- Release Notes and Announcements
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Quick Start
- Cloud Product Monitoring
- Tencent Cloud Service Metrics
- CVM
- CBS
- TencentDB
- TencentDB for SQL Server Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for MySQL Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for Redis Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for MongoDB Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for PostgreSQL Monitoring Metrics
- TDSQL-C for MySQL Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for TcaplusDB Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for MariaDB Monitoring Metrics
- TDSQL for MySQL Monitoring Metrics (Legacy)
- TDSQL for MySQL Monitoring Metrics
- SCF
- CKafka
- TDMQ
- VPC
- NAT Gateway Monitoring Metrics
- VPN Gateway Monitoring Metrics
- VPN Tunnel Monitoring Metrics
- Direct Connect Gateway Monitoring Metrics
- CCN Monitoring Metrics
- Peering Connection Monitoring Metrics
- Bandwidth Packet Monitoring Metrics
- EIP Monitoring Metrics
- Anycast EIP Monitoring Metrics
- Network Detection Monitoring Metrics
- CLB
- COS
- CFS
- CPM
- ECM
- EMR
- CDN
- Edge Security Acceleration Platform EdgeOne
- Direct Connect
- TKE
- GAAP
- CMQ
- API Gateway
- Elasticsearch
- WAF
- CLS
- Tencent Cloud Service Metrics
- Operation Guide
- Prometheus Monitoring
- Best Practice
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- Monitoring Data Query APIs
- Alarm APIs
- DescribeAlarmHistories
- CreateAlarmPolicy
- DeleteAlarmPolicy
- DescribeAlarmPolicies
- DescribeAlarmPolicy
- ModifyAlarmPolicyStatus
- SetDefaultAlarmPolicy
- BindingPolicyObject
- UnBindingPolicyObject
- UnBindingAllPolicyObject
- ModifyAlarmPolicyCondition
- ModifyAlarmPolicyNotice
- ModifyAlarmPolicyTasks
- DescribeMonitorTypes
- DescribeAllNamespaces
- DescribeAlarmMetrics
- DescribeAlarmEvents
- DescribeBindingPolicyObjectList
- ModifyAlarmPolicyInfo
- DescribeConditionsTemplateList
- Legacy Alert APIs
- Notification Template APIs
- Prometheus Service APIs
- DescribePrometheusInstanceUsage
- DescribeServiceDiscovery
- CreateServiceDiscovery
- UpdateAlertRuleState
- UpdateAlertRule
- DescribeAlertRules
- DeleteAlertRules
- CreateAlertRule
- DescribePrometheusInstances
- UpgradeGrafanaDashboard
- UpdatePrometheusScrapeJob
- UpdatePrometheusAgentStatus
- UpdateExporterIntegration
- UninstallGrafanaDashboard
- UnbindPrometheusManagedGrafana
- TerminatePrometheusInstances
- ModifyPrometheusInstanceAttributes
- GetPrometheusAgentManagementCommand
- DestroyPrometheusInstance
- DescribePrometheusScrapeJobs
- DescribePrometheusAgents
- DescribeExporterIntegrations
- DeletePrometheusScrapeJobs
- DeleteExporterIntegration
- CreatePrometheusScrapeJob
- CreatePrometheusAgent
- CreateExporterIntegration
- BindPrometheusManagedGrafana
- UpdateRecordingRule
- DescribeRecordingRules
- DeleteRecordingRules
- CreateRecordingRule
- CreatePrometheusMultiTenantInstancePostPayMode
- DescribePrometheusZones
- Grafana Service APIs
- UpgradeGrafanaInstance
- UpdateSSOAccount
- UpdateGrafanaWhiteList
- UpdateGrafanaNotificationChannel
- UpdateGrafanaIntegration
- UpdateGrafanaEnvironments
- UpdateGrafanaConfig
- UpdateDNSConfig
- UninstallGrafanaPlugins
- ResumeGrafanaInstance
- ModifyGrafanaInstance
- InstallPlugins
- EnableSSOCamCheck
- EnableGrafanaSSO
- EnableGrafanaInternet
- DescribeSSOAccount
- DescribeInstalledPlugins
- DescribeGrafanaWhiteList
- DescribeGrafanaNotificationChannels
- DescribeGrafanaIntegrations
- DescribeGrafanaInstances
- DescribeGrafanaEnvironments
- DescribeGrafanaConfig
- DescribeDNSConfig
- DeleteSSOAccount
- DeleteGrafanaNotificationChannel
- DeleteGrafanaIntegration
- DeleteGrafanaInstance
- CreateSSOAccount
- CreateGrafanaNotificationChannel
- CreateGrafanaIntegration
- CreateGrafanaInstance
- CleanGrafanaInstance
- DescribeGrafanaChannels
- Event Center APIs
- TencentCloud Managed Service for Prometheus APIs
- CheckIsPrometheusNewUser
- CreatePrometheusTemp
- CreatePrometheusAlertPolicy
- CreatePrometheusClusterAgent
- CreatePrometheusGlobalNotification
- DeletePrometheusTemp
- DeletePrometheusTempSync
- DeletePrometheusAlertPolicy
- DeletePrometheusClusterAgent
- DescribePrometheusAgentInstances
- DescribePrometheusAlertPolicy
- DescribePrometheusInstanceDetail
- DescribePrometheusClusterAgents
- DescribePrometheusInstanceInitStatus
- DescribePrometheusGlobalConfig
- DescribePrometheusInstancesOverview
- DescribePrometheusGlobalNotification
- DescribePrometheusRecordRules
- DescribePrometheusTemp
- DescribePrometheusTempSync
- DescribePrometheusTargetsTMP
- ModifyPrometheusTemp
- ModifyPrometheusAgentExternalLabels
- ModifyPrometheusAlertPolicy
- ModifyPrometheusGlobalNotification
- RunPrometheusInstance
- DescribeClusterAgentCreatingProgress
- SyncPrometheusTemp
- Monitoring APIs
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- Troubleshooting
- FAQs
- Alarm Management
- Documentation Guide
- Policy
- Glossary
- Release Notes and Announcements
- Product Introduction
- Purchase Guide
- Quick Start
- Cloud Product Monitoring
- Tencent Cloud Service Metrics
- CVM
- CBS
- TencentDB
- TencentDB for SQL Server Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for MySQL Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for Redis Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for MongoDB Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for PostgreSQL Monitoring Metrics
- TDSQL-C for MySQL Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for TcaplusDB Monitoring Metrics
- TencentDB for MariaDB Monitoring Metrics
- TDSQL for MySQL Monitoring Metrics (Legacy)
- TDSQL for MySQL Monitoring Metrics
- SCF
- CKafka
- TDMQ
- VPC
- NAT Gateway Monitoring Metrics
- VPN Gateway Monitoring Metrics
- VPN Tunnel Monitoring Metrics
- Direct Connect Gateway Monitoring Metrics
- CCN Monitoring Metrics
- Peering Connection Monitoring Metrics
- Bandwidth Packet Monitoring Metrics
- EIP Monitoring Metrics
- Anycast EIP Monitoring Metrics
- Network Detection Monitoring Metrics
- CLB
- COS
- CFS
- CPM
- ECM
- EMR
- CDN
- Edge Security Acceleration Platform EdgeOne
- Direct Connect
- TKE
- GAAP
- CMQ
- API Gateway
- Elasticsearch
- WAF
- CLS
- Tencent Cloud Service Metrics
- Operation Guide
- Prometheus Monitoring
- Best Practice
- API Documentation
- History
- Introduction
- API Category
- Making API Requests
- Monitoring Data Query APIs
- Alarm APIs
- DescribeAlarmHistories
- CreateAlarmPolicy
- DeleteAlarmPolicy
- DescribeAlarmPolicies
- DescribeAlarmPolicy
- ModifyAlarmPolicyStatus
- SetDefaultAlarmPolicy
- BindingPolicyObject
- UnBindingPolicyObject
- UnBindingAllPolicyObject
- ModifyAlarmPolicyCondition
- ModifyAlarmPolicyNotice
- ModifyAlarmPolicyTasks
- DescribeMonitorTypes
- DescribeAllNamespaces
- DescribeAlarmMetrics
- DescribeAlarmEvents
- DescribeBindingPolicyObjectList
- ModifyAlarmPolicyInfo
- DescribeConditionsTemplateList
- Legacy Alert APIs
- Notification Template APIs
- Prometheus Service APIs
- DescribePrometheusInstanceUsage
- DescribeServiceDiscovery
- CreateServiceDiscovery
- UpdateAlertRuleState
- UpdateAlertRule
- DescribeAlertRules
- DeleteAlertRules
- CreateAlertRule
- DescribePrometheusInstances
- UpgradeGrafanaDashboard
- UpdatePrometheusScrapeJob
- UpdatePrometheusAgentStatus
- UpdateExporterIntegration
- UninstallGrafanaDashboard
- UnbindPrometheusManagedGrafana
- TerminatePrometheusInstances
- ModifyPrometheusInstanceAttributes
- GetPrometheusAgentManagementCommand
- DestroyPrometheusInstance
- DescribePrometheusScrapeJobs
- DescribePrometheusAgents
- DescribeExporterIntegrations
- DeletePrometheusScrapeJobs
- DeleteExporterIntegration
- CreatePrometheusScrapeJob
- CreatePrometheusAgent
- CreateExporterIntegration
- BindPrometheusManagedGrafana
- UpdateRecordingRule
- DescribeRecordingRules
- DeleteRecordingRules
- CreateRecordingRule
- CreatePrometheusMultiTenantInstancePostPayMode
- DescribePrometheusZones
- Grafana Service APIs
- UpgradeGrafanaInstance
- UpdateSSOAccount
- UpdateGrafanaWhiteList
- UpdateGrafanaNotificationChannel
- UpdateGrafanaIntegration
- UpdateGrafanaEnvironments
- UpdateGrafanaConfig
- UpdateDNSConfig
- UninstallGrafanaPlugins
- ResumeGrafanaInstance
- ModifyGrafanaInstance
- InstallPlugins
- EnableSSOCamCheck
- EnableGrafanaSSO
- EnableGrafanaInternet
- DescribeSSOAccount
- DescribeInstalledPlugins
- DescribeGrafanaWhiteList
- DescribeGrafanaNotificationChannels
- DescribeGrafanaIntegrations
- DescribeGrafanaInstances
- DescribeGrafanaEnvironments
- DescribeGrafanaConfig
- DescribeDNSConfig
- DeleteSSOAccount
- DeleteGrafanaNotificationChannel
- DeleteGrafanaIntegration
- DeleteGrafanaInstance
- CreateSSOAccount
- CreateGrafanaNotificationChannel
- CreateGrafanaIntegration
- CreateGrafanaInstance
- CleanGrafanaInstance
- DescribeGrafanaChannels
- Event Center APIs
- TencentCloud Managed Service for Prometheus APIs
- CheckIsPrometheusNewUser
- CreatePrometheusTemp
- CreatePrometheusAlertPolicy
- CreatePrometheusClusterAgent
- CreatePrometheusGlobalNotification
- DeletePrometheusTemp
- DeletePrometheusTempSync
- DeletePrometheusAlertPolicy
- DeletePrometheusClusterAgent
- DescribePrometheusAgentInstances
- DescribePrometheusAlertPolicy
- DescribePrometheusInstanceDetail
- DescribePrometheusClusterAgents
- DescribePrometheusInstanceInitStatus
- DescribePrometheusGlobalConfig
- DescribePrometheusInstancesOverview
- DescribePrometheusGlobalNotification
- DescribePrometheusRecordRules
- DescribePrometheusTemp
- DescribePrometheusTempSync
- DescribePrometheusTargetsTMP
- ModifyPrometheusTemp
- ModifyPrometheusAgentExternalLabels
- ModifyPrometheusAlertPolicy
- ModifyPrometheusGlobalNotification
- RunPrometheusInstance
- DescribeClusterAgentCreatingProgress
- SyncPrometheusTemp
- Monitoring APIs
- Data Types
- Error Codes
- Troubleshooting
- FAQs
- Alarm Management
- Documentation Guide
- Policy
- Glossary
CVM Disk Is Read-Only
Last updated: 2020-07-01 11:47:43
This document is currently invalid. Please refer to the documentation page of the product.
Overview
This document describes how to troubleshoot the problem of disks being read-only.
Troubleshooting Approaches
- Check the disk usage to see whether the disk is full.
- Check whether the inode resource of the disk is exhausted (for Linux CVM instances).
- Check whether a disk hardware component is faulty.
Locating and Troubleshooting the Problem
Windows CVM instances
Log in to the Windows CVM instance and perform the following operations.
Disk is full
- In the disk properties dialog box, check whether the disk space is exhausted.
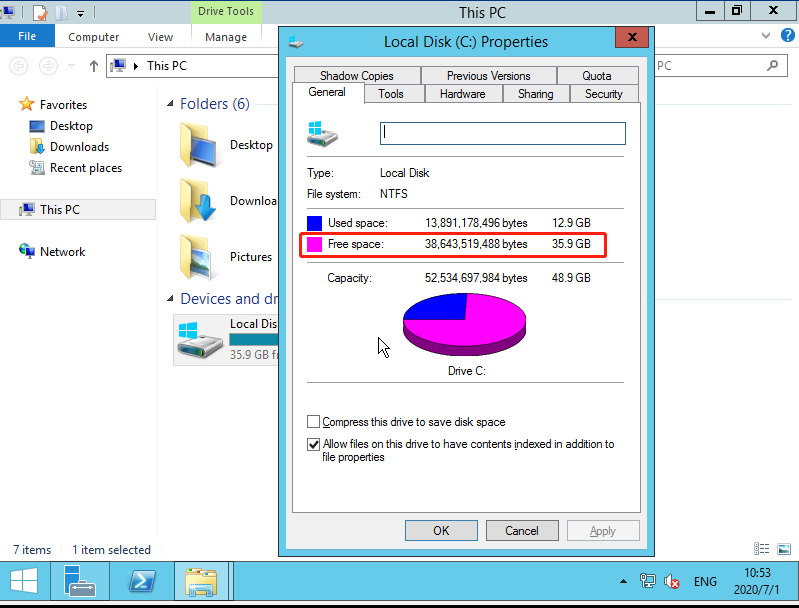
- If the disk space is exhausted, access the disk and delete unnecessary files.
If the disk is full or files cannot be deleted due to an increase in the business volume, we recommend that you expand CBS cloud disks.
Hardware failure
If the failure is caused by a faulty hardware component or other problems, submit a ticket.
Linux CVM instances
Log in to the Linux CVM instance and perform the following operations.
Disk is full
- Run the following command to check the disk usage.
df -m - If the disk usage has reached 100%, access the directory that is already full and run the following command to check the sizes of the files in the directory.
du -f - Delete unnecessary files to release disk space as needed. You can run the following command to delete unnecessary files. To do this, you need to replace
file_namewith the specific file name. We recommend that you do not delete non third-party files.rm -rf file_nameIf the disk is full or files cannot be deleted due to an increase in the business volume, we recommend that you expand CBS cloud disks.
The inode resource has been exhausted
If the disk usage has not reached 100% but the inode resource has been exhausted, it is generally because the generation of many small files exhausted the inode resource.
- Run the following command to check the inode usage.
df -i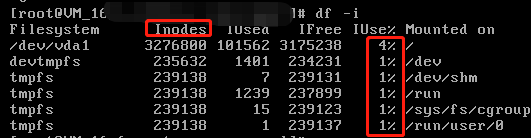
In Linux, the partition for the root directory is generally small. If small files are periodically generated and not cleared in a timely manner, the inode resource will soon be exhausted. If the inode resource usage has reached 100%, complete the following steps:
i. Run the following command to identify the directory with the largest number of files.for i in /*; do echo $i; find $i | wc -l; doneIf the directory is known, replace
/*with the specific directory.ii. More files will consume more inodes. Therefore, access the directory with many files and run the following command to delete unnecessary files. To do this, you need to replace
file_namewith the specific file name. We recommend that you do not delete non third-party files.rm -rf file_nameIf the disk is full or files cannot be deleted due to an increase in the business volume, we recommend that you expand CBS cloud disks.
Hardware failure
If the hardware failure is caused by a faulty hardware component or other problems, submit a ticket.

 Yes
Yes
 No
No
Was this page helpful?