Cluster-Level High Availability
Last updated:2025-12-24 14:51:17
Cross-AZ Deployment of TDMQ for Apache Pulsar
TDMQ for Apache Pulsar supports cross-AZ deployment. When you purchase a TDMQ for Apache Pulsar cluster in a region with 3 or more availability zones (AZs), you can select up to 3 AZs to purchase a cross-AZ instance. The partition replicas of such an instance are forcibly distributed across nodes in different AZs. This deployment method ensures that the instance continues to provide services normally, even if a single AZ becomes unavailable.
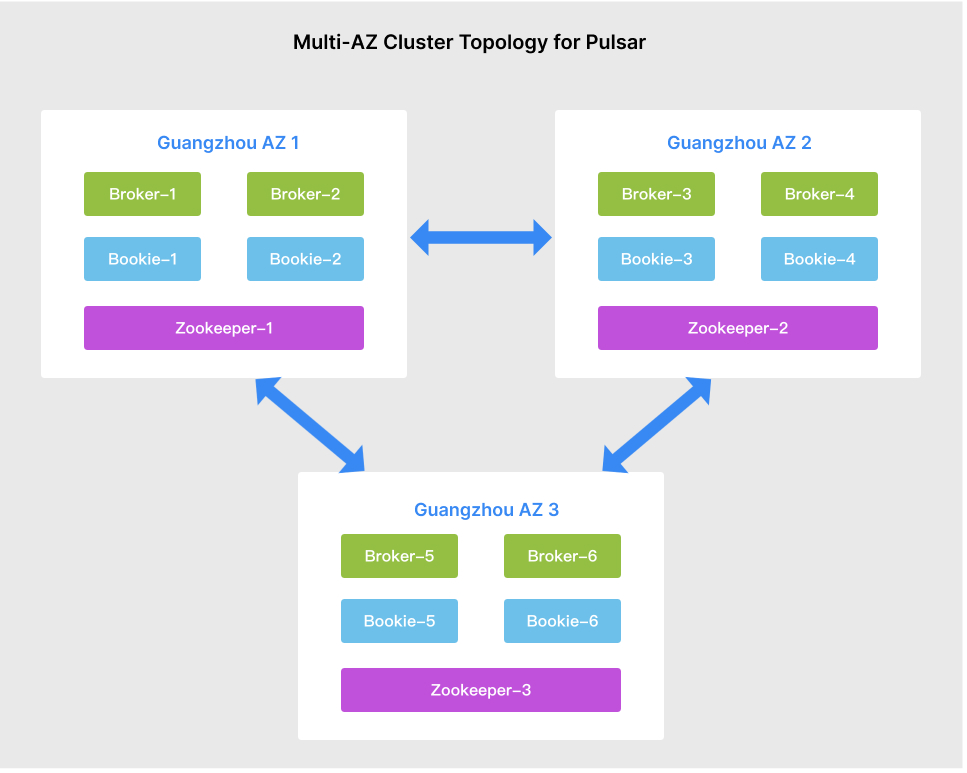
Cross-AZ Deployment Principles
Cross-AZ disaster recovery of TDMQ for Apache Pulsar is achieved through the principle of rack awareness. That is, service nodes of different components are deployed to different racks in different AZs. However, it remains a single TDMQ for Apache Pulsar cluster essentially.
Rack awareness is a type of ensemble placement policy. It is an algorithm used by the BookKeeper client to select ensembles, primarily based on network topology properties.
Bookie Selection
When a bookie cluster is deployed, it registers a temporary zk-node with ZooKeeper. The BookKeeper client discovers the list of bookie nodes through ZooKeeper (watcher). When bookie nodes are changed (for example, crashes), the ensemble placement policy is notified through the onClusterChanged(Set, Set) API. Then, a new network topology is reconstructed, and subsequent operations (such as newEnsemble) are generated based on the new network topology.
NetworkTopology
The network topology uses a tree-like hierarchical structure to represent bookie nodes in a cluster. A bookie cluster can consist of multiple data centers (regions). A data center contains servers distributed across different racks. In the tree structure, the leaf nodes represent bookie information.
Example 1: Region A has three bookie nodes: bk1, bk2, and bk3. Their network locations are /region-a/rack-1/bk1, /region-a/rack-1/bk2, and /region-a/rack-2/bk3, respectively. The network topology is as follows:
root|region-a/ \\rack-1 rack-2/ \\ \\bk1 bk2 bk3
Example 2: Region A and region B have four bookie nodes: bk1, bk2, bk3, and bk4. Their network locations are /region-a/rack-1/bk1, /region-a/rack-1/bk2, /region-b/rack-2/bk3, and /region-b/rack-2/bk4, respectively. The network topology is as follows:
root/ \\region-a region-b| |rack-1 rack-2/ \\ / \\bk1 bk2 bk3 bk4
The network location is resolved through DNSToSwitchMapping, which resolves a domain name or IP address to a network location. The network location should be in the format of /region/rack, where / indicates root, region indicates a data center, and rack indicates rack information.
Note:
In TDMQ for Apache Pulsar, DNSToSwitchMapping is implemented using BookieRackAffinityMapping. The rack information is stored through ZooKeeper. Only the rack-aware capability is implemented.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cross-AZ Deployment
Advantages
It can significantly enhance the disaster recovery capability of a cluster. When force majeure risks, such as unexpected network instability or power outages/restarts occur in a single AZ, it ensures that clients can resume message production and consumption after a brief reconnection wait.
Disadvantages
Cross-AZ deployment will inevitably increase cross-AZ synchronization latency. The cross-AZ latency in major regions, such as Guangzhou, Shanghai, and Beijing, typically ranges from 10 ms to 40 ms.
Usage Instructions
Was this page helpful?
You can also Contact Sales or Submit a Ticket for help.
Yes
No
Feedback

