Modifying Data Replication Mode
Last updated:2025-05-21 15:53:27
Supported Methods to Replicate Data
Database instance replication refers to the process of synchronizing data by configuring one or more backup databases for the server, distributing PostgreSQL data across multiple systems. TencentDB for PostgreSQL supports two kinds of data replication methods: asynchronous replication and semi-synchronous replication.
Asynchronous Replication
Asynchronous replication for TencentDB for PostgreSQL adopts the one-master-one-standby architecture.
After receiving a data update (including insert, update and delete operations) request from an application, the master performs the update operation. When the update is completed, the master immediately responds to the application and replicates the data to the slave.
In the process of data update, the master does not need to wait for the response of the slave. Therefore, the database instances of asynchronous replication usually have higher performance (for specific performance, see Test Results), and the unavailability of the slave does not affect the service provided by the master. However, because the data is not synchronized to the slave in real time, if a fault occurs on the master while the slave is delayed and a switch occurs, there is a slight chance of causing data inconsistency.
Note:
By default, TencentDB for PostgreSQL adopts asynchronous replication for data replication.
Semi-synchronous Replication
Semi-synchronous replication of TencentDB for PostgreSQL adopts a one-master-one-standby architecture.
An application initiates a data update request (including insert, update, delete operations). After the master completes the update operation, it immediately replicates the data to the slave. Only after the slave receives the data and writes it to the WAL (without executing), it returns a success message to the master. The master must only return a response to the application program after receiving the success message from the slave.
Only when an exception occurs in data replication (the Slave node is unavailable or an exception occurs in the network used for data replication), the Master will pause (about 10 seconds by default in PostgreSQL) responding to the application. The system will downgrade the replication mode to asynchronous replication. When data replication returns to normal, the system will restore the replication mode to semi-synchronous replication.
Degradation Description
The operation in which the system automatically changes the data replication mode from semi-synchronous replication to asynchronous replication according to specified conditions is called degradation. Degradation includes two situations: fault degradation and delayed degradation.
Fault Degradation
If the current primary-backup data replication mode of TencentDB for PostgreSQL is semi-synchronous, when an exception occurs in data replication (the Slave node is unavailable or an exception occurs in the network used for data replication), the Master will pause responding to the application (about 10 seconds by default in TencentDB for PostgreSQL) and downgrade the primary-backup replication mode to asynchronous to ensure system availability. When the high-availability system detects that data replication has returned to normal, it will restore the primary-backup data replication mode to semi-synchronous.
Note:
Failure degradation is the default behavior of the high-availability system of TencentDB for PostgreSQL. To ensure system high availability, customizing is not supported at present.
Latency Degradation
If you have specific needs, you can enable latency degradation under semi-synchronous replication. Once delayed degradation is enabled, TencentDB for PostgreSQL's high-availability system will determine the master-slave replication latency based on the conditions you have set. Exceeding the latency will trigger semi-synchronous degradation to asynchronous. It is recommended that only this feature be enabled for highly latency-sensitive businesses.
The conditions for latency degradation are the size or time of master-slave synchronization. You can refer to the metrics of log write delay (bytes) and log write time delay (seconds) on the standby database. For more details, see Master/Slave Latency Monitoring Metrics.
Failover Description
When the primary/replica replication mode of an instance is asynchronous replication or semi-synchronous replication downgrades to asynchronous replication, a primary/standby switch will be triggered if the Master fails and cannot be recovered. Since data is not synchronized to the Slave in real time, there is a slight chance of data inconsistency after the switch. TencentDB for PostgreSQL enables you to flexibly set the failover conditions. By default, switching is allowed when both primary/replica delay <= 10240 MB and primary/secondary delay <= 10 seconds are met. It is advisable that you make settings only when you have special business needs.
Modifying Data Replication Mode
1. Log in to the PostgreSQL Console. In the instance list, click the Instance ID or Operation in the Manage column to open the instance details page.
2. In the Availability Info section of the instance details, detailed availability information of the instance is displayed.
2.1 When the data replication mode is asynchronous, the specific display information is as follows:
Information | Description |
Data Replication Mode | For the data synchronization mode between the master and the slave, the current two-machine high availability (one master and one slave) architecture supports Async ( Asynchronous replication )and Semi-Sync ( Semi-synchronous replication ). |
Instance Status | Display the current accessibility status of the instance. When the status is normal, normally receive user requests. If an abnormal display occurs, it indicates that the instance currently cannot receive application requests. |
| |
Failover Condition | When the Master node fails and cannot be recovered, automatic failover is required, with the Slave providing services. At this point, the system defines the failover conditions, which are the size and time of primary-backup latency. The default system conditions are less than or equal to 10240 MB and 10 seconds. For specific switch conditions, refer to Failover Description. |
Primary AZ | It refers to the availability zone of the master node. |
Standby AZ | It refers to the availability zone of the slave node. |
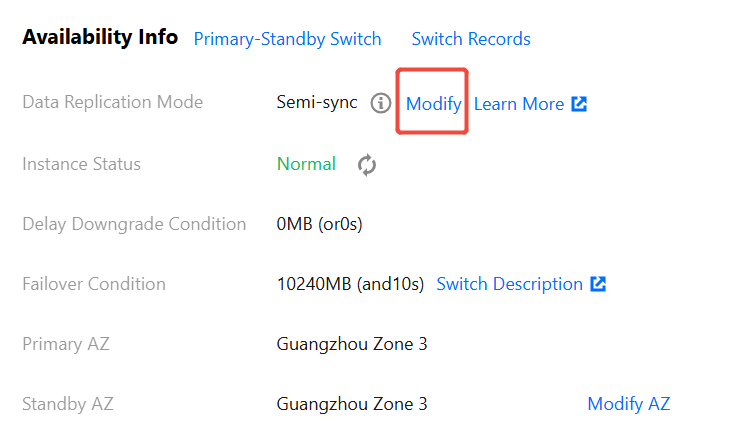
2.2 The specific display information is as follows when the data replication mode is semi-synchronous:
Information | Description |
Data Replication Mode | For the data synchronization mode between the master and the slave, the current two-machine high availability (one master and one slave) architecture supports Async ( Asynchronous replication )and Semi-Sync ( Semi-synchronous replication ). |
Instance Status | It displays the current accessibility status of the instance. When the status is normal, user requests are normally received. If the status is abnormal, the instance currently cannot accept application requests. |
Delay Downgrade Condition | When the data replication mode of the instance is semi-synchronous replication, the system will automatically degrade the master and slave replication method to asynchronous to ensure system availability outside the range of user-set conditions. This degradation condition is the master and standby latency size or latency time. Among them, PostgreSQL instances with a large version number of 9 only support the condition of master and standby latency size. For details, see Degradation Description. |
Failover Condition | When the master node fails and cannot be recovered, an automatic failover is required, to switch to the slave to provide service. At this time, the system has defined the failover conditions, which are the size or time of master-slave latency. Applications can modify the switch conditions based on special needs. For details, see Failover Description. |
Primary AZ | It refers to the availability zone of the master node. |
Standby AZ | It refers to the availability zone of the slave node. |
3. Click Modify to change the current instance's data replication mode.
Note:
Changes to the data replication mode are effective immediately, and modifying the data method may cause a master/slave switch. There will be a momentary disconnection during the master/slave switch, please ensure the application is reconnected.
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

