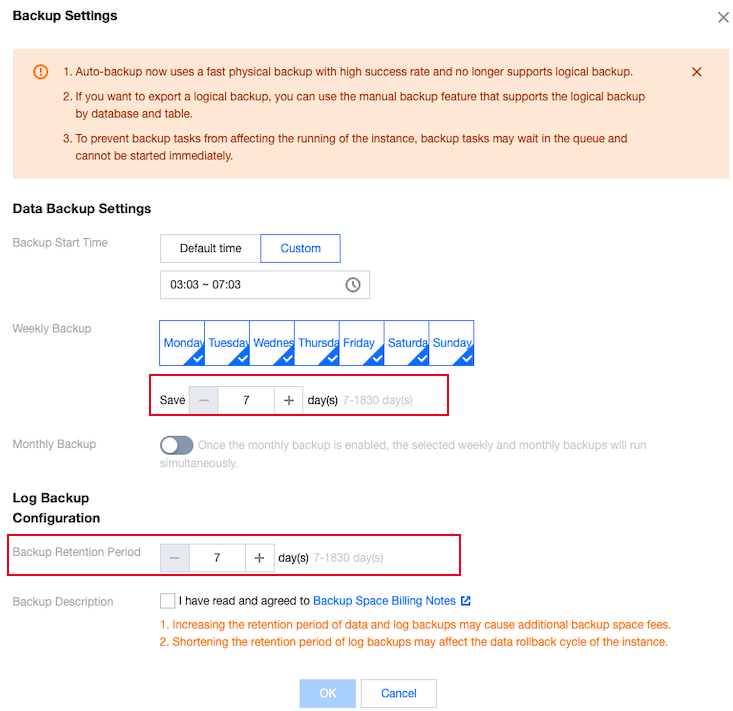
Backup Start Time | Support selecting the default time (to perform backup during idle time of resources throughout the day) or customizing the backup start time. The backup will be initiated within this time range. If the backup fails to be initiated within this time period due to an unexpected reason, this backup will no longer start and will be initiated during the next backup start time period. Default time is the backup initiation time automatically assigned by the system. Support custom selection of backup start time. Set it to the off-peak period. Backup initiation time is merely the time when the backup starts and does not represent the backup end time. For example, if you select 02:00 - 06:00 to enable backup, the system will initiate backup at a certain point within the time range of 02:00 - 06:00, depending on the backend backup policy and backup system status. |
Weekly Backup | Select by the scale of one week, and support consecutive or interval selection from Monday to Sunday. Chosen by default for Monday to Sunday, 7 days. Support custom selection of backup time. However, to ensure the security of your data, please set up at least two backups per week. |
Weekly backup retention time | Weekly backup files can be retained for 7–1830 days. It defaults to 7 days. The backup set will be auto-deleted upon expiry. |
Monthly Backup | Select based on a one-month (31 days) scale. The backup data backed up monthly can be set with a separate retention time. Off by default. After turning on the switch, you can choose any number of days from 1 to 31. Particularly, if the 31st is selected, the backup this time will be skipped directly in months without the 31st. Monthly backup and weekly backup are carried out simultaneously, and all data will be stored. |
Monthly backup retention time | Monthly backup files can be retained for 7–1830 days. It defaults to 7 days. The backup set will be auto-deleted upon expiry. |
log backup retention time | Log backup data retention time setting: Retainable for 7–1830 days, defaults to 7 days. |
Last updated:2025-09-10 22:12:08
mkdir -p /var/lib/pgsql/16/recoverychown postgres /var/lib/pgsql/16/recovery
/var/lib/pgsql/12 for PostgreSQL 12.x.[root@VM-10-5-tencentos postgresql-16.8]# wget -O /var/lib/pgsql/16/recovery/file_name.tar.zst "https://postgres-backup-gz-******.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/pgsql/1030559/data/20**-**-**/automatic-**********.tar.zst?q-sign-algorithm=sha1&q-ak=AKIDjHZcZJpqnqiL0jP4awHZg6McnqiYIwNZ&q-sign-time=1746776185%3B1746819385&q-key-time=1746776185%3B1746819385&q-header-list=host&q-url-param-list=&q-signature=68309d4bbc1bea30fef07776a2aa9fd699c19aa9"
[root@VM-10-5-tencentos postgresql-16.8]# ls -lh /var/lib/pgsql/16/recoverytotal 3952-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4045802 May 7 20:42 manual-20250507204222.tar.zst
[root@VM-10-5-tencentos postgresql-16.8]# zstd –version*** zstd command line interface 64-bits v1.4.4, by Yann Collet ***
[root@VM-10-5-tencentos postgresql-16.8]# sudo yum install epel-release[root@VM-10-5-tencentos postgresql-16.8]# sudo yum install zstd
[root@VM-10-5-tencentos postgresql-16.8]# cd /var/lib/pgsql/16/recovery[root@VM-10-5-tencentos recovery]# tar -I zstd -xvf file_name.tar.zst
[root@VM-10-5-tencentos recovery]# ls -lhtotal 4.0M-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 225 May 7 20:42 backup_label-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 225 May 7 20:31 backup_label.olddrwx------ 6 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 21:13 base-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 56 May 7 20:31 current_audit_logfiles-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 35 May 7 20:31 current_logfilesdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 21:13 global-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3.9M May 7 20:42 manual-20250507204222.tar.zstdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 20:31 pg_commit_tsdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 20:31 pg_dynshmem-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 308 May 7 20:31 pg_hba.conf-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 2.6K May 7 20:31 pg_ident.confdrwx------ 4 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 20:31 pg_logicaldrwx------ 4 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 20:31 pg_multixactdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 20:31 pg_notifydrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 20:42 pg_replslotdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 20:31 pg_serialdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 20:31 pg_snapshotsdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 20:31 pg_statdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 20:31 pg_stat_tmpdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 20:31 pg_subtransdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 20:31 pg_tblspcdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 20:31 pg_twophase-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 3 May 7 20:31 PG_VERSIONdrwx------ 3 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 21:13 pg_waldrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 20:31 pg_xact-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 3.2K May 7 20:31 postgresql.conf-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 0 May 7 20:31 standby.signal-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 0 May 7 20:42 tablespace_map-rw------- 1 postgres postgres. 2 May 7 20:31 TENCENTDB_RELEASE
[root@VM-10-5-tencentos recovery]# rm -rf backup_label
[root@VM-10-5-tencentos recovery]# vi postgresql.conf
pg_stat_statements.tracksynchronous_standby_namesextension_blacklistarchive_modebasebackup_exclude_pathstencentdb_syscache_max_numshared_preload_librariestencentdb_relcache_max_numarchive_commanddisable_dblink_connect_to_othertencentdb_az_fivetencentdb_relcache_evict_numpg_stat_statements.maxsoft_limit_connectionstencentdb_syscache_evict_numtencentdb_enable_trusted_extensionsynchronous_committencentdb_enable_superuser_unsafe_behaviourtencentdb_enable_copy_tolocal_preload_libraries
include = 'standby.conf'.log_destination = ‘csvlog’
port = '5433' ## Change the value of the port parameter to 5433
synchronous_commit = localsynchronous_standby_names = ''
chmod 0700 /var/lib/pgsql/16/recoverychown postgres:postgres /var/lib/pgsql/16/recovery -R
[root@VM-10-5-tencentos recovery]# ls -altotal 4064drwx------ 19 postgres postgres 4096 May 8 09:43 .drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 May 7 20:44 ..-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 225 May 7 20:42 backup_label-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 225 May 7 20:31 backup_label.olddrwx------ 6 postgres postgres 4096 May 7 21:13 base-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 56 May 7 20:31 current_audit_logfiles-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 35 May 7 20:31 current_logfilesdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4096 May 7 21:13 global-rw-r--r-- 1 postgres postgres 4045802 May 7 20:42 manual-20250507204222.tar.zstdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4096 May 7 20:31 pg_commit_tsdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4096 May 7 20:31 pg_dynshmem-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 308 May 7 20:31 pg_hba.conf-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 2640 May 7 20:31 pg_ident.confdrwx------ 4 postgres postgres 4096 May 7 20:31 pg_logicaldrwx------ 4 postgres postgres 4096 May 7 20:31 pg_multixactdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4096 May 7 20:31 pg_notifydrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4096 May 7 20:42 pg_replslotdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4096 May 7 20:31 pg_serialdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4096 May 7 20:31 pg_snapshotsdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4096 May 7 20:31 pg_statdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4096 May 7 20:31 pg_stat_tmpdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4096 May 7 20:31 pg_subtransdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4096 May 7 20:31 pg_tblspcdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4096 May 7 20:31 pg_twophase-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 3 May 7 20:31 PG_VERSIONdrwx------ 3 postgres postgres 4096 May 7 21:13 pg_waldrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4096 May 7 20:31 pg_xact-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 3276 May 7 21:35 postgresql.conf-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 0 May 7 20:31 standby.signal-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 0 May 7 20:42 tablespace_map-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 2 May 7 20:31 TENCENTDB_RELEASE
[root@VM-10-5-tencentos postgresql-16.8]# wget -O /var/lib/pgsql/16/recovery/pg_wal/file_name.tar.zst "download_address"
[root@VM-10-5-tencentos recovery]# cd /var/lib/pgsql/16/recovery/pg_wal[root@VM-10-5-tencentos pg_wal]# ls -lhtotal 33M-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 16M May 7 20:42 000000010000000000000003-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 16M May 7 20:42 000000010000000000000004-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1.5K May 8 10:31 20250508103101_20250508103101-20250508101527-000000010000000000000005_000000010000000000000005.tar.zstdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 21:13 archive_status
[root@VM-10-5-tencentos pg_wal]# tar -I zstd -xvf file_name.tar.zst000000010000000000000005
[root@VM-10-5-tencentos pg_wal]# ls -lhtotal 49M-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 16M May 7 20:42 000000010000000000000003-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 16M May 7 20:42 000000010000000000000004-rw------- 1 1003 users 16M May 8 10:31 000000010000000000000005-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1.5K May 8 10:31 20250508103101_20250508103101-20250508101527-000000010000000000000005_000000010000000000000005.tar.zstdrwx------ 2 postgres postgres 4.0K May 7 21:13 archive_status
/usr/local/pgsql/bin/pg_ctl start -D /var/lib/pgsql/16/recovery -l logfile
/usr/local/pgsql/bin/pg_ctl status -D /var/lib/pgsql/16/recovery

[postgres@VM-0-5-tencentos recovery]$ /usr/local/pgsql/bin/psql -h127.0.0.1 -p 5432 -Udbadmin -dpostgrespsql (16.0)Type "help" for help.postgres=>
Parameter | Description |
host | The connection address of the TencentDB for PostgreSQL instance. |
port | The port of the TencentDB for PostgreSQL instance. |
username | The account name of the TencentDB for PostgreSQL instance. |
-Fc | Output format, which is suitable for pg_restore for restoration. |
dbname | The name of the database to be exported. |
dumpdir | The path and name of the exported backup file. |
pg_dump -h 10.0.13.13 -p 5432 -U dbadmin -Fc testdb > testdb_bkp.dump
Password:, enter the access account password, and the file will be successfully exported. You can run ll testdb_bkp.dump to ensure the file is generated.
[postgres@VM-0-14-tencentos root]$ psql -h127.0.0.1 -p5432 -Upostgres -dpostgrespsql (16.0)Type "help" for help.postgres=# \duList of rolesRole name | Attributes-----------+------------------------------------------------------------postgres | Superuser, Create role, Create DB, Replication, Bypass RLSpostgres=# CREATE USER dbadmin WITH PASSWORD '123456' SUPERUSER;CREATE ROLEpostgres=# \duList of rolesRole name | Attributes-----------+------------------------------------------------------------dbadmin | Superuserpostgres | Superuser, Create role, Create DB, Replication, Bypass RLSpostgres=#
[postgres@VM-0-14-tencentos root]$ psql -h127.0.0.1 -p5432 -Udbadmin -dpostgrespsql (16.0)Type "help" for help.postgres=# select datname from pg_database;datname-----------template1template0postgres(3 rows)postgres=# create database testdb;CREATE DATABASEpostgres=# select datname from pg_database;datname-----------template1template0postgrestestdb(4 rows)postgres=#
Parameter | Description |
host | The connection address of the self-built PostgreSQL instance. |
port | The port of the self-built PostgreSQL instance. |
username | The account name of the self-built PostgreSQL instance. |
dbname | The name of the database to be imported. |
dumpdir | The path and name of the backup file to be imported. |
-c | -c is an optional parameter, indicating that the relevant data in the target database will be cleared before data restoration. |
pg_restore -h 127.0.0.1 -p 5432 -U dbadmin -d testdb testdb_bkp.dump -c
[postgres@VM-0-14-tencentos root]$ psql -h127.0.0.1 -p5432 -Udbadmin -dpostgrespsql (16.0)Type "help" for help.postgres=# \c testdbYou are now connected to database "testdb" as user "dbadmin".testdb=# SELECT table_name FROM information_schema.tables WHERE table_schema = 'public';table_name------------sbtest1sbtest10sbtest2sbtest3sbtest4sbtest5sbtest6sbtest7sbtest8sbtest9(10 rows)testdb=#
Last updated:2025-08-14 16:41:45

Last updated:2025-07-22 20:25:30
Last updated:2025-08-14 16:46:26
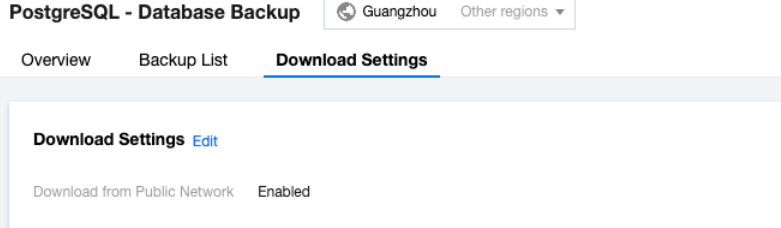
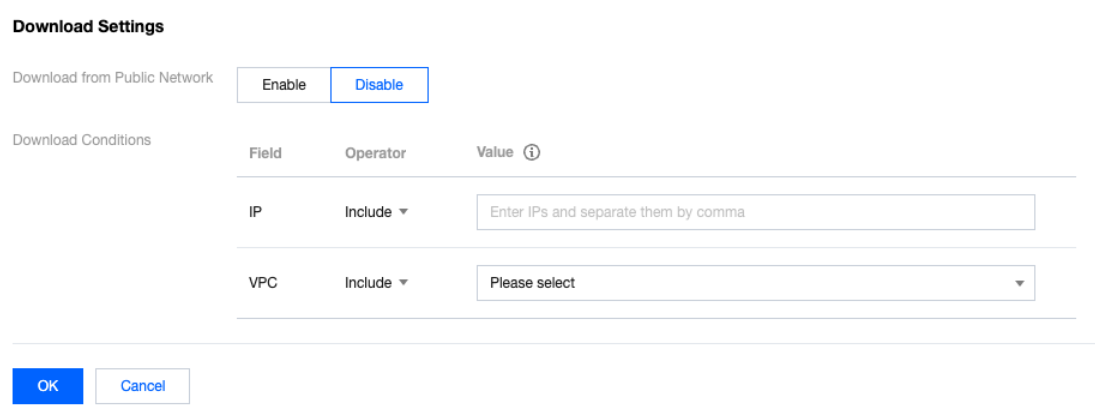
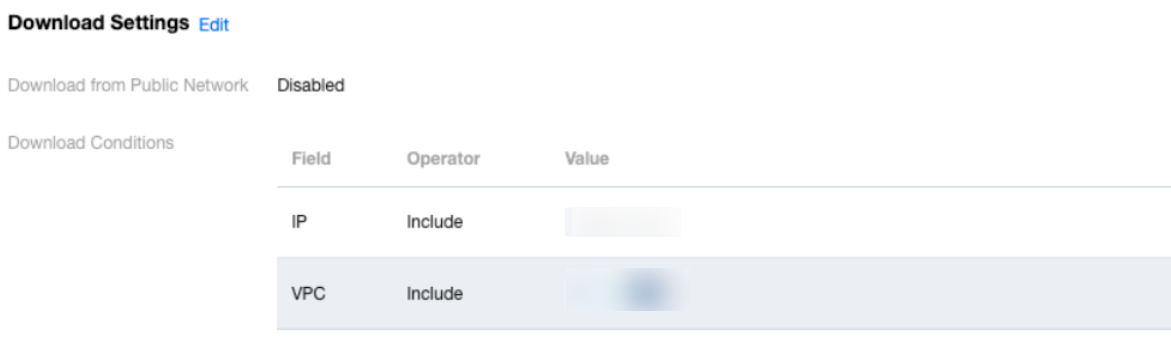
Last updated:2024-03-20 15:43:50
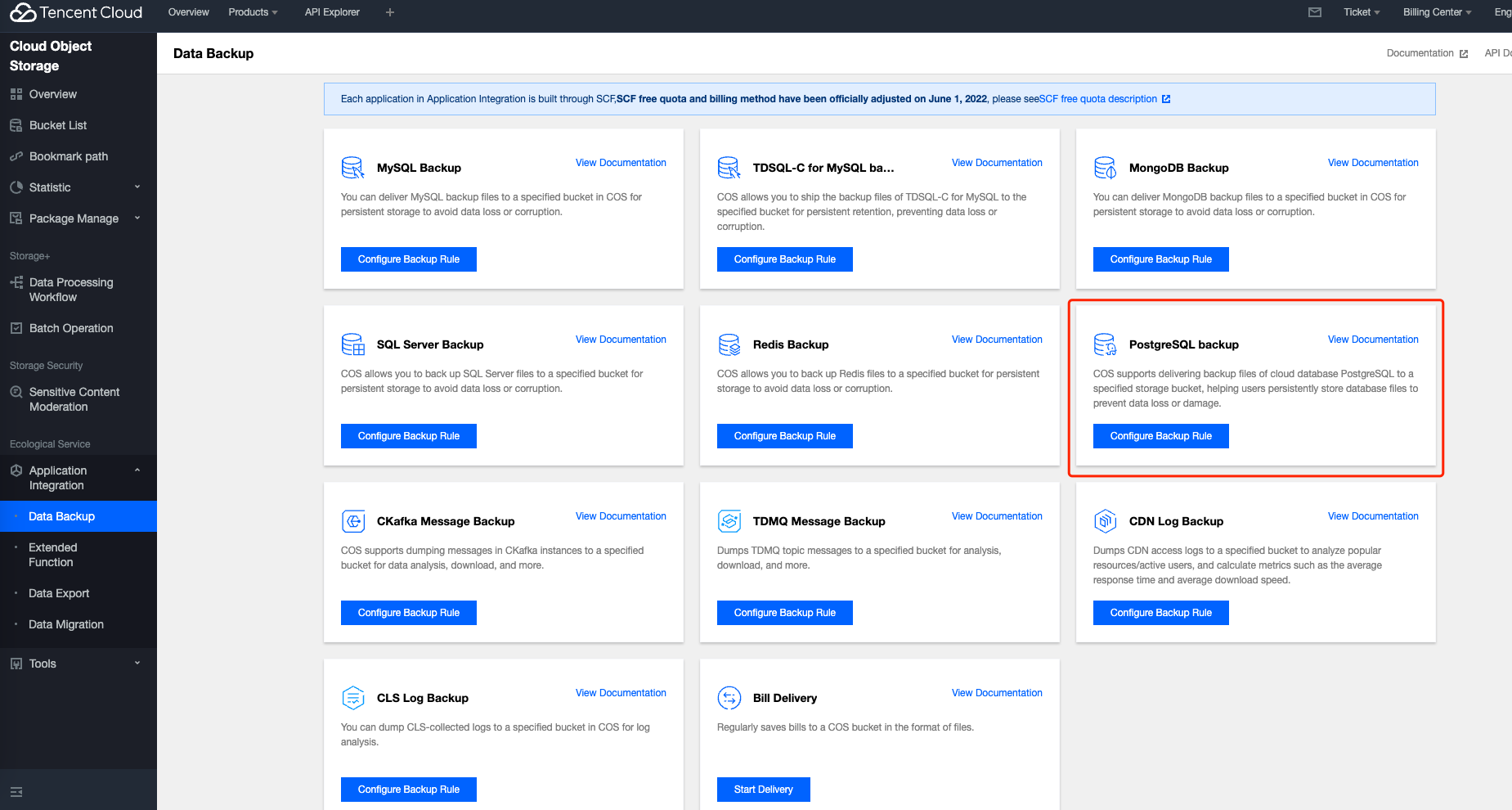
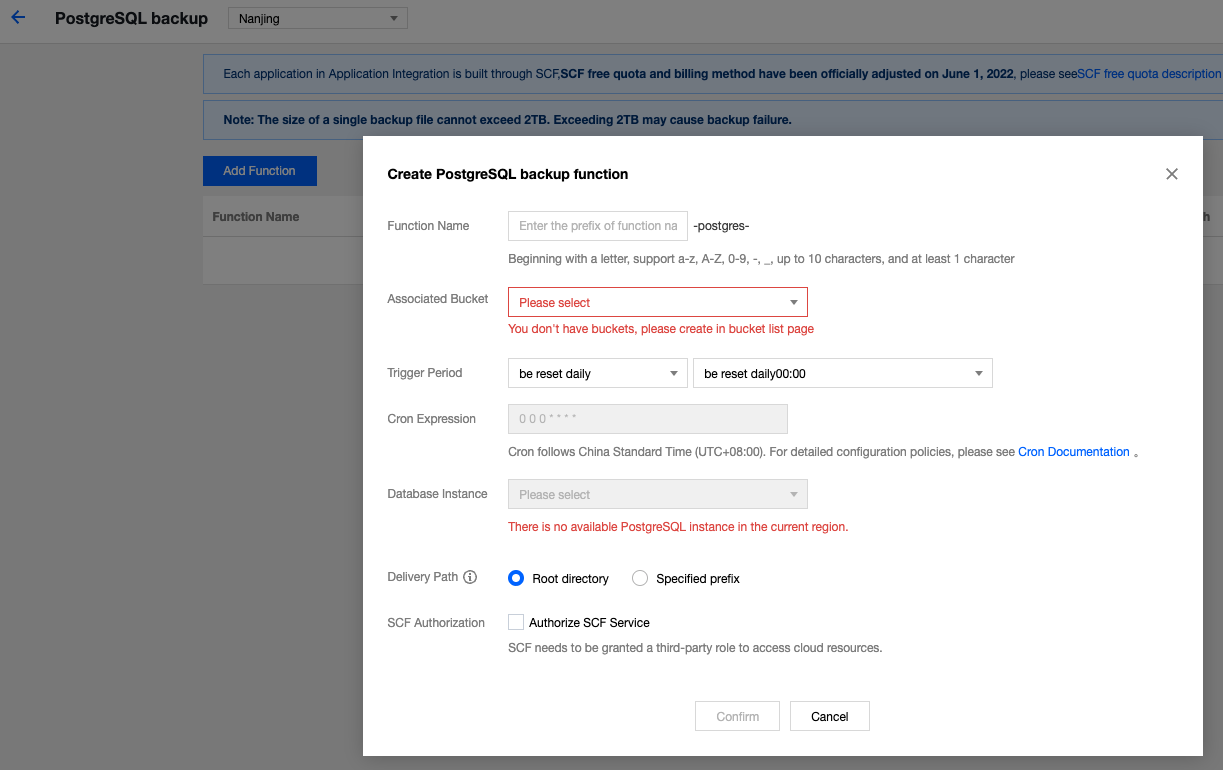
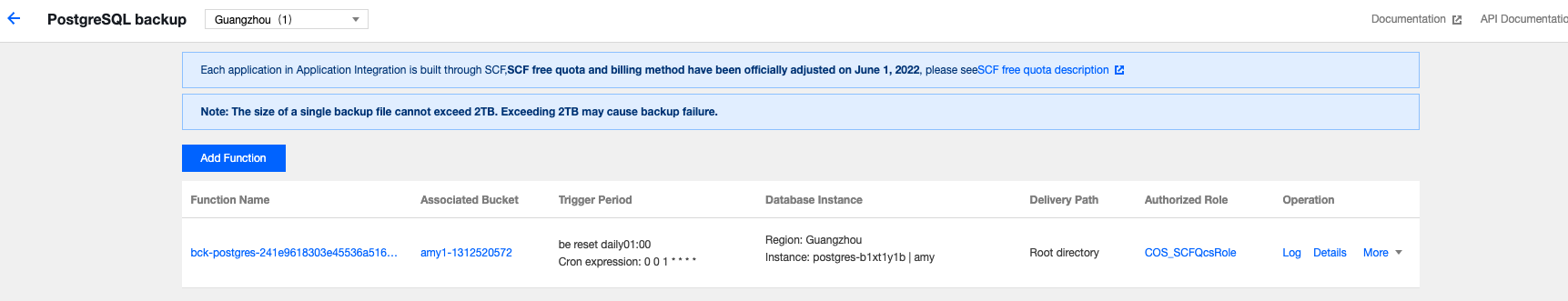
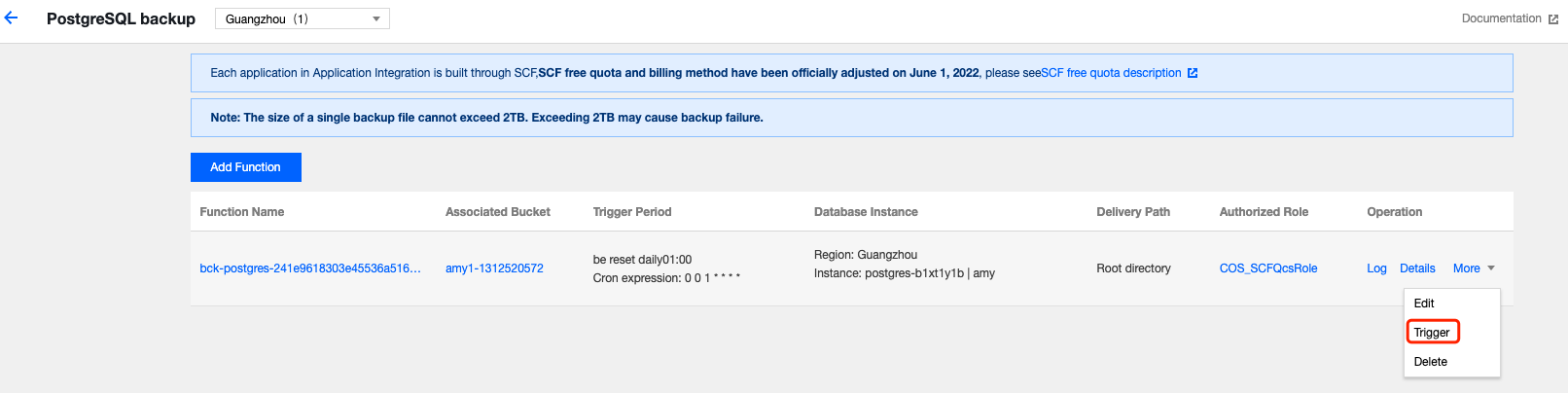
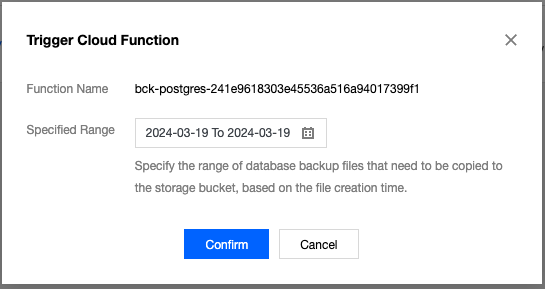
Last updated:2025-08-14 16:53:09
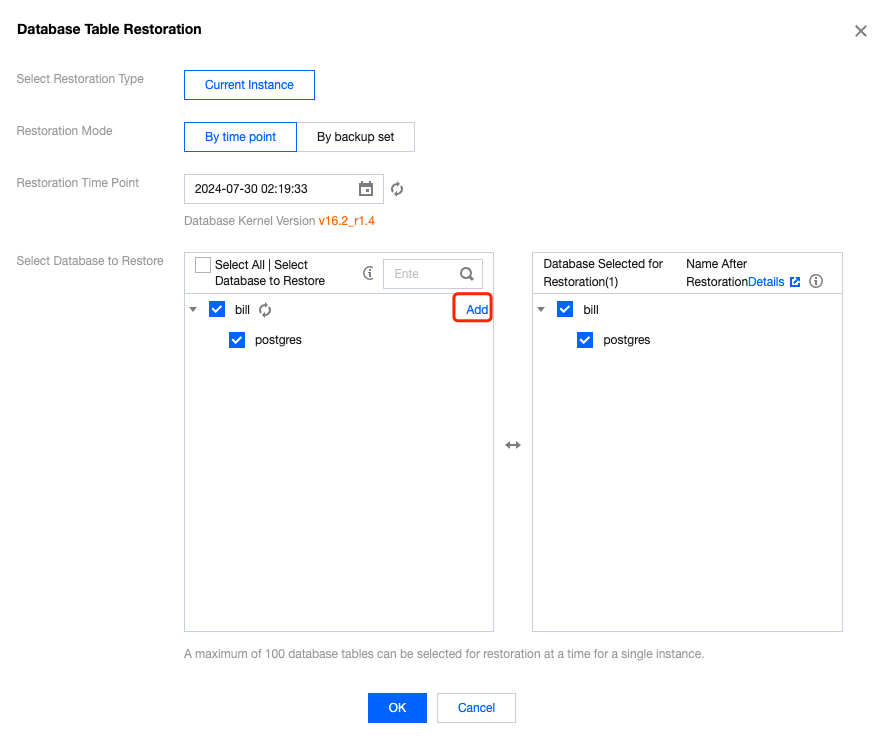
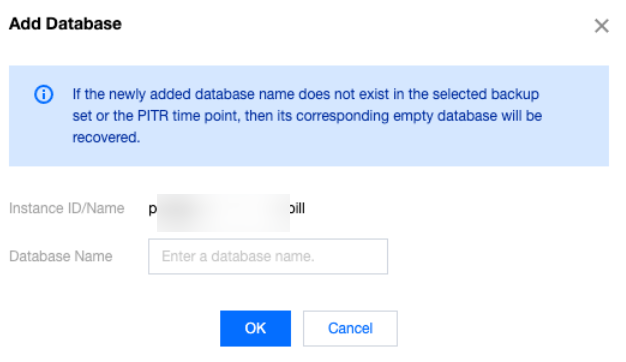
Last updated:2025-07-22 20:25:30
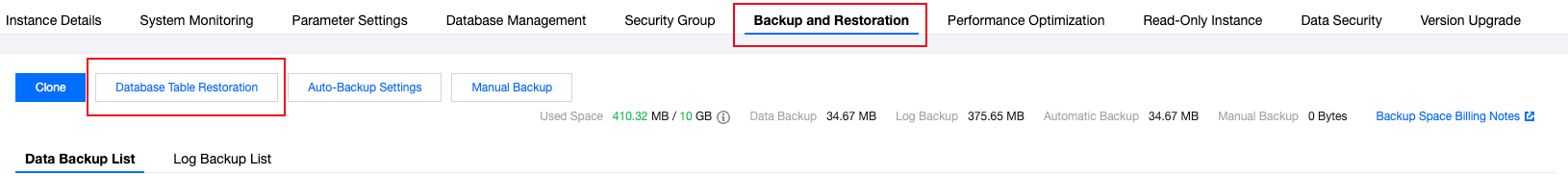
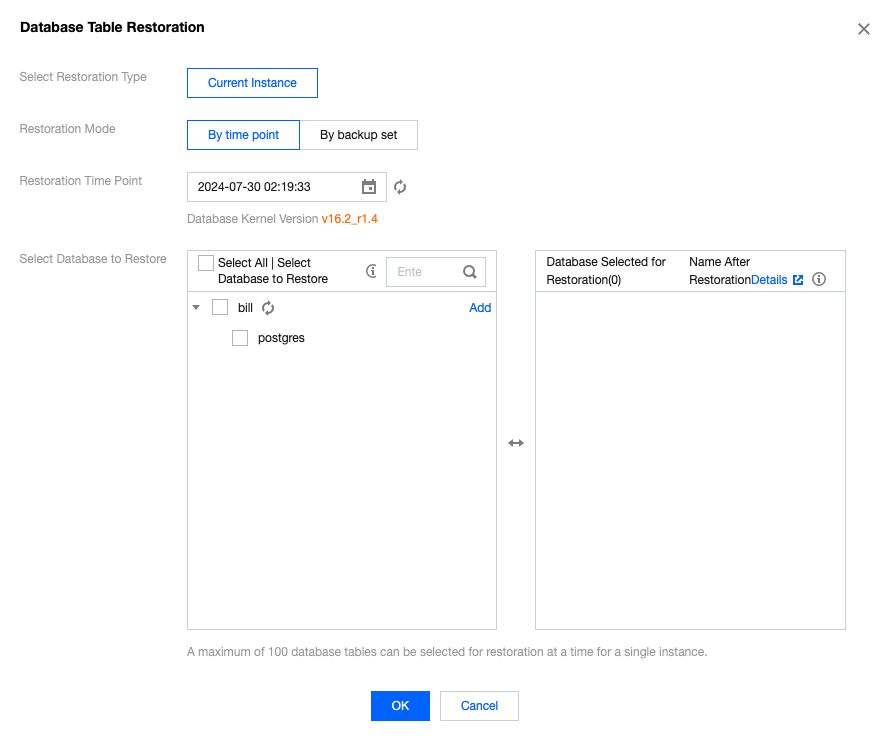
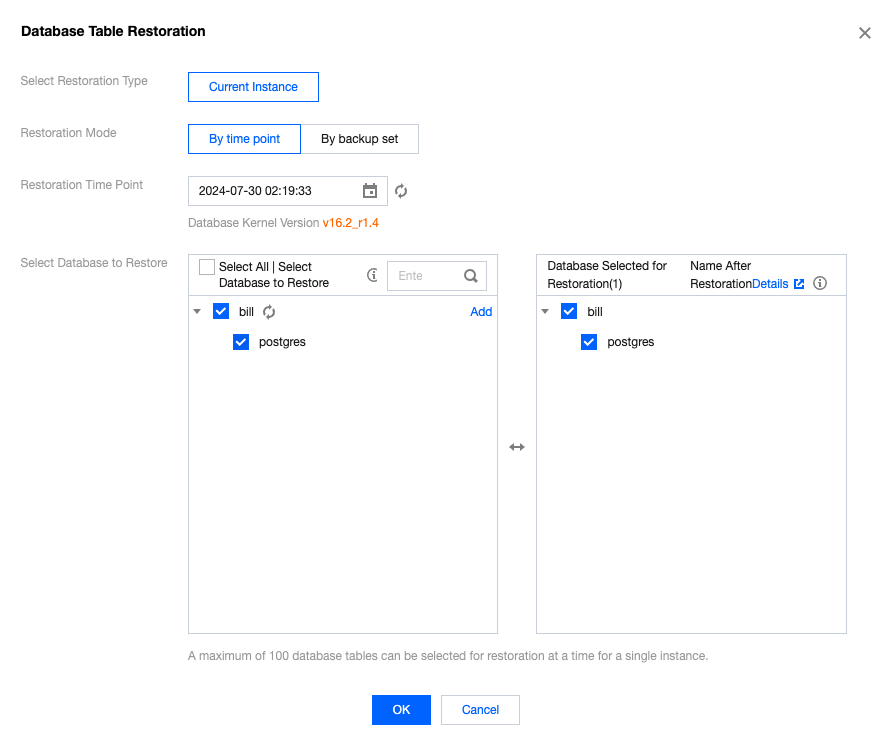
Type | Source | Retention policy | Space Usage Cost | Recovery Operations | Delete Operation |
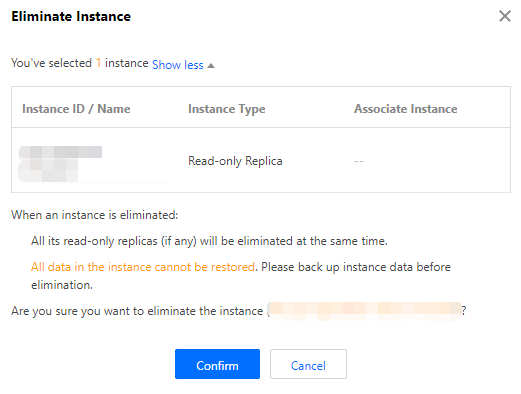
auto | Automatically generated by the system. | By default, backups are retained for 7 days from the generation time. Users can also customize the setting. For details, please refer to Automatic Backup Settings. | Recover by backup set or time point recovery. | If a backup set contains data within 2 days, it cannot be deleted. | |
Manual | Permanent retention. | Recover by backup set or time point recovery. | Self-service deletion. | ||
Final | The instance is automatically generated by the system when it is put into the recycle bin and completely cleared upon expiration. | Retention period: 8 days from generation time. | No charge. | Recover by backup set or time point recovery. | Non-deletable, can only be automatically cleared by the system upon expiration. |
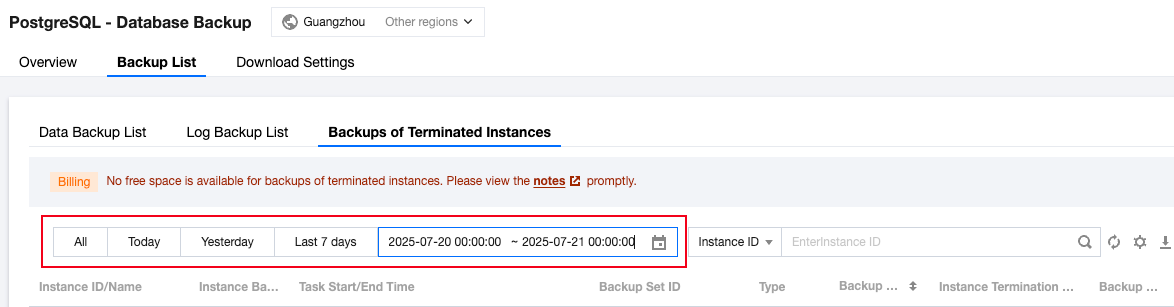
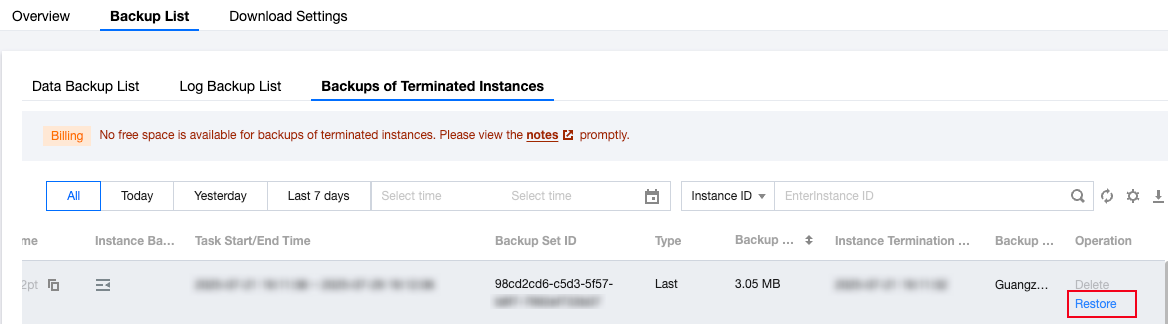
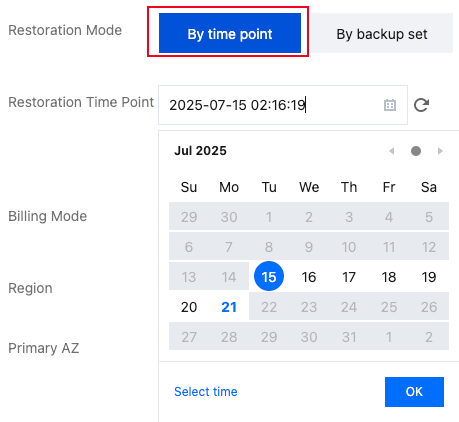
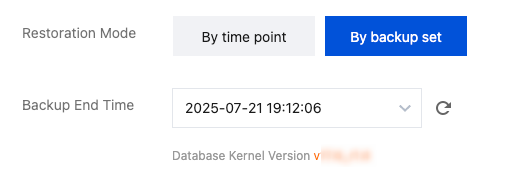

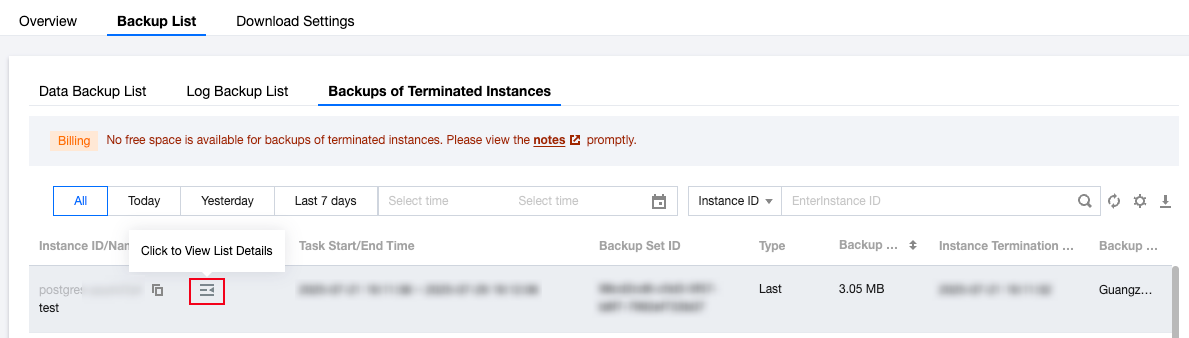
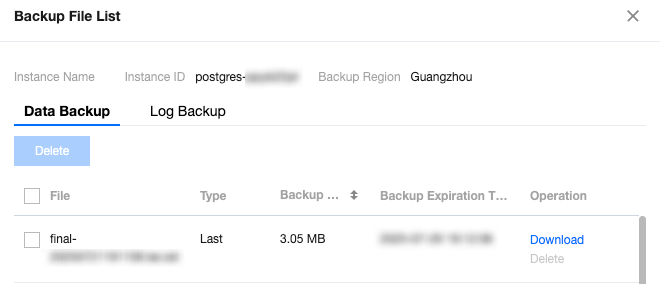
Last updated:2024-11-04 10:04:48
Category | Description |
Supported versions | 1. Source database Self-built databases PostgreSQL 10-16 Third-party cloud vendors 10-16 Alibaba Cloud RDS PostgreSQL AWS RDS PostgreSQL Huawei Cloud RDS for PostgreSQL TencentDB for PostgreSQL 10-16 (Migration within the same root account/Migration between different root accounts) 2. Target database TencentDB for PostgreSQL 10-16 |
Impact on the source database | 1. During full data migration, Data Transfer Service (DTS) consumes certain source instance resources, which may increase the load and pressure of the source database. If your database configuration is low, we recommend you perform the migration during off-peak hours. 2. During the actual migration process, the rate can be influenced by factors such as the read performance of the source instance, network bandwidth between the source and target instances, and the specifications and performance of the target instance. The migration concurrency is determined by the number of cores of the target instance. For example, if the target instance has 2 cores, the concurrency will be 2. |
Migration object | Interrelated data objects need to be migrated together; otherwise, the migration will fail. Common association relationships include: views referencing tables, views referencing views, storage procedures/functions/triggers referencing views/tables, and table association through primary and foreign keys. |
Source database requirements | When Full + Incremental Migration is selected as the migration type, the tables in the source database must have primary keys; otherwise, data inconsistency between the source and target databases may occur. For tables without primary keys, it is recommended to select Full Migration. |
Target database requirements | If the entire instance is to be migrated, the target database must not contain users and roles with the same names as those in the source database. |
Network description | 1. When a migration task is configured, the source database address must use the IP address and port that can directly connect to the PostgreSQL instance. Do not use the IP address and port of proxies like pgpool. 2. To ensure migration efficiency, cross-region migration is not supported for self-built instances on Cloud Virtual Machine (CVM). If cross-region migration is needed, choose the public network access method. |
Operation limits | 1. During the structural migration, full migration, and incremental migration, do not perform DDL operations or Large Object operations; otherwise, data inconsistency will occur. 2. Do not modify or delete user information (including the username, password, and permissions) and port numbers in the source and target databases during migration. |
Last updated:2024-11-04 10:04:25
grant select on table table name to username;grant select on SEQUENCE sequence name to username;grant connect on database database name to username;grant select on large object large object OID to username;GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA schema name to username;
alter database database name owner to migration user;
pg_tencentdb_superuser role user, during verification, you will receive an error message saying "Target instance permission check failed, unable to get Schema List." In this case, use the following statement to grant initialization user permissions to the migration user.grant pg_tencentdb_superuser to migration user;
RHEL/CentOS: rpm -q glibc
ldd --version | grep -i libc
Configuration Item | Description |
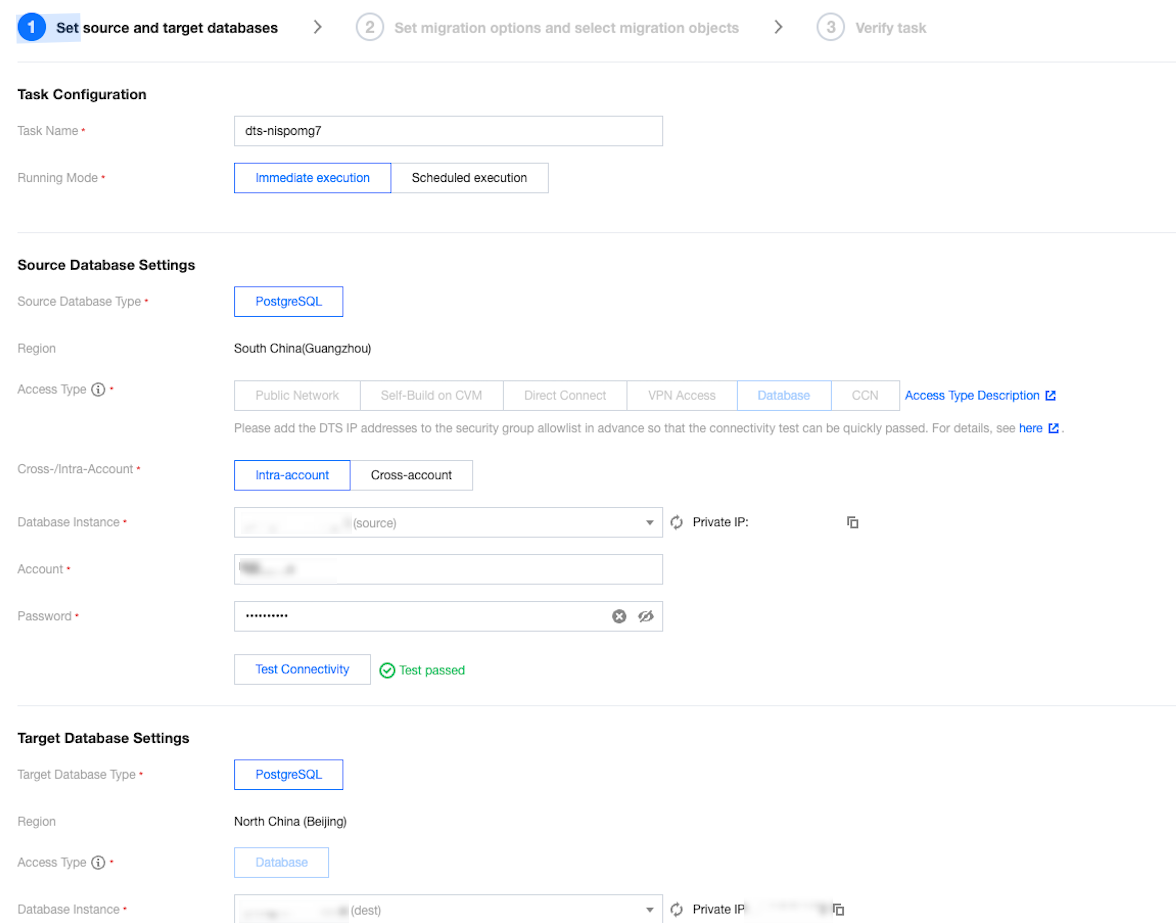
Source Instance Type | Choose according to your source database type. It cannot be modified after purchase. This example uses "PostgreSQL". |
Source Instance Region | Select the region of the source database. If the source database is a self-built one, select a region nearest to it. |
Target Instance Type | Choose according to your target database type. It cannot be modified after purchase. This example uses "PostgreSQL". |
Target Instance Region | Select the region of the target database. |
Specification | Select the specification of a migration link according to your business conditions. For the performance and billing details of different specifications, see Billing Overview. |
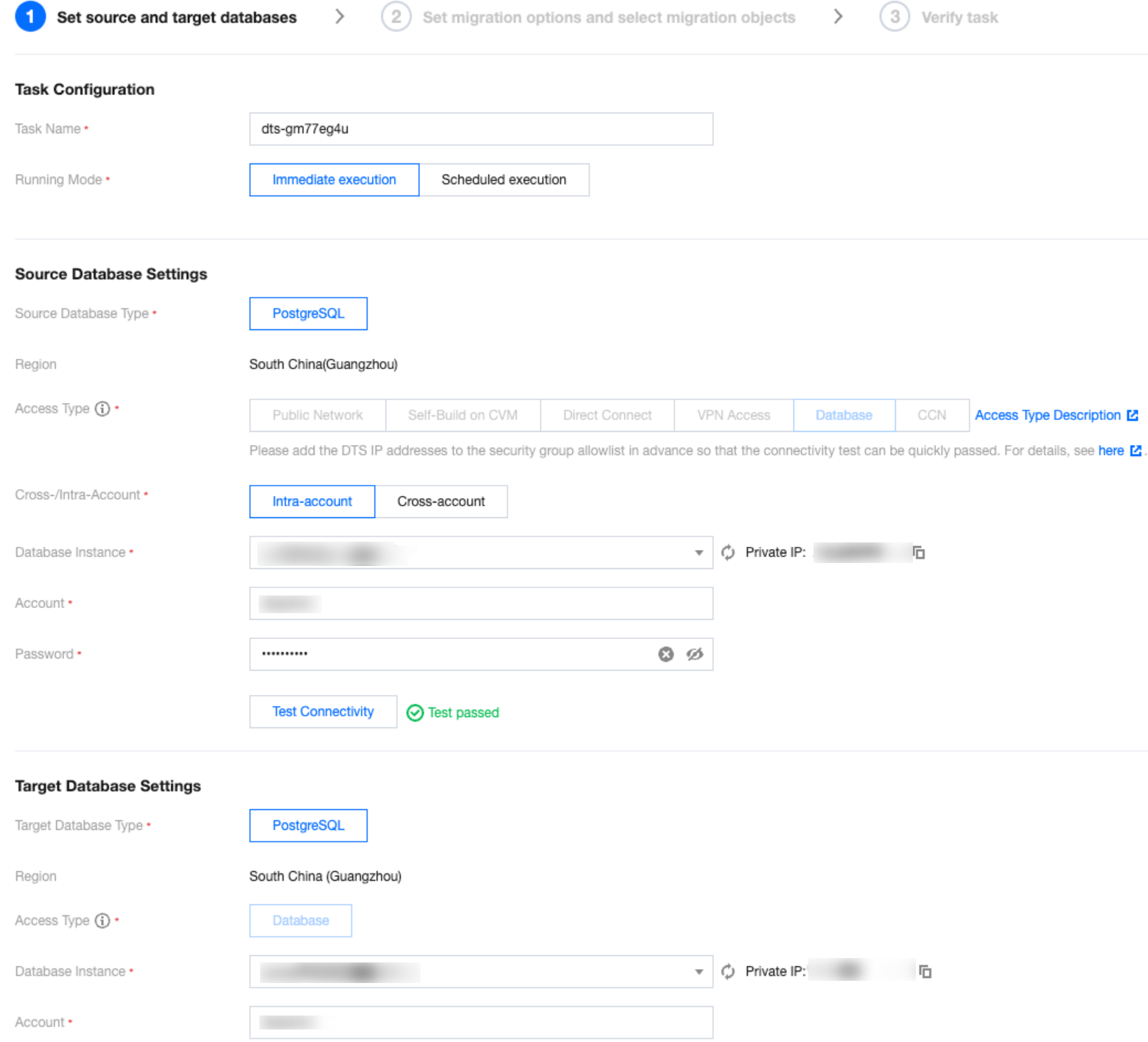
Setting Type | Configuration Item | Description |
Task Configuration | Task Name | Set a business-significant name for easy task identification. |
| Running Mode | Immediate execution: Start a task immediately after passing task verification. Scheduled execution: Set a task execution time, and the task will start when the time is reached. |
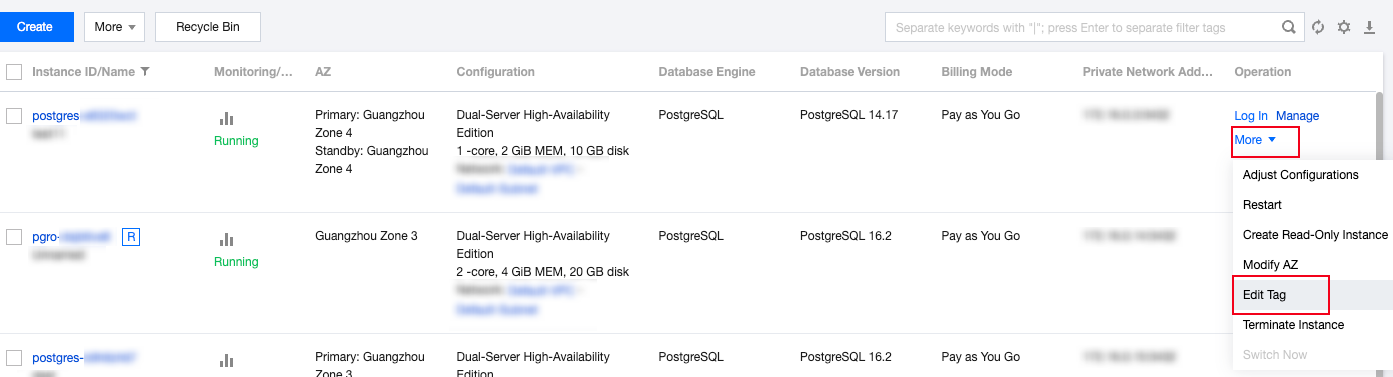
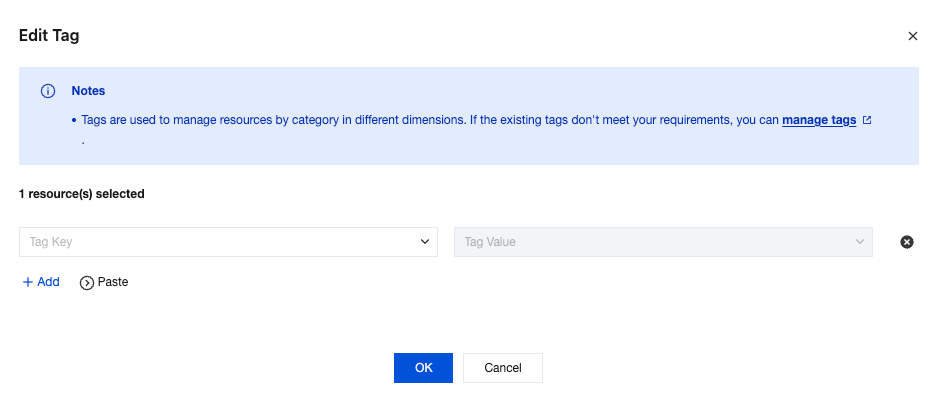
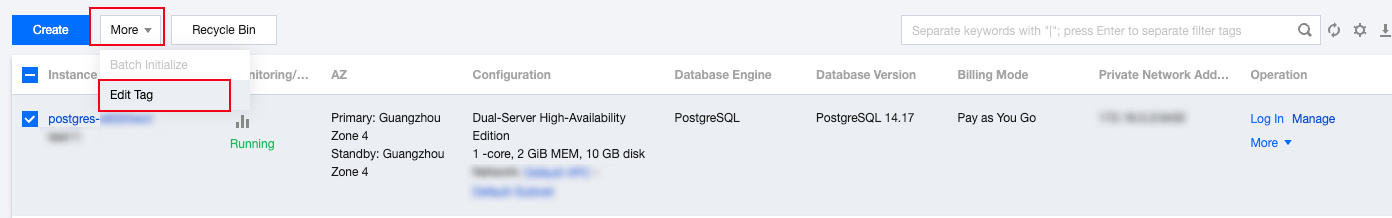
| Tag | Tags are used to manage resources by category from different dimensions. If the existing tags do not meet your requirements, go to the console to manage the tags. |
Source Database Settings | Source Database Type | The source database type selected at the time of purchase, which cannot be modified. |
| Region | The source database region selected at the time of purchase, which cannot be modified. |
| Access Type | Choose according to your scenario. This example uses "Database". For preparation work for different access types, refer to Overview of Preparations Related to Network. To ensure migration efficiency, cross-region migration is not supported for self-built instances on CVM. If cross-region migration is needed, choose the public network access method. Public Network: The source database can be accessed via a public IP address. When migrating via the public network, ensure that the source instance service is accessible under the public network environment and that the public network connection remains stable. Network fluctuations or failures may cause the migration to fail. If the migration fails, a new migration task will need to be initiated. Self-Build on CVM: The source database is deployed on a Tencent CVM. To ensure migration efficiency, cross-region migration is not supported for self-built instances on CVM. If cross-region migration is needed, choose the public network access method. Direct Connect: The source database can be connected to Tencent Virtual Private Cloud via Direct Connect. VPN Access: The source database can be connected to Tencent Virtual Private Cloud via VPN Connections. Database: The source database is a TencentDB instance. CCN: The source database can be connected to Tencent Virtual Private Cloud via Cloud Connect Network. |
| Cross-/Intra-Account | Intra-account: The source database instance and the target database instance belong to the same Tencent Cloud root account. Cross-account: The source database instance and the target database instance belong to different Tencent Cloud root accounts. The following is an example of migration within the same account. For cross-account migration guidance, refer to Cross-Account TencentDB Instance Migration. |
| Database Instance | Select the instance ID of the source PostgreSQL database. |
| Account | The account of the source PostgreSQL database, which must have the required permissions. |
| Password | The password of the source PostgreSQL database account. |
Target Database Settings | Target Database Type | The target database type selected at the time of purchase, which cannot be modified. |
| Region | The target database region selected at the time of purchase, which cannot be modified. |
| Access Type | Choose according to your scenario. This example uses "Database" by default. |
| Database Instance | Select the instance ID of the target database. |
| Account | The account of the target database, which must have the required permissions. |
| Password | The password of the target database account. |
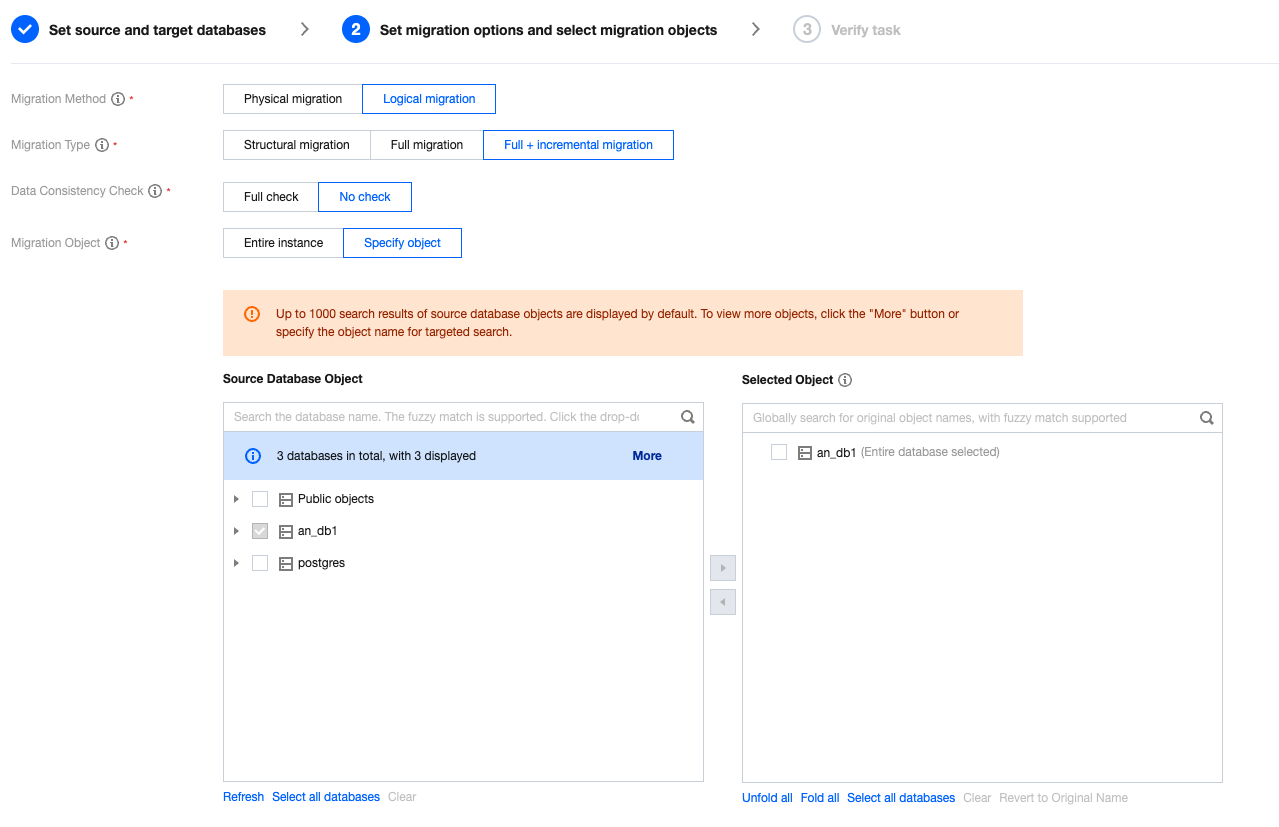
Configuration Item | Description |
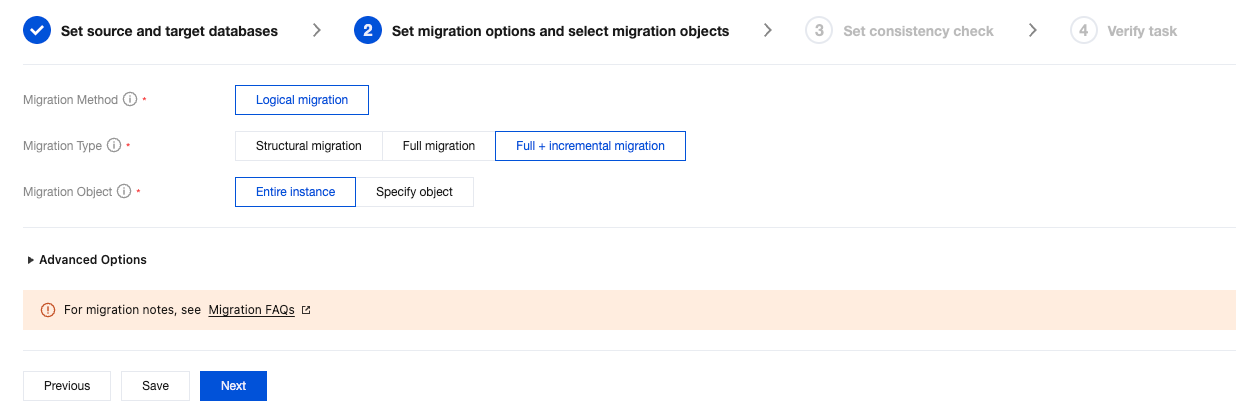
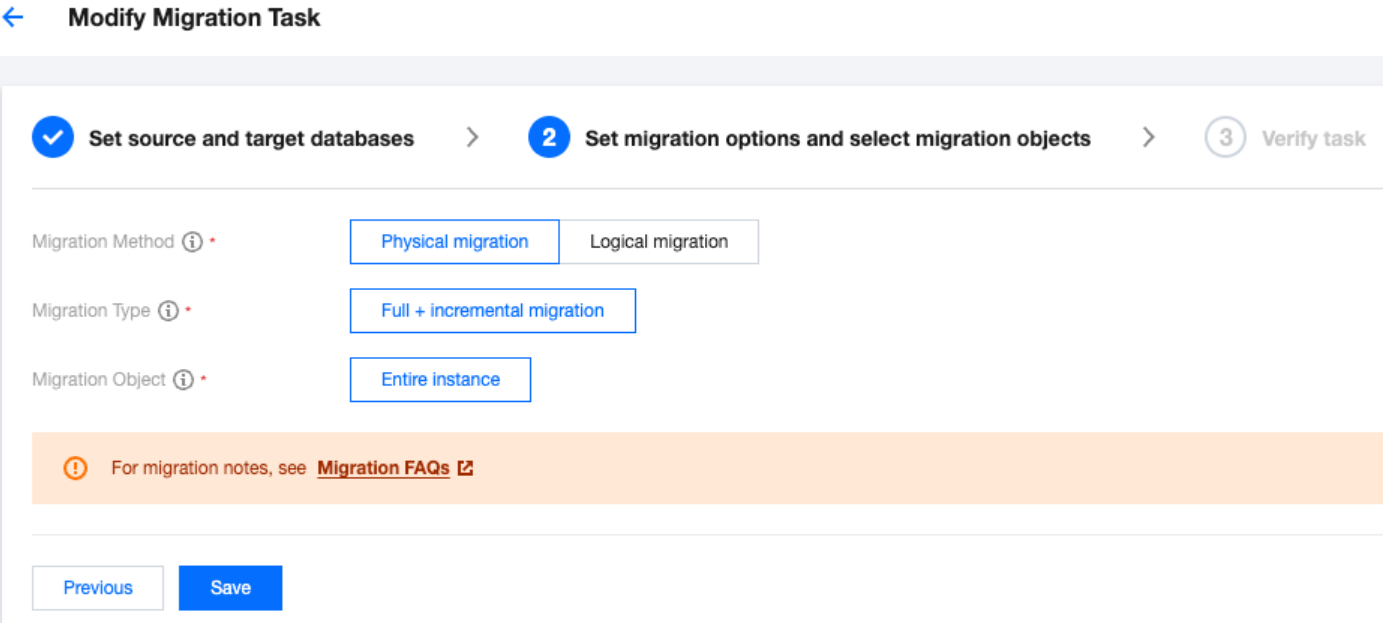
Migration Type | Choose according to your scenario. Structural migration: Migrate structured data such as databases and tables. Full migration: Migrate the entire database. The migrated data includes only the existing data of the source database when a task is initiated and does not include the incremental data written to the source database after a task is initiated. Full + Incremental migration: The migrated data includes the existing data of the source database when a task is initiated as well as the incremental data written to the source database after a task is initiated. If data is being written to the source database during migration, and you want to smoothly migrate the data in a non-stop manner, select this option. |
Migration Object | Entire instance: Migrate the entire instance, excluding system databases such as system objects in PostgreSQL. However, roles and user metadata definitions will be migrated. Specify object: Migrate specified objects. |
Specify object | Select the objects to be migrated in Source Database Object and move them to the Selected Object box. |
Last updated:2024-12-12 20:11:49
Last updated:2024-11-04 10:07:51
Last updated:2024-11-04 10:09:08
Last updated:2024-11-04 10:50:08
wal_level of the source database must be logical.max_replication_slots and max_wal_senders parameters in the source database must be greater than the total number of databases to be migrated (retain extra connections).persistence attribute of the tables to be migrated in the source database must be p (permanent tables); otherwise, replication is not supported, and hence logical migration is not possible.REPLICA IDENTITY attribute is set to NOTHING), the verification task will report a warning.= operator (json/point/polygon/txid_snapshot/xml), the verification will fail. You need to modify the table without a primary key as prompted or deselect the primary key table option; otherwise, the task cannot proceed.wal_level, max_replication_slots, and max_wal_senders is as follows.wal_level = logicalmax_replication_slots = 10 //Modify according to actual needs.max_wal_senders = 10 //Modify according to actual needs.
postgres=> select name,setting from pg_settings where name='wal_level';name | setting-----------+---------wal_level | logical(1 row)postgres=> select name,setting from pg_settings where name='max_replication_slots';name | setting-----------------------+---------max_replication_slots | 10(1 row)postgres=> select name,setting from pg_settings where name='max_wal_senders';name | setting-----------------+---------max_wal_senders | 10(1 row)
REPLICA IDENTITY attribute is set to NOTHING), the verification task will report a warning.ALTER TABLE schemaName.tableName REPLICA IDENTITY FULL;
Last updated:2024-11-04 10:16:55
abstime, reltime, and tinterval, the verification task will report an error.abstime, reltime, and tinterval are old time and date types that have been deprecated in the latest PostgreSQL version. It is recommended to replace them with the following types:abstime: It can be replaced with the timestamp or timestamp with time zone type. These types provide a broader range of capabilities for representing dates and times.reltime: It can be replaced with the interval type. The interval type is used to represent time intervals and can include units such as years, months, days, hours, minutes, and seconds.tinterval: It can be replaced with the tsrange or tstzrange type. These types are used to represent time ranges and can include start and end times.abstime, reltime, and tinterval is similar. First, create a column, convert the old data format to the new data format, and store it in the new column. After verifying the new column data is correct, delete the old column. Finally, if needed, rename the new column to the name of the old column.abstime to timestamp.ALTER TABLE your_table ADD COLUMN new_column TIMESTAMP;
UPDATE your_table SET new_column = your_abstime_column::TIMESTAMP;
SELECT * FROM your_table;
ALTER TABLE your_table DROP COLUMN your_abstime_column;
ALTER TABLE your_table RENAME COLUMN new_column TO your_abstime_column;
Last updated:2024-11-04 10:18:12
Last updated:2024-11-04 10:19:28
create user new user with password 'password';grant pg_tencentdb_superuser to new username;alter user new user with CREATEDB;alter user new user with CREATEROLE;
drop user conflicting user;# If the conflicting user has resource dependencies, run the following statement to modify the owner of the resources first (with a table as an example below):alter table table name owner to new user;
Last updated:2024-11-04 10:24:36
alter system set timezone='parameter value';alter system set lc_monetary='parameter value';alter system set lc_numeric='parameter value';
Last updated:2024-11-04 10:24:17
Last updated:2024-11-04 10:23:49
Last updated:2024-11-04 10:41:06
Last updated:2025-04-07 16:48:07
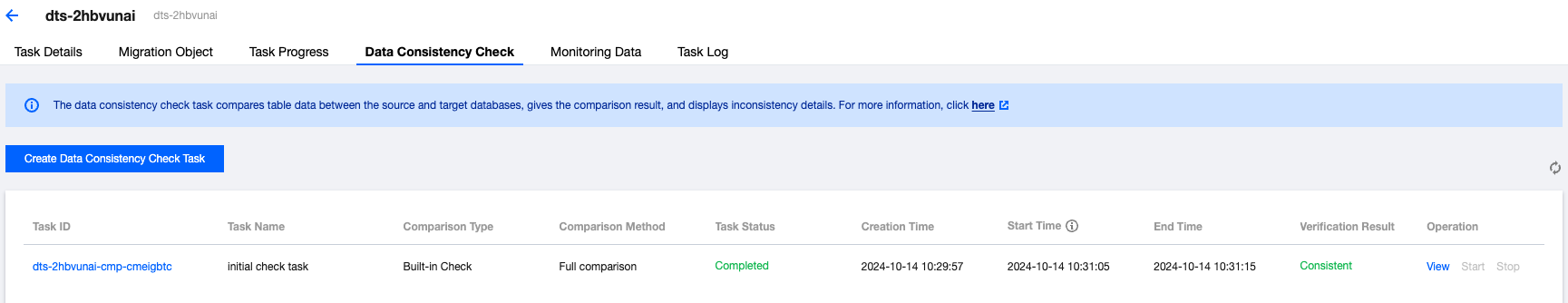
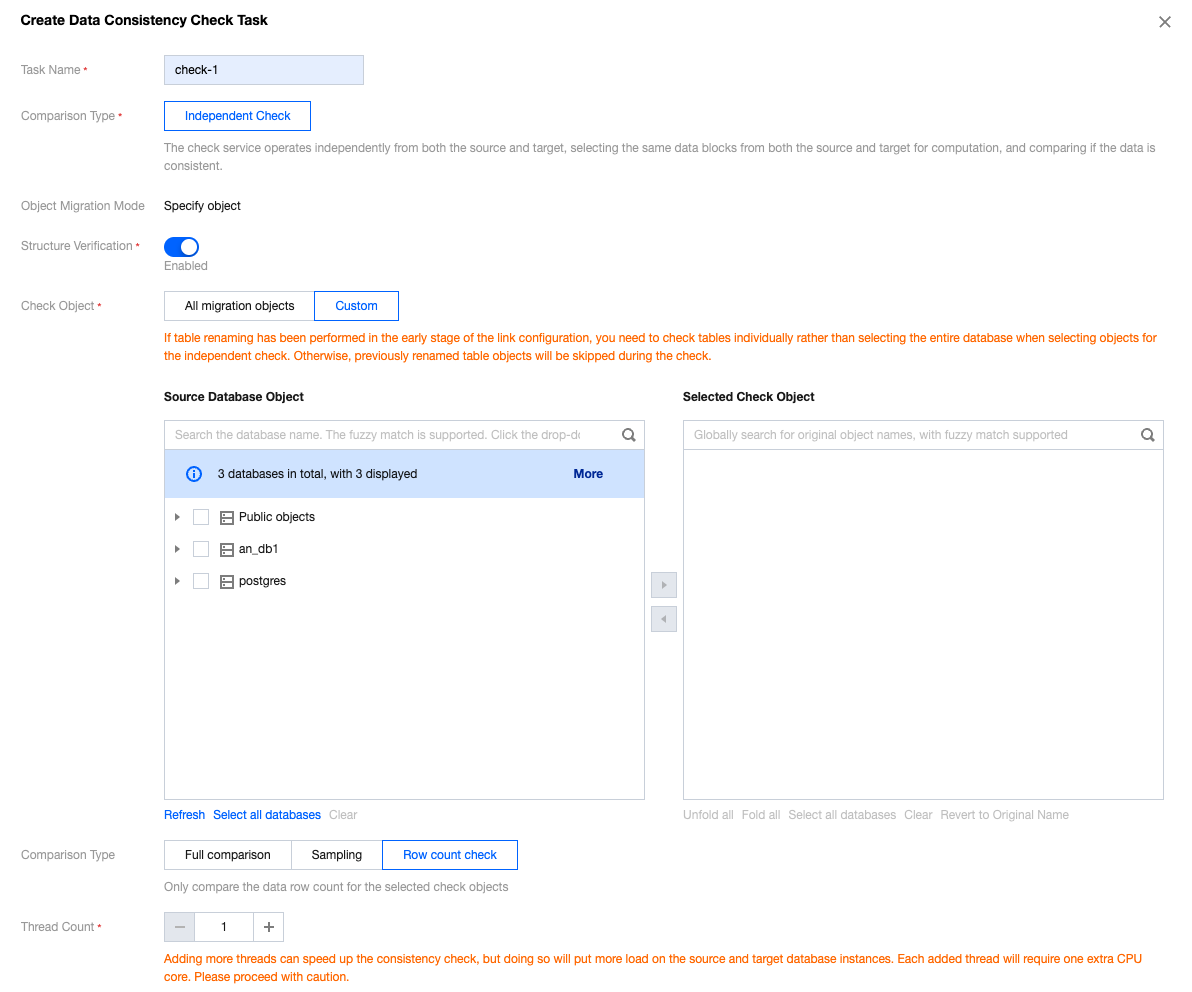
Parameter | Description |
Task Type | Independent Check: The verification service operates independently of a DTS task and can compare other data not involved in the migration. |
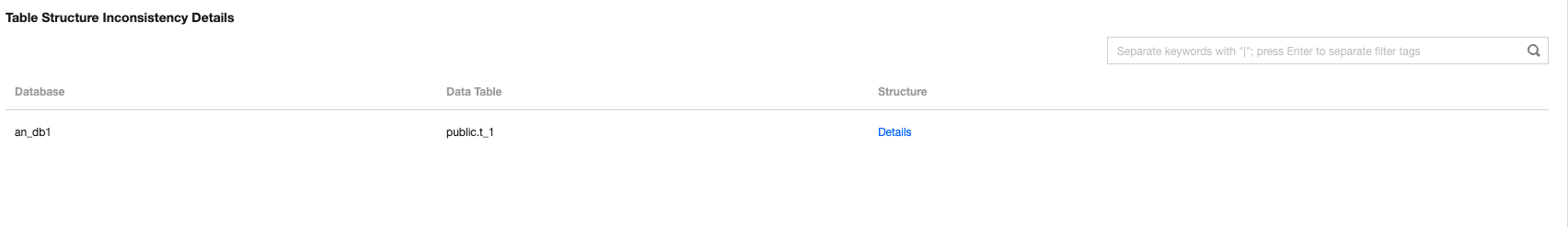
Structure Verification | Verify the data object structures at both the source and target ends. If you have confirmed the structures are consistent, disabling structure verification can save time. |
Check Object | All migration objects: Check all the objects selected in a migration task. Custom: Choose the objects to be verified from the selected migration objects. |
Comparison Type | Full comparison: Check all the data for the selected objects. Sampling: Check the data of a certain proportion (10%, 20%, 30%, ..., 90%) for the selected objects. Row count check: Only compare the data row count for the selected objects. In this case, even tables without primary keys can also be checked. |
Thread Count | The value ranges from 1 to 8 and can be set as needed. Adding more threads can speed up the consistency check, but doing so will put more load on the source and target databases. Each added thread will require one extra CPU core. |
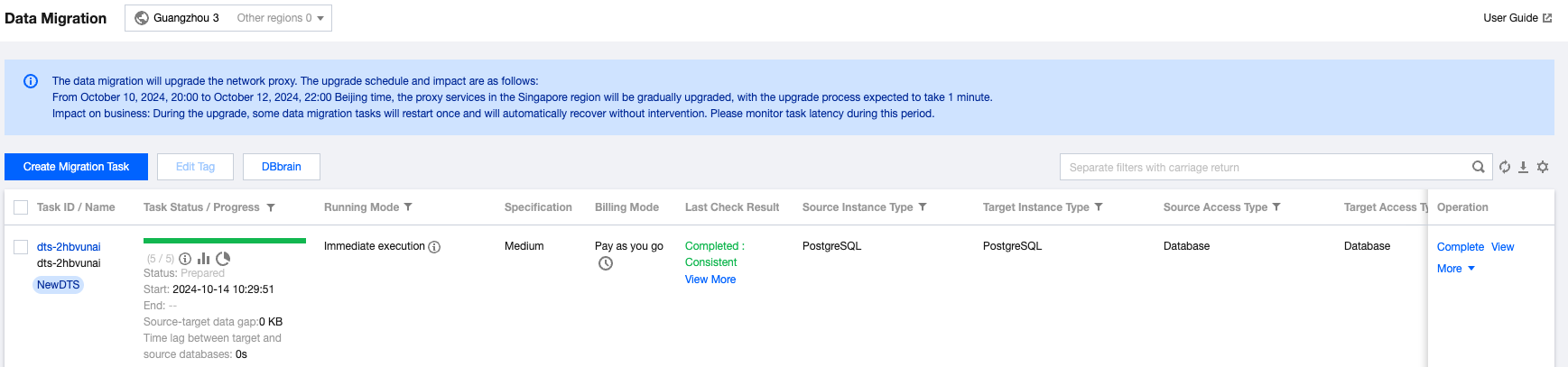
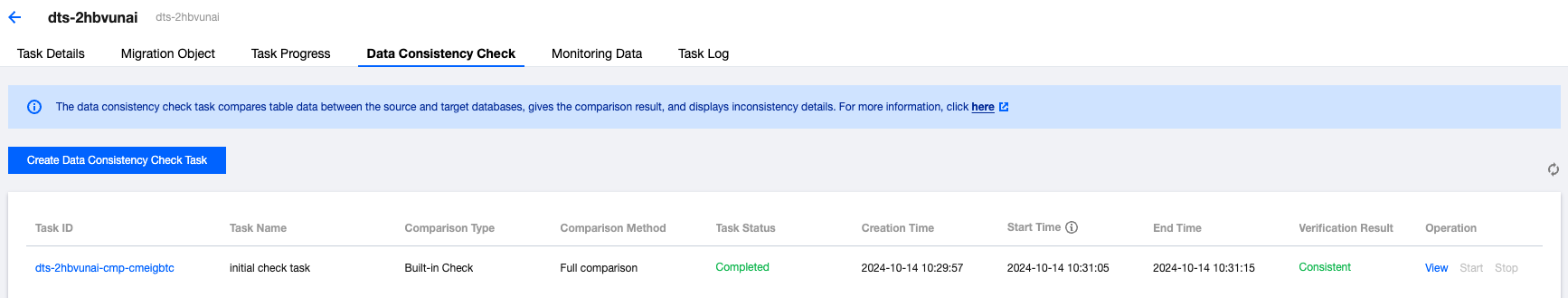
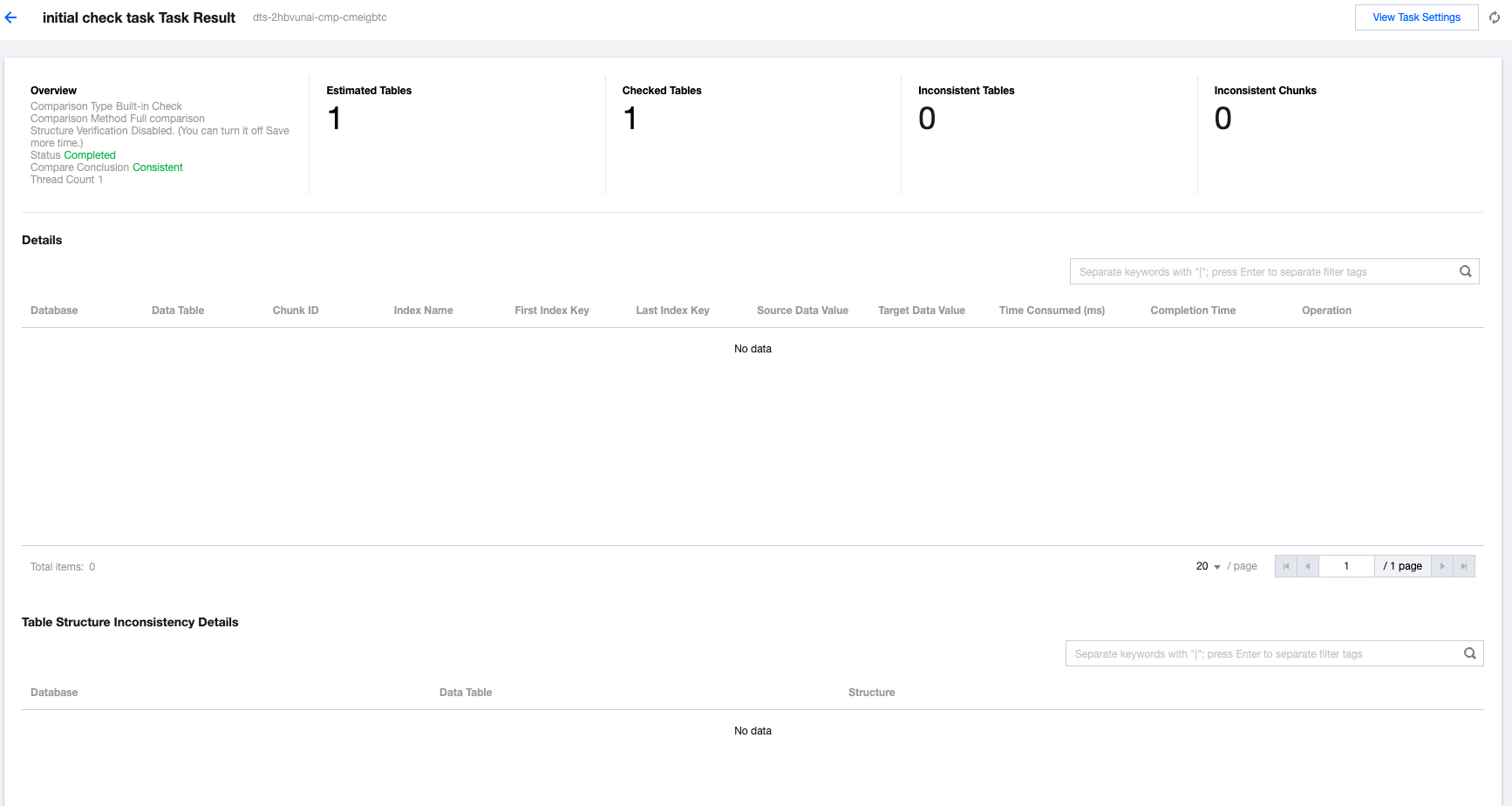
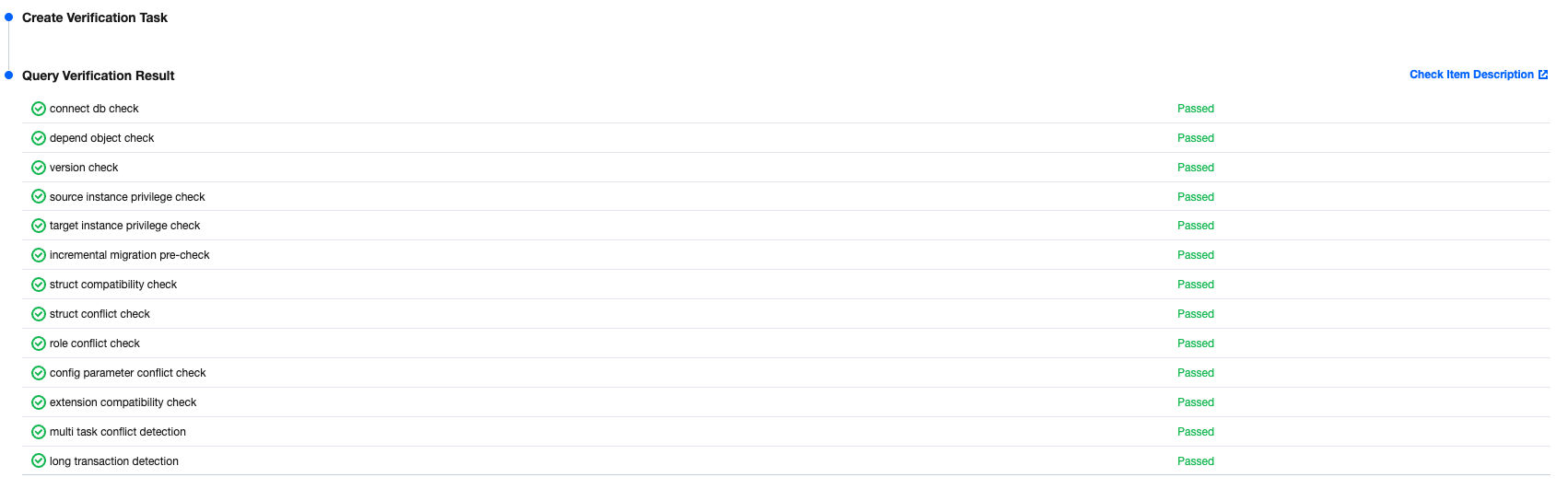
Item | Details |
Overview | Comparison Type: All are currently Independent Check. Comparison Method: The available options are Full comparison, Sampling, and Row count check. Structure Verification: The available options are Enabled and Disabled. Status: The current status of the verification task, which can be Created, Awaiting Execution, Running, or Completed. Compare Conclusion: The result of the current verification task, which can be Inconsistent or Consistent. Thread Count: The number of threads configured for the current task. |
Estimated Tables | The system's estimated total number of tables that need verification. |
Checked Tables | The number of tables that have currently been successfully checked. |
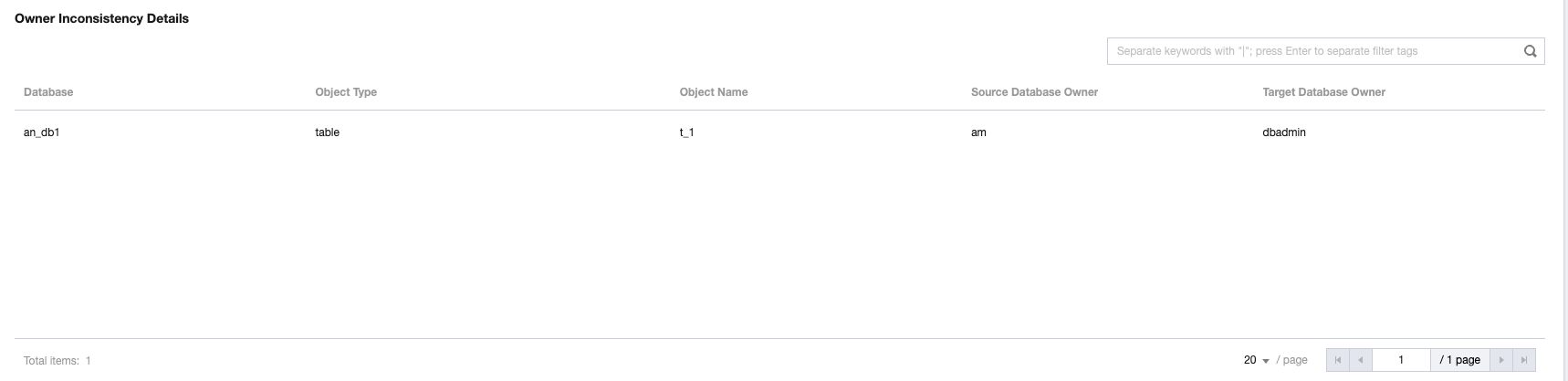
Inconsistent Tables | The number of tables with inconsistencies between the source and target ends among the tables that have already been checked. You can view specific inconsistent tables in Details. |
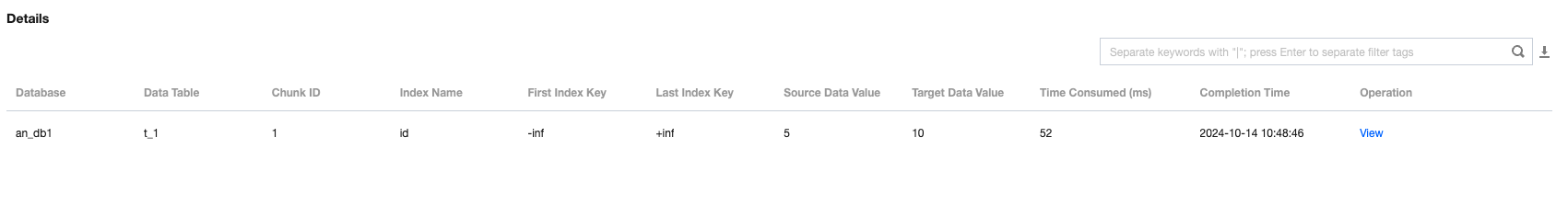
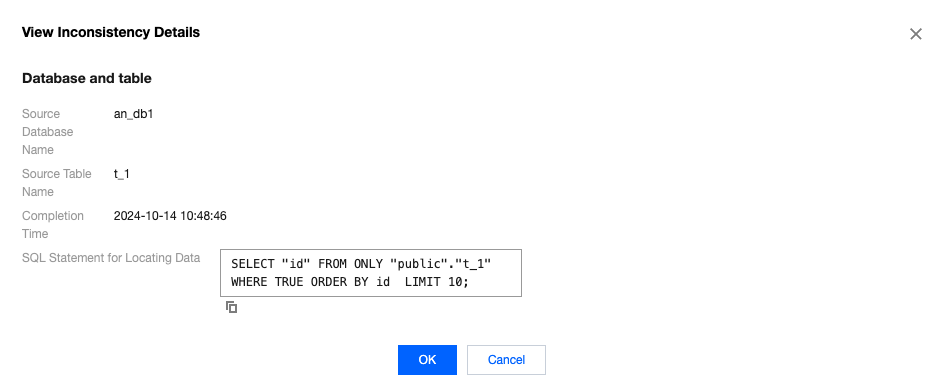
Inconsistent Chunks | The number of chunks with inconsistencies between the source and target ends among the tables that have already been checked. During system verification, chunks are used for verification at both ends, with each chunk containing 10,000 rows of data. |
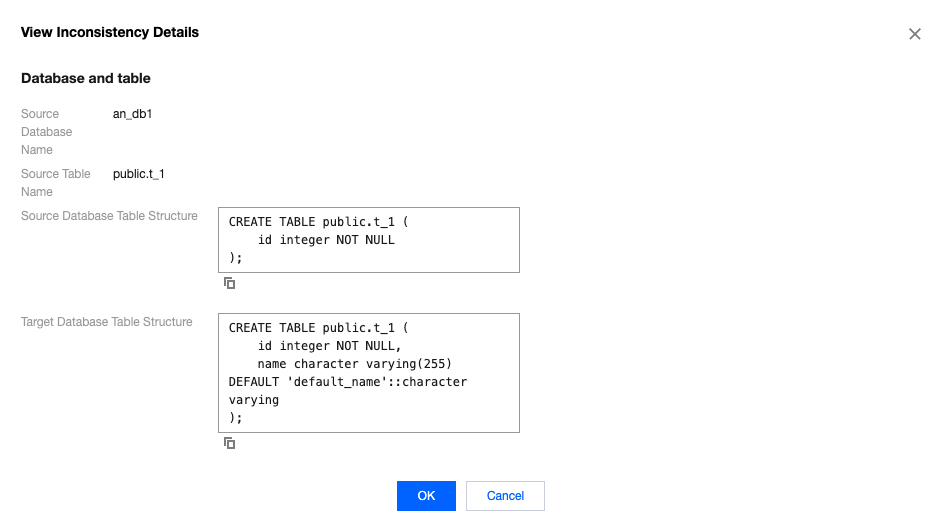
Last updated:2024-07-23 11:56:42
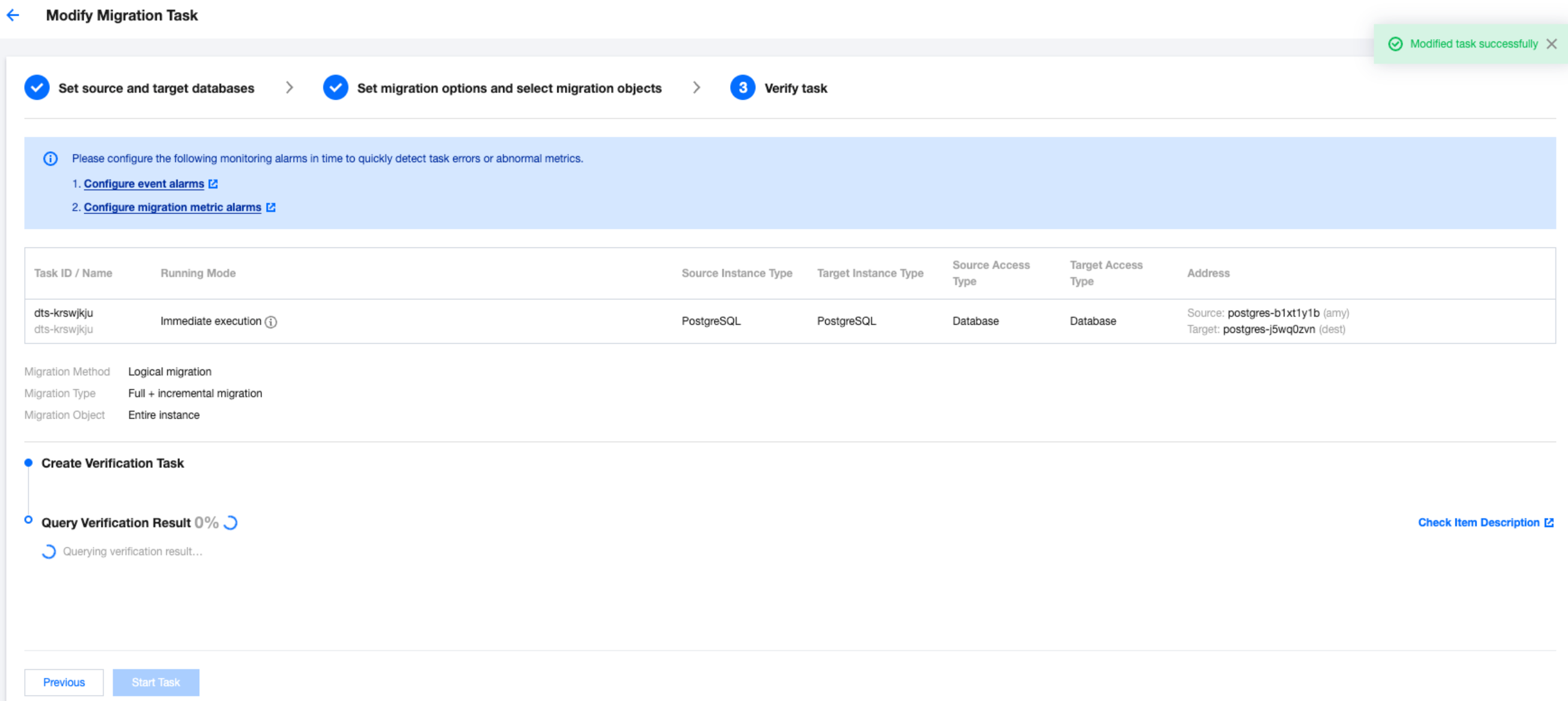
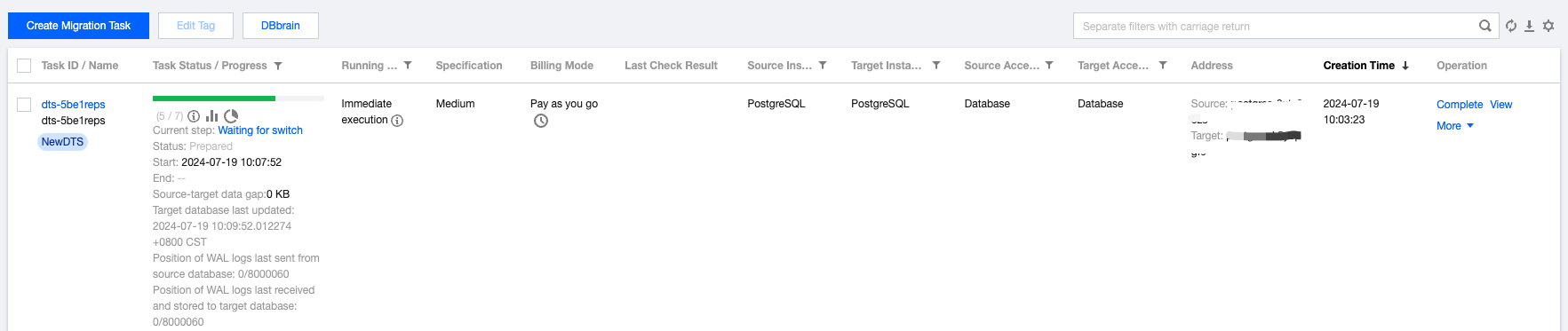
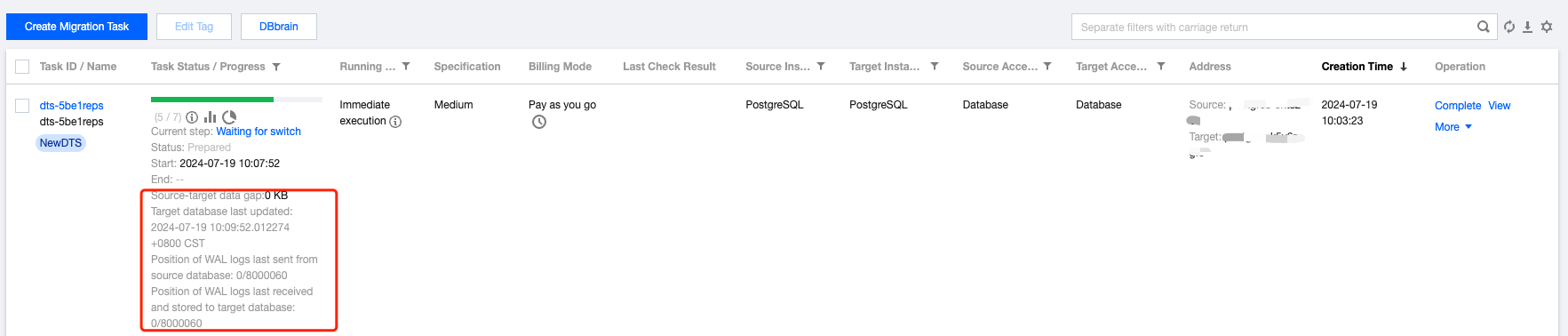
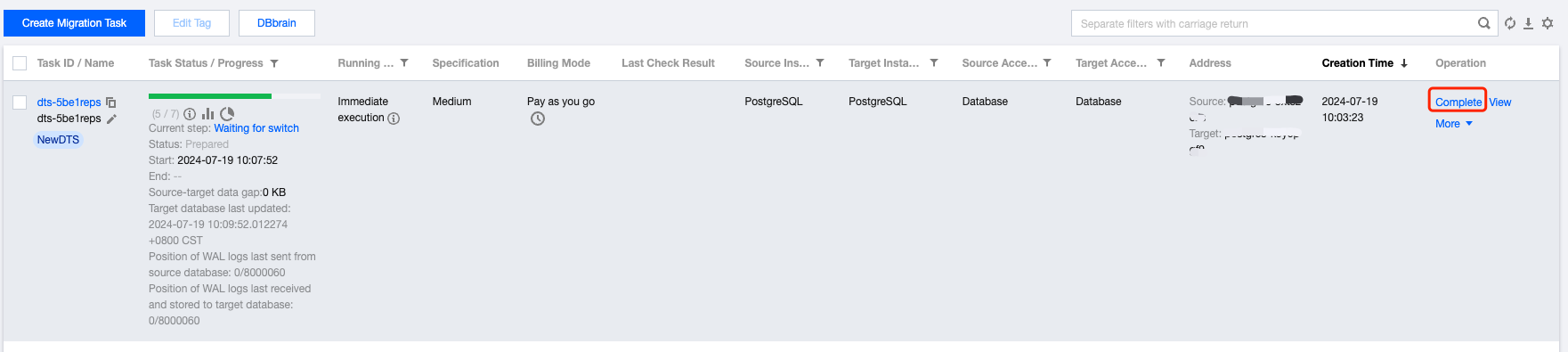
Last updated:2025-04-07 17:03:14
Major Version | Kernel Version |
10 | v10.17_r1.5 |
11 | v11.12_r1.5 |
12 | v12.7_r1.5 |
13 | v13.3_r1.4 |
14 | v14.2_r1.11 |
15 | v15.1_r1.4 |
16 | v16.0_r1.2 |
connect source with replication failed: pq: no pg_hba.conf entry for replication connection from host "xx.xx.xxx.xx", user "xxx" occurs, the configuration of the pg_hba.conf file of the source instance does not meet migration requirements. You can add host replication all 0.0.0.0/0 md5 to the pg_hba.conf file of the source instance, and then restart the instance or execute select pg_reload_conf(); to reload the configuration.Parameter Name | Default Handling for Migration | Verification Action |
data_checksums | Use the parameter value of the source instance. | There is no alert when the parameter values are different. |
enable_partitionwise_aggregate | Use the parameter value of the source instance. | There is no alert when the parameter values are different. |
enable_partitionwise_join | Use the parameter value of the source instance. | There is no alert when the parameter values are different. |
lc_ctype | Use the parameter value of the source instance. | There is no alert when the parameter values are different. |
max_locks_per_transaction | Use the parameter value of the source instance. | There is no alert when the parameter values are different. |
max_prepared_transactions | Use the parameter value of the source instance. | There is no alert when the parameter values are different. |
random_page_cost | Use the parameter value of the source instance. | There is no alert when the parameter values are different. |
max_connections | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
max_wal_senders | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
max_worker_processes | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
array_nulls | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
authentication_timeout | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
autovacuum_analyze_scale_factor | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
autovacuum_analyze_threshold | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
autovacuum_freeze_max_age | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
autovacuum_multixact_freeze_max_age | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
autovacuum_naptime | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
autovacuum_vacuum_cost_delay | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
autovacuum_vacuum_cost_limit | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
autovacuum_vacuum_insert_scale_factor | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
autovacuum_vacuum_insert_threshold | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
autovacuum_vacuum_scale_factor | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
autovacuum_vacuum_threshold | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
bytea_output | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
check_function_bodies | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
constraint_exclusion | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
cursor_tuple_fraction | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
DateStyle | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
deadlock_timeout | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
default_statistics_target | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
default_transaction_isolation | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
exit_on_error | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
extra_float_digits | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
from_collapse_limit | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
geqo | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
geqo_effort | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
geqo_generations | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
geqo_pool_size | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
geqo_seed | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
geqo_selection_bias | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
geqo_threshold | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
idle_in_transaction_session_timeout | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
idle_session_timeout | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
IntervalStyle | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
jit | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
jit_above_cost | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
jit_inline_above_cost | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
jit_optimize_above_cost | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
join_collapse_limit | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
lc_monetary | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
lc_numeric | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
lc_time | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
local_preload_libraries | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
log_filename | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
max_logical_replication_workers | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
max_parallel_workers | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
max_replication_slots | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
max_standby_archive_delay | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
max_standby_streaming_delay | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
recursive_worktable_factor | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
search_path | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
statement_timeout | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
stats_fetch_consistency | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
TimeZone | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
vacuum_cost_delay | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
vacuum_cost_limit | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
vacuum_cost_page_dirty | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
vacuum_cost_page_hit | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
vacuum_cost_page_miss | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
vacuum_freeze_min_age | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
vacuum_freeze_table_age | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
vacuum_multixact_freeze_min_age | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
vacuum_multixact_freeze_table_age | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
wal_level | Use the parameter value of the target instance. | There is an alert for the user to modify the parameter when parameter values are different. If the parameter is not modified, the default handling method for the migration will be adopted. |
Last updated:2025-06-06 15:01:40
Category | Description |
Supported Versions | 1. Source database Self-built database PostgreSQL 10-16 Third-party cloud vendors (Alibaba Cloud RDS PostgreSQL/AWS RDS PostgreSQL/Huawei Cloud RDS for PostgreSQL) 10-16 TencentDB for PostgreSQL 10-16 (Migration between same master accounts / Migration between different main accounts) 2. Target database TencentDB for PostgreSQL 10-16 |
Source database impact | 1. DTS occupies certain source instance resources when executing full data synchronization, which may lead to an increase in the load of the source instance and add pressure on the database itself. If your database configuration is too low, it is recommended that you perform operations during business off-peak hours. 2. Defaults to a lock-free method. No global lock is applied to the source database during the sync process. 3. When performing data synchronization, DTS uses the account executing the synchronization task to create postgres.public.identify and {database}.__tencentdb__sync_*.* in the source database to record task status and configuration information. The target instance uses the {database}.__tencentdb__ schema to record synchronization status information. postgres.public.identify, {database}.__tencentdb__sync_*.*, and {database}.__tencentdb__ schema occupy very little space, about one-thousandth to one-ten-thousandth of the source database storage space. Therefore, they have no impact on the performance of the source database and do not preempt resources. 4. The sync task depends on the max_replication_slots parameter (one replication_slot is occupied when configuring a sync task for each database). You can view the usage status by using the SQL statement "select * from pg_replication_slots". If the number of configured sync databases + replication_slots > max_replication_slots, creating a new sync task will fail. Users are advised to end the task proactively before the system releases the replication_slots (replication_slots will not be released if the failed task is not ended). |
sync object | 1. Unsupported object synchronization: ROLE, PROCEDURE, TRIGGER, FUNCTION, RULE. 2. No support for synchronization of public objects and permission changes. 3. Foreign key import is not supported during structure initialization in the full-load phase. Foreign key constraints will be automatically removed before import. 4. Data sync does not support the FOREIGN TABLE table type. Export and import do not support TEMPORARY TABLE in the full-load phase. Only UNLOGGED TABLE data structure sync is supported in the incremental synchronization phase. 5. The source database updates SEQUENCE objects in the incremental phase. After synchronization to the target database, refreshing the last_value of the SEQUENCE is not supported. Users may need to manually check the sync result and modify the parameter value on the target database. 6. After the objects in the source database are synchronized to the target end, the object owner will be changed to the target database account. For example, if the owner of table 1 was A before, and account B is used for synchronization in the target database, the owner of table 1 will be changed to B after being written into the target database. 7. Cannot select the entire source instance for synchronization. If there is an operation to create a new database (CREATE DATABASE) on the source side in subsequent synchronization tasks, it is recommended to create the repository object on the target side before starting the synchronization task. 8. If there are CREATE TABLE or RENAME TABLE operations on the source during the sync task process, please select the entire database where the table is located when selecting the sync object in the configuration phase. Otherwise, the newly created table or the renamed table will not be synchronized to the target end. |
Data Type | 1. Data types supported Aclitem,Bit,Bool,Box,Bpchar,Bytea,Char,Cid,Cidr,Circle,Date,Float4,Float8,Inet,Int2,Int4,Int8,Interval,Json,Jsonb,Jsonpath,Line,Lseg,Macaddr,Name,Numeric,Oid,Path,Point,Polygon,Record,Text,Tid,Time,Timestamp,Timestamptz,Unknown,Uuid,Varbit,Varchar,XID,Daterange,Int4range,Int8range,Numrange,Tsrange,Tstzrange,Datemultirange,Int4multirange,Int8multirange,Nummultirange, Tsmultirange,Tstzmultirange,XML,Money,Time with time zone,Tsvector,Tsquery,pg_lsn,txid_snapshot. 2. Time zone Fields with time zone (timestamp with time zone) in the source instance will automatically convert to the corresponding value of the target instance time zone after synchronizing to the target instance. |
Supported SQL | 1. DML INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE 2. DDL DROP DATABASE,ALTER DATABASE CREATE SCHEMA,DROP SCHEMA CREATE TABLE,ALTER TABLE,DROP TABLE CREATE VIEW,DROP VIEW CREATE INDEX,DROP INDEX CREATE SEQUENCE,DROP SEQUENCE Note: CREATE TABLE table name AS SELECT statement is not currently supported. SQL Filter Policy with Where condition filtering is not currently supported. |
Limits of Operation | Do not perform the following operations during the sync process, otherwise the synchronization task will fail. 1. Do not modify or delete user information (including username, password and permissions) and port number in the source database and target database. 2. During the incremental synchronization phase, concurrent DDL and DML operations may cause data conflicts. It is recommended to reduce DDL during the incremental phase. 3. Do not perform the operation of purging WAL on the source database. 4. Do not delete the system database and schema postgres.public.identify, __tencentdb__sync_*.*, {database}.__tencentdb__ schema during the synchronous increment stage. 5. When the source and target database types are Tencent Cloud Database, do not modify the network of the database instance. If the network of the source instance and the target instance changes, causing the original VIP to be deleted, the synchronization task to fail, or to remain running unchanged (at this point, the synchronization is no longer working), in this case, the synchronization task cannot be retried. You need to manually end the task and then reestablish a new synchronization task. |
Data Synchronization Description | 1. When DTS initiates a data synchronization task, it sets the REPLICA IDENTITY FULL attribute for tables awaiting synchronization and newly created tables (for tasks with incremental DDL enabled). However, if there are long-running transactions on the table, this may result in a timeout during the setup process, ultimately causing the task to fail. 2. When DTS initiates a data synchronization task, if the database instance contains uncommitted long-running transactions, the creation of the replication slot may time out, thereby leading to task failure. |
Source database HA | HA occurs in the source database and migration of the primary node of the source instance occurs, causing changes in the WAL log. The original synchronization task will fail. The synchronized data in the target database needs cleaning, and then a new synchronization task needs to be established. |
Last updated:2025-04-30 18:29:39
Parameter | Description |
Billing Mode | Support annual and monthly subscription and pay-as-you-go. |
Source instance type | Select PostgreSQL. It cannot be modified after purchase. |
Source instance region | Select the source instance location. It cannot be modified after purchase. |
Types of target instances | Select PostgreSQL. It cannot be modified after purchase. |
Target instance region | Select the target instance location. It cannot be modified after purchase. |
Specification | Select specifications according to business requirements. The higher the specifications, the better the performance. For details, see Billing Overview. |
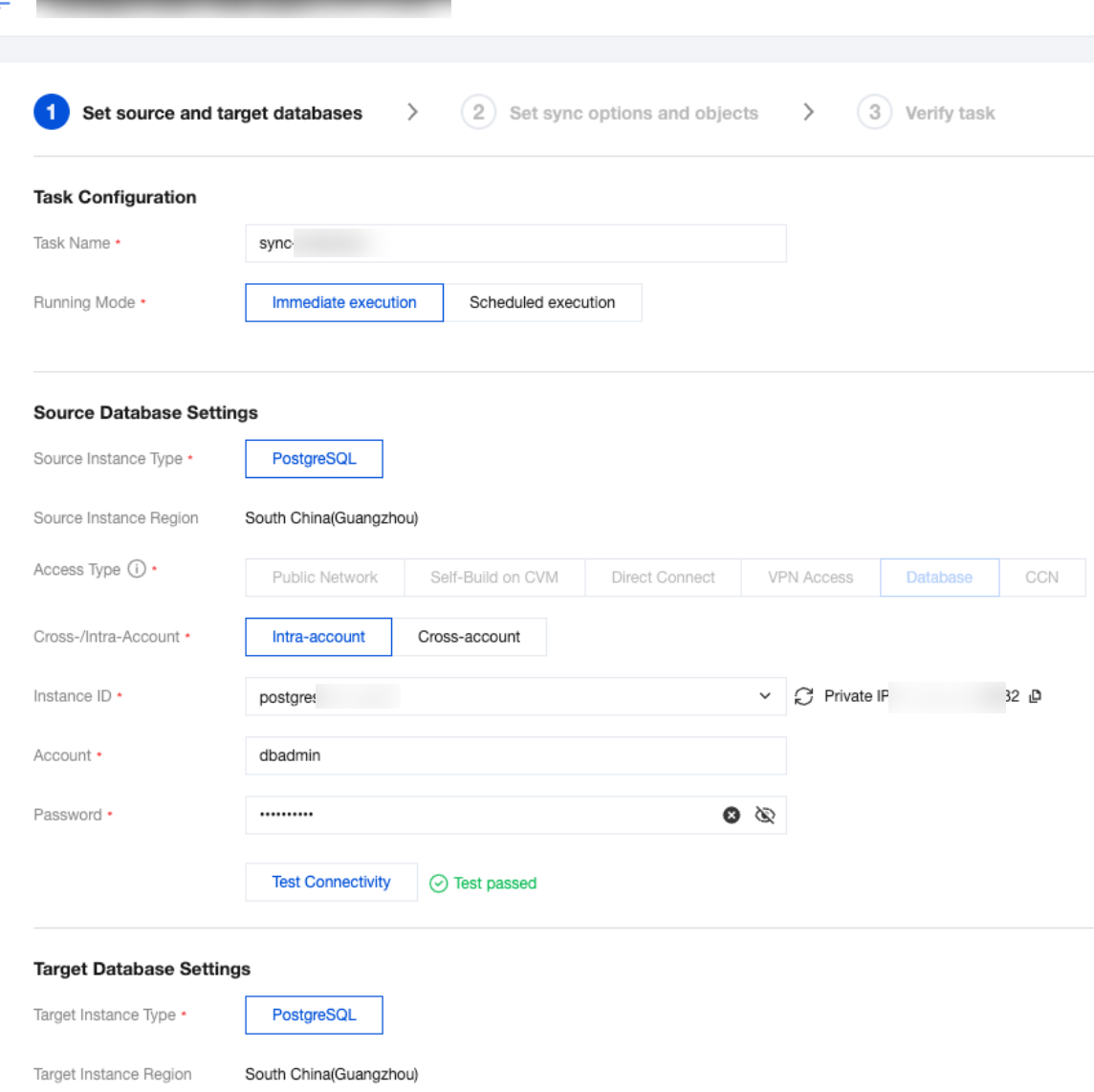
Settings | Parameter | Description |
Task Settings | Task Name | DTS will automatically generate a task name. Users can set it according to the actual situation. |
| Running Mode | Support two modes: immediate execution and scheduled execution. |
Source Instance Setting | Source instance type | The source instance type selected at the time of purchase cannot be modified. |
| Source instance region | The source instance location selected at the time of purchase cannot be modified. |
| Access type | Based on your scenario selection, this scenario chooses "Direct Connect" or "VPN Access". This scenario requires configuring interconnectivity between VPN and IDC. For preparation work of other access types, refer to Preparation Overview. Public network: The source database can be accessed through a public IP address. Self-built cloud host: The source database is deployed on Tencent Cloud CVM. Dedicated line access: The source database can be connected to the Tencent Cloud private network through Dedicated Line Access. VPN access: The source database can be connected to the Tencent Cloud private network through VPN Connections. Cloud database: The source database belongs to a Tencent Cloud database instance. CCN: The source database can be connected to the Tencent Cloud private network through CCN. |
| VPC Direct Connect gateway/VPN gateway | Direct connect only supports VPC direct connect gateway. Please confirm the gateway associated network type. For VPN gateway, please select the VPN gateway instance that accesses via VPN gateway. |
| Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) | Select the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) and subnet associated with the VPC Direct Connect gateway and VPN gateway. |
| Host address | Source instance access IP address or domain name. |
| Port | Source instance access port. |
| Account | Source instance account and account permission should meet the requirements. |
| Password | The password of the source instance account. |
Target instance settings | Types of target instances | The type of target instance selected when purchased cannot be modified. |
| Target instance region | The target instance region selected when purchased cannot be modified. |
| Access type | Based on your scenario selection, this scenario selects "CloudDB". |
| Instance ID | Select the target instance ID. |
| Account | Target instance account and account permission should meet the requirements. |
| Password | The password of the target instance account. |
Settings | Parameter | Description |
Task Settings | Task Name | DTS will automatically generate a task name. Users can set it according to the actual situation. |
| Running Mode | Support two modes: immediate execution and scheduled execution. |
Source Instance Setting | Source instance type | The source instance type selected at the time of purchase cannot be modified. |
| Source instance region | The source instance location selected at the time of purchase cannot be modified. |
| Access type | For this scenario, select "TencentDB". For preparation work for different access types, refer to Preparation Overview. Public network: The source database can be accessed through a public IP address. Self-built cloud host: The source database is deployed on Tencent Cloud CVM. Direct Connect: The source database can be connected to the Tencent Cloud private network through Direct Connect. VPN access: The source database can be connected to the Tencent Cloud private network through VPN Connections. Cloud database: The source database belongs to a Tencent Cloud database instance. CCN: The source database can be connected to the Tencent Cloud private network through CCN. |
| Instance ID | The ID of the source instance. |
| Account | Source instance account and account permission should meet the requirements. |
| Password | The password of the source instance account. |
Target instance settings | Types of target instances | The type of target instance selected when purchased cannot be modified. |
| Target instance region | The target instance region selected when purchased cannot be modified. |
| Access type | Based on your scenario selection, this scenario selects "CloudDB". |
| Instance ID | Select the target instance ID. |
| Account | Target instance account and account permission should meet the requirements. |
| Password | The password of the target instance account. |
Settings | Parameter | Description |
Task Settings | Task Name | DTS will automatically generate a task name. Users can set it according to the actual situation. |
| Running Mode | Support two modes: immediate execution and scheduled execution. |
| Automatic Retry | After configuration, if the migration task is temporarily interrupted due to network exceptions, DTS will automatically retry and recover the task within the set time. No manual intervention is required. The configurable time range is 5 - 720 minutes. |
Source Instance Setting | Source instance type | The source instance type selected at the time of purchase cannot be modified. |
| Source instance region | The source instance location selected at the time of purchase cannot be modified. |
| Access type | For third-party cloud vendor databases, you can generally choose the public network method, or choose VPN access, direct connect, or CCN. You need to choose according to the actual network conditions. This scenario selects "public network". For preparation work for different access types, refer to Overview of Preparation Work. Public network: The source database can be accessed through a public IP address. Self-built cloud host: The source database is deployed on Tencent Cloud CVM. Dedicated line access: The source database can be connected to the Tencent Cloud private network through Dedicated Line Access. VPN access: The source database can be connected to the Tencent Cloud private network through VPN Connections. Cloud database: The source database belongs to a Tencent Cloud database instance. CCN: The source database can be connected to the Tencent Cloud private network through CCN. |
| Host address | Source instance access IP address or domain name. |
| Port | Source instance port. |
| Account | Source instance account and account permission should meet the requirements. |
| Password | The password of the source instance account. |
Target instance settings | Types of target instances | The type of target instance selected when purchased cannot be modified. |
| Target instance region | The target instance region selected when purchased cannot be modified. |
| Access type | Based on your scenario selection, this scenario selects "CloudDB". |
| Instance ID | Select the target instance ID. |
| Account | Target instance account and account permission should meet the requirements. |
| Password | The password of the target instance account. |
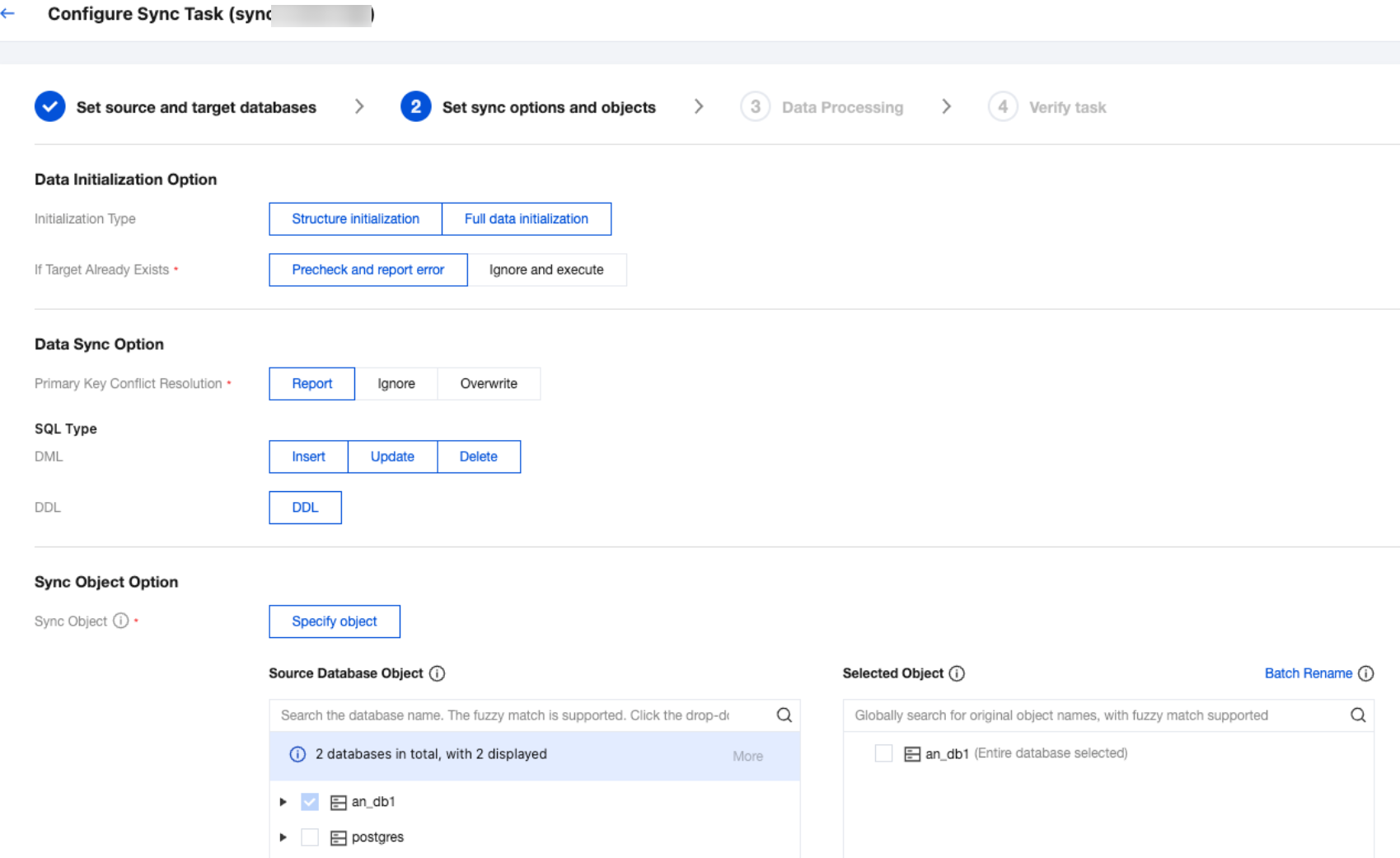
Settings | Parameter | Description |
Data Initialization Option | Initialization Type | Table structure initialization: During synchronous task execution, the table structure in the source instance will be initialized to the target instance first. Full data initialization: During synchronous task execution, the data in the source instance will be initialized to the target instance first. In scenarios where only full data initialization is selected, users need to create the table structure in the target database in advance. Both are selected by default and can be canceled based on the actual situation. |
| Existing homonymous table | Pre-validation and error reporting: If a table with the same name exists, an error will be reported and the process will no longer continue. Ignore and continue execution: Add full data and incremental data directly to the table of the target instance. |
Data Sync Option | Conflict Resolution Mechanism | Conflict Error: When a primary key conflict is detected during synchronization, an error will be reported and the data sync task will be suspended. Conflict ignored: When a primary key conflict is detected during synchronization, retain the primary key record in the target database. Conflict overwrite: When a primary key conflict is detected during synchronization, overwrite the primary key record in the target database with the primary key record in the source database. |
| Sync operation type | Support operations: Insert, Update, Delete, DDL. DDL customization is not supported currently. |
Synchronization object options | Source instance database and table objects | Select objects to be synchronized. Basic tables and views are supported. Only SEQUENCE is supported for advanced objects. |
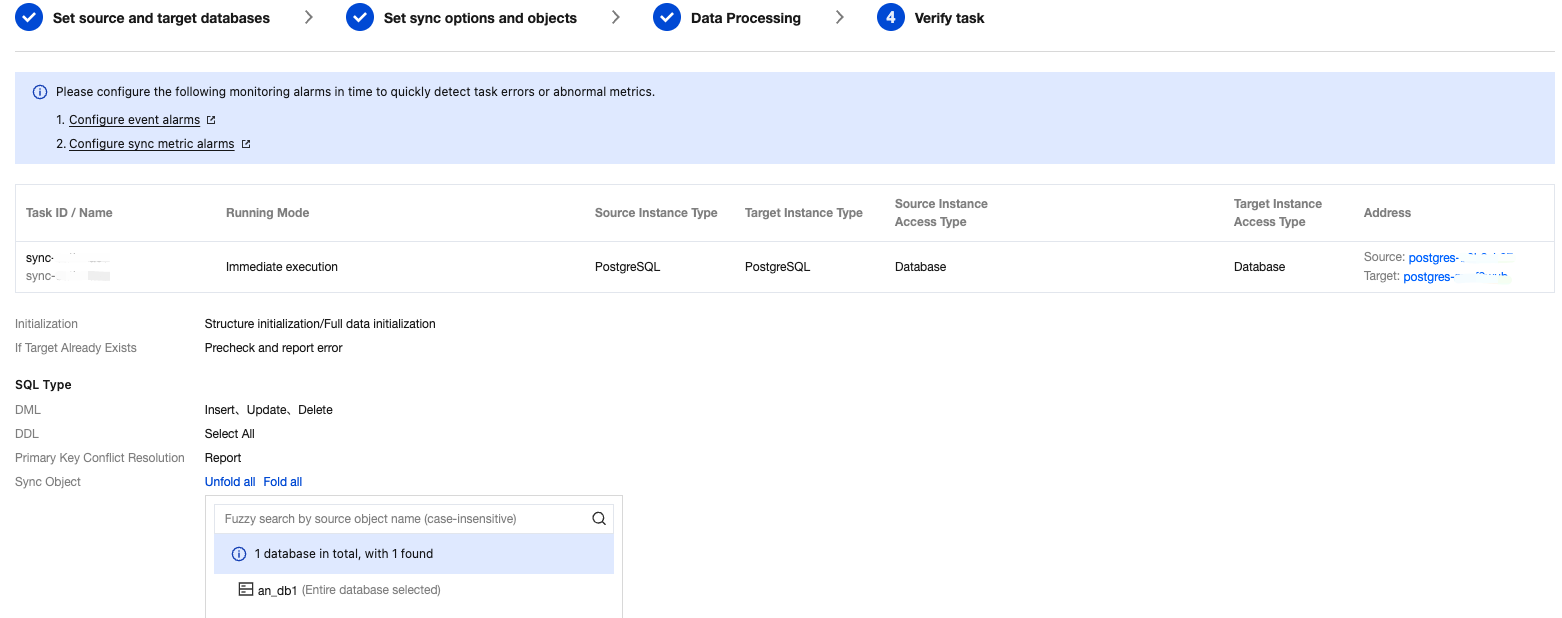
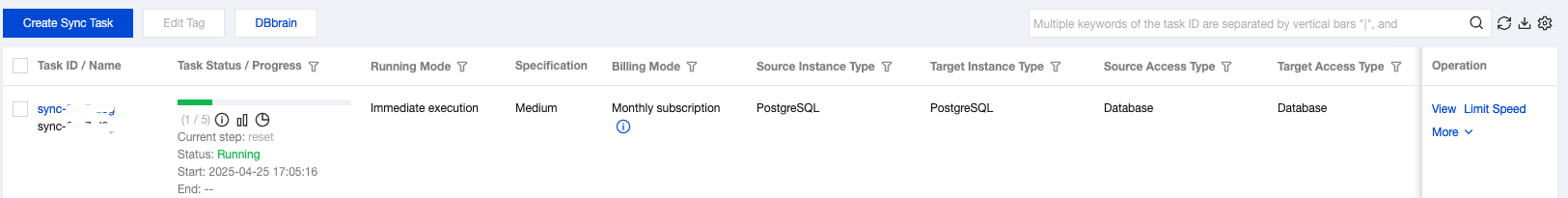
Last updated:2025-04-30 17:53:50
Last updated:2025-04-30 17:54:25
Last updated:2025-04-30 17:55:38
Last updated:2025-04-30 17:56:46
Last updated:2025-04-30 17:57:57
wal_level of the source database must be logical.max_replication_slots and max_wal_senders of the source database must be greater than the total number of libraries to be migrated (reserved additional number of connections).persistence attribute of tables to be migrated in the source database must be p (permanent table). Otherwise, replication is not supported, and logical migration cannot be done.REPLICA IDENTITY attribute is set to NOTHING), the validation task will raise an alarm.= operator, the verification will fail. You need to repair the table without a primary key according to the prompt or uncheck the primary key table. Otherwise, you cannot continue the task.wal_level, max_replication_slots, and max_wal_senders.wal_level = logicalmax_replication_slots = 10 //Change according to actual conditionsmax_wal_senders = 10 //Change according to actual conditions
postgres=> select name,setting from pg_settings where name='wal_level';name | setting-----------+---------wal_level | logical(1 row)postgres=> select name,setting from pg_settings where name='max_replication_slots';name | setting-----------------------+---------max_replication_slots | 10(1 row)postgres=> select name,setting from pg_settings where name='max_wal_senders';name | setting-----------------+---------max_wal_senders | 10(1 row)
REPLICA IDENTITY attribute is set to NOTHING), the validation task will raise an alarm.ALTER TABLE schemaName.tableName REPLICA IDENTITY FULL;
Last updated:2025-04-30 17:58:55
abstime, reltime and tinterval, the verification task will report an error.abstime, reltime and tinterval are some older date and time types which have been deprecated in new PostgreSQL Versions. It is recommend using following types as alternatives:abstime: Can be substituted with timestamp or timestamp with time zone types. These types provide a broader range of date and time representation capabilities.reltime: Can be substituted with interval type. interval type is used to represent time intervals and can include units such as year, month, day, hour, minute, and second.tinterval: Can be substituted with tsrange or tstzrange types. These types are used to represent time ranges and can include start time and end time.abstime, reltime and tinterval are similar. First, create a new column. Convert the old data format to the new data format and store it in the new column. After verifying that the data in the new column is correct, delete the old column. Finally, rename the new column to the name of the old column as needed.abstime to timestamp as an example for introduction.ALTER TABLE your_table ADD COLUMN new_column TIMESTAMP;
UPDATE your_table SET new_column = your_abstime_column::TIMESTAMP;
SELECT * FROM your_table;
ALTER TABLE your_table DROP COLUMN your_abstime_column;
ALTER TABLE your_table RENAME COLUMN new_column TO your_abstime_column;
Last updated:2025-04-30 18:00:05
Last updated:2025-04-30 18:01:00
create user new user with password 'password';grant pg_tencentdb_superuser to new username;alter user new user with CREATEDB;alter user new user with CREATEROLE;
drop user conflicting user;# If the conflicting user has resource dependencies, please first modify the owner of the dependent object. For example, the modification statement for the owner of a table is:alter table table name owner to new user;
Last updated:2025-04-30 18:02:04
alter system set timezone='<parameter value>';alter system set lc_monetary='<parameter value>';alter system set lc_numeric='<parameter value>';
Last updated:2025-04-30 18:03:01
Last updated:2025-04-30 18:03:56
Last updated:2025-04-30 18:04:56
Last updated:2025-04-30 18:06:25
Last updated:2025-04-30 18:07:16
Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51
pg_tencentdb_superuser is temporarily escalated to superuser and passes all permission checks.
TencentDB for PostgreSQL extensions are managed at the database level. You can create different extensions for different databases, but databases cannot use extensions in other databases.
To create an extension, access the database with the client tool and run the following statements:CREATE EXTENSION [ IF NOT EXISTS ] extension_name[ WITH ][ SCHEMA schema_name ][ VERSION version ][ FROM old_version ]
\dx command if you use the psql client.\dxList of installed extensionsName | Version | Schema | Description---------------+---------+------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------amcheck | 1.2 | public | functions for verifying relation integritybloom | 1.0 | public | bloom access method - signature file based indexhstore | 1.6 | public | data type for storing sets of (key, value) pairshstore_plperl | 1.0 | public | transform between hstore and plperljsonb_plperl | 1.0 | public | transform between jsonb and plperlplperl | 1.0 | pg_catalog | PL/Perl procedural languageplpgsql | 1.0 | pg_catalog | PL/pgSQL procedural languagepostgis | 3.0.2 | public | PostGIS geometry, geography, and raster spatial types and functions(8 rows)
select * from pg_available_extensions where installed_version is not null; statement to view the list of installed extensions.name | default_version | installed_version | comment---------------+-----------------+-------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------plperl | 1.0 | 1.0 | PL/Perl procedural languageamcheck | 1.2 | 1.2 | functions for verifying relation integrityhstore_plperl | 1.0 | 1.0 | transform between hstore and plperlplpgsql | 1.0 | 1.0 | PL/pgSQL procedural languagejsonb_plperl | 1.0 | 1.0 | transform between jsonb and plperlhstore | 1.6 | 1.6 | data type for storing sets of (key, value) pairsbloom | 1.0 | 1.0 | bloom access method - signature file based indexpostgis | 3.0.2 | 3.0.2 | PostGIS geometry, geography, and raster spatial types and functions(8 rows)
Last updated:2025-12-19 17:39:23
Range of Kernel Version | list of risk plugins |
less than or equal to v10.23_r1.24 | plv8,plls,plcoffee,pg_cron,age |
less than or equal to v11.22_r1.30 | plv8,plls,plcoffee,pg_cron,age |
less than or equal to v12.22_r1.33 | plv8,plls,plcoffee,pg_cron,age |
less than or equal to v13.22_r1.28 | plv8,plls,plcoffee,pg_cron,age |
less than or equal to v14.19_r1.37 | plv8,plls,plcoffee,pg_cron,age |
less than or equal to v15.14_r1.22 | plv8,plls,plcoffee,pg_cron,age |
less than or equal to v16.10_r1.17 | plv8,plls,plcoffee,pg_cron,age |
less than or equal to v17.6_r1.11 | plv8,plls,plcoffee,pg_cron,age |
less than or equal to v18.0_r1.1 | plv8,plls,plcoffee,pg_cron,age |
Last updated:2025-12-11 14:24:47
Plugin Name | v10 | v11 | v12 | v13 | v14 | v15 | v16 | v17 | v18 |
address_standardizer | 3.0.1 | 3.0.1 | 3.0.2 | 3.0.2 | 3.2.1 | 3.3.2 | 3.4.0 | 3.5.0 | 3.5.0 |
address_standardizer_data_us | 3.0.1 | 3.0.1 | 3.0.2 | 3.0.2 | 3.2.1 | 3.3.2 | 3.4.0 | 3.5.0 | 3.5.0 |
age | - | - | - | 1.5.0 | 1.5.0 | 1.5.0 | 1.5.0 | 1.5.0 | 1.5.0 |
auth_delay | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
auto_explain | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
autoinc | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
bloom | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
bool_plperl | - | - | - | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
btree_gin | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
btree_gist | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.7 | 1.7 |
chkpass | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
citext | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 |
cos_fdw | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
count_distinct | - | 3.0.2 | 3.0.2 | 3.0.2 | 3.0.2 | 3.0.2 | 3.0.2 | 3.0.2 | 3.0.2 |
cube | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
dblink | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
decoder_raw | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
decoderbufs | 0.1.0 | 0.1.0 | 0.1.0 | 0.1.0 | 0.1.0 | 0.1.0 | 0.1.0 | 0.1.0 | 0.1.0 |
dict_int | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
dict_xsyn | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
earthdistance | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
fuzzystrmatch | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
hll | 2.14 | 2.14 | 2.14 | 2.15 | 2.16 | 2.16 | 2.18 | 2.18 | 2.18 |
hstore | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 |
hstore_plperl | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
hypopg | - | 1.4.1 | 1.4.1 | 1.4.1 | 1.4.1 | 1.4.1 | 1.4.1 | 1.4.1 | 1.4.1 |
imgsmlr | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
insert_username | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
intarray | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
isn | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
jsonb_plperl | - | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
lo | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
ltree | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
moddatetime | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
mysql_fdw | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
old_snapshot | - | - | - | - | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | - | - |
orafce | - | - | 3.8 | - | 4.15 | - | - | - | - |
pg_bigm | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
pg_buffercache | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
pg_freespacemap | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
pg_hashids | 1.2.1 | 1.2.1 | 1.2.1 | 1.2.1 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
pg_hint_plan | 1.3.6 | 1.3.6 | 1.3.6 | 1.3.7 | 1.4.1 | 1.4.1 | 1.6.0 | 1.7.0 | 1.7.0 |
pg_ivm | - | - | - | 1.11 | 1.11 | 1.11 | 1.11 | 1.11 | 1.11 |
pg_jieba | - | 1.1.1 | 1.1.1 | 1.1.1 | 1.1.1 | 1.1.1 | 1.1.1 | 1.1.1 | 1.1.1 |
pg_partman | - | 4.7.3 | 4.7.4 | 4.7.4 | 4.7.4 | 4.7.4 | 4.7.4 | 4.7.4 | 4.7.4 |
pg_pathman | - | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | - | - | - | - | - |
pg_prewarm | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
pg_repack | 1.4.4 | 1.5.2 | 1.5.2 | 1.5.2 | 1.5.2 | 1.5.2 | 1.5.2 | 1.5.2 | 1.5.2 |
pg_similarity | - | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
pg_sphere | - | 1.5.1 | 1.5.1 | 1.5.1 | 1.5.1 | 1.5.1 | 1.5.1 | 1.5.1 | 1.5.1 |
pg_stat_log | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
pg_stat_statements | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 1.10 | 1.10 | 1.11 | 1.11 |
pg_trgm | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 |
pgagent | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4.2.3 | 4.2.3 | 4.2.3 | 4.2.3 | 4.2.3 | 4.2.3 |
pgcrypto | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
pglogical | - | 2.4.4 | 2.4.4 | 2.4.4 | 2.4.4 | 2.4.4 | 2.4.4 | 2.4.5 | 2.4.5 |
pgrouting | 3.2.2 | 3.2.2 | 3.2.2 | 3.2.2 | 3.2.2 | 3.2.2 | 3.5.1 | 3.6.2 | 3.6.2 |
pgrowlocks | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
pgstattuple | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
pipelinedb | 1.0.0 | 1.0.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
pldbgapi | - | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
plperl | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
plpgsql | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
postgis | 3.0.1 | 3.0.1 | 3.0.2 | 3.0.2 | 3.2.1 | 3.3.2 | 3.4.0 | 3.5.0 | 3.5.0 |
postgis_raster | 3.0.1 | 3.0.1 | 3.0.2 | 3.0.2 | 3.2.1 | 3.3.2 | 3.4.0 | 3.5.0 | 3.5.0 |
postgis_sfcgal | 3.0.1 | 3.0.1 | 3.0.2 | 3.0.2 | 3.2.1 | 3.3.2 | 3.4.0 | 3.5.0 | 3.5.0 |
postgis_tiger_geocoder | 3.0.1 | 3.0.1 | 3.0.2 | 3.0.2 | 3.2.1 | 3.3.2 | 3.4.0 | 3.5.0 | 3.5.0 |
postgis_topology | 3.0.1 | 3.0.1 | 3.0.2 | 3.0.2 | 3.2.1 | 3.3.2 | 3.4.0 | 3.5.0 | 3.5.0 |
postgres_fdw | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
rdkit | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 4.0.1 | 4.0.1 | 4.0.1 | 4.5.0 | 4.5.0 |
rds_server_handler | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
refint | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
roaringbitmap | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
rum | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
seg | 1.1 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 |
sequential_uuids | 1.0.2 | 1.0.2 | 1.0.2 | 1.0.2 | 1.0.2 | 1.0.2 | 1.0.2 | 1.0.2 | 1.0.2 |
smlar | - | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
sslinfo | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
starrocks_fdw | - | - | - | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
tablefunc | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
tcn | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
tencentdb_ai | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.1 | 1.1 |
tencentdb_failover_slot | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | - | - |
tencentdb_pwdcheck | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
tencentdb_sql_throttling | - | - | - | - | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
tencentdb_stat | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | - | - | - | - |
tencentdb_superuser | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
tencentdb_system_stat | - | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
timetravel | 1.0 | 1.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
timescaledb | 1.7.5 | 1.7.5 | 2.6.0 | 2.9.1 | 2.9.1 | 2.9.1 | 2.13.0 | 2.17.1 | 2.17.1 |
topn | 2.4.0 | 2.4.0 | 2.4.0 | 2.4.0 | 2.4.0 | 2.4.0 | 2.6.0 | 2.6.0 | 2.6.0 |
tsm_system_rows | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
tsm_system_time | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
unaccent | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
uuid-ossp | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
vector | - | - | 0.8.0 | 0.8.0 | 0.8.0 | 0.8.0 | 0.8.0 | 0.8.0 | 0.8.0 |
wal2json | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.5 | 2.6 | 2.6 |
xml2 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
zhparser | 1.0 | 1.0 | 2.2 | 1.0 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 2.2 |
Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51
Extension | v9.3.25_r1.3 | v9.3.25_r1.2 | v9.3.25_r1.1 | v9.3.5_r1.0 |
pg_hint_plan | 1.1.4 | 1.1.4 | 1.1.4 | 1.1.4 |
pg_prewarm | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
pg_stat_error | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
pg_stat_log | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
pg_stat_statements | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
pgrowlocks | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
sslinfo | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
tablefunc | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
tcn | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
unaccent | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
uuid-ossp | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
pg_cron | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
pgagent | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
pg_partman | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
tsearch2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
postgis | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 |
postgis_raster | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
postgis_sfcgal | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | Unsupported |
postgis_tiger_geocoder | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 |
postgis_topology | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 |
pgrouting | 2.4.1 | 2.4.1 | 2.4.1 | 2.4.1 |
address_standardizer | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 |
address_standardizer_data_us | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 |
earthdistance | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
plperl | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
plpgsql | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
pltcl | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
plv8 | 2.0.0 | 2.0.0 | 2.0.0 | 2.0.0 |
bool_plperl | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
jsonb_plperl | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
hstore | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
hstore_plperl | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
plcoffee | 2.0.0 | 2.0.0 | 2.0.0 | 2.0.0 |
plls | 2.0.0 | 2.0.0 | 2.0.0 | 2.0.0 |
timescaledb | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
pipelinedb | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
rdkit | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
imgsmlr | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
zhparser | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
intagg | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
intarray | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
isn | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
xml2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
jsonbx | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
dict_int | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
dict_xsyn | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
citext | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
ltree | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
postgres_fdw | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
orafce | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 |
chkpass | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
bloom | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
btree_gin | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
btree_gist | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
roaringbitmap | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
rum | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
cube | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
decoderbufs | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
pg_bigm | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
fuzzystrmatch | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
hll | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
pg_trgm | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
pg_hashids | 1.2.1 | 1.2.1 | 1.2.1 | 1.2.1 |
pgcrypto | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
cos_fdw | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
topn | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51
Extension | v9.5.25_r1.3 | v9.5.25_r1.2 | v9.5.25_r1.1 | v9.5.4_r1.0 |
pg_hint_plan | 1.1.5 | 1.1.5 | 1.1.5 | 1.1.5 |
pg_prewarm | 1 | 1 | 1 | Unsupported |
pg_stat_error | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
pg_stat_log | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
pg_stat_statements | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
pgrowlocks | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
sslinfo | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
tablefunc | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
tcn | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
unaccent | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
uuid-ossp | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
pg_cron | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
pgagent | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 4 |
pg_partman | 2.6.4, 1.4 | 2.6.4, 1.4 | 2.6.4, 1.4 | 2.6.4, 1.4, 1.0 |
tsearch2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
postgis | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 |
postgis_raster | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
postgis_sfcgal | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | Unsupported |
postgis_tiger_geocoder | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 |
postgis_topology | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 |
pgrouting | 2.4.1 | 2.4.1 | 2.4.1 | 2.4.1 |
address_standardizer | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 |
address_standardizer_data_us | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 | 2.3.0 |
earthdistance | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
plperl | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
plpgsql | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
pltcl | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
plv8 | 2.0.0 | 2.0.0 | 2.0.0 | 2.0.0 |
bool_plperl | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
jsonb_plperl | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
hstore | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
hstore_plperl | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
plcoffee | 2.0.0 | 2.0.0 | 2.0.0 | 2.0.0 |
plls | 2.0.0 | 2.0.0 | 2.0.0 | 2.0.0 |
timescaledb | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
pipelinedb | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
rdkit | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
imgsmlr | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
zhparser | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
intagg | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
intarray | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
isn | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
xml2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
jsonbx | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
dict_int | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
dict_xsyn | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
citext | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
ltree | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
postgres_fdw | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
orafce | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 | 3.3 |
chkpass | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
bloom | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
btree_gin | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
btree_gist | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
roaringbitmap | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
rum | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
cube | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
decoderbufs | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
pg_bigm | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
fuzzystrmatch | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
hll | 2.14 | 2.14 | 2.14 | 2.14 |
pg_trgm | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 |
pg_hashids | 1.2.1 | 1.2.1 | 1.2.1 | 1.2.1 |
pgcrypto | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
cos_fdw | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
topn | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported | Unsupported |
Last updated:2025-08-14 17:04:48
SELECT * FROM pg_available_extensions WHERE name = 'vector';

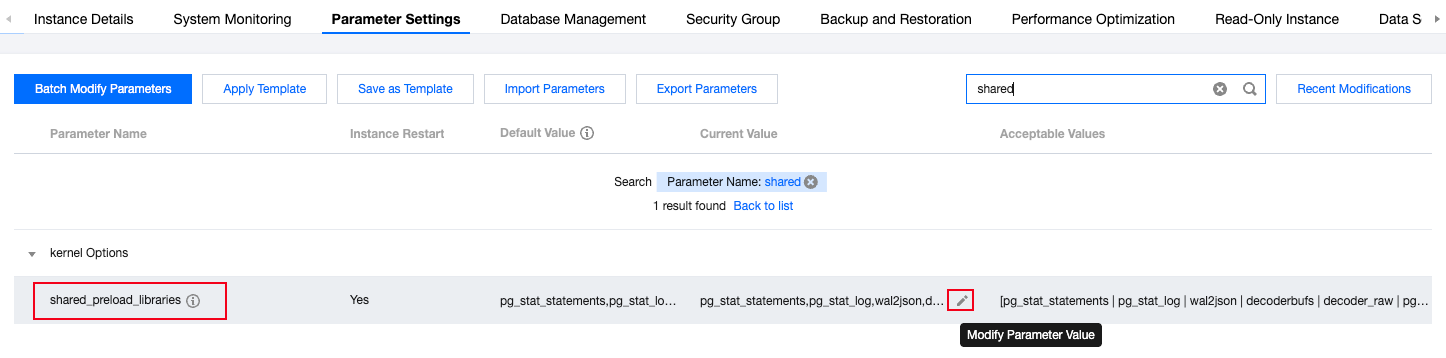

CREATE EXTENSION vector;
SELECT * FROM pg_available_extensions WHERE name = 'vector';
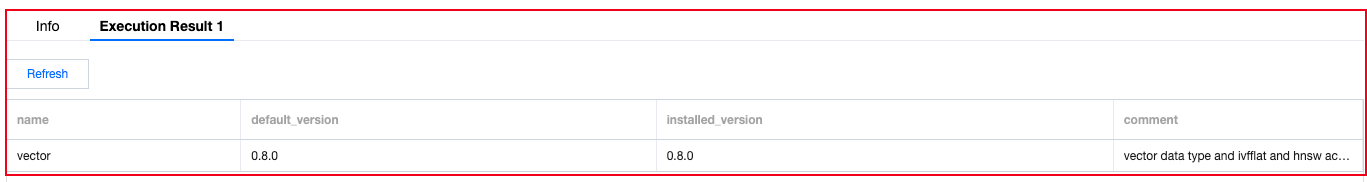
Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51
CREATE EXTENSION.postgres-xxxxxx or pgro-xxxxxx and can be viewed in the console.ins-xxxxx.postgres_fdwpostgres_fdw extension can be used to access data from other databases in the same instance or other instances.postgres=>create role user1 with LOGIN CREATEDB PASSWORD 'password1';postgres=>create database testdb1;CREATE DATABASE
postgres=>create role user2 with LOGIN CREATEDB PASSWORD 'password2';postgres=> create database testdb2;CREATE DATABASEpostgres=> \c testdb2 user2You are now connected to database "testdb2" as user "user2".testdb2=> create table test_table2(id integer);CREATE TABLEtestdb2=> insert into test_table2 values (1);INSERT 0 1
# Createpostgres=> \c testdb1You are now connected to database "testdb1" as user "user1".testdb1=> create extension postgres_fdw;CREATE EXTENSION# Viewtestdb1=> \dxList of installed extensionsName | Version | Schema | Description--------------+---------+------------+----------------------------------------------------plpgsql | 1.0 | pg_catalog | PL/pgSQL procedural languagepostgres_fdw | 1.0 | public | foreign-data wrapper for remote PostgreSQL servers(2 rows)
# Access the data of the target instance's `testdb2` from the current instance's `testdb1`testdb1=>create server srv_test1 foreign data wrapper postgres_fdw options (host 'xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx',dbname 'testdb2', port '5432', instanceid 'postgres-xxxxx');CREATE SERVER
dbname parameter.# Access the data of `testdb2` from `testdb1` in the current instancecreate server srv_test1 foreign data wrapper postgres_fdw options (dbname 'testdb2');
testdb1=>create server srv_test foreign data wrapper postgres_fdw options (host 'xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx', dbname 'testdb2', port '5432', instanceid 'ins-xxxxx', access_type '2', region 'ap-guangzhou',uin 'xxxxxx',own_uin 'xxxxxx');CREATE SERVER
testdb1=>create server srv_test1 foreign data wrapper postgres_fdw options (host 'xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx',dbname 'testdb2', port '5432', instanceid 'ins-xxxxx', access_type '2', region 'ap-guangzhou', uin 'xxxxxx', own_uin 'xxxxxx', vpcid 'vpc-xxxxxx', subnetid 'subnet-xxxxx');CREATE SERVER
testdb1=>create server srv_test1 foreign data wrapper postgres_fdw options (host 'xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx',dbname 'testdb2', port '5432', access_type '3', region 'ap-guangzhou', uin 'xxxxxx', own_uin 'xxxxxx');CREATE SERVER
testdb1=>create server srv_test1 foreign data wrapper postgres_fdw options (host 'xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx',dbname 'testdb2', port '5432', access_type '4', region 'ap-guangzhou', uin 'xxxxxx', own_uin 'xxxxxx', vpngwid 'xxxxxx');
testdb1=>create server srv_test1 foreign data wrapper postgres_fdw options (host 'xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx',dbname 'testdb2', port '5432', access_type '5', region 'ap-guangzhou', uin 'xxxxxx', own_uin 'xxxxxx', vpngwid 'xxxxxx');
testdb1=>create server srv_test1 foreign data wrapper postgres_fdw options (host 'xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx',dbname 'testdb2', port '5432', access_type '6', region 'ap-guangzhou', uin 'xxxxxx', own_uin 'xxxxxx', dcgid 'xxxxxx');CREATE SERVER
testdb1=> create user mapping for user1 server srv_test1 options (user 'user2',password 'password2');CREATE USER MAPPING
testdb1=> create foreign table foreign_table1(id integer) server srv_test1 options(table_name 'test_table2');CREATE FOREIGN TABLE
testdb1=> select * from foreign_table1;id----1(1 row)
dblinkdblink extentionpostgres=> create extension dblink;postgres=> \dxList of installed extensionsName | Version | Schema | Description--------------------+---------+------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------dblink | 1.2 | public | connect to other PostgreSQL databases from within a databasepg_stat_log | 1.0 | public | track runtime execution statistics of all SQL statements executedpg_stat_statements | 1.6 | public | track execution statistics of all SQL statements executedplpgsql | 1.0 | pg_catalog | PL/pgSQL procedural language(4 rows)
dblink linkselect dblink_connect('yunpg1','host=10.10.10.11 port=5432 instanceid=postgres-2123455r dbname=postgres access_type=1 user=dbadmin password=P302!');dblink_connect----------------OK(1 row)
postgres=> select * from dblink('yunpg1','select catalog_name,schema_name,schema_owner from information_schema.schemata') as t(a varchar(50),b varchar(50),c varchar(50));a | b | c----------+--------------------+---------postgres | pg_toast | user_00postgres | pg_temp_1 | user_00postgres | pg_toast_temp_1 | user_00postgres | pg_catalog | user_00postgres | public | user_00postgres | information_schema | user_00(6 rows)
mysql_fdwmysql_fdw extensionpostgres=> create extension mysql_fdw;CREATE EXTENSIONpostgres=> \dx;List of installed extensionsName | Version | Schema | Description--------------------+---------+------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------dblink | 1.2 | public | connect to other PostgreSQL databases from within a databasemysql_fdw | 1.1 | public | Foreign data wrapper for querying a MySQL serverpg_stat_log | 1.0 | public | track runtime execution statistics of all SQL statements executedpg_stat_statements | 1.9 | public | track planning and execution statistics of all SQL statements executedplpgsql | 1.0 | pg_catalog | PL/pgSQL procedural language(5 rows)
postgres=> CREATE SERVER mysql_svr FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER mysql_fdw OPTIONS (host '171.16.10.13',port '3306',instanceid 'cdb-l1d95grp',uin '100026380431');CREATE SERVER
postgres=> CREATE USER MAPPING FOR PUBLIC SERVER mysql_svr OPTIONS (username 'fdw_user',password 'Secret!123');CREATE USER MAPPING
postgres=> IMPORT FOREIGN SCHEMA hrdb FROM SERVER mysql_svr INTO public;
cos_fdwLast updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51
pg_roaringbitmap extension to use the bitwise operation feature to improve the query performance.CREATE EXTENSION roaringbitmap;
roaringbitmap type:CREATE TABLE t1 (id integer, bitmap roaringbitmap);
rb_build function to insert the roaringbitmap data:-- Set the bit value of the array to 1.INSERT INTO t1 SELECT 1,RB_BUILD(ARRAY[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,200]);-- Set the bit values of multiple records to 1 and aggregate the bit values into a Roaring bitmap.INSERT INTO t1 SELECT 2,RB_BUILD_AGG(e) FROM GENERATE_SERIES(1,100) e;
-- Set the bit value of the array to 1.SELECT RB_OR(a.bitmap,b.bitmap) FROM (SELECT bitmap FROM t1 WHERE id = 1) AS a,(SELECT bitmap FROM t1 WHERE id = 2) AS b;
SELECT RB_OR_AGG(bitmap) FROM t1;SELECT RB_AND_AGG(bitmap) FROM t1;SELECT RB_XOR_AGG(bitmap) FROM t1;SELECT RB_BUILD_AGG(e) FROM GENERATE_SERIES(1,100) e;
SELECT RB_CARDINALITY(bitmap) FROM t1;
SELECT RB_ITERATE(bitmap) FROM t1 WHERE id = 1;
Function | Input | Output | Description | Example | Result |
rb_build | integer[] | roaringbitmap | Create roaringbitmap from integer array | rb_build('{1,2,3,4,5}') | {1,2,3,4,5} |
rb_index | roaringbitmap,integer | bigint | Return the 0-based index of element in this roaringbitmap, or -1 if do not exsits | rb_index('{1,2,3}',3) | 2 |
rb_cardinality | roaringbitmap | bigint | Return cardinality of the roaringbitmap | rb_cardinality('{1,2,3,4,5}') | 5 |
rb_and_cardinality | roaringbitmap,roaringbitmap | bigint | Return cardinality of the AND of two roaringbitmaps | rb_or_cardinality('{1,2,3}','{3,4,5}') | 1 |
rb_xor_cardinality | roaringbitmap,roaringbitmap | bigint | Return cardinality of the XOR of two roaringbitmaps | rb_xor_cardinality('{1,2,3}','{3,4,5}') | 4 |
rb_andnot_cardinality | roaringbitmap,roaringbitmap | bigint | Return cardinality of the ANDNOT of two roaringbitmaps | rb_andnot_cardinality('{1,2,3}','{3,4,5}') | 2 |
rb_is_empty | roaringbitmap | boolean | Check if roaringbitmap is empty. | rb_is_empty('{1,2,3,4,5}') | t |
rb_fill | roaringbitmap,range_start bigint,range_end bigint | roaringbitmap | Fill the specified range (not include the range_end) | rb_fill('{1,2,3}',5,7) | {1,2,3,5,6} |
rb_clear | roaringbitmap,range_start bigint,range_end bigint | roaringbitmap | Clear the specified range (not include the range_end) | rb_clear('{1,2,3}',2,3) | {1,3} |
rb_flip | roaringbitmap,range_start bigint,range_end bigint | roaringbitmap | Negative the specified range (not include the range_end) | rb_flip('{1,2,3}',2,10) | {1,4,5,6,7,8,9} |
rb_range | roaringbitmap,range_start bigint,range_end bigint | roaringbitmap | Return new set with specified range (not include the range_end) | rb_range('{1,2,3}',2,3) | {2} |
rb_range_cardinality | roaringbitmap,range_start bigint,range_end bigint | bigint | Return the cardinality of specified range (not include the range_end) | rb_range_cardinality('{1,2,3}',2,3) | 1 |
rb_min | roaringbitmap | integer | Return the smallest offset in roaringbitmap. Return NULL if the bitmap is empty | rb_min('{1,2,3}') | 1 |
rb_max | roaringbitmap | integer | Return the greatest offset in roaringbitmap. Return NULL if the bitmap is empty | rb_max('{1,2,3}') | 3 |
rb_rank | roaringbitmap,integer | bigint | Return the number of elements that are smaller or equal to the specified offset | rb_rank('{1,2,3}',3) | 3 |
rb_jaccard_dist | roaringbitmap,roaringbitmap | double precision | Return the jaccard distance(or the Jaccard similarity coefficient) of two bitmaps | rb_jaccard_dist('{1,2,3}','{3,4}') | 0.25 |
rb_select | roaringbitmap,bitset_limit bigint,bitset_offset bigint=0,reverse boolean=false,range_start bigint=0,range_end bigint=4294967296 | roaringbitmap | Return subset [bitset_offset,bitset_offset+bitset_limit) of bitmap between range [range_start,range_end) | rb_select('{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}',5,2) | {3,4,5,6,7} |
rb_to_array | roaringbitmap | integer[] | Convert roaringbitmap to integer array | rb_to_array(roaringbitmap('{1,2,3}')) | {1,2,3} |
rb_iterate | roaringbitmap | SET of integer | Return set of integer from a roaringbitmap data. | SELECT rb_iterate(rb_build('{1,2,3}')) | 1 2 3 |
Aggregate Function | Input | Output | Description | Example | Result |
rb_build_agg | integer | roaringbitmap | Build a roaringbitmap from a integer set | select rb_build_agg(id) from (values (1),(2),(3)) t(id) | {1,2,3} |
rb_or_agg | roaringbitmap | roaringbitmap | AND Aggregate calculations from a roaringbitmap set | select rb_or_agg(bitmap) from (values (roaringbitmap('{1,2,3}')), (roaringbitmap('{2,3,4}')) ) t(bitmap) | {1,2,3,4} |
rb_and_agg | roaringbitmap | roaringbitmap | AND Aggregate calculations from a roaringbitmap set | select rb_and_agg(bitmap) from (values (roaringbitmap('{1,2,3}')), (roaringbitmap('{2,3,4}')) ) t(bitmap) | {2,3} |
rb_xor_agg | roaringbitmap | roaringbitmap | XOR Aggregate calculations from a roaringbitmap set | select rb_xor_agg(bitmap) from (values (roaringbitmap('{1,2,3}')), (roaringbitmap('{2,3,4}')) ) t(bitmap) | {1,4} |
rb_or_cardinality_agg | roaringbitmap | bigint | OR Aggregate calculations from a roaringbitmap set, return cardinality. | select rb_or_cardinality_agg(bitmap) from (values (roaringbitmap('{1,2,3}')),(roaringbitmap('{2,3,4}'))) t(bitmap) | 4 |
rb_and_cardinality_agg | roaringbitmap | bigint | AND Aggregate calculations from a roaringbitmap set, return cardinality | select rb_and_cardinality_agg(bitmap) from (values (roaringbitmap('{1,2,3}')), (roaringbitmap('{2,3,4}'))) t(bitmap) | 2 |
rb_xor_cardinality_agg | roaringbitmap | bigint | XOR Aggregate calculations from a roaringbitmap set, return cardinality | select rb_xor_cardinality_agg(bitmap) from (values (roaringbitmap('{1,2,3}')), (roaringbitmap('{2,3,4}')) ) t(bitmap) | 2 |
Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51
Feature | Classic Network | VPC |
Custom network | Unsupported | Supported |
Custom routing | Unsupported | Supported |
Custom IP | Unsupported | Supported |
Interconnection rule | Interconnection in the same region | Interconnection between subnets in the same VPC in the same region |
Security control | Security group | Security group |
Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51
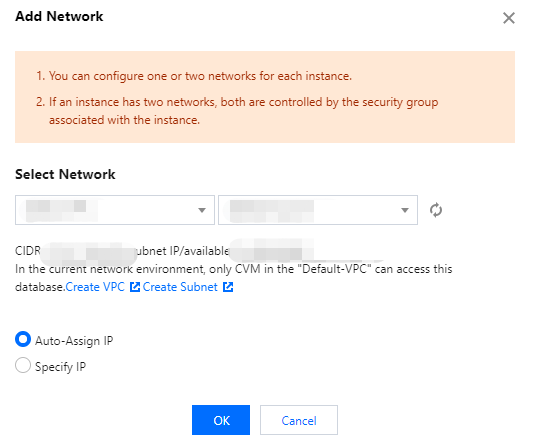
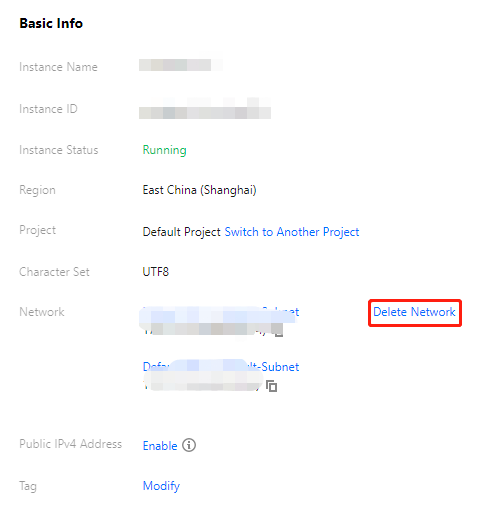
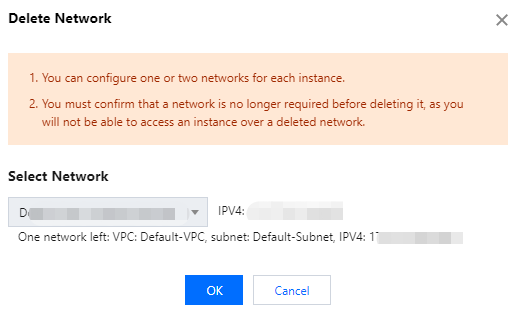
Last updated:2025-04-23 21:44:46

Last updated:2025-11-11 19:04:10
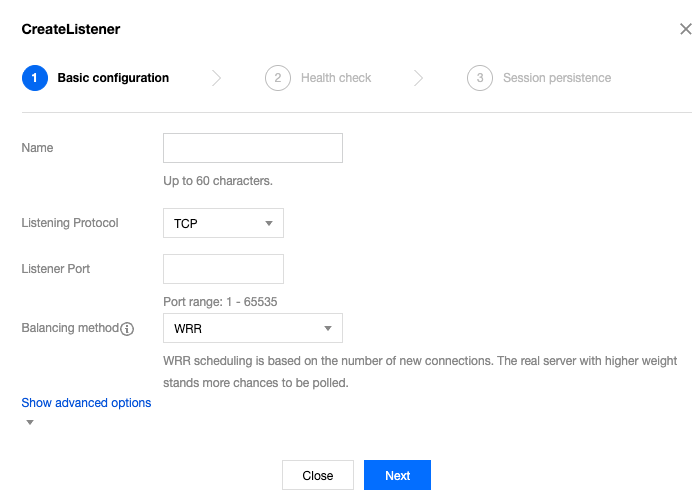
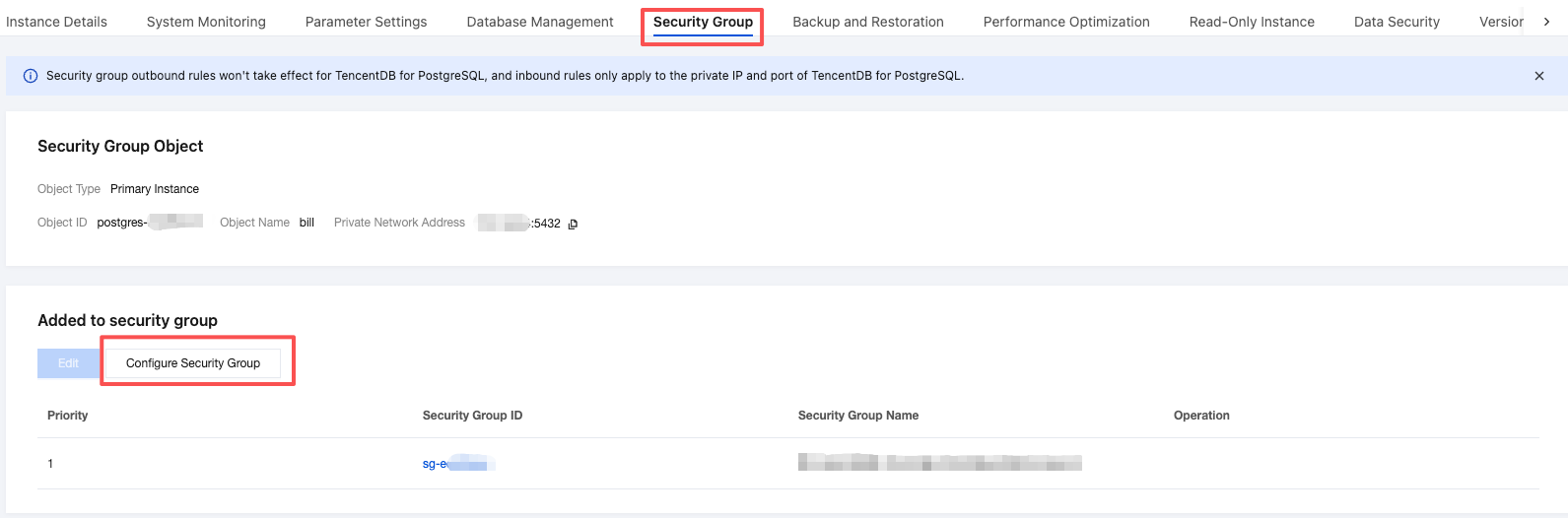
Parameter | Description |
Host name/address | Enter the address of the CLB instance. You can view the VIP information in the basic info on the CLB instance details page. |
Port | Enter the port of the CLB instance. You can view the TCP port number under Monitor Management on the CLB instance details page. |
Username | Enter the account name of the PostgreSQL instance to be connected. The account is created under Instance Management > Database Management > Account Management. |
Password | Enter the password corresponding to the filled-in Username, then click Save. |
Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51
Task | Link |
Understand the basic structure of policies | |
Define operations in a policy | |
Define resources in a policy | |
View supported resource-level permissions | |
View console examples |
Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51
{"version":"2.0","statement":[{"effect":"effect","action":["action"],"resource":["resource"],"condition": {"key":{"value"}}}]}
effect, action, resource, and condition. One policy has only one statement."action":["postgres:action1","postgres:action2"]
"action":["postgres:Describe*"]
"action":["postgres:*"]
qcs:project_id:service_type:region:account:resource
Resource | Resource Description Method in Access Policies |
Instance | qcs::postgres:$region:$account:DBInstanceId/$DBInstanceId |
"resource":[ "qcs::postgres:ap-shanghai:164xxx472:DBInstanceId/postgres-0xssvm8e"]
"resource":[ "qcs::postgres:ap-shanghai:164xxx472:DBInstanceId/*"]
resource element as shown below:"resource": ["*"]
"resource":["qcs::postgres::164xxx472:DBInstanceId/postgres-0xf1f41e","qcs::postgres::164xxx472:DBInstanceId/postgres-0xssvm8e"]
Last updated:2024-01-24 11:16:51
Resource Type | Resource Description Method in Access Policies |
qcs::postgres:$region:$account:DBInstanceId/$DBInstanceId qcs::postgres:$region:$account:DBInstanceId/* |
$region and $account with your actual values. You can also use the wildcard (*) in the path. For more information, please see Console Examples.* as the resource element in the policy statement.API Operation | API Description |
CreateDBInstances | Creates an instance |
CreateServerlessDBInstance | Creates a PostgreSQL for Serverless instance |
DescribeOrders | Obtains order information |
DescribeRegions | Queries available regions |
DescribeZones | Queries available availability zones |
DescribeProductConfig | Queries product specifications |
InquiryPriceCreateDBInstances | Queries prices |
DescribeServerlessDBInstances | Queries the list of PostgreSQL for Serverless instances |
API Name | API Description |
CloseServerlessDBExtranetAccess | Disables the public network access for a PostgreSQL for Serverless instance |
DeleteServerlessDBInstance | Deletes a PostgreSQL for Serverless instance |
OpenServerlessDBExtranetAccess | Enables the public network access for a PostgreSQL for Serverless instance |
API Name | API Description |
DescribeDBBackups | Queries the list of instance backups |
DescribeDBErrlogs | Obtains error logs |
DescribeDBSlowlogs | Obtains slow query logs |
DescribeDBXlogs | Obtains the Xlog list |
API Name | API Description |
CloseDBExtranetAccess | Disables the public network address for an instance |
DescribeDBInstanceAttribute | Queries instance details |
DescribeDatabases | Pulls the instance list |
DestroyDBInstance | Terminates an instance |
InitDBInstances | Initializes an instance |
InquiryPriceRenewDBInstance | Queries the instance renewal price |
InquiryPriceUpgradeDBInstance | Queries the instance upgrade price |
ModifyDBInstanceName | Modifies the instance name |
ModifyDBInstancesProject | Transfers an instance to another project |
OpenDBExtranetAccess | Enables public network access |
RenewInstance | Renews an instance |
RestartDBInstance | Restarts an instance |
SetAutoRenewFlag | Sets auto-renewal |
UpgradeDBInstance | Upgrades an instance |
DescribeDBInstances | Queries the instance list |
API Name | API Description |
DescribeAccounts | Obtains the list of instance users |
ModifyAccountRemark | Modifies the account password |
ResetAccountPassword | Resets the account password |
Last updated:2025-09-10 22:18:28
"action": ["postgres:DescribeProductConfig","postgres:InquiryPriceCreateDBInstances","postgres:DescribeRegions","postgres:DescribeZones"]
{"effect": "allow","action": ["monitor:Get*","monitor:Describe*"],"resource": "*"}
QcloudPostgreSQLFullAccess policy with the user.
This policy grants the user permissions to operate all PostgreSQL resources. You can find more details below:
Associate the default policy QcloudPostgreSQLFullAccess with the user as instructed in Authorization Management.QcloudPostgreSQLReadOnlyAccess policy with the user. Users assigned will not have the access to create, delete, or modify PostgreSQL instances.
This policy grants the user permissions of all PostgreSQL operations that begin with the word "Describe" or "Inquiry". The detailed steps are as follows:
Associate the default policy PostgreSQL with the user as instructed in Authorization Management.{"version": "2.0","statement": [{"action": "postgres:*","resource": "qcs::postgres:ap-shanghai:103xxx1481:DBInstanceId/postgres-0xxxx8e","effect": "allow"}]}
{"version": "2.0","statement": [{"action": "postgres:*","resource": "qcs::postgres:::*","effect": "allow"}]}
{"version": "2.0","statement": [{"action": "postgres:*","resource": ["qcs::postgres::16xxx472:DBInstanceId/postgres-c8xxxa4","qcs::postgres::16xxx472:DBInstanceId/postgres-d8xxxb4",],"effect": "deny"}]}
Last updated:2024-12-04 12:53:23
c can be encrypted from any plaintext m, and its relevance to the plaintext cannot be found in itself.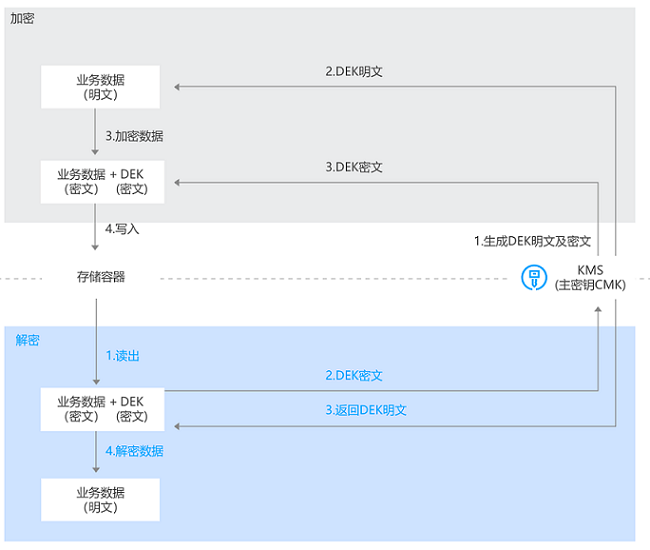
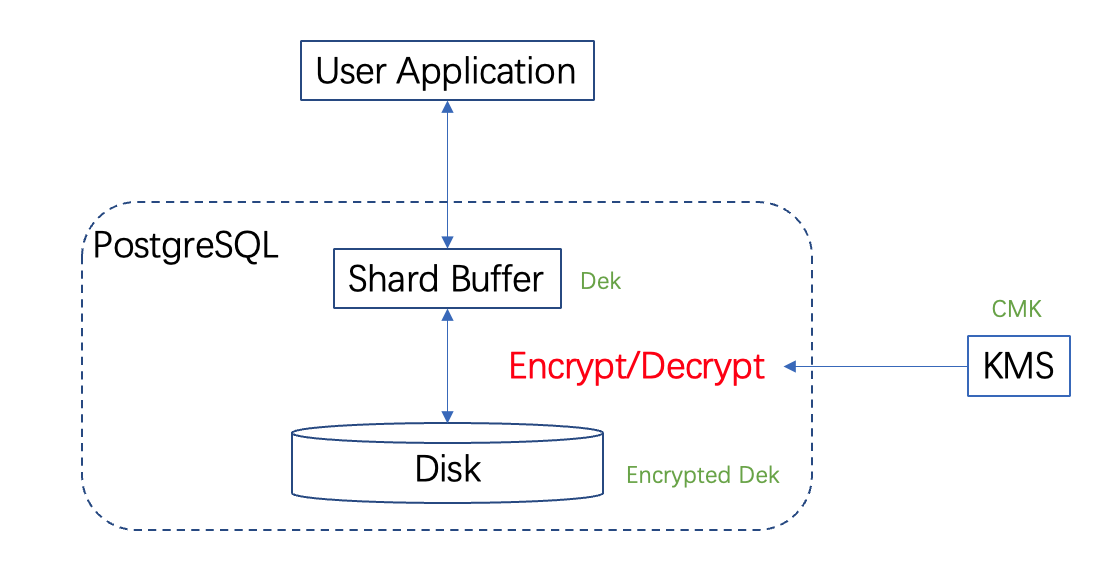
Last updated:2024-12-04 12:52:28
cam:PassRole, kms:GetServiceStatus, and kms:GetRegions permissions. If a permission is not granted, use the root account to grant it to the sub-account.Last updated:2025-02-13 17:02:07
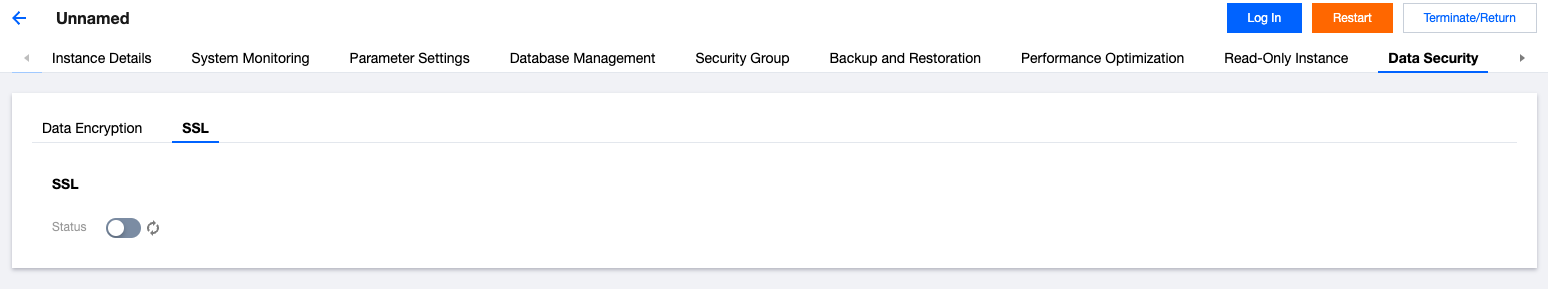
.postgresql folder under the /usr/local/pgsql/ directory.mkdir -p /usr/local/pgsql/.postgresql
ca.pem to the .postgresql folder.[root@VM-0-6-tencentos .postgresql]# lltotal 4-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 2681 Feb 6 11:13 ca.pem
.postgresql folder.chown postgres:postgres /usr/local/pgsql/.postgresql/*chmod 600 /usr/local/pgsql/.postgresql/*
postgres user.[root@VM-0-6-tencentos .postgresql]# export PGSSLROOTCERT="/usr/local/pgsql/.postgresql/ca.pem"[root@VM-0-6-tencentos .postgresql]# echo $PGSSLROOTCERT/usr/local/pgsql/.postgresql/ca.pem
[root@VM-0-6-tencentos .postgresql]# export PGSSLMODE="require"[root@VM-0-6-tencentos .postgresql]# echo $PGSSLMODErequire
[root@VM-0-6-tencentos .postgresql]# psql -h10.6.0.20 -p5432 -Udbadmin -dpostgresPassword for user dbadmin:psql (16.4, server 11.22)SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.3, cipher: TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, compression: off)Type "help" for help.postgres=>
SSL connection, it indicates that the current connection uses SSL encryption..postgresql folder under the /usr/local/pgsql/ directory.mkdir -p /usr/local/pgsql/.postgresql
.postgresql folder.[root@VM-0-6-tencentos .postgresql]# lltotal 8-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 2840 Feb 6 19:55 ca.jks-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 2681 Feb 6 11:13 ca.pem
.postgresql folder.chown postgres:postgres /usr/local/pgsql/.postgresql/*chmod 600 /usr/local/pgsql/.postgresql/*
.pem certificate is as follows. Specific parameters are configured based on your business details.import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.ResultSet;import java.sql.Statement;import java.util.Properties;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {try {Class.forName("org.postgresql.Driver");Properties props = new Properties();props.setProperty("user", "dbadmin");props.setProperty("password", "xxxxxxxx");props.setProperty("ssl", "true");props.setProperty("sslmode", "verify-ca");props.setProperty("sslrootcert", "/usr/local/pgsql/.postgresql/ca.pem");Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:postgresql://10.6.0.10:5432/postgres",props);Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM mytable");while (rs.next()) {System.out.println(rs.getString("id"));}conn.close();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.ResultSet;import java.sql.Statement;import java.util.Properties;public class Main1 {public static void main(String[] args) {try {Class.forName("org.postgresql.Driver");System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.trustStore", "/usr/local/pgsql/.postgresql/ca.jks");System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword","tencentdb_pg");System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.keyStore","/usr/local/pgsql/.postgresql/ca.jks");System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.keyStorePassword","tencentdb_pg");Properties props = new Properties();props.setProperty("user", "dbadmin");props.setProperty("password", "xxxxx");props.setProperty("ssl", "true");props.setProperty("sslmode", "require");props.setProperty("sslfactory", "org.postgresql.ssl.DefaultJavaSSLFactory");Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:postgresql://10.6.0.10:5432/postgres",props);Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM mytable");while (rs.next()) {System.out.println(rs.getString("id"));}conn.close();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}
.postgresql folder under the /usr/local/pgsql/ directory.mkdir -p /usr/local/pgsql/.postgresql
ca.pem to the .postgresql folder.[root@VM-0-6-tencentos .postgresql]# lltotal 4-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 2681 Feb 6 11:13 ca.pem
.postgresql folder.chown postgres:postgres /usr/local/pgsql/.postgresql/*chmod 600 /usr/local/pgsql/.postgresql/*
package mainimport ("database/sql""fmt""log"_ "github.com/lib/pq")func main() {connStr := "user=dbadmin password=Lxh202405! dbname=postgres host=10.6.0.20 port=5432 sslmode=verify-full sslrootcert=/usr/local/pgsql/.postgresql/ca.pem"db, err := sql.Open("postgres", connStr)if err != nil {log.Fatal(err)}err = db.Ping()if err != nil {log.Fatal(err)}fmt.Println("Successfully connected!")}
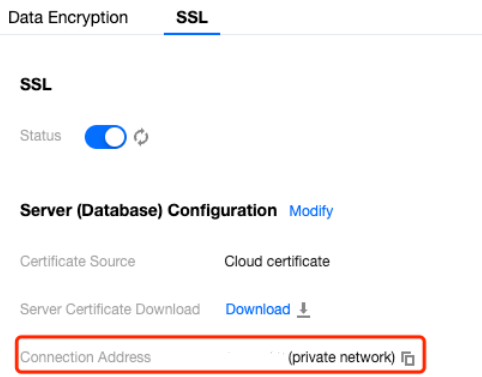
Last updated:2025-03-11 14:29:44
postgres=> \dx;List of installed extensionsName | Version | Schema | Description-----------------------+---------+------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------pg_stat_log | 1.0 | public | track runtime execution statistics of all SQL statements executedpg_stat_statements | 1.9 | public | track planning and execution statistics of all SQL statements executedplpgsql | 1.0 | pg_catalog | PL/pgSQL procedural languagetencentdb_serverless | 1.0 | public | extension for serverless modetencentdb_system_stat | 1.0 | public | track execution statistics of querssy executed(5 rows)
postgres=> show tencentdb_serverless.min_cpu_cores;tencentdb_serverless.min_cpu_cores------------------------------------8(1 row)postgres=> show tencentdb_serverless.max_cpu_cores;tencentdb_serverless.max_cpu_cores------------------------------------8(1 row)
tencentdb_serverless.set_database_cpu_limit(database_name text [, min_cpu_cores numeric(5,1), max_cpu_cores numeric(5,1)])
postgres=> select tencentdb_serverless.set_database_cpu_limit('tenant_001',2,2.5);set_database_cpu_limit------------------------(1 row)
tencentdb_serverless.reset_database_limit(database_name text)
postgres=> select tencentdb_serverless.reset_database_limit('tenant_001');reset_database_limit----------------------(1 row)
tencentdb_serverless.reset_all_database_limit()
postgres=> select tencentdb_serverless.reset_all_database_limit();reset_all_database_limit--------------------------(1 row)
Column name | Meaning |
database_name | The name of the database |
min_cpu_cores | The minimum number of CPU cores that the current database can use |
max_cpu_cores | The maximum number of CPU cores that the current database can use |
min_mem_kilobytes | The maximum memory size that the current database can use, measured in kB. Reserved field, currently not in use. |
max_mem_kilobytes | The maximum memory size that the current database can use, measured in kB. Reserved field, currently not in use. |
postgres=> select * from tencentdb_serverless.resource_limit_view;database_name | min_cpu_cores | max_cpu_cores | min_mem_kilobytes | max_mem_kilobytes---------------+---------------+---------------+-------------------+-------------------tenant_001 | 2.0 | 2.5 | |tenant_002 | 2.0 | 2.5 | |(2 rows)
postgres=> select datname,sum(cpu_usage) as cpu_usage from tencentdb_process_system_usage where datname !='NULL' group by datname;datname | cpu_usage------------+-----------postgres | 3tenant_001 | 1.99tenant_002 | 1(3 rows)
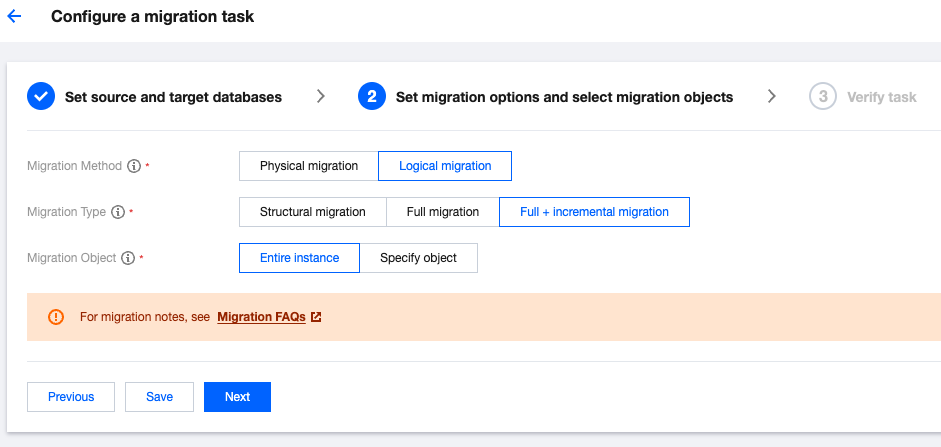
Last updated:2024-12-04 12:50:48
Template | Description | Remarks |
Open all ports | All ports are open. May present security issues. | - |
Open ports 22, 80, 443, and 3389 and the ICMP protocol | Ports 22, 80, 443, and 3389 and the ICMP protocol are opened to the internet. All ports are opened to the private network. | This template does not take effect for TencentDB. |
Custom | You can create a security group and then add custom rules. For detailed directions, please see "Step 2. Add a security group rule" below. | The custom template is recommended. |
Source or Target | Description |
A single IPv4 address or an IPv4 range | In CIDR notation, such as 203.0.113.0, 203.0.113.0/24 or 0.0.0.0/0, where 0.0.0.0/0 indicates all IPv4 addresses will be matched. |
A single IPv6 address or an IPv6 range | In CIDR notation, such as FF05::B5, FF05:B5::/60, ::/0 or 0::0/0, where ::/0 or 0::0/0 indicates all IPv6 addresses will be matched. |
ID of referenced security group. You can reference the ID of: Current security group Other security group | To reference the current security group, please enter the ID of security group associated with the CVM. You can also reference another security group in the same region and belongs to the same project by entering the security group ID. |
- |
Inbound or Outbound | Type | Source | Protocol and Port | Policy |
Inbound | Custom | All IPs: 0.0.0.0/0 Specific IPs: specify IPs or IP ranges | TCP:5432 | Allow |
Last updated:2024-12-04 12:51:31
Last updated:2025-09-10 22:19:27
Metric Name | Monitoring Metric Name | Unit | Metric Type |
CPU utilization | cpu | % | Actual CPU utilization |
used storage space | storage | GB | Instance space size |
Memory Usage | memory | MBytes | Actual memory usage. |
Memory usage | memory_rate | % | Actual memory utilization |
QPS | qps | Times/second | Number of executed SQL statements per second. |
Number of Connections | connections | Counts | Number of database connections during collection. |
Number of requests | read_write_calls | Times | Number of read/write requests in a statistical period. |
Number of read requests | read_calls | Times | Number of read requests in a statistical period. |
Number of write requests | write_calls | Times | Number of write requests in a statistical period. |
Other Requests | other_calls | Times | Number of other requests in a statistical period (requests other than SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE). |
Buffer cache hit rate | hit_percent | % | Hit rate of all SQL statements executed in a statistical period |
Average execution latency | sql_runtime_avg | ms | Average execution latency of all SQL statements in one statistical period. |
Longest TOP10 Execution Latency | sql_runtime_max | ms | Longest TOP10 average execution latency of SQL statements in a statistical period. |
Shortest TOP10 Execution Latency | sql_runtime_min | ms | Shortest TOP10 average execution latency of SQL statements in a statistical period. |
The number of remaining XIDs | remain_xid | Counts | During database collection, display the remaining xid count of the database with the least xid. No such metric for read-only instances. |
Standby log shipping and playback position difference | xlog_diff | Byte | The size difference between logs sent from the primary database to the standby and replay completed reflects the speed of log application on the standby. This metric can help evaluate standby performance and network transmission speed. No such metric for read-only instances. |
Storage Usage | storage_rate | % | Total storage utilization, including temporary files, data files, log files, and other database files. |
Number of Slow Queries | slow_query_cnt | Counts | The number of slow queries in a collection cycle. |
log write delay | xlog_diff | Byte | The size difference between logs sent from the primary database to the standby and replay completed reflects the speed of log application on the standby. This metric can help evaluate standby performance and network transmission speed. No such metric for read-only instances. |
log write time delay | xlog_diff_time | Seconds | The time difference between logs sent from the primary database to the standby and logs received and written to disk. No such metric for read-only instances, and this metric is only available for instance versions 10.x or later. |
Primary-standby data synchronization delay | slave_apply_delay | Byte | The size difference between standby database replay LSN and current LSN of primary instance. For the primary instance, this metric reflects the RTO for fault switch. For read-only instances, it reflects data latency. |
Primary-standby data sync delay time | replay_lag | Seconds | The delay time of data sync between the primary and replica databases. A shorter delay means the primary-replica data is more consistent. During primary database failure, less data is lost after the switch. |
Number of Active Connections | active_conns | Counts | Trigger database collection during instantaneous active connections (non-idle connection). |
Number of idle connections | idle_conns | Counts | Query instantaneous idle connections in the database during collection. |
Number of SQL statements with execution duration exceeding 1 second | long_query | Counts | Number of SQL statements being executed with execution time exceeding 1 second during database collection. |
Number of transactions with execution duration exceeding 1 second | long_xact | Counts | Number of transactions with execution time exceeding 1 second during database collection. |
Number of idle transactions | idle_in_xact | Counts | Number of transactions in idle in transaction state when triggering database collection. |
Number of idle transactions exceeding 5 seconds | long_idle_in_xact | Counts | Number of transactions in idle in transaction state exceeding 5 seconds during database collection. |
Number of waiting sessions | waiting | Counts | Number of database connections in a waiting state. |
Number of sessions waiting exceeding 5 seconds | long_waiting | Counts | The number of database connections with a waiting time exceeding 5 seconds. |
Number of 2PC transactions | 2PC | Counts | Number of 2PC transactions during database collection. |
Number of 2PC transactions unsubmitted for over 5 seconds | long_2pc | Counts | Number of 2PC transactions with execution time exceeding 5 seconds during database collection. |
Number of new connections within 5 seconds | new_conn_in5s | Counts | Query all connection counts established within the last 5 seconds when triggering database collection. |
TPS | tps | Times/second | Number of successful transactions per second (including rollbacks and submissions). |
Number of transaction commits | xact_commit | Times/second | Average transactions per second in a statistical period. |
Transaction rollback count | xact_rollback | Times/second | The average number of rolled-back transactions per second in a statistical period. |
Number of record deletions per second | tup_deleted | Counts | Average number of tuples deletions per second in a statistical period. No Such Metric for read-only instances. |
Number of insertions per second | tup_inserted | Counts | Average number of tuples insertions per second in a statistical period. No Such Metric for read-only instances. |
Number of record updates per second | tup_updated | Counts | Average number of tuples updates per second in a statistical period. No Such Metric for read-only instances. |
Number of index scan records per second | tup_fetched | Counts | Average number of index scan tuples per second in a statistical period. |
Number of full-table scan records per second | tup_returned | Counts | The number of full-table scan tuples per second in a statistical period. |
Number of deadlocks | deadlocks | Counts | Number of deadlocks in a statistical period. |
log file size | log_file_size | GB | WAL log file occupied space size. |
Size of data files | data_file_size | GB | Data file occupied space size. |
Temporary file size | temp_file_size | MB | Temporary file size. |
throughput rate | throughput | KBytes/s | Disk read/write speed per instance per second. |
Read Throughput | throughput_read | KBytes/s | Instance disk read speed per second. |
Write Throughput | throughput_write | KBytes/s | Disk write speed per instance per second. |
connection utilization | conn_utilization | % | Current number of instance connections/Maximum number of connections. |
instance port inbound traffic | cluster_in_flow | KBytes/s | Inbound traffic on the database instance listening port. |
instance port outbound traffic | cluster_out_flow | KBytes/s | Outbound traffic on the database instance listening port. |
Last updated:2024-01-24 11:20:59
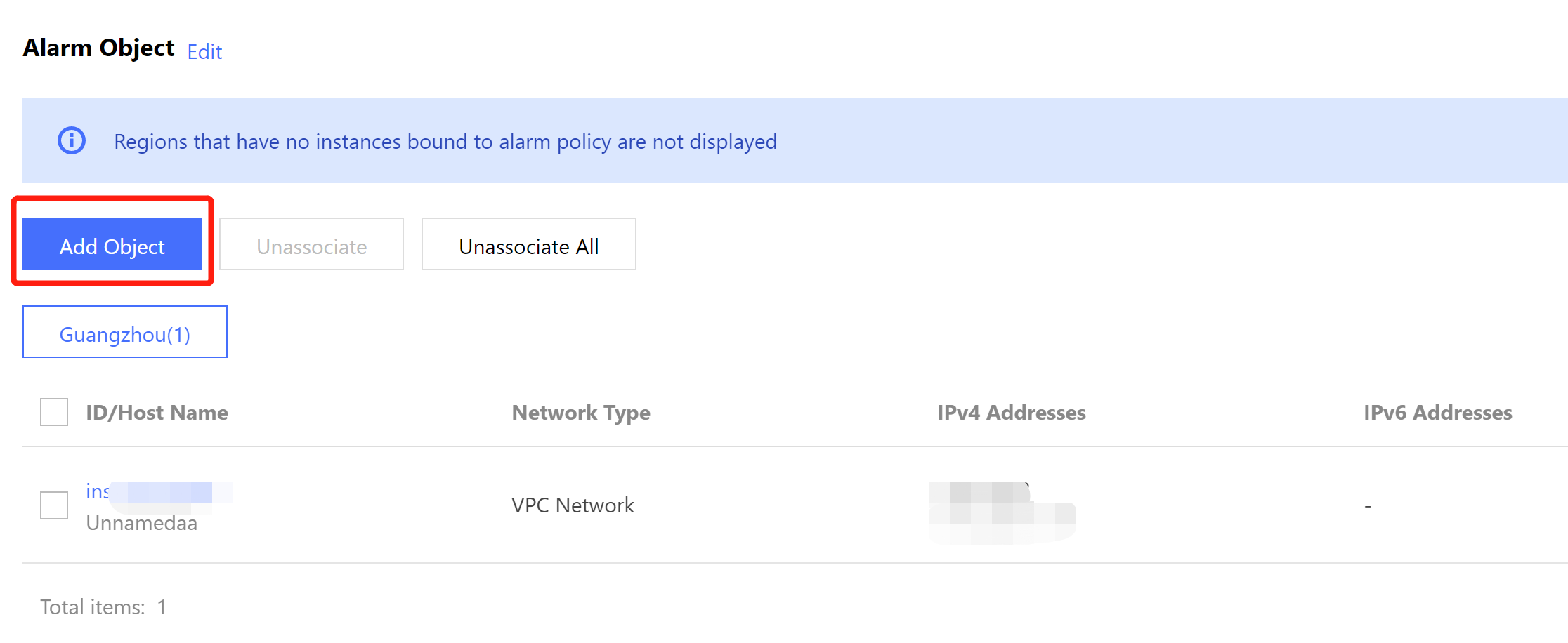
Last updated:2024-01-24 11:20:59
Tag Key | Tag Value |
Business | Game 1, game 2, and game 3 |
OPS owner | John, Jane, and Harry |
instance-id | Business | OPS Owner |
postgres-abcdef1 | Game 1 | Harry |
postgres-abcdef2 | Game 2 | Jane |
postgres-abcdef3 | Game 3 | John |
Last updated:2025-09-10 22:15:38