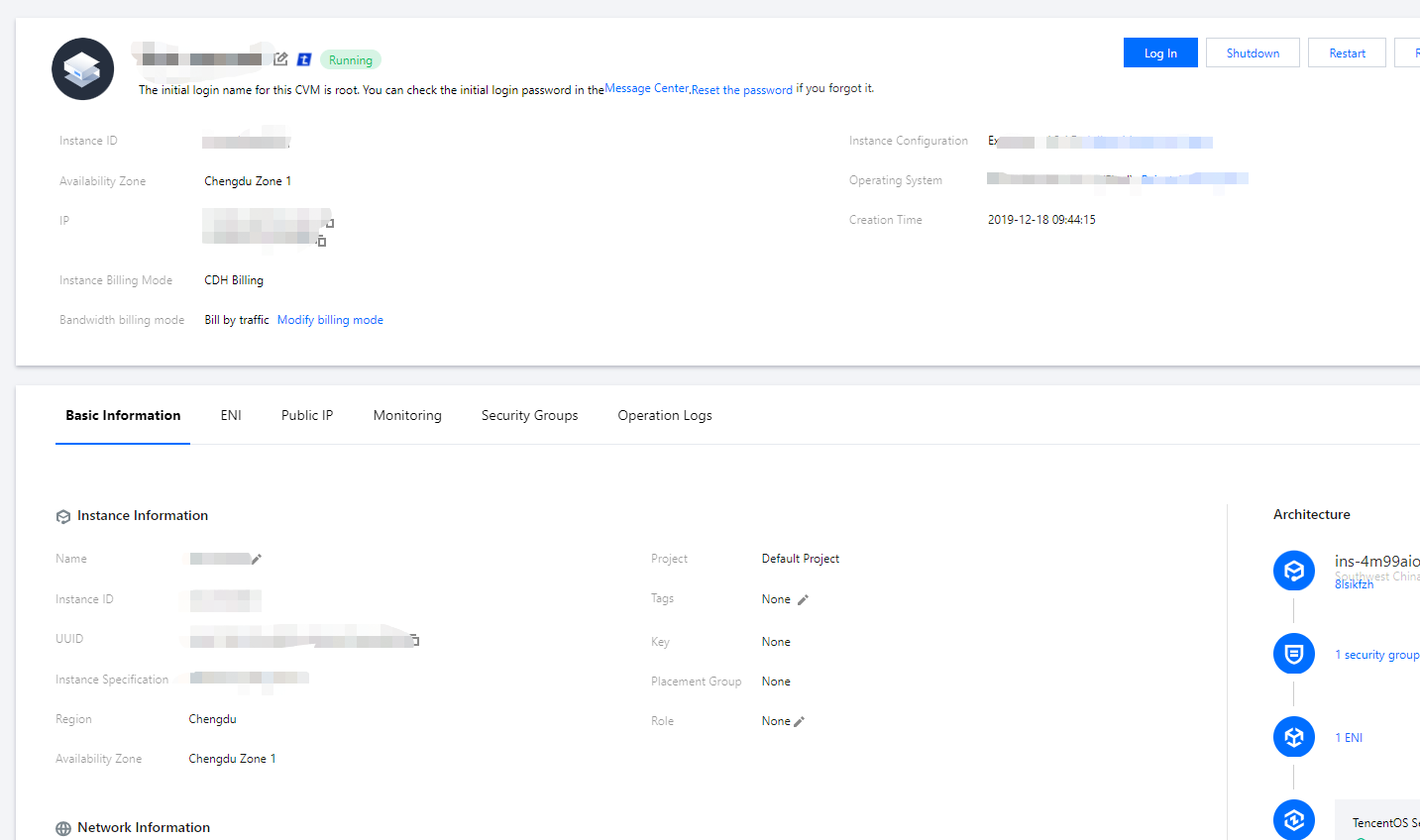
Cloud Virtual Machine
User Guide
Product Documentation


Copyright Notice
©2013-2025 Tencent Cloud. All rights reserved.
Copyright in this document is exclusively owned by Tencent Cloud. You must not reproduce, modify, copy or distribute in any way, in whole or in part, the contents of this document without Tencent Cloud's the prior written consent.
Trademark Notice

All trademarks associated with Tencent Cloud and its services are owned by the Tencent corporate group, including its parent, subsidiaries and affiliated companies, as the case may be. Trademarks of third parties referred to in this document are owned by their respective proprietors.
Service Statement
This document is intended to provide users with general information about Tencent Cloud's products and services only and does not form part of Tencent Cloud's terms and conditions. Tencent Cloud's products or services are subject to change. Specific products and services and the standards applicable to them are exclusively provided for in Tencent Cloud's applicable terms and conditions.
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
Last updated:2025-09-04 15:31:52
Model | Instance Type | Number of ENIs | |||||||||
| | CPU: 1 core | CPU: 2 cores | CPU: 4 cores | CPU: 6 cores | CPU: 8 cores | CPU: 10 cores | CPU: 12 cores | CPU: 14 cores | CPU: 16 cores | CPU: >16 cores |
Standard | Standard S5 | 2 | 4 | 4 | - | 6 | - | - | - | 8 | 8 |
| Standard Storage Optimized S5se | - | - | 4 | - | 6 | - | - | - | 8 | 8 |
| Standard SA2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | - | 6 | - | - | - | 8 | 8 |
| Standard S4 | 2 | 4 | 4 | - | 6 | - | - | - | 8 | 8 |
| Standard Network-optimized SN3ne | 2 | 4 | 4 | - | 6 | - | 8 | - | 8 | 8 |
| Standard S3 | 2 | 4 | 4 | - | 6 | - | 8 | - | 8 | 8 |
| Standard SA1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | - | 6 | - | - | - | 8 | 8 |
| Standard S2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | - | 6 | - | 8 | - | 8 | 8 |
| Standard S1 | 2 | 4 | 4 | - | 6 | - | 8 | - | 8 | 8 |
High IO | High IO IT5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 8 | 8 |
| High IO IT3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 8 | 8 |
Memory Optimized | Memory Optimized M5 | 2 | 4 | 4 | - | 6 | - | 8 | - | 8 | 8 |
| Memory Optimized M4 | 2 | 4 | 4 | - | 6 | - | 8 | - | 8 | 8 |
| Memory Optimized M3 | 2 | 4 | 4 | - | 6 | - | 8 | - | 8 | 8 |
| Memory Optimized M2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | - | 6 | - | 8 | - | 8 | 8 |
| Memory Optimized M1 | 2 | 4 | 4 | - | 6 | - | 8 | - | 8 | 8 |
Compute | Compute Optimized C4 | - | - | 4 | - | 6 | - | - | - | 8 | 8 |
| Compute Network-optimized CN3 | - | - | 4 | - | 6 | - | - | - | 8 | 8 |
| Compute C3 | - | - | 4 | - | 6 | - | - | - | 8 | 8 |
| Compute C2 | - | - | 4 | - | 6 | - | - | - | 8 | 8 |
GPU-based | GPU Compute GN6 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 8 |
| GPU Compute GN6S | - | - | 4 | - | 6 | - | - | - | - | - |
| GPU Compute GN7 | - | - | 4 | - | 6 | - | - | - | - | 8 |
| GPU Compute GN8 | - | - | - | 4 | - | - | - | 8 | - | 8 |
| GPU Compute GN10X | - | - | - | - | 6 | - | - | - | - | 8 |
| GPU Compute GN10Xp | - | - | - | - | - | 6 | - | - | - | 8 |
FPGA-based | FPGA Accelerated FX4 | - | - | - | - | - | 6 | - | - | - | 8 |
Big Data | Big Data D3 | - | - | - | - | 6 | - | - | - | 8 | 8 |
| Big Data D2 | - | - | - | - | 6 | - | - | - | 8 | 8 |
| Big Data D1 | - | - | - | - | 6 | - | - | - | - | 8 |
CPM | | Not supported | | | | | | | | | |
Model | Instance Type | Private IPs bound to a single ENI | |||||||||
| | CPU: 1 core | CPU: 2 cores | CPU: 4 cores | CPU: 6 cores | CPU: 8 cores | CPU: 10 cores | CPU: 12 cores | CPU: 14 cores | CPU: 16 cores | CPU: >16 cores |
Standard | Standard S5 | 6 | 10 | 10 | - | 20 | - | - | - | 30 | 30 |
| Standard Storage Optimized S5se | - | - | 20 | - | 20 | - | - | - | 30 | 30 |
| Standard SA2 | 6 | 10 | 10 | - | 20 | - | - | - | 30 | 30 |
| Standard S4 | 6 | 10 | 10 | - | 20 | - | - | - | 30 | 30 |
| Standard Network-optimized SN3ne | 6 | 10 | 10 | - | 20 | - | 30 | - | 30 | 30 |
| Standard S3 | 6 | 10 | 10 | - | 20 | - | 30 | - | 30 | 30 |
| Standard SA1 | 1 GB memory: 2>1 GB memory: 6 | 10 | 8 GB memory: 1016 GB memory: 20 | - | 20 | - | - | - | 30 | 30 |
| Standard S2 | 6 | 10 | 10 | - | 20 | - | 30 | - | 30 | 30 |
| Standard S1 | 6 | 10 | 10 | - | 20 | - | 30 | - | 30 | 30 |
High IO | High IO IT5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 30 | 30 |
| High IO IT3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 30 | 30 |
Memory Optimized | Memory Optimized M5 | 6 | 10 | 10 | - | 20 | - | 30 | - | 30 | 30 |
| Memory Optimized M4 | 6 | 10 | 10 | - | 20 | - | 30 | - | 30 | 30 |
| Memory Optimized M3 | 6 | 10 | 10 | - | 20 | - | 30 | - | 30 | 30 |
| Memory Optimized M2 | 6 | 10 | 10 | - | 20 | - | 30 | - | 30 | 30 |
| Memory Optimized M1 | 6 | 10 | 10 | - | 20 | - | 30 | - | 30 | 30 |
Compute | Compute Optimized C4 | - | - | 10 | - | 20 | - | - | - | 30 | 30 |
| Compute Network-optimized CN3 | - | - | 10 | - | 20 | - | - | - | 30 | 30 |
| Compute C3 | - | - | 10 | - | 20 | - | - | - | 30 | 30 |
| Compute C2 | - | - | 10 | - | 20 | - | - | - | 30 | 30 |
GPU-based | GPU Compute GN2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 30 |
| GPU Compute GN6 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 30 |
| GPU Compute GN6S | - | - | 10 | - | 20 | - | - | - | - | - |
| GPU Compute GN7 | - | - | 10 | - | 20 | - | - | - | - | 30 |
| GPU Compute GN8 | - | - | - | 10 | - | - | - | 30 | - | 30 |
| GPU Compute GN10X | - | - | - | - | 20 | - | - | - | - | 30 |
| GPU Compute GN10Xp | - | - | - | - | - | 20 | - | - | - | 30 |
FPGA-based | FPGA Accelerated FX4 | - | - | - | - | - | 20 | - | - | - | 30 |
Big Data | Big Data D3 | - | - | - | - | 20 | - | - | - | 30 | 30 |
| Big Data D2 | - | - | - | - | 20 | - | - | - | 30 | 30 |
| Big Data D1 | - | - | - | - | 20 | - | - | - | - | 30 |
CPM | | Not supported | | | | | | | | | |
Network Billing Method | Instance | Maximum Bandwidth Range (Mbps) | |
| | Instance Billing Method | Instance Configuration |
Bill-by-traffic | Pay-as-you-go instances | All | 0-100 |
Bill-by-bandwidth | Pay-as-you-go instances | All | 0-100 |
Bandwidth package | All | | 0-2000 |
Network Billing Method | Instance | Range of Bandwidth Cap (Mbps) | |
| | Instance Billing Method | Instance Configuration |
Bill-by-traffic | Pay-as-you-go instances | All | 0-100 |
Bill-by-bandwidth | Pay-as-you-go instances | All | 0-100 |
Bandwidth package | All | | 0-2000 |
Limitations | Description |
Elastic cloud disk capability | Starting from May 2018, all data disks purchased with CVM instances are elastic cloud disks, which can be unmounted from and remounted to CVM instances. This feature is supported in all availability zones. |
Cloud disk performance | I/O specification applies to both input and output performance at the same time.For example, if a 1-TB SSD has a maximum random IOPS of 26,000, it means that both its read and write performance can reach this value. Due to performance limits, if the block size in this example is 4 KB or 8 KB, the maximum IOPS can be reached. If the block size is 16 KB, the maximum IOPS cannot be reached (throughput has already reached the limit of 260 MB/s). |
Elastic cloud disks per CVM | A maximum of 20 |
Snapshots per region | 64 + Number of cloud disks in the region x 64 |
Attaching cloud disks to a CVM | The CVM instance and cloud disks must be in the same availability zone. |
Snapshot rollback | Snapshot data can only be rolled back to the cloud disk where the snapshot was created. |
Creating cloud disks using snapshot - Type limit | Only snapshots of data disks can be used to create new elastic cloud disks. |
Creating cloud disks using snapshot - Size limit | The capacity of new cloud disk must be larger than the source disk of the snapshot. |
Item | Limit |
Security groups | 50 per region |
Rules in a security group | 100 for inbound rules and 100 for outbound rules |
CVM instances associated with a security group | 2,000 |
Security groups associated with a CVM instance | 5 |
Security groups referenced by a security group | 10 |
Resource | Limit |
VPCs per region per account | 20 |
Subnets per VPC | 100 |
Classic network-based CVMs associated with each VPC | 100 |
Route tables per VPC | 10 |
Route tables associated with each subnet | 1 |
Routes per route table | 50 |
HAVIPs per VPC | 10 |
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:12:28
Last updated:2025-09-08 16:27:47
Type | Sub-type | Description |
Standard instances provide a balance of compute, memory, and network resources to accommodate most applications. | ||
Memory optimized instances feature large memory and are suitable for applications that require extensive memory operations, searches, and computations, such as high-performance databases and distributed memory caching. | ||
High I/O instances feature high random IOPS, high throughput and low latency. They are suitable for I/O-intensive applications that require high disk read/write performance and low latency, such as high-performance databases. | ||
This instance family is equipped with massive storage resources, features high throughput, and is suitable for throughput-intensive applications such as Hadoop distributed computing, massive log processing, distributed file systems, and large data warehouses. | ||
This family comes with a turbo frequency up to 3.8 GHz, and provides the highest single-core computing performance. It is suitable for compute-intensive applications such as batch processing, high performance computing, and dedicated game servers. | ||
BeFast 1 | BeFast 1 instances provide cost-effective, balanced and stable computing, memory and network resources. Instances of this family are dynamically managed through the Tencent Cloud's intelligent scheduling capability, meeting the needs for application resources in most scenarios. | |
- | This family is equipped with heterogeneous hardware such as GPU and FPGA to deliver real-time, fast parallel computing and floating-point computing capabilities. It is suitable for high-performance applications such as deep learning, scientific computing, video encoding/decoding, and graphics workstations. |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Network Packet Receive and Send (pps) (Outbound + Inbound) | Number of Connections | Number of Queues | Standard Bandwidth/Burst Bandwidth (Gbps) (Outbound + Inbound) | Cloud Block Storage Standard Bandwidth (Gbps) (Read + Write) | Cloud Block Storage Standard IOPS (Read + Write) | Remarks |
S8.MEDIUM8 | 2 | 8 | 400,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5/10 | 2 | 20,000 | - |
S8.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 800,000 | 250,000 | 4 | 2/10 | 2.5 | 30,000 | - |
S8.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 800,000 | 250,000 | 4 | 2/10 | 2.5 | 30,000 | - |
S8.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 1,600,000 | 500,000 | 8 | 4/10 | 4 | 40,000 | - |
S8.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 1,600,000 | 500,000 | 8 | 4/10 | 4 | 40,000 | - |
S8.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 3,200,000 | 1,100,000 | 16 | 9/10 | 6 | 60,000 | - |
S8.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 3,200,000 | 1,100,000 | 16 | 9/10 | 6 | 60,000 | - |
S8.8XLARGE64 | 32 | 64 | 6,400,000 | 2,200,000 | 32 | 17/25 | 10 | 80,000 | - |
S8.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 6,400,000 | 2,200,000 | 32 | 17/25 | 10 | 80,000 | - |
S8.14XLARGE256 | 56 | 256 | 11,200,000 | 4,000,000 | 48 | 30 | 16 | 100,000 | - |
S8.16XLARGE256 | 64 | 256 | 12,800,000 | 4,500,000 | 48 | 34 | 20 | 125,000 | - |
S8.28XLARGE512 | 112 | 512 | 22,500,000 | 8,000,000 | 48 | 60 | 32 | 200,000 | - |
S8.56XLARGE1024 | 224 | 1024 | 45,000,000 | 16,000,000 | 48 | 120 | 64 | 400,000 | |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Network Packet Receive and Send (pps) (Outbound + Inbound) | Number of Connections | Number of Queues | Standard Bandwidth/Burst Bandwidth (Gbps) (Outbound + Inbound) | Cloud Block Storage Standard Bandwidth (Gbps) (Read + Write) | Cloud Block Storage Standard IOPS (Read + Write) | Remarks |
SA5.MEDIUM2 | 2 | 2 | 250,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5/10 | 1 | 10,000 | - |
SA5.MEDIUM4 | 2 | 4 | 250,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5/10 | 1 | 10,000 | - |
SA5.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 300,000 | 250,000 | 4 | 1.5/10 | 1.5 | 15,000 | - |
SA5.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 300,000 | 250,000 | 4 | 1.5/10 | 1.5 | 15,000 | - |
SA5.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 700,000 | 250,000 | 8 | 3/10 | 2 | 20,000 | - |
SA5.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 700,000 | 250,000 | 8 | 3/10 | 2 | 20,000 | - |
SA5.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 1,400,000 | 500,000 | 16 | 5/10 | 2.5 | 30,000 | - |
SA5.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1,400,000 | 500,000 | 16 | 5/10 | 2.5 | 30,000 | - |
SA5.8XLARGE64 | 32 | 64 | 2,800,000 | 1,000,000 | 32 | 10/25 | 3 | 40,000 | - |
SA5.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 2,800,000 | 1,000,000 | 32 | 10/25 | 3 | 40,000 | - |
SA5.12XLARGE96 | 48 | 96 | 4,200,000 | 1,500,000 | 48 | 15/25 | 3.5 | 45,000 | - |
SA5.12XLARGE192 | 48 | 192 | 4,200,000 | 1,500,000 | 48 | 15/25 | 3.5 | 45,000 | - |
SA5.16XLARGE256 | 64 | 256 | 5,600,000 | 2,000,000 | 48 | 20/25 | 4 | 50,000 | - |
SA5.16XLARGE288 | 64 | 288 | 5,600,000 | 2,000,000 | 48 | 20/25 | 4 | 50,000 | - |
SA5.32XLARGE576 | 128 | 576 | 11,200,000 | 4,000,000 | 48 | 40/- | 8 | 100,000 | - |
SA5.64XLARGE1152 | 256 | 1152 | 22,500,000 | 8,000,000 | 48 | 80/- | 16 | 200,000 | - |
SA5.128XLARGE2304 | 512 | 2304 | 45,000,000 | 16,000,000 | 48 | 160/- | 32 | 400,000 | |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Network Packet Receive and Send (pps) (Outbound + Inbound) | Number of Connections | Number of Queues | Private Network Bandwidth Capacity (Gbps) (Outbound + Inbound) | Remarks |
SA4.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 900,000 | 300,000 | 8 | 2 | - |
SA4.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 900,000 | 300,000 | 8 | 2 | - |
SA4.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 1,800,000 | 600,000 | 16 | 4 | - |
SA4.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1,800,000 | 600,000 | 16 | 4 | - |
SA4.8XLARGE64 | 32 | 64 | 3,700,000 | 1,300,000 | 32 | 8 | - |
SA4.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 3,700,000 | 1,300,000 | 32 | 8 | - |
SA4.16XLARGE128 | 64 | 128 | 7,500,000 | 2,600,000 | 48 | 17 | - |
SA4.16XLARGE256 | 64 | 256 | 7,500,000 | 2,600,000 | 48 | 17 | - |
SA4.24XLARGE192 | 96 | 192 | 11,200,000 | 4,000,000 | 48 | 25 | - |
SA4.48XLARGE384 | 192 | 384 | 22,500,000 | 8,000,000 | 48 | 50 | - |
SA4.96XLARGE768 | 384 | 768 | 45,000,000 | 16,000,000 | 48 | 100 | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of connections | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
S6.SMALL1 | 1 | 1 | 260,000 | 260,000 | 1 | 1.6 | 2.7GHz | - |
S6.SMALL2 | 1 | 2 | 260,000 | 260,000 | 1 | 1.6 | 2.7GHz | - |
S6.SMALL4 | 1 | 4 | 260,000 | 260,000 | 1 | 1.6 | 2.7GHz | - |
S6.MEDIUM4 | 2 | 4 | 300,000 | 260,000 | 2 | 2 | 2.7GHz | - |
S6.MEDIUM8 | 2 | 8 | 300,000 | 260,000 | 2 | 2 | 2.7GHz | - |
S6.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 600,000 | 600,000 | 4 | 4 | 2.7GHz | - |
S6.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 600,000 | 600,000 | 4 | 4 | 2.7GHz | - |
S6.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 1,200,000 | 1,000,000 | 8 | 7 | 2.7GHz | - |
S6.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 1,200,000 | 1,000,000 | 8 | 7 | 2.7GHz | - |
S6.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 2,600,000 | 2,000,000 | 16 | 13 | 2.7GHz | - |
S6.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 2,600,000 | 2,000,000 | 16 | 13 | 2.7GHz | - |
S6.8XLARGE64 | 32 | 64 | 6,000,000 | 4,000,000 | 32 | 26 | 2.7GHz | - |
S6.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 6,000,000 | 4,000,000 | 32 | 26 | 2.7GHz | - |
S6.12XLARGE96 | 48 | 96 | 7,000,000 | 6,000,000 | 48 | 39 | 2.7GHz | - |
S6.12XLARGE192 | 48 | 192 | 7,000,000 | 6,000,000 | 48 | 39 | 2.7GHz | - |
S6.16XLARGE266 | 64 | 266 | 10,000,000 | 8,000,000 | 48 | 62 | 2.7GHz | - |
S6.31MEDIUM216 | 62 | 216 | 10,000,000 | 6,000,000 | 48 | 60 | 2.7GHz | - |
S6.16XLARGE216 | 64 | 216 | 10,000,000 | 8,000,000 | 48 | 50 | 2.7GHz | - |
S6.32XLARGE432 | 128 | 432 | 19,000,000 | 16,000,000 | 48 | 100 | 2.7GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of connections | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
SA3.SMALL1 | 1 | 1 | 250,000 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.SMALL2 | 1 | 2 | 250,000 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.SMALL4 | 1 | 4 | 250,000 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.MEDIUM4 | 2 | 4 | 300,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.MEDIUM8 | 2 | 8 | 300,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 500,000 | 250,000 | 4 | 2 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 500,000 | 250,000 | 4 | 2 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 32 | 800,000 | 500,000 | 8 | 4 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 800,000 | 500,000 | 8 | 4 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 1,500,000 | 1,100,000 | 16 | 7 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1,500,000 | 1,100,000 | 16 | 7 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.8XLARGE64 | 32 | 64 | 2,500,000 | 2,200,000 | 32 | 14 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 2,500,000 | 2,200,000 | 32 | 14 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.12XLARGE96 | 48 | 96 | 4,000,000 | 3,300,000 | 48 | 21 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.12XLARGE192 | 48 | 192 | 4,000,000 | 3,300,000 | 48 | 21 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.16XLARGE128 | 64 | 128 | 5,200,000 | 4,400,000 | 48 | 28 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.16XLARGE256 | 64 | 256 | 5,200,000 | 4,400,000 | 48 | 28 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.20XLARGE160 | 80 | 160 | 6,500,000 | 5,500,000 | 48 | 35 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.20XLARGE320 | 80 | 320 | 6,500,000 | 5,500,000 | 48 | 35 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.24XLARGE192 | 96 | 192 | 7,800,000 | 6,600,000 | 48 | 42 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.24XLARGE384 | 96 | 384 | 7,800,000 | 6,600,000 | 48 | 42 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.29XLARGE216 | 116 | 216 | 9,500,000 | 8,000,000 | 48 | 50 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.29XLARGE470 | 116 | 470 | 9,500,000 | 8,000,000 | 48 | 50 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.32XLARGE256 | 128 | 256 | 10,000,000 | 8,800,000 | 48 | 56 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.32XLARGE512 | 128 | 512 | 10,000,000 | 8,800,000 | 48 | 56 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.40XLARGE320 | 160 | 320 | 13,000,000 | 11,000,000 | 48 | 69 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.40XLARGE640 | 160 | 640 | 13,000,000 | 11,000,000 | 48 | 69 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.58XLARGE432 | 232 | 432 | 19,000,000 | 16,000,000 | 48 | 100 | 2.55GHz | - |
SA3.58XLARGE940 | 232 | 940 | 19,000,000 | 16,000,000 | 48 | 100 | 2.55GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound bandwidth) | Clock rate | Notes |
SR1.SMALL1 | 1 | 1 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.8GHz | - |
SR1.SMALL2 | 1 | 2 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.8GHz | - |
SR1.MEDIUM4 | 2 | 4 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.8GHz | - |
SR1.MEDIUM8 | 2 | 8 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.8GHz | - |
SR1.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.8GHz | - |
SR1.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.8GHz | - |
SR1.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 500,000 | 2 | 3 | 2.8GHz | - |
SR1.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 500,000 | 2 | 3 | 2.8GHz | - |
SR1.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 1,100,000 | 4 | 6 | 2.8GHz | - |
SR1.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1,100,000 | 4 | 6 | 2.8GHz | - |
SR1.8XLARGE64 | 32 | 64 | 2,200,000 | 8 | 12 | 2.8GHz | - |
SR1.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 2,200,000 | 8 | 12 | 2.8GHz | - |
SR1.16XLARGE128 | 64 | 128 | 4,500,000 | 16 | 16 | 2.8GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of connections | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
S5.SMALL1 | 1 | 1 | 250,000 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S5.SMALL2 | 1 | 2 | 250,000 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S5.SMALL4 | 1 | 4 | 250,000 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S5.MEDIUM4 | 2 | 4 | 300,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S5.MEDIUM8 | 2 | 8 | 300,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S5.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 500,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S5.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 500,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S5.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 800,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 3.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S5.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 800,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 3.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S5.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 1,500,000 | 300,000 | 4 | 6.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S5.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1,500,000 | 300,000 | 4 | 6.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S5.6XLARGE48 | 24 | 48 | 2,000,000 | 400,000 | 6 | 9.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S5.6XLARGE96 | 24 | 96 | 2,000,000 | 400,000 | 6 | 9.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S5.8XLARGE64 | 32 | 64 | 2,500,000 | 600,000 | 8 | 12 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S5.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 2,500,000 | 600,000 | 8 | 12 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S5.12XLARGE96 | 48 | 96 | 4,000,000 | 900,000 | 12 | 17.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S5.12XLARGE192 | 48 | 192 | 4,000,000 | 900,000 | 12 | 17.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S5.16XLARGE256 | 64 | 256 | 5,000,000 | 1,200,000 | 16 | 23.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of connections | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
S5se.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 500,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.5GHz | - |
S5se.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 800,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 3.0 | 2.5GHz | - |
S5se.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 800,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 3.0 | 2.5GHz | - |
S5se.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 1,500,000 | 300,000 | 4 | 6.0 | 2.5GHz | - |
S5se.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1,500,000 | 300,000 | 4 | 6.0 | 2.5GHz | - |
S5se.8XLARGE64 | 32 | 64 | 2,500,000 | 600,000 | 8 | 12.0 | 2.5GHz | - |
S5se.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 2,500,000 | 600,000 | 8 | 12.0 | 2.5GHz | - |
S5se.17XLARGE316 | 68 | 316 | 5,000,000 | 1,200,000 | 16 | 25.0 | 2.5GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
SA2.SMALL1 | 1 | 1 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.6 GHz | - |
SA2.SMALL2 | 1 | 2 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.6 GHz | - |
SA2.SMALL4 | 1 | 4 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.6 GHz | - |
SA2.MEDIUM4 | 2 | 4 | 300,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.6 GHz | - |
SA2.MEDIUM8 | 2 | 8 | 300,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.6 GHz | - |
SA2.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 500,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.6 GHz | - |
SA2.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 500,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.6 GHz | - |
SA2.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 700,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.6 GHz | - |
SA2.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 700,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.6 GHz | - |
SA2.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 1,000,000 | 4 | 3.0 | 2.6GHz | - |
SA2.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1,000,000 | 4 | 3.0 | 2.6GHz | - |
SA2.8XLARGE64 | 32 | 64 | 1,400,000 | 8 | 5.0 | 2.6GHz | - |
SA2.12XLARGE96 | 48 | 96 | 2,100,000 | 12 | 7.0 | 2.6GHz | - |
SA2.16XLARGE128 | 64 | 128 | 2,800,000 | 16 | 9.0 | 2.6GHz | - |
SA2.20XLARGE160 | 80 | 160 | 3,500,000 | 16 | 12.0 | 2.6GHz | - |
SA2.22XLARGE224 | 90 | 224 | 3,750,000 | 16 | 13.0 | 2.6GHz | - |
SA2.24XLARGE192 | 96 | 192 | 4,200,000 | 16 | 14.0 | 2.6GHz | - |
SA2.32XLARGE256 | 128 | 256 | 5,600,000 | 32 | 18.0 | 2.6GHz | - |
SA2.40XLARGE320 | 160 | 320 | 7,100,000 | 32 | 23.0 | 2.6GHz | - |
SA2.45XLARGE464 | 180 | 464 | 7,500,000 | 32 | 25.0 | 2.6GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory(GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
S4.SMALL1 | 1 | 1 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.4GHz | - |
S4.SMALL2 | 1 | 2 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.4GHz | - |
S4.SMALL4 | 1 | 4 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.4GHz | - |
S4.MEDIUM4 | 2 | 4 | 300,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.4GHz | - |
S4.MEDIUM8 | 2 | 8 | 300,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.4GHz | - |
S4.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 500,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.4GHz | - |
S4.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 500,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.4GHz | - |
S4.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 800,000 | 2 | 3.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S4.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 800,000 | 2 | 3.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S4.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 1,500,000 | 4 | 6.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S4.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1,500,000 | 4 | 6.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S4.6XLARGE48 | 24 | 48 | 2,000,000 | 6 | 8.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S4.6XLARGE96 | 24 | 96 | 2,000,000 | 6 | 8.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S4.8XLARGE64 | 32 | 64 | 2,500,000 | 8 | 11.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S4.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 2,500,000 | 8 | 11.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S4.12XLARGE96 | 48 | 96 | 4,000,000 | 12 | 16.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S4.12XLARGE192 | 48 | 192 | 4,000,000 | 12 | 16.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S4.16XLARGE256 | 64 | 256 | 5,000,000 | 16 | 22.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S4.18XLARGE288 | 72 | 288 | 6,000,000 | 16 | 24.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
SN3ne.SMALL2 | 1 | 2 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
SN3ne.MEDIUM4 | 2 | 4 | 300,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
SN3ne.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 500,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
SN3ne.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 500,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
SN3ne.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 800,000 | 2 | 3.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
SN3ne.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 800,000 | 2 | 3.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
SN3ne.3XLARGE24 | 12 | 24 | 1,000,000 | 3 | 4.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
SN3ne.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 1,500,000 | 4 | 6.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
SN3ne.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1,500,000 | 4 | 6.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
SN3ne.6XLARGE48 | 24 | 48 | 2,000,000 | 6 | 8.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
SN3ne.6XLARGE96 | 24 | 96 | 2,000,000 | 6 | 8.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
SN3ne.8XLARGE64 | 32 | 64 | 2,500,000 | 8 | 11.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
SN3ne.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 2,500,000 | 8 | 11.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
SN3ne.12XLARGE96 | 48 | 96 | 4,000,000 | 12 | 16.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
SN3ne.12XLARGE192 | 48 | 192 | 4,000,000 | 12 | 16.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
SN3ne.16XLARGE128 | 64 | 128 | 5,000,000 | 16 | 22.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
SN3ne.16XLARGE256 | 64 | 256 | 5,000,000 | 16 | 22.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
SN3ne.18XLARGE288 | 72 | 288 | 6,000,000 | 16 | 24.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
S3.SMALL1 | 1 | 1 | 200,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.SMALL2 | 1 | 2 | 200,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.SMALL4 | 1 | 4 | 200,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.MEDIUM8 | 2 | 8 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 450,000 | 4 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 450,000 | 4 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 850,000 | 8 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 850,000 | 8 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.3XLARGE24 | 12 | 24 | 850,000 | 12 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.3XLARGE48 | 12 | 48 | 850,000 | 12 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 850,000 | 16 | 2.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 850,000 | 16 | 2.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.6XLARGE48 | 24 | 48 | 850,000 | 16 | 3.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.6XLARGE96 | 24 | 96 | 850,000 | 16 | 3.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.8XLARGE64 | 32 | 64 | 850,000 | 16 | 4.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 850,000 | 16 | 4.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.12XLARGE96 | 48 | 96 | 850,000 | 16 | 6.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.12XLARGE192 | 48 | 192 | 850,000 | 16 | 6.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.16XLARGE256 | 64 | 256 | 850,000 | 16 | 8.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
S3.20XLARGE320 | 80 | 320 | 850,000 | 16 | 10.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
SA1.SMALL1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1.5 | 2.0 GHz | - |
SA1.SMALL2 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 | 1.5 | 2.0 GHz | - |
SA1.SMALL4 | 1 | 4 | - | 1 | 1.5 | 2.0 GHz | - |
SA1.MEDIUM4 | 2 | 4 | - | 2 | 1.5 | 2.0 GHz | - |
SA1.MEDIUM8 | 2 | 8 | - | 2 | 1.5 | 2.0 GHz | - |
SA1.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | - | 4 | 1.5 | 2.0 GHz | - |
SA1.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | - | 4 | 1.5 | 2.0 GHz | - |
SA1.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | - | 8 | 1.5 | 2.0 GHz | - |
SA1.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | - | 8 | 1.5 | 2.0 GHz | - |
SA1.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | - | 16 | 1.5 | 2.0 GHz | - |
SA1.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | - | 16 | 1.5 | 2.0 GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
S2ne.SMALL2 | 1 | 2 | 120,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2ne.MEDIUM4 | 2 | 4 | 150,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2ne.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 300,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2ne.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 300,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2ne.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 600,000 | 2 | 2.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2ne.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 600,000 | 2 | 2.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2ne.3XLARGE24 | 12 | 24 | 900,000 | 3 | 2.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2ne.3XLARGE48 | 12 | 48 | 900,000 | 3 | 2.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2ne.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 1,200,000 | 4 | 3.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2ne.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1,200,000 | 4 | 3.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2ne.6XLARGE48 | 24 | 48 | 1,800,000 | 6 | 5.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2ne.6XLARGE96 | 24 | 96 | 1,800,000 | 6 | 5.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2ne.8XLARGE64 | 32 | 64 | 2,400,000 | 8 | 6.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2ne.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 2,400,000 | 8 | 6.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2ne.12XLARGE192 | 48 | 192 | 3,600,000 | 12 | 9.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
S2.SMALL1 | 1 | 1 | 200,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2.SMALL2 | 1 | 2 | 200,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2.SMALL4 | 1 | 4 | 200,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2.MEDIUM2 | 2 | 2 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2.MEDIUM4 | 2 | 4 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2.MEDIUM8 | 2 | 8 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 450,000 | 4 | 1.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 450,000 | 4 | 1.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 500,000 | 8 | 1.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 500,000 | 8 | 1.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2.3XLARGE24 | 12 | 24 | 500,000 | 8 | 2.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2.3XLARGE48 | 12 | 48 | 500,000 | 8 | 2.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 500,000 | 8 | 3.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 500,000 | 8 | 3.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2.6XLARGE48 | 24 | 48 | 700,000 | 8 | 4.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2.6XLARGE96 | 24 | 96 | 700,000 | 8 | 4.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2.8XLARGE64 | 32 | 64 | 700,000 | 8 | 6.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 700,000 | 8 | 6.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
S2.14XLARGE224 | 56 | 224 | 700,000 | 8 | 10.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
S1.SMALL1 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1.5 | - | - |
S1.SMALL2 | 1 | 2 | - | 1 | 1.5 | - | - |
S1.SMALL4 | 1 | 4 | - | 1 | 1.5 | - | - |
S1.MEDIUM2 | 2 | 2 | - | 2 | 1.5 | - | - |
S1.MEDIUM4 | 2 | 4 | - | 2 | 1.5 | - | - |
S1.MEDIUM8 | 2 | 8 | - | 2 | 1.5 | - | - |
S1.MEDIUM12 | 2 | 12 | - | 2 | 1.5 | - | - |
S1.LARGE4 | 4 | 4 | - | 4 | 1.5 | - | - |
S1.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | - | 4 | 1.5 | - | - |
S1.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | - | 4 | 1.5 | - | - |
S1.2XLARGE8 | 8 | 8 | - | 8 | 2.0 | - | - |
S1.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | - | 8 | 2.0 | - | - |
S1.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | - | 8 | 2.0 | - | - |
S1.3XLARGE24 | 12 | 24 | - | 8 | 2.5 | - | - |
S1.3XLARGE48 | 12 | 48 | - | 8 | 2.5 | - | - |
S1.4XLARGE16 | 16 | 16 | - | 8 | 3.5 | - | - |
S1.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | - | 8 | 3.5 | - | - |
S1.4XLARGE48 | 16 | 48 | - | 8 | 3.5 | - | - |
S1.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | - | 8 | 3.5 | - | - |
S1.6XLARGE48 | 24 | 48 | - | 8 | 5.0 | - | - |
S1.8XLARGE64 | 32 | 64 | - | 8 | 7.0 | - | - |
S1.12XLARGE96 | 48 | 96 | - | 8 | 10.0 | - | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Network Packet Receive and Send (pps) (Outbound + Inbound) | Number of Connections | Number of Queues | Standard Bandwidth/Burst Bandwidth (Gbps) (Outbound + Inbound) | Cloud Block Storage Standard Bandwidth (Gbps) | Cloud Block Storage Standard IOPS (Read + Write) | Remarks |
M8.MEDIUM16 | 2 | 16 | 400,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5/10 | 2 | 20,000 | |
M8.LARGE32 | 4 | 32 | 800,000 | 250,000 | 4 | 2/10 | 2.5 | 30,000 | - |
M8.2XLARGE64 | 8 | 64 | 1,400,000 | 500,000 | 8 | 4/10 | 4 | 40,000 | - |
M8.4XLARGE128 | 16 | 128 | 3,200,000 | 1,100,000 | 16 | 9/10 | 6 | 60,000 | - |
M8.8XLARGE256 | 32 | 256 | 6,400,000 | 2,200,000 | 32 | 17/25 | 10 | 80,000 | - |
M8.16XLARGE512 | 64 | 512 | 12,800,000 | 4,500,000 | 48 | 34 | 20 | 125,000 | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Network Packet Receive and Send (pps) (Outbound + Inbound) | Number of Connections | Number of Queues | Standard Bandwidth/Burst Bandwidth (Gbps) (Outbound + Inbound) | Cloud Block Storage Standard Bandwidth (Gbps) | Cloud Block Storage Standard IOPS (Read + Write) | Remarks |
MA5.LARGE32 | 4 | 32 | 300,000 | 250,000 | 4 | 1.5/10 | 1.5 | 15,000 | - |
MA5.2XLARGE64 | 8 | 64 | 700,000 | 250,000 | 8 | 3/10 | 2 | 20,000 | - |
MA5.4XLARGE128 | 16 | 128 | 1,400,000 | 500,000 | 16 | 5/10 | 2.5 | 30,000 | - |
MA5.8XLARGE256 | 32 | 256 | 2,800,000 | 1,000,000 | 32 | 10/25 | 3 | 40,000 | - |
MA5.16XLARGE512 | 64 | 512 | 5,600,000 | 2,000,000 | 48 | 20/25 | 4 | 50,000 | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of connections | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | Cloud Block Storage Standard Bandwidth (Gbps) | Cloud Block Storage Standard IOPS (Read + Write) | Remarks |
MA4.LARGE32 | 4 | 32 | 400,000 | 250,000 | 4 | 1.5 | 2 | 30,000 | - |
MA4.2XLARGE64 | 8 | 64 | 900,000 | 300,000 | 8 | 2 | 2.5 | 40,000 | - |
MA4.4XLARGE128 | 16 | 128 | 1,800,000 | 600,000 | 16 | 4 | 3 | 50,000 | - |
MA4.8XLARGE256 | 32 | 256 | 3,700,000 | 1,300,000 | 32 | 8 | 4 | 60,000 | - |
MA4.16XLARGE512 | 64 | 512 | 7,500,000 | 2,600,000 | 48 | 17 | 6 | 90,000 | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
MA3.SMALL8 | 1 | 8 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.55GHz | - |
MA3.MEDIUM16 | 2 | 16 | 300,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.55GHz | - |
MA3.LARGE32 | 4 | 32 | 500,000 | 4 | 2 | 2.55GHz | - |
MA3.2XLARGE64 | 8 | 64 | 800,000 | 8 | 4 | 2.55GHz | - |
MA3.4XLARGE128 | 16 | 128 | 1,500,000 | 16 | 7 | 2.55GHz | - |
MA3.8XLARGE256 | 32 | 256 | 2,500,000 | 32 | 14 | 2.55GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of connections | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
M6.SMALL8 | 1 | 8 | 250,000 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.7 GHz | - |
M6.MEDIUM16 | 2 | 16 | 300,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 2 | 2.7 GHz | - |
M6.LARGE32 | 4 | 32 | 600,000 | 500,000 | 4 | 4 | 2.7 GHz | - |
M6.2XLARGE64 | 8 | 64 | 1,200,000 | 1,000,000 | 8 | 7 | 2.7 GHz | - |
M6.4XLARGE128 | 16 | 128 | 2,500,000 | 2,000,000 | 16 | 13 | 2.7 GHz | - |
M6.8XLARGE256 | 32 | 256 | 5,000,000 | 4,000,000 | 32 | 26 | 2.7 GHz | - |
M6.16XLARGE512 | 64 | 512 | 10,000,000 | 8,000,000 | 48 | 52 | 2.7 GHz | - |
M6.31MEDIUM470 | 62 | 470 | 10,000,000 | 8,000,000 | 48 | 50 | 2.7 GHz | - |
M6.31XLARGE940 | 124 | 940 | 19,000,000 | 16,000,000 | 48 | 100 | 2.7 GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) |
With encrypted memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of connections | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
M6ce.MEDIUM16 | 2 | 16 | 8 | 300,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 2 | 2.7/3.3GHz | - |
M6ce.LARGE32 | 4 | 32 | 16 | 600,000 | 500,000 | 4 | 4 | 2.7/3.3GHz | - |
M6ce.2XLARGE64 | 8 | 64 | 32 | 1,200,000 | 1,000,000 | 8 | 7 | 2.7/3.3GHz | - |
M6ce.4XLARGE128 | 16 | 128 | 64 | 2,500,000 | 2,000,000 | 16 | 13 | 2.7/3.3GHz | - |
M6ce.8XLARGE256 | 32 | 256 | 128 | 5,000,000 | 4,000,000 | 32 | 26 | 2.7/3.3GHz | - |
M6ce.31MEDIUM428 | 62 | 428 | 214 | 10,000,000 | 8,000,000 | 48 | 50 | 2.7/3.3GHz | - |
M6ce.31XLARGE856 | 124 | 856 | 428 | 19,000,000 | 8,000,000 | 48 | 100 | 2.7/3.3GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of connections | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
M5.SMALL8 | 1 | 8 | 250,000 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.5GHz | - |
M5.MEDIUM16 | 2 | 16 | 300,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.5GHz | - |
M5.LARGE32 | 4 | 32 | 500,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.5GHz | - |
M5.2XLARGE64 | 8 | 64 | 800,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 3.0 | 2.5GHz | - |
M5.3XLARGE96 | 12 | 96 | 1,000,000 | 250,000 | 3 | 5.0 | 2.5GHz | - |
M5.4XLARGE128 | 16 | 128 | 1,500,000 | 300,000 | 4 | 6.0 | 2.5GHz | - |
M5.8XLARGE256 | 32 | 256 | 2,500,000 | 600,000 | 8 | 12.0 | 2.5GHz | - |
M5.16XLARGE512 | 64 | 512 | 5,000,000 | 1,200,000 | 16 | 23.0 | 2.5GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of connections | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
MA2.SMALL8 | 1 | 8 | 250,000 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.6GHz | - |
MA2.LARGE32 | 4 | 32 | 500,000 | 250,000 | 4 | 1.5 | 2.6GHz | - |
MA2.2XLARGE64 | 8 | 64 | 700,000 | 250,000 | 8 | 1.5 | 2.6GHz | - |
MA2. 2XLARGE384 | 8 | 384 | 700,000 | 250,000 | 8 | 1.5 | 2.6GHz | - |
MA2.4 XLARGE128 | 16 | 128 | 1,000,000 | 300,000 | 16 | 3 | 2.6GHz | - |
MA2.8 XLARGE256 | 32 | 256 | 1,400,000 | 700,000 | 32 | 5 | 2.6GHz | - |
MA2.12XLARGE384 | 48 | 384 | 2,100,000 | 1,000,000 | 48 | 7 | 2.6GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
M4.SMALL8 | 1 | 8 | 250,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.4GHz | - |
M4.MEDIUM16 | 2 | 16 | 300,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.4GHz | - |
M4.LARGE32 | 4 | 32 | 500,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.4GHz | - |
M4.2XLARGE64 | 8 | 64 | 800,000 | 2 | 3.0 | 2.4GHz | - |
M4.3XLARGE96 | 12 | 96 | 1,000,000 | 3 | 4.0 | 2.4GHz | - |
M4.3XLARGE144 | 12 | 144 | 1,000,000 | 3 | 4.0 | 2.4GHz | - |
M4.4XLARGE128 | 16 | 128 | 1,500,000 | 4 | 6.0 | 2.4GHz | - |
M4.4XLARGE192 | 16 | 192 | 1,500,000 | 4 | 6.0 | 2.4GHz | - |
M4.8XLARGE256 | 32 | 256 | 2,500,000 | 8 | 11.0 | 2.4GHz | - |
M4.8XLARGE384 | 32 | 384 | 2,500,000 | 8 | 11.0 | 2.4GHz | - |
M4.16XLARGE512 | 64 | 512 | 5,000,000 | 16 | 22.0 | 2.4GHz | - |
M4.18XLARGE648 | 72 | 648 | 6,000,000 | 16 | 24.0 | 2.4GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
M3.SMALL8 | 1 | 8 | 300,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
M3.MEDIUM16 | 2 | 16 | 400,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
M3.LARGE32 | 4 | 32 | 800,000 | 4 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
M3.2XLARGE64 | 8 | 64 | 1,200,000 | 8 | 1.5 | 2.5GHz | - |
M3.3XLARGE96 | 12 | 96 | 1,200,000 | 12 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
M3.3XLARGE144 | 12 | 144 | 1,200,000 | 12 | 1.5 | 2.5 GHz | - |
M3.4XLARGE128 | 16 | 128 | 1,200,000 | 16 | 2.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
M3.4XLARGE192 | 16 | 192 | 1,200,000 | 16 | 2.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
M3.8XLARGE256 | 32 | 256 | 1,200,000 | 16 | 4.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
M3.8XLARGE384 | 32 | 384 | 1,200,000 | 16 | 4.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
M3.16XLARGE512 | 64 | 512 | 1,200,000 | 16 | 8.0 | 2.5 GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
M2.SMALL8 | 1 | 8 | 200,000 | 1 | 1.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
M2.MEDIUM16 | 2 | 16 | 250,000 | 2 | 1.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
M2.LARGE32 | 4 | 32 | 450,000 | 4 | 1.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
M2.2XLARGE64 | 8 | 64 | 500,000 | 8 | 1.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
M2.3XLARGE96 | 12 | 96 | 500,000 | 8 | 2.5 | 2.4 GHz | - |
M2.4XLARGE128 | 16 | 128 | 500,000 | 8 | 3.0 | 2.4 GHz | - |
M2.6XLARGE192 | 24 | 192 | 700,000 | 8 | 4.5 | 2.4GHz | - |
M2.8XLARGE256 | 32 | 256 | 700,000 | 8 | 6.0 | 2.4GHz | - |
M2.12XLARGE384 | 48 | 384 | 700,000 | 8 | 9.0 | 2.4GHz | - |
M2.14XLARGE448 | 56 | 448 | 700,000 | 8 | 10.0 | 2.4GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
M1.SMALL8 | 1 | 8 | - | 1 | 1.5 | 2.3GHz | - |
M1.MEDIUM16 | 2 | 16 | - | 2 | 1.5 | 2.3GHz | - |
M1.LARGE32 | 4 | 32 | - | 4 | 1.5 | 2.3GHz | - |
M1.2XLARGE64 | 8 | 64 | - | 8 | 2.0 | 2.3GHz | - |
M1.3XLARGE96 | 12 | 96 | - | 8 | 2.5 | 2.3GHz | - |
M1.4XLARGE128 | 16 | 128 | - | 8 | 3.5 | 2.3GHz | - |
M1.6XLARGE192 | 24 | 192 | - | 8 | 5.0 | 2.3GHz | - |
M1.8XLARGE256 | 32 | 256 | - | 8 | 7.0 | 2.3GHz | - |
M1.12XLARGE368 | 48 | 368 | - | 8 | 10.0 | 2.3GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Network packet transmission (pps) (Outbound + Inbound) | Number of connections | Queue count | Private Network Standard/Burst Bandwidth (Gbps) (Outbound + Inbound) | Remarks |
ITA5.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1.4 million | 500,000 | 16 | 5/10 | 1 × 7140GB local NVMe SSD drive |
ITA5.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 2.8 million | 1 million | 32 | 10/25 | 2 × 7140GB local NVMe SSD drive |
ITA5.16XLARGE256 | 64 | 256 | 5.6 million | 2 million | 48 | 20/25 | 4 × 7140GB Local NVMe SSD drives |
ITA5.32XLARGE512 | 128 | 512 | 11.2 million | 4 million | 48 | 40/- | 8 × 7140GB Local NVMe SSD drives |
ITA5.64XLARGE1024 | 256 | 1024 | 22.5 million | 8 million | 48 | 80/- | 16 × 7140GB Local NVMe SSD drives |
ITA5.128XLARGE2304 | 512 | 2304 | 45 million | 16 million | 48 | 160/- | 24 × 7140GB Local NVMe SSD drives |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
IT5.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1,500,000 | 4 | 6 | 2.5GHz | 1 x 3570 GB local NVMe SSD |
IT5.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 2,500,000 | 8 | 12 | 2.5GHz | 2 x 3570 GB local NVMe SSDs |
IT5.16XLARGE256 | 64 | 256 | 5,000,000 | 16 | 23 | 2.5GHz | 4 x 3570 GB local NVMe SSDs |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
IT3.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1,500,000 | 4 | 6 | 2.5GHz | 1 × 3720 GB local NVMe SSD |
IT3.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 2,500,000 | 8 | 12 | 2.5GHz | 2 × 3720 GB local NVMe SSDs |
IT3.16XLARGE256 | 64 | 256 | 5,000,000 | 16 | 23 | 2.5GHz | 4 × 3720 GB local NVMe SSDs |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of connections | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
D3.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 800,000 | 250,000 | 2 | 4.0 | 2.5GHz | 4 x 3720 GB local SATA HDDs |
D3.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1,500,000 | 300,000 | 4 | 7.0 | 2.5 GHz | 8 x 3720 GB local SATA HDDs |
D3.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 2,500,000 | 600,000 | 8 | 14.0 | 2.5 GHz | 12 x 3720 GB local SATA HDDs |
D3.16XLARGE256 | 64 | 256 | 5,000,000 | 1,200,000 | 12 | 27.0 | 2.5GHz | 24 x 3720 GB local SATA HDDs |
D3.21XLARGE320 | 84 | 320 | 6,000,000 | 1,600,000 | 16 | 32.0 | 2.5 GHz | 24 x 3720 GB local SATA HDDs |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
D2.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 800,000 | 2 | 3.0 | 2.4GHz | 1 x 11176 GB local SATA HDD |
D2.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1,500,000 | 4 | 6.0 | 2.4GHz | 2 x 11176 GB local SATA HDDs |
D2.6XLARGE96 | 24 | 96 | 2,000,000 | 6 | 8.0 | 2.4GHz | 3 x 11176 GB local SATA HDDs |
D2.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 2,500,000 | 8 | 11.0 | 2.4GHz | 4 x 11176 GB local SATA HDDs |
D2.16XLARGE256 | 64 | 256 | 5,000,000 | 16 | 22.0 | 2.4GHz | 8 x 11176 GB local SATA HDDs |
D2.19XLARGE320 | 76 | 320 | 6,000,000 | 16 | 25.0 | 2.4GHz | 12 x 11176 GB local SATA HDDs |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of connections | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
C6.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 800,000 | 600,000 | 4 | 5 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C6.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 800,000 | 600,000 | 4 | 5 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C6.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 1,600,000 | 1,300,000 | 8 | 9 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C6.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 1,600,000 | 1,300,000 | 8 | 9 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C6.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 3,300,000 | 2,700,000 | 16 | 18 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C6.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 3,300,000 | 2,700,000 | 16 | 18 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C6.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 6,600,000 | 5,500,000 | 32 | 35 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C6.23MEDIUM216 | 46 | 216 | 9,500,000 | 8,000,000 | 46 | 50 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C6.16XLARGE256 | 64 | 256 | 13,000,000 | 11,000,000 | 48 | 70 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C6.20XLARGE320 | 80 | 320 | 16,000,000 | 13,900,000 | 48 | 87 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C6.23XLARGE432 | 92 | 432 | 19,000,000 | 16,000,000 | 48 | 100 | 3.2 GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of connections | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
C5.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 500,000 | 250,000 | 4 | 1.5 | 3.4GHz | - |
C5.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 500,000 | 250,000 | 4 | 1.5 | 3.4GHz | - |
C5.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 800,000 | 250,000 | 8 | 3.0 | 3.4GHz | - |
C5.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 800,000 | 250,000 | 8 | 3.0 | 3.4GHz | - |
C5.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 1,500,000 | 300,000 | 8 | 6.0 | 3.4GHz | - |
C5.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1,500,000 | 300,000 | 8 | 6.0 | 3.4GHz | - |
C5.8XLARGE64 | 32 | 64 | 2,500,000 | 600,000 | 16 | 12.0 | 3.4GHz | - |
C5.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 2,500,000 | 600,000 | 16 | 12.0 | 3.4GHz | - |
C5.12XLARGE96 | 48 | 96 | 4,000,000 | 900,000 | 24 | 18.0 | 3.4GHz | - |
C5.12XLARGE192 | 48 | 192 | 4,000,000 | 900,000 | 24 | 18.0 | 3.4GHz | - |
C5.13XLARGE184 | 52 | 184 | 4,000,000 | 1,000,000 | 32 | 19.0 | 3.4GHz | - |
C5.16XLARGE256 | 64 | 256 | 5,000,000 | 1,200,000 | 32 | 24.0 | 3.4GHz | - |
C5.26XLARGE368 | 104 | 368 | 6,000,000 | 2,000,000 | 32 | 36.0 | 3.4GHz | - |
Specifications | vCPU | MEM (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
C4.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 600,000 | 4 | 2.0 | 3.2GHz | - |
C4.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 600,000 | 4 | 2.0 | 3.2GHz | - |
C4.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 1,000,000 | 8 | 4.0 | 3.2GHz | - |
C4.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 1,000,000 | 8 | 4.0 | 3.2GHz | - |
C4.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1,000,000 | 16 | 7.0 | 3.2GHz | - |
C4.8XLARGE174 | 32 | 174 | 1,000,000 | 16 | 13.0 | 3.2GHz | - |
C4.16XLARGE348 | 64 | 348 | 1,000,000 | 16 | 25.0 | 3.2GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
CN3.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 600,000 | 4 | 3.0 | 3.2 GHz | - |
CN3.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 600,000 | 4 | 3.0 | 3.2 GHz | - |
CN3.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 1,000,000 | 8 | 5.0 | 3.2 GHz | - |
CN3.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 1,000,000 | 8 | 5.0 | 3.2 GHz | - |
CN3.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 1,000,000 | 16 | 9.0 | 3.2 GHz | - |
CN3.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1,000,000 | 16 | 9.0 | 3.2 GHz | - |
CN3.8XLARGE64 | 32 | 64 | 1,000,000 | 16 | 17.0 | 3.2 GHz | - |
CN3.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 1,000,000 | 16 | 17.0 | 3.2 GHz | - |
CN3.12XLARGE160 | 48 | 160 | 1,000,000 | 16 | 25.0 | 3.2 GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
C3.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 600,000 | 2 | 2.5 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C3.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 600,000 | 2 | 2.5 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C3.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 1,000,000 | 2 | 3.0 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C3.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 1,000,000 | 2 | 3.0 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C3.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 1,000,000 | 4 | 4.5 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C3.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1,000,000 | 4 | 4.5 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C3.8XLARGE64 | 32 | 64 | 1,000,000 | 8 | 8.0 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C3.8XLARGE128 | 32 | 128 | 1,000,000 | 8 | 8.0 | 3.2 GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | CPU clock rate | Notes |
C2.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 550,000 | 4 | 2.5 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C2.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 550,000 | 4 | 2.5 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C2.LARGE32 | 4 | 32 | 550,000 | 4 | 2.5 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C2.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 550,000 | 8 | 3.5 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C2.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 550,000 | 8 | 3.5 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C2.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 850,000 | 8 | 6.0 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C2.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 850,000 | 8 | 6.0 | 3.2 GHz | - |
C2.8XLARGE96 | 32 | 96 | 850,000 | 8 | 10.0 | 3.2 GHz | - |
Specification | vCPU | Memory (GB) | Throughput (pps) (received and sent packets) | Number of Connections | Number of Queues | Private network bandwidth (Gbps) (outbound and inbound) | Notes |
BF1.MEDIUM2 | 2 | 2 | 250,000 or more | 250,000 or more | 2 | 1.5 or higher | - |
BF1.MEDIUM4 | 2 | 4 | 250,000 or more | 250,000 or more | 2 | 1.5 or higher | - |
BF1.MEDIUM8 | 2 | 8 | 250,000 or more | 250,000 or more | 2 | 1.5 or higher | - |
BF1.LARGE4 | 4 | 4 | 300,000 or more | 250,000 or more | 2 | 1.5 or higher | - |
BF1.LARGE8 | 4 | 8 | 300,000 or more | 250,000 or more | 2 | 1.5 or higher | - |
BF1.LARGE16 | 4 | 16 | 300,000 or more | 250,000 or more | 2 | 1.5 or higher | - |
BF1.2XLARGE8 | 8 | 8 | 600,000 or more | 250,000 or more | 2 | 1.5 or higher | - |
BF1.2XLARGE16 | 8 | 16 | 600,000 or more | 250,000 or more | 2 | 1.5 or higher | - |
BF1.2XLARGE32 | 8 | 32 | 600,000 or more | 250,000 or more | 2 | 1.5 or higher | - |
BF1.4XLARGE16 | 16 | 16 | 1.3 million or more | 500,000 or more | 4 | 3 or higher | - |
BF1.4XLARGE32 | 16 | 32 | 1.3 million or more | 500,000 or more | 4 | 3 or higher | - |
BF1.4XLARGE64 | 16 | 64 | 1.3 million or more | 500,000 or more | 4 | 3 or higher | - |
BF1.8XLARG64 | 32 | 64 | 2.6 million or more | 1 million or more | 8 | 5 or higher | - |
BF1.8XLARG128 | 32 | 128 | 2.6 million or more | 1 million or more | 8 | 5 or higher | - |
BF1.12XLARG96 | 48 | 96 | 3.9 million or more | 1.5 million or more | 12 | 7 or higher | - |
BF1.12XLARG192 | 48 | 192 | 3.9 million or more | 1.5 million or more | 12 | 7 or higher | - |
BF1.16XLARG128 | 64 | 128 | 5.2 million or more | 2 million or more | 16 | 9 or higher | - |
BF1.16XLARG256 | 64 | 256 | 5.2 million or more | 2 million or more | 16 | 9 or higher | - |
Last updated:2025-08-05 18:59:50
Status Name | Status Attributes | Description |
Creating | Intermediate status | The instance has been created but is not running yet. |
Running | Steady status | The instance is running normally, and you can run your services on this instance. |
Restarting | Intermediate status | A restart operation has been performed for the instance via the console or APIs, but the instance is not running yet. If this status lasts for a long time, there may be an exception. |
Reinstalling | Intermediate status | The instance's system has been reinstalled or its disk has been reconfigured via the console or APIs, but the instance is not running yet. |
Shutting Down | Intermediate status | A shutdown operation has been performed for the instance via the console or APIs, but the instance has not been shut down yet. If this status lasts for a long time, there may be an exception. We do not recommend forced shutdown. |
Shutdown | Steady status | The instance has been shut down normally and cannot provide external services. Some instance attributes can only be modified when the instance is in shutdown status. |
Terminating | Intermediate status | The instance has expired for 15 days or the user has performed the termination operation, but it has not completed yet. |
Reclaimed | Steady status | A pay-as-you-go instance has been manually terminated for less than 2 hours and put into the recycle bin. In this status, the instance does not provide external services. |
Released | Steady status | The release operation has been completed. The original instance no longer exists, cannot provide services, and its data is completely cleared. |

Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
Last updated:2024-06-25 15:45:04
Type | Required | Configuration Description |
Billing mode | Yes | Select one as needed: Pay-as-you-go: It is an elastic billing method of CVM applicable to scenarios such as e-commerce flash sales, where demand will fluctuate significantly in an instant. Spot instance: A novel operational mode for instances, aptly suited for scenarios such as big data computing, and load-balanced online services and website services. As market supply and demand dynamics shift, the price of spot instances fluctuates accordingly, typically ranging from 3% to 20% of the pay-as-you-go price. |
Region/Availability Zone | Yes | Region: We recommend you select the region closest to your end users to minimize the access latency and improve the access speed. Availability zone: Select one as needed. If you want to purchase multiple CVM instances, we recommend you select different AZs to implement disaster recovery. |
Instance | Yes | Tencent Cloud provides different instance types based on the underlying hardware. For more information on instances, see Instance Types. |
Image | Yes | Tencent Cloud provides public images, custom images, and shared images. For more information on images, see Image Types. |
Yes | It is used for OS installation and defaults to 50 GB. Available cloud disk types vary by region. Select one as instructed on the page. | |
No | It is used to scale up the storage capacity of the CVM instance to ensure high efficiency and reliability. It is not added by default. | |
Scheduled Snapshot | No | A scheduled snapshot policy can be set for the system disk or data disk. For more information, see Scheduled Snapshots. |
Quantity | Yes | It indicates the quantity of CVM instances to be purchased. |
Type | Required | Configuration Description |
Network | Yes | It is a logically isolated network space built in Tencent Cloud. A VPC includes at least one subnet. The system provides a default VPC and subnet for each region. If the existing VPC or subnet does not meet your requirements, you can create a VPC or subnet in the VPC console. Note: By default, resources in the same VPC are interconnected over the private network. When purchasing a CVM instance, make sure that the CVM instance and its subnet are in the same AZ. |
Public IP | No | If your CVM instance needs to access the public network, you need to assign a public IP for it. You can assign the public IP when creating the CVM instance or configure an Note: The dedicated public IP that is assigned free of charge cannot be unbound from the instance. To unbind this IP address, convert it to an EIP first. For more information on EIPs, see Elastic IP (EIP). No dedicated public IP can be assigned in the following two cases, subject to the information on the purchase page: The IP resources have been sold out. Resources are only available in certain regions. |
Bill-by-bandwidth mode | Yes | Tencent Cloud provides two network billing modes. Configure a value greater than 0 Mbps as needed. Bill-by-traffic: Billing is based on traffic that is actually used. You can specify a peak bandwidth to prevent charges incurred by unexpected traffic. Packet loss will occur when the instantaneous bandwidth exceeds this value. This is applicable to scenarios where the network connection fluctuates significantly. Bill-by-bandwidth package: Select this aggregated billing mode when your public network instances have traffic peaks at different times. It is applicable to large-scale businesses where traffic can be staggered between different instances using the public network. BWP is currently in beta test. To try it out, submit a ticket for application. |
Bandwidth value | No | You can set the maximum public network bandwidth of the CVM instance as needed. For more information, see Public Network Bandwidth Cap. |
Security group | Yes | If there is no available security group, you can choose New security group. If there are available security groups, you can choose Existing Security Groups. |
Tag | No | You can add tags for the instance as needed, which can be used to categorize, search for, and aggregate cloud resources. For more information, see Overview. |
Instance name | No | You can customize the name of the CVM instance to be created. If no instance name is specified, Unnamed will be used by default. An instance name can contain up to 128 characters. Batch sequential naming or pattern string-based naming is also supported. Note: This name is displayed only in the console. It is not the hostname of the CVM instance. |
Login Methods | Yes | Configure the method to log in to the CVM as needed. Set Password: Customize the password for logging in to the instance. SSH Key Pair (only for Linux instances): Associate the instance with an SSH key to ensure secure login to the CVM instance.If no key is available or existing keys are inappropriate, click Create Now to create a key. For more information on SSH keys, see SSH Keys. Random Password: A password will be automatically generated and sent to you in Message Center. |
Instance Termination Protection | No | It is not enabled by default. You can enable it as needed. Then, you cannot terminate an instance in the console or via the API. For more information, see Enabling Instance Termination Protection. |
Security Enhancement | No | By default, Anti-DDoS and Cloud Workload Protection are enabled free of charge to help you build a CVM security system to prevent data leakage. |
Tencent Cloud Observability Platform | No | CM is activated by default. You can install add-ons to get CVM monitoring metrics and display them in visual charts. You can also specify custom alarm thresholds. In addition, you can configure three-dimensional CVM data monitoring, smart data analysis, real-time fault alarms, and custom data reports to precisely monitor Tencent Cloud services and the health conditions of CVM instances. |
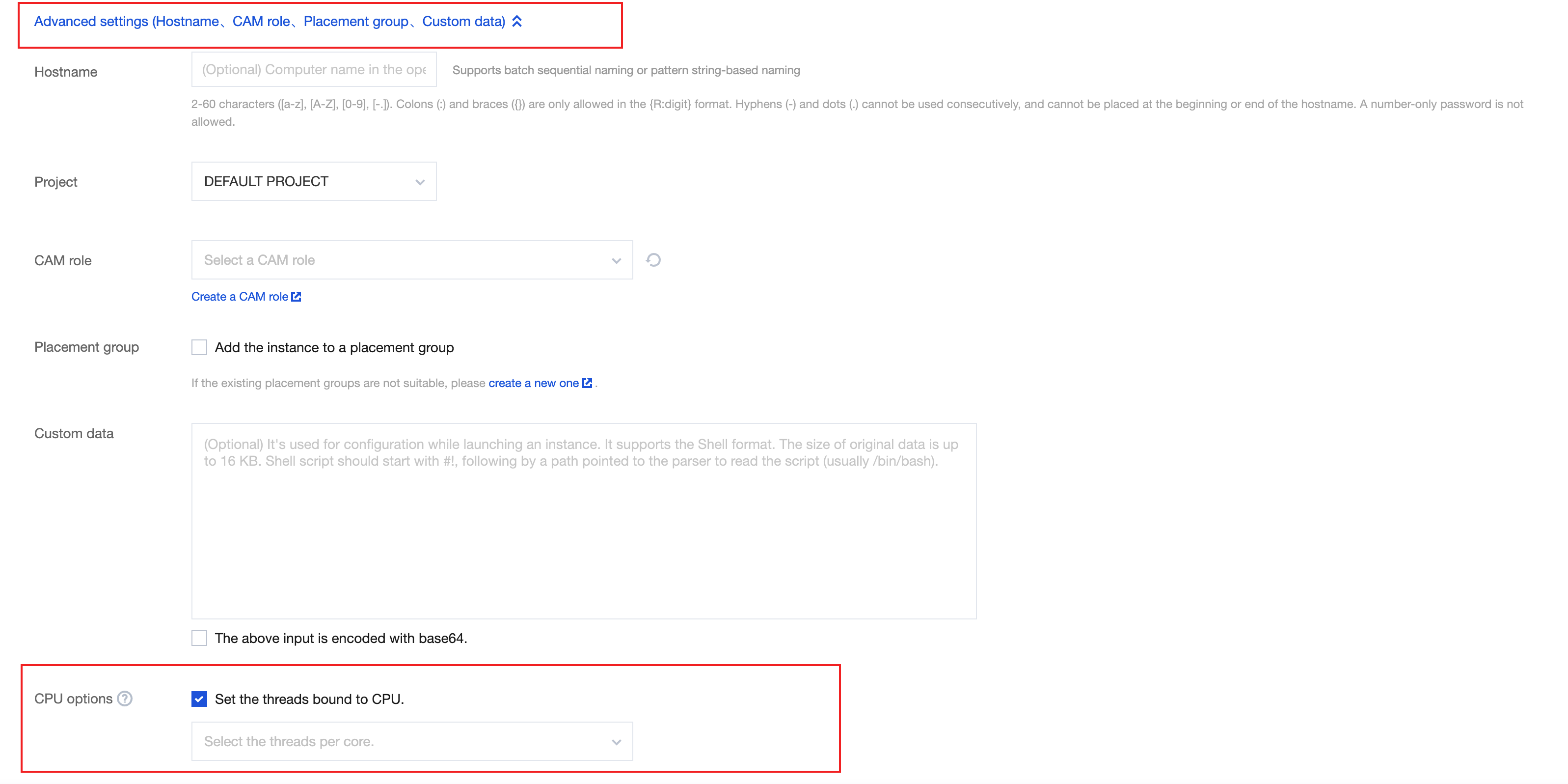
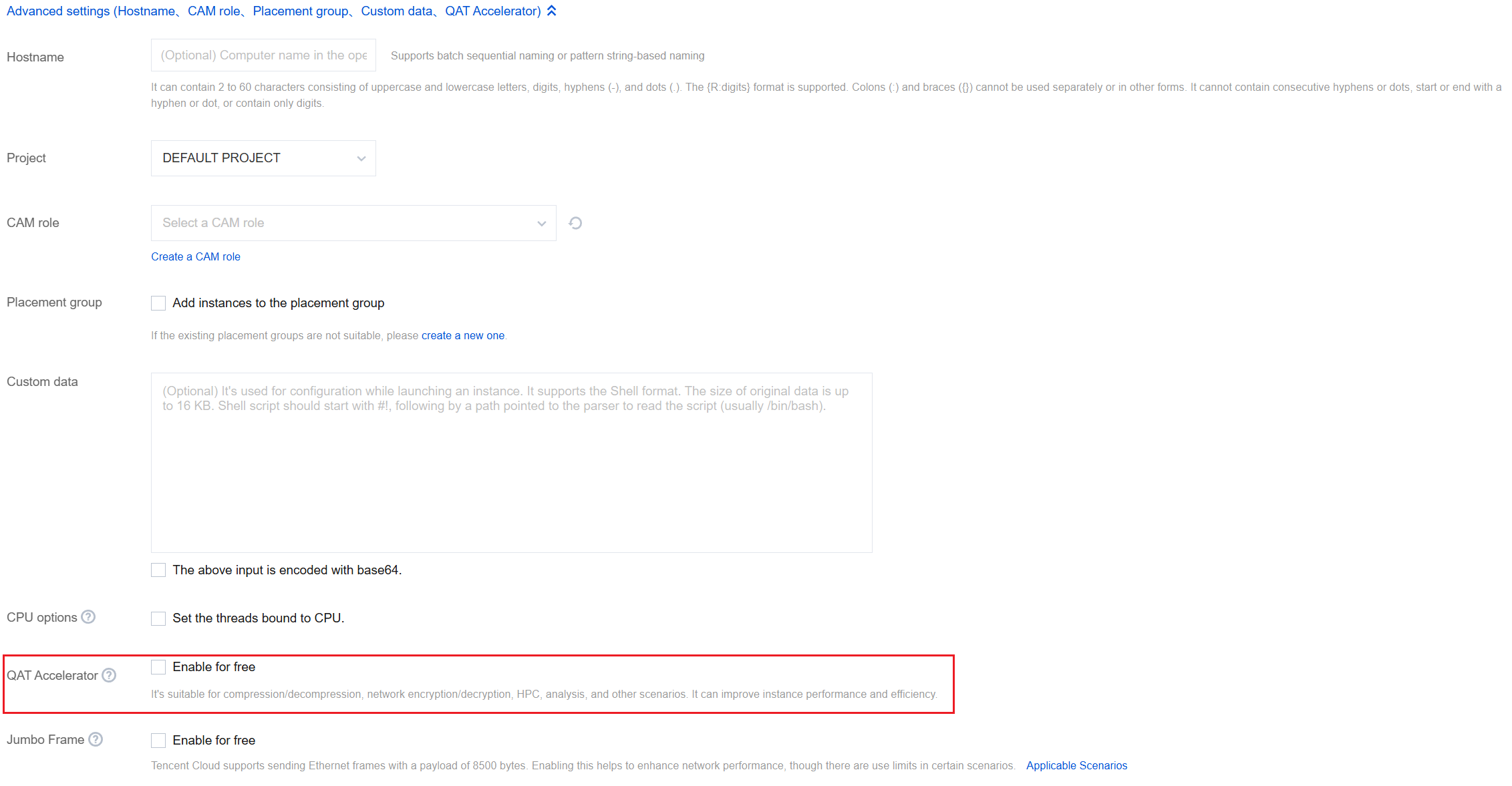
Advanced Settings | No | Configure additional settings for the instance as needed. Hostname: You can customize the name of the computer in the CVM operating system. After a CVM instance is created, you can log in to it to view the hostname. Project: The default project is selected. You can select an existing project as needed to manage different CVM instances. CAM Role: You can set a role and use it to grant a role entity the permissions to access CVM services and resources and perform operations in Tencent Cloud. For detailed directions, see Managing Roles. Placement Group: You can add the instances to placement groups to improve your business availability. For detailed directions, see Placement Group. Custom Data: You can configure an instance by specifying custom data, and the configured scripts will run when an instance is started. If multiple CVM instances are purchased at a time, the custom data will run on all of them. The Linux operating system supports the Shell format, while the Windows operating system supports the PowerShell format and a maximum of 16 KB of raw data. For more information, see Configuring Custom Data (Linux CVM). Note: Custom data configuration applies only to certain public images with the cloud-init service. For more information, see Cloud-Init & Cloudbase-Init. |
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
Image Status | Solution |
Images on local computers or other platforms | Import the system disk image on local computers or other platforms to the custom image on CVM. For more information, see Overview. |
There are template instances but no custom images | |
Custom images in other regions | Copy the custom image to the target region where you want to create an instance. For more information, see Copying Images. |
Custom images under another account | Share the custom image with the account under which you want to create an instance. For more information, see Sharing Custom Images. |
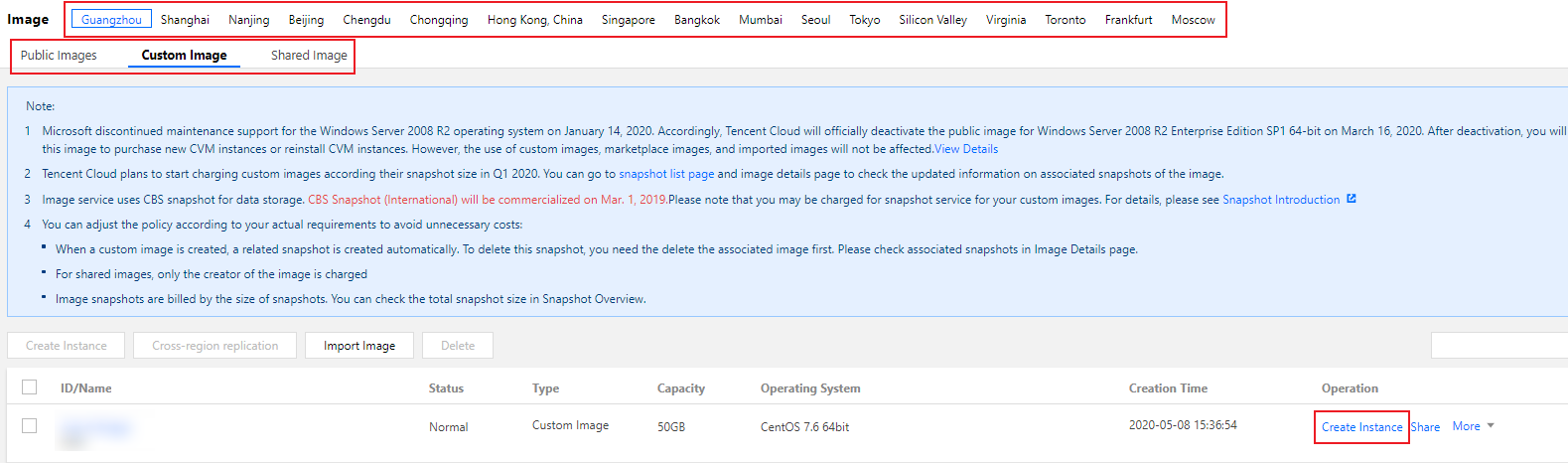
RunInstances API to pass in the snapshot ID parameter; otherwise, the created cloud disk cannot match the snapshot ID, the snapshot data cannot be rolled back, the data disk has no data, and mounting cannot be performed.Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
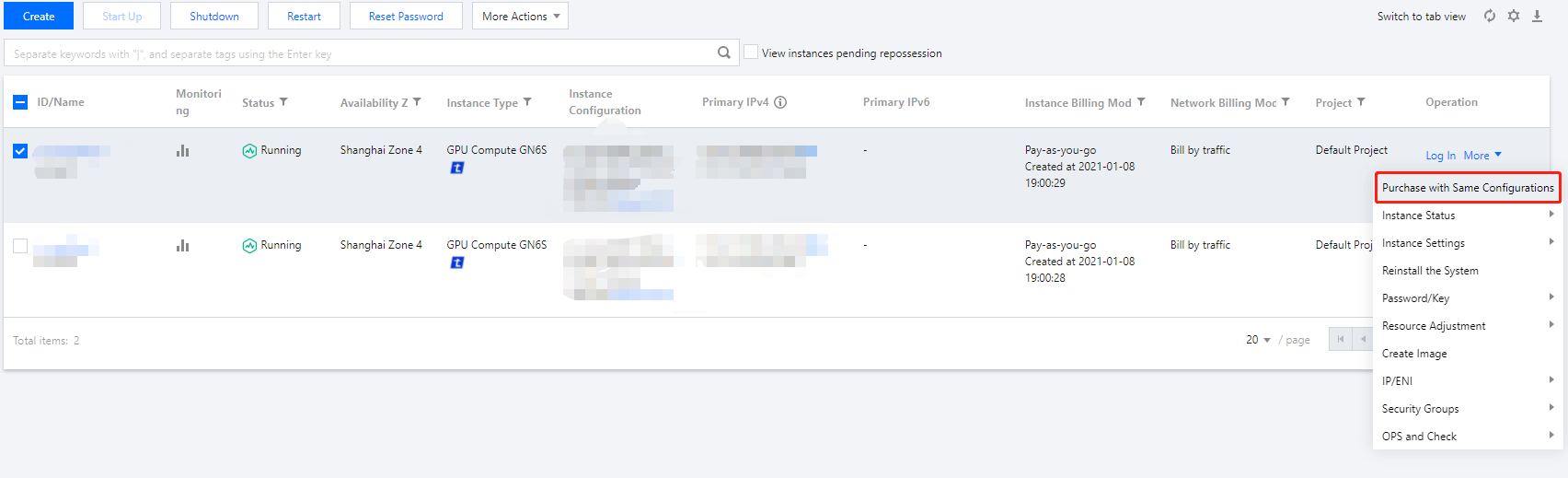
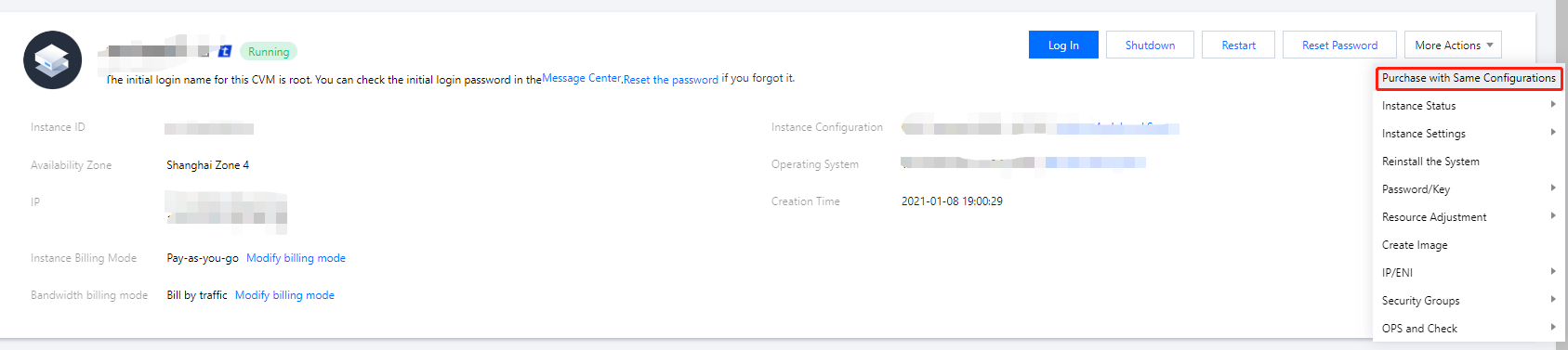
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
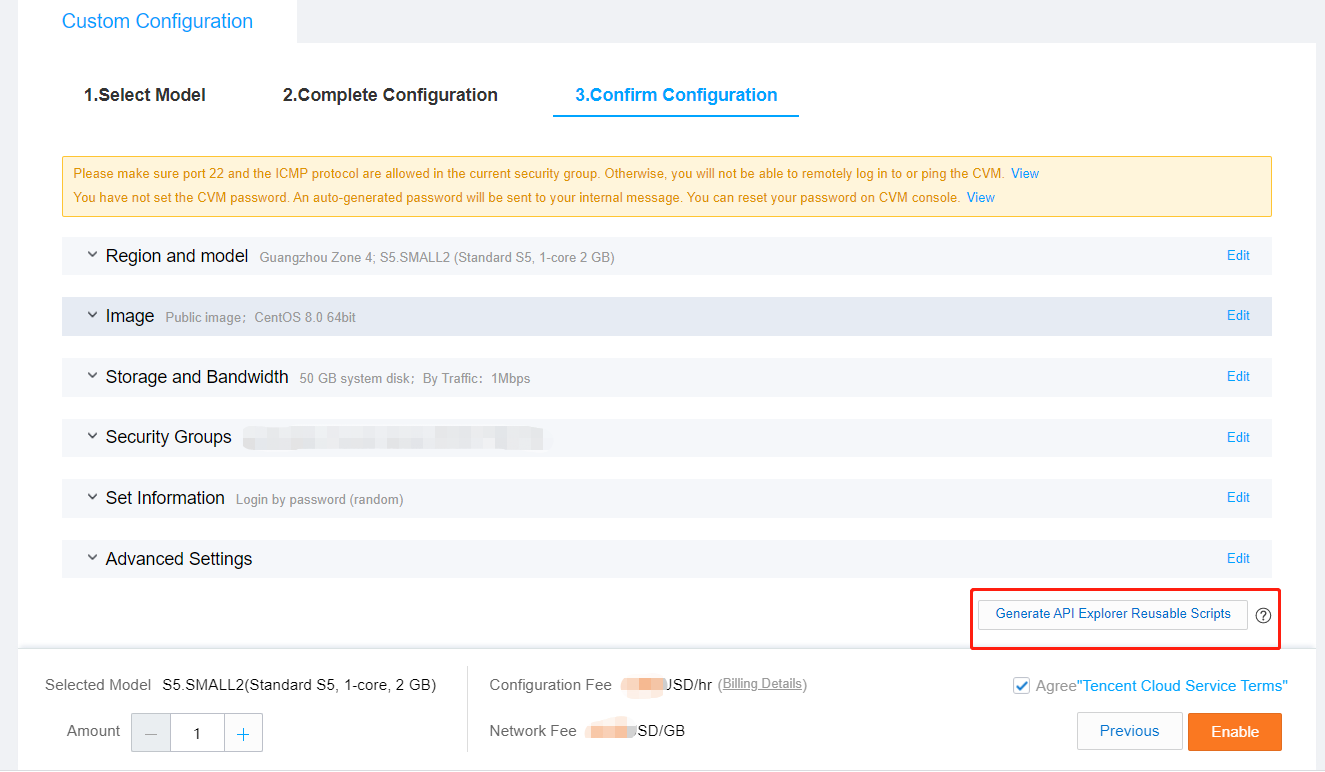
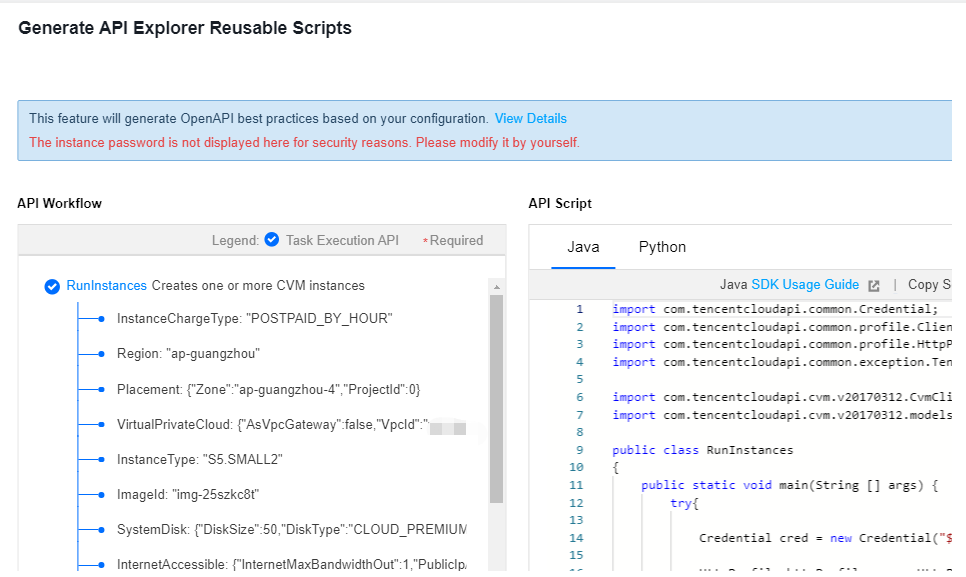
RunInstances API based on the selected configurations. The parameters marked with “*” are required for the API. You can hover over the data to display it completely.Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
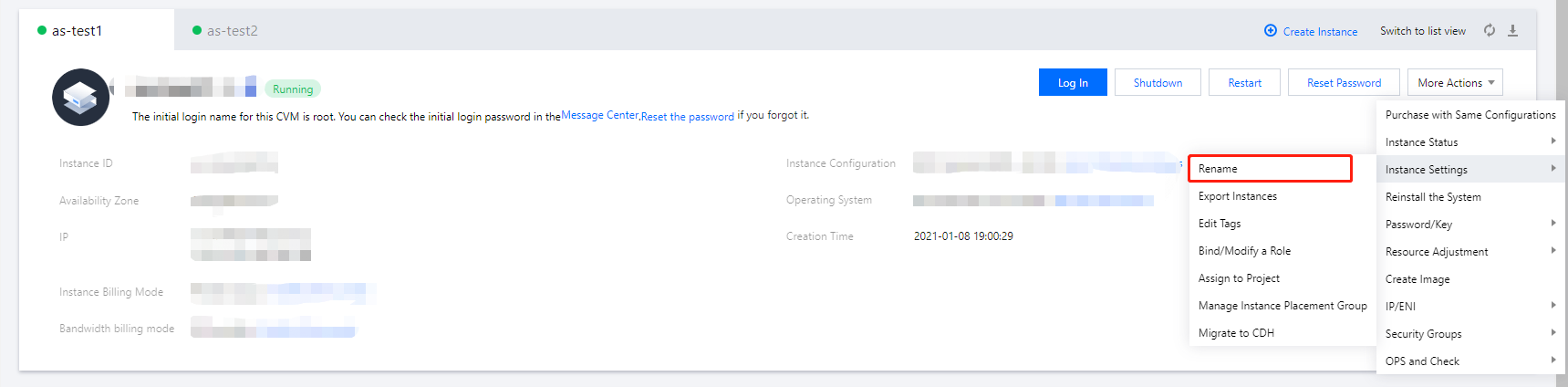
CVM as the instance name.
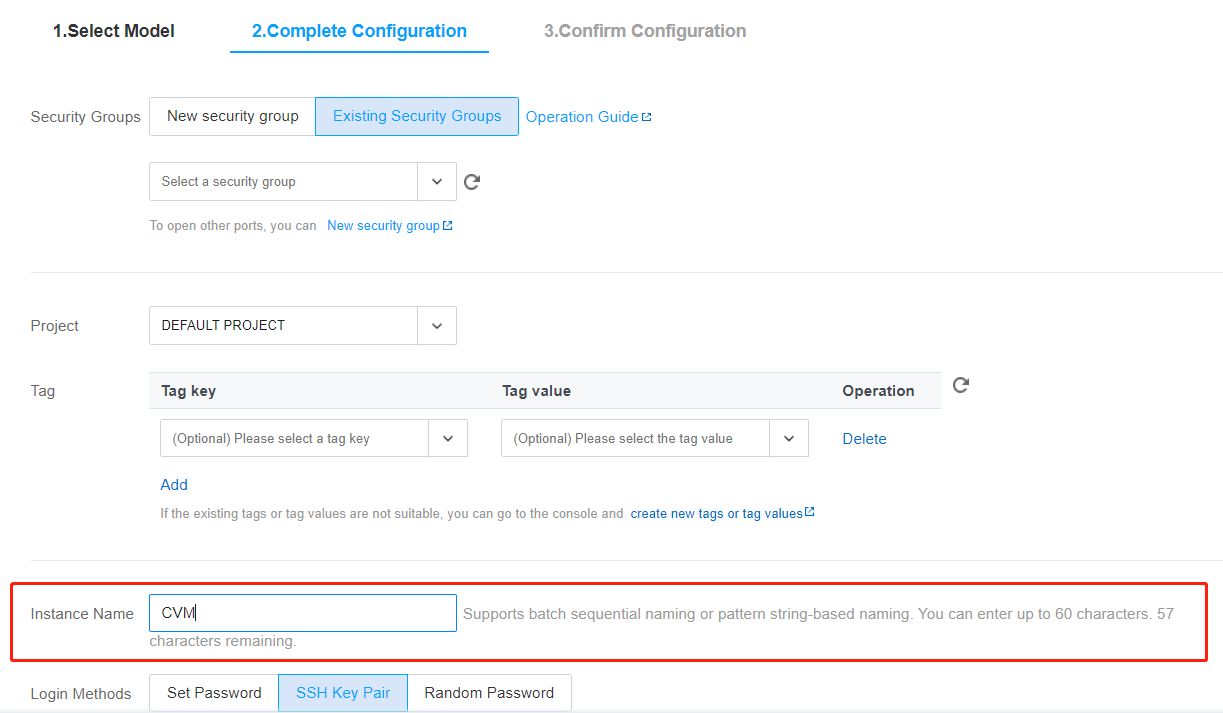
InstanceName to CVM.HostName to CVM.CVM{R:3} as the instance name.
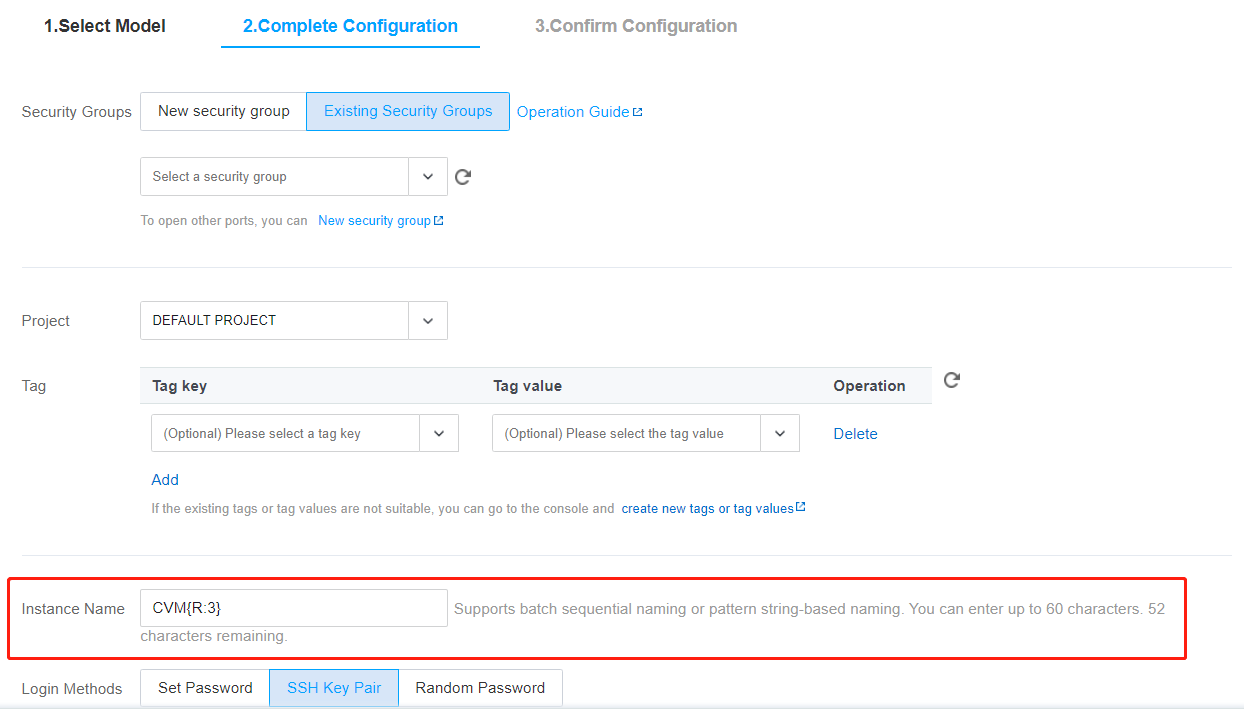
InstanceName to CVM{R:3}.HostName to CVM{R:3}.cvm{R:13}-Big{R:2}-test as the instance name.
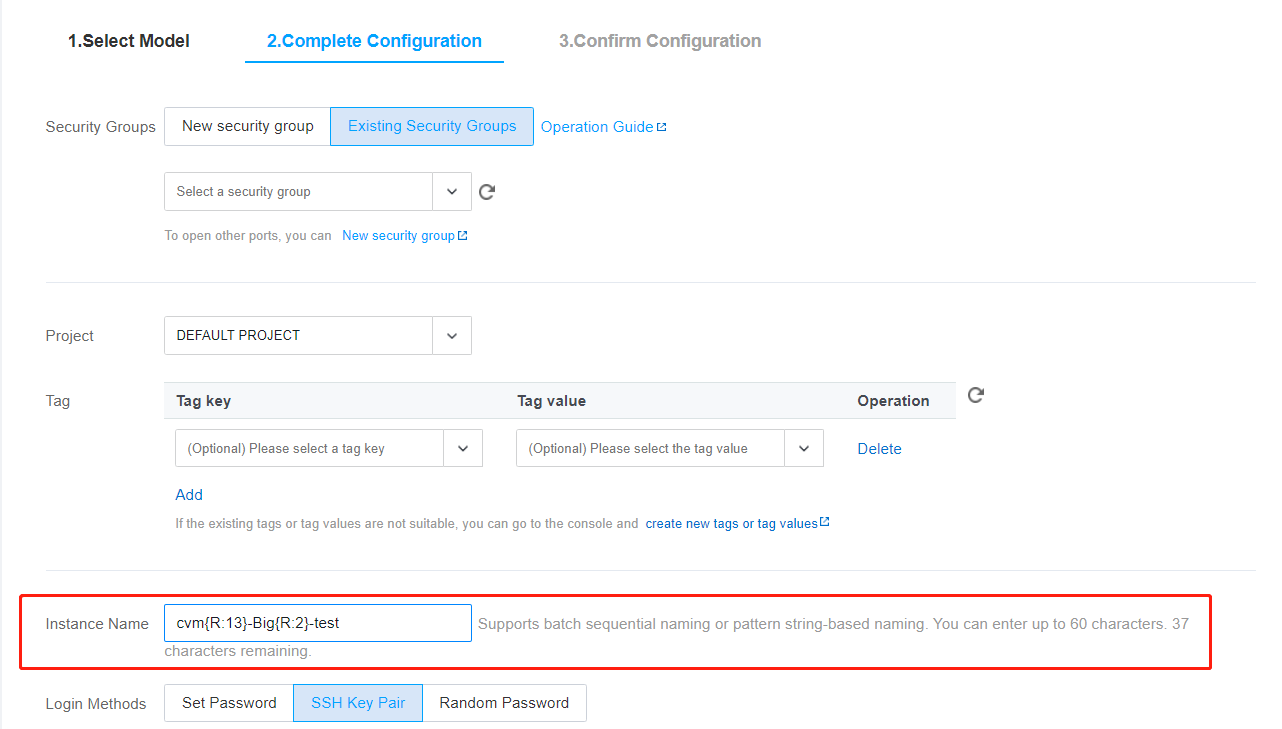
InstanceName to cvm{R:13}-Big{R:2}-test.HostName to cvm{R:13}-Big{R:2}-test.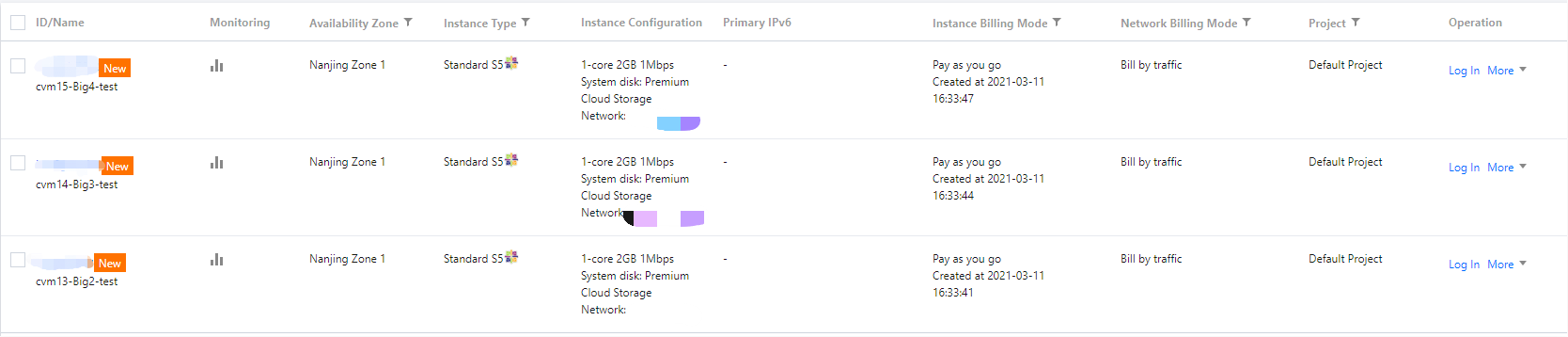
hostname
hostname
hostname command.cvm13-Big2-test
Last updated:2025-09-28 15:10:06
Last updated:2025-09-30 16:39:06

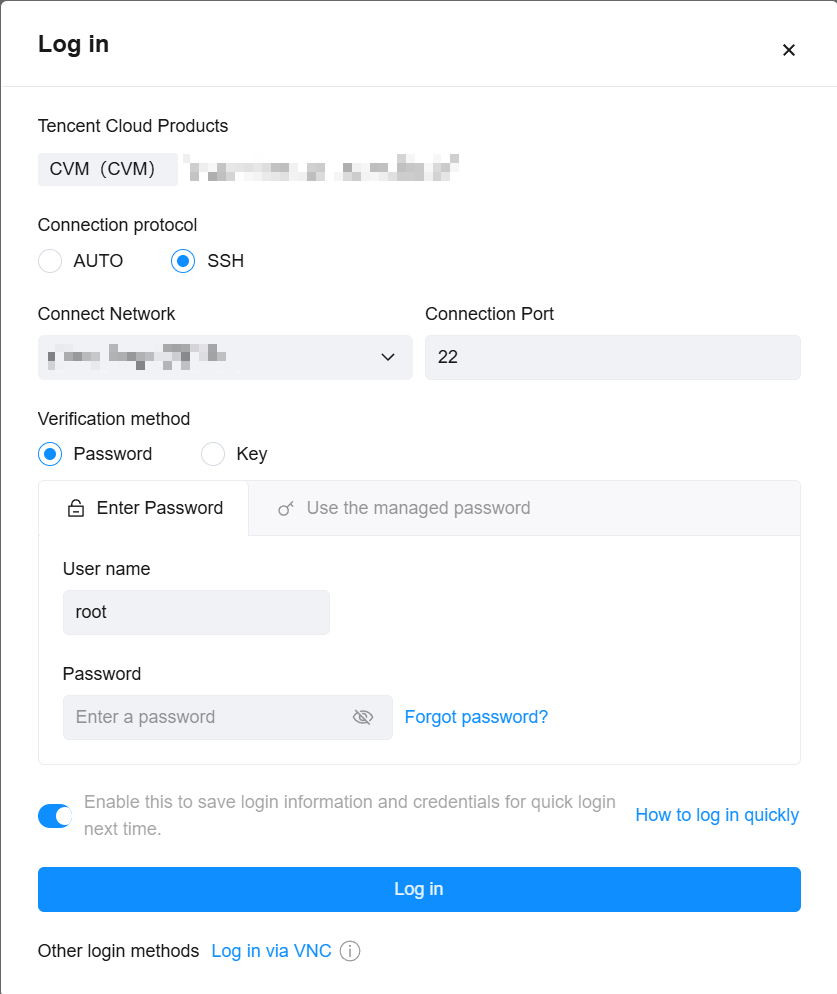
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
root for the Linux instance, and is ubuntu for the Ubuntu system. You can modify it according to the actual situation.ssh <username>@<hostname or IP address>
username refers to the default account as mentioned in “Prerequisites”.hostname or IP address refers to the public IP address or custom domain name of your Linux instance.chmod 400 <The absolute path of the private key downloaded to be associated with the CVM>
icacls <The absolute path of the private key downloaded to be associated with the CVM> /grant <Windows user account>:F
icacls <The absolute path of the private key downloaded to be associated with the CVM> /inheritancelevel:r
ssh -i <The absolute path of the private key downloaded to be associated with the CVM> <username>@<hostname or IP address>
username refers to the default account as mentioned in “Prerequisites”.hostname or IP address refers to the public IP address or custom domain name of your Linux instance.ssh -i "Mac/Downloads/shawn_qcloud_stable.pem" ubuntu@192.168.11.123 command to remotely log in to the Linux CVM.Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
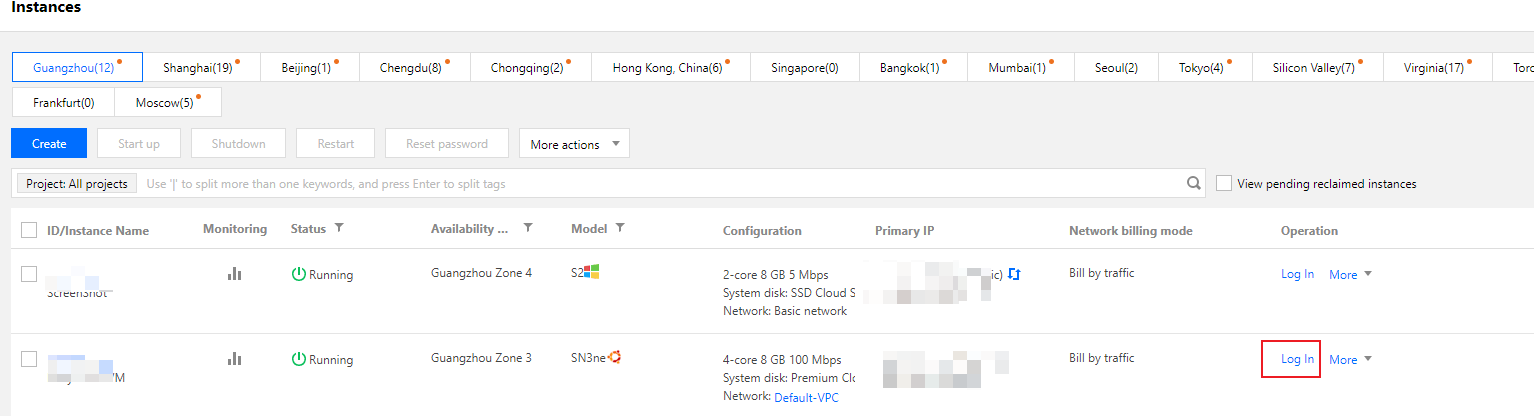
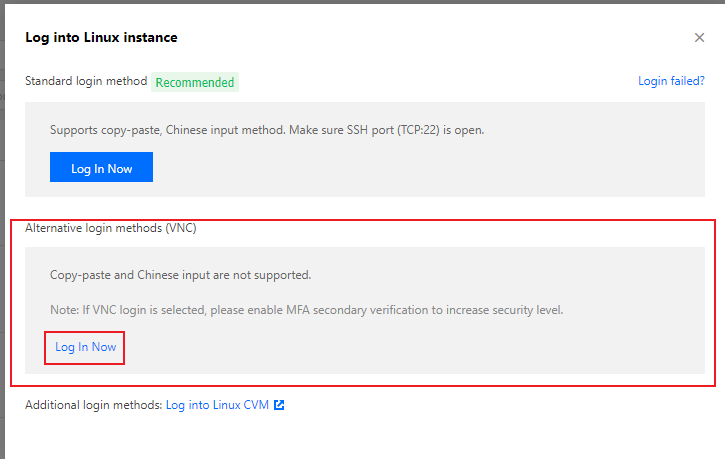
root, and the default username of Ubuntu instances is ubuntu. Please enter as needed.
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
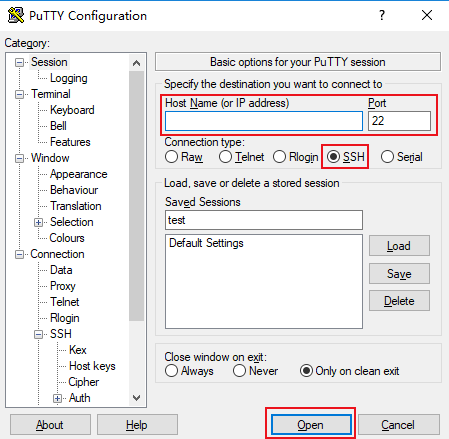
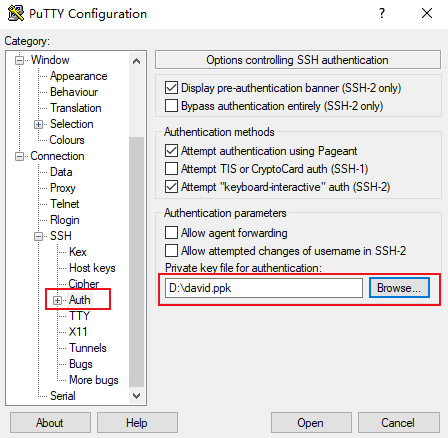
test.
After configuring Host Name, configure and save Saved Sessions. You can double-click the session name saved under Saved Sessions to log in to CVM.
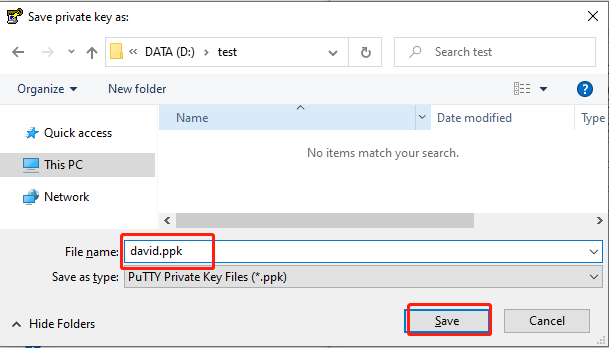
david, as shown below:
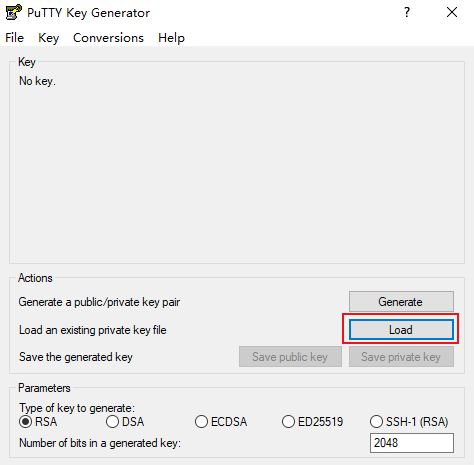
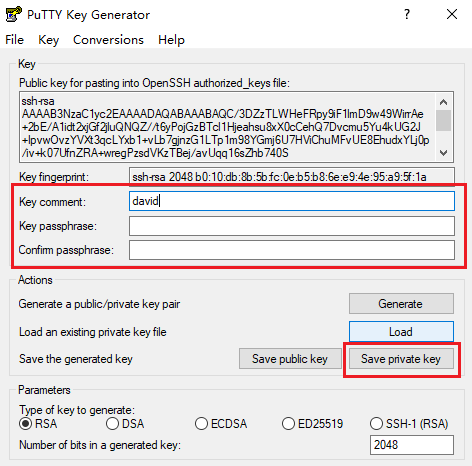
david as david.ppk, as shown below:

test.
After configuring Host Name, configure and save Saved Sessions. You can double-click the session name saved under Saved Sessions to log in to CVM.
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
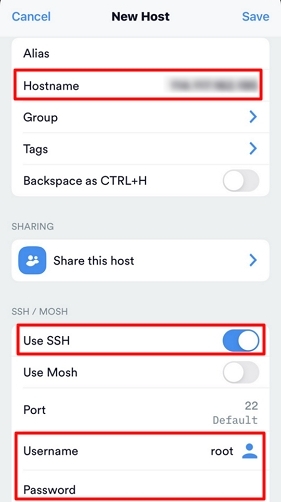
root, or ubuntu if your instance uses the Ubuntu operating system.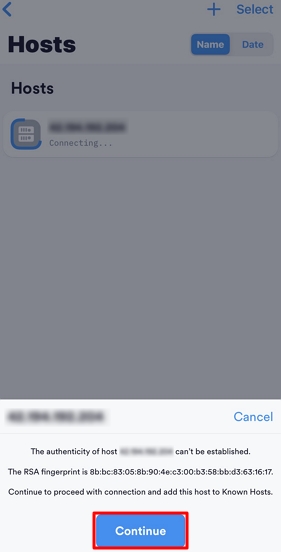
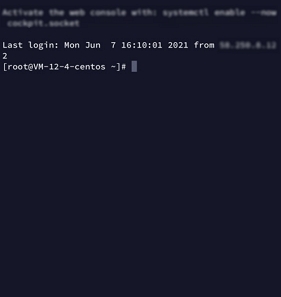
root, or ubuntu if your instance uses the Ubuntu operating system.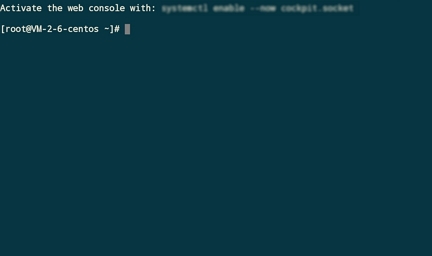
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
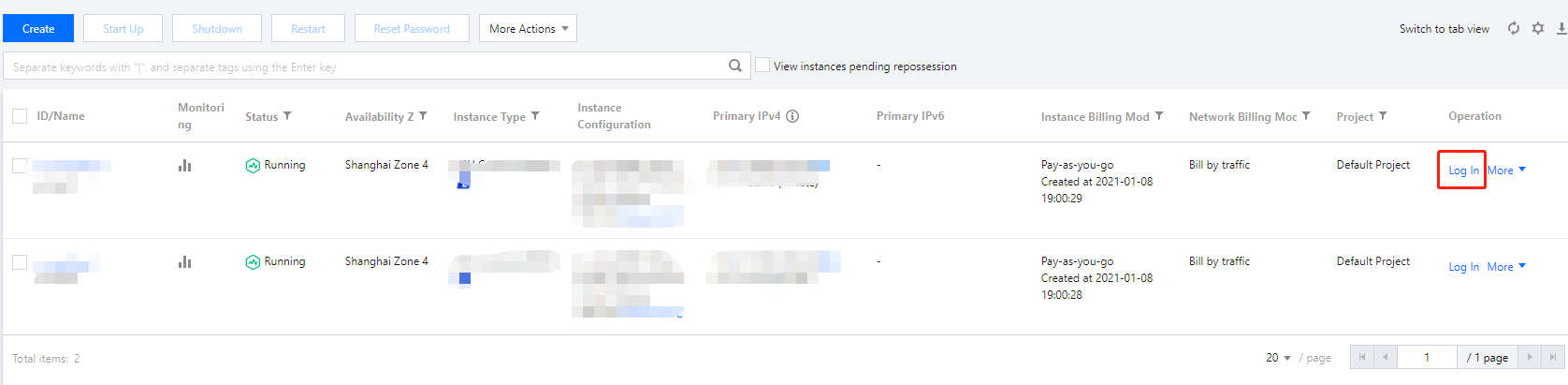
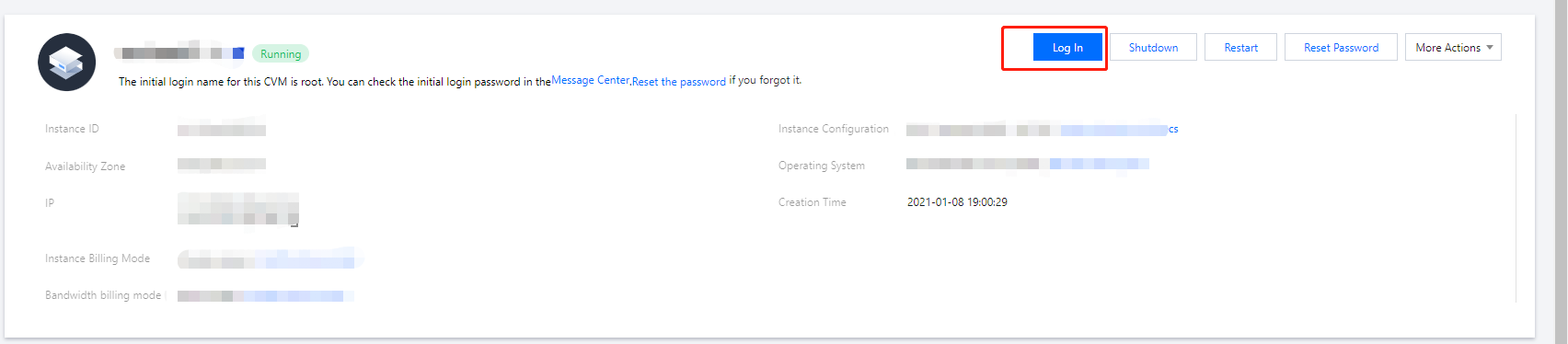
Administrator. Enter a value as needed.
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
:port in the RDP file.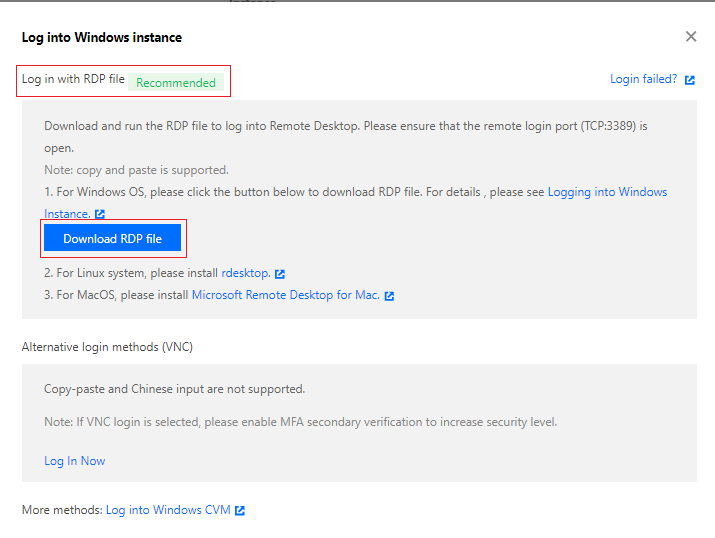
rdesktop
wget https://github.com/rdesktop/rdesktop/releases/download/v1.8.3/rdesktop-1.8.3.tar.gz
tar xvzf rdesktop-<x.x.x>.tar.gz ## Replace x.x.x with the version number of the downloaded rdesktop.cd rdesktop-1.8.3./configuremakemake install
rdesktop -u Administrator -p <your-password> <hostname or IP address>
Administrator refers to the admin account mentioned in the prerequisites section.<your-password> refers to the login password that you set.
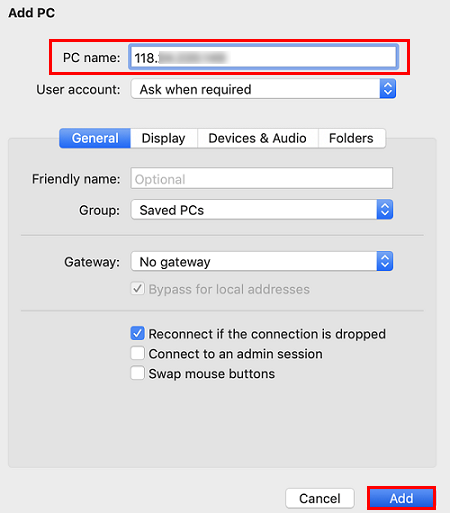
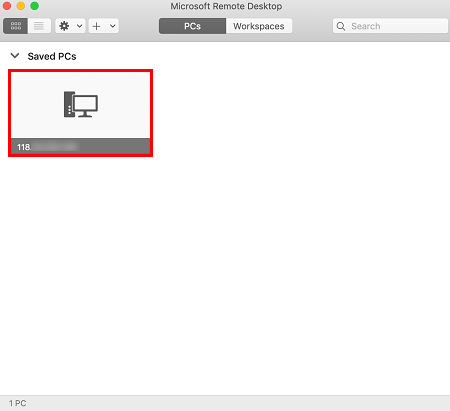
If you use a system default password to log in to the instance, you can obtain the password at the Message Center. If you forgot your password, please reset the instance password.<hostname or IP address> is the public IP or custom domain name of your Windows instance. For more information on how to get the public IP, please see Getting Public IP Addresses.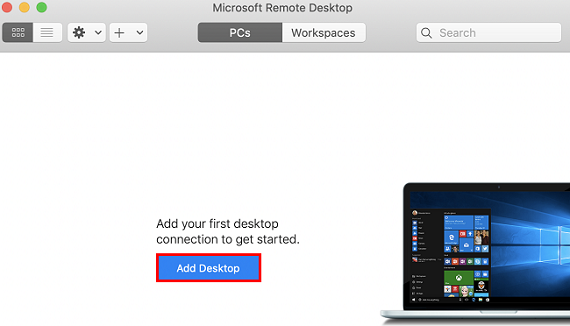


Scenario | Default Mode | H.264/AVC 444 Mode | Description |
Idle | 0.3 Kbps | 0.3 Kbps | User has paused their work, and there's no active screen updates. |
Microsoft Word | 100–150 Kbps | 200–300 Kbps | User is actively working with Microsoft Word, typing, pasting graphics, and switching between documents. |
Microsoft Excel | 150–200 Kbps | 400–500 Kbps | User is actively working with Microsoft Excel and updating multiple cells with formulas and charts simultaneously. |
Microsoft PowerPoint | 4–4.5 Mbps | 1.6–1.8 Mbps | User is actively working with Microsoft PowerPoint, typing, and pasting. User is also modifying rich graphics and using slide transition effects. |
Web browsing | 6–6.5 Mbps | 0.9–1 Mbps | User is actively working with a graphically rich website that contains multiple static and animated images. User scrolls the pages both horizontally and vertically. |
Image gallery | 3.3–3.6 Mbps | 0.7–0.8 Mbps | User is actively working with the image gallery application, browsing, zooming, resizing, and rotating images. |
Video playback | 8.5–9.5 Mbps | 2.5–2.8 Mbps | User is watching a 30 FPS video that consumes 1/2 of the screen. |
Fullscreen video playback | 7.5–8.5 Mbps | 2.5–3.1 Mbps | User is watching a 30 FPS video that is maximized to a fullscreen. |
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02

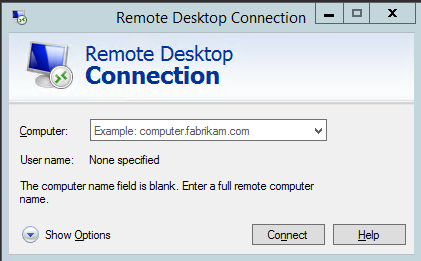
Administrator, and the password can be obtained as instructed in Prerequisites.
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
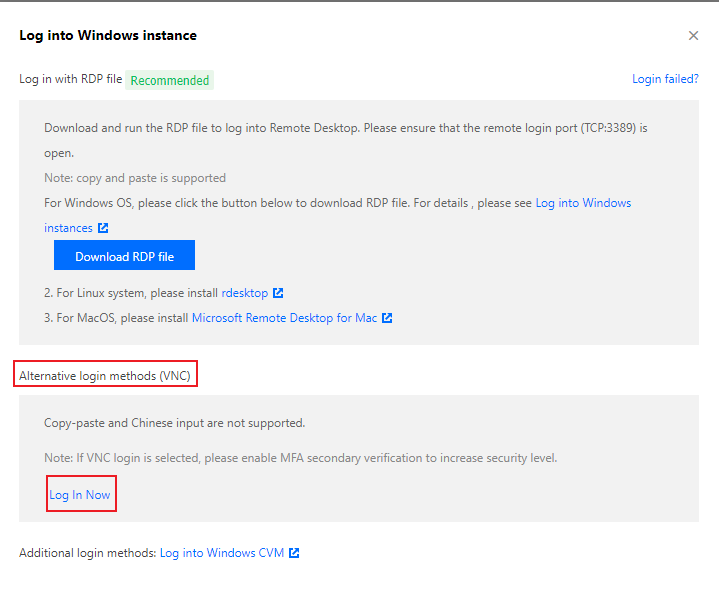
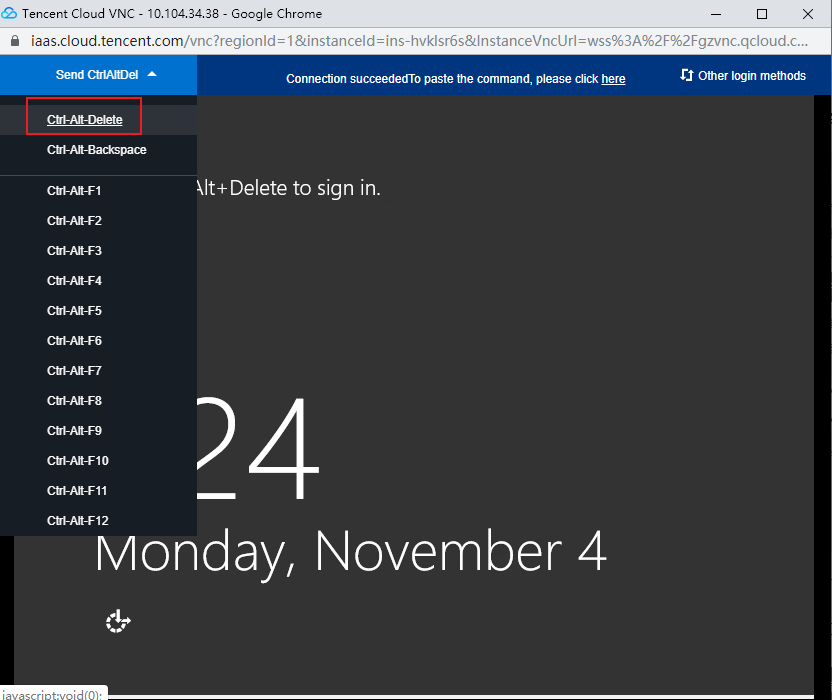
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
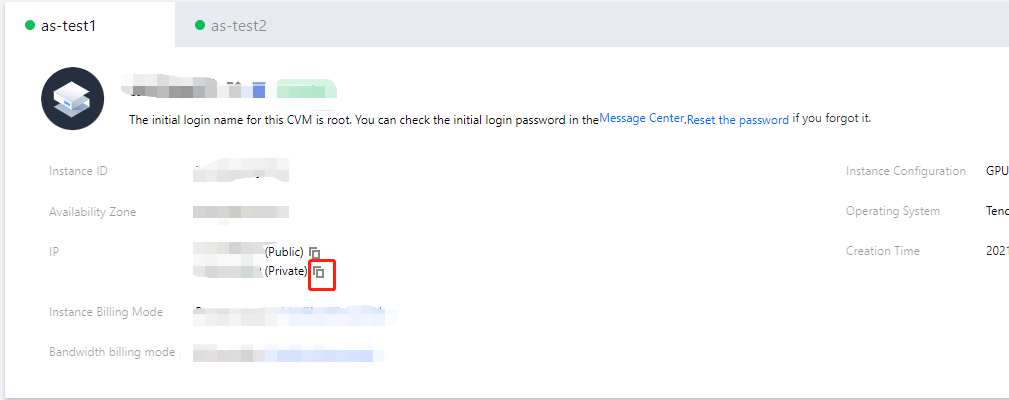
Administrator.
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02

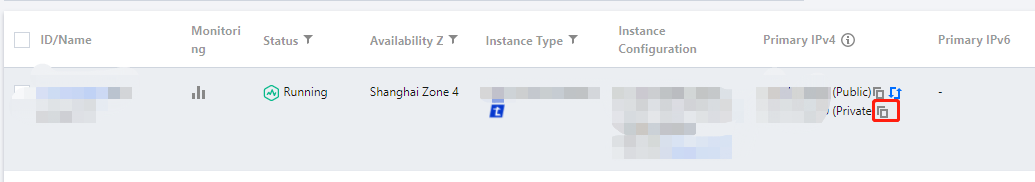

curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/meta-data/local-ipv4

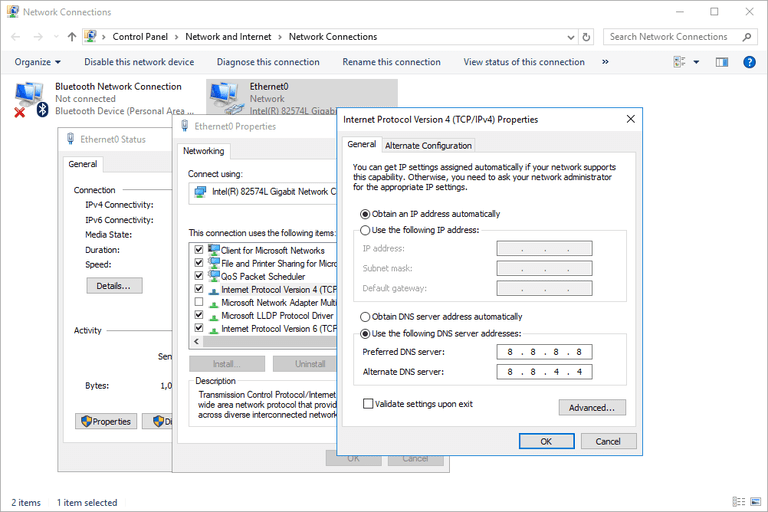
/etc/grub.conf file.vi /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 10.53.216.182nameserver 10.53.216.198options timeout:1 rotate
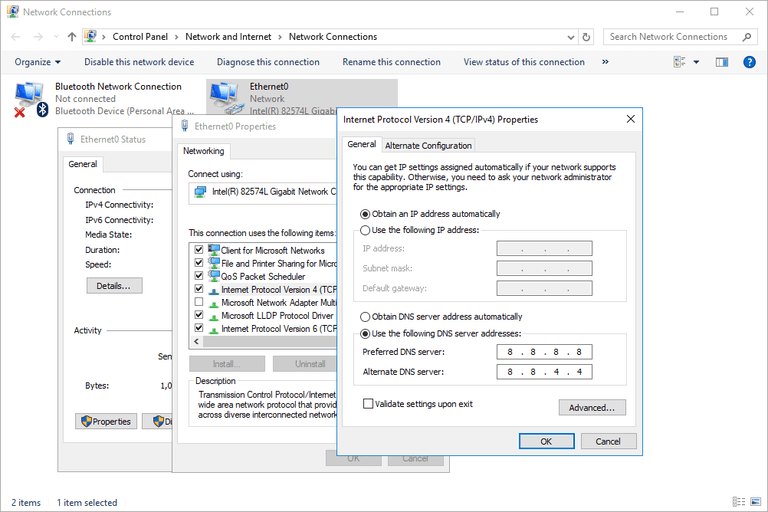
Last updated:2024-07-10 09:55:57

Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02

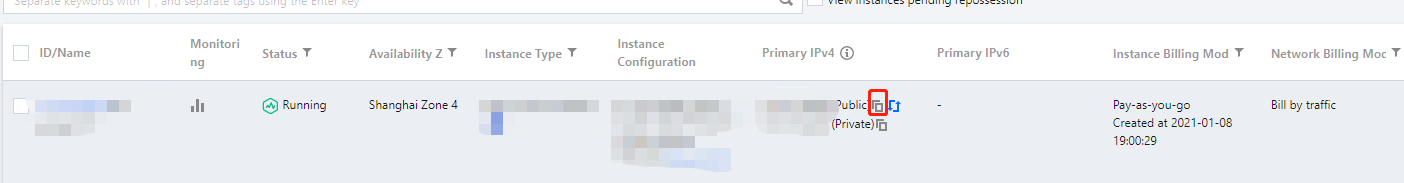

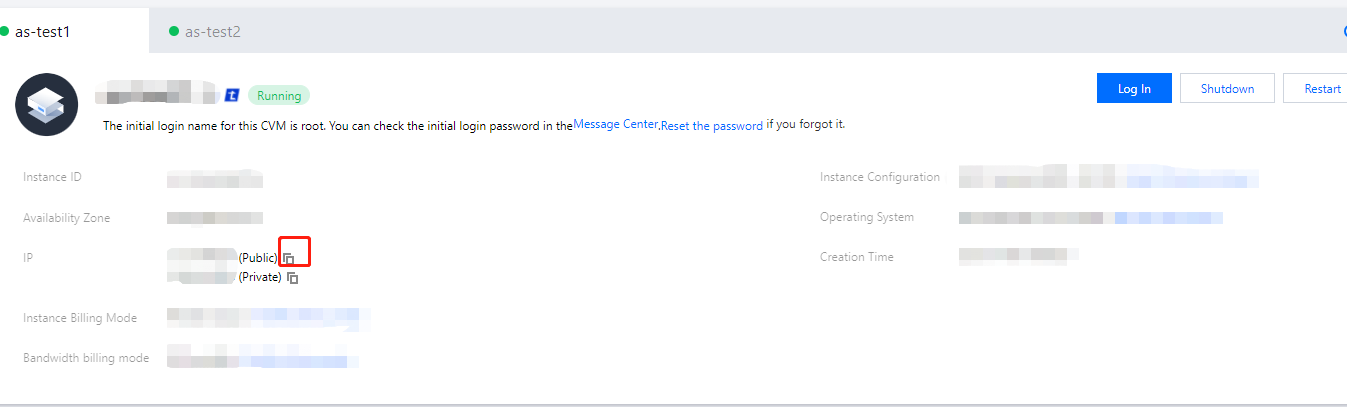
ifconfig (Linux) or ipconfig (Windows) commands), the public IP address is not displayed. To obtain the public IP from within the instance, you need to check the instance metadata.curlhttp://metadata.tencentyun.com/meta-data/public-ipv4
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
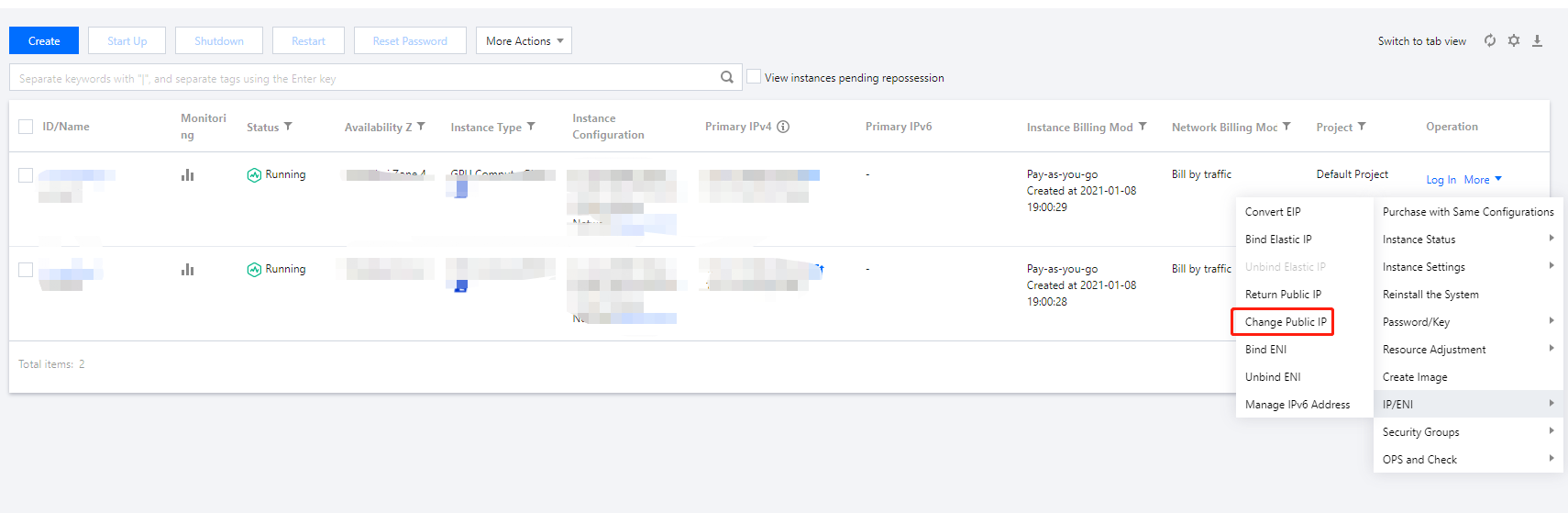
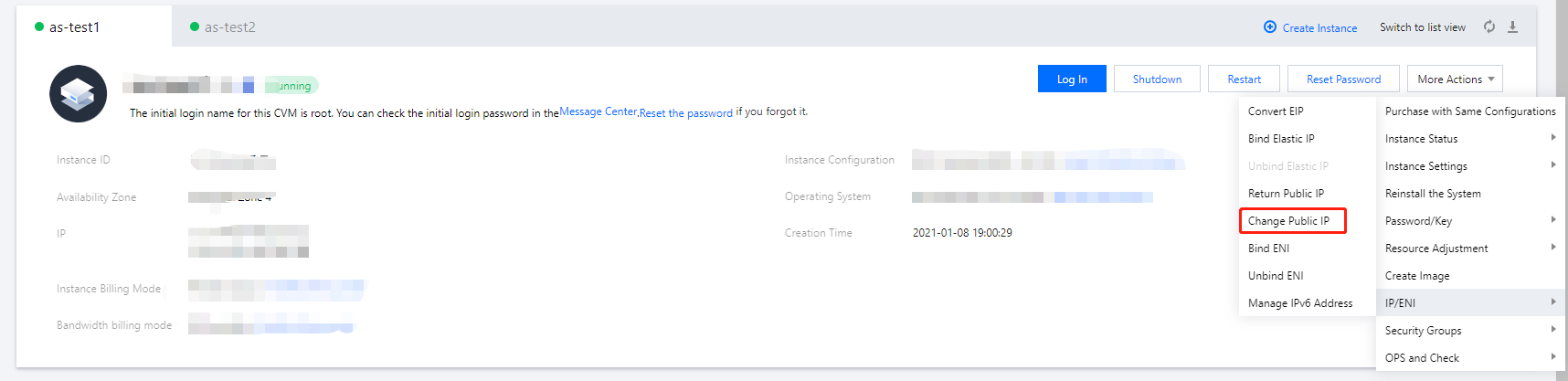
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
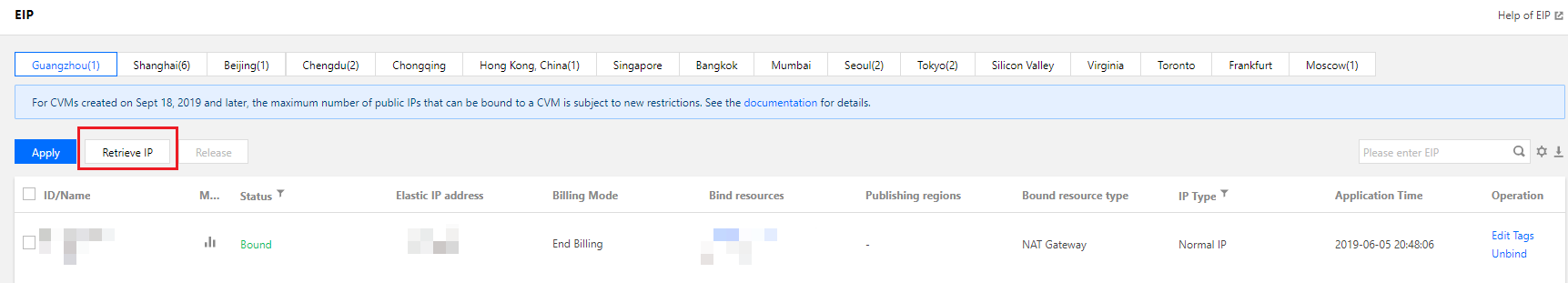

Last updated:2025-08-14 17:22:23
Concept | Description |
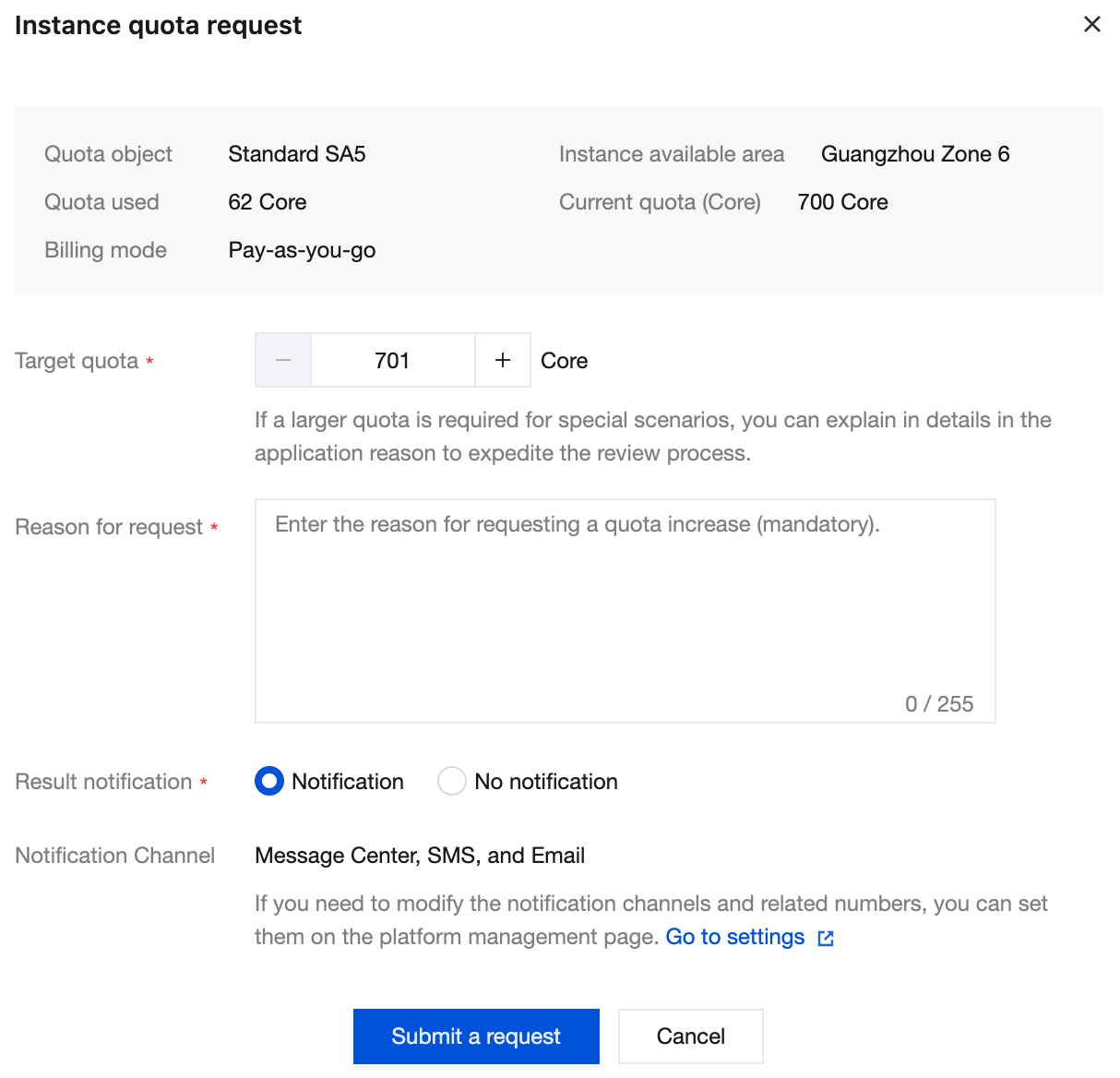
Instance Quota | A Tencent Cloud account can apply for the maximum value of instance purchases. |
Quota Unit | Quota units are distinguished by instance specifications: Instance specifications with vCPU < 64 cores, quota unit is number of cores. Instance specifications with vCPU ≥ 64 cores, quota unit is number of CVM instances. |
Current Quota | Current maximum value of instances that can be applied for purchase. |
Quota Used | Quota of purchased and used instances. |
Apply for Quota | You can apply for a quota increase on the quota management page. |
Target Quota | Target quota value applied for. Once the quota application is approved, it will override the original quota value. |
If you need to understand | Please Refer to |
Query Each Instance's Current Quota and Usage | |
Process for Applying for Instance Quota Increase | |
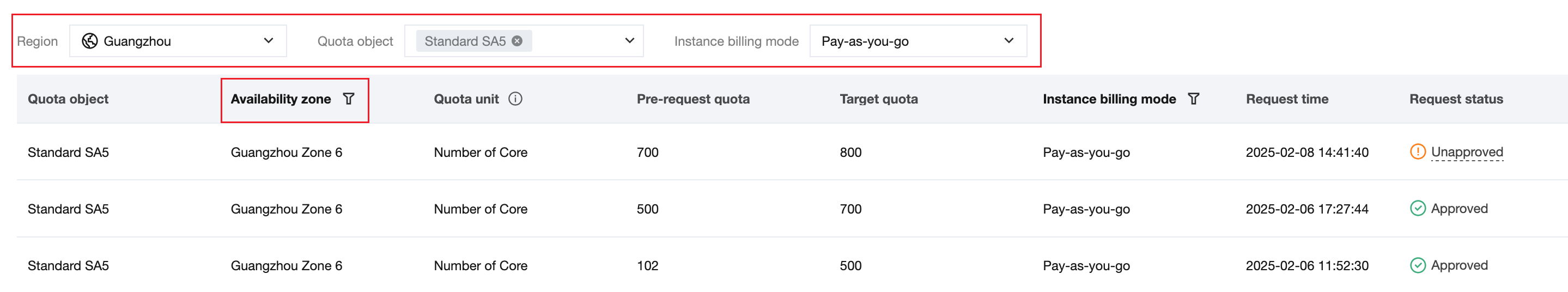
Query Quota Request Records |
Last updated:2025-10-29 18:05:09
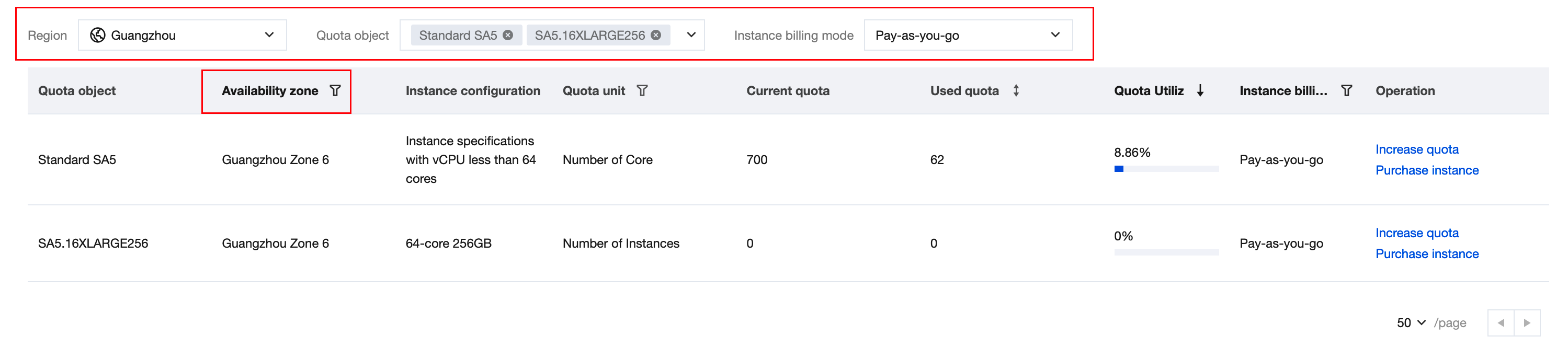
Last updated:2025-10-29 18:08:45
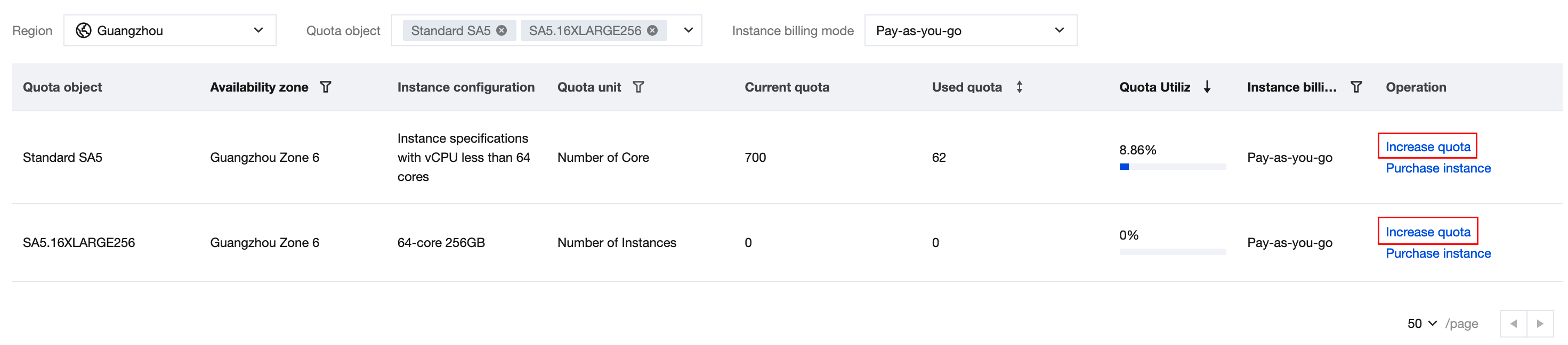
Last updated:2025-10-29 18:05:45
Last updated:2024-05-17 10:55:19
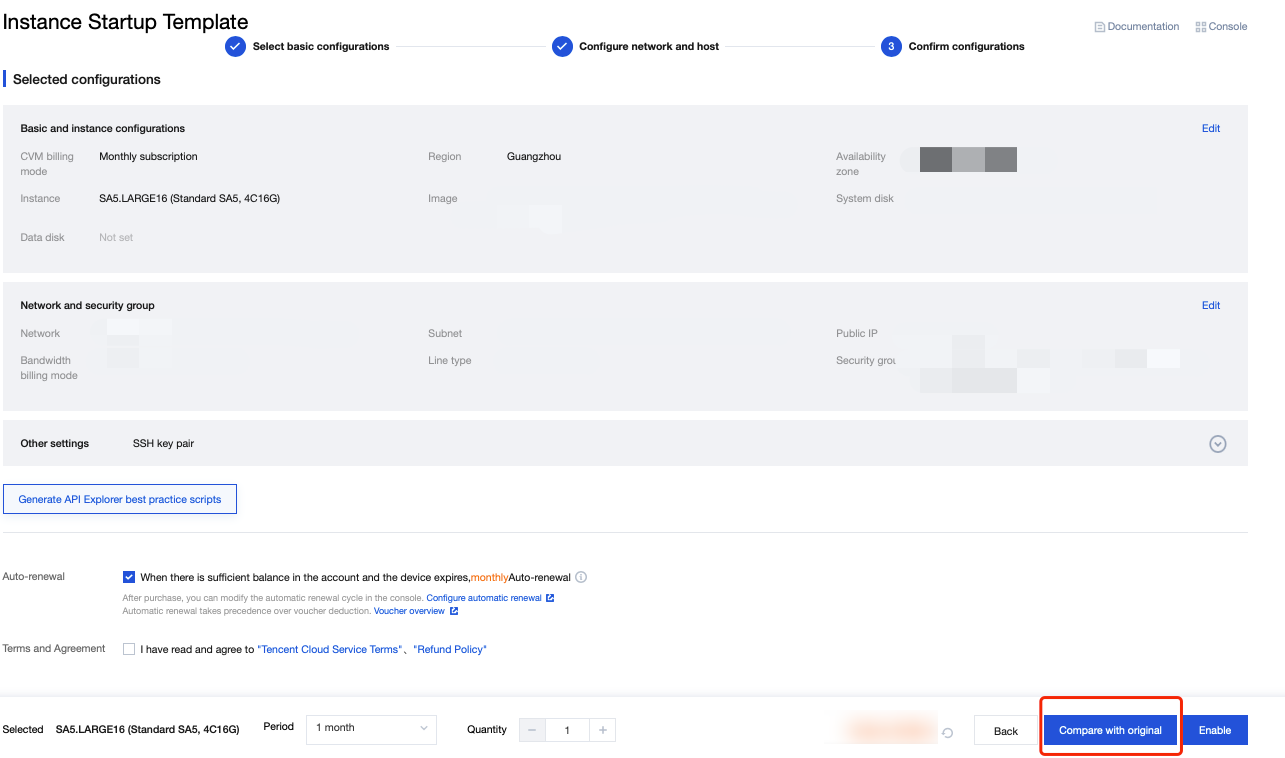
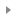
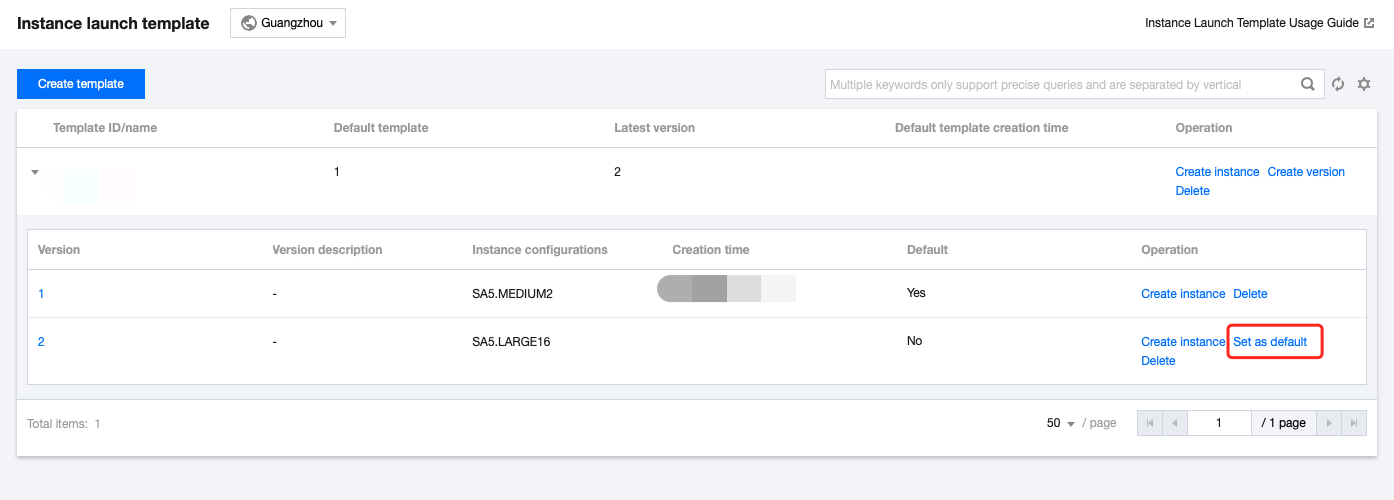
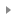
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02


Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
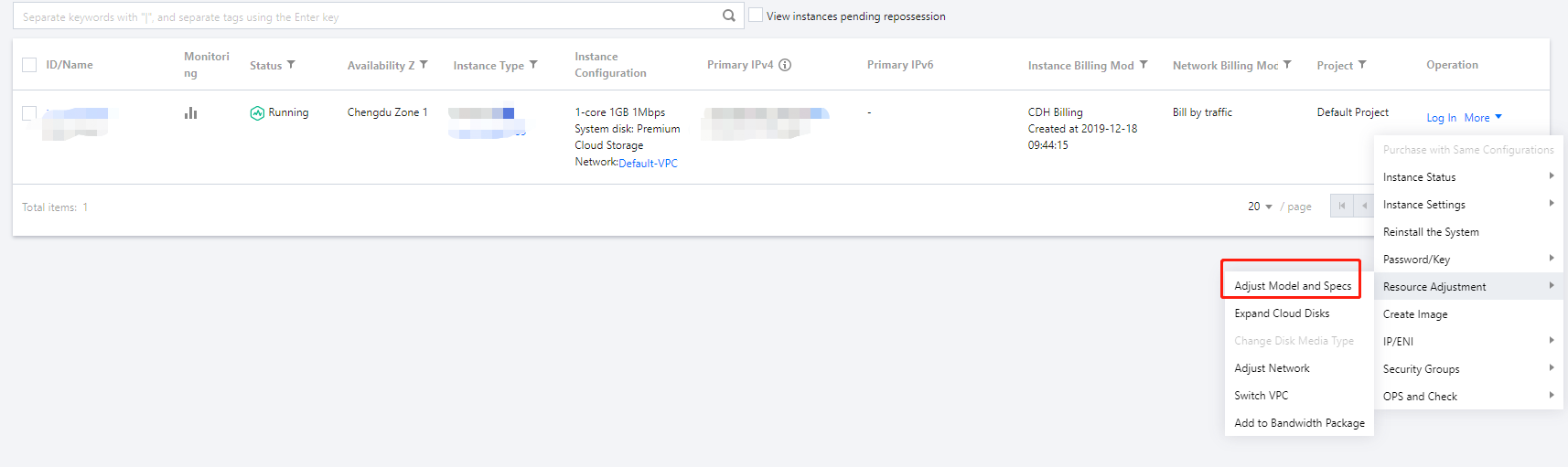

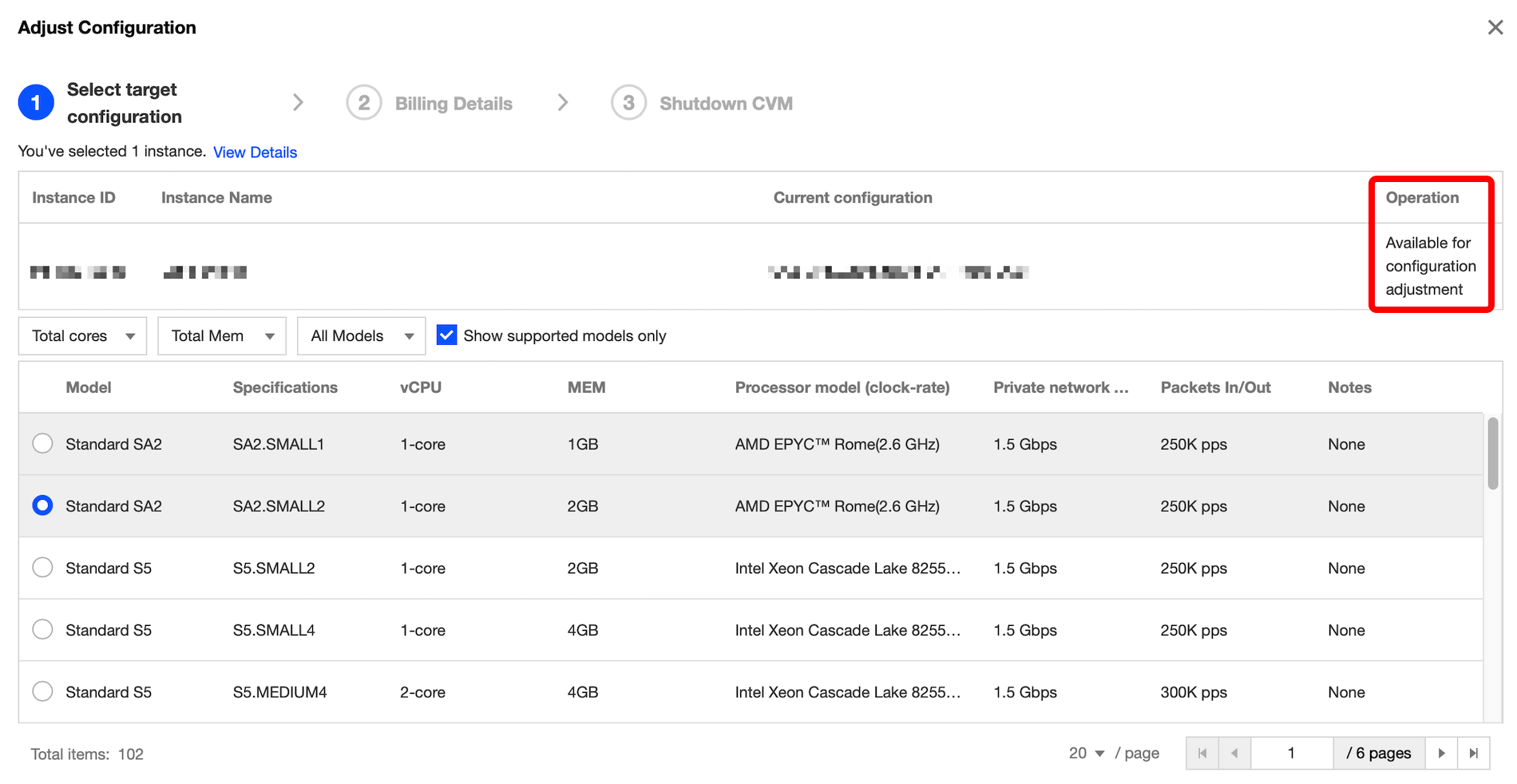

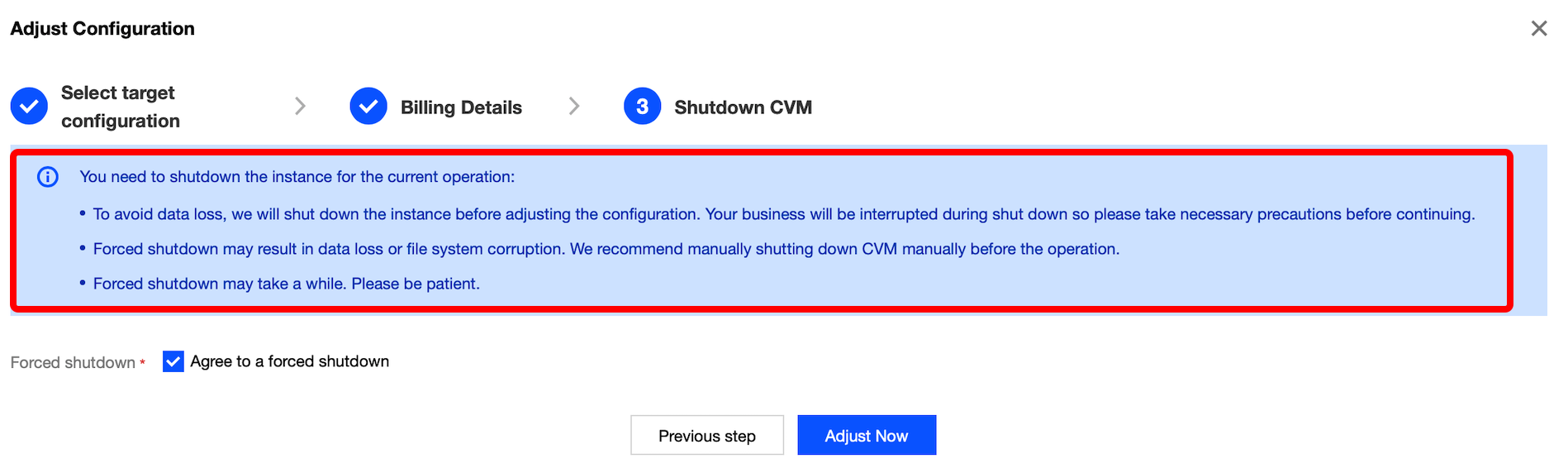

Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
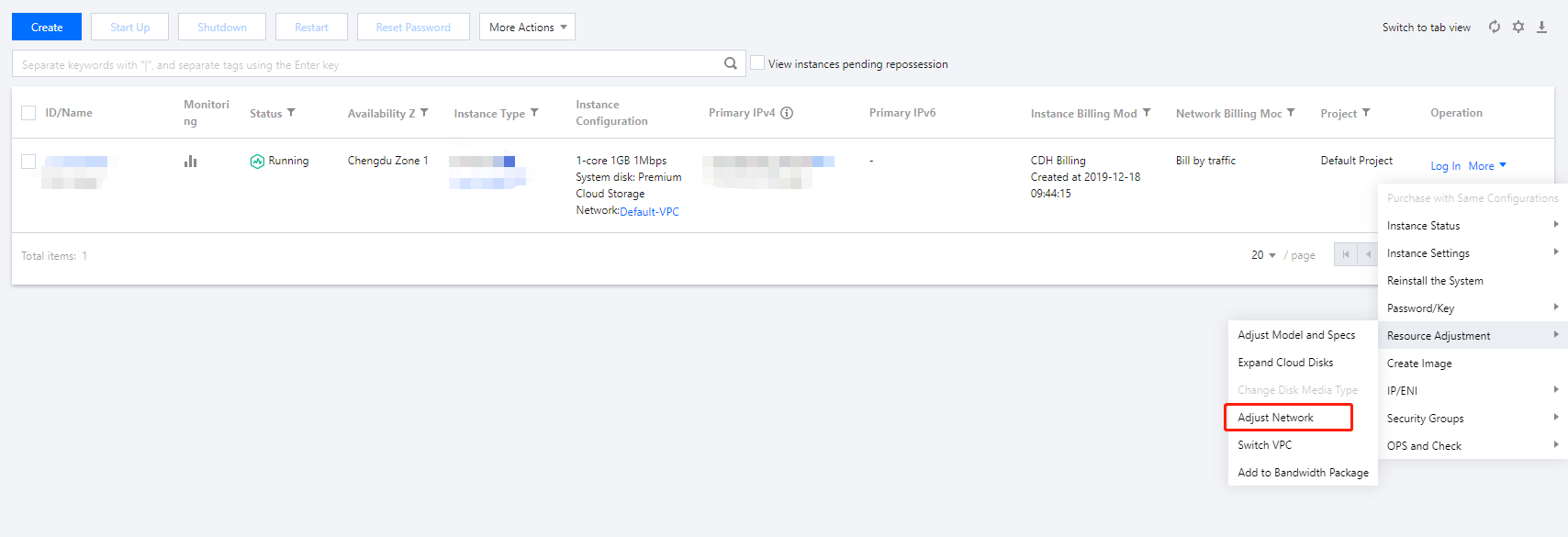
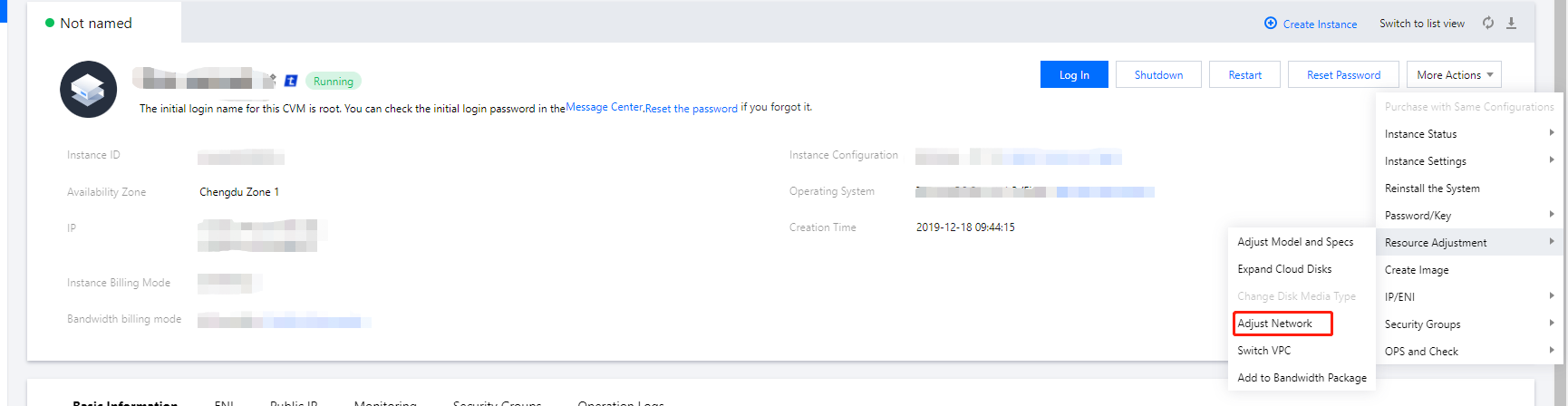
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
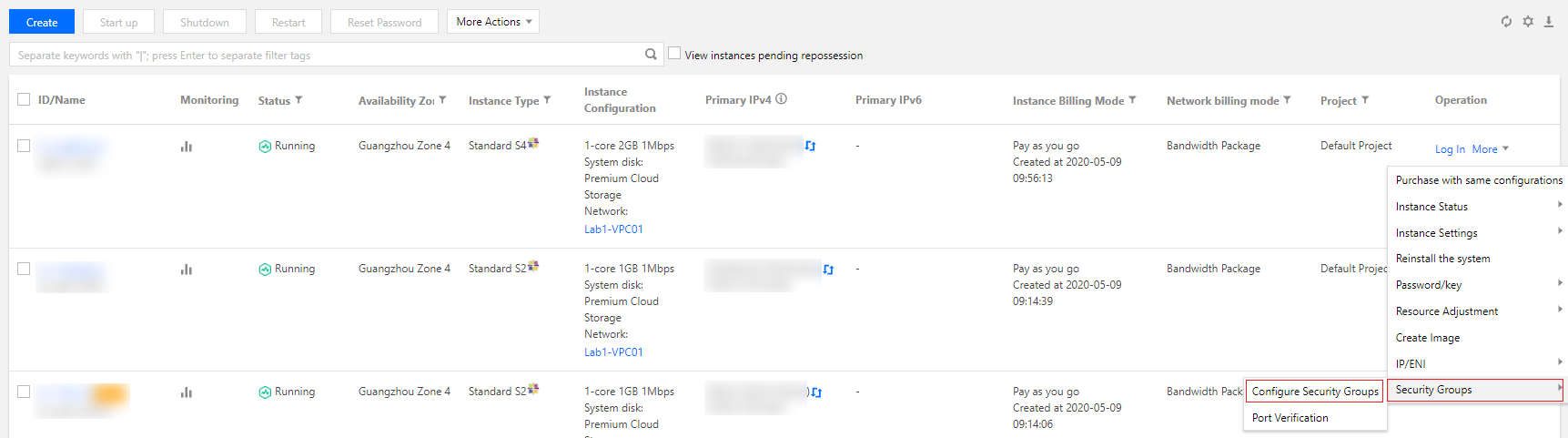
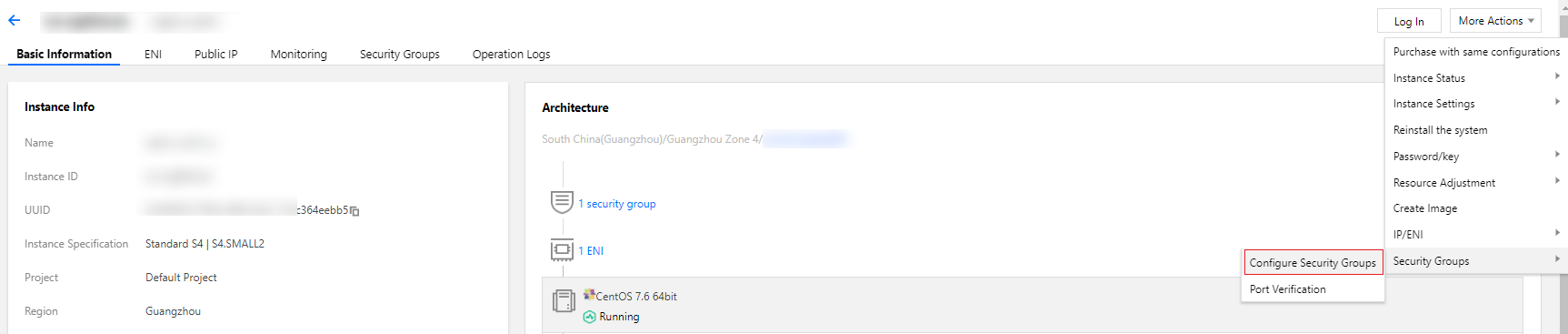
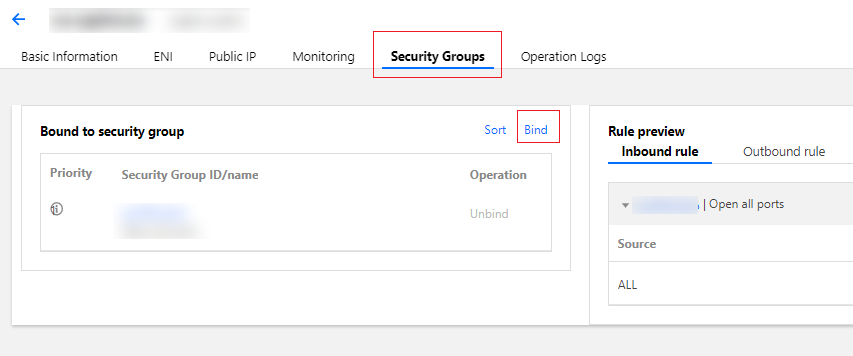
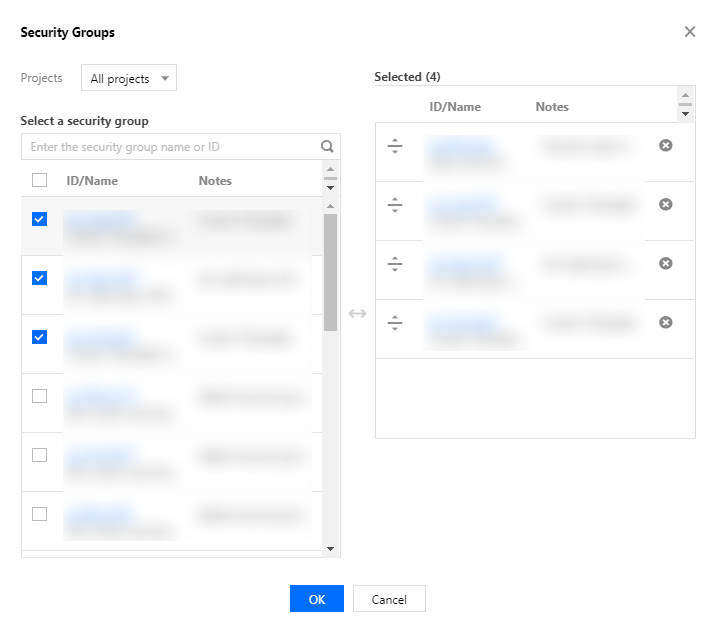
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:00
cvm.qcloud.com to assume the role. For more information, see Concepts.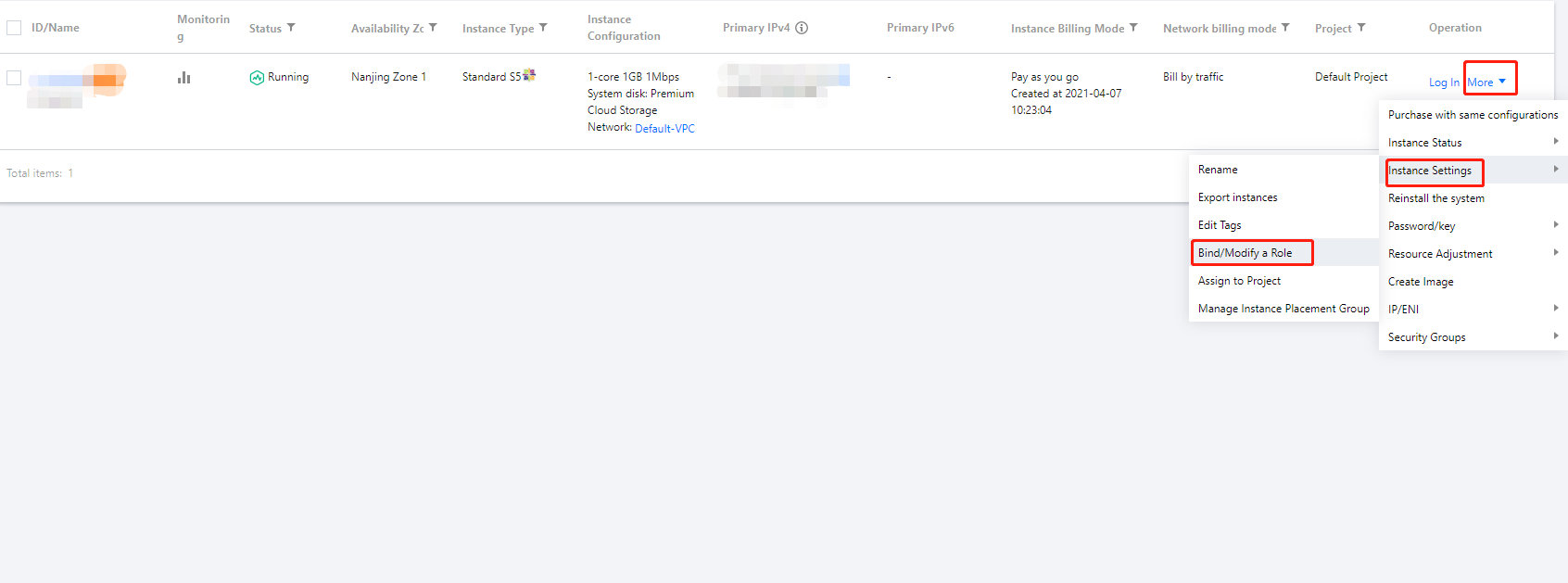
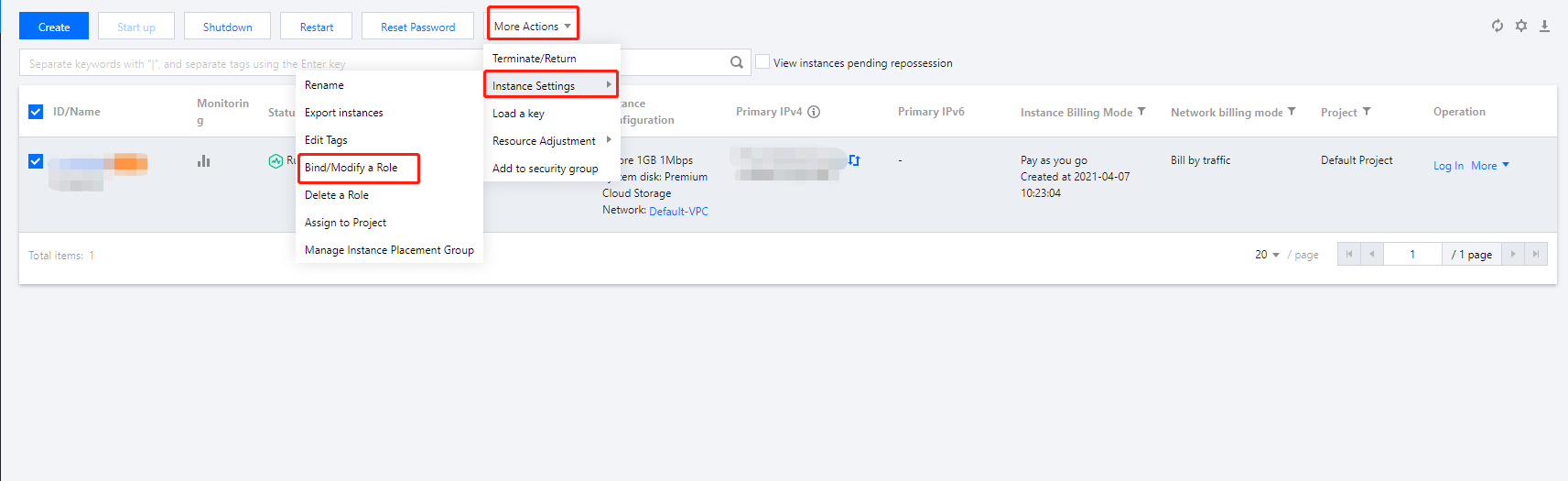
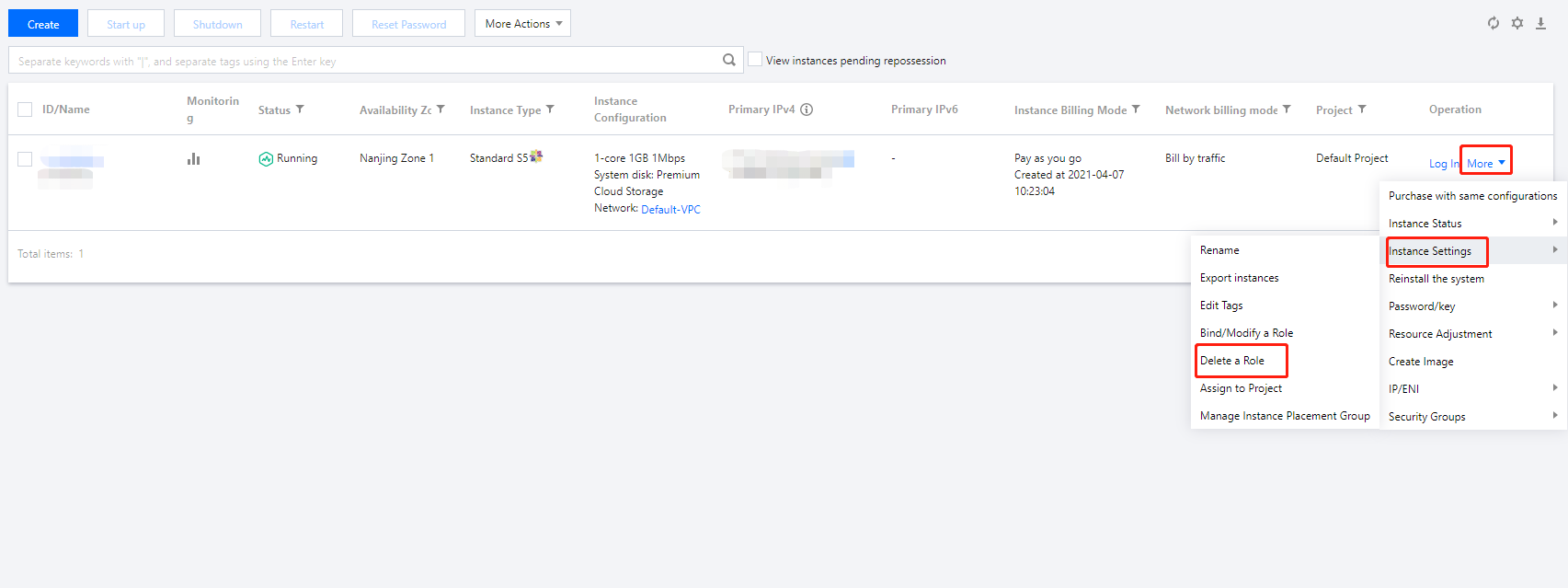
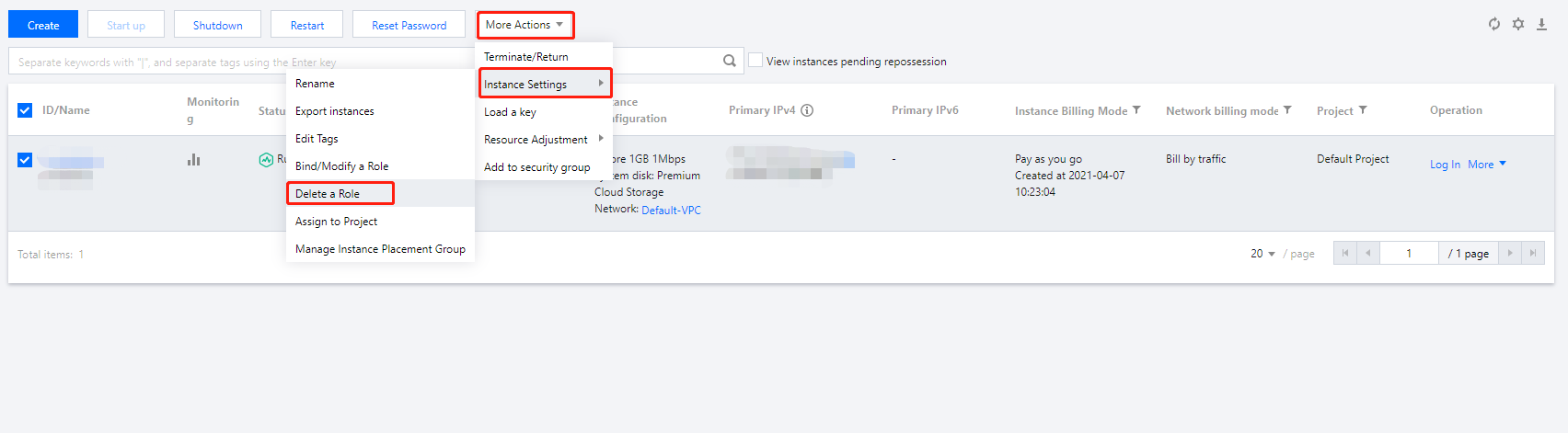
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
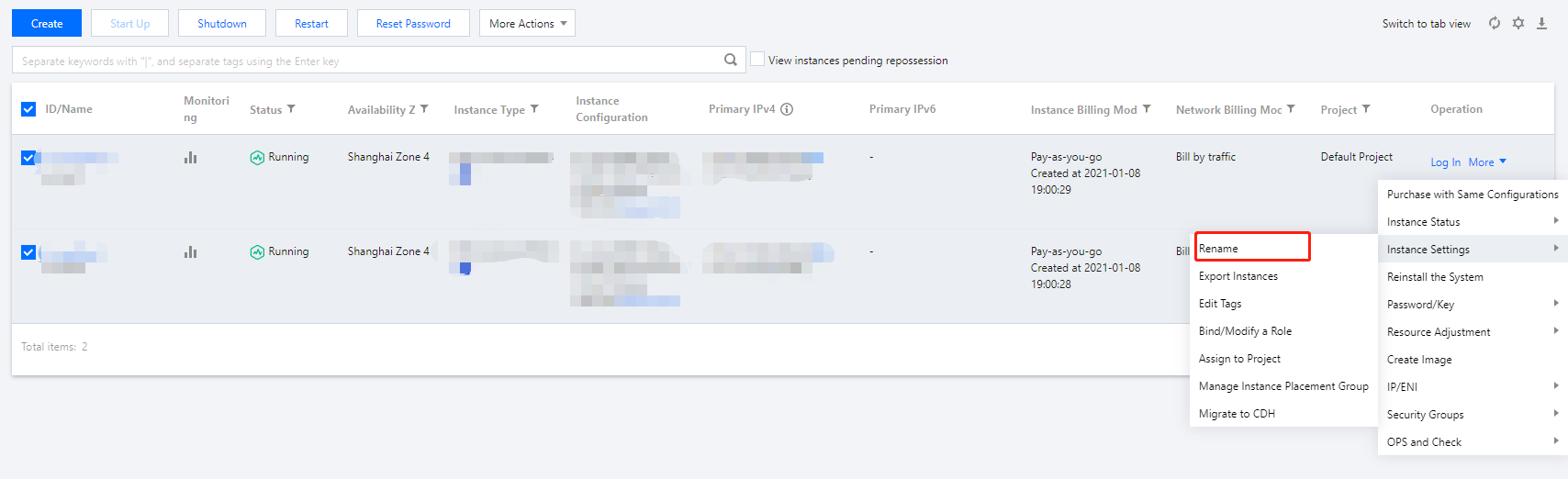
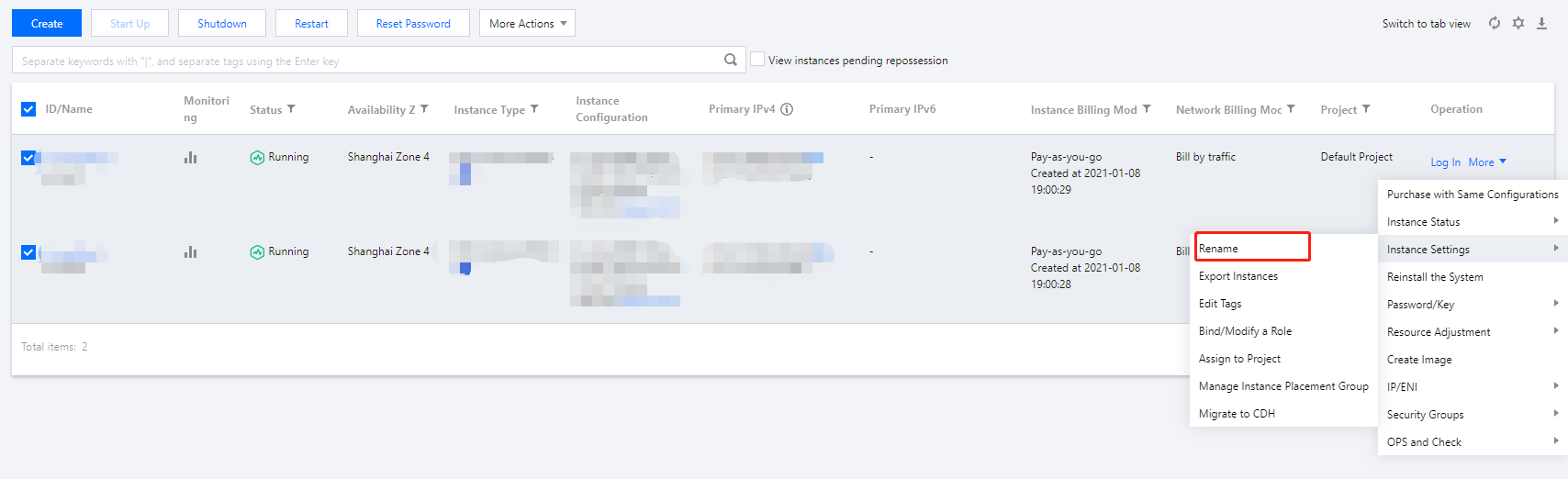
Last updated:2024-03-26 09:46:28

Last updated:2025-12-10 15:36:57
[root@VM-0-16-tencentos ~]# lspci00:00.0 Host bridge: Intel Corporation 82G33/G31/P35/P31 Express DRAM Controller00:01.0 VGA compatible controller: Cirrus Logic GD 544600:02.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 7500/5520/5500/X58 I/O Hub PCI Express Root Port 0 (rev 02)00:03.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 7500/5520/5500/X58 I/O Hub PCI Express Root Port 0 (rev 02)00:04.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 7500/5520/5500/X58 I/O Hub PCI Express Root Port 0 (rev 02)00:05.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 7500/5520/5500/X58 I/O Hub PCI Express Root Port 0 (rev 02)00:1f.0 ISA bridge: Intel Corporation 82801IB (ICH9) LPC Interface Controller (rev 02)00:1f.2 SATA controller: Intel Corporation 82801IR/IO/IH (ICH9R/DO/DH) 6 port SATA Controller [AHCI mode] (rev 02)00:1f.3 SMBus: Intel Corporation 82801I (ICH9 Family) SMBus Controller (rev 02)01:00.0 PCI bridge: Red Hat, Inc. Device 000e02:01.0 Ethernet controller: Red Hat, Inc. Virtio network device02:02.0 USB controller: NEC Corporation uPD720200 USB 3.0 Host Controller (rev 03)02:03.0 SCSI storage controller: Red Hat, Inc. Virtio block device02:04.0 Unclassified device [00ff]: Red Hat, Inc. Virtio memory balloon03:00.0 PCI bridge: Red Hat, Inc. Device 000e05:00.0 Co-processor: Intel Corporation Device 0da5 (rev 02)06:00.0 Co-processor: Intel Corporation Device 0da5 (rev 02)
0da5 indicates the existence of a QAT accelerator within the instance.yum install intel-qat20 kmod-intel-qat20 -y
[root@VM-0-16-tencentos ~]# systemctl restart qat[root@VM-0-16-tencentos ~]# systemctl status qat
Started QAT service is displayed, it indicates that the status of the QAT device is normal./usr/bin/cpa_sample_code to verify whether the QAT is operating normally.Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
qcloud, tencent, or project.+=.@-.+=.@-. It can be left empty if necessary.Instance ID | Business Group | Business Scope | Owner |
ins-abcdef1 | E-commerce | Marketing campaigns | John Smith |
ins-abcdef2 | E-commerce | Marketing campaigns | Chris |
ins-abcdef3 | Games | Game A | Jane Smith |
ins-abcdef4 | Games | Game B | Chris |
ins-abcdef5 | Entertainment | Post-production | Chris |
ins-abcdef6 | Entertainment | Post-production | John Smith |
Tag Key | Tag Value |
dept | ecommerce |
business | mkt |
owner | John Smith |
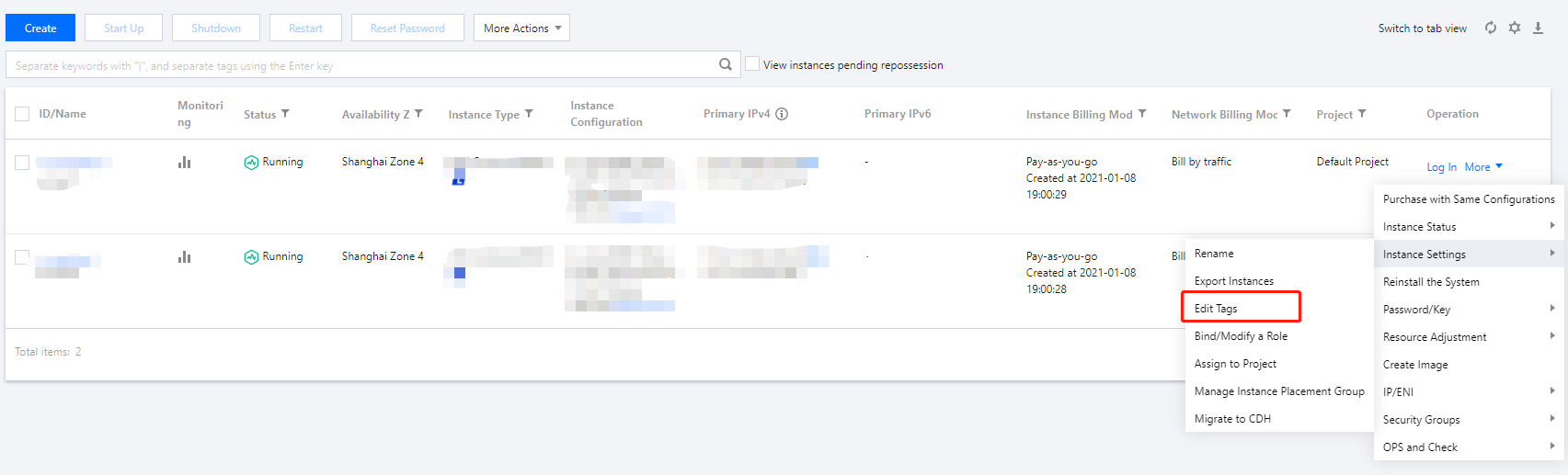
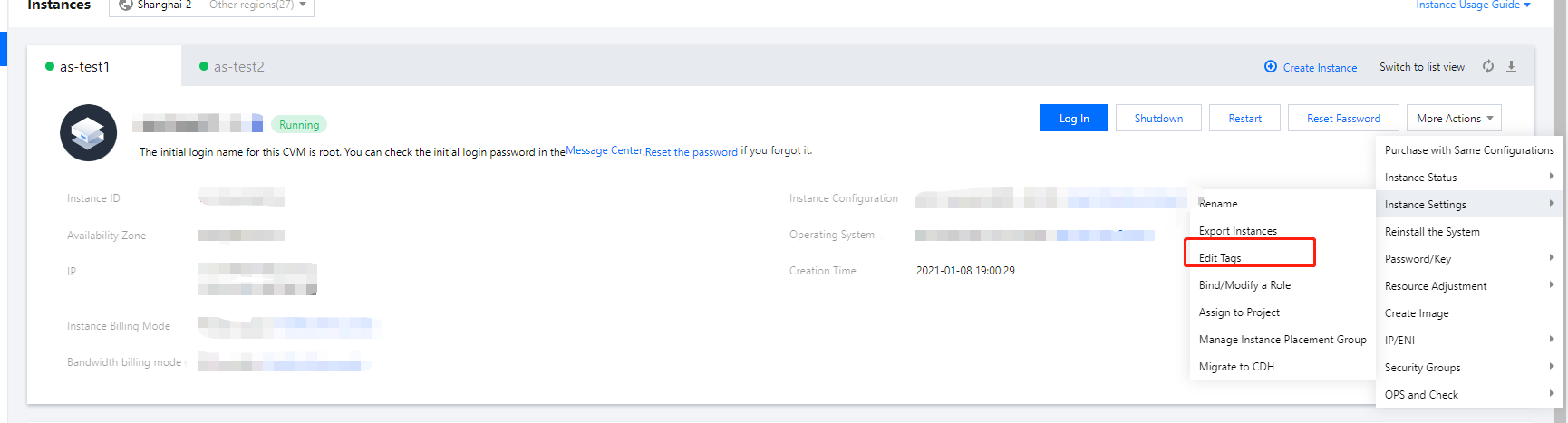
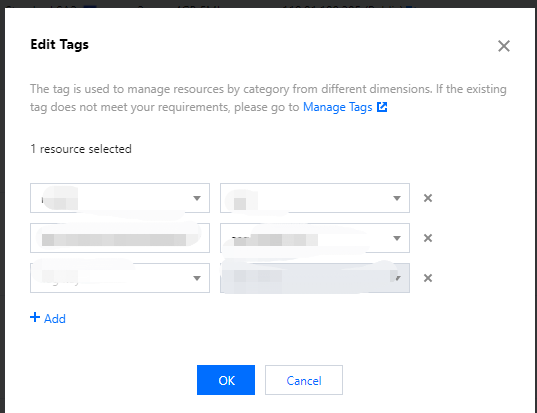

key1 or key2 by entering Tag: key1|key2 in the search box.Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
qcloud, tencent, or project.+=.@-.+=.@-. It can be left empty if necessary.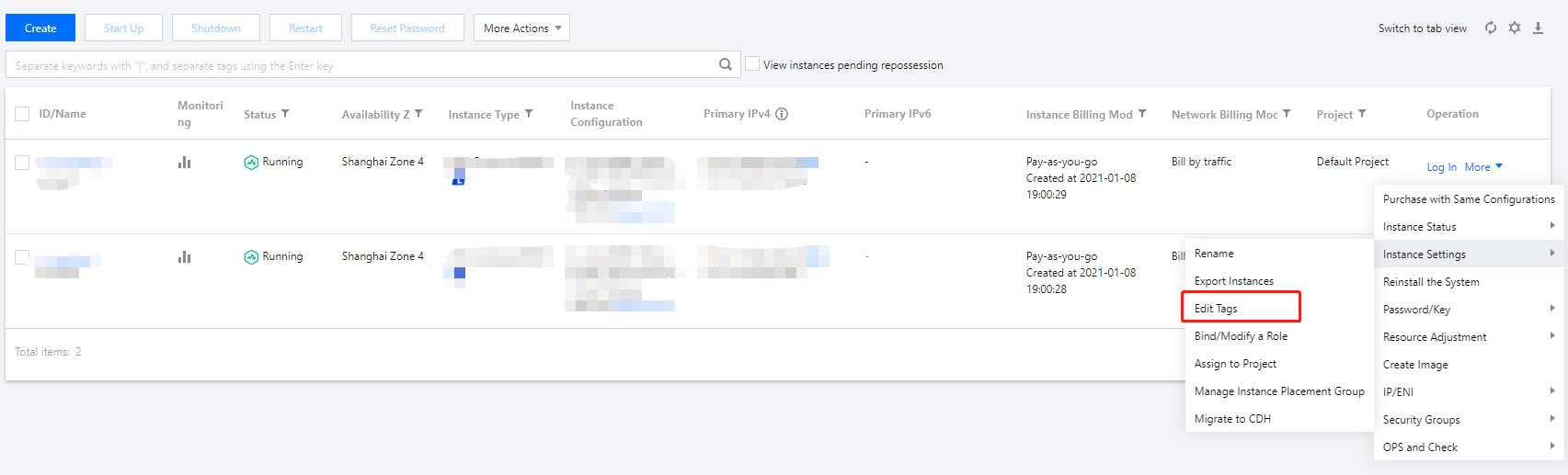
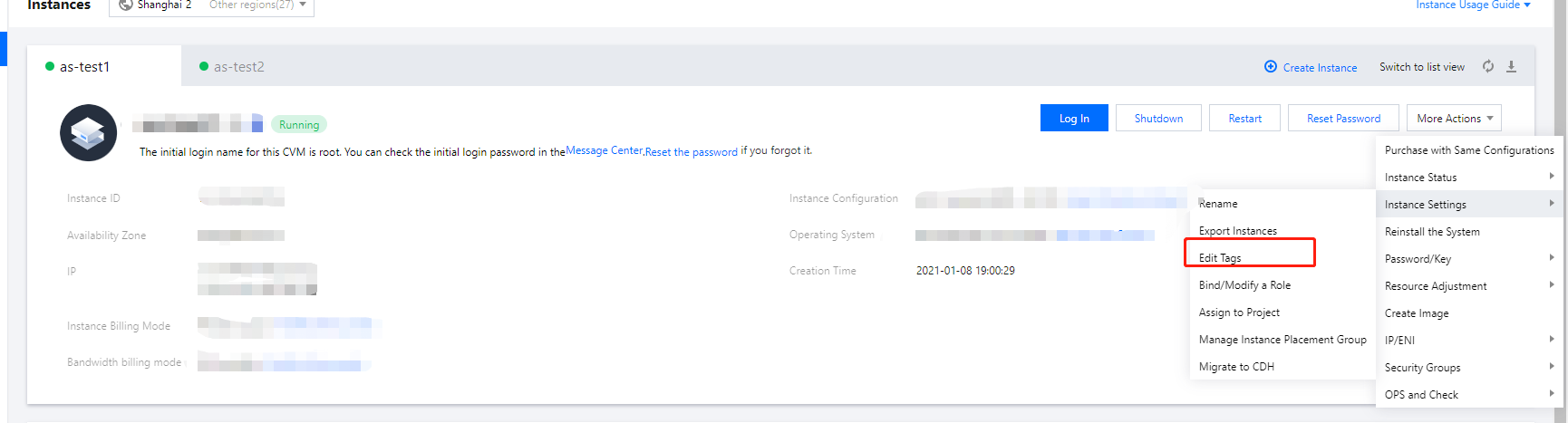
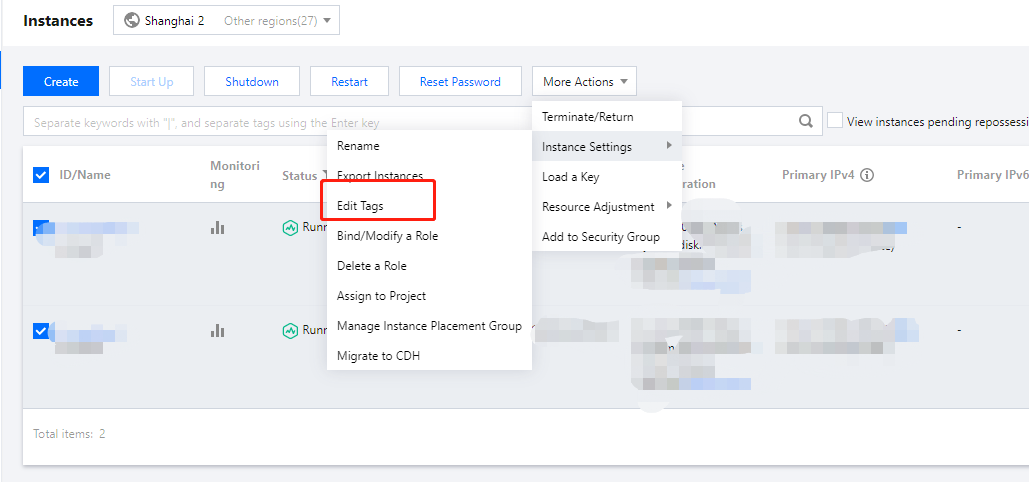
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
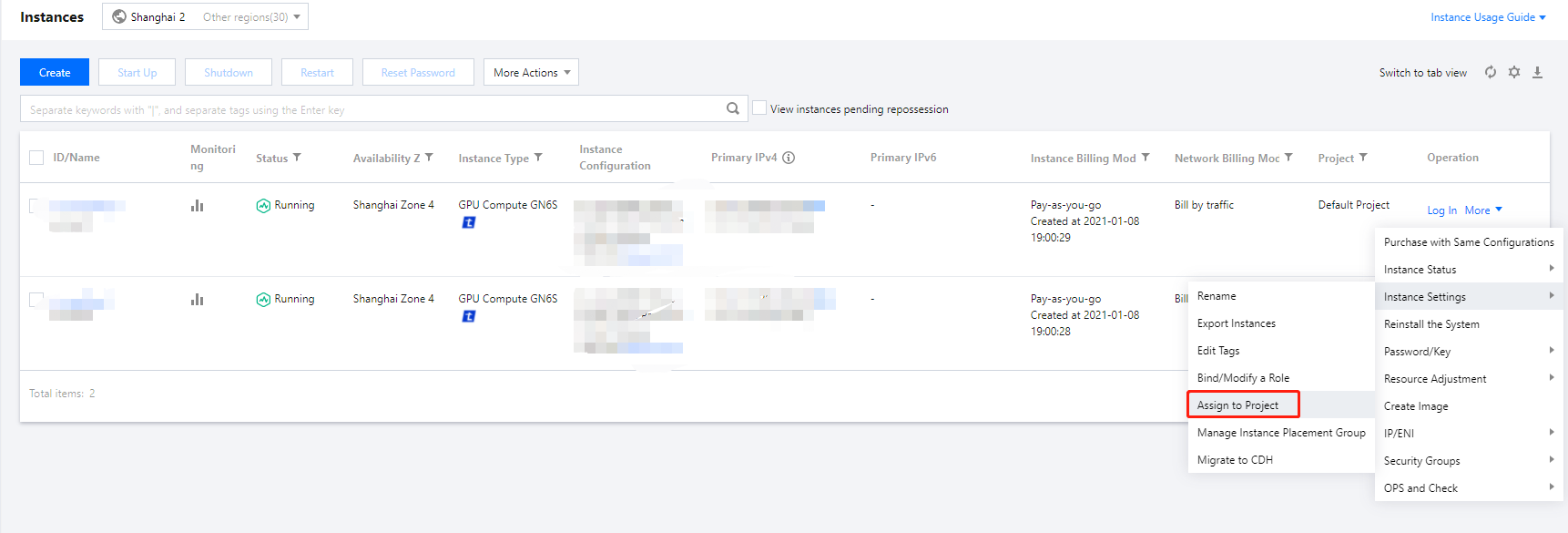
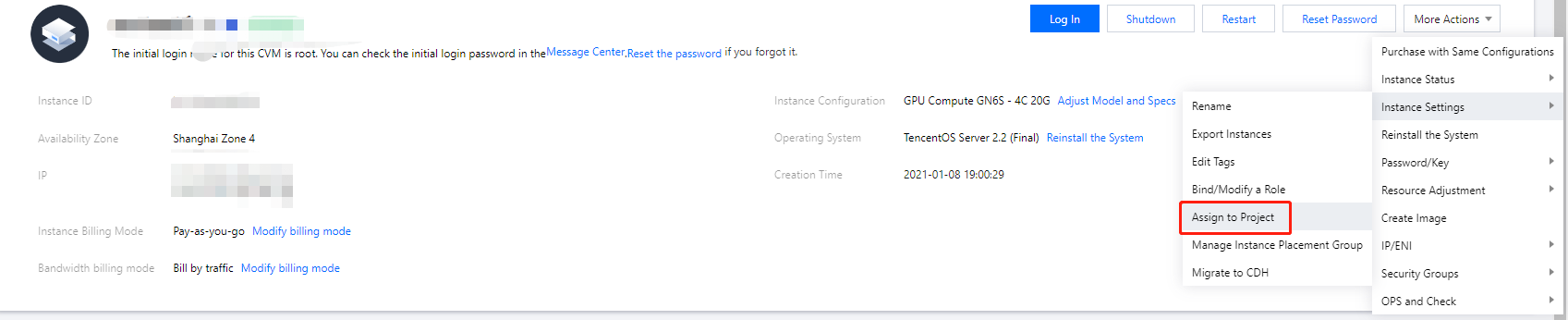
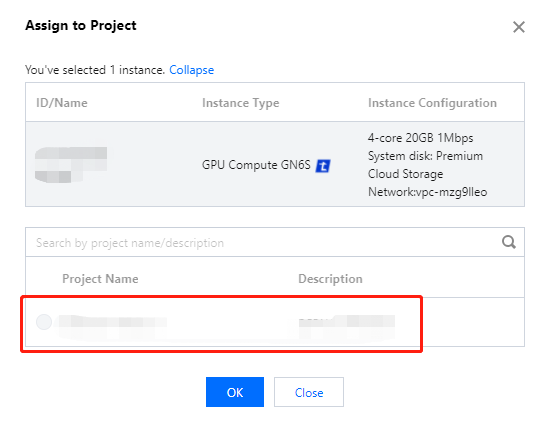
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
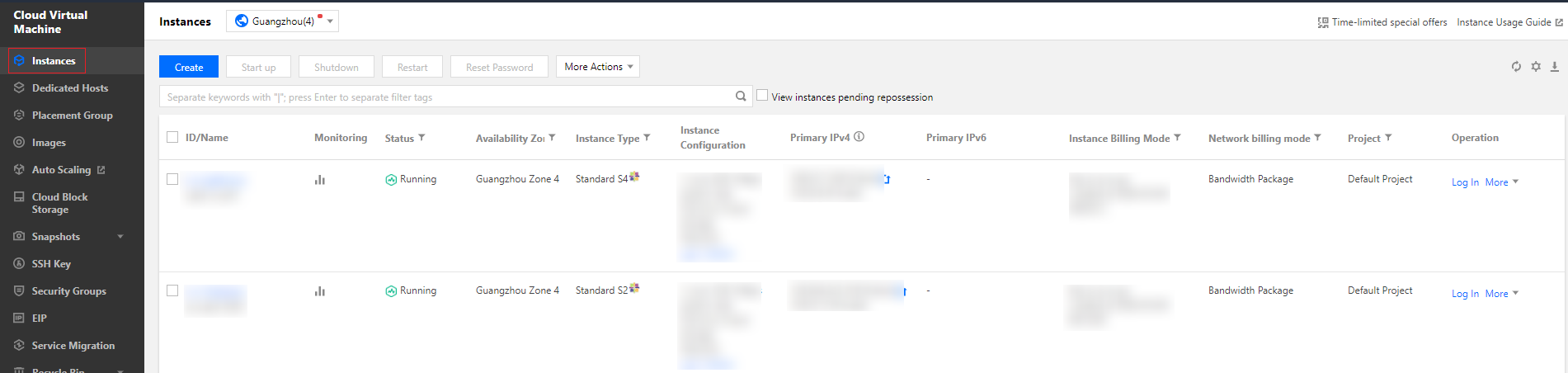

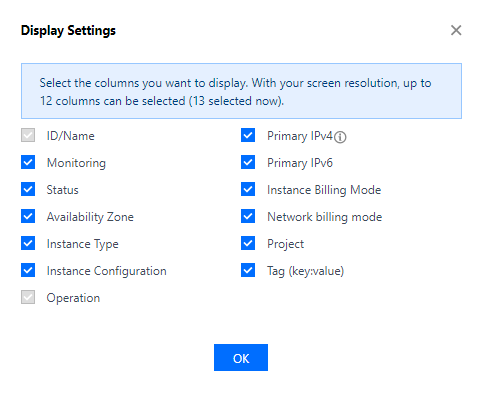
Last updated:2024-11-08 16:02:50
Name | Description | Version |
instance-id | Instance ID | 1.0 |
instance-name | Instance name | 1.0 |
uuid | Instance ID | 1.0 |
local-ipv4 | Instance private IP address | 1.0 |
public-ipv4 | Instance public IP address | 1.0 |
mac | MAC address of the instance's eth0 device | 1.0 |
placement/region | Instance region | Updated on September 19, 2017 |
placement/zone | Instance availability zone | Updated on September 19, 2017 |
network/interfaces/macs/${mac}/mac | MAC address of the instance’s network interface | 1.0 |
network/interfaces/macs/${mac}/primary-local-ipv4 | Primary private IP of the instance’s network interface | 1.0 |
network/interfaces/macs/${mac}/public-ipv4s | Public IP address of the instance’s network interface | 1.0 |
network/interfaces/macs/${mac}/vpc-id | VPC ID of the instance’s network interface | Updated on September 19, 2017 |
network/interfaces/macs/${mac}/subnet-id | Subnet ID of the instance’s network interface | Updated on September 19, 2017 |
network/interfaces/macs/${mac}/local-ipv4s/${local-ipv4}/gateway | Gateway address of the instance’s network interface | 1.0 |
network/interfaces/macs/${mac}/local-ipv4s/${local-ipv4}/local-ipv4 | Private IP address of the instance’s network interface | 1.0 |
network/interfaces/macs/${mac}/local-ipv4s/${local-ipv4}/public-ipv4 | Public IP address of the instance’s network interface | 1.0 |
network/interfaces/macs/${mac}/local-ipv4s/${local-ipv4}/public-ipv4-mode | Public network mode of the instance’s network interface | 1.0 |
network/interfaces/macs/${mac}/local-ipv4s/${local-ipv4}/subnet-mask | Subnet mask of the instance’s network interface | 1.0 |
payment/charge-type | Instance billing plan | Updated on September 19, 2017 |
payment/create-time | Instance creation time | Updated on September 19, 2017 |
payment/termination-time | Instance termination time | Updated on September 19, 2017 |
app-id | AppID of the user to which the instance belongs | Updated on September 19, 2017 |
as-group-id | Auto scaling group ID of the instance | Updated on September 19, 2017 |
spot/termination-time | Spot instance termination time | Updated on September 19, 2017 |
instance/instance-type | Instance type | Updated on September 19, 2017 |
instance/image-id | Instance image ID | Updated on September 19, 2017 |
instance/security-group | Information of the security group bound to the instance | Updated on September 19, 2017 |
instance/bandwidth-limit-egress | Instance private network outbound bandwidth limit, in Kbit/s | Updated on 9/29/2019 |
instance/bandwidth-limit-ingress | Instance private network inbound bandwidth limit, in Kbit/s | Updated on 9/29/2019 |
cam/security-credentials/${role-name} | Temporary credential generated by the CAM role policy, which can be obtained only when the instance is associated with the CAM role. Change `${role-name}` to the actual CAM role name; otherwise, `404` will be returned | Updated on 12/11/2019 |
volumes | Instance storage | 1.0 |
${mac} and ${local-ipv4} in the above table indicate the MAC address and private IP address of the network interface specified for the instance, respectively.http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/
curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/1.09/19/2017latestmeta-data
/ represent directories and other lines represent the accessed data. For the description of accessed data, see the Overview section described above.[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/instance-idinstance-namelocal-ipv4macnetwork/placement/public-ipv4uuid
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/placement/regionap-guangzhou[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/placement/zoneap-guangzhou-3
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/local-ipv410.104.13.59
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/public-ipv4139.199.11.29
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/instance-idins-3g445roi
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/uuidcfac763a-7094-446b-a8a9-b995e638471a
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/mac52:54:00:BF:B3:51
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/network/interfaces/macs/52:54:00:BF:B3:51/
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/network/interfaces/macs/52:54:00:BF:B3:51/local-ipv4s/macvpc-idsubnet-idowner-idprimary-local-ipv4public-ipv4slocal-ipv4s/
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/network/interfaces/macs/52:54:00:BF:B3:51/vpc-idvpc-ja82n9op[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/network/interfaces/macs/52:54:00:BF:B3:51/subnet-idsubnet-ja82n9op
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/network/interfaces/macs/52:54:00:BF:B3:51/local-ipv4s/10.104.13.59/
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/network/interfaces/macs/52:54:00:BF:B3:51/local-ipv4s/10.104.13.59gatewaylocal-ipv4public-ipv4public-ipv4-modesubnet-mask
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/network/interfaces/macs/52:54:00:BF:B3:51/local-ipv4s/10.104.13.59/gateway10.15.1.1
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/network/interfaces/macs/52:54:00:BF:B3:51/local-ipv4s/10.104.13.59/public-ipv4-modeNAT
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/network/interfaces/macs/52:54:00:BF:B3:51/local-ipv4s/10.104.13.59/public-ipv4139.199.11.29
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/network/interfaces/macs/52:54:00:BF:B3:51/local-ipv4s/10.104.13.59/subnet-mask255.255.192.0
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/payment/charge-typePOSTPAID_BY_HOUR
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/payment/create-time2018-09-18 11:27:33
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/spot/termination-time2018-08-18 12:05:33
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/app-id123456789
CVMas.[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/cam/security-credentials/CVMas{TmpSecretId": "************************************","TmpSecretKey": "********************************","ExpiredTime": 1615590047,"Expiration": "2021-03-12T23:00:47Z","Token": "******","Code": "Success"}
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/volumesdisk-xxxxxxxx/
[qcloud-user]# curl http://metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/user-data179, client, shanghai
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02


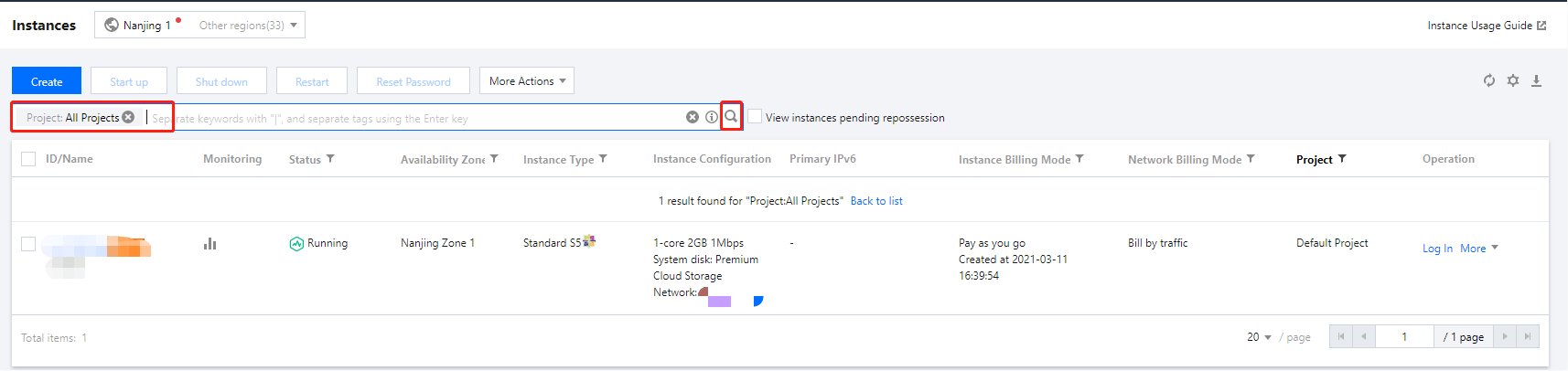

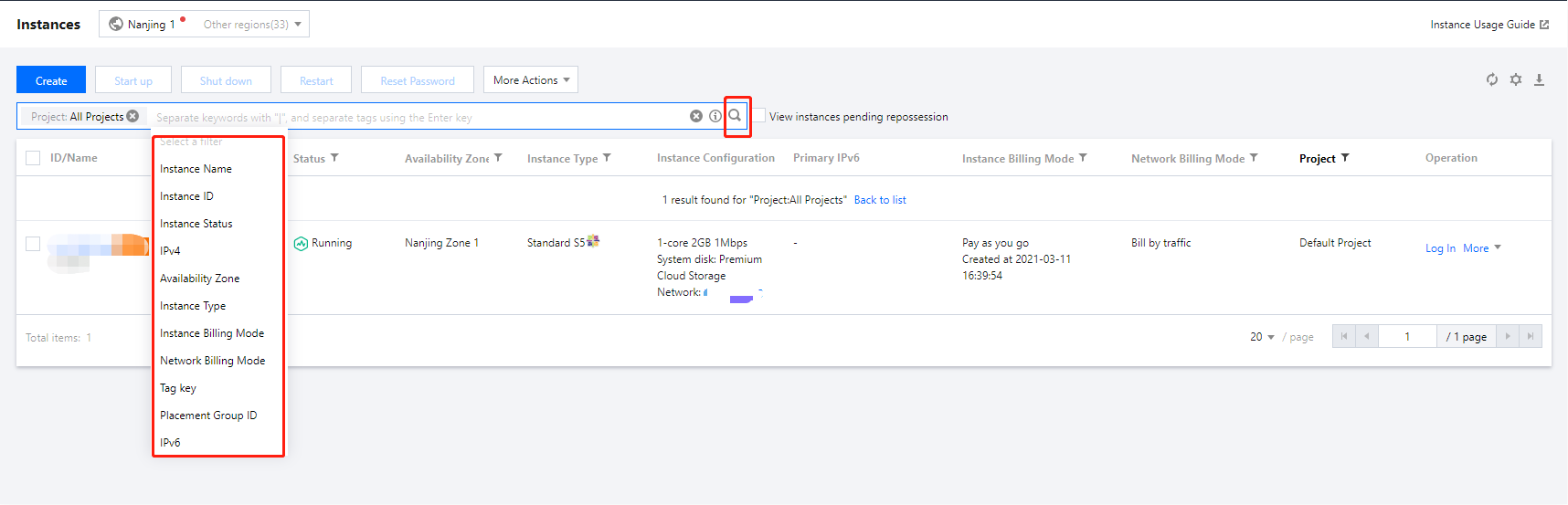

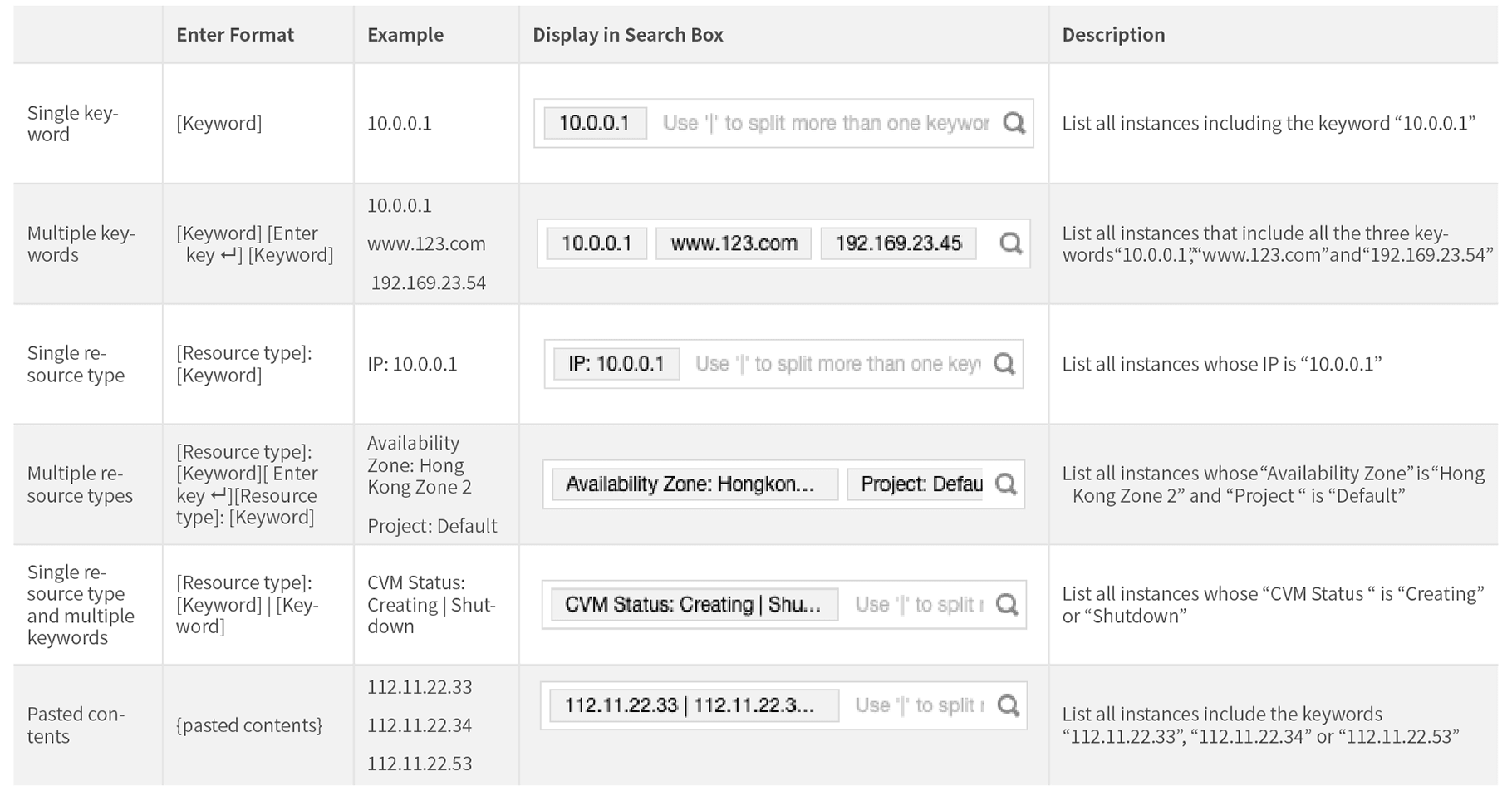
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02

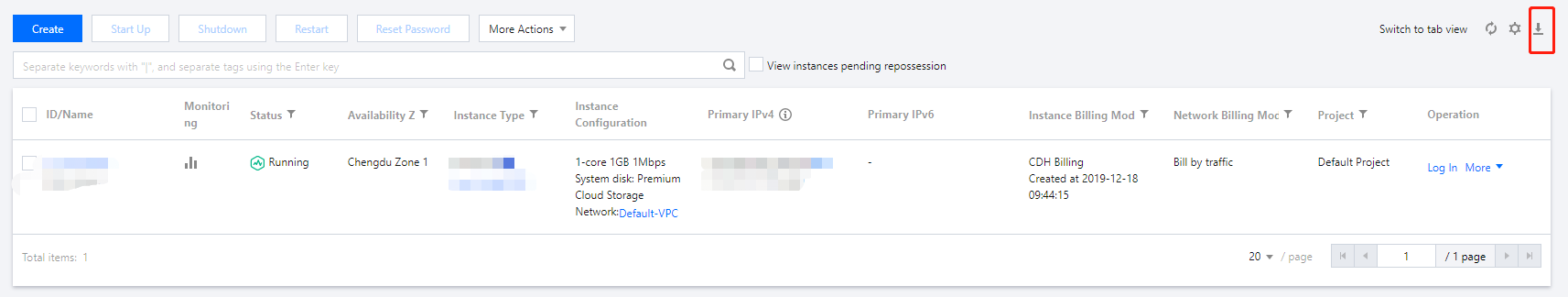

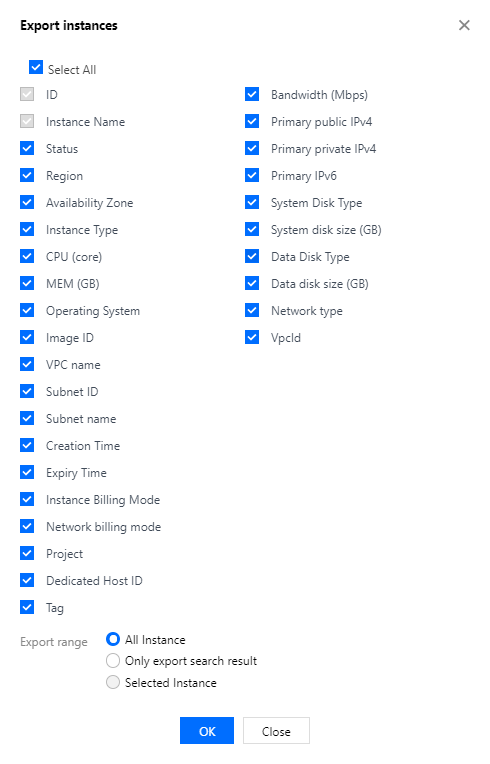
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
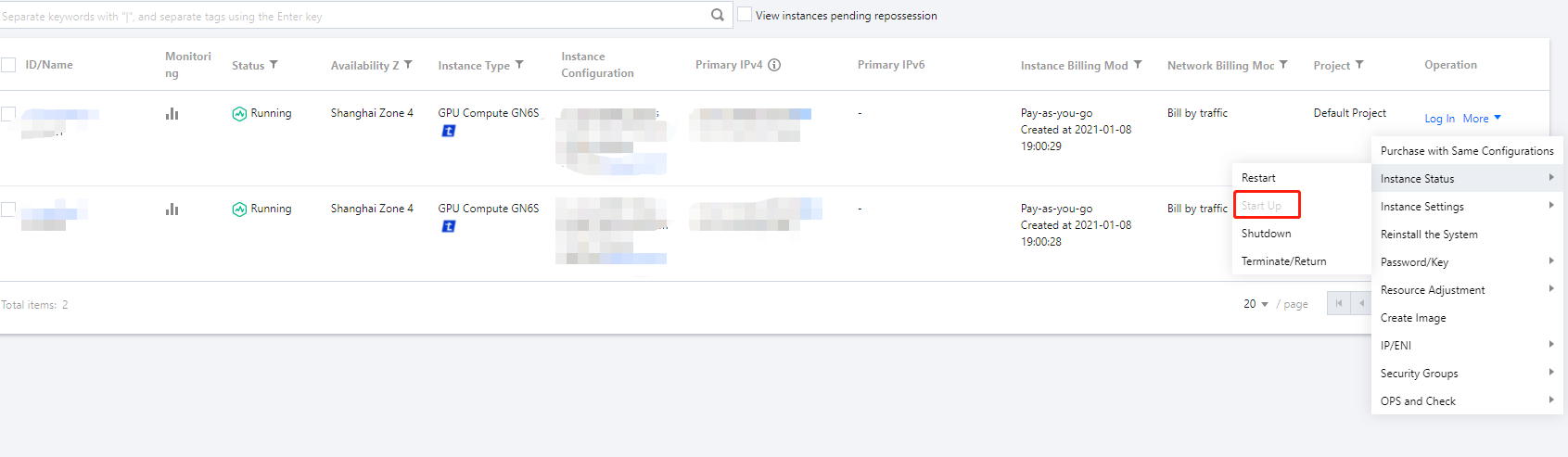
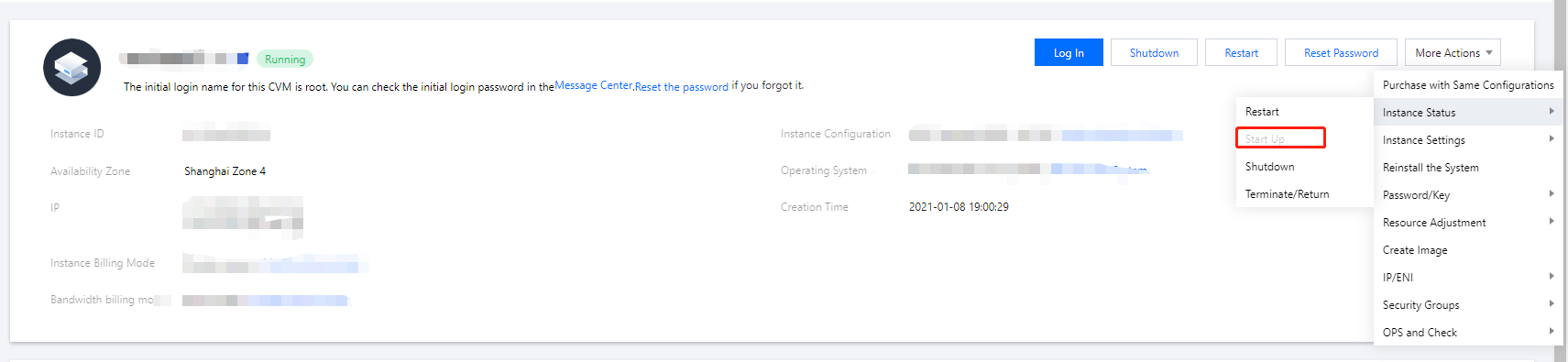
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
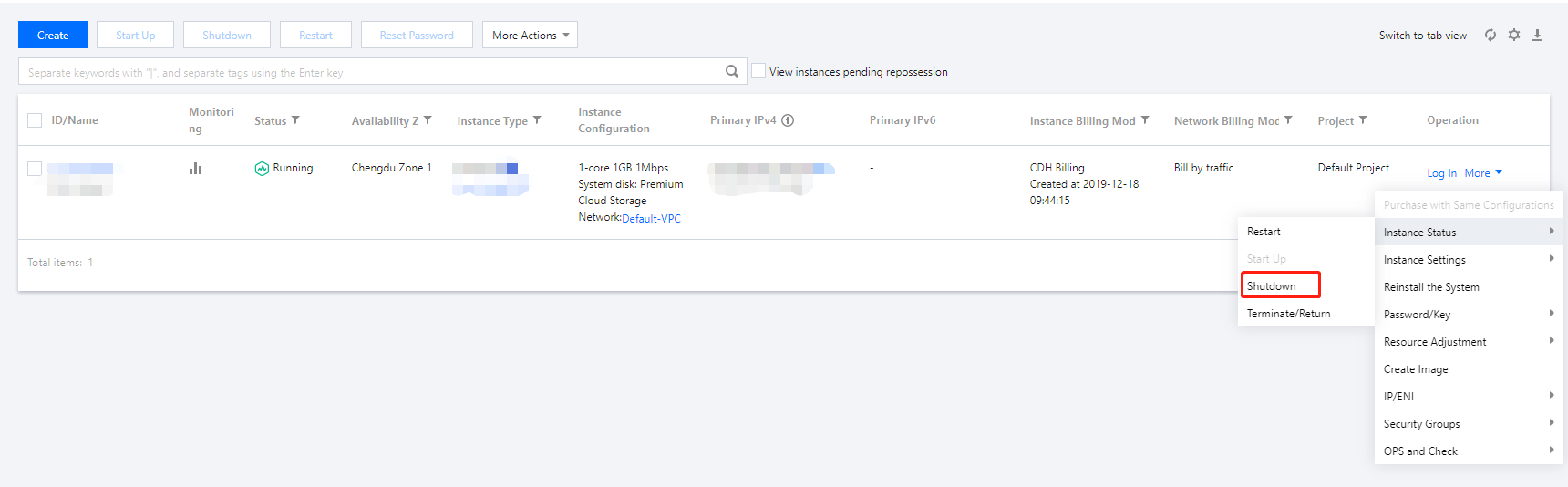
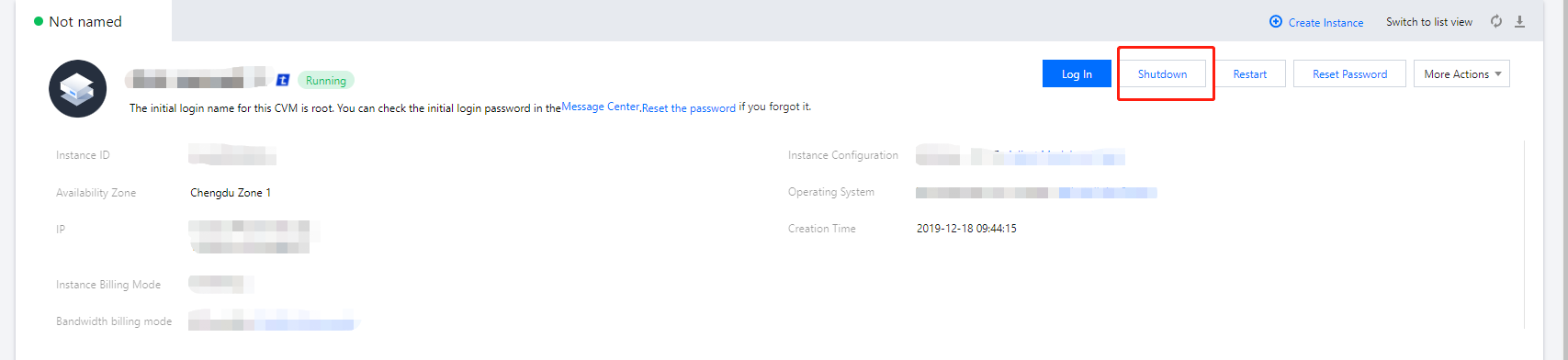
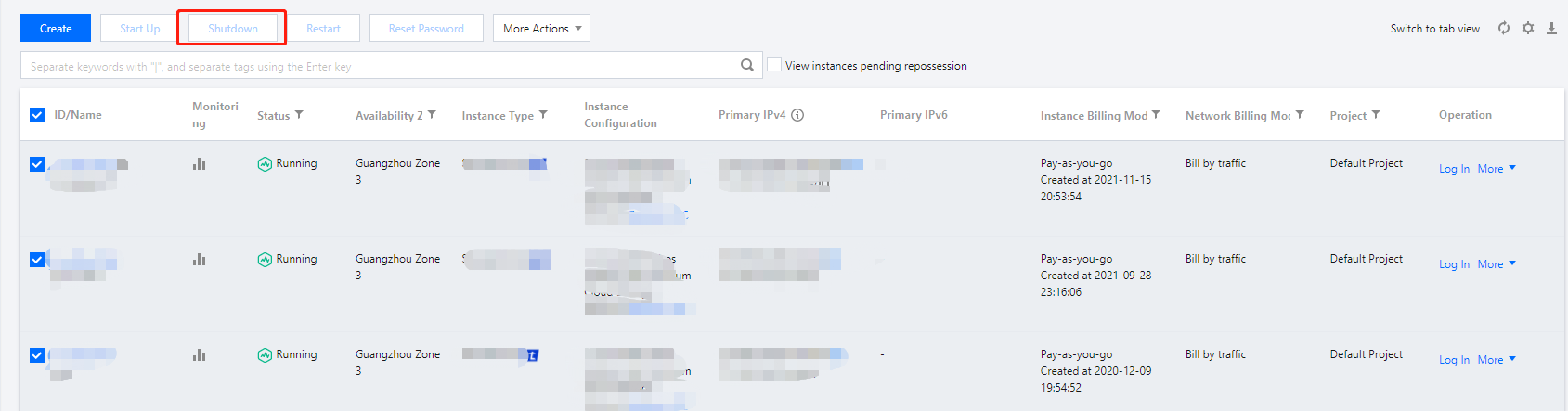
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:25:40
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
StopInstances API to shut down an instance. For details, please see StopInstances. To enable this feature via API, please add the following parameter:Parameter Name | Required | Type | Description |
StoppedMode | No | String | The "No Charge when Shut down" feature is only available for pay-as-you-go instances. Valid values: KEEP_CHARGING: the instance incurs fees after shutdown STOP_CHARGING: no charges when shut down Default value: KEEP_CHARGING |
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
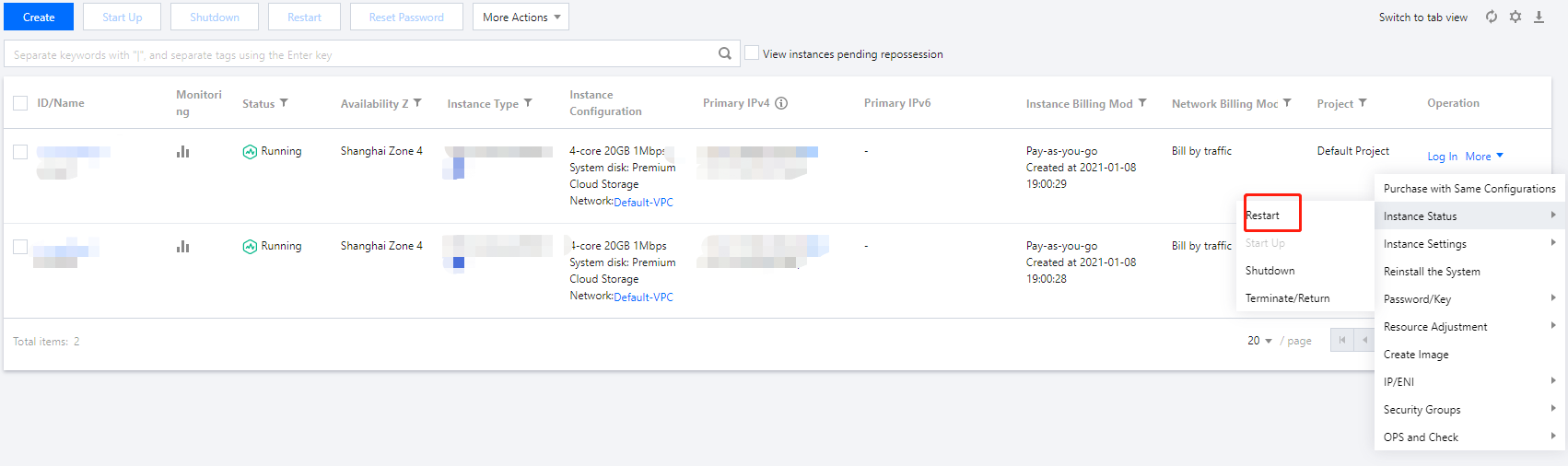
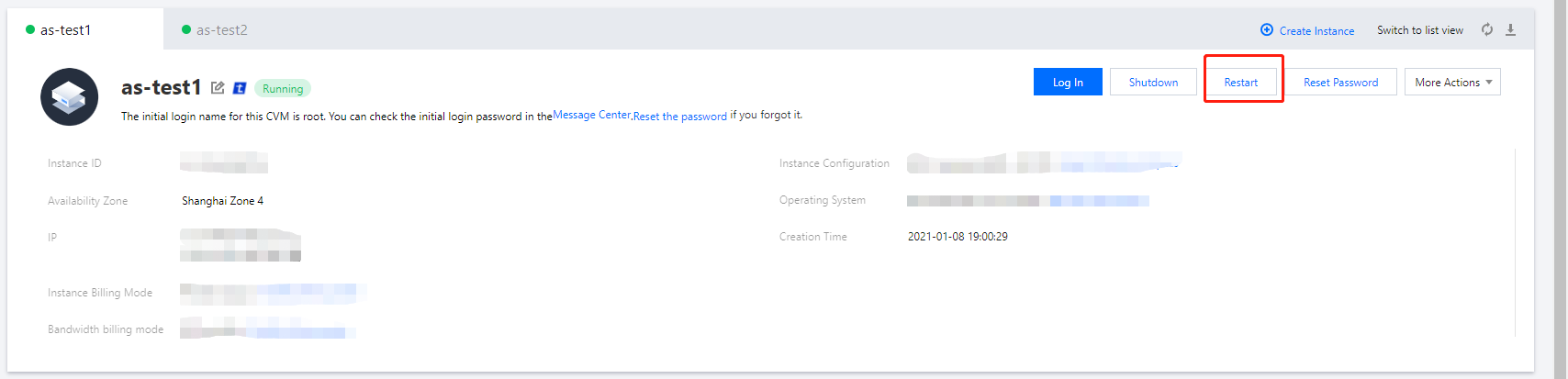
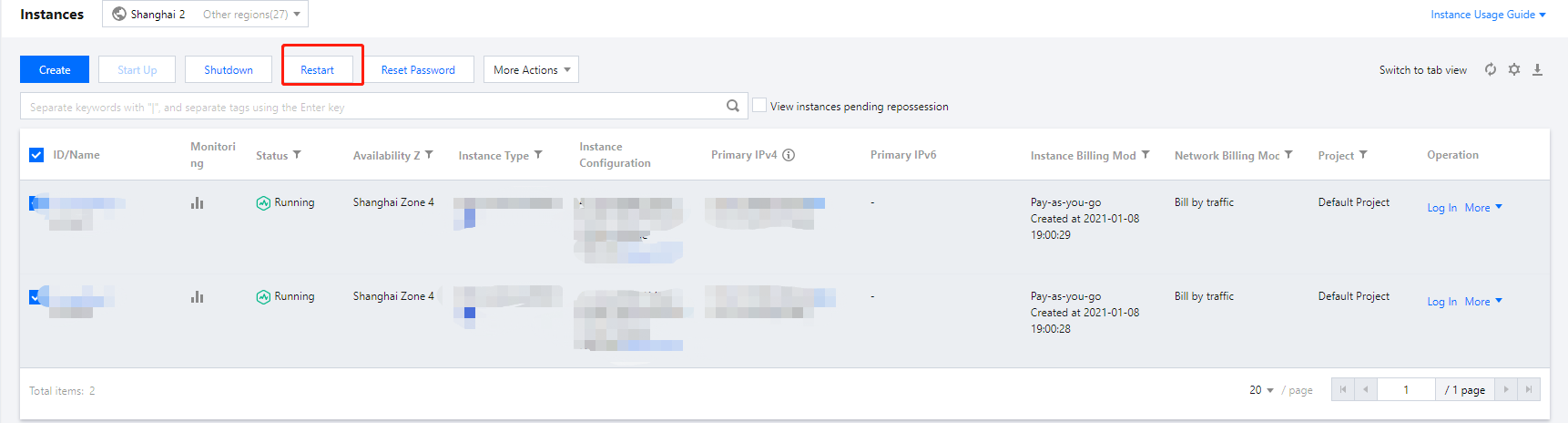
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
Last updated:2025-09-30 14:11:57
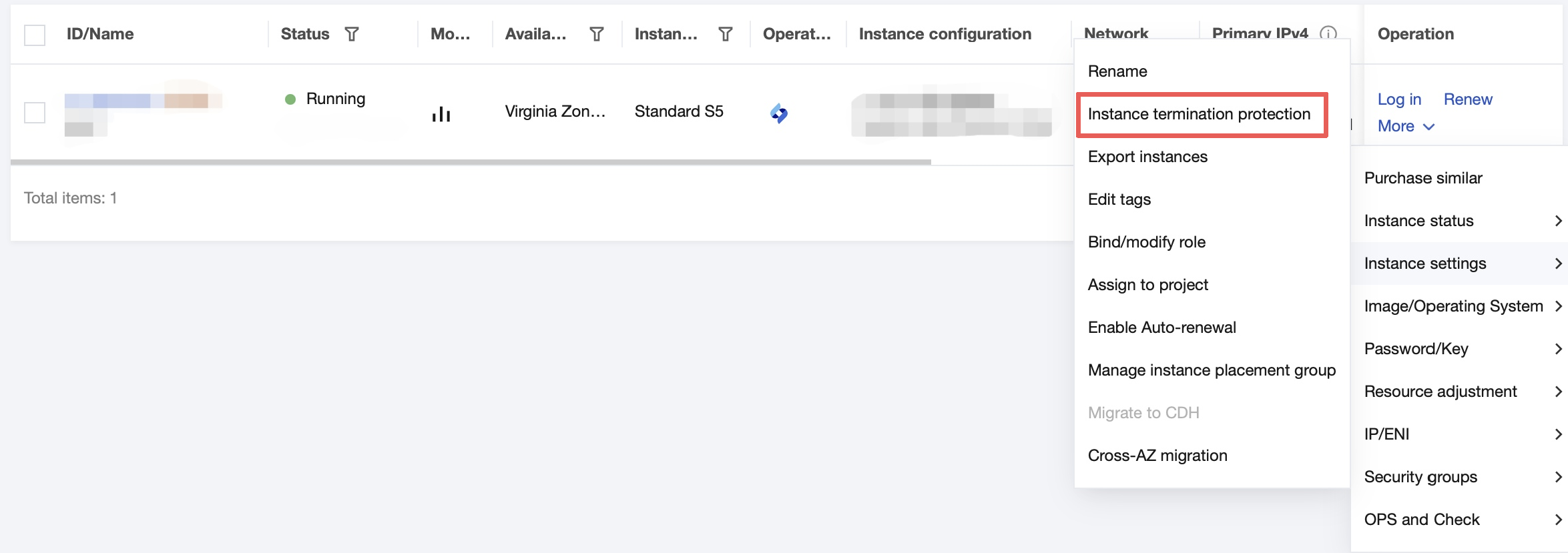
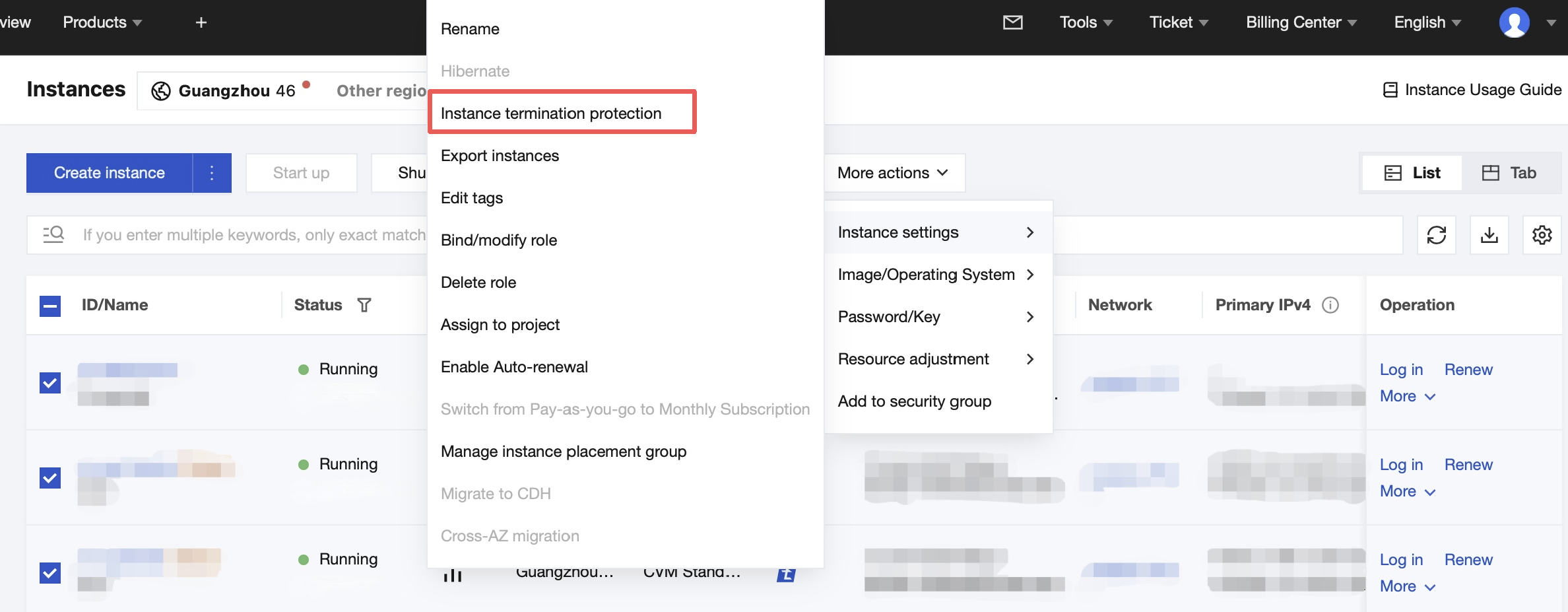
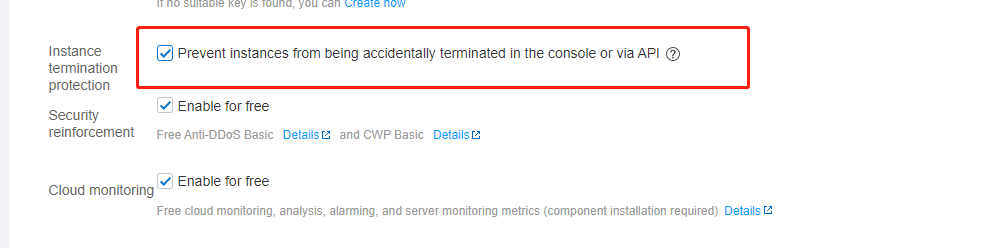
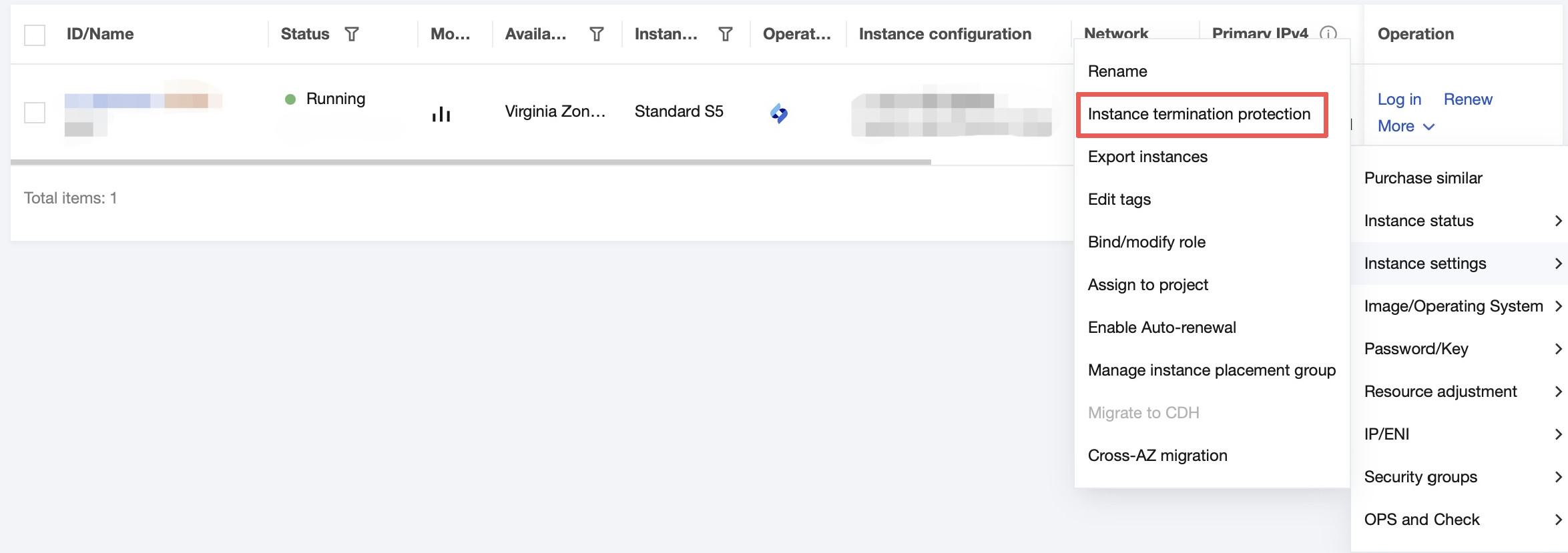
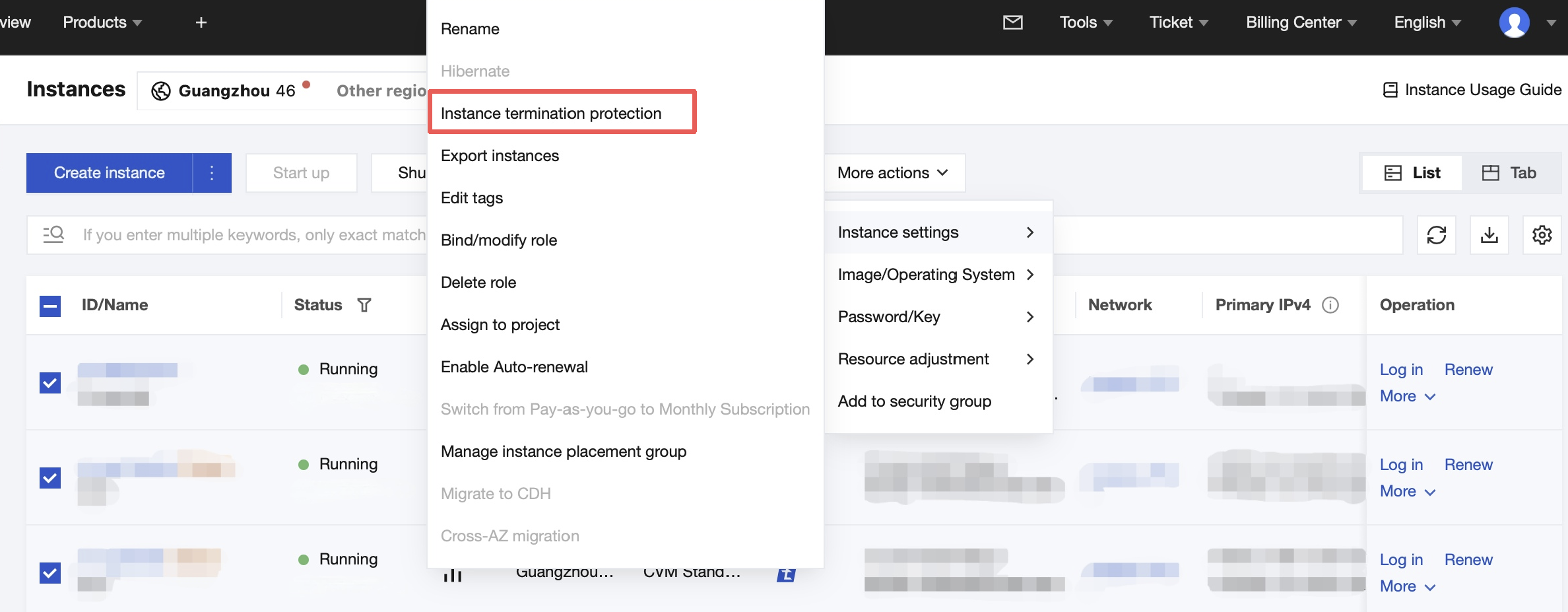
Last updated:2025-08-05 19:00:31
type | Manual termination (not in arrears) | Timed termination (not in arrears) | Automatic termination upon expiration or when in arrears |
Pay-as-you-go instances | After termination, the instance is stored in the recycle bin for 2 hours, and if it is not restored within these 2 hours, it will be released. | Instances for which timed termination is set will be released immediately as scheduled, instead of going into the recycle bin. | After an instance enters into arrears, for the first 2 hours, billing will continue and the instance can still be used normally. In the next 15 days, however, the instance will be shut down, and billing will stop. Pay-as-you-go instances in arrears will not be put into the recycle bin. If the instance is not renewed within the aforementioned period, the instance will be released. |
Monthly-Subscribed Instance | Early Destruction Not Supported | Scheduled Termination Not Involved | After expiration, terminated instances enter the recycle bin and are retained for a maximum of 15 days; if not restored upon expiration, the instance will be released. |
Last updated:2025-09-05 15:40:05
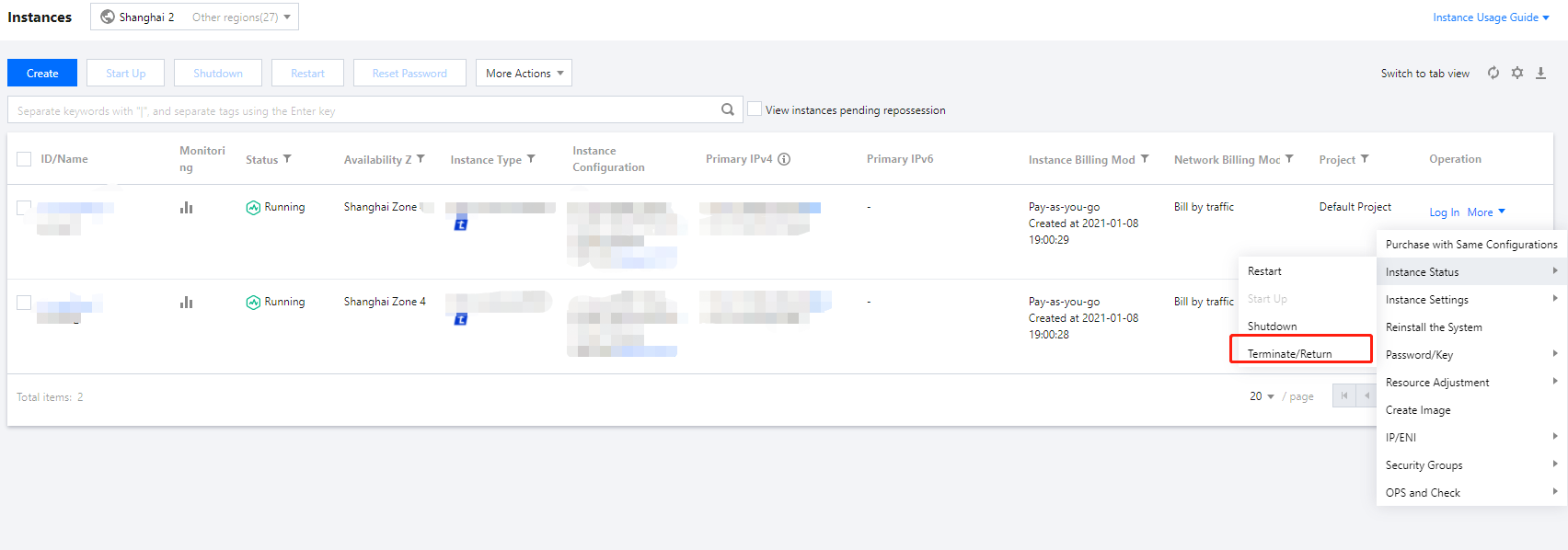

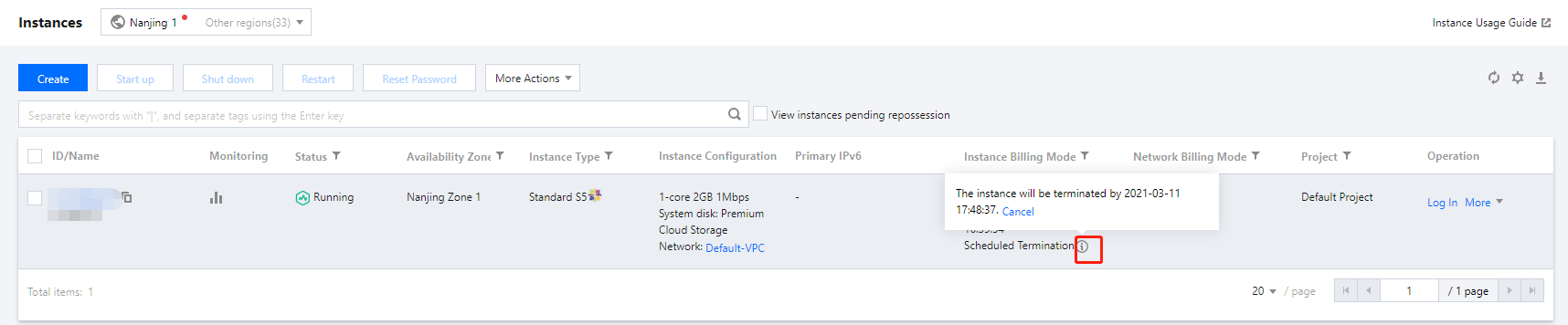
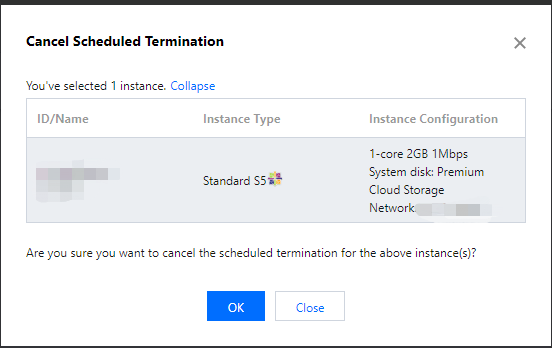
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
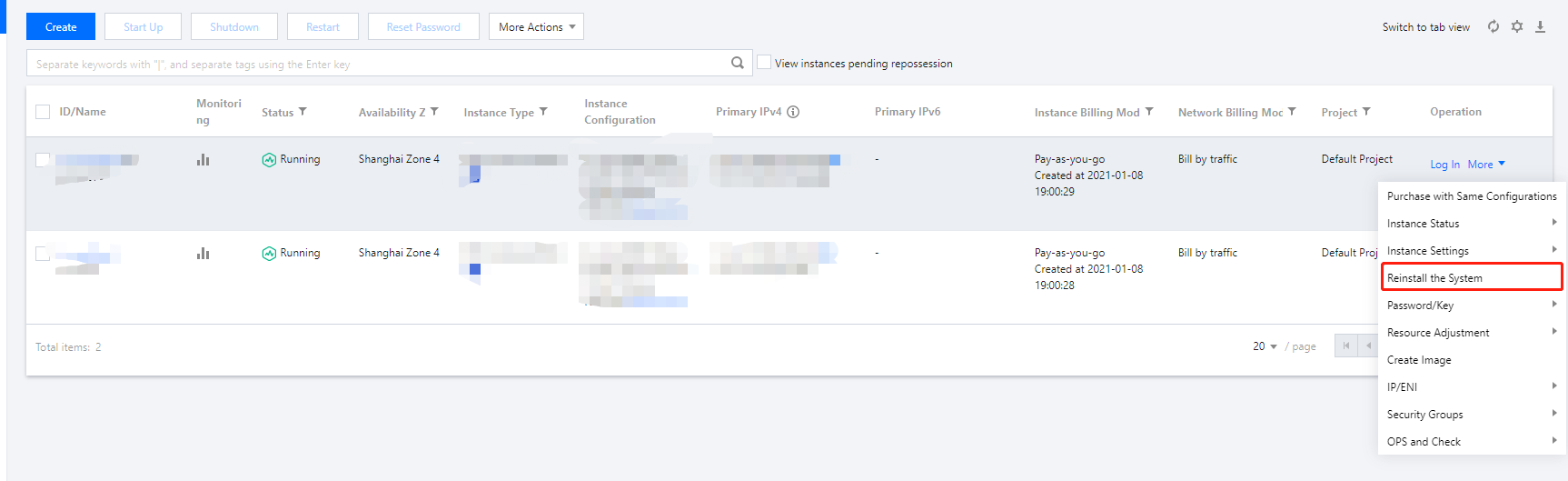
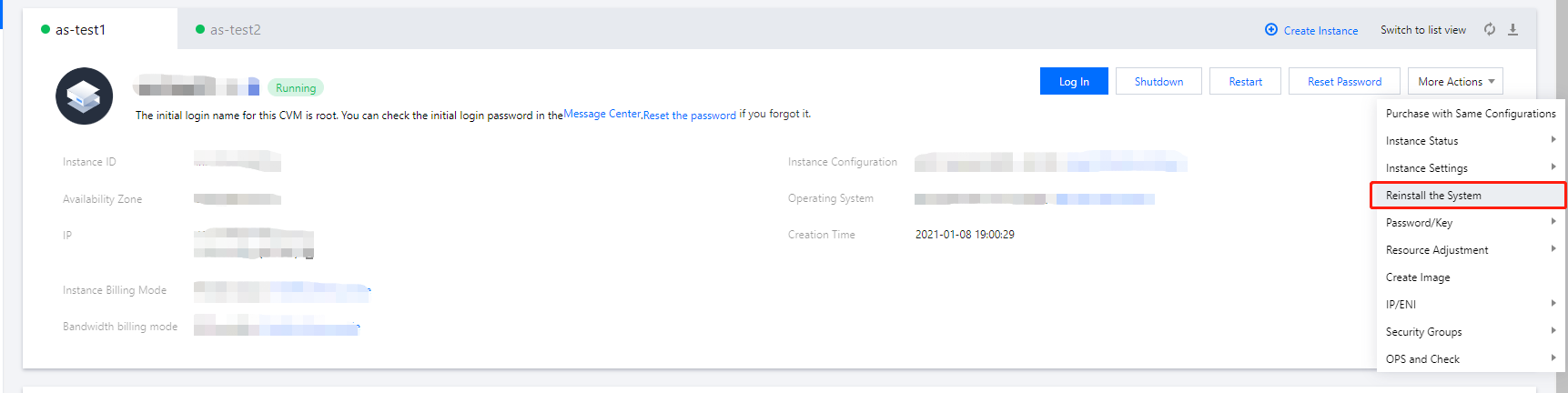
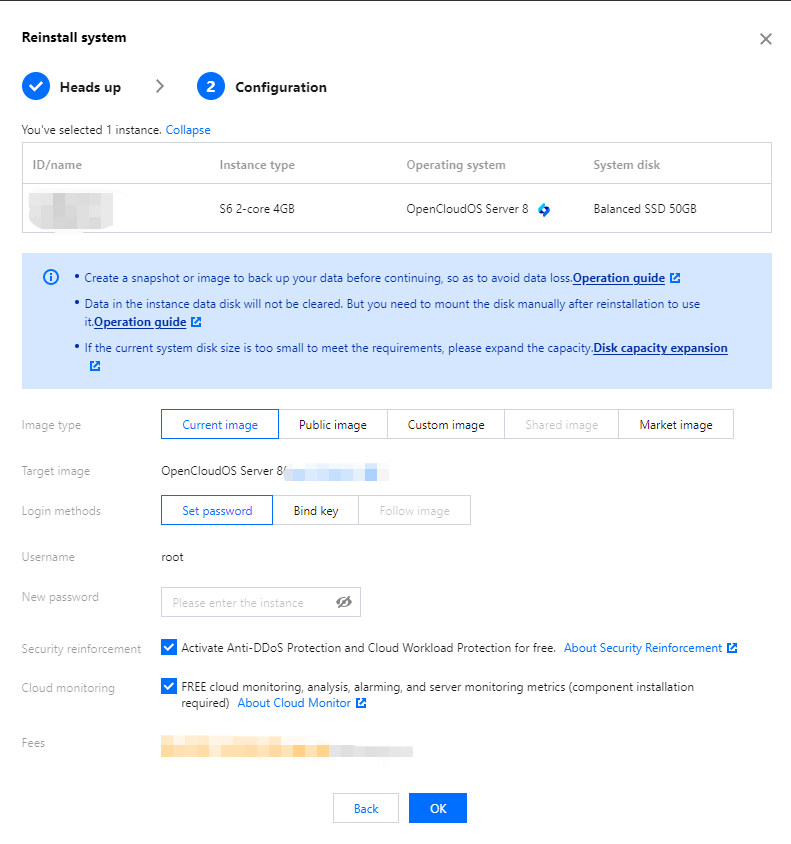
Last updated:2025-11-20 10:45:11
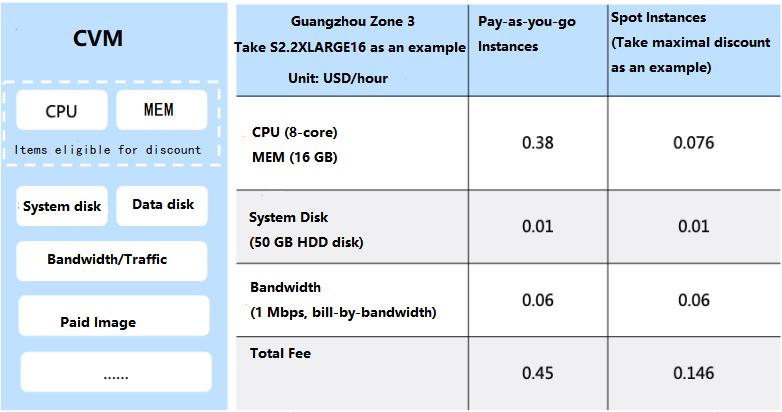
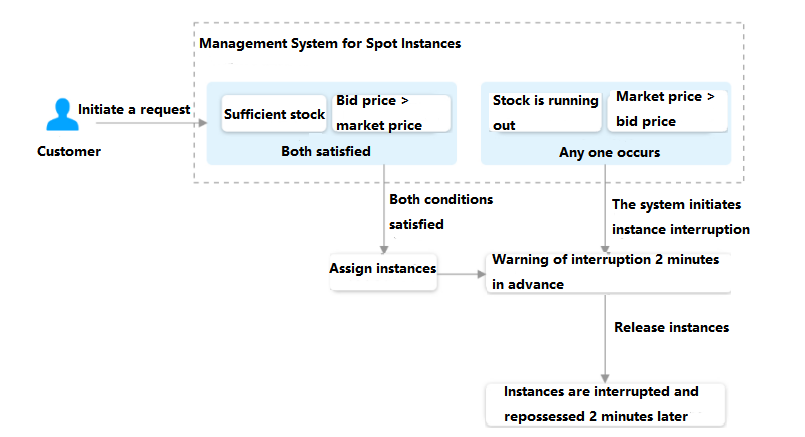
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
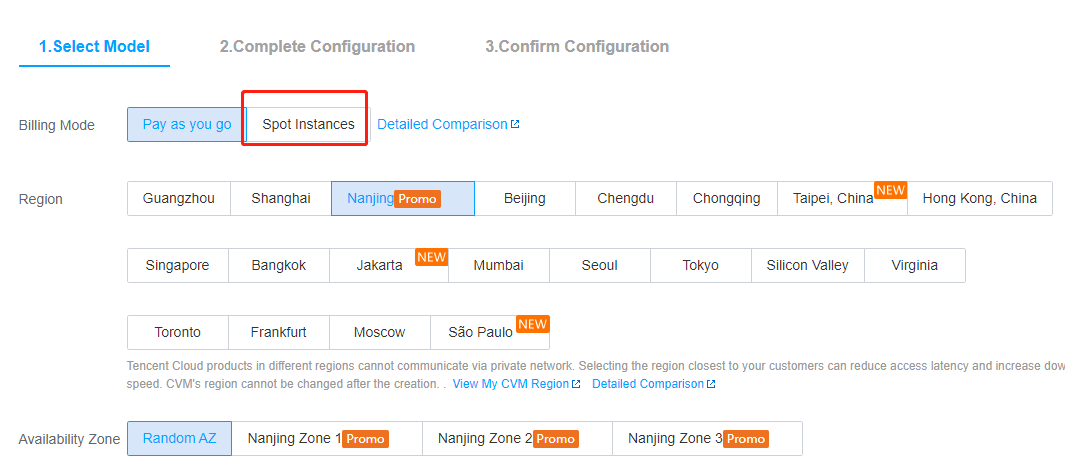

RunInstance API, you can specify the InstanceMarketOptionsRequest parameter to enable or disable the spot instance mode and configure the information about spot instances.RunInstance provides a one-time sync request API. This means that if the application fails because the inventory is insufficient or the requested price is lower than the market price, the RunInstance API will immediately return a failure code and no longer apply for the spot instance again.https://cvm.tencentcloudapi.com/?Action=RunInstances&Placement.Zone=ap-guangzhou-3&InstanceChargeType=SPOTPAID&InstanceMarketOptions.MarketType=spot&InstanceMarketOptions.SpotOptions.MaxPrice=0.0923&InstanceMarketOptions.SpotOptions.SpotInstanceType=one-time&ImageId=img-pmqg1cw7&InstanceType=S2.MEDIUM4&InstanceCount=1&<Common request parameters>
{"Response": {"InstanceIdSet": ["ins-1vogaxgk"],"RequestId": "3c140219-cfe9-470e-b241-907877d6fb03"}}
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
curl metadata.tencentyun.com/latest/meta-data/spot/termination-time
2018-08-18 12:05:33
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:25:40
Item | RI | Pay-as-you-go instance |
Concept | A discount for pay-as-you-go instances. | |
Usage | RIs cannot be used separately; instead, they can only be used with matched pay-as-you-go instances to offset part of the pay-as-you-go bill. | CVMs can be managed and configured independently as a simple web server or as part of a powerful cloud solution together with other Tencent Cloud products. |
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:25:40
Parameter | Required/Optional | Description |
Region/Availability Zone | Required | The region and availability zone where the matched pay-as-you-go instances reside. |
Operating System | Required | Linux OS,Windows. |
Validity | Required | RI term: 1 year. |
Instance | Required | The type of pay-as-you-go instances that you want to match the RI. These pay-as-you-go instances must exactly match RI attributes to benefit from the billing discount during the RI term. |
RI Name | Optional | User-defined. The RI name defaults to “unnamed” if this parameter is left empty. You can enter any name within 60 characters. |
Billing Mode | Required | Select a billing option as needed: All Upfront: you pay for the entire RI term with one upfront payment. This option provides you with the largest discount compared to the other two options below. Partial Upfront: you make a low upfront payment and then pay for instance fees at a monthly rate or discounted hourly rate during the RI term. |
Quantity | Required | Number of RIs you want to purchase |
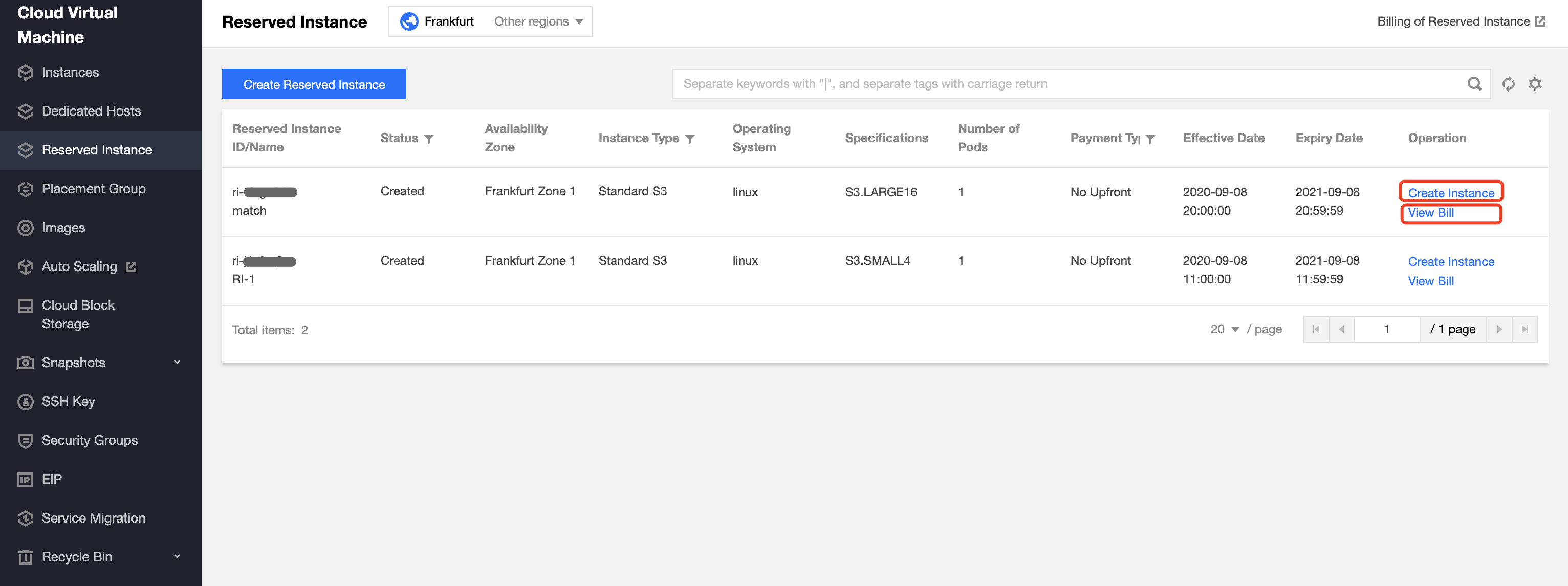
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:00
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:00
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:25:40
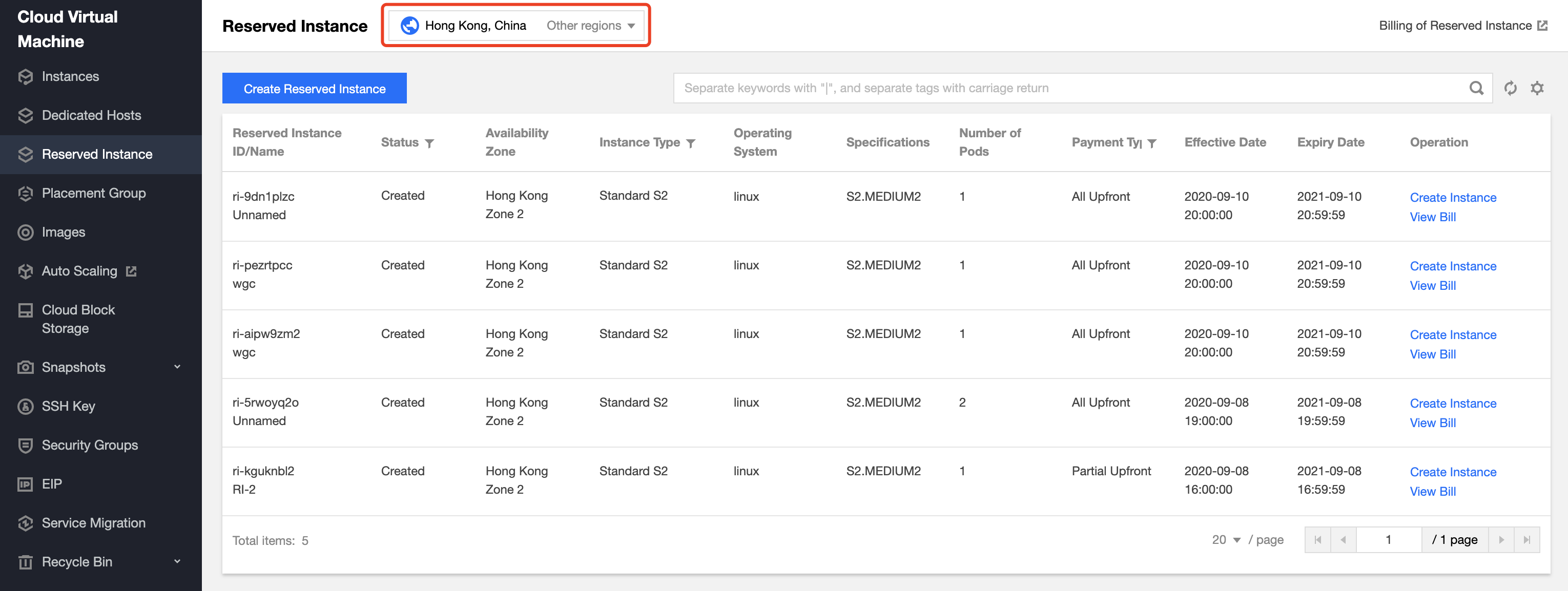

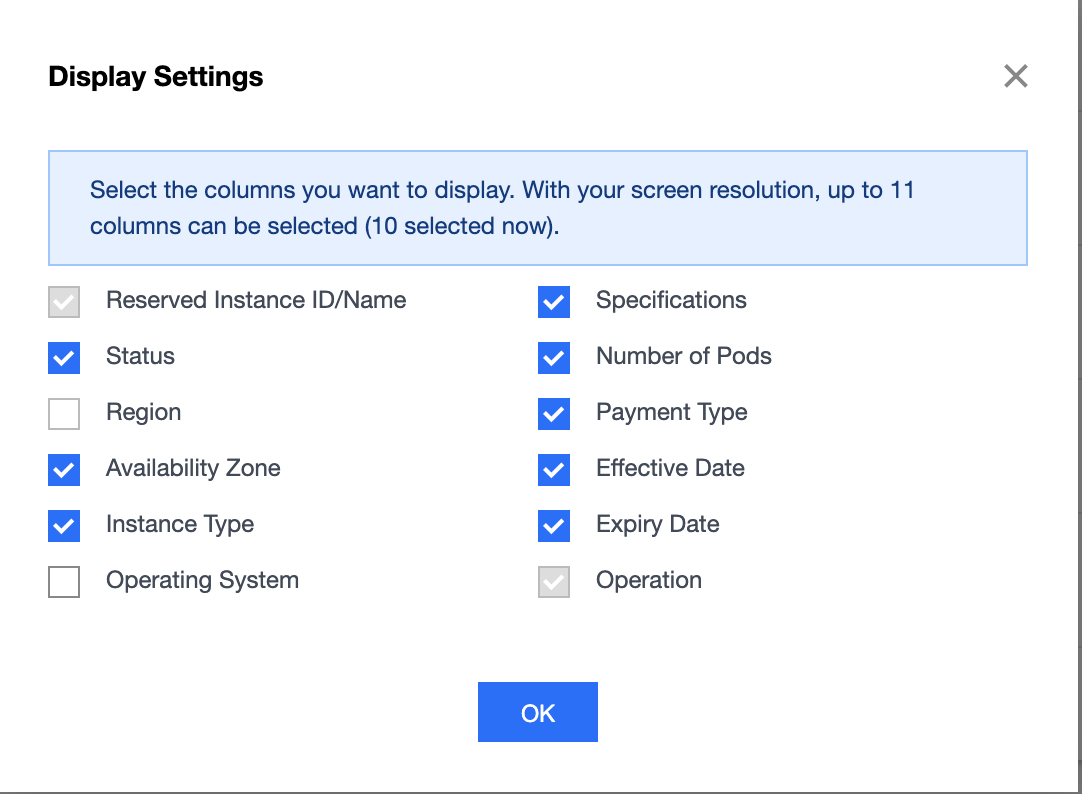
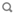
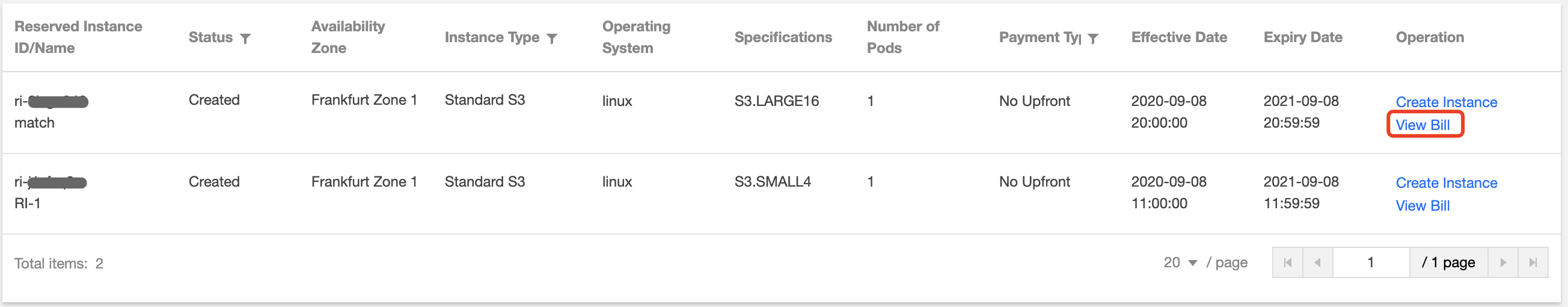
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:12:28
Mode/Item | Deployment with Images | Manual Deployment |
Deployment duration | 3 to 5 minutes | 1 to 2 days |
Deployment process | Quickly create a suitable CVM based on mature marketplace solutions or the already used solutions. | Select the appropriate operating system, database, application software and plugins to create a CVM, and installation and debugging is required. |
Security | Public images and custom images have been tested and audited by Tencent Cloud. The sources of shared images need to be identified by users. | It depends on the development and deployment personnel. |
Applicable scenarios | Public images: Genuine operating systems, which contain the initialized add-ons provided by Tencent Cloud.Custom images: Quickly create the same software environment as an existing CVM, or perform environment backup.Shared images: Quickly create the same software environment as other users' CVMs. | Configure a CVM completely by yourself, without basic settings provided. |
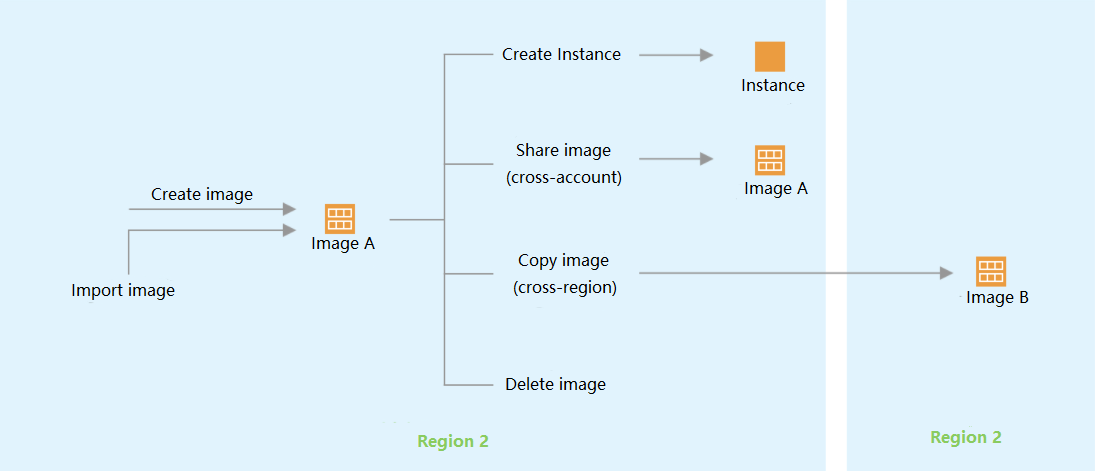
Last updated:2024-05-16 10:23:34
Last updated:2025-01-03 16:53:32
Image Version | Description |
TencentOS Server 4 | TencentOS Server 4 is Tencent's new generation commercial distribution version of the server operating system. The kernel and user-mode software of the upstream distribution version that TencentOS Server 4 depends on are independently evolved based on the upstream community, with independent selection and maintenance, no longer relying on any third-party distribution. This version realizes independent compilation and maintenance of 3000+ (BaseOS, AppStream repository) user-mode software and 8000+ (EPOL) additional software packages. It features high performance, security, and support for multiple hardware platforms, providing reliable basic environments and service capabilities for cloud-based products and businesses. |
TencentOS Server 3 | It is compatible with the CentOS 8 user mode and uses the tkernel4 version deeply optimized based on the community 5.4 LTS kernel. |
TencentOS Server 2.4 | It is compatible with the CentOS 7 user mode and uses the tkernel4 version deeply optimized based on the community 5.4 LTS kernel. |
Last updated:2025-03-04 14:24:16
Last updated:2025-01-21 18:01:27
Update Summary | Update Date |
Incorporate into the file located at /etc/rc.local -> /etc/rc.d/rc.local, and configure it with executable permissions. Install glibc-langpack-en and glibc-langpack-zh to address compatibility issues with language configurations following the subdivision of the glibc-common package. | 2024-12-23 |
Updated the kernel to 6.6.47-12, incorporating the Hygon patch to rectify the issue preventing the Metasequoia model from booting properly. Upgraded additional user-mode software packages. | 2024-11-28 |
Public version first conversion test rootfs uses XFS file system | 2024-09-03 |
Last updated:2024-11-22 17:16:57
mount -t cgroupfs cgroupfs /cgroupfs/
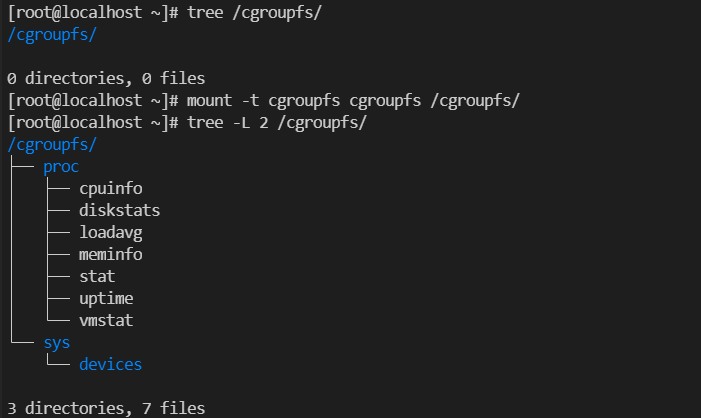
cgroupfs to a specified container by using the option of -v. The command for enabling the docker is as follows:docker run -itd --cpus 2 --cpuset-cpus 0,1,2,4 -v/cgroupfs/sys/devices/system/cpu/:/sys/devices/system/cpu -v/cgroupfs/proc/cpuinfo:/proc/cpuinfo -v/cgroupfs/proc/stat:/proc/stat -v/cgroupfs/proc/meminfo:/proc/meminfo <image-id> /bin/bash
sysctl -w vm.memory_qos=1sysctl -w vm.pagecache_limit_global=1
echo x > /proc/sys/vm/pagecache_limit_ratio#(0 < x < 100) enables the page cache limit. When it is not 0, for example, 30, it means the page cache is limited to 30% of the total system memory.
pagecache_limit_ignore_dirty is used to determine whether to ignore dirty pages when the memory occupation of page cache is calculated. Its location is as follows:/proc/sys/vm/pagecache_limit_ignore_dirty./proc/sys/vm/pagecache_limit_async
sysctl -w vm.memory_qos=1
sysctl -w vm.pagecache_limit_global=0
echo value > memory.limit_in_bytes
echo 10 > memory.pagecache.max_ratio
echo 5 > memory.pagecache.reclaim_ratio
FILE | VAL |
blkio.throttle.readwrite_bps_device | Total Throttle of Read-Write Bps |
blkio.throttle.readwrite_iops_device | Total Throttle of Read-Write iops |
blkio.throttle.readwrite_dynamic_ratio | Dynamic Prediction of Read-Write Ratio: 0: Disabled. A fixed ratio of (Read: Write - 3:1) is used. 1-5: The dynamic prediction scheme is enabled. |
sysctl -w kernel.io_qos=1 # Enable IO QoS feature sysctl -w kernel.io_cgv1_buff_wb=1 # Enable Buffer IO feature (enabled by default)
echo /sys/fs/cgroup/blkio/A > /sys/fs/cgroup/memory/A/memory.bind_blkio
cgroup, with the basic usage as follows:echo 1 > <cgroup directory>/memory.async_fork # Enable the asynchronous fork feature for the current cgroup directory echo 0 > <cgroup directory>/memory.async_fork # Disable the asynchronous fork feature for the current cgroup directory
Last updated:2025-01-03 16:55:14
yum command, as well as the t command that comes with TencentOS Server to manage software packages. In addition, TencentOS Server 3 supports running the dnf command to manage software packages.yumdownloader --source kernel command in the system to obtain it.Last updated:2024-01-08 09:12:28
Last updated:2024-10-14 11:31:53
Updated Feature | Update Date |
Upgraded the user-mode software packages. | 2024-09-11 |
Updated the user mode to 8.10. Added virtio_scsi in /etc/dracut.conf. | 2024-08-16 |
Upgraded the kernel to 5.4.119-20.0009.32. Upgraded the user-mode software packages. | 2024-06-26 |
Optimized the crashkernel value configured in /etc/default/grub. Upgraded the user-mode software packages. | 2024-05-07 |
Updated Feature | Update Date |
Rectified the i8042.noaux parameter issue. Rectified the issue of an empty keymap. Rectified the issue of certain repository URLs lacking mirrors.tencentyun.com. | 2023-07-15 |
Upgraded the kernel to kernel-5.4.119-20.0009.20.oc8. Upgraded the user mode software. Upgraded the dracut-related software to rectify the startup exceptions of the kdump service. Launched OpenCloudOS 8.6 to the public cloud. | 2023-03-15 |
Updated Feature | Update Date |
Disabled the firewalld\sssd\rngd service. Uninstalled the microcode_ctl/nss-softokn/avahi package. Set keymap. Set timezone. Set the cloudinit.target dependency for the boot of kdump. Configured mirrors.tencentyun.com as the first URL in repo. Modified the /etc/rc.d/rc.local file permission to 755. Fixed permission errors of some directories in /var/lib/. | 2022-09-16 |
Updated the kernel version to 5.4.119-19.0010. Updated other user mode software. Updated the image timestamp. | 2022-07-27 |
Launched OpenCloudOS 8.5 to the public cloud. | 2022-03-04 |
Last updated:2024-10-14 11:30:34
Updated Feature | Update Date |
Upgraded the user-mode software packages. | 2024-09-10 |
Upgraded the kernel to 6.6.34-9. Upgraded openssh to openssh-9.3p2-12.oc9.x86_64.rpm, fixing CVE-2024-6387. Upgraded the user-mode software packages. | 2024-07-09 |
Changed the rootfs file system to XFS. Upgraded the user-mode software packages. | 2024-06-27 |
Upgraded the kernel to 6.6.6-2401.0.1.oc9.4. Upgraded other user-mode software packages. Fixed the issue of two duplicate URLs in the yum configuration. Optimized the crashkernel value configured in /etc/default/grub. | 2024-05-07 |
Updated Feature | Update Date |
Configured dracut.conf to adapt to specific device models. | 2023-08-04 |
Disabled irqbalance.service. Configured selinux = disable. Set locale to en_US.UTF-8. | 2023-04-19 |
Rectified cloud-init. Rectified locale. | 2023-03-27 |
Launched OpenCloudOS 9.0 to the public cloud. | 2023-03-17 |
Last updated:2025-09-05 17:50:41
/etc/fstab does not include data disk configuration. Otherwise, instances created with this image cannot be started normally.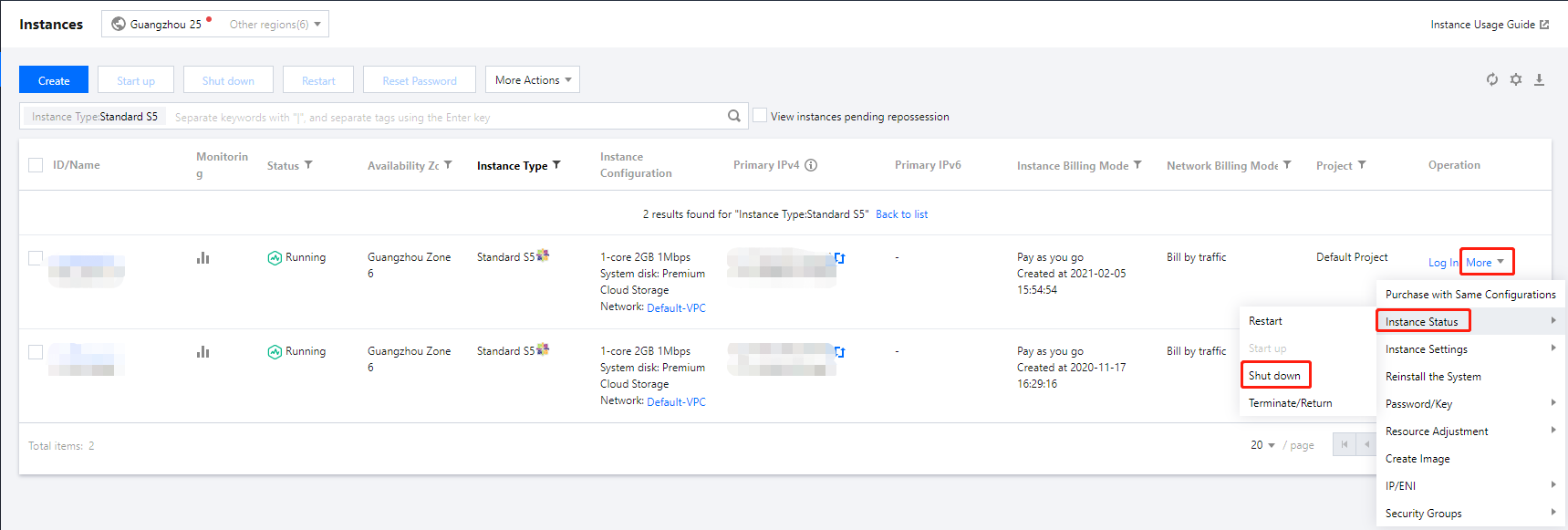
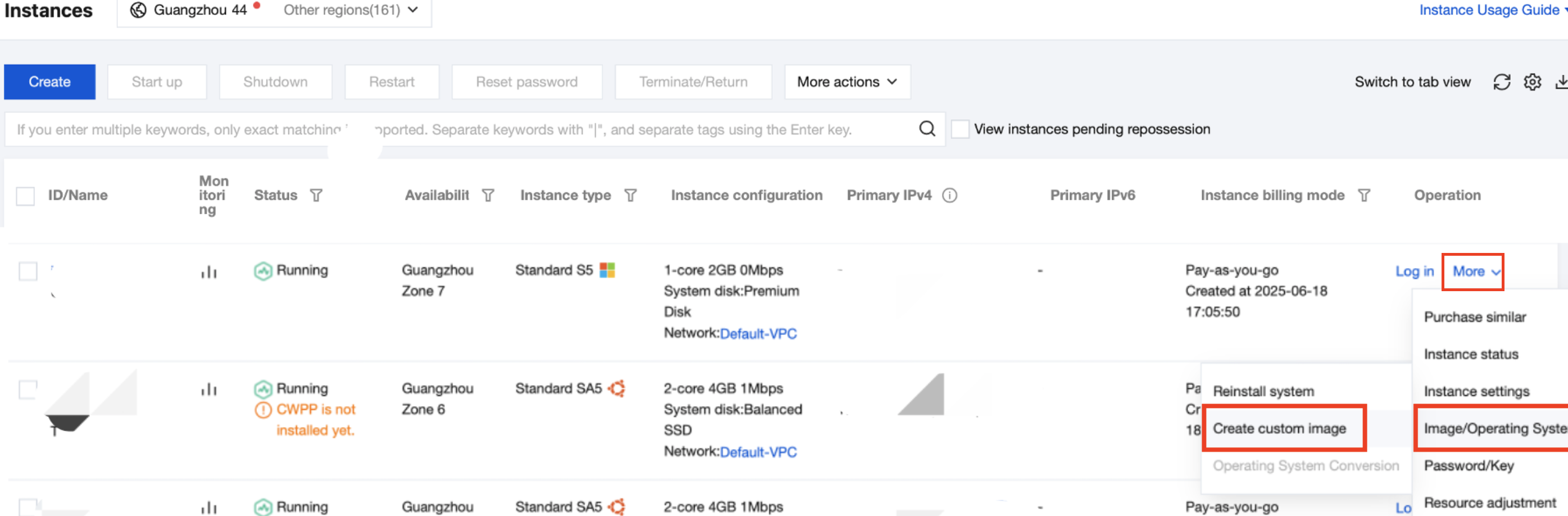
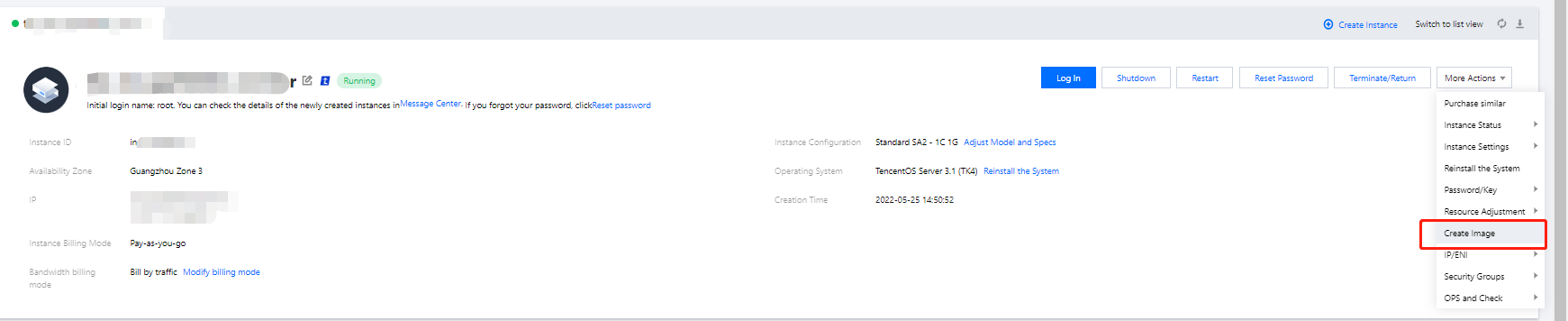
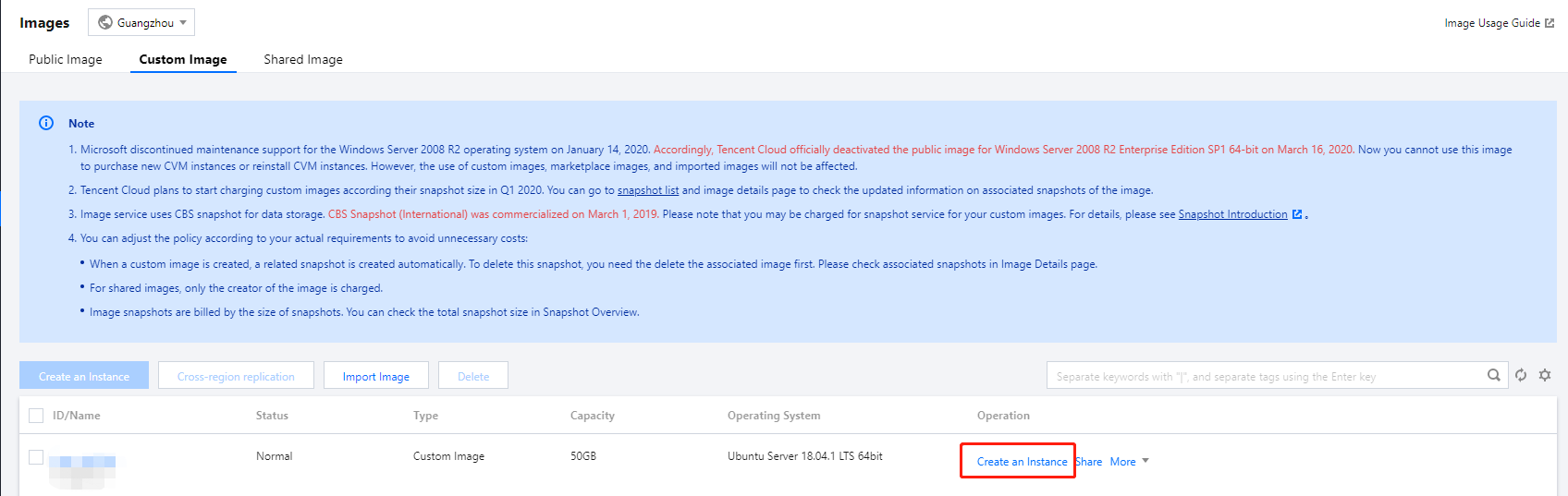
Last updated:2024-05-16 10:47:13
Last updated:2024-05-16 10:46:51
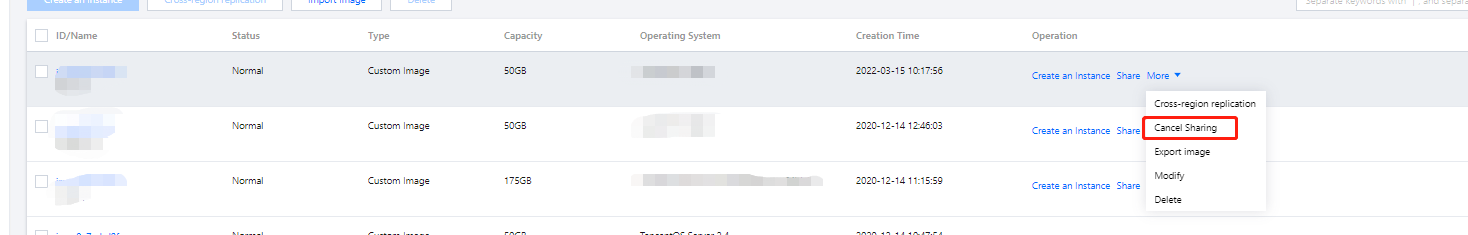
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:00
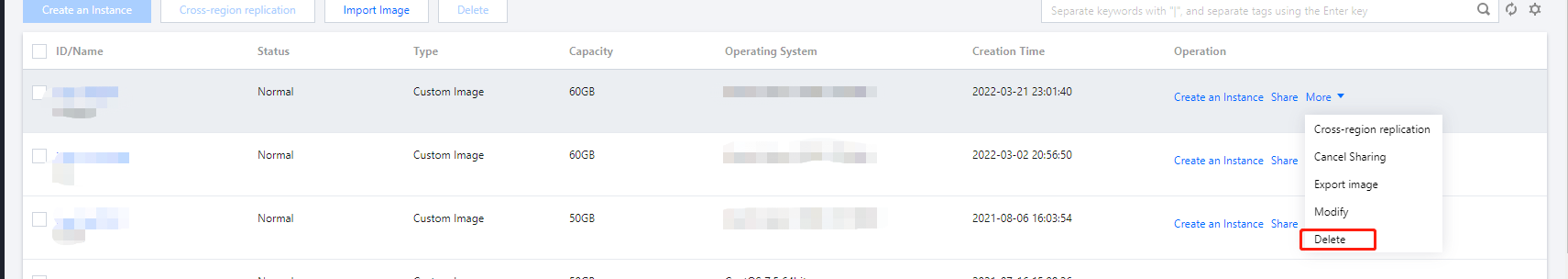

Last updated:2025-12-12 15:35:34
sudo parted -l /dev/sda | grep 'Partition Table'
msdos is returned, it's an MBR partition and you can proceed to the next step.gpt is returned, it's a GPT partition.sudo ls /sys/firmware/efi
/etc/grub2.cfg: It’s recommended to use uuid in the kernel parameter for root mounting. Other methods (such as root=/dev/sda) may cause a system startup failure. The mounting steps are as follows:/root.df -TH
/root is /dev/vda1.
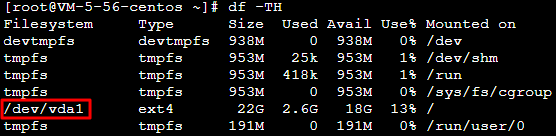
sudo blkid /dev/vda1
/etc/fstab file.vi /etc/fstab
UUID=d489ca1c-xxxx-4536-81cb-ceb2847f9954 / ext4 defaults 0 0
/etc/fstab: Do not attach other disks here, which may cause the system startup failure after migration because the disk is not found./etc/shadow: Granted with the read-write permissions.mount
proc on /proc type proc (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime)sys on /sys type sysfs (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime)dev on /dev type devtmpfs (rw,nosuid,relatime,size=4080220k,nr_inodes=1020055,mode=755)run on /run type tmpfs (rw,nosuid,nodev,relatime,mode=755)/dev/sda1 on / type ext4 (rw,relatime,data=ordered)securityfs on /sys/kernel/security type securityfs (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime)tmpfs on /dev/shm type tmpfs (rw,nosuid,nodev)devpts on /dev/pts type devpts (rw,nosuid,noexec,relatime,gid=5,mode=620,ptmxmode=000)tmpfs on /sys/fs/cgroup type tmpfs (ro,nosuid,nodev,noexec,mode=755)cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/unified type cgroup2 (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,nsdelegate)cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/systemd type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,xattr,name=systemd)pstore on /sys/fs/pstore type pstore (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime)cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/cpu,cpuacct type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,cpu,cpuacct)cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/cpuset type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,cpuset)cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/rdma type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,rdma)cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/blkio type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,blkio)cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/hugetlb type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,hugetlb)cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/memory type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,memory)cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/devices type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,devices)cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/pids type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,pids)cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/freezer type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,freezer)cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/net_cls,net_prio type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,net_cls,net_prio)cgroup on /sys/fs/cgroup/perf_event type cgroup (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,perf_event)systemd-1 on /home/libin/work_doc type autofs (rw,relatime,fd=33,pgrp=1,timeout=0,minproto=5,maxproto=5,direct,pipe_ino=12692)systemd-1 on /proc/sys/fs/binfmt_misc type autofs (rw,relatime,fd=39,pgrp=1,timeout=0,minproto=5,maxproto=5,direct,pipe_ino=12709)debugfs on /sys/kernel/debug type debugfs (rw,relatime)mqueue on /dev/mqueue type mqueue (rw,relatime)hugetlbfs on /dev/hugepages type hugetlbfs (rw,relatime,pagesize=2M)tmpfs on /tmp type tmpfs (rw,nosuid,nodev)configfs on /sys/kernel/config type configfs (rw,relatime)tmpfs on /run/user/1000 type tmpfs (rw,nosuid,nodev,relatime,size=817176k,mode=700,uid=1000,gid=100)gvfsd-fuse on /run/user/1000/gvfs type fuse.gvfsd-fuse (rw,nosuid,nodev,relatime,user_id=1000,group_id=100)
/dev/sda1, no independent partitions reside in /boot or /home, sda1 contains the boot partition, and mbr is missing. Therefore, we only need to copy the entire sda./boot and /home are independent partitions in the current operating system, the exported image should also contain them.qemu-img commandqemu-img for CentOS.apt-get install qemu-utils
/dev/sda to /mnt/sdb/test.qcow2.sudoqemu-img convert -f raw -O qcow2 /dev/sda /mnt/sdb/test.qcow2
/mnt/sdb indicates the mounted new disk or another network storage.
To convert its format, modify the value of the -O parameter to one of the following:Parameter Value | Description |
qcow2 | qcow2 format |
vhd | vhd format |
vmdk | vmdk format |
raw | No format |
dd commandsudo dd if=/dev/sda of=/mnt/sdb/test.imag bs=1K count=$count
count parameter specifies the number of partitions to be copied, which can be queried by running the fdisk command. To copy all partitions, ignore count./dev/sda.fdisk -lu /dev/sda
Disk /dev/sda: 1495.0 GB, 1494996746240 bytes 255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 181756 cylinders, total 2919915520 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 4096 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes Disk identifier: 0x0008f290
dd command is in RAW format. We recommend that you convert it to qcow2, vhd, or other image formats.qemu-img to convert the original image into a supported format.qemu-nbd to open QCOW2 images, and the Xen platform allows you to directly open VHD files. This document uses the Linux platform as an example:modprobe nbd
lsmod | grep nbd
CONFIG_BLK_DEV_NBD is enabled. If not, enable it or change the system before compiling the kernel again.
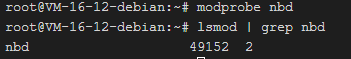
qemu-nbd -c /dev/nbd0 xxxx.qcow2
mount /dev/nbd0p1 /mnt
qemu-nbd command, /dev/nbd0 maps to xxx.qcow2, and /dev/nbd0p1 indicates the first partition of the virtual disk. If nbd0p1 does not exist or mount fails, the image may be incorrect.
You can also start the CVM to check whether the image file works before uploading the image.Last updated:2025-09-08 16:50:31
virtio_blk and the ENI driver virtio_net. To ensure that a CVM instance created with a custom image can start up properly, check whether your image supports virtio drivers in the source server before importing the image. This document uses CentOS as an example to describe how to check whether an image supports virtio drivers.grep -i virtio /boot/config-$(uname -r)
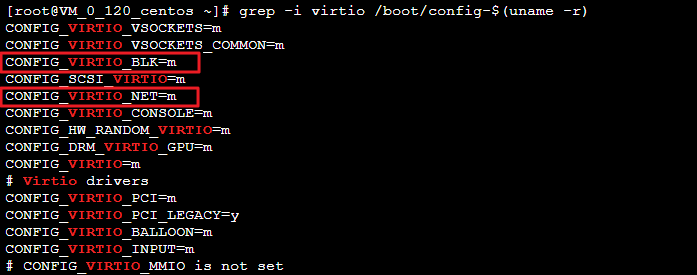
CONFIG_VIRTIO_BLK and CONFIG_VIRTIO_NET is m in the response,please go to Step 2.CONFIG_VIRTIO_BLK and CONFIG_VIRTIO_NET is y in the response, which means the operating system contains the virtio drivers, you can import the custom image to Tencent Cloud. For detailed directions, see Overview.CONFIG_VIRTIO_BLK and CONFIG_VIRTIO_NET in the response, it means that images with the OS cannot be imported to Tencent Cloud. Please download and compile kernel.m in Step 1, you need to check whether initramfs or initrd contains the virtio drivers. Please execute the corresponding command according to the operating system:lsinitrd /boot/initramfs-$(uname -r).img | grep virtio
lsinitrd /boot/initramfs-$(uname -r).img | grep virtio
mkdir -p /tmp/initrd && cd /tmp/initrdzcat /boot/initrd-$(uname -r).img | cpio -idmvfind . -name "virtio*"
lsinitramfs /boot/initrd.img-$(uname -r) | grep virtio
lsinitrd /boot/initrd-$(uname -r) | grep virtio
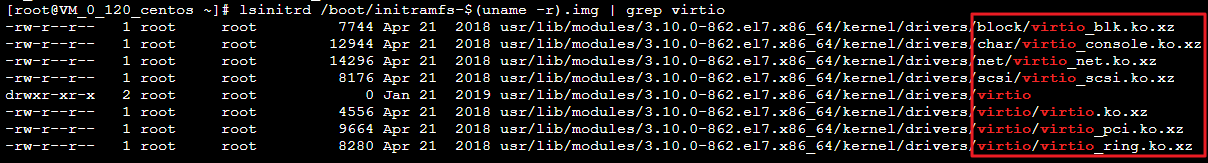
initramfs or initrd does not contain the virtio drivers in Step 2, you will need to reconfigure the temporary file system to ensure that initramfs or initrd contains the virtio drivers. Run the corresponding command according to the operating system:mkinitrd -f --allow-missing --with=virtio_blk --preload=virtio_blk --with=virtio_net --preload=virtio_net --with=virtio_console --preload=virtio_console /boot/initramfs-$(uname -r).img $(uname -r)
mkinitrd -f --allow-missing --with=virtio_blk --preload=virtio_blk --with=virtio_net --preload=virtio_net --with=virtio_console --preload=virtio_console /boot/initramfs-$(uname -r).img $(uname -r)
mkinitrd -f --allow-missing --with=xen-blkfront --preload=xen-blkfront --with=virtio_blk --preload=virtio_blk --with=virtio_pci --preload=virtio_pci --with=virtio_console --preload=virtio_console /boot/initramfs-$(uname -r).img $(uname -r)
mkinitrd -f --allow-missing --with=xen-vbd --preload=xen-vbd --with=xen-platform-pci --preload=xen-platform-pci --with=virtio_blk --preload=virtio_blk --with=virtio_pci --preload=virtio_pci --with=virtio_console --preload=virtio_console /boot/initrd-$(uname -r).img $(uname -r)
echo -e 'xen-blkfront\nvirtio_blk\nvirtio_pci\nvirtio_console' >> /etc/initramfs-tools/modulesmkinitramfs -o /boot/initrd.img-$(uname -r)
mkinitrd -m "virtio_blk virtio_net"
yum install -y ncurses-devel gcc make wget
uname -r

2.6.32-642.6.2.el6.x86_64 version, you should download linux-2.6.32.tar.gz at https://mirrors.edge.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v2.6/linux-2.6.32.tar.gz.cd /usr/src/
wget https://mirrors.edge.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v2.6/linux-2.6.32.tar.gz
tar -xzf linux-2.6.32.tar.gz
ln -s linux-2.6.32 linux
cd /usr/src/linux
make mrpropercp /boot/config-$(uname -r) ./.configmake menuconfig
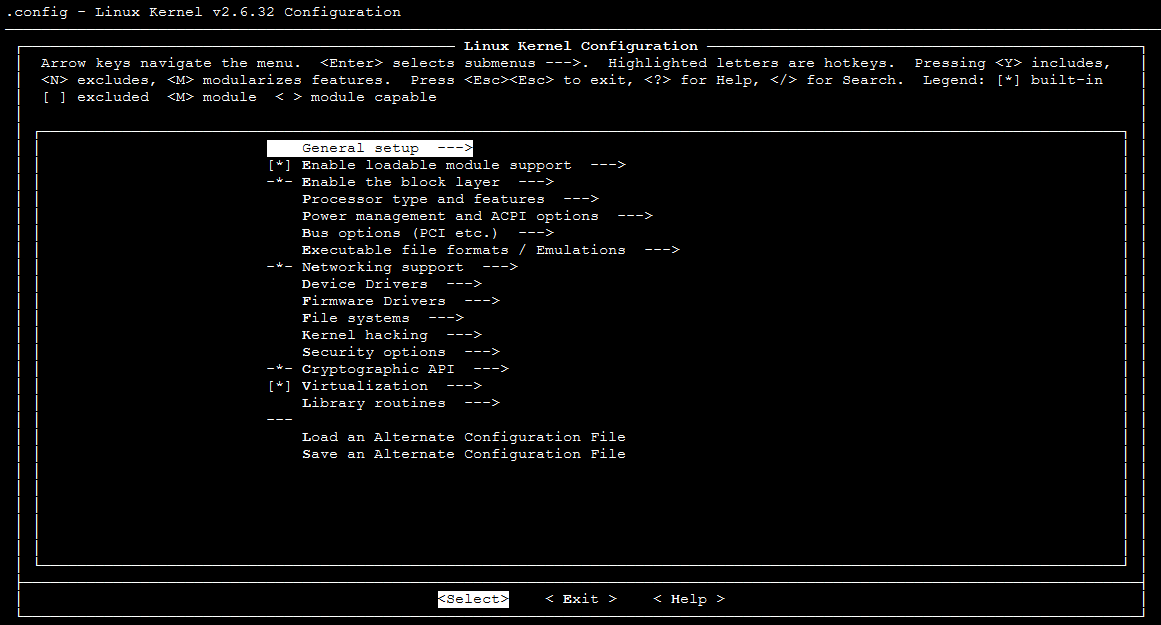
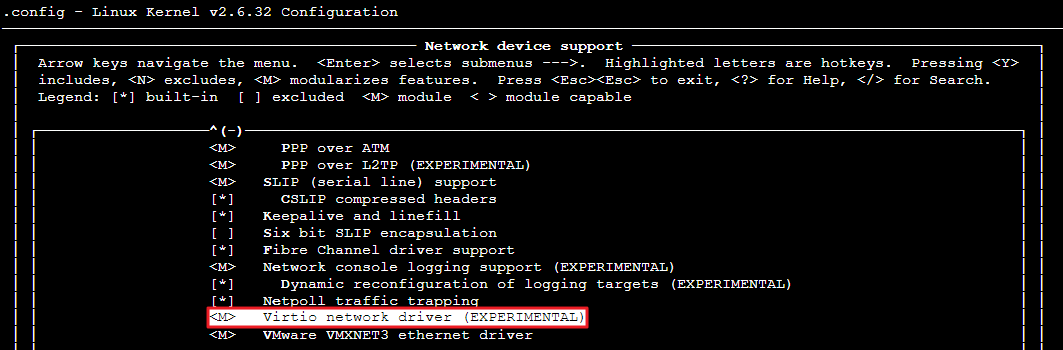
.config file..config file..config file.make oldconfigmake preparemake scriptsmakemake install
find /lib/modules/"$(uname -r)"/ -name "virtio.*" | grep -E "virtio.*"grep -E "virtio.*" < /lib/modules/"$(uname -r)"/modules.builtin
virtio_blk, virtio_pci.virtio_console, it indicates that you have installed the virtio drivers correctly.Last updated:2025-07-14 15:20:53
/usr/local/qcloud/python, and it does not conflict with the default python in the system.Type | OS | Version | x86_64 | arm64 | ||
| | | qcloud-python | cloud-init | qcloud-python | cloud-init |
rpm | CentOS | 7 | ||||
| | 8 | ||||
| Fedora | 36 | N/A | N/A | ||
| Kylin | 20sp1 | ||||
| openSUSE | 15.4 | N/A | N/A | ||
deb | Debian | 11 | ||||
| | 10 | N/A | N/A | ||
| | 9 | N/A | N/A | ||
| | 8 | N/A | N/A | ||
| Ubuntu | 22.04 | N/A | N/A | ||
| | 20.04 | ||||
| | 18.04 | ||||
| | 16.04 | N/A | N/A | ||
rm -rf /var/lib/cloudrm -rf /etc/cloudrm -rf /usr/local/bin/cloud*
dpkg -i *.deb
rpm -ivh *.rpm
cloud-init qcloud -v/usr/bin/cloud-init qcloud 0011
wget https://gerryguan-1306210569.cos.ap-chongqing.myqcloud.com/cloud-init/src/cloud-init-20.1.0011.tar.gz
tar -zxvf cloud-init-20.1.0011.tar.gz
cd cloud-init
yum install python3-pip -y
apt-get -y install python3-pip
python3 -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install 'requests<2.20.0' command to install requests 2.20.0 or later before installing the cloud-init dependencies.pip3 install -r requirements.txt
yum install cloud-utils-growpart dracut-modules-growroot -ydracut -f
yum install cloud-utils-growpart -y
apt-get install cloud-guest-utils -y
python3 setup.py build
python3 setup.py install --init-system systemd
--init-system can be followed by any of systemd, sysvinit, sysvinit_deb, sysvinit_freebsd, sysvinit_openrc, sysvinit_suse, upstart, or None (default). Choose one according to the auto-start service management method of the operating system. Otherwise the cloud-init service cannot automatically start upon system startup.sysvinit for the CentOS 6 and earlier versions, and select systemd for CentOS 7 and later versions. This document uses systemd as an example./etc/cloud/cloud.cfg with that of the downloaded cloud.cfg file.useradd syslog
strings /sbin/init | grep "/lib/system" command, and you will receive a return message.ln -s /usr/local/bin/cloud-init /usr/bin/cloud-init
systemctl enable cloud-init-local.servicesystemctl start cloud-init-local.servicesystemctl enable cloud-init.servicesystemctl start cloud-init.servicesystemctl enable cloud-config.servicesystemctl start cloud-config.servicesystemctl enable cloud-final.servicesystemctl start cloud-final.servicesystemctl status cloud-init-local.servicesystemctl status cloud-init.servicesystemctl status cloud-config.servicesystemctl status cloud-final.service
/lib/systemd/system/cloud-init-local.service with the following:[Unit]Description=Initial cloud-init job (pre-networking)Wants=network-pre.targetAfter=systemd-remount-fs.serviceBefore=NetworkManager.serviceBefore=network-pre.targetBefore=shutdown.targetConflicts=shutdown.targetRequiresMountsFor=/var/lib/cloud[Service]Type=oneshotExecStart=/usr/bin/cloud-init init --localExecStart=/bin/touch /run/cloud-init/network-config-readyRemainAfterExit=yesTimeoutSec=0# Output needs to appear in instance console outputStandardOutput=journal+console[Install]WantedBy=cloud-init.target
/lib/systemd/system/cloud-init.service with the following:[Unit]Description=Initial cloud-init job (metadata service crawler)Wants=cloud-init-local.serviceWants=sshd-keygen.serviceWants=sshd.serviceAfter=cloud-init-local.serviceAfter=systemd-networkd-wait-online.serviceAfter=networking.serviceAfter=systemd-hostnamed.serviceBefore=network-online.targetBefore=sshd-keygen.serviceBefore=sshd.serviceBefore=systemd-user-sessions.serviceConflicts=shutdown.target[Service]Type=oneshotExecStart=/usr/bin/cloud-init initRemainAfterExit=yesTimeoutSec=0# Output needs to appear in instance console outputStandardOutput=journal+console[Install]WantedBy=cloud-init.target
strings /sbin/init | grep "sysvinit" command, and you will receive a return message.chkconfig --add cloud-init-localchkconfig --add cloud-initchkconfig --add cloud-configchkconfig --add cloud-finalchkconfig cloud-init-local onchkconfig cloud-init onchkconfig cloud-config onchkconfig cloud-final on
apt-get/yum install cloud-init
apt-get or yum is the default cloud-init version in the software source configured for the operating system. Some configuration items of instances created by using the image whose cloud-init is installed this way may not be initialized as expected. Therefore, we recommend that you install the service by manually downloading the cloud-init source package./etc/cloud/cloud.cfg with that of the downloaded cloud.cfg file.cloud-init init --local
Cloud-init v. 20.1.0011 running 'init-local' at Fri, 01 Apr 2022 01:26:11 +0000. Up 38.70 seconds.
rm -rf /var/lib/cloud
rm -rf /etc/network/interfaces.d/50-cloud-init.cfg
/etc/network/interfaces to the following:# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system# and how to activate them. For more information, see interfaces(5).source /etc/network/interfaces.d/*
yum install epel-release -y
yum install python3-pip -y
apt-get clean all
apt-get update -y
apt-get -y install python3-pip
Last updated:2024-10-22 12:01:24

bcdedit /enum {current}
Windows boot loaderID {current}device partition=C:path \WINDOWS\system32\winload.exedescription Windows 10locale zh-CNinherit {bootloadersettings}recoverysequence {f9dbeba1-1935-11e8-88dd-ff37cca2625c}displaymessageoverride Recoveryrecoveryenabled Yesflightsigning Yesallowedinmemorysettings 0x15000075osdevice partition=C:systemroot \WINDOWSresumeobject {1bcd0c6f-1935-11e8-8d3e-3464a915af28}nx OptInbootmenupolicy Standard
http://mirrors.tencent.com/install/windows/virtio_64_1.0.9.exehttp://mirrors.tencentyun.com/install/windows/virtio_64_1.0.9.exe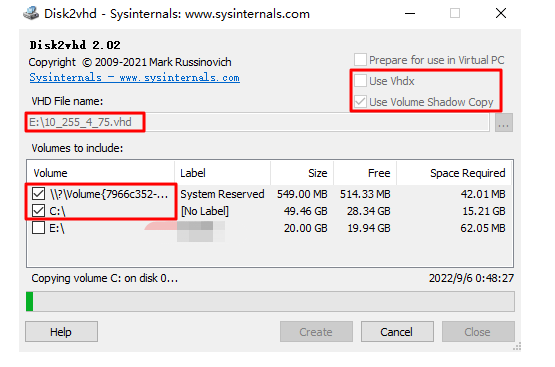

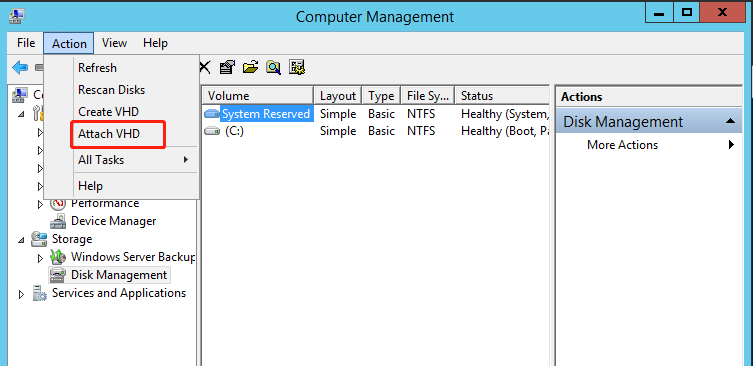
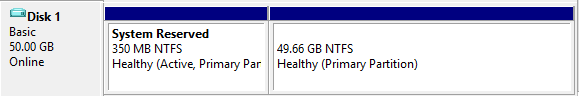
qemu-img to convert the image file format to a supported format.Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:01
Software | Download Link | Description |
CloudbaseInitSetup_X_X_XX_xXX.msi | Download the Cloudbase-Init installation package based on the operating system used. Stable version (recommended) Windows 64-bit operating system: Click here to download the installation package. Windows 32-bit operating system: Click here to download the installation package. Beta version | Used to install Cloudbase-Init |
TencentCloudRun.ps1 | Click here to download the installation package. | - |
localscripts.py | Click here to download the installation package. | Used to ensure that Cloudbase-Init starts properly |

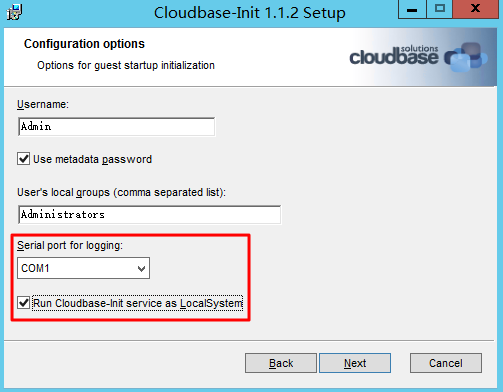
cloudbase-init.conf configuration file.
The cloudbase-init.conf configuration file is saved in C:\Program Files\Cloudbase Solutions\Cloudbase-Init\conf by default. cloudbase-init.conf configuration file with the following:[DEFAULT]username=Administratorgroups=Administratorsinject_user_password=trueconfig_drive_raw_hhd=trueconfig_drive_cdrom=trueconfig_drive_vfat=truebsdtar_path=C:\Program Files\Cloudbase Solutions\Cloudbase-Init\bin\bsdtar.exemtools_path=C:\Program Files\Cloudbase Solutions\Cloudbase-Init\bin\san_policy=OnlineAllmetadata_services=cloudbaseinit.metadata.services.configdrive.ConfigDriveService,cloudbaseinit.metadata.services.ec2service.EC2Service#,cloudbaseinit.metadata.services.httpservice.HttpService#,cloudbaseinit.metadata.services.maasservice.MaaSHttpServicemetadata_base_url=http://169.254.0.23/ec2_metadata_base_url=http://169.254.0.23/retry_count=2retry_count_interval=5plugins=cloudbaseinit.plugins.windows.extendvolumes.ExtendVolumesPlugin,cloudbaseinit.plugins.common.networkconfig.NetworkConfigPlugin,cloudbaseinit.plugins.common.sethostname.SetHostNamePlugin,cloudbaseinit.plugins.common.setuserpassword.SetUserPasswordPlugin,cloudbaseinit.plugins.common.localscripts.LocalScriptsPlugin,cloudbaseinit.plugins.common.userdata.UserDataPluginverbose=truedebug=truelogdir=C:\Program Files\Cloudbase Solutions\Cloudbase-Init\log\logfile=cloudbase-init.logdefault_log_levels=comtypes=INFO,suds=INFO,iso8601=WARN,requests=WARN#logging_serial_port_settings=COM1,115200,N,8mtu_use_dhcp_config=truentp_use_dhcp_config=truefirst_logon_behaviour=nonetbios_host_name_compatibility=falseallow_reboot=trueactivate_windows=truekms_host="kms.tencentyun.com"local_scripts_path=C:\Program Files\Cloudbase Solutions\Cloudbase-Init\LocalScripts\C:\powershellPS C:\Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestrictedvolumes_to_extend=1,2
TencentCloudRun.ps1 script to C:\Program Files\Cloudbase Solutions\Cloudbase-Init\LocalScripts.TencentCloudRun.ps1 script, select Properties, and check for its executable permission in the pop-up window, as shown below:
localscripts.py in C:\Program Files\Cloudbase Solutions\Cloudbase-Init\Python\Lib\site-packages\cloudbaseinit\plugins\common with the localscripts.py file in Required Software.Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:01
C:\Program Files\qemu as the installation path as an example.Path in System variables and click Edit as shown below:

C:\Program Files\qemu, and click OK.qemu-img --help
cd <directory of the source image file>
qemu-img convert -f <source image file format> -O <target image format> <source image filename> <target image filename>
-f: source image file format. -O (in uppercase): target image format and source and target image filenames.
For example, run the following command to convert the test.qcow2 image file to test.raw:qemu-img convert -f qcow2 -O raw test.qcow2 test.raw
apt-get update # Update the package list
apt-get install qemu-utils # Install qemu-img
yum install qemu-img
qemu-img convert -f qcow2 -O raw test.qcow2 test.raw
-f: source image file format. -O (in uppercase): target image format and source and target image filenames.
After conversion, the target file will be displayed in the directory of the source image file.Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:00
/dev/vda1, /dev/vdb1 and so forth) to identify disk partitions. However, these device names may change due to the change in the actual operating environment after an image is imported. To guarantee the correct booting of the system even when the device name changes, you can modify the disk identification method in the GRUB file to the Universally Unique Identifier (UUID). /boot/grub/menu.lst or /boot/grub/grub.conf./boot/grub/grub.cfg or /boot/grub2/grub.cfg.menu.lst or grub.conf file in the /boot/grub directory, you are probably using GRUB (GRUB Legacy). If you find the grub.cfg file in the /boot/grub or /boot/grub2 directory, you are probably using GRUB2.blkid command can be used. Running the blkid command will display the detailed information of all the available partitions, including the UUIDs. Run the following command in the terminal: sudo blkid
/dev/vda1 is c0b9ecd8-f922-4e5d-bccb-83fbc94ad23b. /dev/vda1: UUID="c0b9ecd8-f922-4e5d-bccb-83fbc94ad23b" BLOCK_SIZE="4096" TYPE="ext4" PARTUUID="bcfcb5cb-01"
/boot/grub/grub.cfg directory is made. If you are using GRUB, or if the GRUB2 configuration file for distribution is located in the /boot/grub2/grub.cfg directory, you can adjust the configuration according to the actual situation. /boot/grub/grub.cfg file to the /home directory.sudo cp /boot/grub/grub.cfg /home
/boot/grub/grub.cfg file and confirm the root partition marked in the configuration file. In this case, the root partition is located on the /dev/vda1 device. sudo vi /boot/grub/grub.cfg
# /boot/grub/grub.cfg...echo 'Loading Linux 6.1.0-13-amd64 ...'linux /boot/vmlinuz-6.1.0-13-amd64 root=/dev/vda1 roecho 'Loading initial ramdisk ...'...
grub.cfg file, and change the root=/dev/vda1 device name to the root=UUID=xxx format. The content after root=UUID= is the UUID value corresponding to the device returned by running the blkid command. This configuration may appear for multiple times in the grub.cfg file. The modifcation is required for each configuration. # Before modification...echo 'Loading Linux 6.1.0-13-amd64 ...'linux /boot/vmlinuz-6.1.0-13-amd64 root=/dev/vda1 roecho 'Loading initial ramdisk ...'...# After modification...echo 'Loading Linux 6.1.0-13-amd64 ...'linux /boot/vmlinuz-6.1.0-13-amd64 root=UUID=c0b9ecd8-f922-4e5d-bccb-83fbc94ad23b roecho 'Loading initial ramdisk ...'...
sudo cat /boot/grub/grub.cfg
...linux /boot/vmlinuz-6.1.0-13-amd64 root=UUID=c0b9ecd8-f922-4e5d-bccb-83fbc94ad23b ro...
grub.cfg backup file in the /home directory.Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:01
/etc/fstab file supports the use of device names (such as /dev/vda1) to identify file systems. However, device names may change due to the change in the actual operating environment after an image is imported, so there may be some problems using device names to identify file systems. To avoid these problems, you can change the file system identification method in the /etc/fstab file to UUID. The UUID is a unique characteristic string that identifies a disk partition and won't be affected by the change in device names. Using a UUID as the fstab file disk identification can ensure that the system can still correctly mount the file system when the device name changes.sudo cat /etc/fstab
UUID=c0b9ecd8-f922-4e5d-bccb-83fbc94ad23b / ext4 defaults 1 1
/dev/vda1), it indicates that the current fstab is using a device name. You can refer to the subsequent operation to switch to the UUID method. /dev/vda1 / ext4 defaults 1 1
blkid command can be used. Running the blkid command will display the detailed information of all the available partitions including the UUIDs. Run the following command in the terminal: sudo blkid
/dev/vda1 is c0b9ecd8-f922-4e5d-bccb-83fbc94ad23b. /dev/vda1: UUID="c0b9ecd8-f922-4e5d-bccb-83fbc94ad23b" BLOCK_SIZE="4096" TYPE="ext4" PARTUUID="bcfcb5cb-01"
/etc/fstab file to the /home directory.sudo cp /etc/fstab /home
/etc/fstab file.sudo vi /etc/fstab
UUID=xxx format. The content after UUID= is the UUID value corresponding to the device returned by running the blkid command. # Before modification/dev/vda1 / ext4 defaults 1 1# After modificationUUID=c0b9ecd8-f922-4e5d-bccb-83fbc94ad23b / ext4 defaults 1 1
sudo cat /etc/fstab
UUID=c0b9ecd8-f922-4e5d-bccb-83fbc94ad23b / ext4 defaults 1 1
sudo mount -a
/home directory.sudo mv /home/fstab /etc/fstab
Last updated:2025-09-05 14:44:51
Type | Use Case | Description |
Cross-region replication of custom image | Deploy the same CVM instance across regions quickly. | Copy a custom image to another region, and use the created copy to create a CVM in the new region. |
Intra-region replication of shared image | Make a copy of a shared image and use it as a custom image. | The created custom image is not subject to the limits of shared images. |
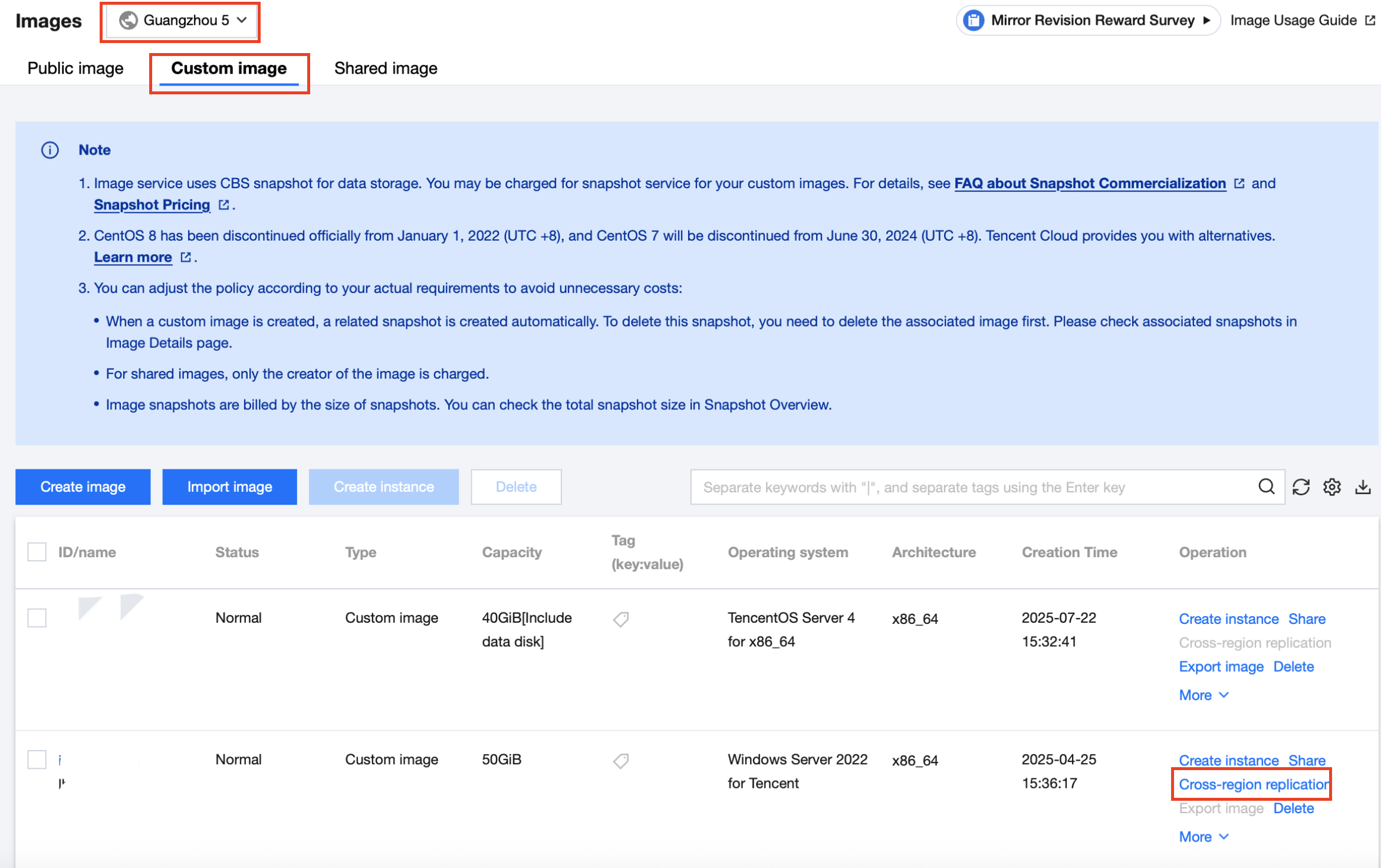
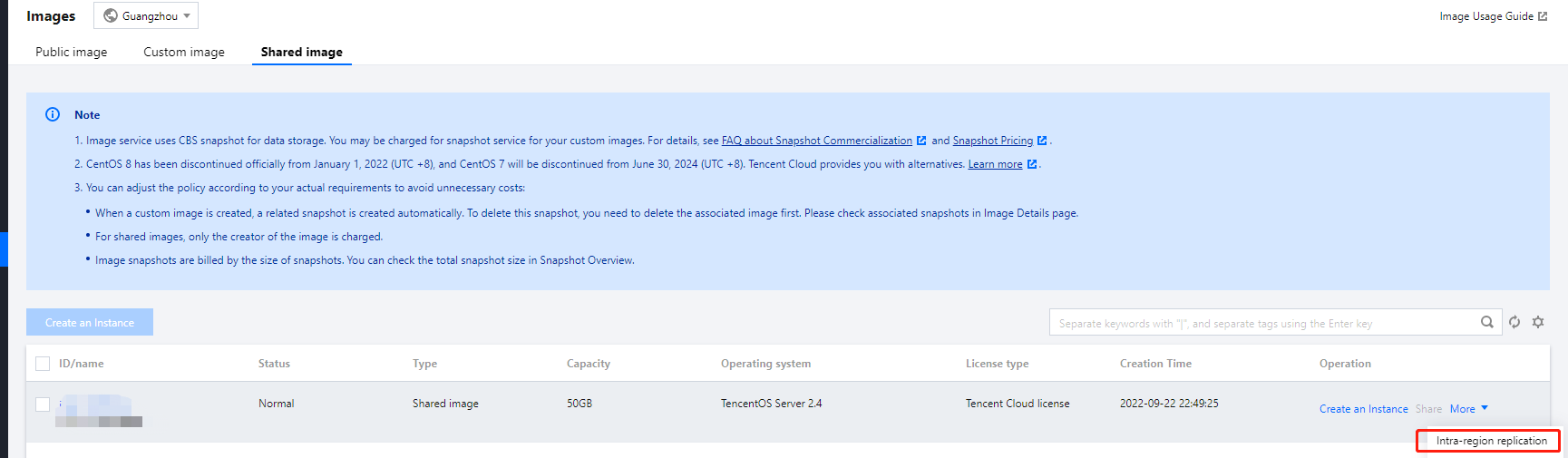
Last updated:2025-09-08 16:44:15
Image Attributes | Condition |
Operating system | Images based on CentOS, CentOS Stream, Ubuntu, Debian, RedHat, OpenSUSE, CoreOS, FreeBSD, Kylin (Kirin), UnionTech, TencentOS, Fedora, AlmaLinux, Rocky Linux, OpenCloudOS, and Other Linux release version Support 32-bit, 64-bit, and arm_64-bit. |
Image format | Support image formats of RAW, VHD, QCOW2, and VMDK. Use qemu-img info imageName | grep 'file format' to check the image format. For image files of other formats, you may refer to Converting Image Format to convert and then import them. |
File system and partition | Support xfs, ext3, and ext4 file systems, and support MBR and GPT partitions. Note: Support the ext4 file system, but cannot include the feature 64bit. The features project and quota cannot appear in pairs. You can run the following command to view the list of features included in the ext4 file system.
It is not recommended for the system disk to have multiple partitions. We recommend a single root partition only. If there are multiple partitions, it is not recommended to have other partitions after the one where the system resides. Otherwise, disk expansion will fail. It is not recommended to use LVM to create system disk partitions (root partition), as it may lead to issues such as instance startup, password modification, and SSH login via password. |
Image size | The actual image size must not exceed 1024 GB. Use qemu-img info imageName | grep 'disk size' to check the actual image size;The image vsize must not exceed 1024 GB. Use qemu-img info imageName | grep 'virtual size' to check the image vsize.Note: When importing an image, review the size of the image after converting it to QCOW2 format. |
Network | Tencent Cloud provides the eth0 network interface by default for instances.Users can query the instance's network configuration through the metadata service within the instance. For details, see Instance Metadata. |
Driver | The image must install the Virtio driver for the virtualization platform KVM. For details, see Linux Import Image Check Virtio Driver. If the image cannot install cloud-init for other reasons, refer to Force Importing Image to configure the instance manually. |
File system | To ensure that the Linux system can correctly identify the disk when the file system is started, check and correctly configure the GRUB file disk identification method. For details, see Configure the GRUB file disk identification method to UUID. To ensure that the Linux system can correctly identify the disk when the file system is mounted, check and correctly configure the fstab file disk identification method. For details, see Configure the fstab file disk identification method to UUID. |
Kernel | We recommend a native kernel for the image. Kernel modification may cause the CVM to fail to import. |
Region limit | The image import service outside the Chinese mainland only supports COS files in the same region. That is, a COS link in the same region needs to be used for import. |
Image Attributes | Condition |
Operating system | Windows Server 2022, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008, and Other Windows-related versions Support 32-bit, 64-bit, and arm_64-bit. |
Image format | Support RAW, VHD, QCOW2, and VMDK image formats. Use qemu-img info imageName | grep 'file format' to check the image format. |
File system and partition | Support NTFS file system, and support MBR and GPT partitions. Support creation of multiple partitions on the system disk. Ensure that no other partitions exist after the boot partition (C Drive) on the disk where the system resides, otherwise the instance may fail to start or the disk expansion may fail. |
Image size | The actual image size must not exceed 1024 GB. Use qemu-img info imageName | grep 'disk size' to check the actual image size. The image vsize must not exceed 1024 GB. Use qemu-img info imageName | grep 'virtual size' to check the image vsize. Note: When importing an image, review the size of the image after converting it to qcow2 format. |
Network | Tencent Cloud provides the local connection network interface for instances by default. Users can query the instance's network configuration through the metadata service within the instance. For details, see Instance Metadata. |
Driver | Images must install the Virtio driver for the virtualization platform KVM. Windows system by default does not have the Virtio driver installed. Users can install the Windows Virtio driver and then export the local image. The download address for the Windows Virtio driver is as follows (download according to your actual network environment): Public network download address: http://mirrors.tencent.com/install/windows/virtio_64_1.0.9.exePrivate network download address: http://mirrors.tencentyun.com/install/windows/virtio_64_1.0.9.exe |
Region limit | The image import service outside the Chinese mainland only supports COS files in the same region. That is, a COS link in the same region needs to be used for import. |
Others |
Parameter | Required | Description |
Region | Yes | Ensure that the region of the custom image you need to import matches the region where you need to create an instance. Custom images from this region cannot be directly used to create instances in other regions. If you need to use the current image in another region, you can replicate your custom image across regions through image replication. |
System Disk Files | Yes | The system disk files contain the critical components such as the kernel, library files, and drivers needed for the server operating system. By using the system disk files, the server can start and run the operating system to provide basic services and features. Import method: Select the storage from the COS list. In the drop-down list, select the COS bucket where the file is contained, and then select the corresponding image file. The system will automatically obtain the URL of the image file. Note that only COS files within the local domain can be selected in this way. Enter the COS object address. Go to the COS console, find the bucket from Bucket List where the image file is located, and find the image file step by step. On the image file details page, click Copy Temporary Link to copy the URL of the image file. |
Operating System | Yes | 1. Linux and Windows operating systems are supported. Ensure that it matches the operating system type of the image file. 2. System platform Identifies the operating system platform to which the image file is imported. Ensure that it matches the operating system platform of the image file. Linux operating system: CentOS, CentOS Stream,Ubuntu, Debian, RedHat, and other commonly used system platforms can be selected. If the system platform is not listed, select Other Linux. Windows operating system: Windows Server 2022, Windows Server 2019, and other commonly used system platforms can be selected. If the system platform is not listed, select Other Windows. 3. System Version Identifies the version of the Linux operating system to which the image file is imported. For example, CentOS supports multiple versions, including 8, 7, 6, and 5. Ensure that it matches the operating system version of the image file. 4. System Architecture 32-bit, 64-bit, and ARM 64-bit are supported. Ensure that it matches the system architecture of the image file. |
Data Disk Files | No | The data disk files are used to store user data such as application data, user documents and database files. If your image has data disk files, add a data disk by configuring this. Import method: Select the storage from the COS list. In the drop-down list, select the COS bucket where the file is contained, and then select the corresponding image file. The system will automatically obtain the URL of the image file. Note that only COS files within the local domain can be selected in this way. Enter the COS object address. Go to the COS console, find the bucket from Bucket List where the image file is located, and find the image file step by step. On the image file details page, click Copy Temporary Link to copy the URL of the image file. |
Image Name | Yes | The image name displayed after the image file is imported. Note that the image name only supports Chinese characters, letters, digits, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and periods (.), with a maximum of 60 characters. |
Image Description | No | Add image description for easy management. |
Tag | No | Set a tag to facilitate search and management. |
Parameter | Required | Description |
Import Method | No | If your image cannot be imported correctly, you can select the Enable Forcible Import option. This method only checks the integrity of the file and will not block the import process due to driver or configuration issues. For details, see Forcibly Importing Image. |
Boot Mode | Yes | Ensure that the selected boot mode matches the boot mode of the image file. Otherwise, using this image may affect the normal startup of your instance. For details, see Best Practices for Boot Mode Legacy BIOS and UEFI. |
Error Code | Reason | Recommended Solution |
InvalidUrl | The entered COS link is invalid. Possible reasons are as follows: The entered image file link is not a Tencent Cloud COS link. The object address of the COS has no permission for public read and private write. The access permission of COS files is private read, but the signature has expired. When an image is imported outside the Chinese mainland, a COS link not in the same region was used; the image import service outside the Chinese mainland only supports COS servers in the same region. The current COS file has been deleted. | Check whether the COS link matches the imported image link. |
InvalidFormatSize | The format or size of the imported image does not conform to the restrictions of Tencent Cloud image import feature. Imported images support image file formats of qcow2, vhd, vmdk, and raw. The size of the system disk image should not exceed 1024 GB, and a single data disk should not exceed 2048 GiB (based on the image file converted to qcow2 format) | The image must meet the restrictions on image format and image size specified in Import Preparation.According to the image format conversion content of Linux Image Creation, convert the image file into an appropriate file format and simplify the image content to meet the size requirements, and then re-import the image. For files exceeding the size limit, images can also be migrated using the Offline Instance Migration feature. |
VirtioNotInstall | Virtio driver not installed: Tencent Cloud uses KVM virtualization technology and requires users to install the Virtio driver in the image to be imported. Except for a few customized Linux operating systems, most Linux operating systems have the Virtio driver installed; Windows operating systems require users to manually install the Virtio driver. | For Linux image import, see Checking Virtio Drivers in Linux. For Windows image import, see Creating Windows Images to install the Virtio driver. |
CloudInitNotInstalled | cloud-init not installed: Tencent Cloud uses the open-source program cloud-init for CVM initialization. Therefore, CVM initialization will fail if the cloud-init program is not installed. | For Linux image import, see Installing Cloud-Init on Linux. For Windows image import, see Installing Cloudbase-Init on Windows. |
PartitionNotPresent | Partition information is not found, and the imported image is incomplete. | The image is corrupted. Check if the boot partition was included when creating the image. It may be caused due to an incorrect image creation method. |
RootPartitionNotFound | The imported image does not contain a root partition. Possible reasons are as follows: The installation package was uploaded; The data disk image was uploaded; The boot partition image was uploaded; An incorrect file was uploaded. | The image is corrupted. It may be caused due to an incorrect image creation method. |
InternalError | Other errors |
Inspection Items | Inspection Instructions | Test Results | Suggestions for Fix |
Virtio | Whether the Virtio driver is installed in the image | Supported - Satisfied KernelNotSupported - Kernel not supported BlkDriverNotFound - Disk driver not found NetDriverNotFound - Network driver not found | Strongly recommended to fix: |
CloudInit | Whether cloud-init is installed in the image | Supported - Satisfied NotSupported - Not supported | Strongly recommended to fix: |
CloudinitConfig | Whether cloud-init is configured correctly | Supported - Satisfied Invalid - cloud.cfg content cannot be loaded InvalidCloudFinalModules - scripts-user not found in the cloud_final_modules configuration InvalidDatasourceList - ConfigDrive not found in datasource_list | Strongly recommended to fix: 1. Modify the cloud-init configuration file:
Download cloud.cfg based on different operating systems. Click here to download cloud.cfg for Ubuntu operating system. Click here to download cloud.cfg for CentOS operating system. Click here to download cloud.cfg for OpenSUSE / SUSE operating system. 2. Replace the content of /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg
with that of the downloaded cloud.cfg file. |
Fstab | The file /etc/fstab in the image is configured with system disk device mounting information. Incorrect configurations may cause system startup exceptions, such as device mounting information not existing or incorrect device UUID. | Supported - Satisfied DeviceNotFound - The configuration contains a non-existent device DeviceConfig - /dev/vd* configuration is used | Recommended fix: 1. If your operating system is not FreeBSD, refer to Configure the fstab file disk identification method to UUID to fix. 2. If your operating system is FreeBSD. Add Label.
Modify /etc/fstab.
Modify the result.
|
Grub | Whether the grub boot file in the image is normal. For example, if device configurations are abnormal, related devices do not exist, or there are UUID errors, it may cause a system startup anomaly. Do not check this item when the image is FreeBSD. | Supported - Satisfied NotSupported - Not configured using UUID | Recommended fix: |
Selinux | Whether SELinux is disabled for the image. It is not recommended to enable SELinux for cloud images, as it may cause a system startup anomaly. Do not check this item when the image is FreeBSD. | Supported - Satisfied ConfigNotFound - The /etc/selinux/config file does not exist when SELinux is enabled Enforcing - Highest level enabled | Recommended fix: Suggestions for fix
Change to
|
OnlineResizeFS | Whether the image supports root partition automatic scaling. The image has cloud-init, growpart (gpart, parted, growpart) commands installed. After the image is used to create an instance, the root partition will automatically scale. For example, if your image space size is 20 GB, and the system disk size is 100 GB during instance creation, the root partition will automatically scale to 100 GB after the instance is created. | Supported - Satisfied NotSupported - Not supported | Recommended fix: When the operating system is CentOS 6, CentOS 7, or TencentOS Server 2 version.
When the operating system is CentOS 8, CentOS Stream, Rocky Linux, or TencentOS Server 3 version.
When the operating system is Ubuntu.
|
Network | Whether the network configuration in the image complies with the cloud-init standard. Only Debian and Ubuntu operating systems need to checked. | Supported - Satisfied Unsupported - Not supported | Recommended fix: /etc/network/interfaces must contain source /etc/network/interfaces.d/* |
SupportBareMachine | Whether the image supports Bare Metal. | Supported - Satisfied Unsupported - Not supported | Optional fix: If you are not using Bare Metal instances, do not need to pay attention to; if the image does not meet the requirements for Bare Metal instances, you can contact customer service for assistance. |
TimeSync | Whether NTP is installed to maintain time synchronization. | Supported - Satisfied Unsupported - Not supported | Optional fix: When the operating system is CentOS 6, CentOS 7, or TencentOS Server 2 version.
When the operating system is CentOS 8, CentOS Stream, Rocky Linux, or TencentOS Server 3 version.
When the operating system is Ubuntu.
|
Inspection Items | Inspection Instructions | Test Results | Suggestions for Fix |
Virtio | Whether the Virtio driver is installed in the image | Supported - Satisfied BlkDriverNotFound - Disk driver not found | Strongly recommended to fix: For details about how to fix, refer to section Checking or Installing Virtio Drivers in Creating Windows Images. |
Cloudbase | Whether cloudbase is installed in the image | Supported - Satisfied NotSupported - Not supported | Strongly recommended to fix: |
CloudbaseConfig | Whether cloudbase is configured correctly | Supported - Satisfied NotSupported - Not supported | Strongly recommended to fix: |
SupportBareMachine | Whether the image supports Bare Metal | Supported - Satisfied NotSupported - Not supported | Optional fix: If you are not using Bare Metal instances, do not need to pay attention to; if the image does not meet the requirements for Bare Metal instances, you can contact customer service for assistance. Self-service driver download address: The downloaded file is a ZIP file. After extraction, right-click the bnxtnd.inf file and select Install. |
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:01
mount_point/qcloud_action/os.conf for configuration. If other configuration data or UserData needs to be used, the user can directly read files under mount_point/.hostname=VM_10_20_xxxxpassword=GRSgae1fw9frsG.rfrFeth0_ip_addr=10.104.62.201eth0_mac_addr=52:54:00:E1:96:EBeth0_netmask=255.255.192.0eth0_gateway=10.104.0.1dns_nameserver="10.138.224.65 10.182.20.26 10.182.24.12"
Parameter Name | Description |
hostname | CVM name |
password | Encrypted password |
eth0_ip_addr | LAN IP of eth0 |
eth0_mac_addr | MAC address of eth0 |
eth0_netmask | Subnet mask of eth0 |
eth0_gateway | Gateway of eth0 |
dns_nameserver | DNS resolution server |
/dev/cdrom and read qcloud_action/os.conf file under the mount point to obtain the configuration information.chpasswd -e.
Note that the encrypted password may contain special characters. We recommend you place it in a file and then set the password with chpasswd -e < passwd_file.os_config script based on the following script sample.
You can modify the script as needed.#!/bin/bash### BEGIN INIT INFO# Provides: os-config# Required-Start: $local_fs $network $named $remote_fs# Required-Stop:# Should-Stop:# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5# Default-Stop: 0 1 6# Short-Description: config of os-init job# Description: run the config phase without cloud-init### END INIT INFO###################user settings#####################cdrom_path=`blkid -L config-2`load_os_config() {mount_path=$(mktemp -d /mnt/tmp.XXXX)mount /dev/cdrom $mount_pathif [[ -f $mount_path/qcloud_action/os.conf ]]; then. $mount_path/qcloud_action/os.confif [[ -n $password ]]; thenpasswd_file=$(mktemp /mnt/pass.XXXX)passwd_line=$(grep password $mount_path/qcloud_action/os.conf)echo root:${passwd_line#*=} > $passwd_filefireturn 0elsereturn 1fi}cleanup() {umount /dev/cdromif [[ -f $passwd_file ]]; thenecho $passwd_filerm -f $passwd_filefiif [[ -d $mount_path ]]; thenecho $mount_pathrm -rf $mount_pathfi}config_password() {if [[ -f $passwd_file ]]; thenchpasswd -e < $passwd_filefi}config_hostname(){if [[ -n $hostname ]]; thensed -i "/^HOSTNAME=.*/d" /etc/sysconfig/networkecho "HOSTNAME=$hostname" >> /etc/sysconfig/networkfi}config_dns() {if [[ -n $dns_nameserver ]]; thendns_conf=/etc/resolv.confsed -i '/^nameserver.*/d' $dns_conffor i in $dns_nameserver; doecho "nameserver $i" >> $dns_confdonefi}config_network() {/etc/init.d/network stopcat << EOF > /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0DEVICE=eth0IPADDR=$eth0_ip_addrNETMASK=$eth0_netmaskHWADDR=$eth0_mac_addrONBOOT=yesGATEWAY=$eth0_gatewayBOOTPROTO=staticEOFif [[ -n $hostname ]]; thensed -i "/^${eth0_ip_addr}.*/d" /etc/hostsecho "${eth0_ip_addr} $hostname" >> /etc/hostsfi/etc/init.d/network start}config_gateway() {sed -i "s/^GATEWAY=.*/GATEWAY=$eth0_gateway" /etc/sysconfig/network}###################init#####################start() {if load_os_config ; thenconfig_passwordconfig_hostnameconfig_dnsconfig_networkcleanupexit 0elseecho "mount ${cdrom_path} failed"exit 1fi}RETVAL=0case "$1" instart)startRETVAL=$?;;*)echo "Usage: $0 {start}"RETVAL=3;;esacexit $RETVAL
os_config script in the /etc/init.d/ directory and execute the following command.chmod +x /etc/init.d/os_configchkconfig --add os_config
os_config has been added to the startup service.chkconfig --list
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:00
Use Case | Billing | Document |
Exporting an image to a COS bucket | Storage usage fees. Storing an image in a COS bucket will incur storage usage fees. COS will calculate the object size and charge fees based on the storage type and region of the target object. | |
| Request fees. Exporting an image to a COS bucket will incur write request fees. COS will calculate the number of write requests and charge fees accordingly. | |
| Traffic fees. Exporting an image to a COS bucket will generate upstream traffic. COS will calculate the traffic volume. Private network upstream traffic and public network upstream traffic are free of charge. | |
Downloading an image from a COS bucket | Request fees. Downloading an image from a COS bucket will incur write request fees. COS will calculate the number of write requests and charge fees accordingly. | |
| Traffic fees. Downloading an image from a COS bucket will generate downstream traffic. COS will calculate the traffic volume. Private network downstream traffic is free of charge, while public network downstream traffic is not. | |
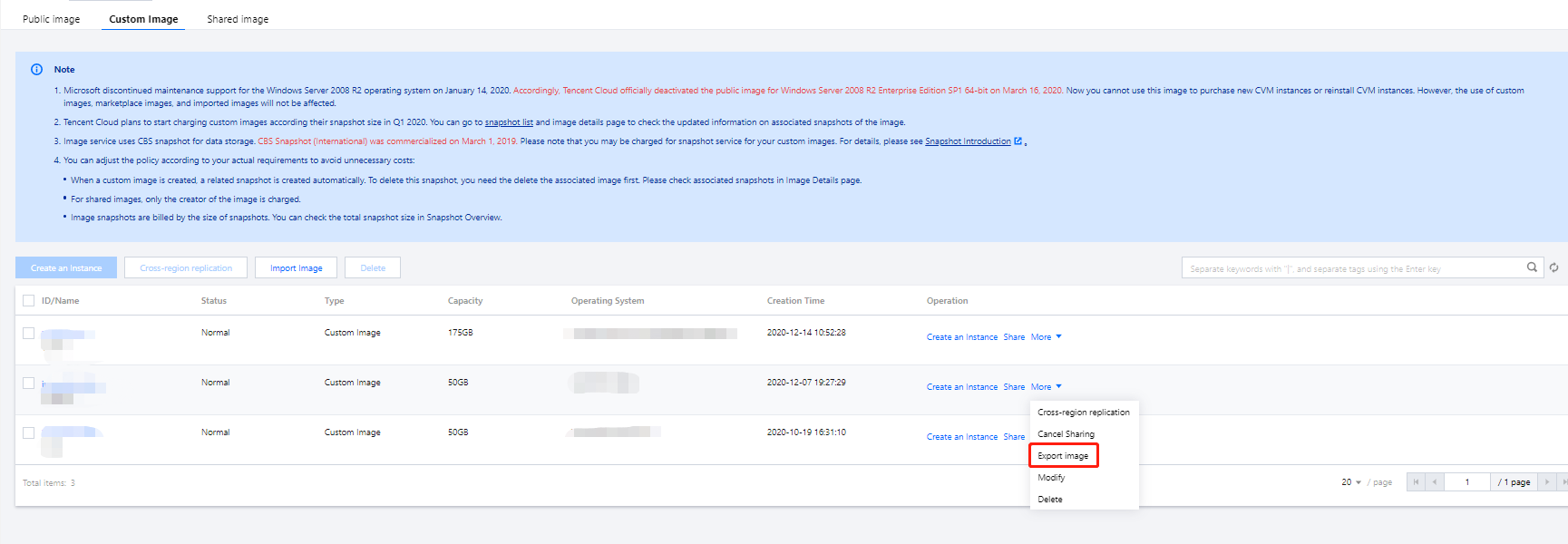
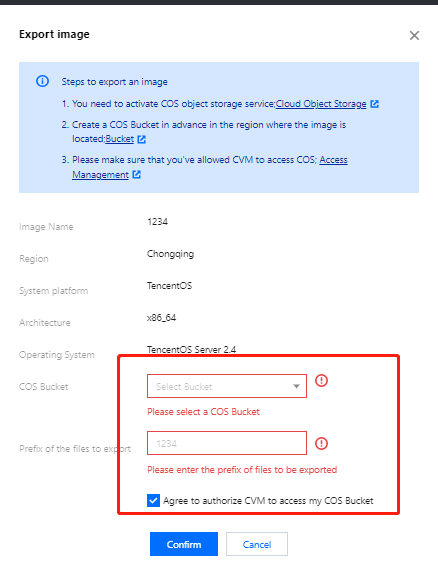
Custom prefix_xvda.raw.Last updated:2024-01-08 09:12:28
Dimension | Category | Description |
Storage Medium | HDD disk | Uses hard disk drive (HHD) as the storage medium. It features a low price and fast read/write speeds. |
| SSD disk | Uses solid state drive (SSD) as the storage medium. It features excellent IOPS and read/write speeds, with an IOPS and throughput of up to 20 times and 16 times higher than those of the HDD disk. It is more expensive than the HDD disk. |
Use Cases | System disk | Used to store the collection of systems that control and schedule the operation of CVM. It uses images. |
| Data disk | Used to store all user data. |
Architecture | Cloud Block Storage (CBS) is an elastic, highly available, highly reliable, low-cost, and customizable network block device that can be used as a standalone scalable disk for CVM. It provides data storage at a data block level and employs a 3-copy distributed mechanism to ensure data reliability. You can adjust the hardware, disk, and network of a CVM with CBS. | |
| Cloud Object Storage (COS) is a data storage device on the Internet. It allows data retrieval from any location on the CVM instance or the Internet, reducing storage costs. It is unsuitable for low-latency and high-IO scenarios. | |
/dev/vda to the system disk and maps the two data disks to /dev/vdb and /dev/vdc, respectively.
The CVM instance can automatically create block storage device mapping for local disks and cloud disks mounted to itself.Last updated:2024-01-08 09:12:28
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:12:28
Last updated:2025-09-08 16:15:45
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:01
Last updated:2024-01-06 17:43:10
Last updated:2025-09-05 10:51:47
Destination Host | Allowed Maximum MTU | Description |
Within the same VPC, CVM instances with Jumbo Frames enabled | 8500 | No |
Within the VPCs interconnected through CCN, CVM instances with Jumbo Frames enabled | | The Jumbo Frame capability needs to be enabled on the CCN. CCN's support for the Jumbo Frame capability is in beta testing. If needed, you can submit a ticket to apply. |
Hosts within the offline IDC connected through dedicated channels | | The Jumbo Frame capability needs to be enabled on the Direct Connect Gateway. Direct Connect Gateway's support for the Jumbo Frame capability is in beta testing. For details, see Change Channel. |
Within the same VPC, CVM instances without enabling Jumbo Frames | 1500 | No |
Within the VPCs interconnected through CCN, CVM instances without enabling Jumbo Frames | | No |
Hosts within the offline IDC connected through dedicated channels | | No |
Access external hosts through EIP | | No |
Network Product | Supported Maximum MTU | Description |
NAT Gateway | 1500 | No |
CLB (including ALB, NLB, and CLB) | 1500 | No |
Direct Connect Gateway | 8500 | The Jumbo Frame capability needs to be enabled on the Direct Connect Gateway. Direct Connect Gateway's support for the Jumbo Frame capability is in beta testing. For details, refer to Change Channel. |
Cloud Connect Network | 8500 | The Jumbo Frame capability needs to be enabled on the CCN. CCN's support for the Jumbo Frame capability is in beta testing. If needed, you can Submit a Ticket to apply. |
Peering connection | 1500 | No |
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:01
Feature | Overview | Documentation |
Recovering public IP addresses | If you release or return a public IP (including EIP and common public IP) by mistake, you can recover it in the console, and the recovered public IP will be an EIP. | - |
Converting common public IPs to EIPs | You can convert a common public IP of CVM to an EIP. After conversion, the EIP can be bound to and unbound from CVM at any time, making it easier to manage the public IP. | - |
Changing the public IP | Change the common public IP of the CVM and release the original public IP. | |
Adjusting the network bandwidth | Adjust the bandwidth or billing mode as needed. This feature will take effect in real time. |
Last updated:2025-09-08 16:14:30
Parameter | Description |
IP Address Type | Tencent Cloud supports various types of EIPs, such as general BGP IP, premium BGP IP, accelerated IP, static single-line IP, and anti-DDoS EIP. General BGP IP: The domestic multi-line BGP network covers more than twenty ISPs (including the three major ISPs, CERNET, and China Broadnet). The BGP public network outbound supports switchover across regions within seconds, providing your users with high-speed and secure networks. Premium BGP IP: Dedicated lines can avoid the use of international ISP services. The latency is lower, which effectively improves the quality of overseas services for users in Chinese Mainland. Accelerated IP: Anycast is used for acceleration to ensure more stable and reliable public network access with a low latency. Static single-line IP: Users can access the public network using services of a single ISP, featuring low cost and convenient scheduling. Anti-DDoS EIP: This type of GBP IP provides Tbps-level cloud-native DDoS protection capability and should be used together with Anti-DDoS Pro for Enterprise. After the IP address is bound to business resources and Anti-DDoS Pro resources, uses can enjoy the anti-DDoS capability. |
IP Resource Pool | If certain adjacent IP addresses need to be reserved for your services or IP addresses in a specific network segment should be allocated, you can submit a ticket for consultation. A dedicated IP resource pool will be assigned for you. Dedicated resource pools are supported for general and premium BGP IPs and static single-line IPs currently. For the fees, please consult your business manager. |
Billing Mode | General BGP IPs support billing by traffic and bandwidth package. For details, see Public Network Fees. Premium BGP IPs support billing by bandwidth package. For details, see Public Network Fees and Bandwidth Packages for Premium BGP IPs in Billing Overview. Accelerated IPs, static single-line IPs, and anti-DDoS EIPs support only billing by bandwidth package. Other billing modes are not supported now. |
Bandwidth Cap | Set the bandwidth cap based on your needs and allocate bandwidth resources reasonably. |
Amount | Determine the amount of EIPs to be applied as needed and make sure that the amount does not exceed the total quota. For details, see Quota Limit in Usage Restrictions. |
Name | Specify the EIP instance name. This parameter is optional. |
Tag | You can add a tag for permission management. |
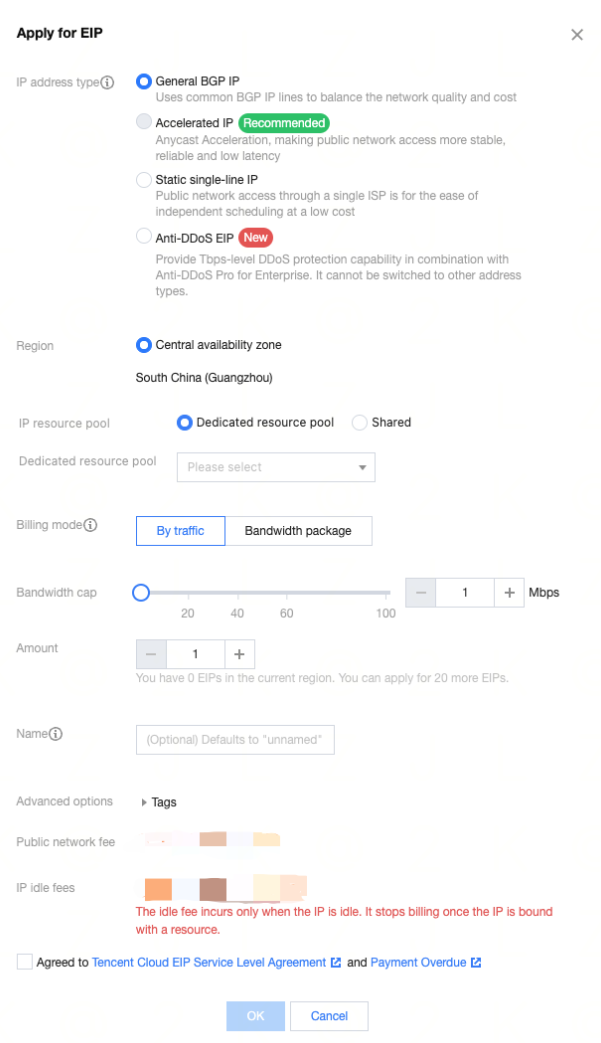

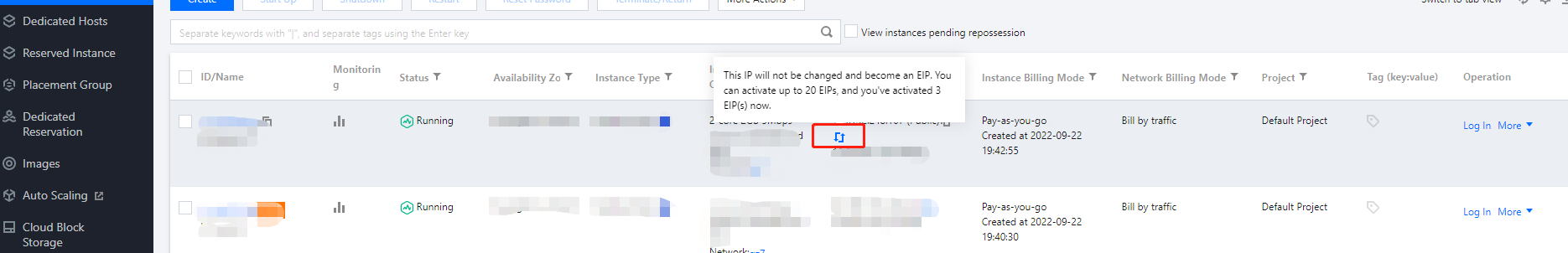
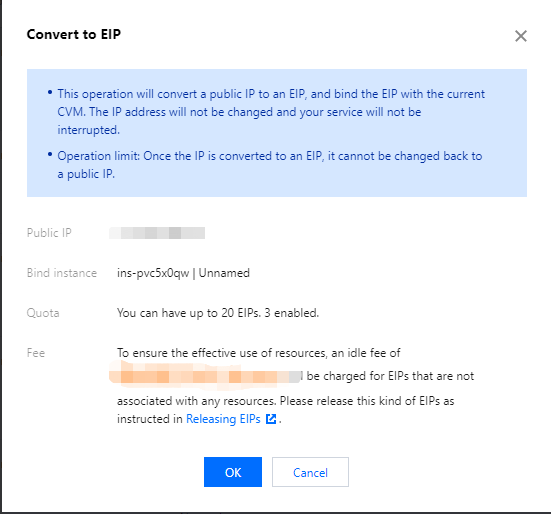
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:01
wget https://network-data-1255486055.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/eip_direct.sh
wget https://network-data-1255486055.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/eip_direct.sh
chmod +x eip_direct.sh
ip addr command to check the name of the ENI that requires EIP direct connection.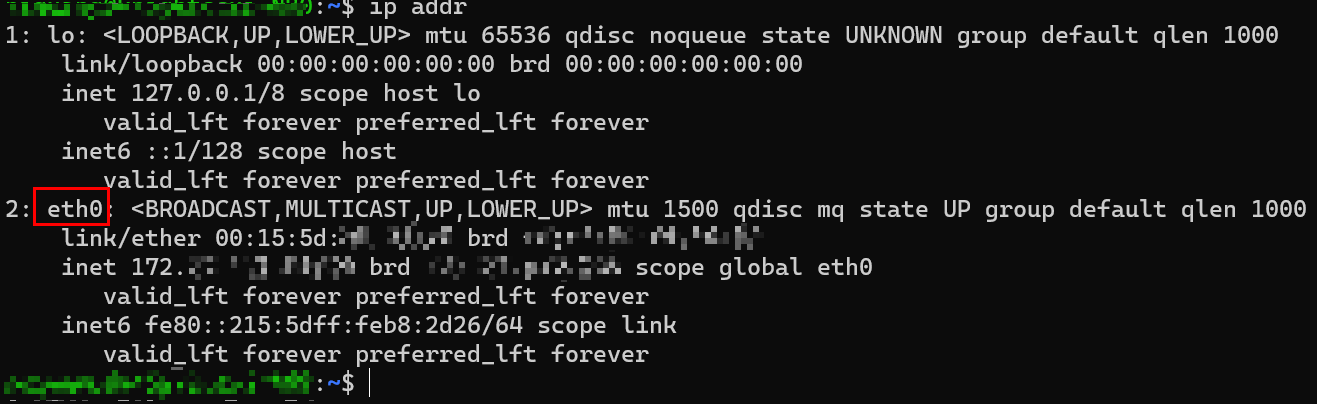
ethx indicates the name of the ENI (required). XX.XX.XX.XX indicates the EIP address (optional). You may leave it blank and run ./eip_direct.sh install ethx directly../eip_direct.sh install ethx XX.XX.XX.XX



firewall.cpland press Enter to open the Windows Firewall page.

ipconfig in the Windows PowerShell window and press Enter. You can see that the IPv4 address on the primary ENI changes to the public network address.
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:01
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:01
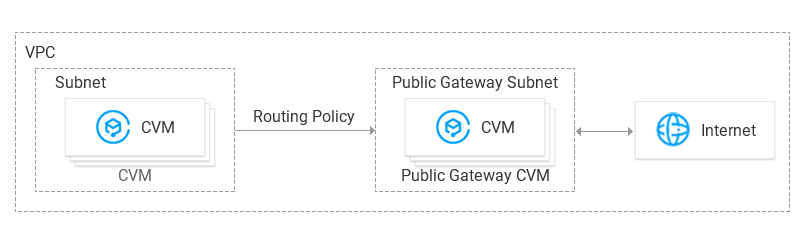

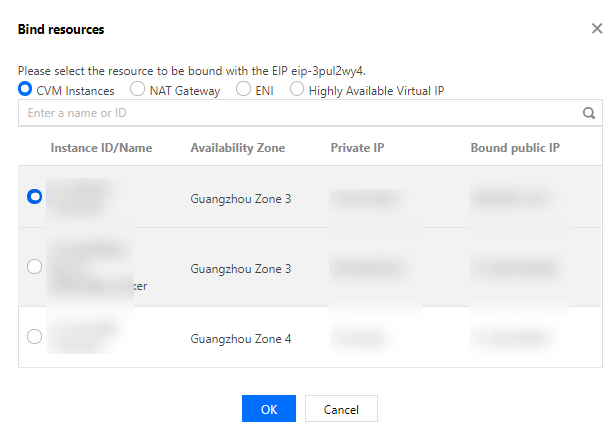
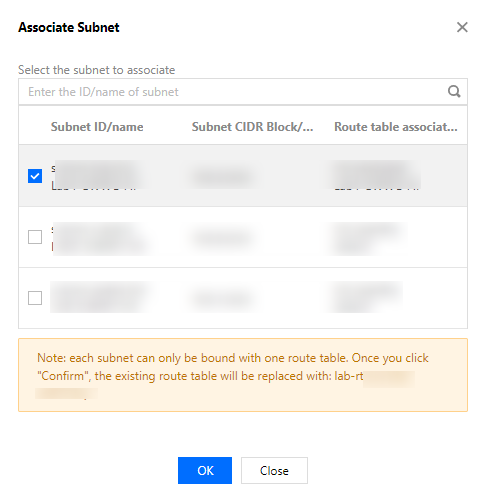
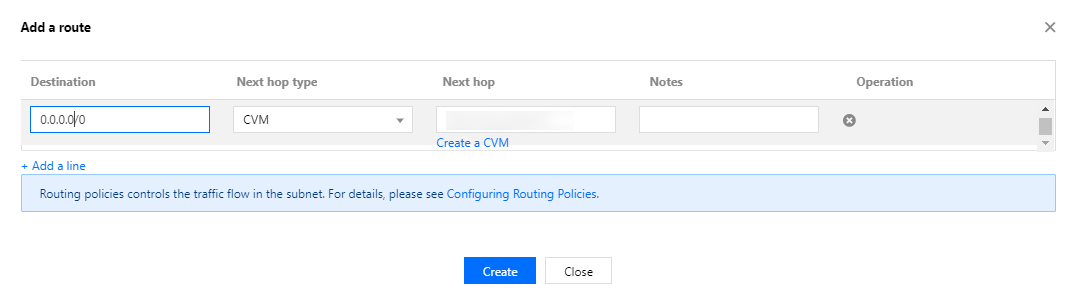
vpcGateway.sh script in usr/local/sbin.vim /usr/local/sbin/vpcGateway.sh
#!/bin/bashecho "----------------------------------------------------"echo " `date`"echo "(1)ip_forward config......"file="/etc/sysctl.conf"grep -i "^net\.ipv4\.ip_forward.*" $file &>/dev/null && sed -i \'s/net\.ipv4\.ip_forward.*/net\.ipv4\.ip_forward = 1/' $file || \echo "net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1" >> $fileecho 1 >/proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward[ `cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward` -eq 1 ] && echo "-->ip_forward:Success" || \echo "-->ip_forward:Fail"echo "(2)Iptables set......"iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -j MASQUERADE && echo "-->nat:Success" || echo "-->nat:Fail"iptables -t mangle -A POSTROUTING -p tcp -j TCPOPTSTRIP --strip-options timestamp && \echo "-->mangle:Success" || echo "-->mangle:Fail"echo "(3)nf_conntrack config......"echo 262144 > /sys/module/nf_conntrack/parameters/hashsize[ `cat /sys/module/nf_conntrack/parameters/hashsize` -eq 262144 ] && \echo "-->hashsize:Success" || echo "-->hashsize:Fail"echo 1048576 > /proc/sys/net/netfilter/nf_conntrack_max[ `cat /proc/sys/net/netfilter/nf_conntrack_max` -eq 1048576 ] && \echo "-->nf_conntrack_max:Success" || echo "-->nf_conntrack_max:Fail"echo 10800 >/proc/sys/net/netfilter/nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established \[ `cat /proc/sys/net/netfilter/nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established` -eq 10800 ] \&& echo "-->nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established:Success" || \echo "-->nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established:Fail"
chmod +x /usr/local/sbin/vpcGateway.shecho "/usr/local/sbin/vpcGateway.sh >/tmp/vpcGateway.log 2>&1" >> /etc/rc.local
set_rps.sh script in usr/local/sbin.vim /usr/local/sbin/set_rps.sh
# !/bin/bashecho "--------------------------------------------"datemask=0i=0total_nic_queues=0get_all_mask() {local cpu_nums=$1if [ $cpu_nums -gt 32 ]; thenmask_tail=""mask_low32="ffffffff"idx=$((cpu_nums / 32))cpu_reset=$((cpu_nums - idx * 32))if [ $cpu_reset -eq 0 ]; thenmask=$mask_low32for ((i = 2; i <= idx; i++)); domask="$mask,$mask_low32"doneelsefor ((i = 1; i <= idx; i++)); domask_tail="$mask_tail,$mask_low32"donemask_head_num=$((2 ** cpu_reset - 1))mask=$(printf "%x%s" $mask_head_num $mask_tail)fielsemask_num=$((2 ** cpu_nums - 1))mask=$(printf "%x" $mask_num)fiecho $mask}set_rps() {if ! command -v ethtool &>/dev/null; thensource /etc/profilefiethtool=$(which ethtool)cpu_nums=$(cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep processor | wc -l)if [ $cpu_nums -eq 0 ]; thenexit 0fimask=$(get_all_mask $cpu_nums)echo "cpu number:$cpu_nums mask:0x$mask"ethSet=$(ls -d /sys/class/net/eth*)for entry in $ethSet; doeth=$(basename $entry)nic_queues=$(ls -l /sys/class/net/$eth/queues/ | grep rx- | wc -l)if (($nic_queues == 0)); thencontinueficat /proc/interrupts | grep "LiquidIO.*rxtx" &>/dev/nullif [ $? -ne 0 ]; then # not smartnic#multi queue don't set rpsmax_combined=$($ethtool -l $eth 2>/dev/null | grep -i "combined" | head -n 1 | awk '{print $2}')#if ethtool -l $eth goes wrong.[[ ! "$max_combined" =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]] && max_combined=1if [ ${max_combined} -ge ${cpu_nums} ]; thenecho "$eth has equally nic queue as cpu, don't set rps for it..."continuefielseecho "$eth is smartnic, set rps for it..."fiecho "eth:$eth queues:$nic_queues"total_nic_queues=$(($total_nic_queues + $nic_queues))i=0while (($i < $nic_queues)); doecho $mask >/sys/class/net/$eth/queues/rx-$i/rps_cpusecho 4096 >/sys/class/net/$eth/queues/rx-$i/rps_flow_cnti=$(($i + 1))donedoneflow_entries=$((total_nic_queues * 4096))echo "total_nic_queues:$total_nic_queues flow_entries:$flow_entries"echo $flow_entries >/proc/sys/net/core/rps_sock_flow_entries}set_rps
chmod +x /usr/local/sbin/set_rps.shecho "/usr/local/sbin/set_rps.sh >/tmp/setRps.log 2>&1" >> /etc/rc.localchmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
Last updated:2024-03-26 14:58:42
HostName of the instance.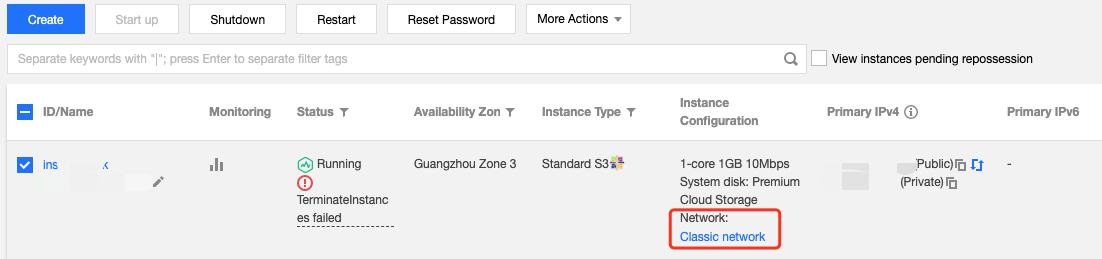

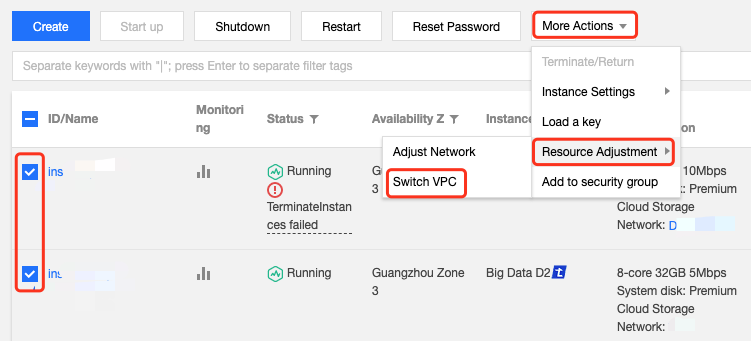

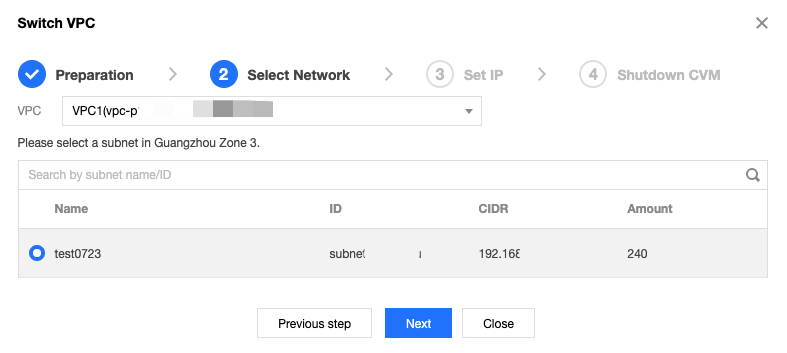
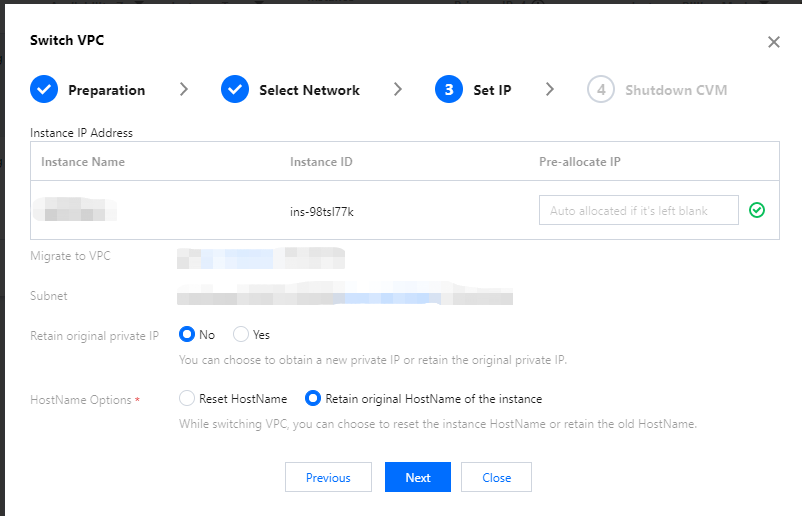

Last updated:2025-11-20 16:59:48

Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
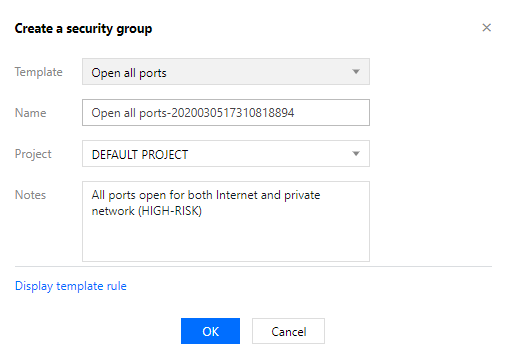
Template | Description | Notes |
Open all ports | All ports are open. May present security issues. | - |
Open TCP port 22,80,443,3389 and ICMP | TCP port 22, 80, 443 and 3389, and the ICMP are open. All ports are open internally. | Suitable for instances with web services. |
Custom | Creates a blank security group in which rules are added afterwards. For details on how to add rules, refer to this article. | - |
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
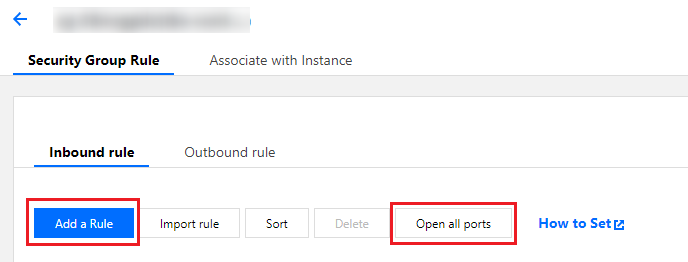
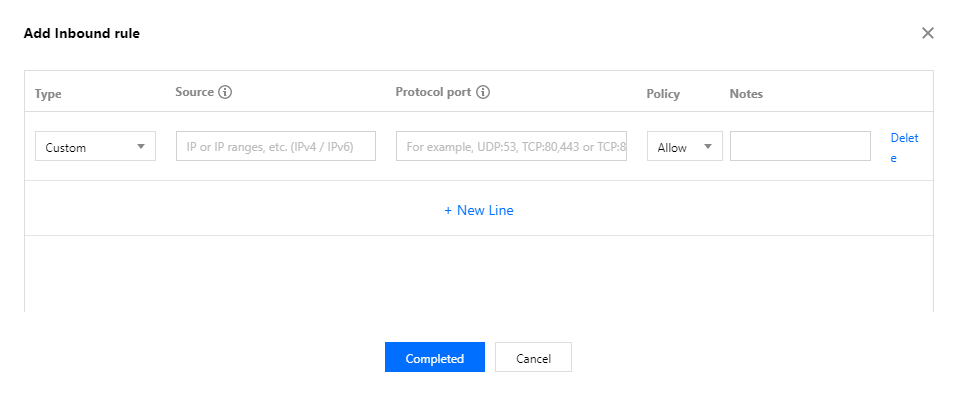
Source or Destination | Description |
A single IPv4 address or an IPv4 range | In CIDR notation, such as 203.0.113.0, 203.0.113.0/24 or 0.0.0.0/0, where 0.0.0.0/0 indicates all IPv4 addresses will be matched. |
A single IPv6 address or an IPv6 range | In CIDR notation, such as FF05::B5, FF05:B5::/60, ::/0 or 0::0/0, where ::/0 or 0::0/0 indicates all IPv6 addresses will be matched. |
ID of the referenced security group. You can reference the ID of: Current security group Other security group | To reference the current security group, please enter the ID of security group associated with the CVM. You can also reference another security group in the same region and belongs to the same project by entering the security group ID. Note: The referenced security group is available to you as an advanced feature. The rules of the referenced security group are not added to the current security group. If you enter the security group ID in Source/Destination when configuring security group rules, the private IP addresses of the CVM instances and the ENIs that are associated with this security group ID are used as the source/destination. This does not include public IP addresses. |
- |
TCP:80.TCP:80,443.TCP:3306-20000.TCP:ALL.Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35




Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
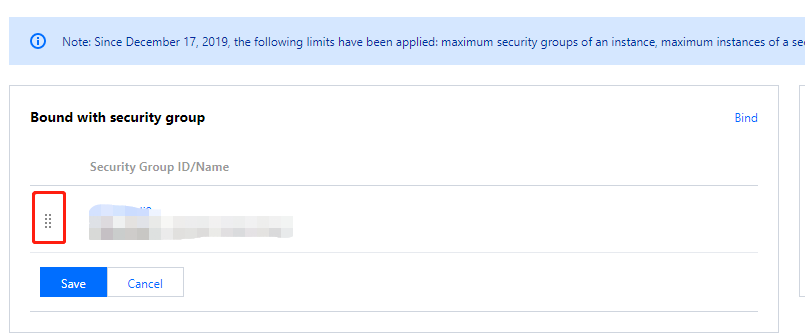
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35

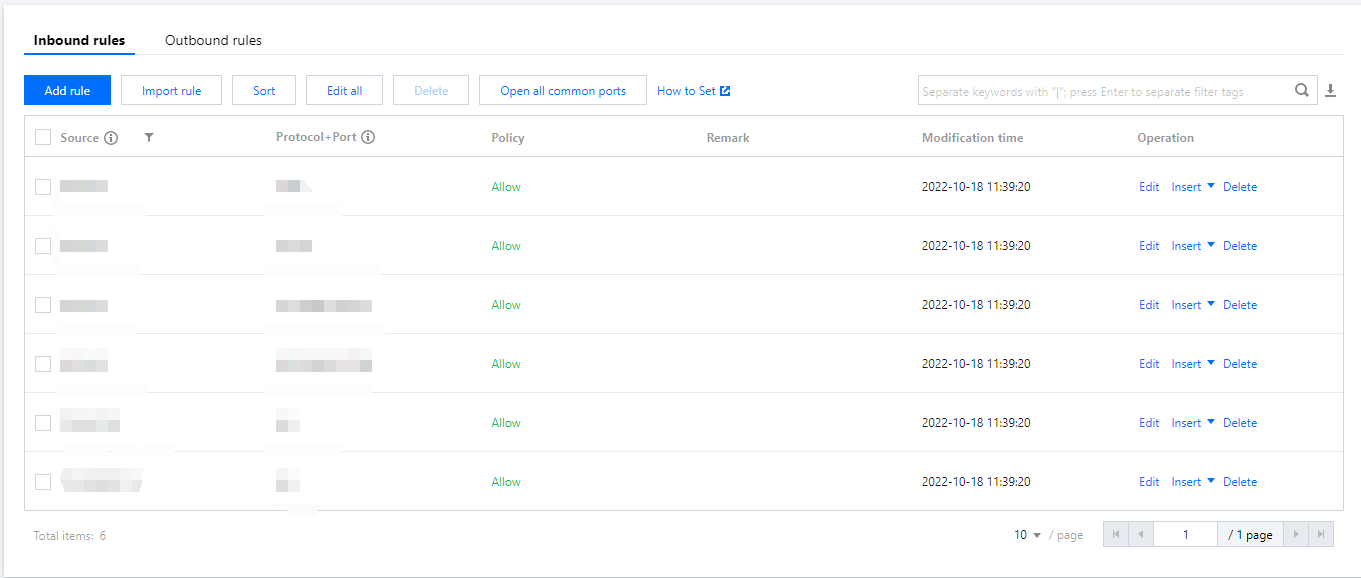
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
Direction | Type | Source | Protocol Port | Policy |
Inbound | Linux login | All IP addresses: 0.0.0.0/0 WebShell proxy IP addresses: as detailed in Orcaterm Proxy IP Addresses Updates Specified IP address: enter your specified IP address or IP range | TCP:22 | Allow |
Direction | Type | Source | Protocol Port | Policy |
Inbound | Windows login | All IP addresses: 0.0.0.0/0 WebRDP proxy IP addresses: 81.69.102.0/24 106.55.203.0/24 101.33.121.0/24 101.32.250.0/24 Specified IP address: enter your specified IP address or IP range | TCP:3389 | Allow |
ping command. Specifically, when adding a security group rule, set Type to Ping and open Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) ports to the Internet to enable other CVMs to access this CVM through ICMP.
You can open all IP addresses or a specified IP address (or IP range) to the Internet as required. This allows you to configure the source IP addresses of the CVMs that can access this CVM through ICMP.Direction | Type | Source | Protocol Port | Policy |
Inbound | Ping | All IP addresses: 0.0.0.0/0 Specified IP address: enter your specified IP address or IP range | ICMP | Allow |
Direction | Type | Source | Protocol Port | Policy |
Inbound | Custom | All IP addresses: 0.0.0.0/0 Specified IP address: enter your specified IP address or IP range | TCP: 23 | Allow |
Direction | Type | Source | Protocol Port | Policy |
Inbound | HTTP (80) | 0.0.0.0/0 | TCP: 80 | Allow |
Inbound | HTTPS (443) | 0.0.0.0/0 | TCP: 443 | Allow |
Direction | Type | Source | Protocol Port | Policy |
Inbound | HTTP (80) | IP address or IP range that is allowed to access your website | TCP: 80 | Allow |
Inbound | HTTPS (443) | IP address or IP range that is allowed to access your website | TCP: 443 | Allow |
Direction | Type | Source | Protocol Port | Policy |
Inbound | Custom | All IP addresses: 0.0.0.0/0 Specified IP address: enter your specified IP address or IP range | TCP: 1101 | Allow |
Direction | Type | Source | Protocol Port | Policy |
Inbound | Custom | All IP addresses: 0.0.0.0/0 Specified IP address: enter your specified IP address or IP range | TCP: 1102 | Reject |
Direction | Type | Source | Protocol Port | Policy |
Outbound | Custom | Specified public IP address that the CVM can access | Required protocol and port number | Allow |
Outbound | Custom | 0.0.0.0/0 | All | Reject |
Direction | Type | Source | Protocol Port | Policy |
Outbound | Custom | Specified public IP address that your CVM instance cannot access | All | Reject |
Direction | Type | Source | Protocol Port | Policy |
Inbound | Custom | 0.0.0.0/0 | TCP: 20 to 21 | Allow |
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
Port | Service | Description |
21 | FTP | An open FTP server port for uploading and downloading. |
22 | SSH | An SSH port for remotely connecting to Linux servers in CLI mode. |
25 | SMTP | An open SMTP server port for sending emails. |
80 | HTTP | A port for web services, such as IIS, Apache, and Nginx, to provide external access. |
110 | POP3 | A port for the POP3 (email protocol 3) service. |
137, 138, 139 | NetBIOS protocol | Ports 137 and 138 are UDP ports for transferring files through My Network Places. Port 139: connections established through port 139 attempt to access the NetBIOS/SMB service. This protocol is used for file and printer sharing on Windows and SAMBA. |
143 | IMAP | A port for Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) v2, which is a protocol for receiving emails like POP3. |
443 | HTTPS | A port for web browsing. HTTPS is a variant of HTTP that provides encryption and transmission over secure ports. |
1433 | SQL Server | Default port for SQL Server. The SQL Server service uses two ports: TCP-1433 and UDP-1434. Port 1433 is used to provide external services, and port 1434 is used to return a response to the requester to indicate the TCP/IP port used by SQL Server. |
3306 | MySQL | Default port for MySQL databases, which is used by MySQL to provide external services. |
3389 | Windows Server Remote Desktop Services | Service port for the Windows Server remote desktop, through which you can connect to a remote server by using the "Remote Desktop" connection tool. |
8080 | Proxy port | Similar to port 80, port 8080 is used in the WWW proxy service for web browsing. The port number ":8080" is often appended to the URL when you visit a website or use a proxy. In addition, after the Apache Tomcat web server is installed, its default service port is port 8080. |
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
Last updated:2024-03-21 09:19:57
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35

Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
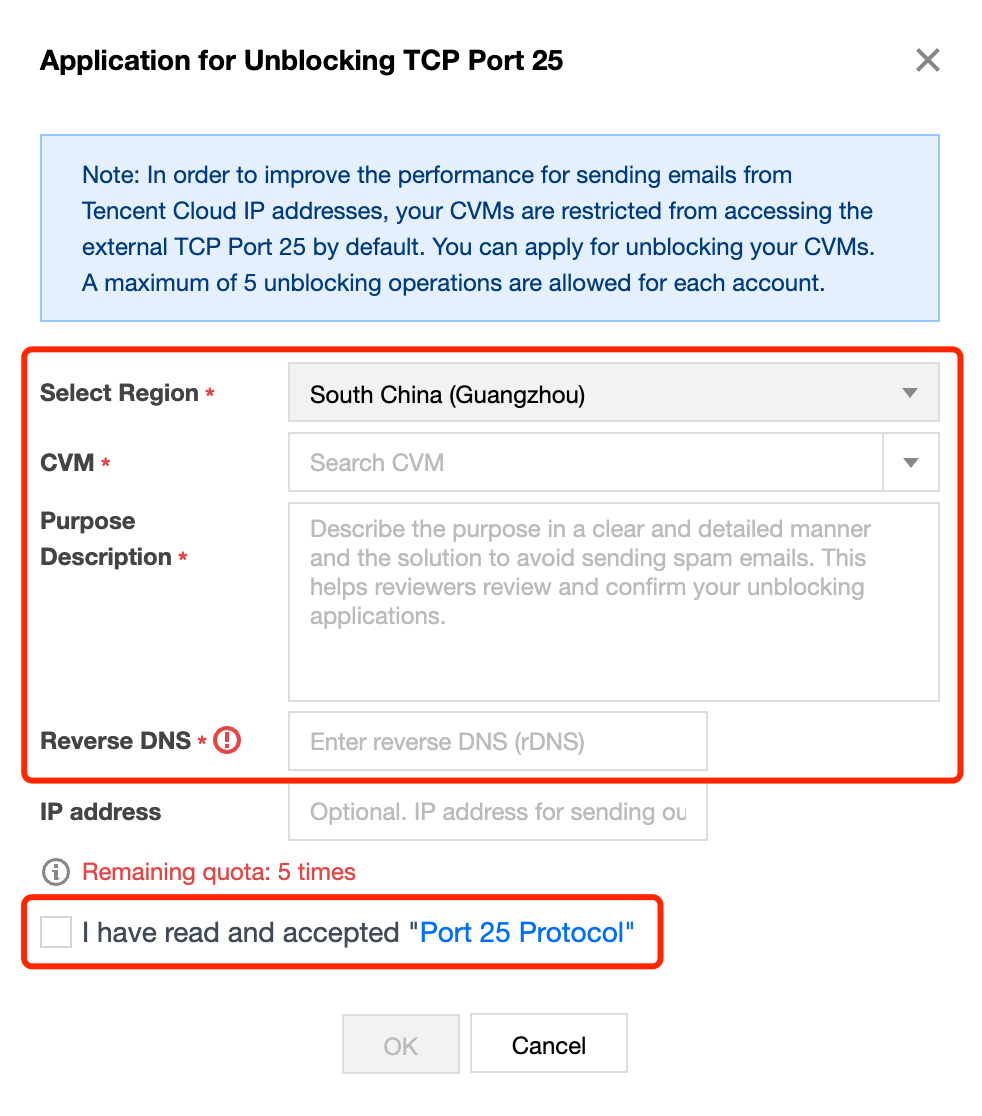
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:12:28
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:12:28
~/.ssh/authorized_keys file.Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
a-z, A-Z, 0-9 and special characters ()`~!@#$%^&*-+=_|{}[]:;'<>,.?/).a-z, A-Z, 0-9 and special characters ()`~!@#$%^&*-+=_|{}[]:;'<>,.?/), excluding user names.Login Method | Description |
Random Password | |
Password Associated with Key | The login with username and password is disabled by default. To use the password, you can log in to the CVM console to reset it, see Resetting Instance Password. |
Custom Password | The password you set is the initial password. |


Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
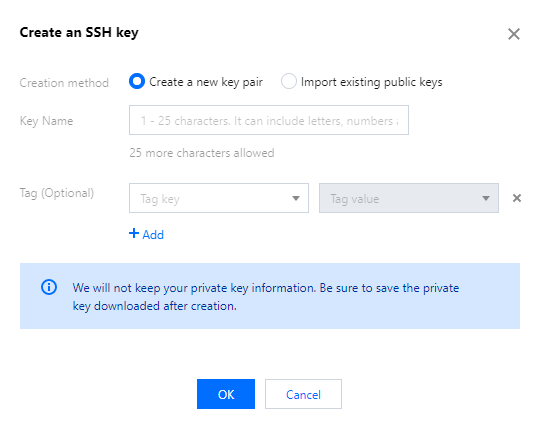
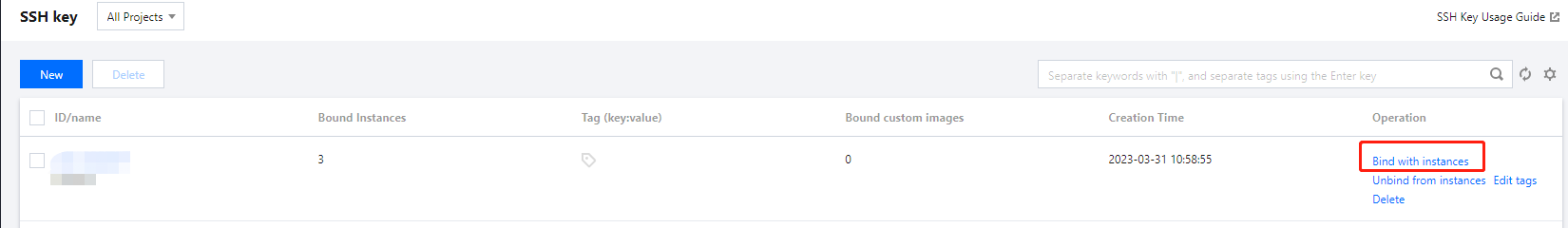
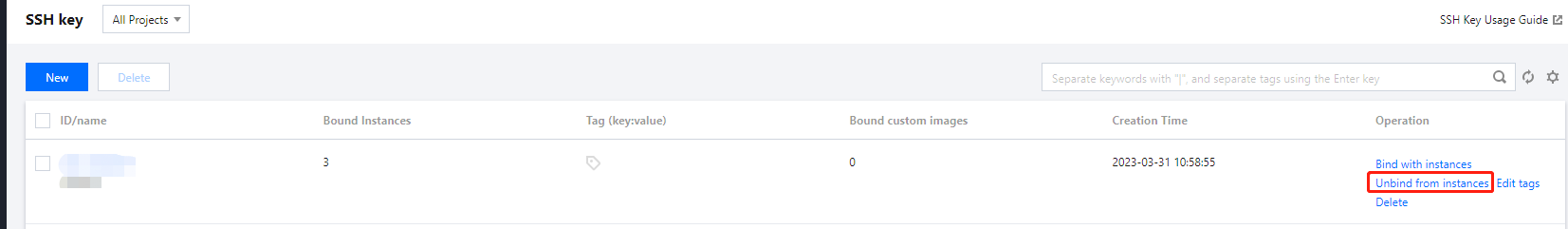

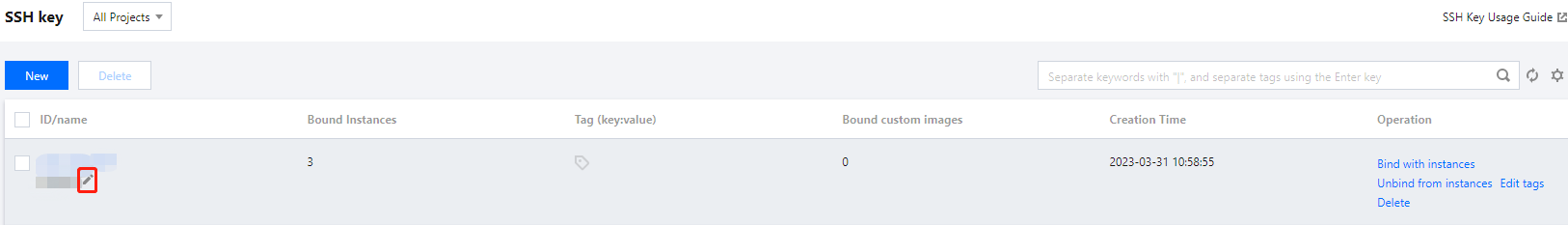
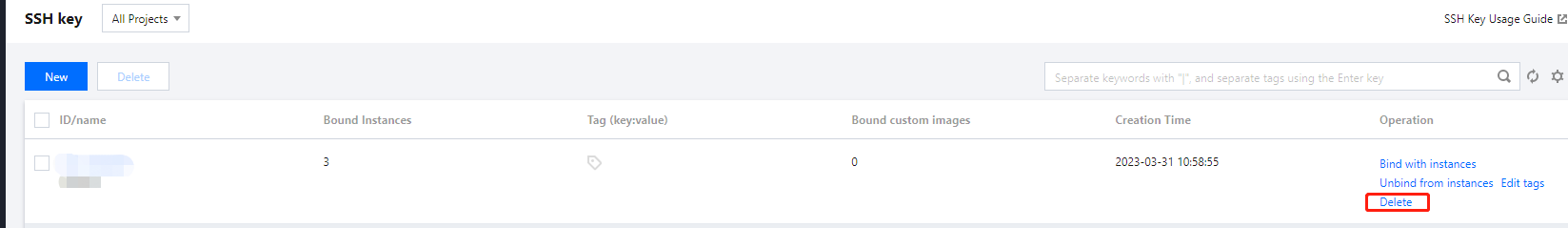
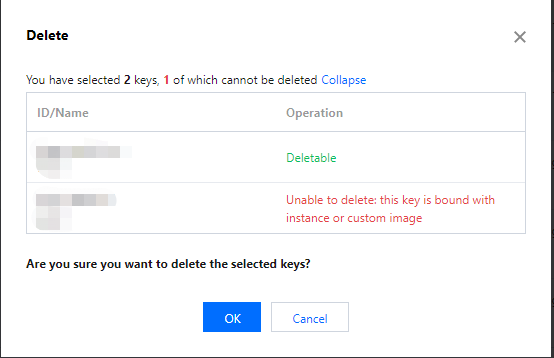
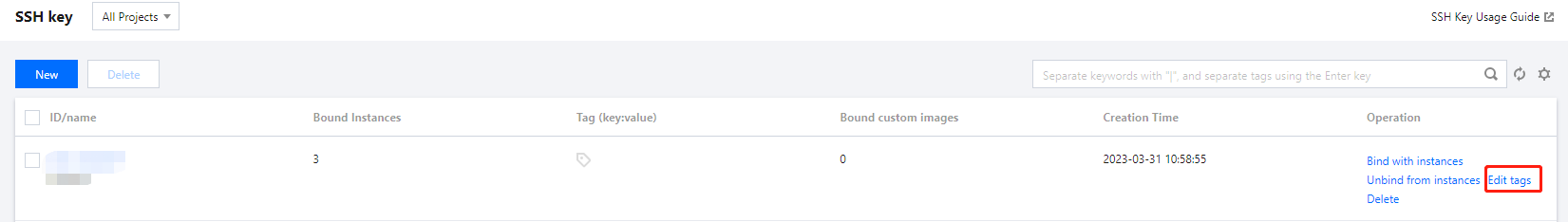
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
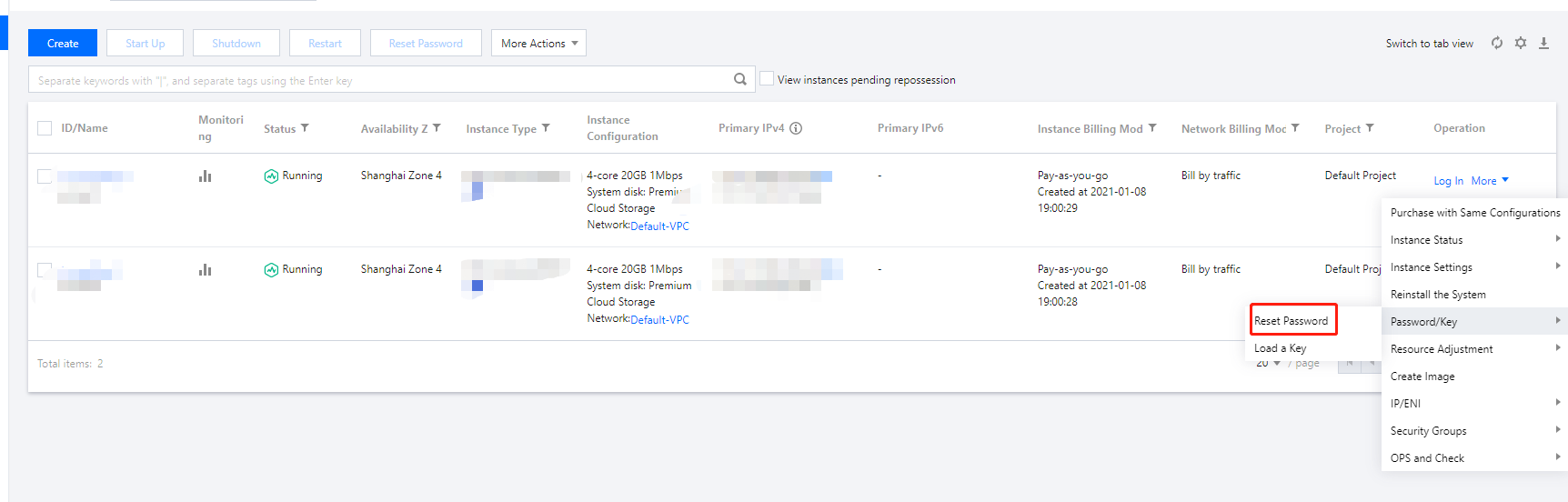
Administrator for Windows, ubuntu for Ubuntu, and root for other Linux distributions. You can select Specified user name and enter the username.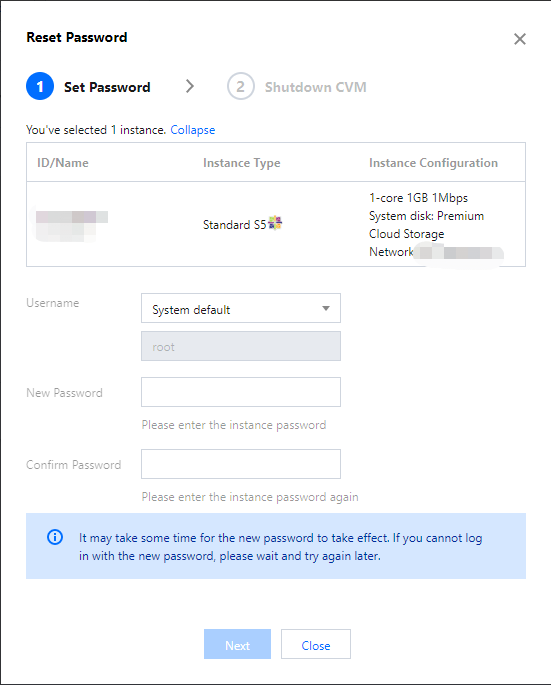
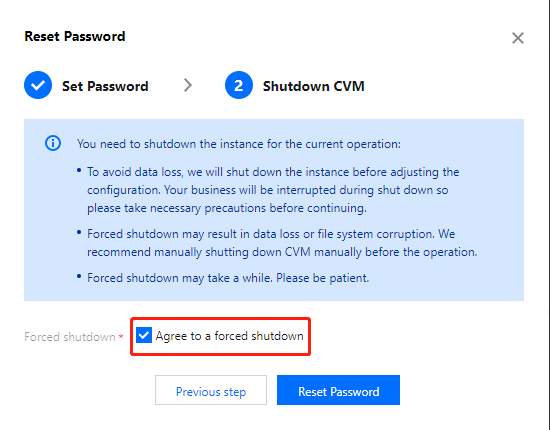
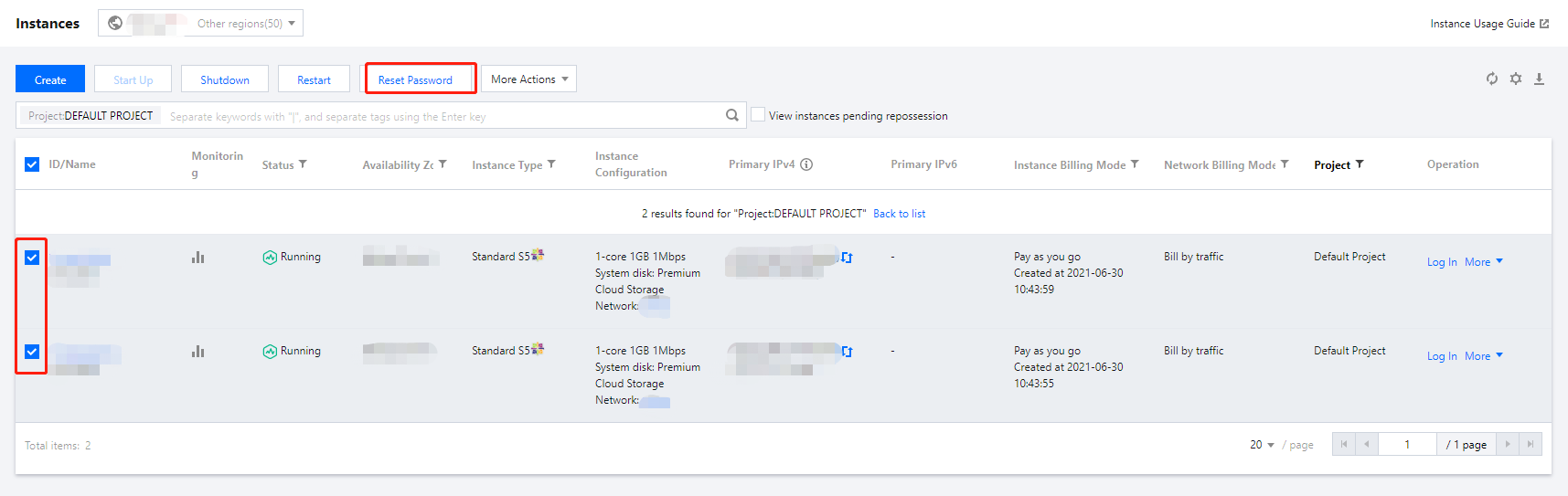
Administrator for Windows, ubuntu for Ubuntu, and root for other Linux distributions. You can select Specified user name and enter the username.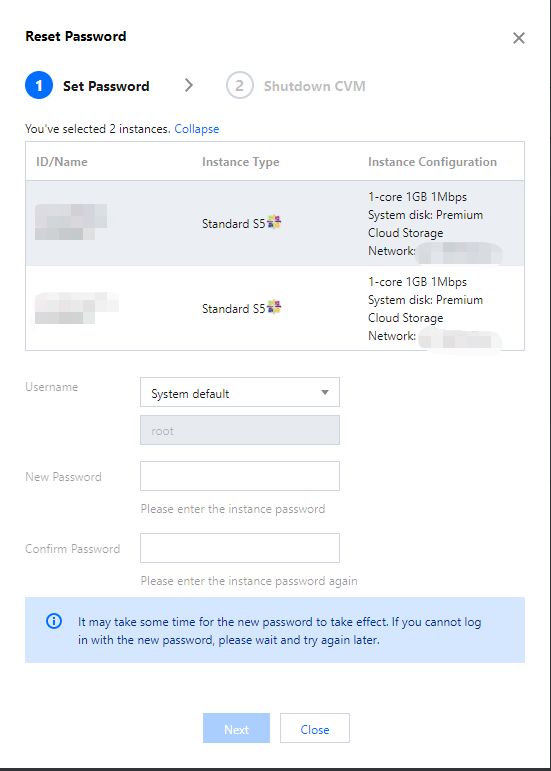
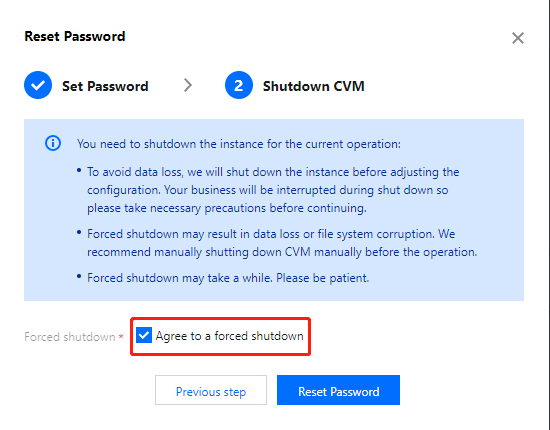
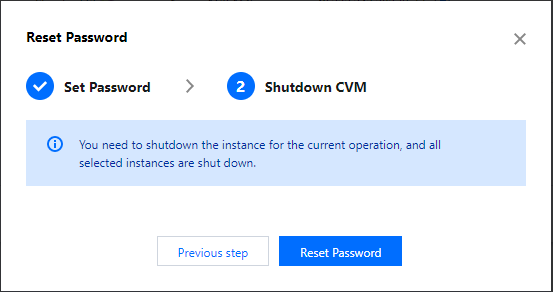
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:12:28
Component | Capability | Main Features |
Displays the overall monitoring information for Tencent Cloud services | Provides the overall information and alarms for Tencent Cloud services | |
Displays the custom alarm policy list | Supports alarm configuration for CVM | |
Displays the specific CVM monitoring information | Allows you to view the CVM monitoring data | |
Displays the custom monitoring dashboard | Graphically displays monitoring data to facilitate the dynamic metric analysis | |
Displays the custom monitoring metrics | Allows you to view the predefined custom monitoring metrics and reported data | |
Displays the traffic monitoring | Allows you to view your overall bandwidth usage |
Monitoring Item | Monitoring Metric | Description |
CPU usage | cpu_usage | CPU usage ratio. The data is collected and reported by the internal monitoring component of the server, making the data more accurate. |
Memory utilization | mem_usage | The ratio of the actual amount of memory used by the user to the total amount of memory, excluding the memory occupied by buffer and system cache. |
Private network outbound bandwidth | lan_outtraffic | Average outbound traffic per second of private ENI. |
Private network inbound bandwidth | lan_intraffic | Average inbound traffic per second of private ENI. |
Public network outbound bandwidth | wan_outtraffic | Average outbound traffic per second over the public network. The minimum granularity for bandwidth statistics is 10 seconds (bandwidth calculation method: total traffic in 10 seconds divided by 10 seconds). |
Public network inbound bandwidth | wan_intraffic | Average inbound traffic per second of the public network. |
Disk usage | disk_usage | Disk usage. |
Disk I/O wait time | disk_io_await | Average wait time per disk I/O operation. |
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
GetMonitorData API to get the monitoring data for all Tencent Cloud products. For more information, see GetMonitorData.Last updated:2024-01-08 09:12:28
Check Item | Description | RiskLevel | Solution |
Network latency | An HTTP request is sent to check whether the network latency of the instance is high based on the following criteria: If the latency is above 600 ms, the network quality is considered poor. If no response is received within 5s, the request is considered timed out. If all requests time out, the network is considered disconnected. | Exception | Check your local network and solve the problem. |
| Network jitter | The average of the differences between the latency values of adjacent requests is the network jitter value. If the network jitter/latency is below or equal to 0.15, the network is stable; otherwise, the network is jittering. | - |
| Upstream bandwidth | Data packets are uploaded to the instance to calculate its upstream bandwidth. | - |
| Downstream bandwidth | Data packets are downloaded from the instance to calculate its downstream bandwidth. | - |
Check Item | Description | RiskLevel | Solution |
Common ports | Checks whether requests to common ports such as ports 22 and 3389 used by the TCP protocol for the inbound traffic are blocked in the security group. | Warning | If requests to port 22 used by the TCP protocol are blocked in an ingress rule in the security group, SSH login may be abnormal. You can open the required ports as instructed in Security Group Use Cases. |
Check Item | Description | RiskLevel | Solution |
Cloud disk status | Checks whether cloud disks associated with the instance have expired and whether they can be read/written. | Exception | A cloud disk associated with the instance has expired. Go to the CBS console to renew it as soon as possible. |
| Checks whether cloud disks associated with the pay-as-you-go instance are unavailable due to expiration. | Warning | Auto-Renewal is not enabled for the cloud disks attached to the instance. Go to the CBS console to configure auto-renewal for the cloud disk. |
| | ||
| |||
Check Item | Description | Risk Level | Solution |
High cloud disk latency | Checks whether the I/O performance metric svctm is abnormal. | Warning | A cloud disk associated with the instance has a high latency. We recommend you pay attention to the cloud disk usage. |
Cloud disk I/O | Checks for cloud disk I/O hang | Warning | A cloud disk associated with the instance has an I/O hang. We recommend you pay attention to the cloud disk usage. |
System disk inode utilization | Checks whether the inode utilization of the cloud disk has reached 100%. | Warning | |
System disk read-only | Checks whether the cloud disk is read-only. | Exception | |
System disk space utilization | Checks whether the utilization of the cloud disk has reached 100%. | Warning | |
Partition I/O utilization | Checks whether the io_util of the cloud disk has reached 100%. | Warning | |
Check Item | Description | RiskLevel | Solution |
Instance shutdown | Checks whether the instance is shut down. | Warning | |
Instance restart history | Checks whether the instance has been restarted in the last 12 hours. | Warning | The instance has been restarted in the last 12 hours. Pay attention to the instance running status. |
Instance kernel crash | Checks whether a hung task has occurred in the instance in the last 12 hours. | Exception | A hung task, panic, or soft deadlock has occurred in the instance in the last 12 hours. Pay attention to the instance running status and troubleshoot as instructed in Kernel and I/O Issues. |
| | Checks whether a panic has occurred in the instance in the last 12 hours. | Exception |
| | Checks whether a soft deadlock occurred in the instance in the last 12 hours. | Exception |
Check Item | Description | RiskLevel | Solution |
CPU utilization | Checks whether the instance has experienced a high CPU utilization in the last 12 hours. | Warning | Check your CPU utilization and adjust the configuration according. Troubleshoot it as instructed below: Windows instance: Login Failure Due To High CPU and Memory Usage (Windows) Linux instance: Login Failure Due To High CPU and Memory Usage (Linux) |
| Memory utilization | Checks whether the instance has experienced a high memory utilization in the last 12 hours. | Warning |
| Basic CPU utilization | Checks whether the instance has experienced a high CPU utilization in the last 12 hours. | Warning |
Check Item | Description | RiskLevel | Solution |
Public EIP connection | Checks whether the EIP is isolated due to overdue payments. | Exception | An EIP may be disconnected from the public network due to overdue payments. You need to go to the Billing Center to make the overdue payment. |
Existence of EIP | Checks whether the instance has an EIP. | Warning | The instance has no EIPs. If you want to use an EIP to access the public network, go to the EIP console to bind one. |
EIP blocked | Checks whether the EIP is blocked due to DDoS attacks | Exception | An instance EIP is blocked due to DDoS attacks. |
Public network bandwidth utilization | Checks whether the instance has experienced a high public network inbound bandwidth utilization in the last 12 hours. | Warning | Check the network usage and troubleshoot as instructed in Login Failure Due to High Bandwidth Utilization. |
| | Checks whether the instance has experienced a high public network outbound bandwidth utilization in the last 12 hours. | Warning |
| Private network bandwidth utilization | Checks whether the instance has experienced a high private network inbound bandwidth utilization in the last 12 hours. | Warning |
| | Checks whether the instance has experienced a high private network outbound bandwidth utilization in the last 12 hours. | Warning |
Packet loss | Checks whether the instance has experienced TCP packet loss due to triggering of traffic throttling in the last 12 hours. | Warning | |
| | Checks whether the instance has experienced UDP packet loss due to triggering of traffic throttling in the last 12 hours. | Warning |
| | Checks whether the instance has experienced packet loss due to a soft interrupt in the last 12 hours. | Warning |
| Kernel network conditions | Checks whether the instance has experienced a full UDP send buffer in the last 12 hours. | Warning |
| | Checks whether the instance has experienced a full UDP receive buffer in the last 12 hours. | Warning |
| | Checks whether the instance has experienced a full TCP complete connection queue in the last 12 hours. | Warning |
| | Checks whether the instance has experienced TCP request overflow in the last 12 hours. | Warning |
| Connection utilization | Checks whether the number of connections of the instance has reached the upper limit in the last 12 hours. | Warning |
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:41:35
Configuration Type | Configuration Item | Description | |
Basic Info | Policy Name | | A custom policy name |
| Remarks | | Remarks for the policy |
| Monitor Type | | Choose Cloud Product Monitoring |
| Policy Type | | Select the desired policy type for monitoring Tencent Cloud services. |
| Project | | Choose a project as needed. You can later find this policy quickly by filtering by the project. |
Configure Alarm Policies | Alarm Object | | Instance ID: associate the policy with the specified CVM instance Tag: associate the policy with CVM instances bound with the specified tag Instance Group: associate the policy with the selected instance group All Objects: associate the policy with all instances under the current account (permission required) |
| Trigger Condition | Manual Configuration (Metric Alarm) | Trigger condition: specify the metric, comparison, threshold, statistical period, and the number of consecutive periods. You can expand the trigger condition to view the metric trend, and based on which, set a proper threshold. |
| | Manual Configuration (Event Alarm) | Create an event alarm policy to get notifications in case of service resources or underlying infrastructure exceptions |
| | Select template | Choose a configured template as needed. For more information about the configurations, please see Configuring Trigger Condition Template. |
Configure Alarm Notification (optional) | Notification Template | | It defaults to the preset notification template (sending the notification to the root account admin via SMS and email). Up to 3 notification templates can be bound to each alarm policy. For more information about the configurations of notification templates, see Creating Notification Template. |
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:01
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:01
Task Type | Description | Suggestion | Applicable Authorization Policies |
Instance running exception | Sudden software and hardware failures or system errors of the underlying host of the instance, which cause abnormal downtime or restart of the instance. | When a maintenance task of abnormal instance running is triggered, the platform immediately performs relevant maintenance and tries to restart the abnormal instance.It is recommended to wait for the completion of instance restarting, and check the update progress of maintenance task. | Choose the policy based on the current status of the maintenance task: When the task is in "Processing" status, the platform is urgently performing related maintenance on the abnormal instance. After the maintenance is completed, the task status will be updated immediately, and relevant notifications will be pushed to you. When the task is in "Ended" status, the abnormal instance has automatically restarted and restored. You can verify whether the instance and application have been restored to normal mode. |
Instance running risk | The instance is currently running normally, but there are risks on software and hardware of the host or the underlying platform, which may cause the fluctuation of the instance performance or the abnormal downtime. | To complete the maintenance as soon as possible to avoid risks of the underlying software and hardware and potential downtime, it is recommended to back up your business data in advance and go to the Maintenance Task console to perform the following operations: 1. (Optional) Back up the instance data. 2. Authorize the platform to initiate maintenance immediately, or reserve a planned maintenance within 48 hours in advance. 3. Wait for the system to automatically initiate maintenance at the scheduled maintenance time. | According to the fixing method of the underlying risks of the instance, the following authorization methods can be selected: Authorization for migration without CVM shutdown (the instance does not need to be shut down, and the CVM may experience short-term high load or network jitter during the migration). Authorization for shutdown maintenance (the instance is fast restored after restart). Note: 1. If the user does not authorize within 48 hours, the system will initiate maintenance at the scheduled maintenance time. 2. Local disk instances do not support fast restoration after restart, and require a longer maintenance period to fix underlying hardware risks. Users can choose to redeploy local disk instances to quickly avoid the risks (local disk data cannot be retained). |
Instance disk exception | A sudden failure occurs on the local disk, which may cause reduced I/O performance of the instance or damage to the disk. | To complete the maintenance as soon as possible to restore the disk, it is recommended to back up your business data in advance and go to the Maintenance Task console to perform the following operations: 1. (Optional) Back up the instance data. 2. Authorize the platform to change the abnormal disk immediately, or reserve a planned maintenance within 48 hours in advance. 3. Wait for the platform to replace the abnormal disk, and reattach and use the replaced disk according to the prompts in the restoration notification. | According to the fixing method of the abnormal disk, the following authorization methods can be selected: Change disk without CVM shutdown (replace the abnormal disk without CVM shutdown. During the maintenance, the I/O of the abnormal disk is temporarily unavailable. After the maintenance is completed, you can attach and use the new disk). Shut down to change disk (the instance needs to be shut down to replace the abnormal disk. The local disk data may be retained. A long maintenance period is required). (Optional) Migrate without the disk: The local disk instance is redeployed, and the local disk data cannot be retained. The instance availability can be restored in minutes. |
Instance disk warning | The local disk of the instance may be damaged, or its service life is about to end, which may cause instance I/O exceptions or disk offline. | To complete the maintenance as soon as possible to eliminate the potential failure risks of the local disk, it is recommended to back up your business data in advance and go to the Maintenance Task console to perform the following operations: 1. (Optional) Back up the instance data. 2. Authorize the platform to change the disk with potential failure risks immediately, or reserve a planned maintenance within 48 hours in advance. 3. Wait for the platform to replace the abnormal disk, and reattach and use the replaced local disk according to the prompts in the restoration notification. | According to the fixing method of the abnormal disk, the following authorization methods can be selected: Change disk without CVM shutdown (replace the abnormal disk without CVM shutdown. During the maintenance, the I/O of the abnormal disk is temporarily unavailable. After the maintenance is completed, you can attach and use the new disk). Shut down to change disk (the instance needs to be shut down to replace the abnormal disk. The local disk data may be retained. A long maintenance period is required). (Optional) Migrate without the disk: The local disk instance is redeployed, and the local disk data cannot be retained. The instance availability can be restored in minutes. |
Instance network connection exception | A sudden failure occurs at the underlying network connection of the instance, which may cause network jitter or abnormal network connection. | When a maintenance task of an abnormal instance network connection is triggered, the platform immediately performs relevant maintenance on the underlying network and tries to restore the network connection of the abnormal instance. It is recommended to wait for the completion of the automatic fixing of the network connection, and check the update progress of the maintenance task. | Choose the policy based on the current status of the maintenance task: When the task is in "Processing" status, the platform is urgently performing related maintenance on the underlying network of the abnormal instance. After the maintenance is completed, the task status will be updated immediately, and relevant notifications will be pushed to you. When the task is in "Ended" status, the network connection of the abnormal instance has been recovered. You can verify whether the instance and application have been restored to normal mode. |
Instance maintenance and upgrade | Maintenance without CVM shutdown is initiated due to reasons such as underlying host architecture and software upgrades to improve instance performance and security. | To complete maintenance as soon as possible to improve instance performance and security, it is recommended to back up your business data in advance, and go to the Maintenance Task console to perform the following operations: 1. (Optional) Back up the instance data. 2. Authorize the platform to initiate maintenance immediately, or reserve a planned maintenance within 48 hours in advance. 3. Wait for the system to automatically initiate maintenance at the scheduled maintenance time. | You can choose from the following authorization methods: Maintenance without CVM shutdown (the instance does not need to be shut down, and the CVM may experience short-term high load or network jitter during the maintenance). Note: If the user does not authorize within 48 hours, maintenance starts at the next scheduled maintenance time. |
Task Status | Description |
Pending authorization | Wait for user authorization. The user can choose the maintenance method and time. If the user does not authorize for a non-disk maintenance task within 48 hours, the system will initiate maintenance at the scheduled maintenance time and the maintenance task status will be changed into “Processing”. |
Scheduled | The user has authorized for maintenance and reserved a maintenance time. The default scheduled maintenance time can be modified within 48 hours after the task is created. |
Processing | The maintenance task is being processed. |
Ended | The maintenance task is completed. |
Avoided | If the instance has an unfinished maintenance task, when the user returns or terminates the instance, or adjusts the instance configuration, the avoidance of the maintenance task will be interrupted. |
Canceled | The maintenance task is canceled by the system. |
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:01
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:01
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:01
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:37:01
Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11
http://mirrors.tencent.comhttp://mirrors.tencentyun.com/pip install pip -i the directory where PyPI is located in
http://mirrors.tencent.com/pypi/simple directory, run the following command:pip install 17monip -i http://mirrors.tencent.com/pypi/simple --trusted-host mirrors.tencent.com
index-url parameter in the ~/.pip/pip.conf file to the source path of the Tencent Cloud software repository.[global]index-url = the directory where PyPI is located intrusted-host = public network/private network access address
http://mirrors.tencent.com/pypi/simple directory, execute the following command:[global]index-url = http://mirrors.tencent.com/pypi/simpletrusted-host = mirrors.tencent.com
settings.xml configuration file of Maven.<mirrors> ... </ mirrors> code block and configure the following content into it.<mirror><id>nexus-tencentyun</id><mirrorOf>*</mirrorOf><name>Nexus tencentyun</name><url>http://mirrors.tencent.com/nexus/repository/maven-public/</url></mirror>
npm config set registry http://mirrors.tencent.com/npm/
/etc/default/docker configuration file.vim /etc/default/docker
DOCKER_OPTS="--registry-mirror=https://mirror.ccs.tencentyun.com"
/etc/docker/daemon.json configuration file.vim /etc/docker/daemon.json
{"registry-mirrors": ["https://mirror.ccs.tencentyun.com"]}
sudo su echo "EXTRA_ARGS=\"–registry-mirror=https://mirror.ccs.tencentyun.com\"" >> /var/lib/boot2docker/profile exit
MariaDB.repo file under /etc/yum.repos.d/.vi /etc/yum.repos.d/MariaDB.repo
# MariaDB 10.2 CentOS7-amd64[mariadb]name = MariaDBbaseurl = http://mirrors.tencent.com/mariadb/yum/10.2/centos7-amd64/gpgkey = http://mirrors.tencent.com/mariadb/yum/RPM-GPG-KEY-MariaDBgpgcheck=1
yum clean all
yum install MariaDB-client MariaDB-server
mongodb.repo file under /etc/yum.repos.d/.vi /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb.repo
[mongodb-org-4.0]name=MongoDB Repositorybaseurl=http://mirrors.tencent.com/mongodb/yum/el7-4.0gpgcheck=0enabled=1
yum install -y mongodb-org
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv 68818C72E52529D4
mirror path.#Debian 8echo "deb http://mirrors.tencent.com/mongodb/apt/debian jessie/mongodb-org/4.0 main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-4.0.list#Debian 9echo "deb http://mirrors.tencent.com/mongodb/apt/debian stretch/mongodb-org/4.0 main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-4.0.list
sudo apt-get clean all
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 --recv 68818C72E52529D4
mirror path.#Ubuntu 14.04echo "deb [ arch=amd64 ] http://mirrors.tencent.com/mongodb/apt/ubuntu trusty/mongodb-org/4.0 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-4.0.list#Ubuntu 16.04echo "deb [ arch=amd64 ] http://mirrors.tencent.com/mongodb/apt/ubuntu xenial/mongodb-org/4.0 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-4.0.list#Ubuntu 18.04echo "deb [ arch=amd64 ] http://mirrors.tencent.com/mongodb/apt/ubuntu bionic/mongodb-org/4.0 multiverse" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-4.0.list
sudo apt-get clean all
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org
gem source -r https://rubygems.org/gem source -a http://mirrors.tencent.com/rubygems/
Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11
sudo apt-cache search all
sudo apt-get install nginx
Y to approve the installation. Wait until the software installation is complete, as shown in the figure below:

sudo dpkg -L software_name
sudo dpkg -l software_name

Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11
yum command to install software in the CentOS environment. Tencent Cloud provides a YUM repository so you can directly install software packages without adding sources.dnf install [software name]
dnf install php command to install PHP, the following prompt will appear:
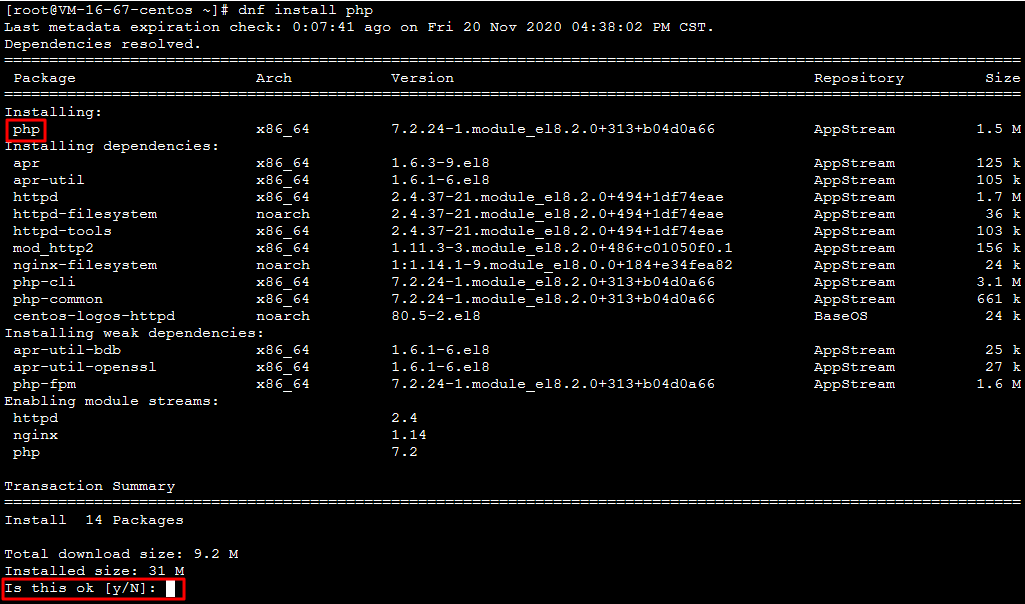
y and press Enter to start the installation.
The Complete prompt indicates the installation is completed.yum will be unusable. You can use the fully compatible MariaDB, or click here to learn about how to install an older version of MySQL.yum install [software name]
yum install PHP command to install PHP, the following prompt will appear:
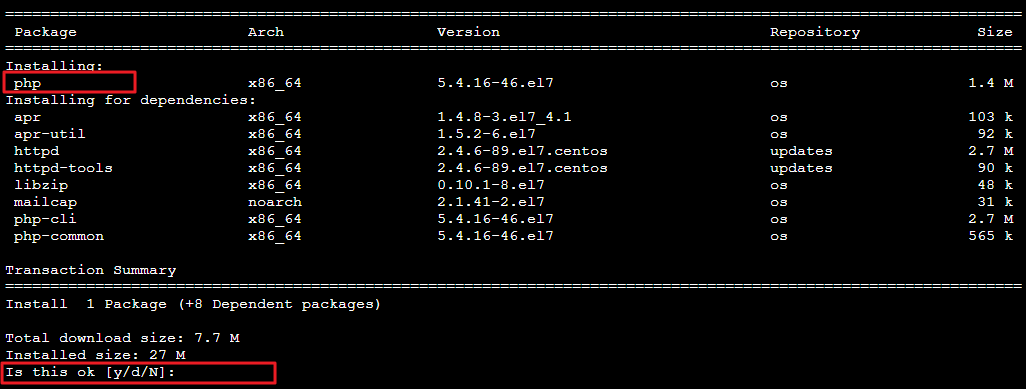
y and press Enter to start the installation.
The Complete prompt indicates the installation is completed.rpm -ql [software name]
rpm -ql php to view the installation directory of PHP, as shown in the figure below:
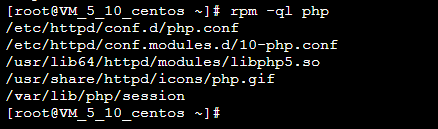
rpm -q
rpm -q php to view the version of PHP, as shown in the figure below:
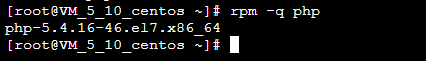
Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11
service nginx restart
wget http://127.0.0.1
--2013-02-20 17:07:26-- http://127.0.0.1/Connecting to 127.0.0.1:80... connected.HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OKLength: 151 [text/html]Saving to: 'index.html'100%[==========================================================================================>] 151 --.-K/s in 0s2013-02-20 17:07:26 (37.9 MB/s) - 'index.html' saved [151/151]
vim /etc/php5/fpm/php-fpm.conf
[global]error_log = /var/log/php-fpm.log[www]user = nobodygroup = nobodylisten = 127.0.0.1:9000pm = dynamicpm.max_children = 5pm.start_servers = 2pm.min_spare_servers = 1pm.max_spare_servers = 3
/etc/init.d/mysql start; /etc/init.d/php-fpm start; /etc/init.d/nginx start

vim /usr/share/nginx/html/index.php
<?phpecho "<title>Test Page</title>";echo "hello world";?>
Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11
http://mirror.centos.org/centos-6/, a third-party image site, or Tencent Cloud at http://mirrors.tencent.com/ and http://mirrors.tencentyun.com/. If you continue to use the default CentOS 6 source configured in Tencent Cloud, an error may occur.cat /etc/centos-release

CentOS-Base.repo file.vim /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo
baseurl according to the CentOS version and network environment.http://mirrors.tencentyun.com/centos-vault/6.x/http://mirrors.tencent.com/centos-vault/6.x/CentOS-Base.repo file is as follows:

[extras]gpgcheck=1gpgkey=http://mirrors.tencentyun.com/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6enabled=1baseurl=http://mirrors.tencentyun.com/centos-vault/6.9/extras/$basearch/name=Qcloud centos extras - $basearch[os]gpgcheck=1gpgkey=http://mirrors.tencentyun.com/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6enabled=1baseurl=http://mirrors.tencentyun.com/centos-vault/6.9/os/$basearch/name=Qcloud centos os - $basearch[updates]gpgcheck=1gpgkey=http://mirrors.tencentyun.com/centos/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-6enabled=1baseurl=http://mirrors.tencentyun.com/centos-vault/6.9/updates/$basearch/name=Qcloud centos updates - $basearch
CentOS-Epel.repo file.vim /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Epel.repo
baseurl based on the network environment.
In this example, change baseurl=http://mirrors.tencentyun.com/epel/$releasever/$basearch/ to baseurl=http://mirrors.tencentyun.com/epel-archive/6/$basearch/. The result is as follows:

[epel]name=epel for redhat/centos $releasever - $basearchfailovermethod=prioritygpgcheck=1gpgkey=http://mirrors.tencentyun.com/epel/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-6enabled=1baseurl=http://mirrors.tencentyun.com/epel-archive/6/$basearch/
yum install command to install the required software.Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11
yum -y install chrony
chrony.conf configuration file.vim /etc/chrony.conf
#log measurements statistics tracking.server time1.tencentyun.com iburstserver time2.tencentyun.com iburstserver time3.tencentyun.com iburstserver time4.tencentyun.com iburstserver time5.tencentyun.com iburst

systemctl restart chronyd
systemctl enable chronyd
date
chronyc sourcestats -v
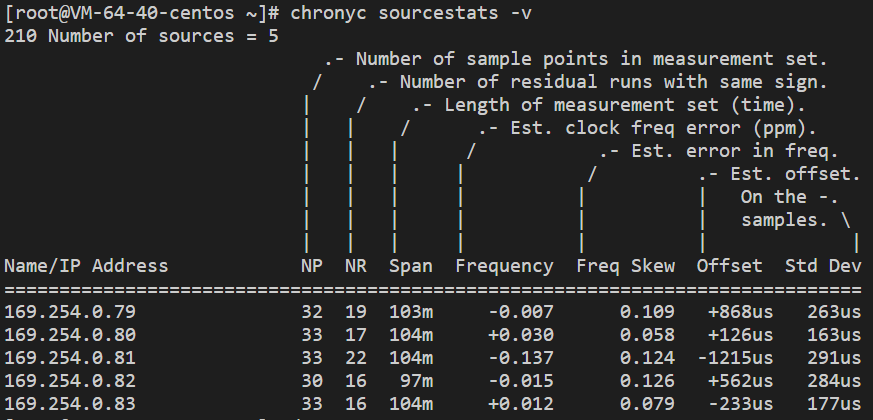
Command | Description |
chronyc sources -v | Check the clock source. |
chronyc sourcestats -v | Check the clock source status. |
timedatectl set-local-rtc 1 | Set the real time clock. The default format is UTC. |
timedatectl set-ntp yes | Enable the NTP service for synchronization. |
chronyc tracking | Calibrate the NTP server. |
chronyc -a makestep | Force synchronization of the system clock. |
Last updated:2025-08-14 17:12:48
root. Therefore, the sudo command is not required in the script. The root user can access all the files you created. If you need to grant other users with the access permission, modify the permission in the script.#! and the path directing to the interpreter of the script to be read (generally starting with /bin/bash).vi script_text.sh
#!/bin/bashecho "Hello Tencent Cloud."
#! and the path directing to the interpreter of the script to be read (generally starting with /bin/bash). For more information on the shell script, see BASH Programming - Introduction HOW-TO.# Base64-encode the scriptbase64 script_text.sh
# Result returned after the encodingIyEvYmluL2Jhc2gKZWNobyAiSGVsbG8gVGVuY2VudCBDbG91ZC4iCg==
# Base64-decode the returned result to verify the commandecho "IyEvYmluL2Jhc2gKZWNobyAiSGVsbG8gVGVuY2VudCBDbG91ZC4iCg==" | base64 -d
script_text script with Base64 is IyEvYmluL2Jhc2gKZWNobyAiSGVsbG8gVGVuY2VudCBDbG91ZC4iCg==.
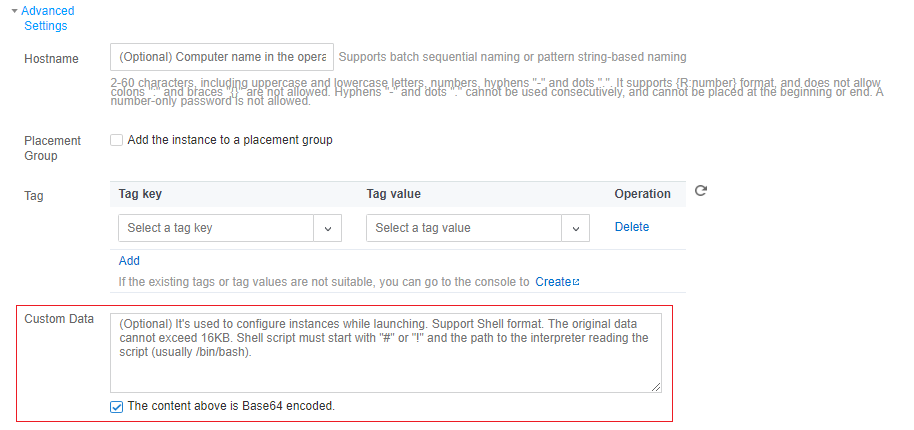
UserData parameter of the RunInstances API.
The following is an sample CVM creation request with UserData:https://cvm.tencentcloudapi.com/?Action=RunInstances&Version=2017-03-12&Placement.Zone=ap-guangzhou-6&ImageId=img-pmqg1cw7&UserData=IyEvYmluL2Jhc2gKZWNobyAiSGVsbG8gVGVuY2VudCBDbG91ZC4iCg==&<Common Request Parameters>
cat /var/log/cloud-init-output.log
Last updated:2025-08-14 16:47:36
<powershell>"Hello Tencent Cloud." | Out-File C:\tencentcloud.txt</powershell>
vi script_text.ps1
<powershell>"Hello Tencent Cloud." | Out-File C:\tencentcloud.txt</powershell>
base64 script_text.ps1
PHBvd2Vyc2hlbGw+CiJIZWxsbyBUZW5jZW50IENsb3VkLiIgfCBPdXQtRmlsZSAgQzpcdGVuY2VudGNsb3VkLnR4dAo8L3Bvd2Vyc2hlbGw+Cg==
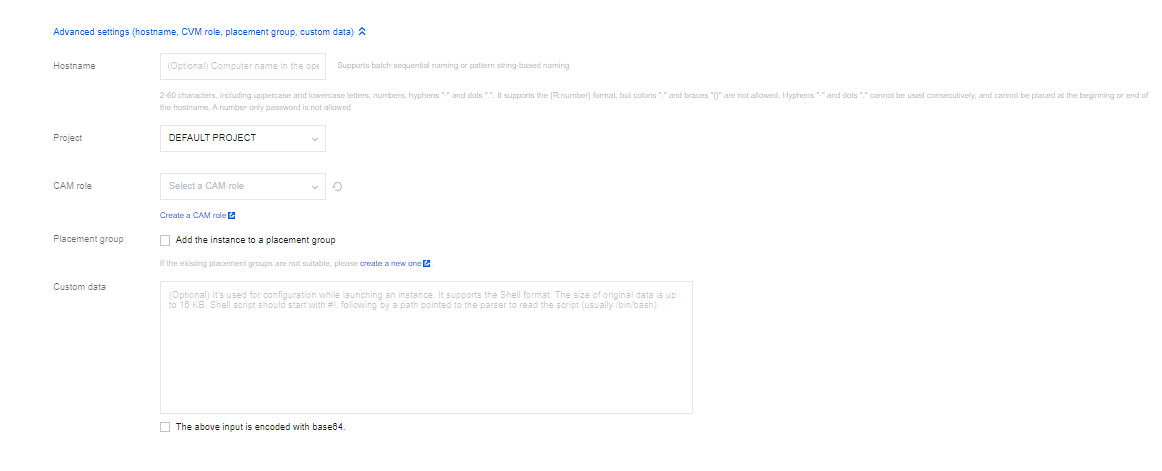
https://cvm.tencentcloudapi.com/?Action=RunInstances&Version=2017-03-12&Placement.Zone=ap-guangzhou-6&ImageId=img-pmqg1cw7&UserData=PHBvd2Vyc2hlbGw+CiJIZWxsbyBUZW5jZW50IENsb3VkLiIgfCBPdXQtRmlsZSAuXHRlbmNlbnRjbG91ZC50go=&<Common Request Parameters>
tencentcloud.txt text file exists.
If the tencentcloud.txt text file exists, the configuration is successful, as shown in the following figure:
C:\Program Files\Cloudbase Solutions\Cloudbase-Init\log\cloudbase-init.log file to get the execution logs of the script.Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11

slmgr /upk
slmgr /ipk <ProductKey>
slmgr /skms kms.tencentyun.com
slmgr /ato
<ProductKey> in the slmgr /ipk <ProductKey> command should be replaced as follows:489J6-VHDMP-X63PK-3K798-CPX3YW3GGN-FT8W3-Y4M27-J84CP-Q3VJ9CB7KF-BWN84-R7R2Y-793K2-8XDDGWMDGN-G9PQG-XVVXX-R3X43-63DFGWX4NM-KYWYW-QJJR4-XV3QB-6VM33
For more information, see Key Management Services (KMS) client activation and product keys.HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\ProductOptions registry key is damaged. You can run the following command to determine whether to reactivate the system.(Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\ProductOptions\).ProductPolicy.count
slmgr.vbs /ipk <ProductKey>
Get-ItemProperty... command again for verification. The returned value is 56184.slmgr.vbs /ato
slmgr.vbs /rilc
Get-ItemProperty... command again for verification, and the returned value is still 1960.slmgr.vbs /ato
Get-ItemProperty... command again for verification, and the returned value may change. However, after the system is restarted, the memory limit is still 2 GB.slmgr.vbs /ato
Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11
cmd.exe in the Run dialog box to open the console window.w32tm /config /syncfromflags:manual /manualpeerlist:"ntpupdate.tencentyun.com"w32tm /resync
cmd.exe in the Run dialog box to open the console window.cscript /nologo %windir%/system32/slmgr.vbs -skms kms.tencentyun.com:1688cscript /nologo %windir%/system32/slmgr.vbs -ato
Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11

Last updated:2025-11-20 20:48:40
qemu component.qemu component transfers the shutdown command to the CVM by interrupting ACPI (for more information, see technical documents on VMCS).Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11
http://mirrors.tencentyun.com/install/windows/power-set-win.bat.
For example, download the Tencent Cloud power modification and configuration tool (power-set-win.bat) to the C: drive.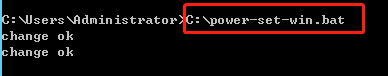
powercfg -L



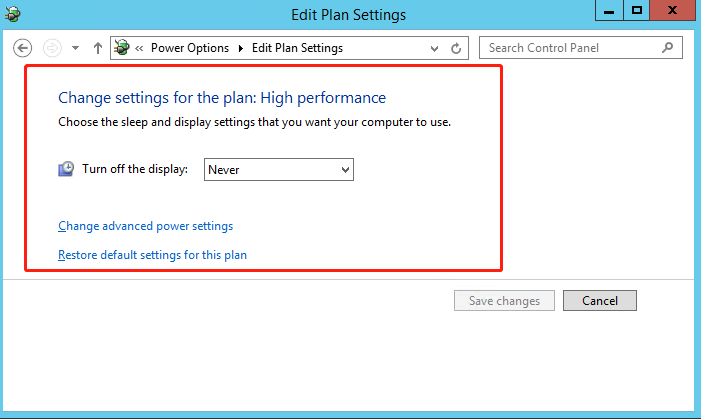
Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11





Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11

cmd in the pop-up window and press Enter.systeminfo command to view the system information.
This document uses Windows Server 2016 Datacenter Edition 64-bit as an example.

http://mirrors.tencent.com/install/windows/virtio_64_1.0.9.exehttp://mirrors.tencentyun.com/install/windows/virtio_64_1.0.9.exe

Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11

ipconfig /all
C:\Windows\System32\Sysprep\sysprep.exe

whoami /user

http://www.stratesave.com/html/sidchg.html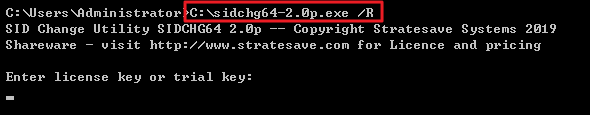
/R means automatic restart after modification, and /S means shutdown after modification. For details, please see SIDCHG Official Instructions.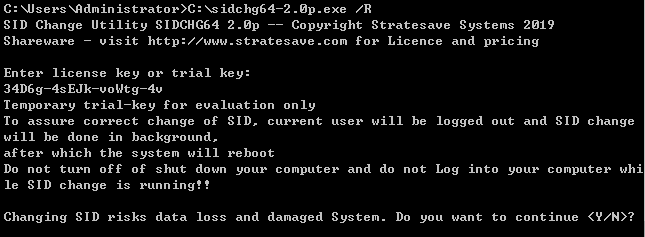


whoami /user

Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11
grub.

grub as follows:/etc/grub.conf file.vi /etc/grub.conf
vga=792 to the parameter grub, as shown below:
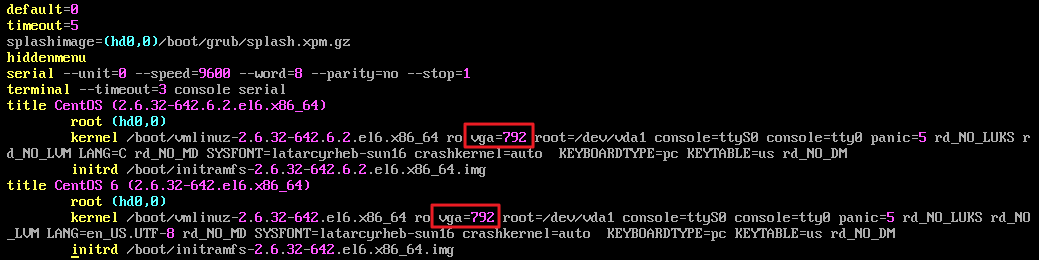
reboot
grub as follows:grub file.vim /etc/default/grub
vga=792 to the end of the parameter value GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT, as shown below:

grub.cfg file.grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg
reboot
Resolution | 640 * 480 | 800 * 600 | 1024 * 768 |
VGA | 786 | 789 | 792 |
Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11
https://technet.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/cc721940(v=ws.10).aspx.%WINDIR%\system32\sysprep.slmgr.vbs /dlv.
C:\Program Files\Cloudbase Solutions\.cd 'C:\Program Files\Cloudbase Solutions\Cloudbase-Init\conf'
/unattend:Unattend.xml in the following command, otherwise your current username, password and other configurations of the CVM will be reset. If you choose Follow image for the login, you will need to manually reset the username and account after launch.C:\Windows\System32\sysprep\sysprep.exe /generalize /oobe /unattend:Unattend.xml
whoami /user.Last updated:2025-09-08 17:02:17
yuminstallatop -y
Complete! indicates that atop has been successfully installed.vim /etc/sysconfig/docker
LOGINTERVAL=600 to LOGINTERVAL=30. This means to modify the monitoring period of 600s by default to a recommended value-30s. You can modify it to other values as needed.LOGGENERATIONS=28 to LOGGENERATIONS=7. This means to modify the log retention time of 28 days by default to 7 days. To prevent overmuch disk storage space from being occupied due to the long-term running of atop, it’s recommended to modify it to 7 days. You can modify it to other values as needed.
The result should be as follows:
systemctl restart atop
/var/log/atop directory. Please check the required log file name, execute the following command to view the log file, and analyze the data with reference to atop Common Commands and System Resource Monitoring Field Description.atop -r /var/log/atop/atop_2021xxxx
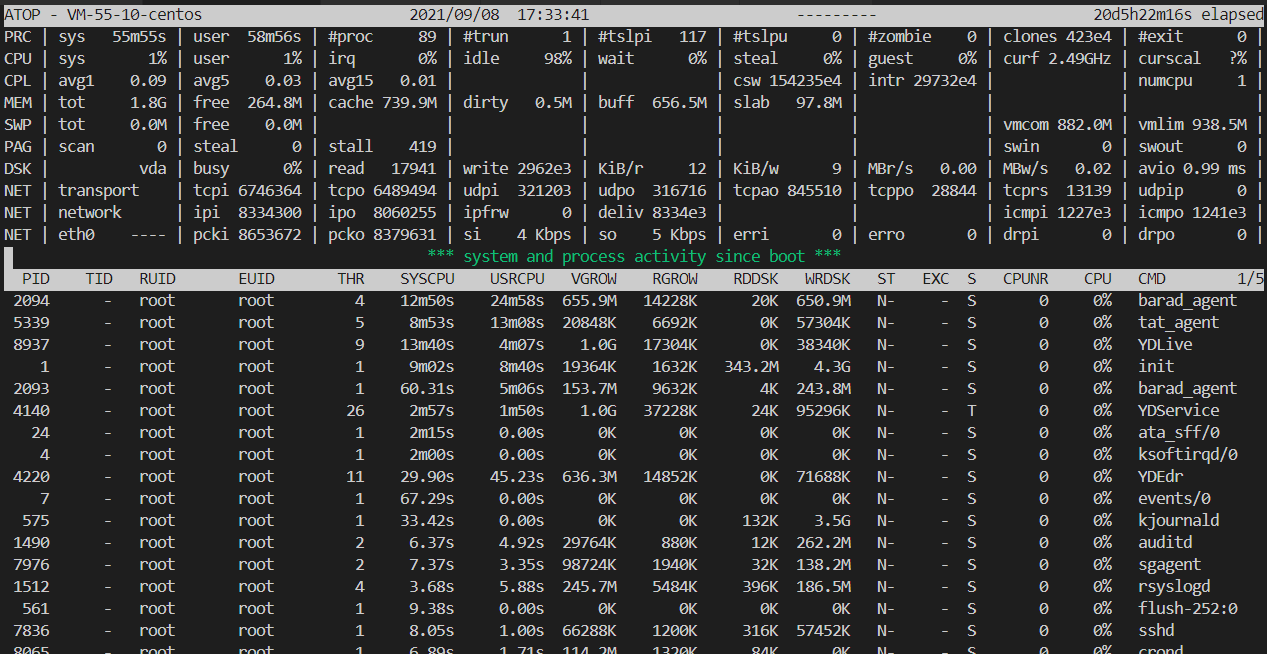
systemctl stop atop
Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11
sysctl to adapt to your specific business. This document describes the default and optimal configurations of Tencent Cloud Linux public images and helps you manually tune them as needed.sysctl -w command only makes the configurations take effect temporarily, while parameters wrote to /etc/sysctl.conf take effect permanently.Parameter | Description | Initial Configuration |
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle | This parameter is used to quickly recycle the TIME_WAIT connection. If enabled, kernel will check the packet timestamp.We do not recommend enabling this parameter, because packet loss may occur when the timestamp is not monotonically increasing. This parameter is disused in later kernel versions. | 0 |
net.core.somaxconn | This parameter is used to define the ESTABLISH state at the end of the three-way handshake when there is no ACCEPT queue. A longer ACCEPT queue indicates low processing rate of the client, or a burst of new connections in a short time. Setting net.core.somaxconn too low may cause packet loss because the new SYN connection will be discarded when the server receives SYN packet and the somaxconn table is full. Setting it too high is only necessary for high concurrence service, but the latency may increase. | 128 |
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog | This parameter specifies the maximal number of connections in SYN_RECV queue, which was once used to defend the common synflood attacks. However, if tcp_syncookies=1, connections in SYN_RECV queue will exceed the upper limit. | - |
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies | This parameter is used to enable SYN Cookies, which prevents some SYN attacks. If enabled, the connections can still be established when the SYN queue is overflowed. However, SHA1 will be used to verify Cookies, which theoretically increases the CPU utilization. | 1 |
net.core.rmem_defaultnet.core.rmem_maxnet.ipv4.tcp_memnet.ipv4.tcp_rmem | These parameters are used to configure the cache size of received data. Setting this too high may waste memory resources, while setting it too low may cause packet loss. You can tune them according to the concurrence and throughput of your business. rmem_default: the theoretically optimal configuration is equal to the value of bandwidth divided by RTT, which will overwrite the configurations of tcp_rmem and tcp_rmem rmem_max: approximately five times of rmem_default tcp_mem: total TCP memory consumed, which is automatically set to to 3/32, 1/8 or 3/16 of the CVM’s available memory. The parameters tcp_mem and rmem_default also determine the maximum number of concurrent connections. | rmem_default=655360rmem_max=3276800 |
net.core.wmem_defaultnet.core.wmem_maxnet.ipv4.tcp_wmem | These parameters are used to configure the data transmission cache. Data sending on Tencent Cloud usually does not have bottlenecks, so these configurations are optional. | - |
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_intvlnet.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_probesnet.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time | These parameters are relevant to TCP Keepalive, which default to 75/9/7200. The default settings mean that the kernel will initiate detection when a TCP connection is idle for 7,200 seconds, and will send RST after 9 failed detections (each for 75 seconds). These values are too high for a server. You can adjust them to 30/3/1800 as needed. | - |
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range | This parameter is used to configure the available port range, which can be adjusted as needed. | - |
tcp_tw_reuse | This parameter is used to reuse a socket in TIME-WAIT state for new TCP connections. This help you quickly restart links that use fixed ports, but may involve risks in the NAT-based network. Later kernel versions support values 0, 1, and 2 and configure it to 2. | - |
net.ipv4.ip_forwardnet.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding | This parameter is used to specify the IP forwarding. You can configure it to 1 in the Docker’s route forwarding scenario. | 0 |
net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter | This parameter is used to specify the reverse path validation rule of ENI on received data packets. Valid values include 0, 1 (recommended by RFC3704), and 2. The recommended configuration is a strict mode that can prevent DDoS attacks and IP spoofing acts. | - |
net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_source_route | This parameter is used to specify whether to accept IP packets containing source routes, which is not allowed by default, as recommended on the CentOS website. | 0 |
net.ipv4.conf.all.promote_secondariesnet.ipv4.conf.default.promote_secondaries | This parameter is used to specify whether a secondary IP address will become a primary IP after the original primary IP address is deleted. | 1 |
net.ipv6.neigh.default.gc_thresh3net.ipv4.neigh.default.gc_thresh3 | This parameter is used to define the maximum records stored in the ARP cache. The garbage collector immediately starts once the stored records exceed the set value. | 4096 |
Parameter | Description | Initial Configuration |
vm.vfs_cache_pressure | This controls the tendency of the kernel to reclaim the memory. At the default value of 100, the kernel will attempt to reclaim dentries back to memory. The curl-based services usually accumulate dentries, which may use up all the free memory and cause OOM or kernel bug. We configure it to 250 to balance the reclaiming frequency and performance, which is tunable. | 250 |
vm.min_free_kbytes | This parameter is used to force the Linux MEM to keep a minimum number of kilobytes free memory for use by kernel threads. The value is automatically calculated according to the free physical memory (MEM) at startup by: 4*sqrt (MEM). When the server receives microbursts of packets, your server may become subtly broken and cause OOM. On a high-configuration server, we recommend configuring vm.min_free_kbytes at about 1% of the total memory by default. | - |
kernel.printk | This specifies the level for kernel’s printk printing function. The default configuration is five or above. | 5 4 1 7 |
kernel.numa_balancing | This indicates that kernel can automatically move processes to the corresponding NUMA node, but it is actually ineffective and affects performance. You can try to enable it in the Redis use cases. | 0 |
kernel.shmallkernel.shmmax | shmmax: defines the maximum size of a single shared memory segment (in bytes) a Linux process can allocate. shmall: defines system-wide total amount of shared memory pages. | kernel.shmmax=68719476736kernel.shmall=4294967296 |
Parameter | Description | Initial Configuration |
fs.file-maxfs.nr_open | They denote the maximum number of file-handles that the Linux kernel or a process can allocate, respectively. file-max: automatically configures to approximate 100,000/GB when OS starts. nr_open: sets to the fixed value of 1048576, which limits the maximum open file handles in a user-mode environment. Generally, keep this value unchanged. To modify the maximum open file handles, configure the ulimit -n parameter in the /etc/security/limits.conf configuration file. | ulimit -n=100001fs.nr_open=1048576 |
kernel.pid_max | This specifies maximum processes in a system. The official image uses the default value of 32768, which can be adjusted as needed. | - |
kernel.core_uses_pid | This determines whether the generated coredump filename will contain .PID. | 1 |
kernel.sysrq | This enables you to operate on /proc/sysrq-trigger later. | 1 |
kernel.msgmnbkernel.msgmax | They defines the maximum size in bytes of a single message queue and the maximum allowable size in bytes of any single message in a message queue, respectively | 65536 |
kernel.softlockup_panic | This controls whether the kernel will panic when a soft lockup is detected. If enabled, a vmcore will be generated based on the kdump configuration, which can be used to analyze the cause of soft lockup. | - |
Parameter | Description | Initial Configuration |
vm.dirty_background_bytesvm.dirty_background_ratiovm.dirty_bytesvm.dirty_expire_centisecsvm.dirty_ratiovm.dirty_writeback_centisecs | These parameters are mainly used to configure the policy for IO being written back to the disk. dirty_background_bytes/dirty_bytes and dirty_background_ratio/dirty_ratio refer to the amount and percentage of system memory that can be filled with “dirty” pages, respectively. In general, the ratio will be specified. dirty_background_ratio: refers to a percentage of dirty pages in the system memory (10% by default) at which the background kernel flush processes will start writing back to the disk. dirty_ratio: refers to the absolute maximum amount of system memory that can be filled with dirty pages before everything must get committed to disk. When the system gets to this point, all new I/O blocks until dirty pages have been written to disk, causing long I/O pauses. The system will first get to the `vm.dirty_background_ratio` condition at which the flush processes will start asynchronous writeback, and applications continue writing. When the system gets to the specified value of ` vm.dirty_ratio`, OS will handle dirty pages synchronously, blocking applications. vm.dirty_expire_centisecs: specifies how long dirty page can be in cache before it needs to be written. It is expressed in 100'ths of a second. Data which has been dirty in-memory for longer than this interval will be written out next time a flush process wakes up. vm.dirty_writeback_centisecs: specifies how often kernel flush processes wake up. It is expressed in 100'ths of a second. | - |
Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11
ps -ef|grep -w "acpid"|grep -v "grep"
sudo apt-get install acpid
yum install acpid
in apcid
Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11
/etc/hosts file according to the /etc/cloud/templates/hosts.${os_type}.tmpl template and overwrites the original /etc/hosts file of the instance involved. Hence, after you manually modify the internal /etc/hosts configuration of the instance and restart it, the /etc/hosts configuration goes back to the original default configuration./etc/hosts configuration will not be overwritten.
For instance created before September 2018, follow the steps below for modification.- update_etc_hosts in the /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg configuration file to - ['update-etc-hosts', 'once-per-instance']:sed -i "/update_etc_hosts/c \ - ['update_etc_hosts', 'once-per-instance']" /etc/cloud/cloud.cfg
config_update_etc_hosts file under the /var/lib/cloud/instance/sem/ path:touch /var/lib/cloud/instance/sem/config_update_etc_hosts
hosts template file pathhosts template file:cat /etc/hosts
hosts template file is as shown in the following figure:
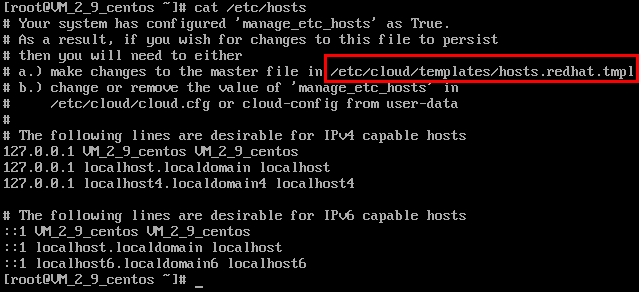
hosts template file127.0.0.1 test test as an example, you can modify the hosts template and /etc/hosts file as needed.hosts template file:vim /etc/cloud/templates/hosts.redhat.tmpl
127.0.0.1 test test
/etc/hosts file/etc/hosts file:vim /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 test test
Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11

root by default in the rescue mode.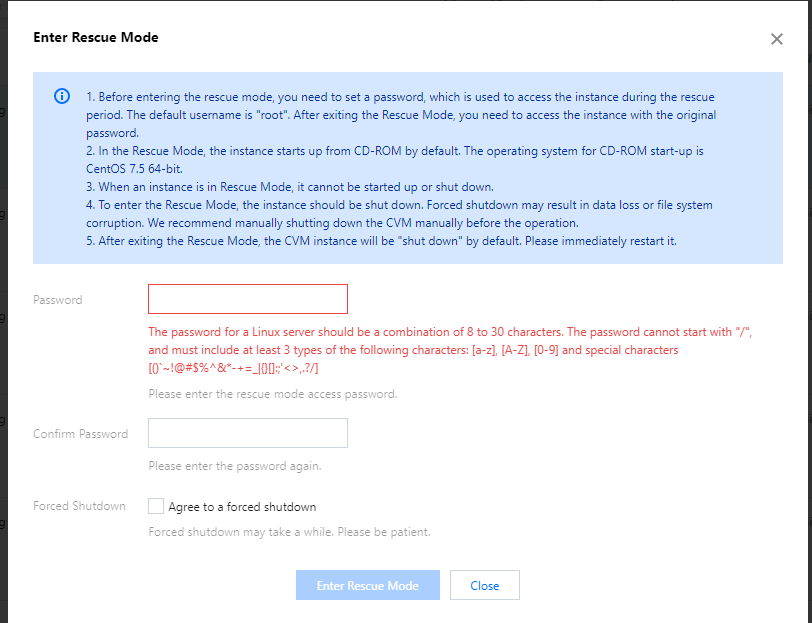
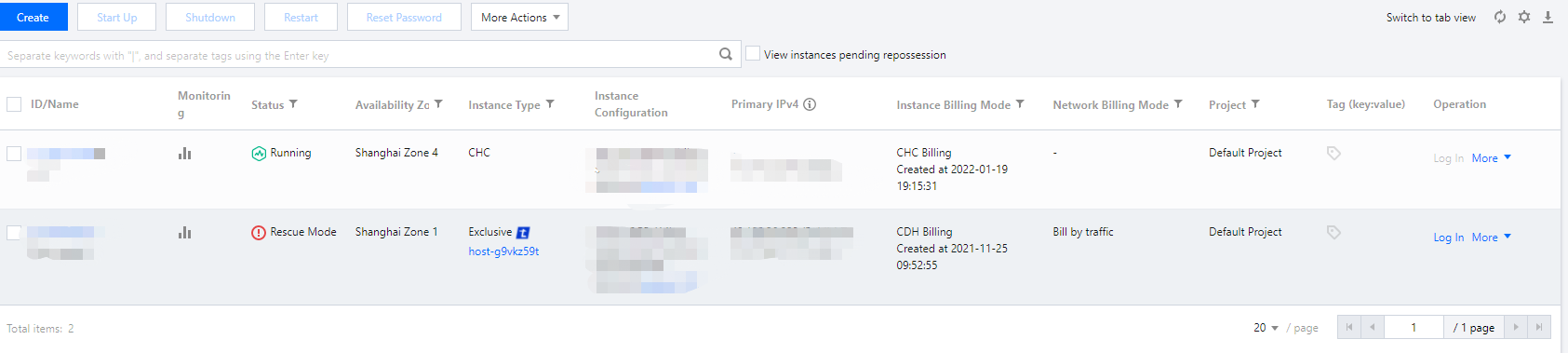
root account and the password set in step 3 to log in to the instance as follows:vda, and its root partition is vda1, which is unmounted by default.mkdir -p /mnt/vm1
mount /dev/vda1 /mnt/vm1
mount -o bind command to mount some sub-directories in the original file system and use the chroot command to run commands in the specified root directory. Below are the specific commands:mount -o bind /dev /mnt/vm1/devmount -o bind /dev/pts /mnt/vm1/dev/ptsmount -o bind /proc /mnt/vm1/procmount -o bind /run /mnt/vm1/runmount -o bind /sys /mnt/vm1/syschroot /mnt/vm1 /bin/bash


Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11
grub menu, as shown below.
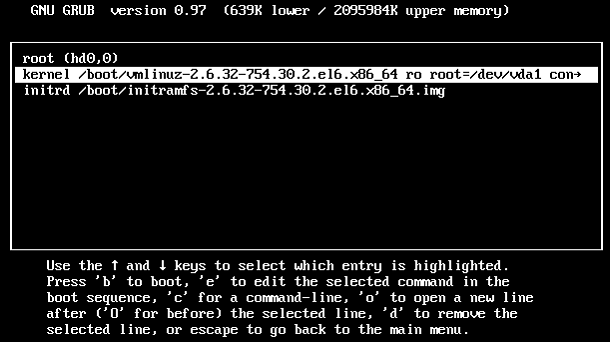
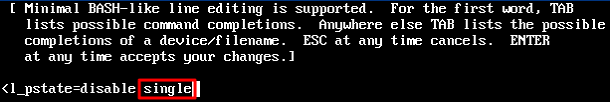
exec /sbin/init command to exit the single user mode.
ro with rw init=/bin/bash or /usr/bin/bash, as shown below.
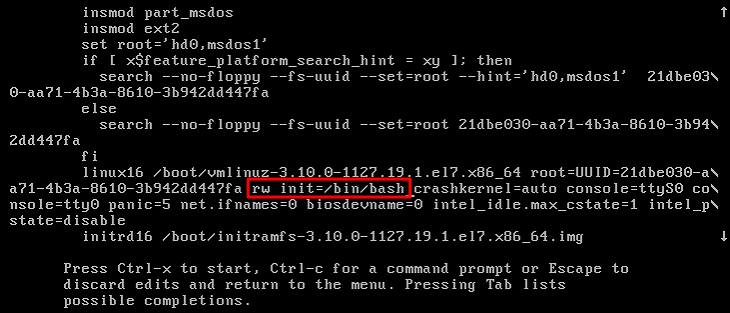
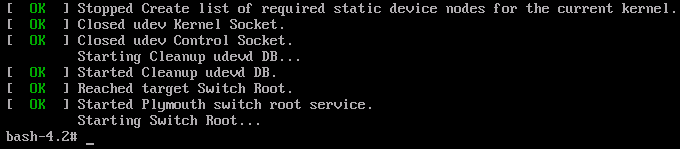
exec /sbin/init command to exit the single user mode.
ro with rw init=/sysroot/bin/bash, as shown below.
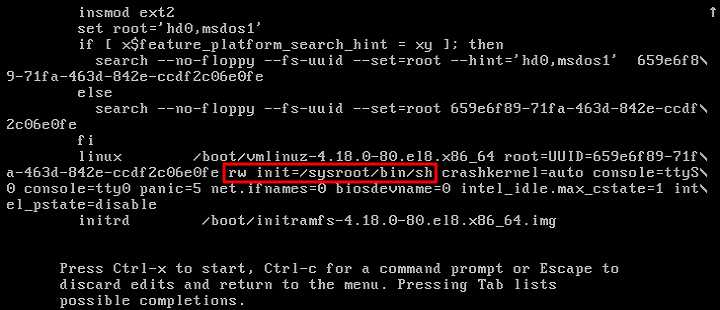
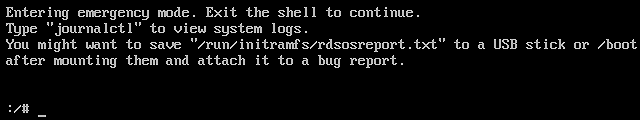
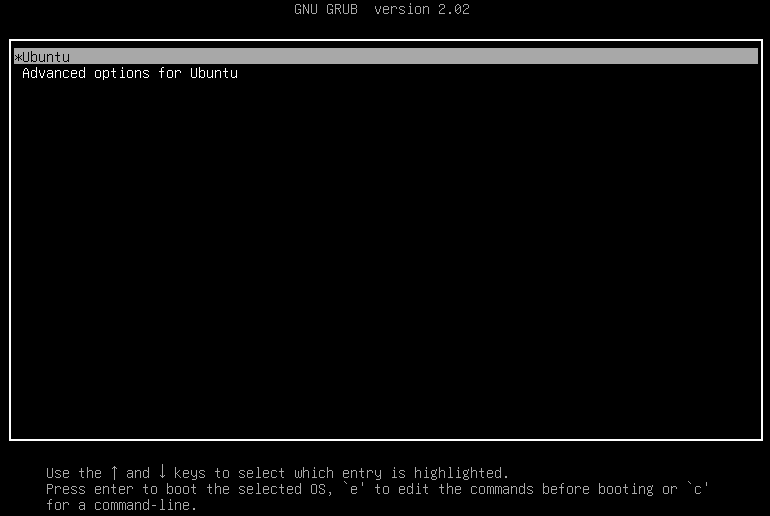
quiet splash rw init=/bin/bash to the end of the line, as shown below.
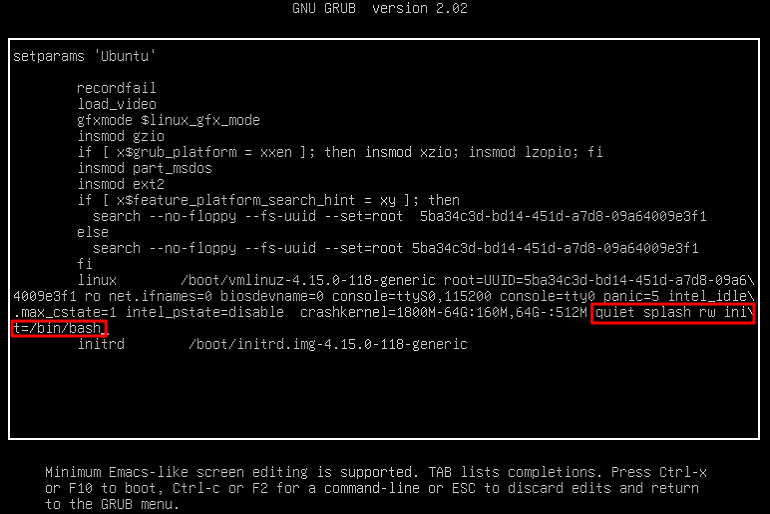
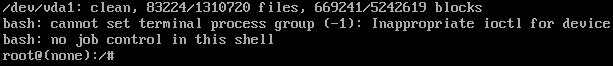
rw to the beginning and 1 to the end of the splash parameter, as shown below.
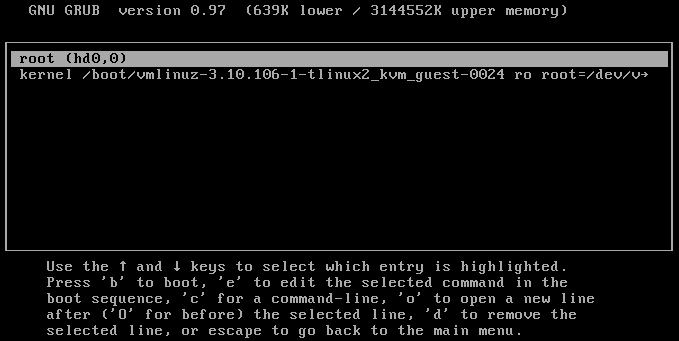
Last updated:2025-09-08 16:57:09

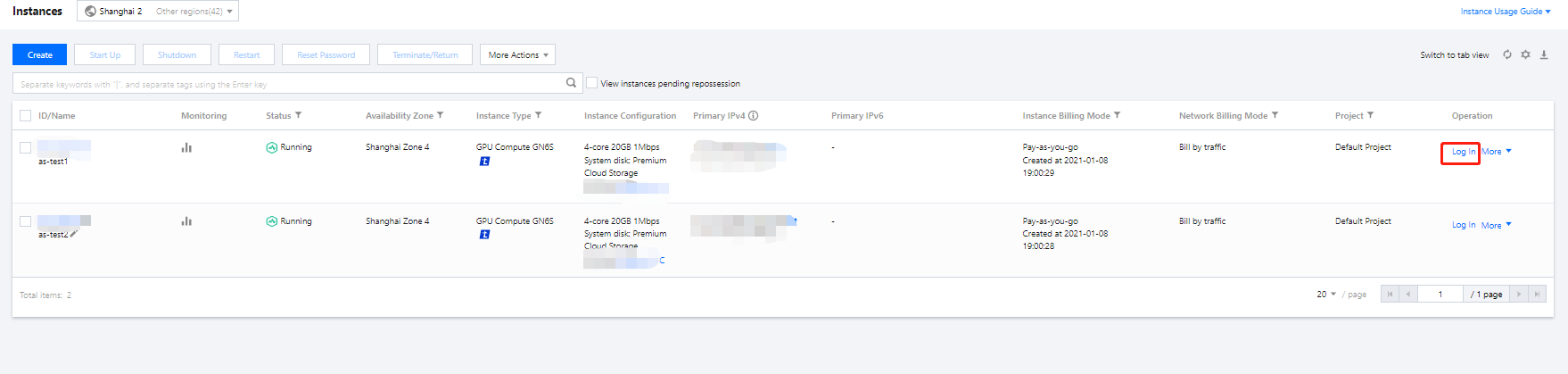
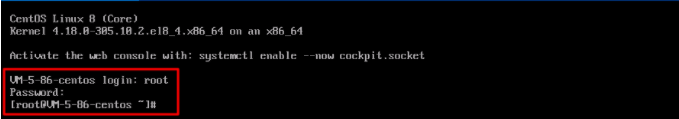
ps -ef | grep sshd
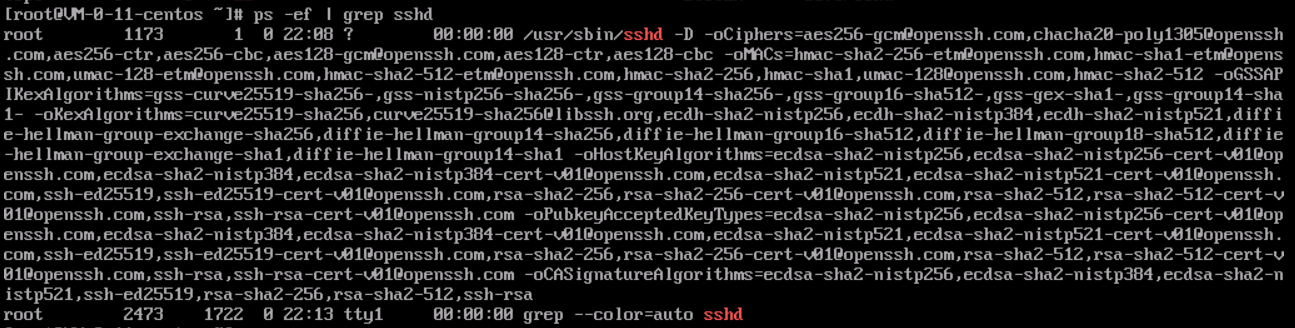
sshd -t
/var/empty/sshd/ permission issue.

/var/log/secure logs to facilitate troubleshooting.
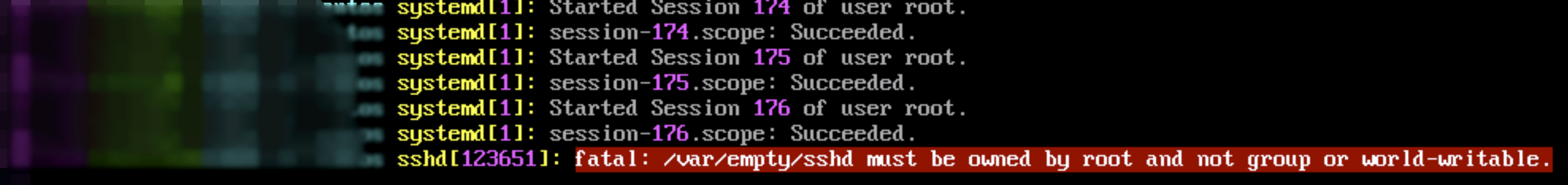
/var/empty/sshd directory.ll -d /var/empty/sshd/
777.

/var/empty/sshd/ file.chmod 711 /var/empty/sshd/
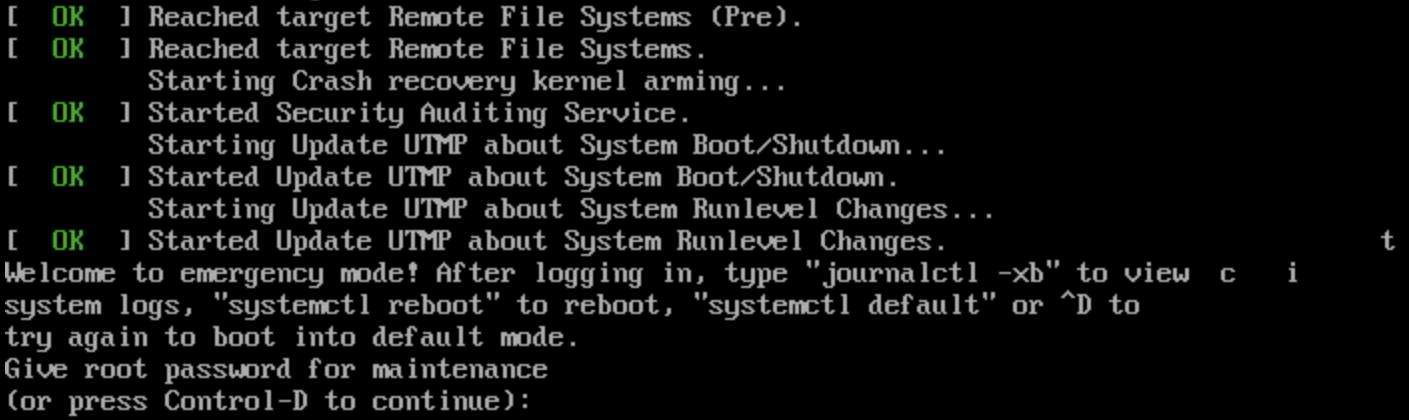
/etc/fstab is not properly configured.
For example, you've configured the auto-attaching of disk based on device name in the /etc/fstab file. If the device name is changed when the CVM restarts, this configuration will cause the system to fail to start up normally./etc/fstab configuration file. Then, restart the CVM to verify the repaired file.
fstab file is correct.lsblk
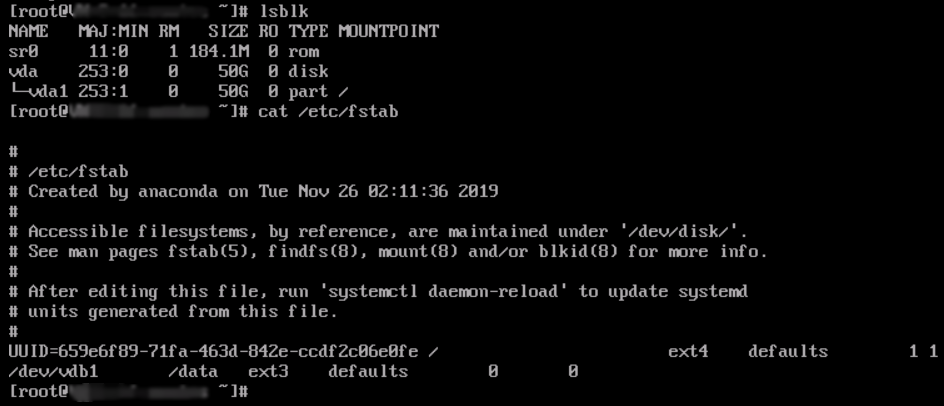
fstab file.cp /etc/fstab /home
/etc/fstab file.vi /etc/fstab
# to comment out this configuration.
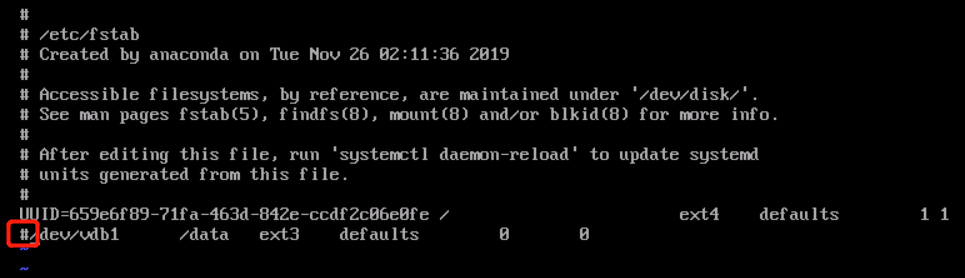
FAILED startup failure items in the prompt message.
.bin and .lib files are missing.
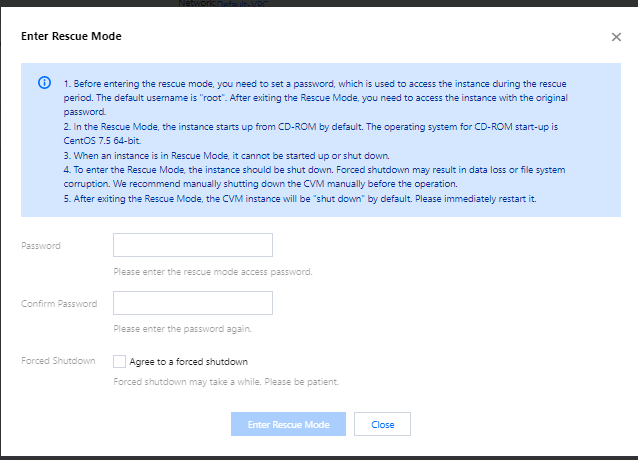

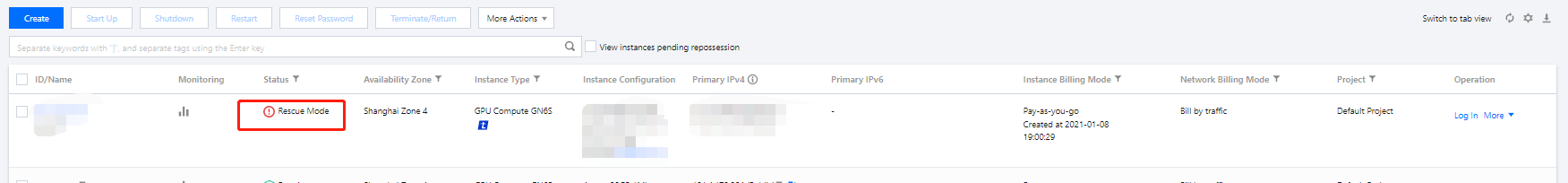
root account and the password set in step 3 to log in to the instance as follows:vda, and its root partition is vda1, which is unmounted by default.mkdir -p /mnt/vm1
mount /dev/vda1 /mnt/vm1

mount -o bind command to mount some sub-directories in the original file system and use the chroot command to run commands in the specified root directory. Below are the specific commands:mount -o bind /dev /mnt/vm1/devmount -o bind /dev/pts /mnt/vm1/dev/ptsmount -o bind /proc /mnt/vm1/procmount -o bind /run /mnt/vm1/runmount -o bind /sys /mnt/vm1/syschroot /mnt/vm1 /bin/bash
chroot command:cd / command.cd /mnt/vm1 to view the root partition data.
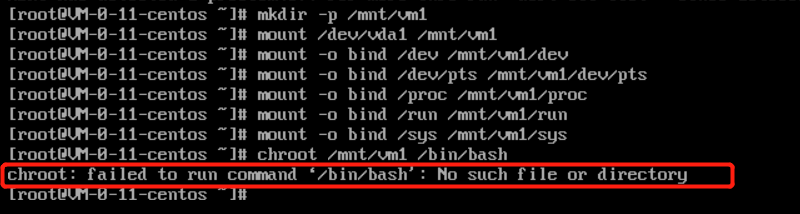
/usr/bin directory in the original system root partition have been deleted.
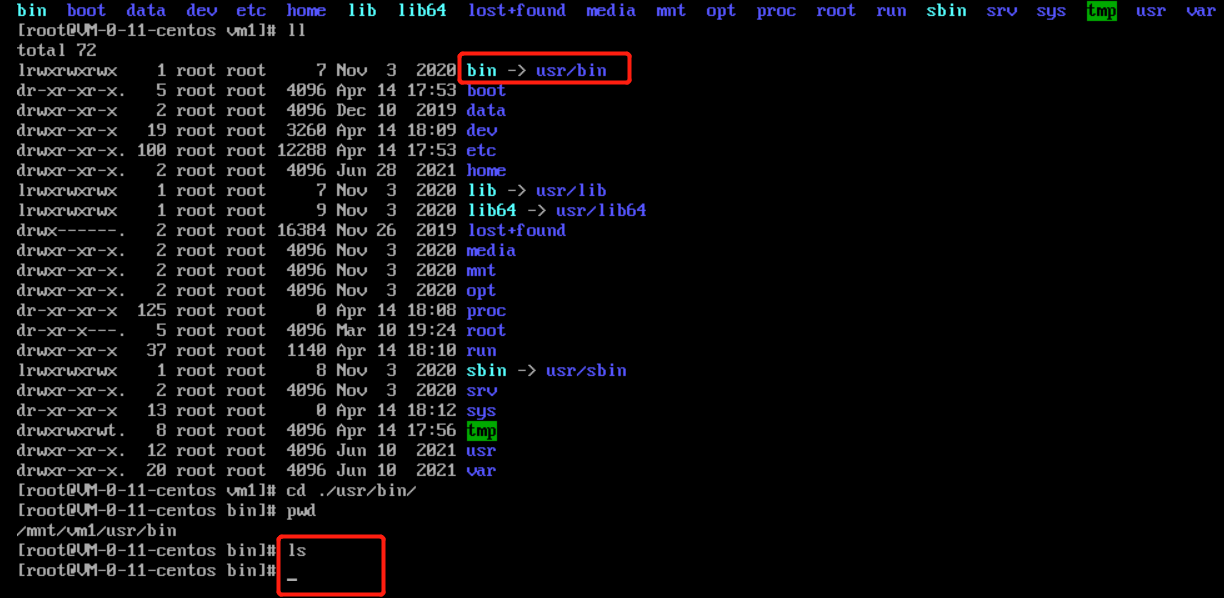
/usr/bin directory of the normal system to the abnormal instance.cd /usr/bin/ && tar -zcvf bin.tar.gz *
scp bin.tar.gz root@abnormal instance ip:/mnt/vm1/usr/bin/
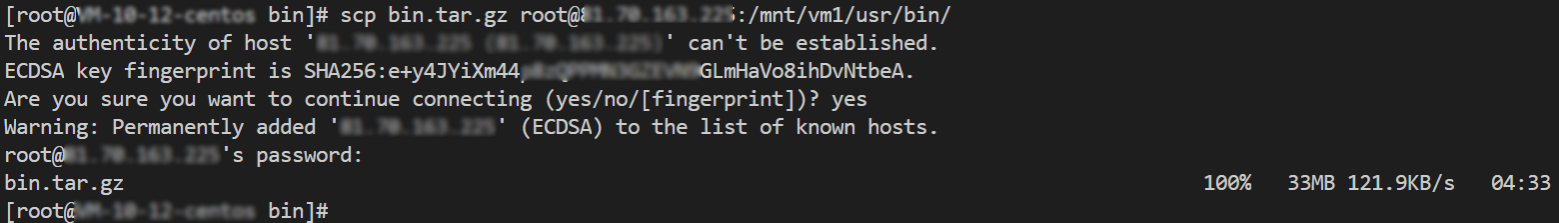
cd /mnt/vm1/usr/bin/
tar -zxvf bin.tar.gz
chroot /mnt/vm1 /bin/bash
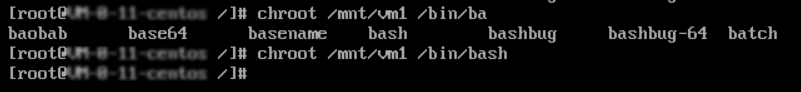
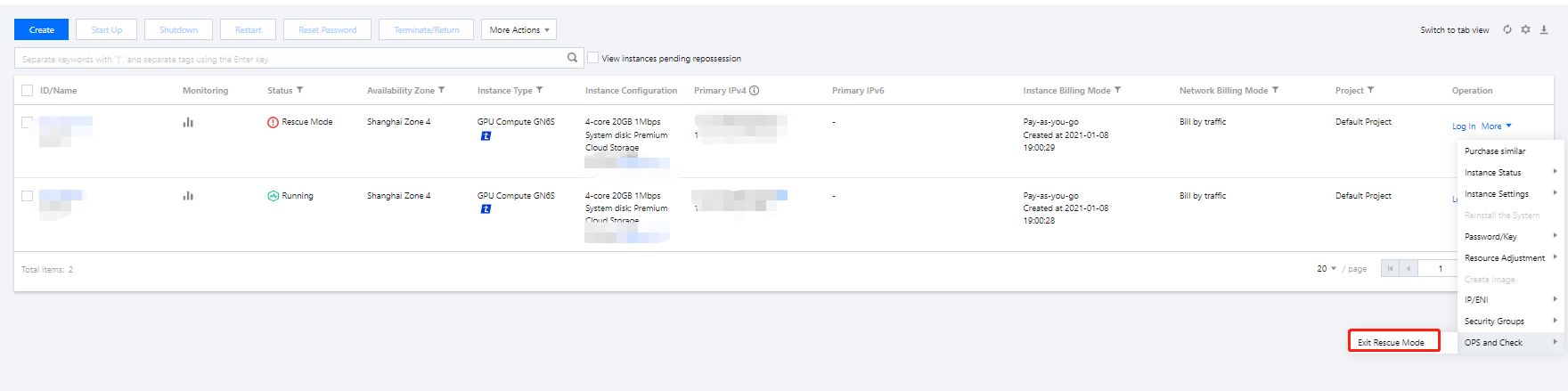
Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11
mstsc /admin command but not Remote Desktop. Windows Server allows two users to log in at the same time by default, which meets most needs. Evaluate your needs based on your actual business scenarios, and if you strongly need to configure multi-user remote login, proceed as instructed in this document.

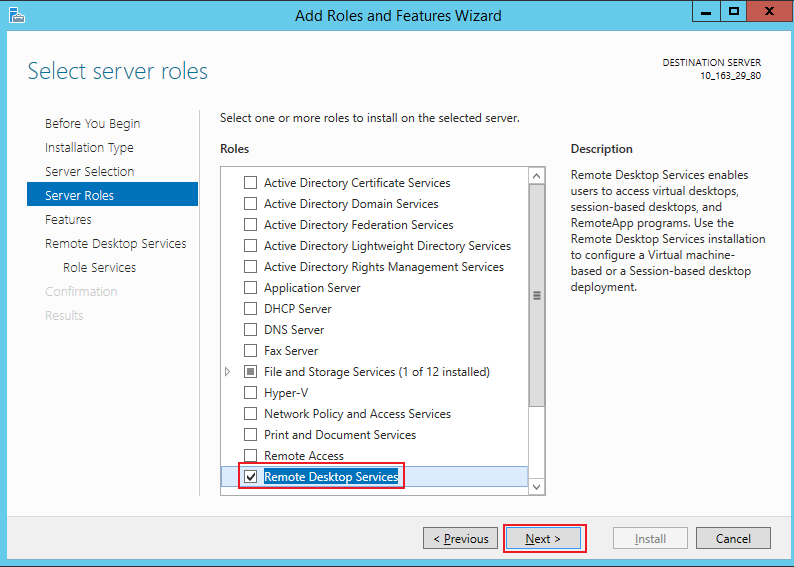
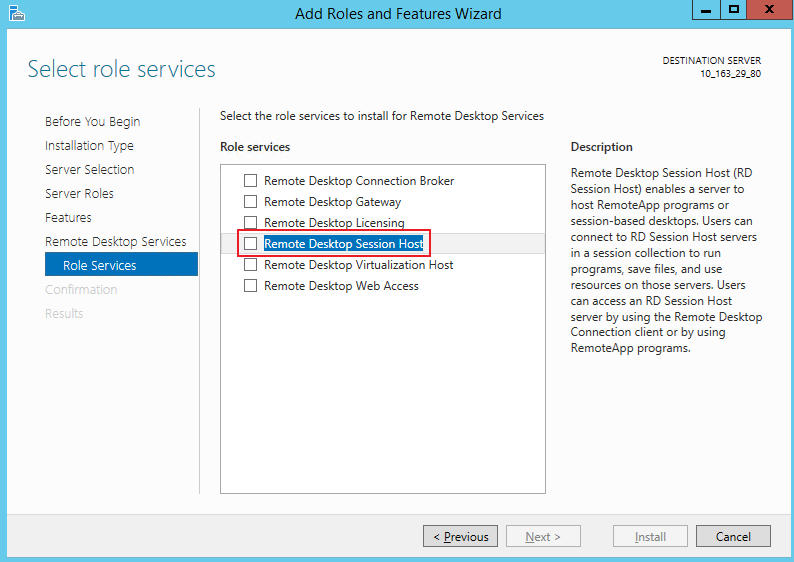
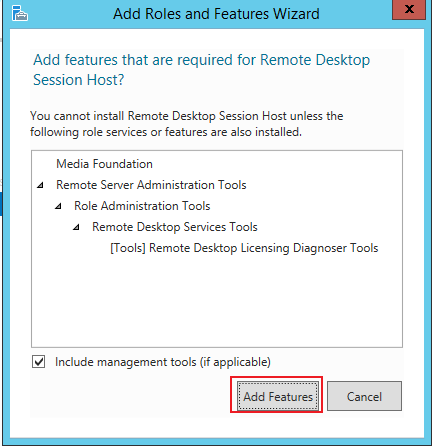
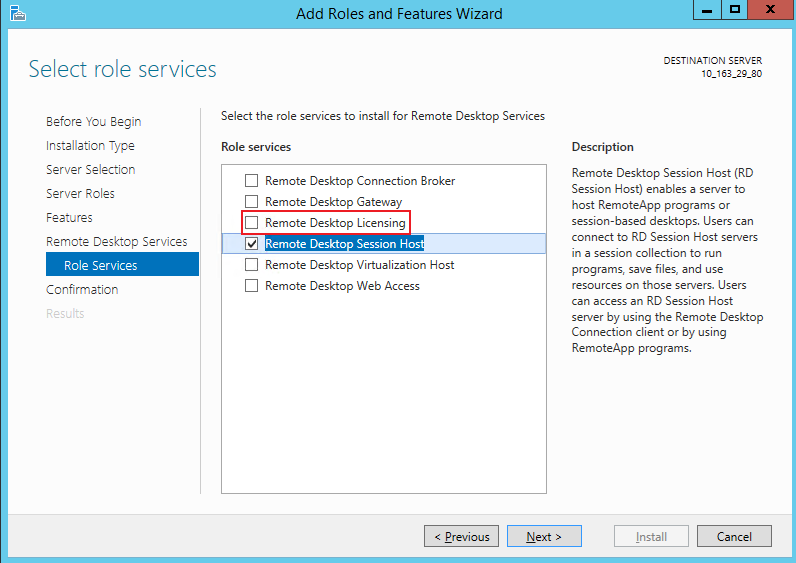
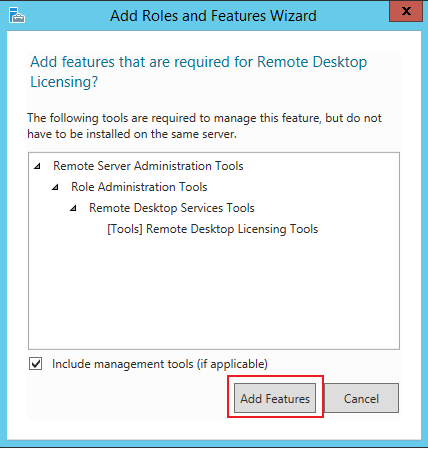







Last updated:2025-09-05 15:18:20

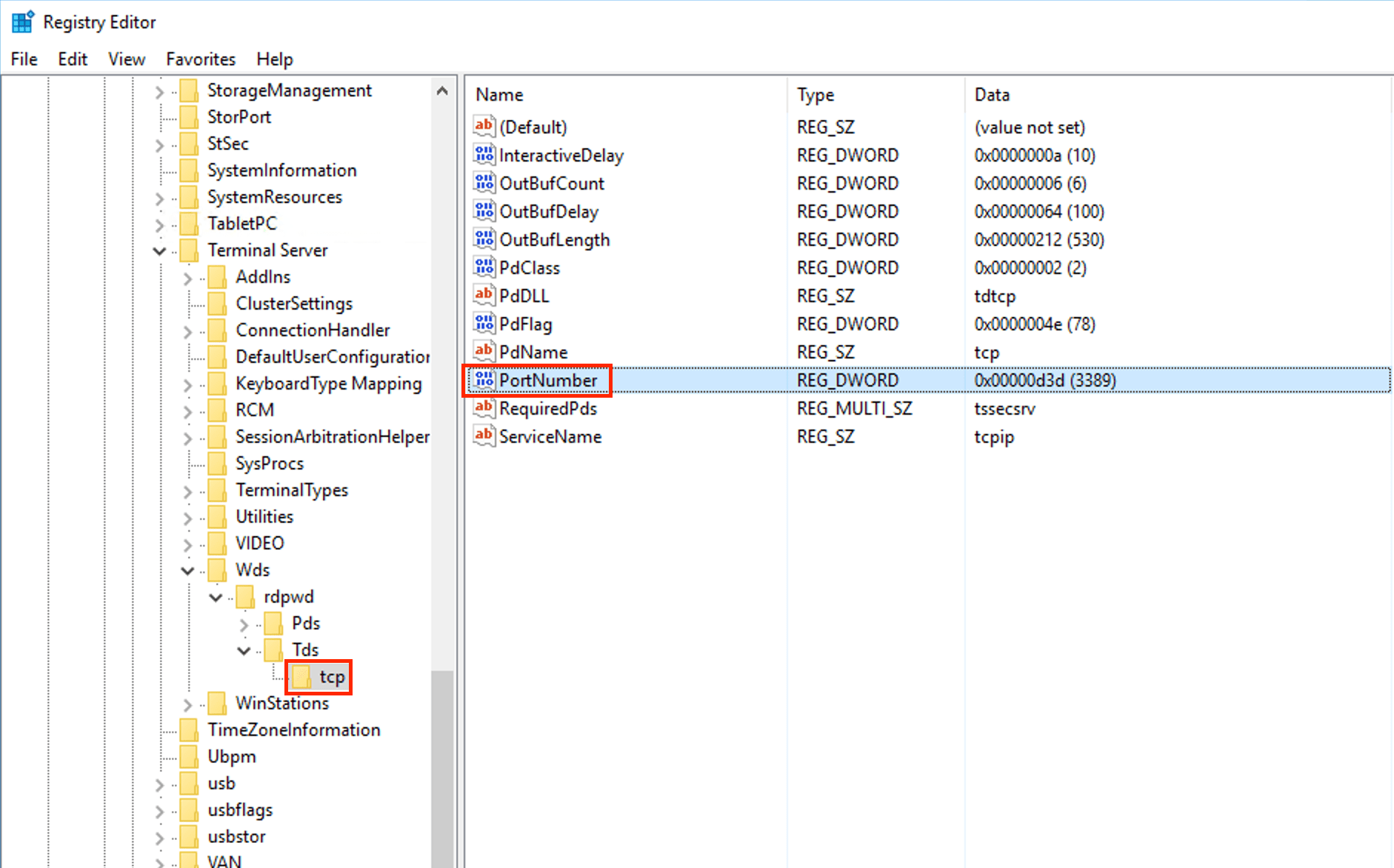
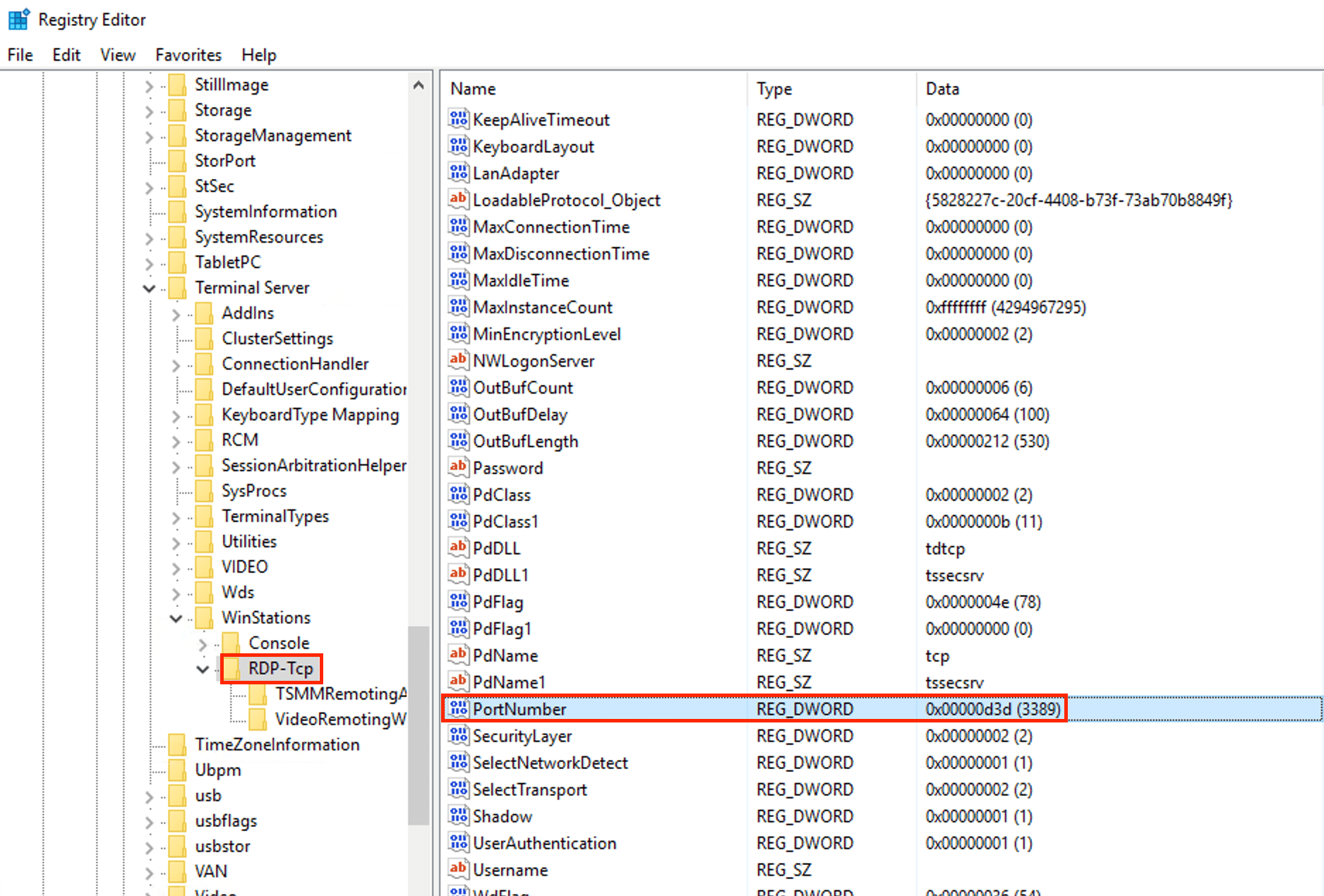
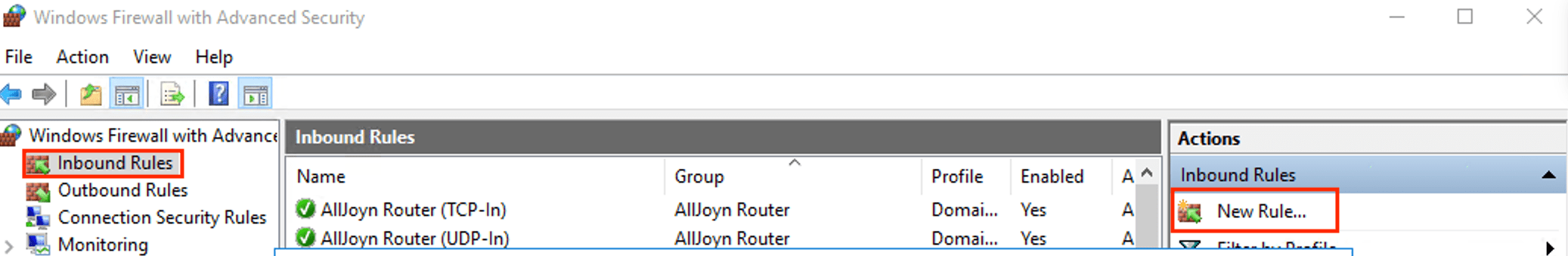
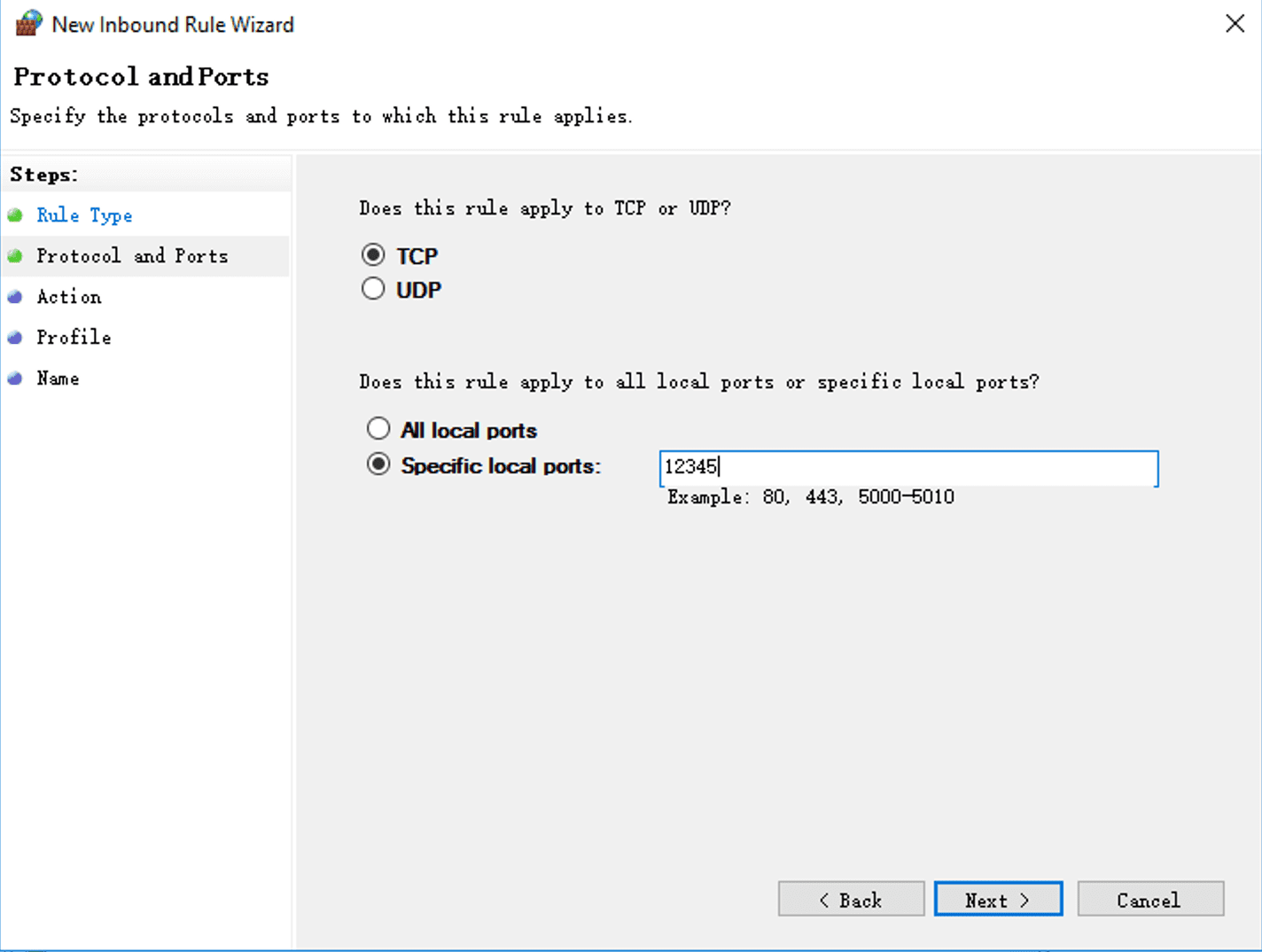
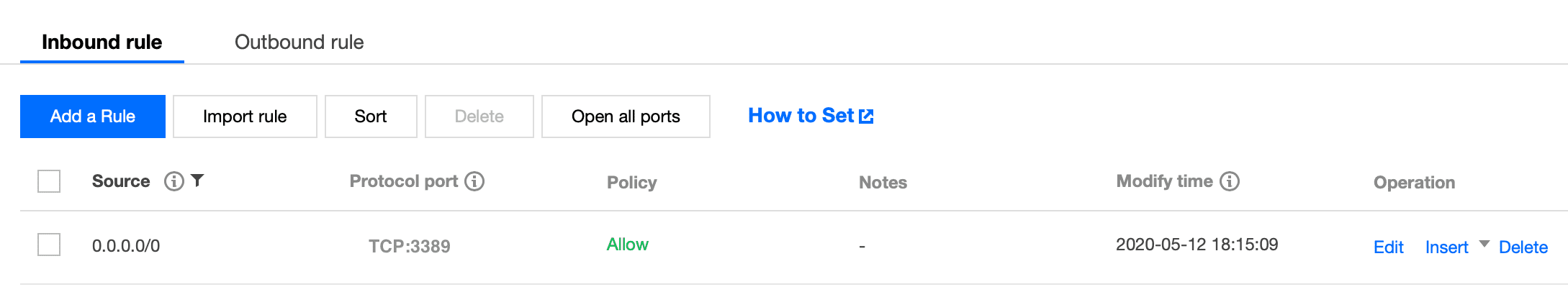
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Port x (where x is the port number of the new port) in a new row below #Port 22, and delete # to comment off Port 22, as shown in the following figure.
For example, add Port 23456 in the row.
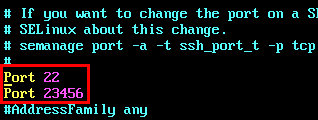
systemctl restart sshd.service
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport <New port number> -j ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 23456 -j ACCEPT
service iptables restart
firewall-cmd --add-port=<New port number>/tcp --permanent
firewall-cmd --add-port=23456/tcp --permanent
success is returned, the port was successfully configured.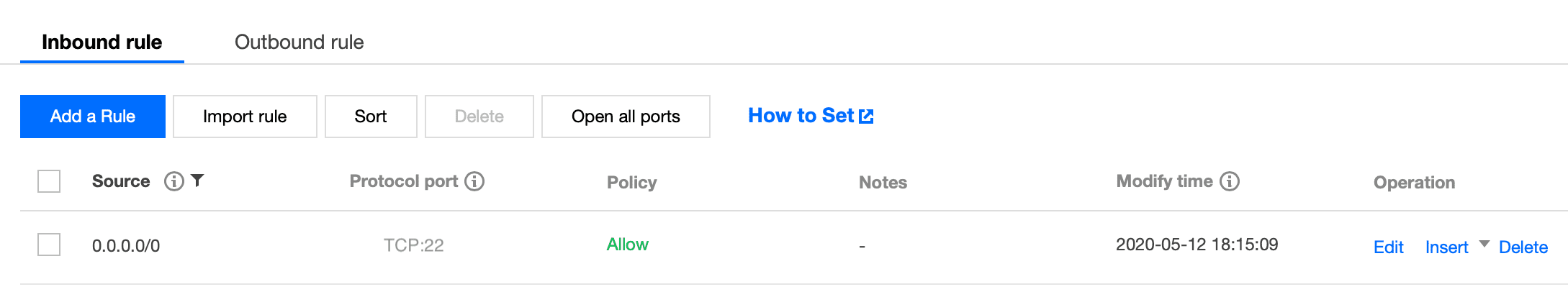
Internet IP of Windows server: port number after modification after Computer and click Connect, as shown in the following figure.
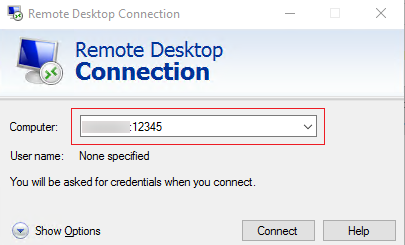
full address:s parameter in the RDP file.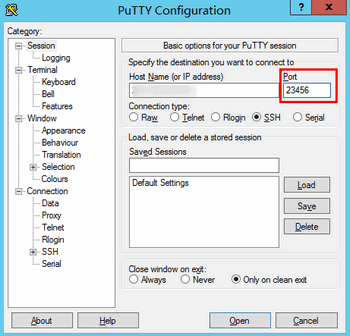

vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# in front of Port 22 to comment off the port.systemctl restart sshd.service
Last updated:2024-01-06 17:38:11
/var/run/utmp, /var/log/wtmp, /var/log/btmp, and /var/log/lastlog files.who command to view the information of the currently logged-in user in the /var/run/utmp file. The returned result is as follows:

w command to view the username of the currently logged-in user and display the currently executed tasks of the user in the /var/run/utmp file. The returned result is as follows:

users command to view the username of the currently logged-in user in the /var/run/utmp file. The returned result is as follows:

last command to view the information of the currently and historically logged-in users in the /var/log/wtmp file. The returned result is as follows:
lastb command to view the information of all the users who failed to log in to the system in the /var/log/btmp file. The returned result is as follows:
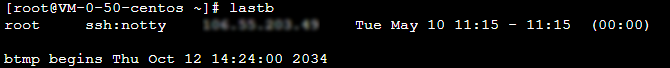
lastlog command to view the last user login information in the /var/log/lastlog file. The returned result is as follows:
cat /var/log/secure command to view the login information. The returned result is as follows:


4648 in <All Event IDs> and click OK.Last updated:2025-11-20 10:34:20
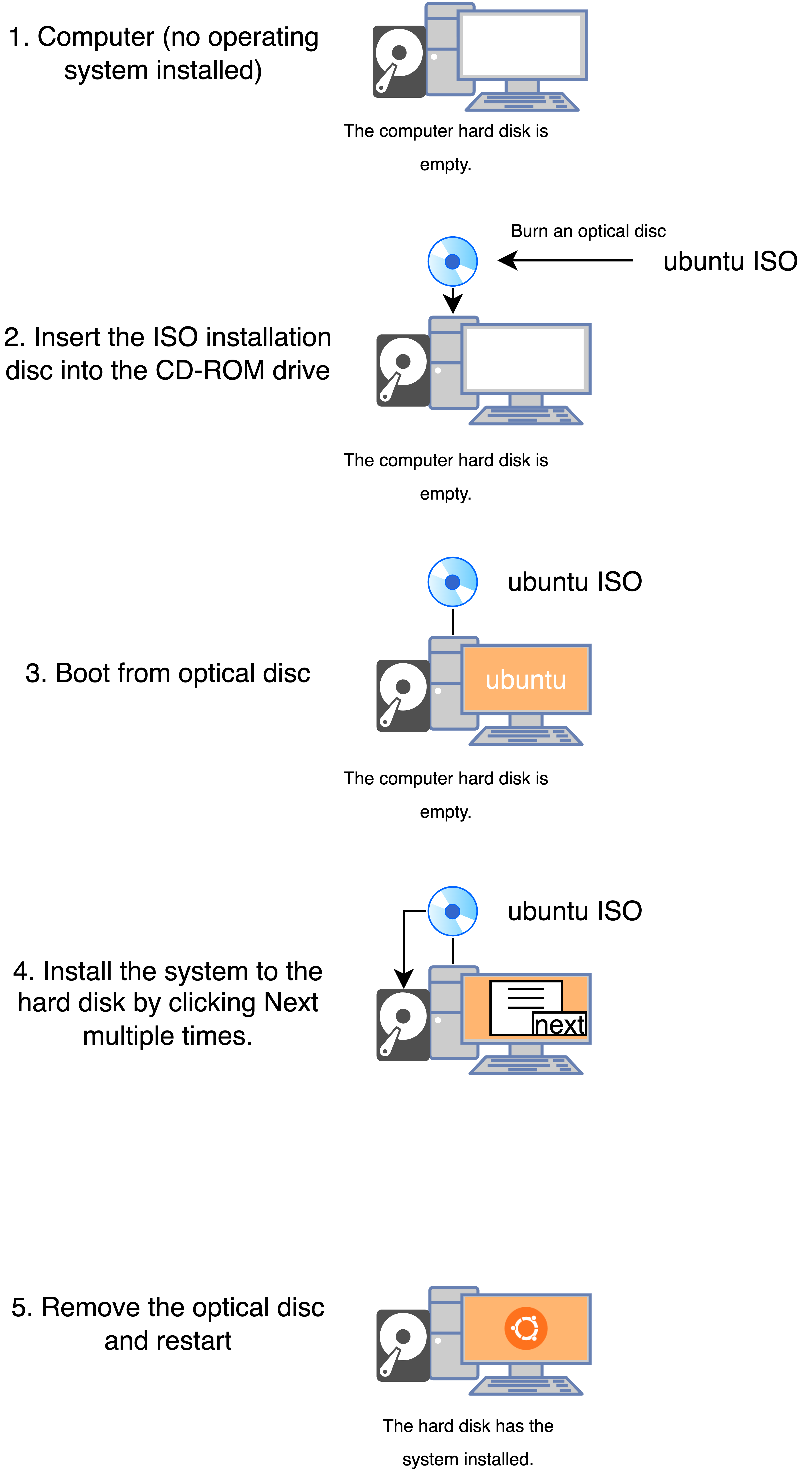

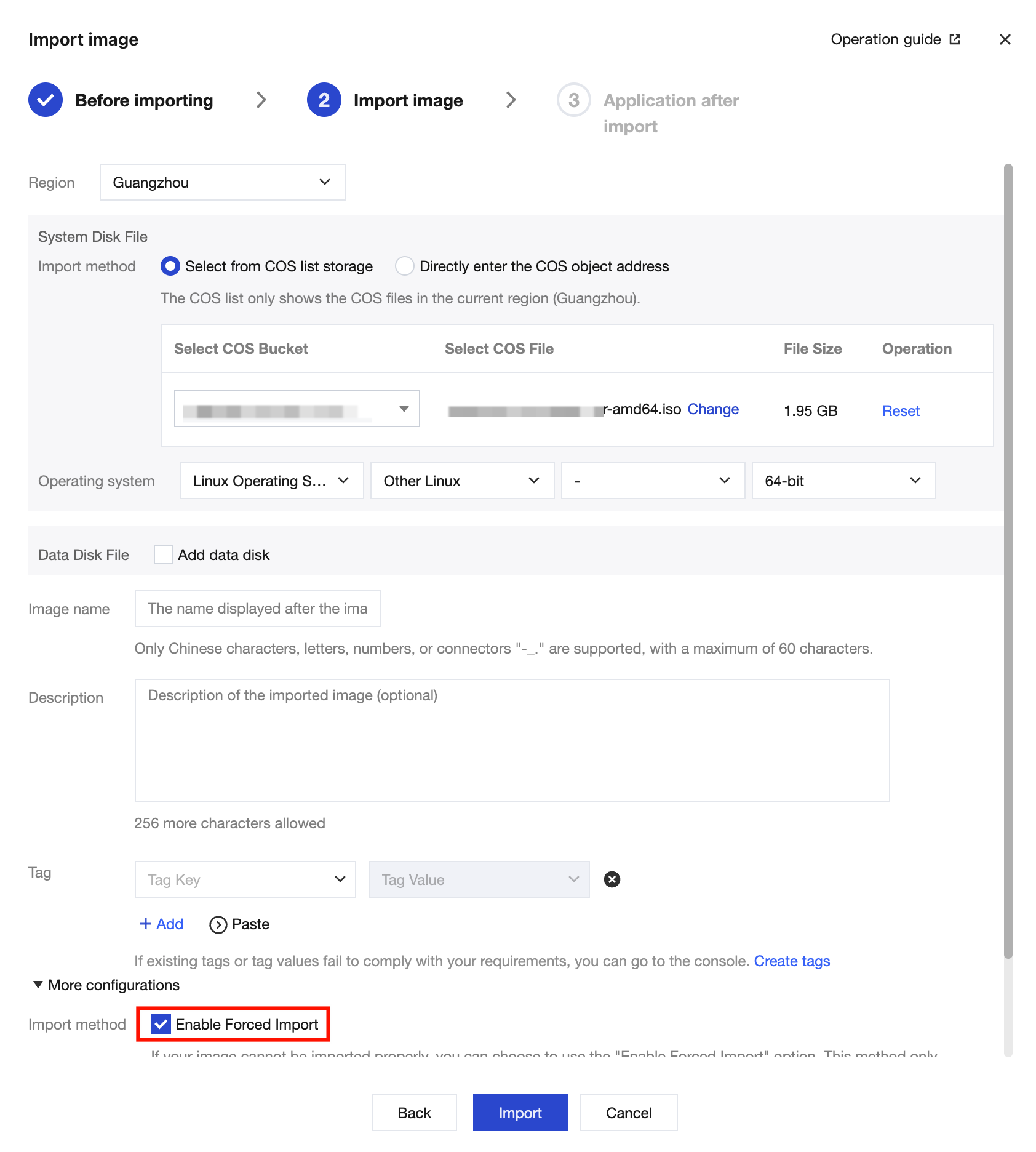
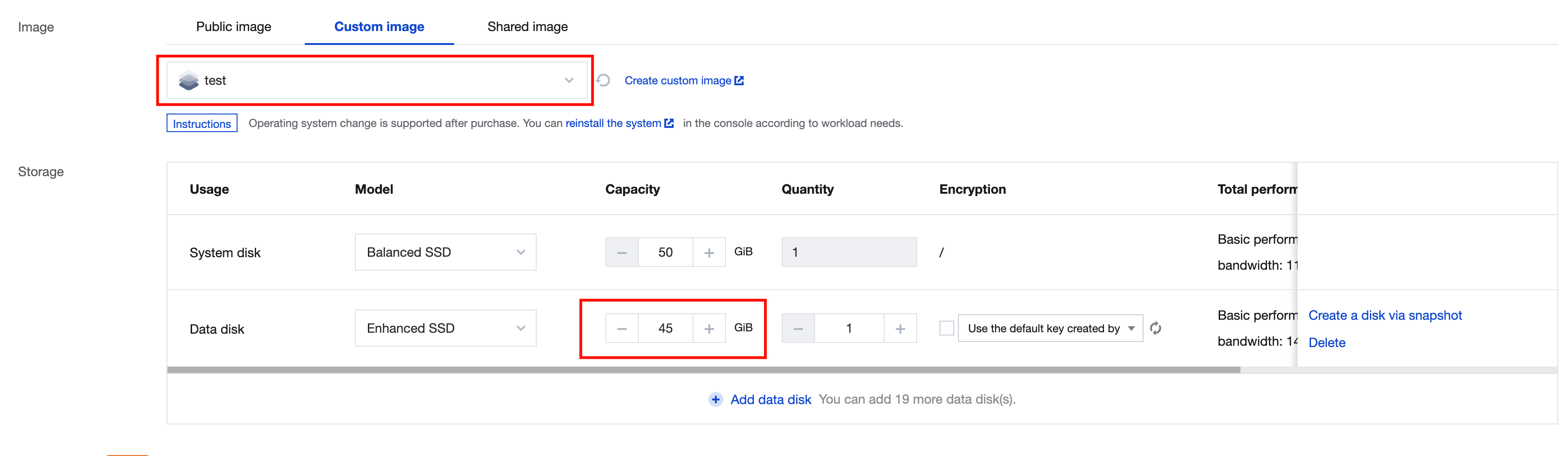
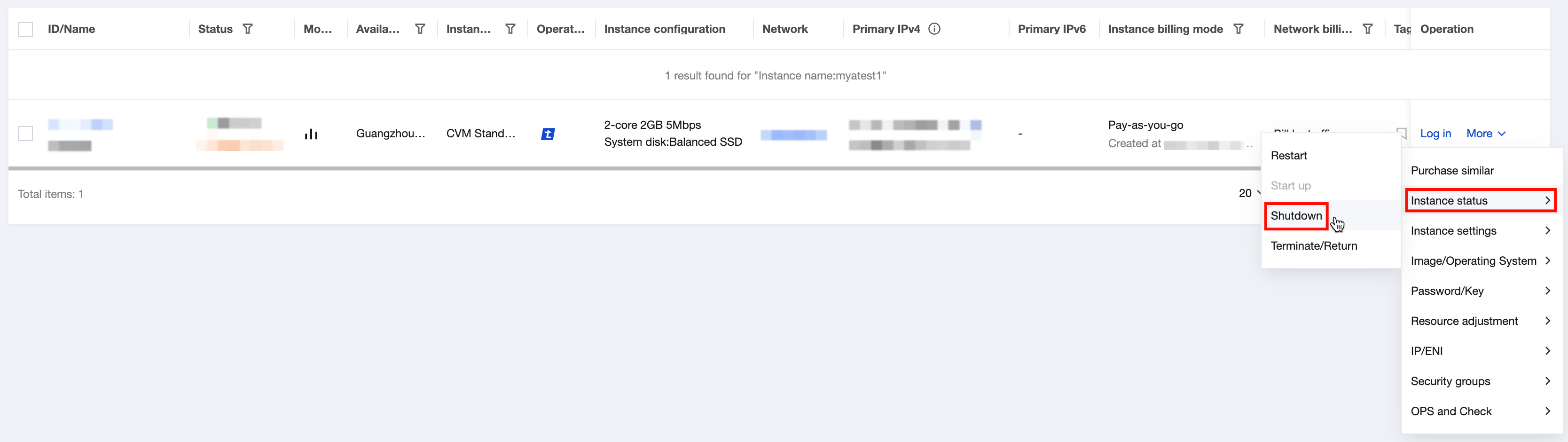
dd command.dd if=/dev/vdb of=/dev/vda bs=2M status=progress
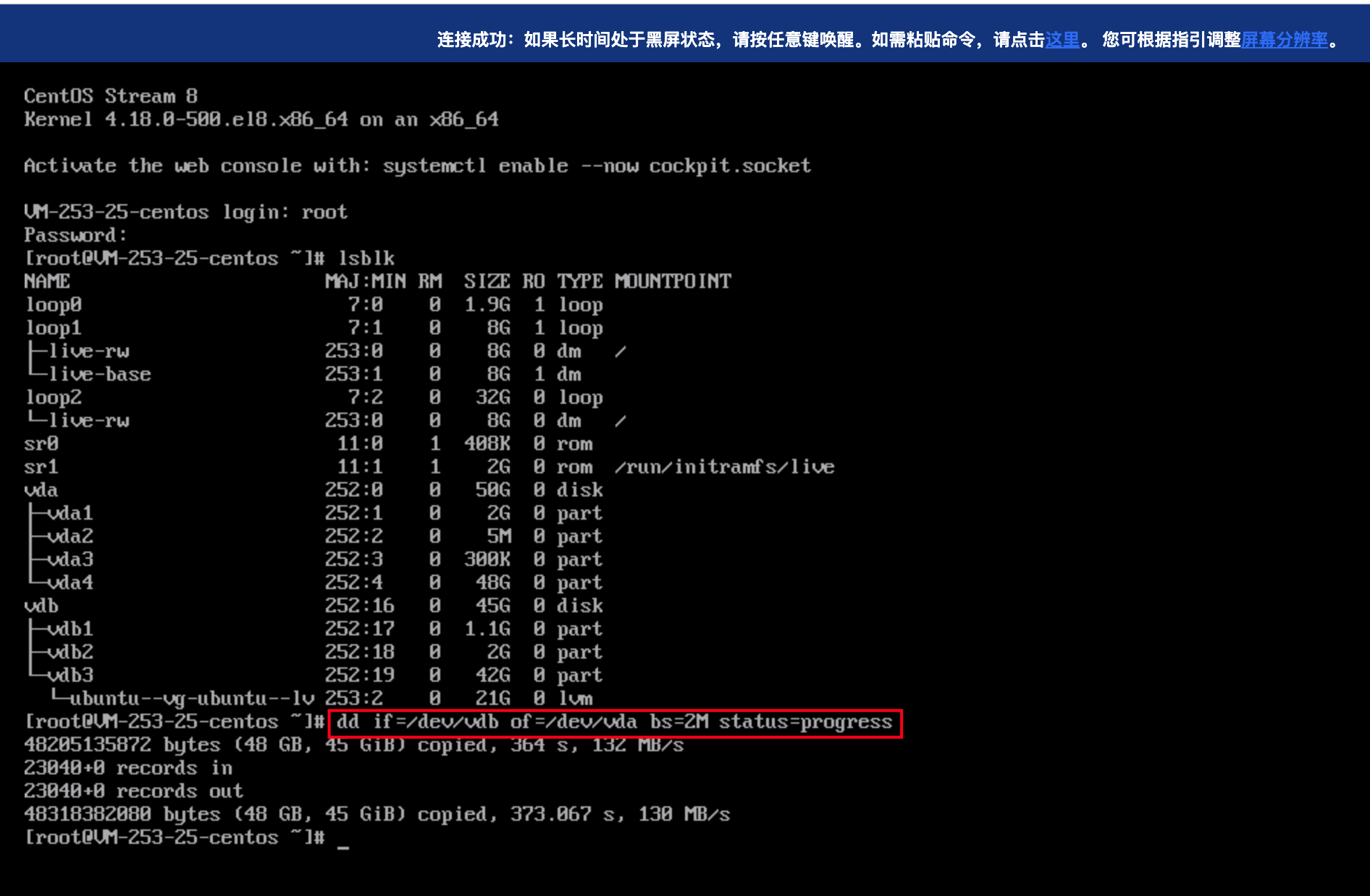
dd command. This prevents issues caused by duplicate UUIDs between the data disk and the system disk.dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/vdb bs=2M count=32
Operating System: Ubuntu 24.04.3 LTS / x86_64
Runtime Version: GNU bash, version 5.2.21(1)-release (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)
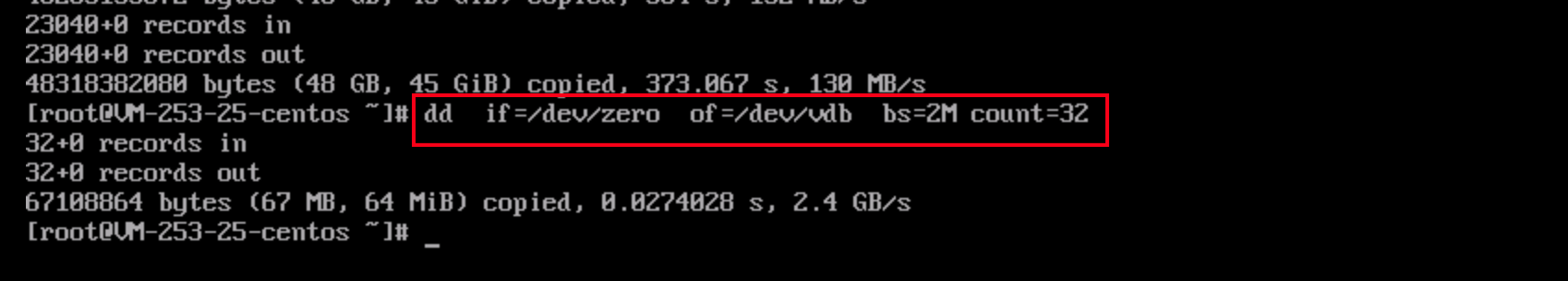

dd command, and installation of additional tools is required.
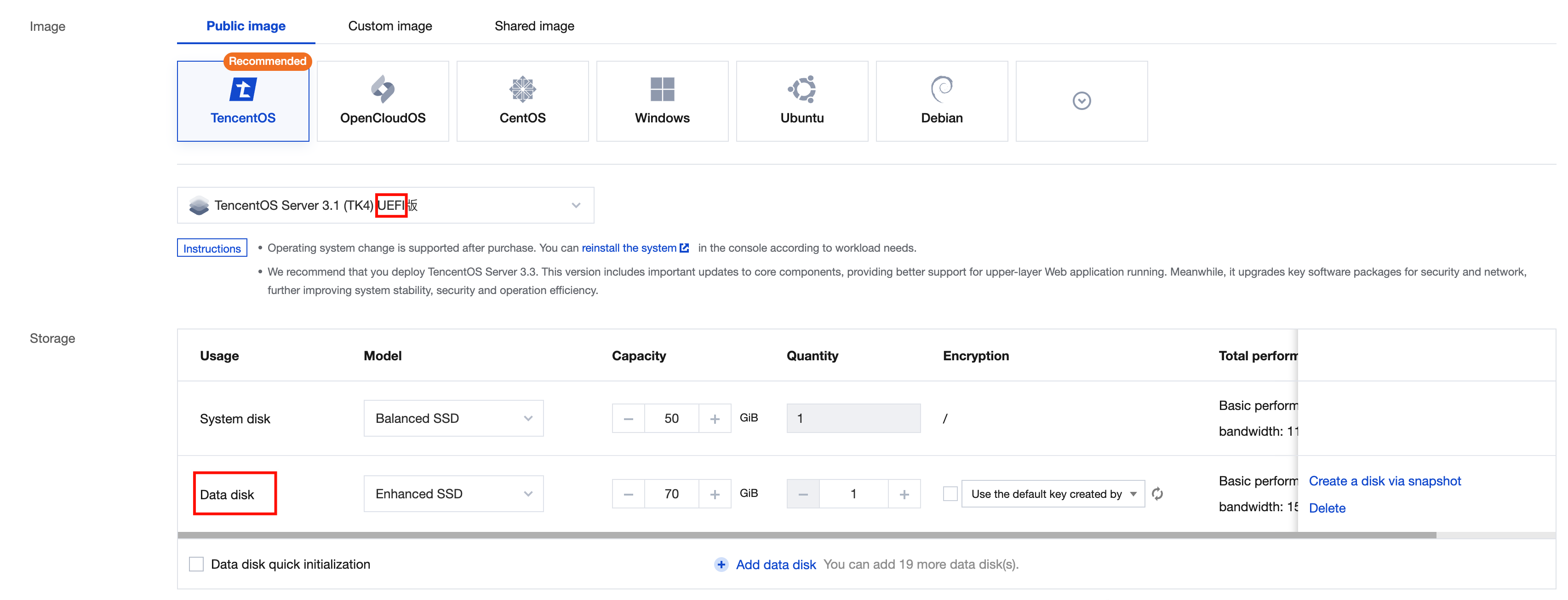
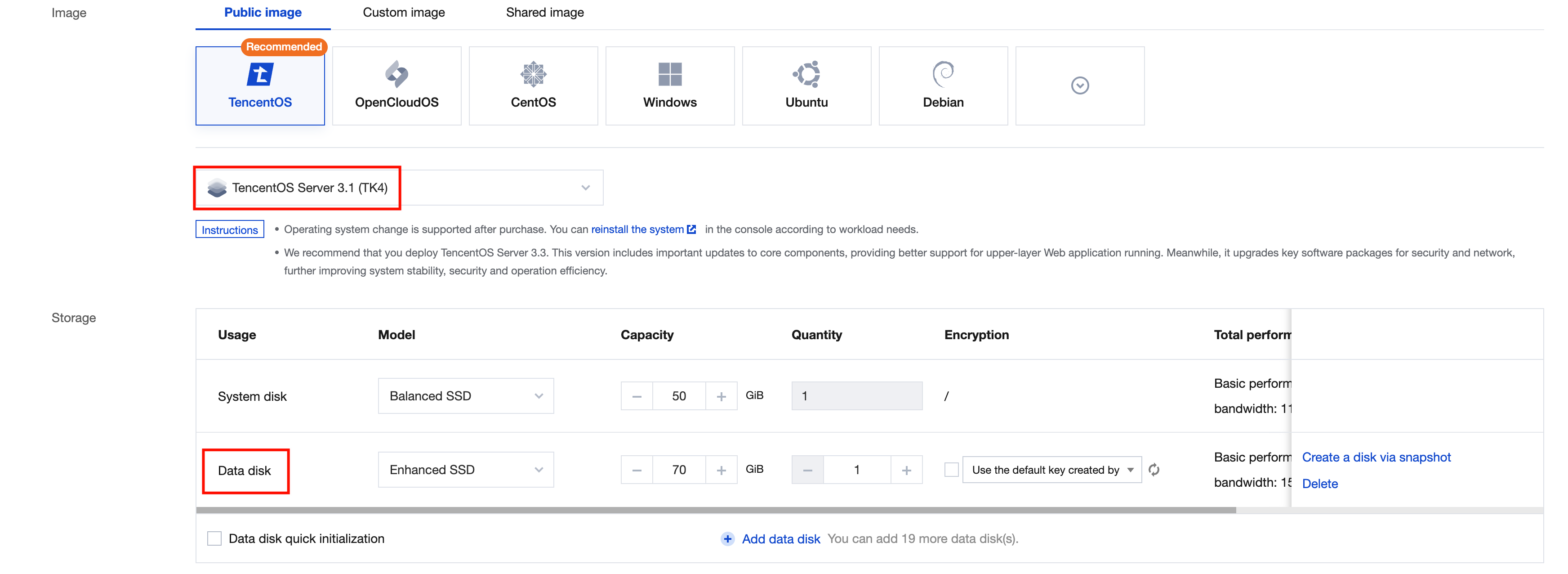

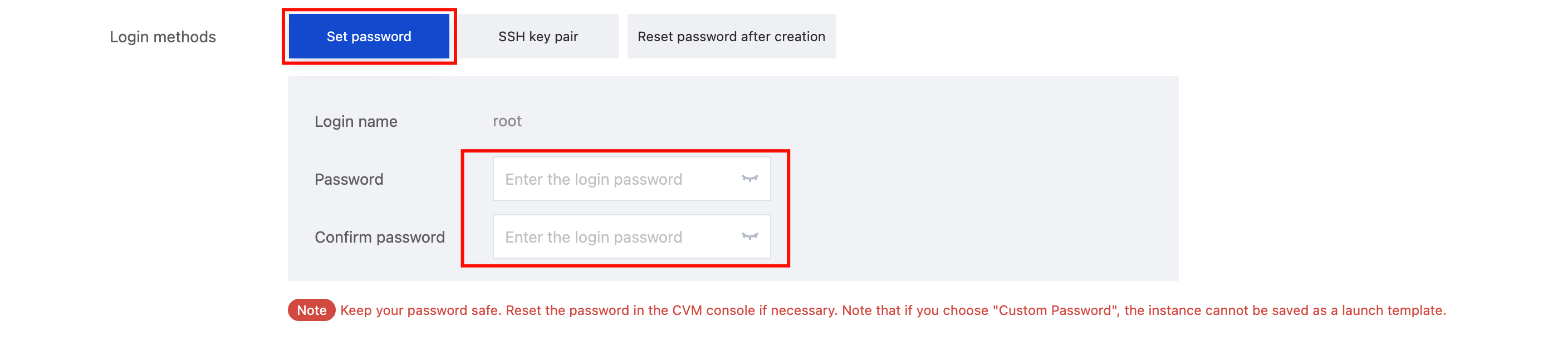
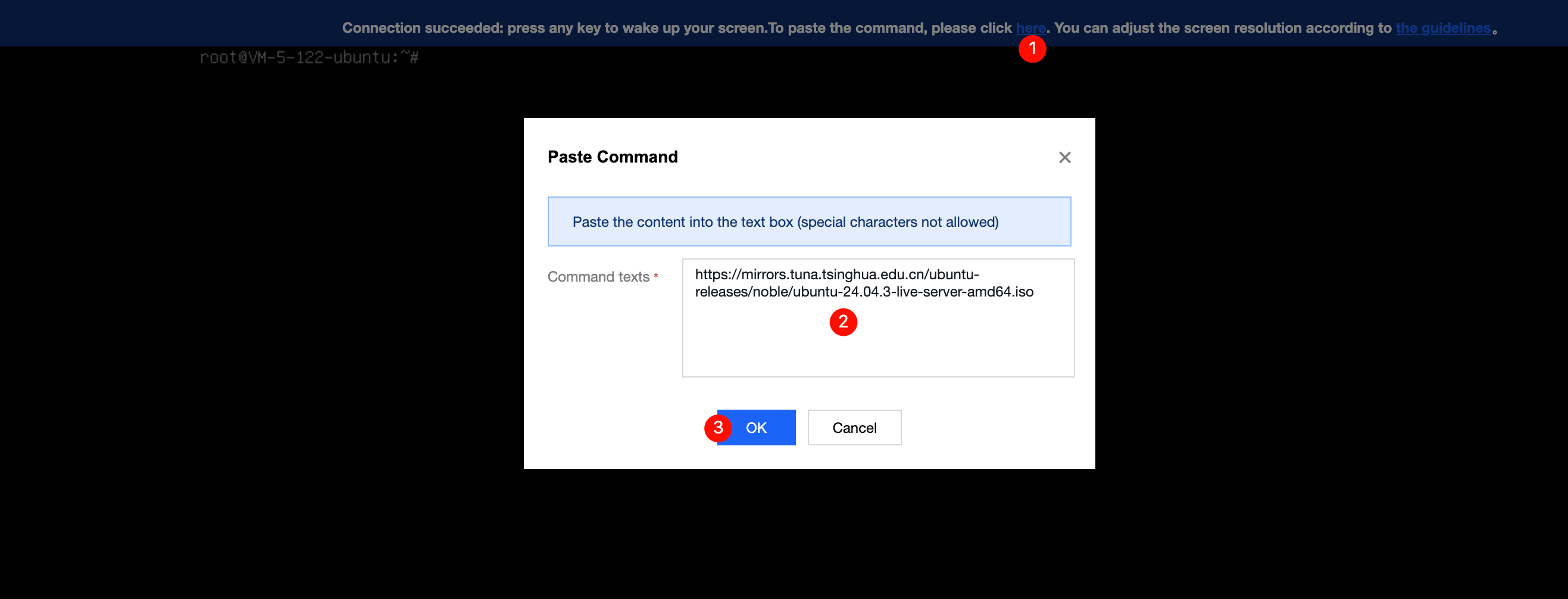
dd command.dd if=<ISO file name> of=/dev/vdb bs=2M status=progress
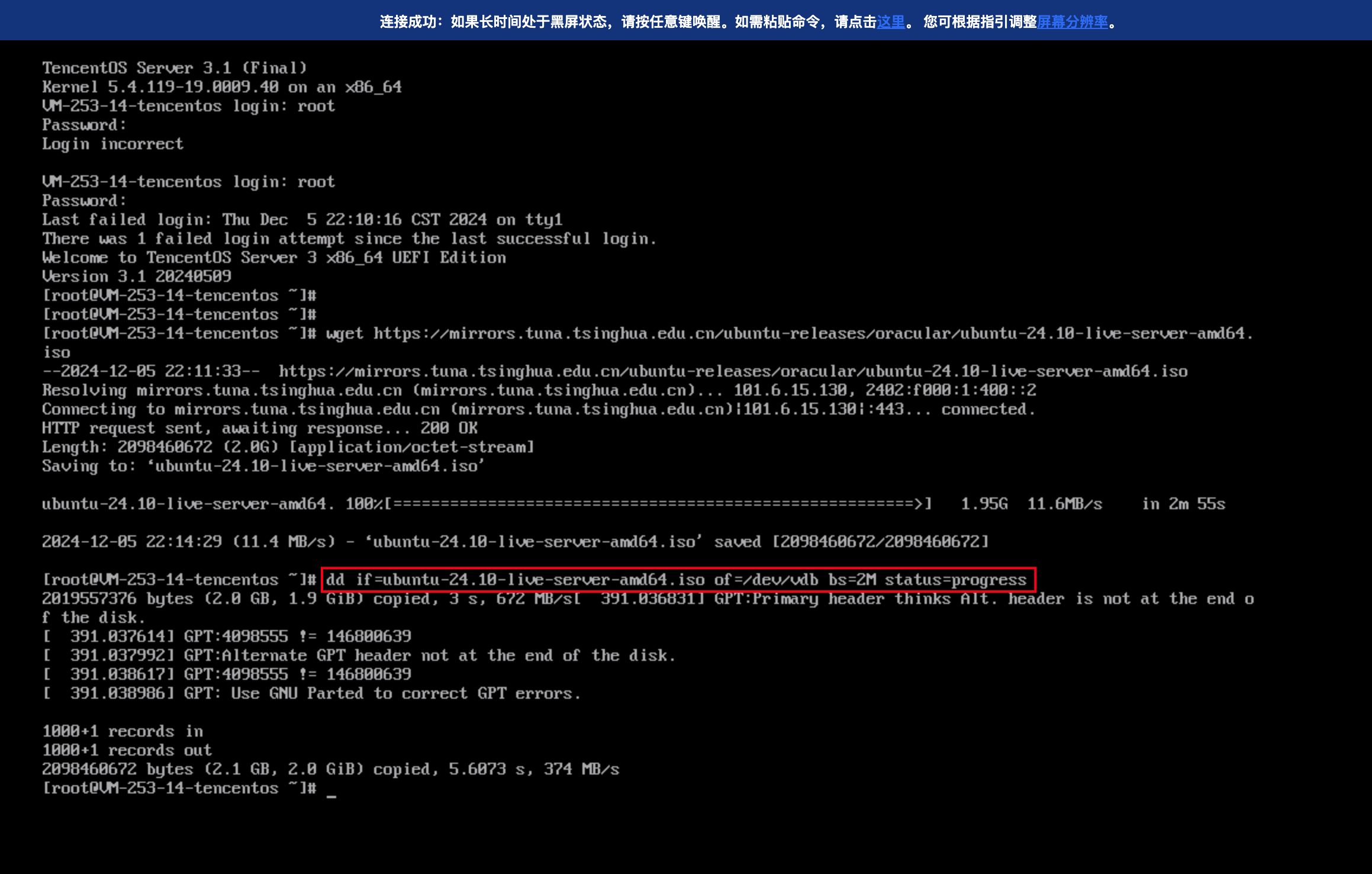
c key to access the grub cmdline interface. You can also enter the fwsetup command on the grub interface to access the firmware interface.

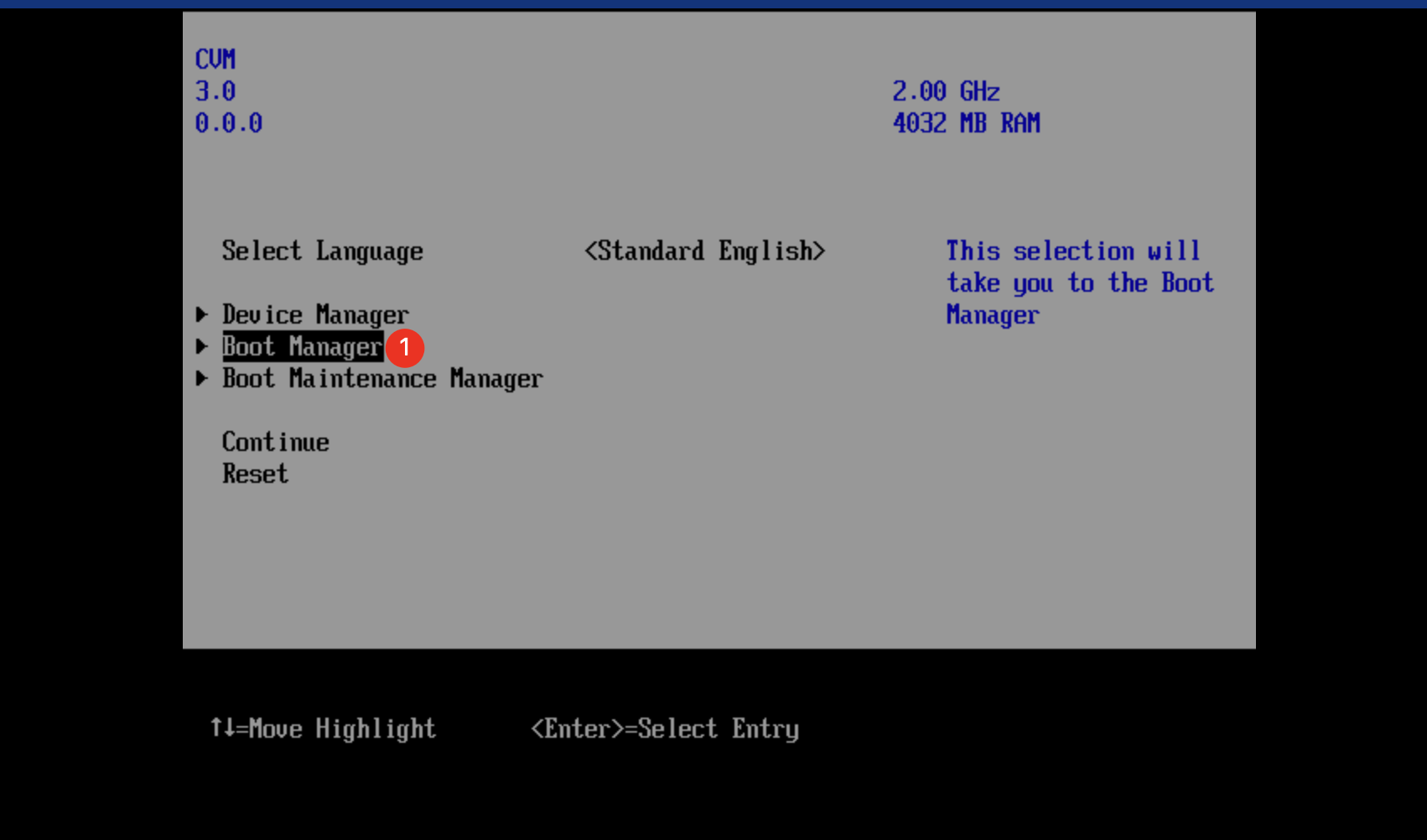
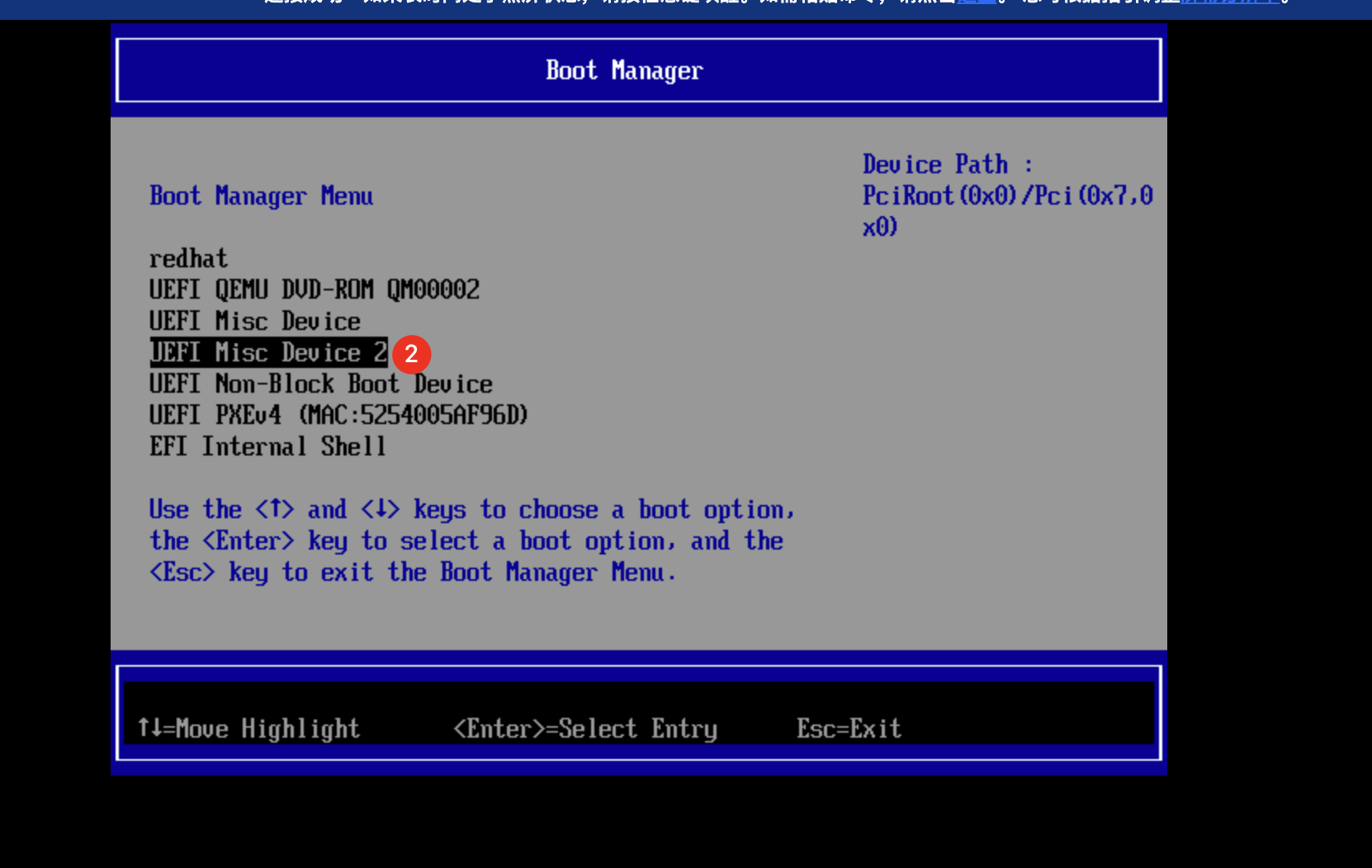
grub> set root=(hd1) # Set the root variable to (hd1), which is Disk 1. Disks are indexed from 0, so Disk 1 is the second disk.grub> chainloader +1 # This is a fixed writing method. +1 indicates loading the MBR from the location specified by the root variable.grub> boot # Boot.
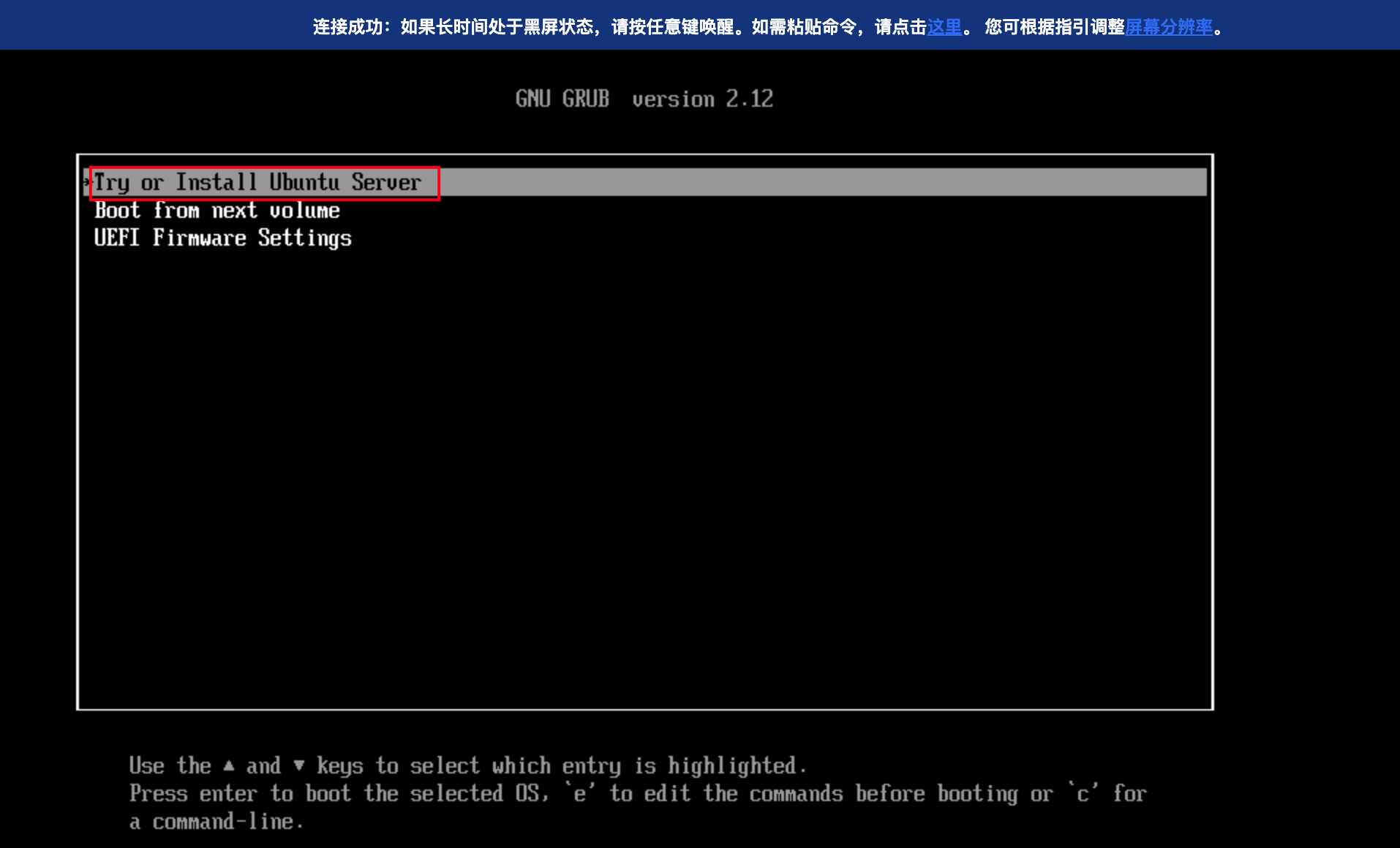

ip addr, the eth NIC does not have an IP address.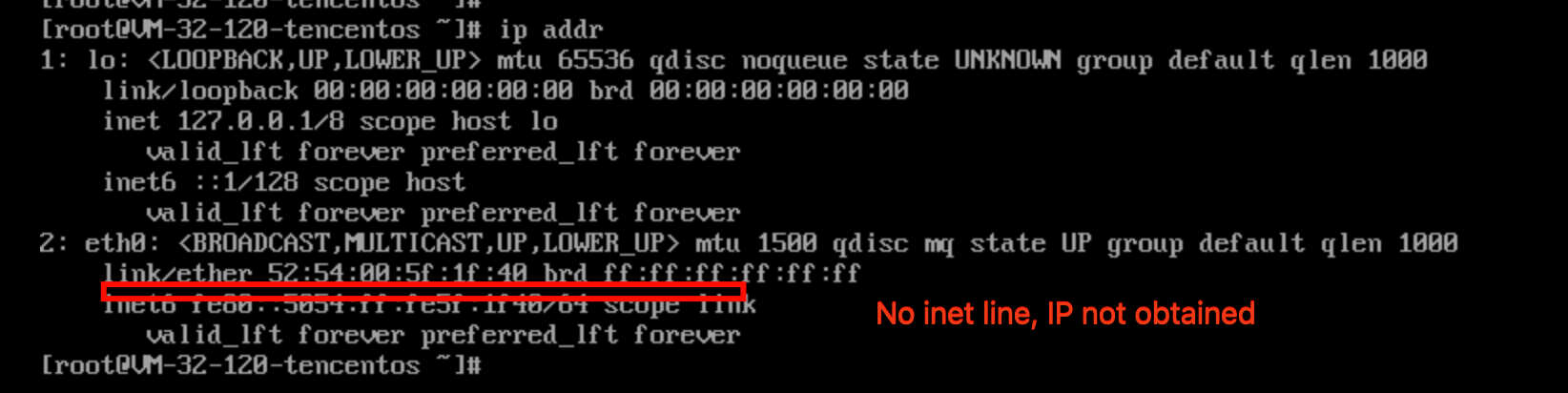
nmtui command to adjust the network configuration of the machine. After configuration adjustment, the machine automatically obtains an IP address through DHCP.
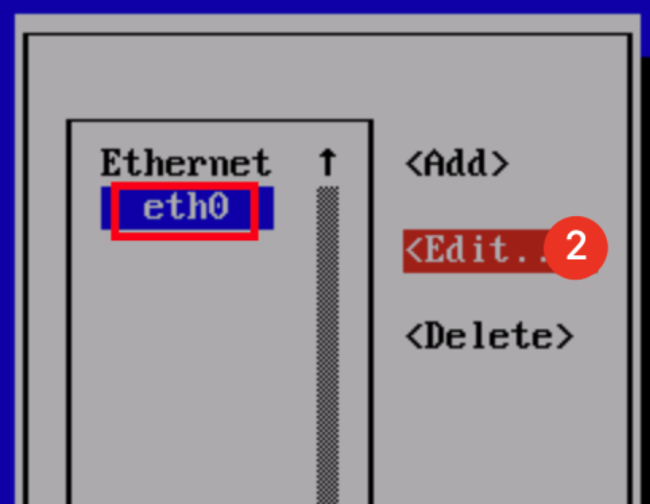
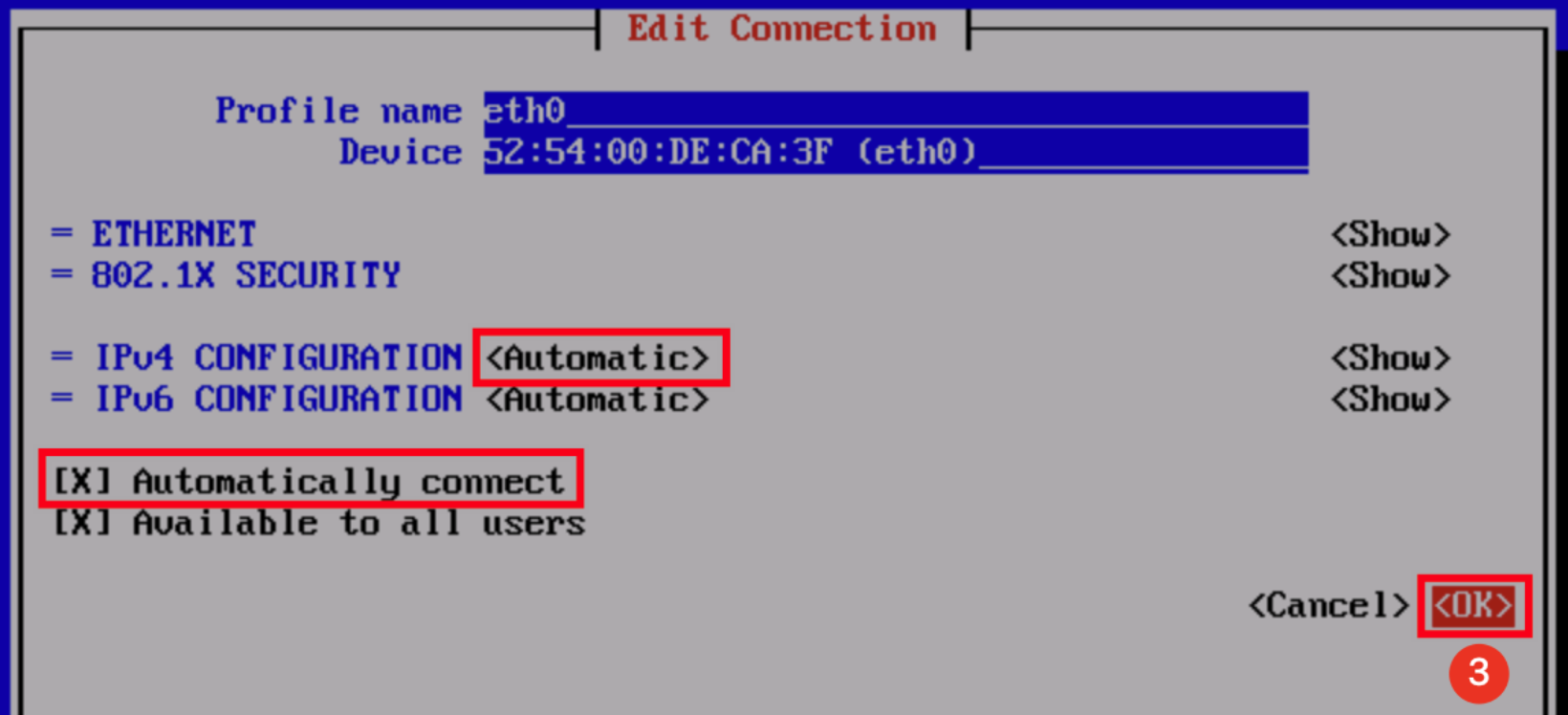
dhclient command, you can obtain an IP address by running dhclient -1 -d <NIC name>. After the IP address is obtained, you can exit the dhclient process using Ctrl + C.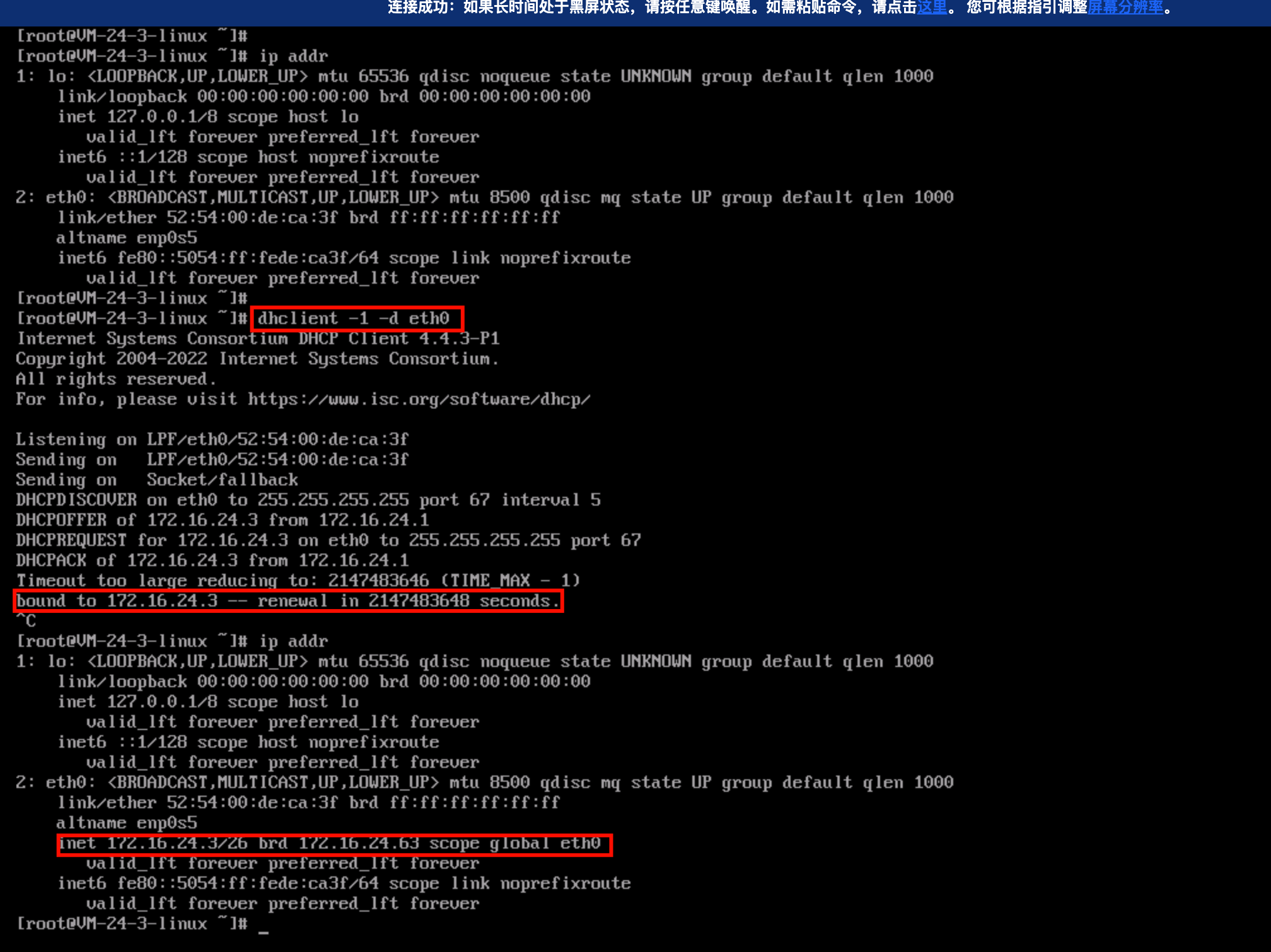
dhclient command, you can consider obtaining IP address information directly from /dev/sr0 and performing manual configuration.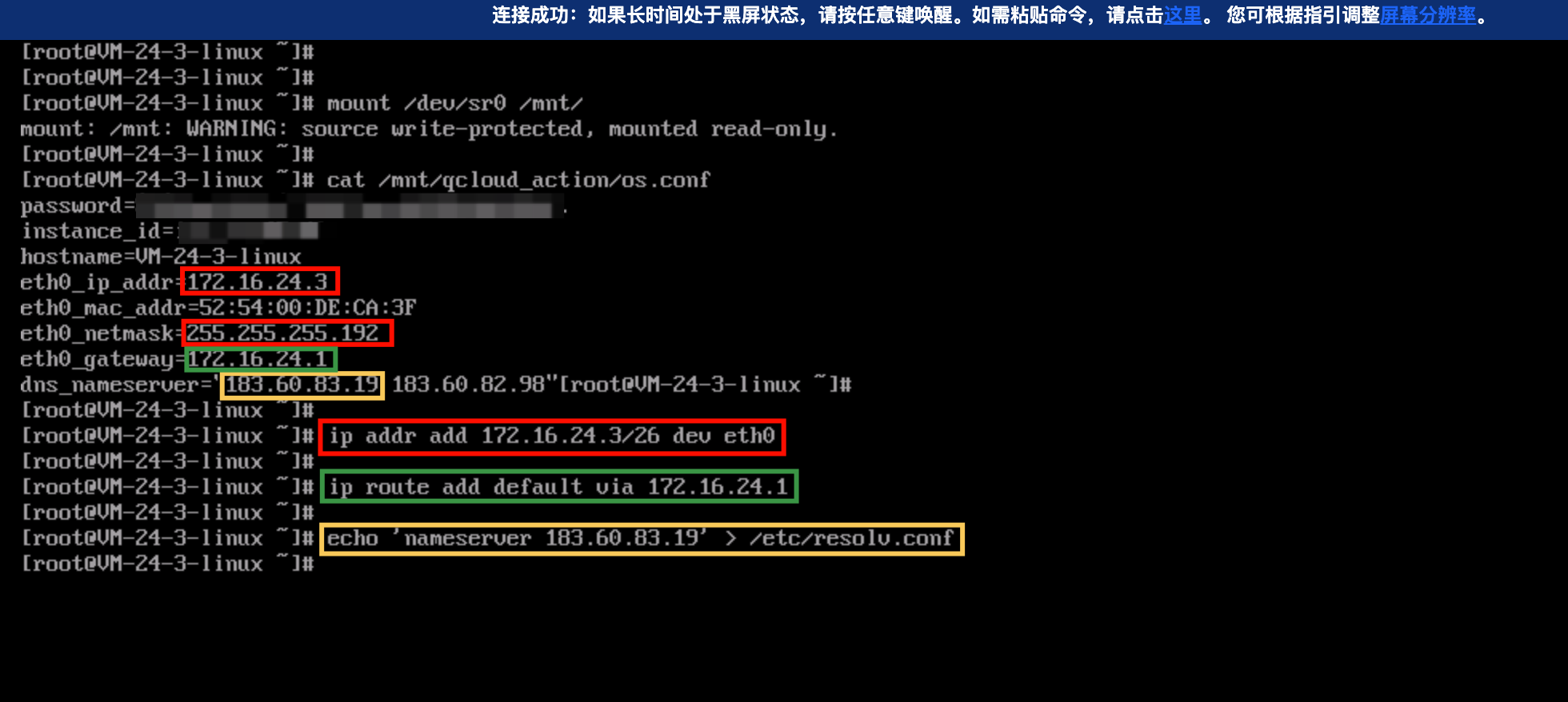
/sys/firmware directory. If the /sys/firmware directory contains an efi directory, UEFI boot is used; otherwise, BIOS boot is used.

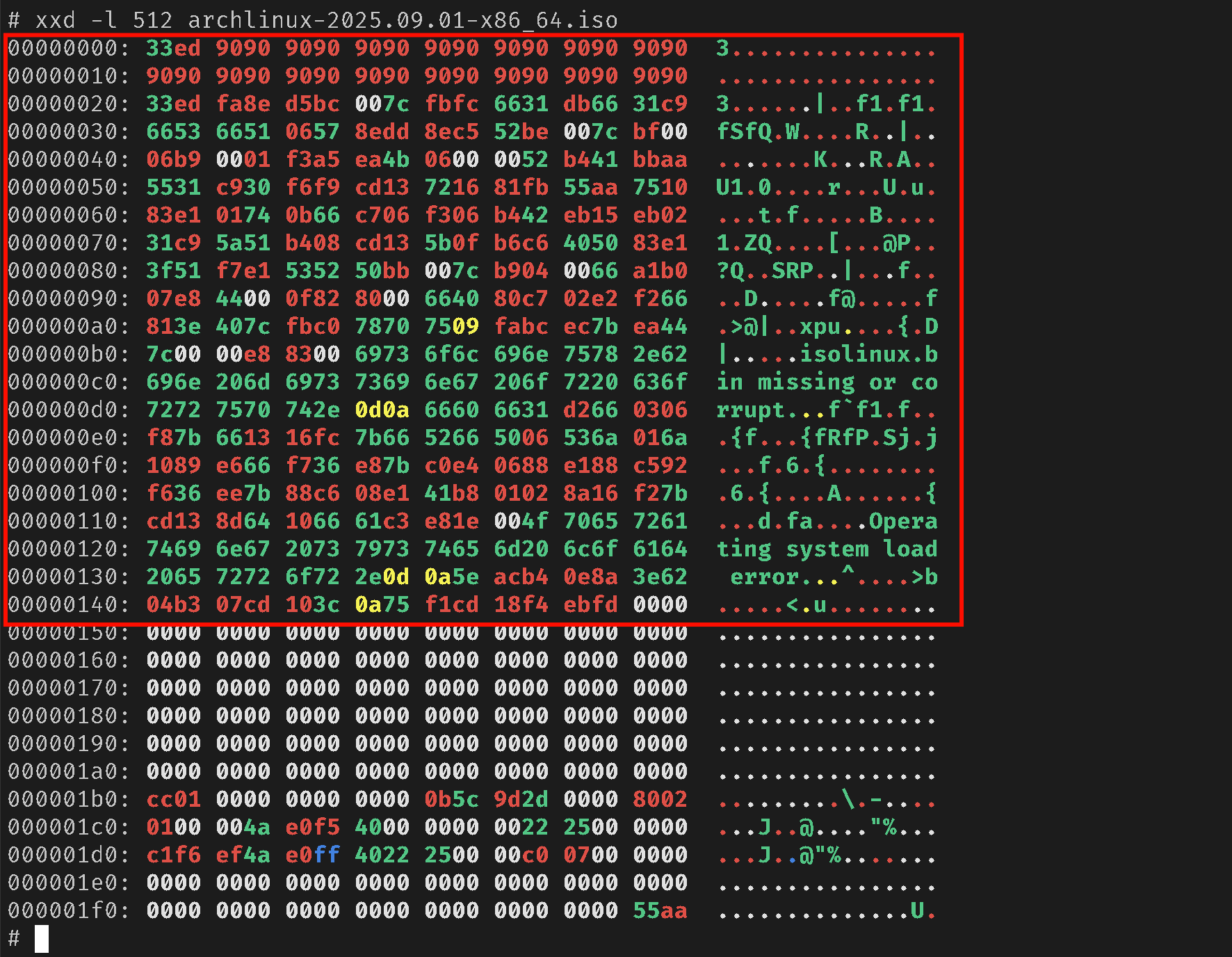
efi/boot/bootx64.efi file. The bootx64.efi file is required to be stored in a UEFI boot partition in the FAT format or in the ISO file system. Below is a check method for reference: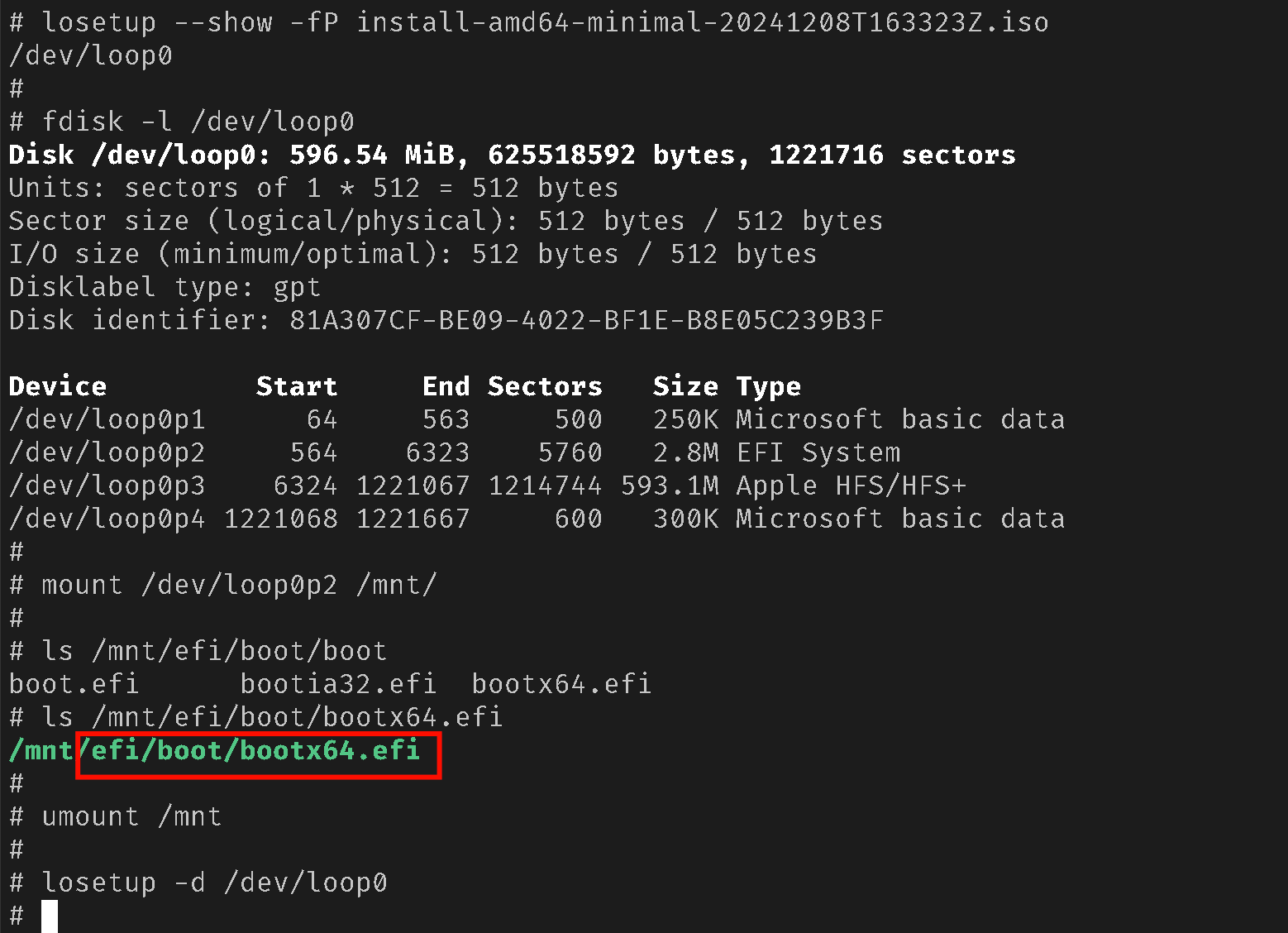
Last updated:2025-11-21 16:29:48
systemctl disable kdump --nowsystemctl status kdump.servicesystemctl is-enabled kdump.service
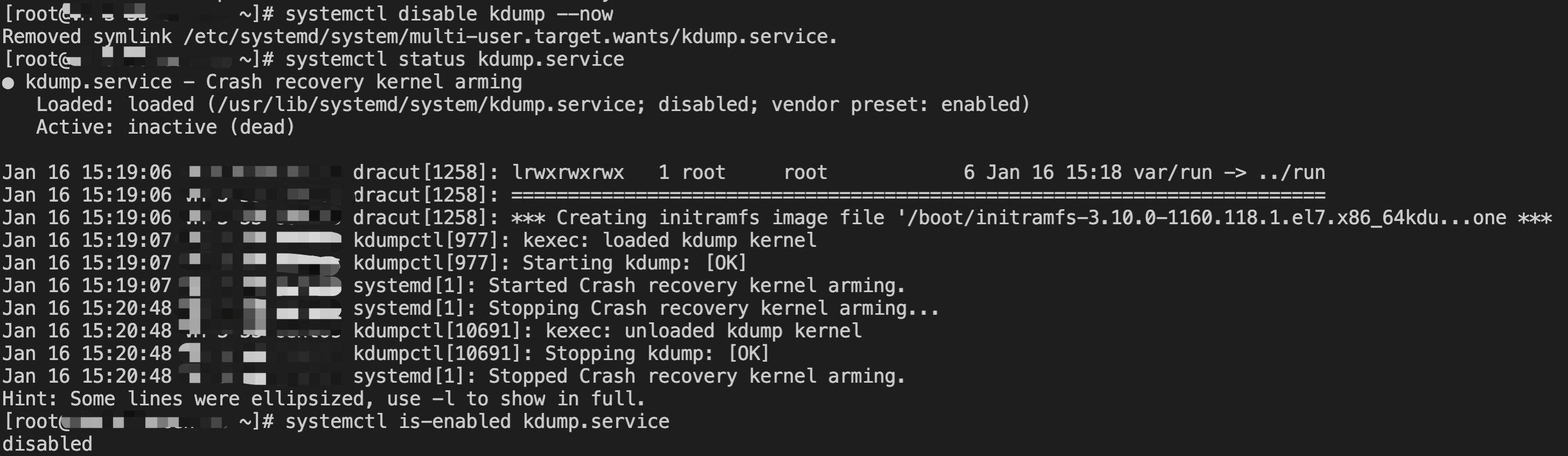
grubby --info=ALL|tee -a grubby.bak.$(date +%Y%m%d)
Operating System: Ubuntu 24.04.3 LTS / x86_64
Runtime Version: GNU bash, version 5.2.21(1)-release (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)
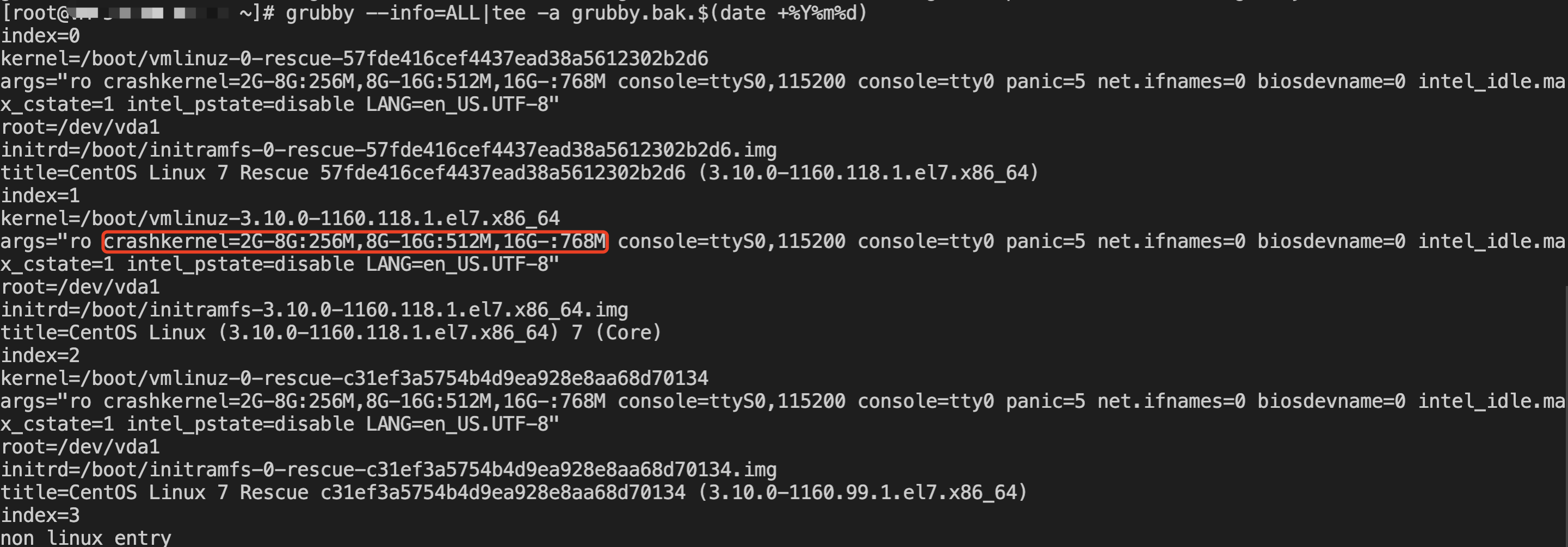
grubby --update-kernel=ALL --remove-args="crashkernel"grubby --info=ALL
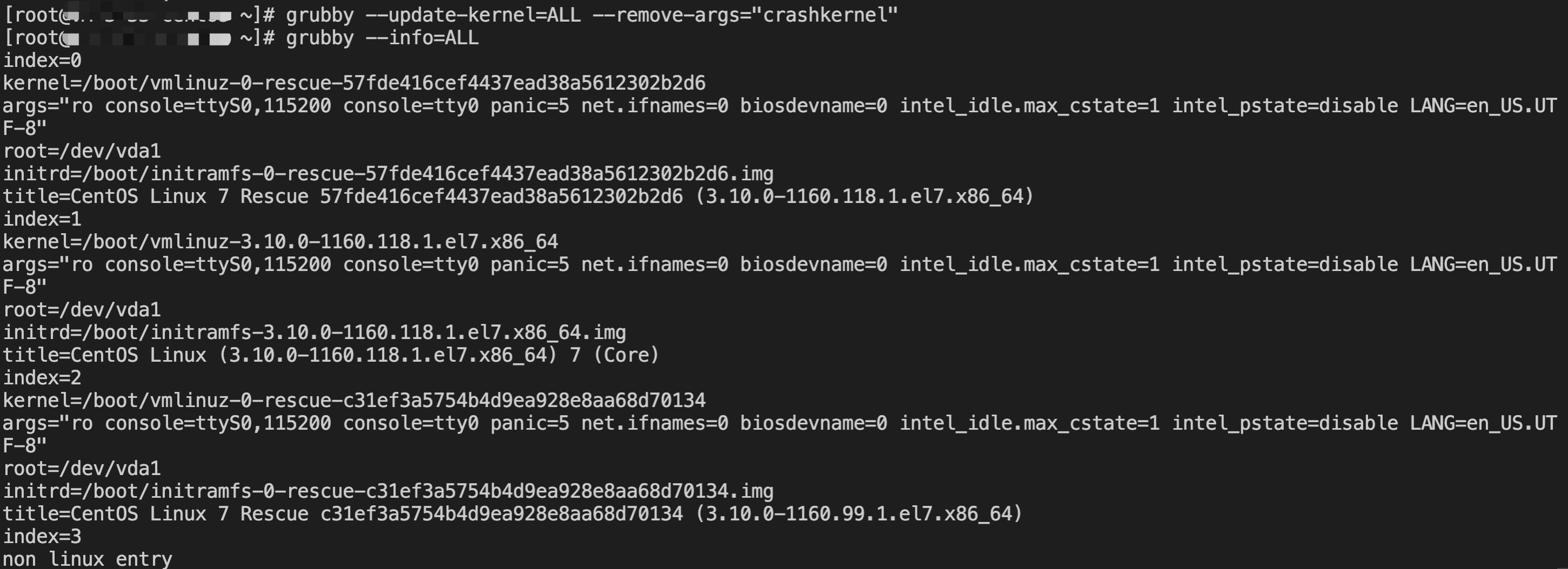
/sys/kernel/kexec_crash_size) is 0, and whether the Linux boot command line parameter /proc/cmdline contain configuration items related to crashkernel.uptimesystemctl status kdump.servicecat /sys/kernel/kexec_crash_sizecat /proc/cmdline
Operating System: Ubuntu 24.04.3 LTS / x86_64
Runtime Version: GNU bash, version 5.2.21(1)-release (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)
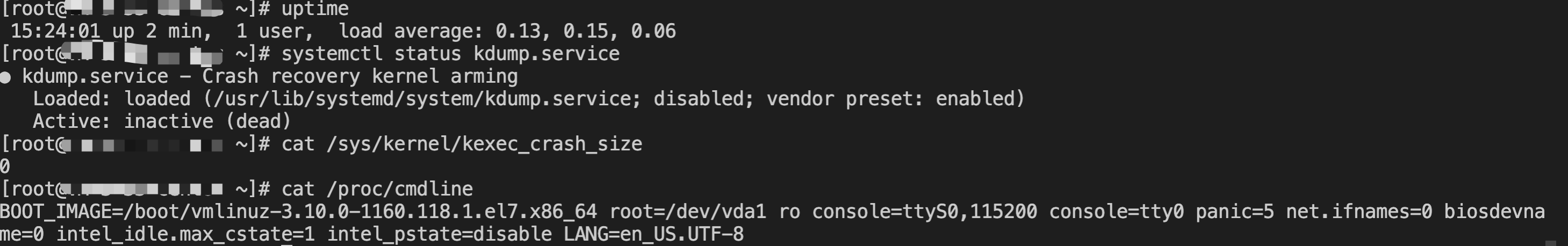
echo 0 >/sys/kernel/kexec_crash_size
cat /sys/kernel/kexec_crash_size
Operating System: Ubuntu 24.04.3 LTS / x86_64
Runtime Version: GNU bash, version 5.2.21(1)-release (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)
systemctl disable kdump --nowsystemctl status kdumpsystemctl is-enabled kdump
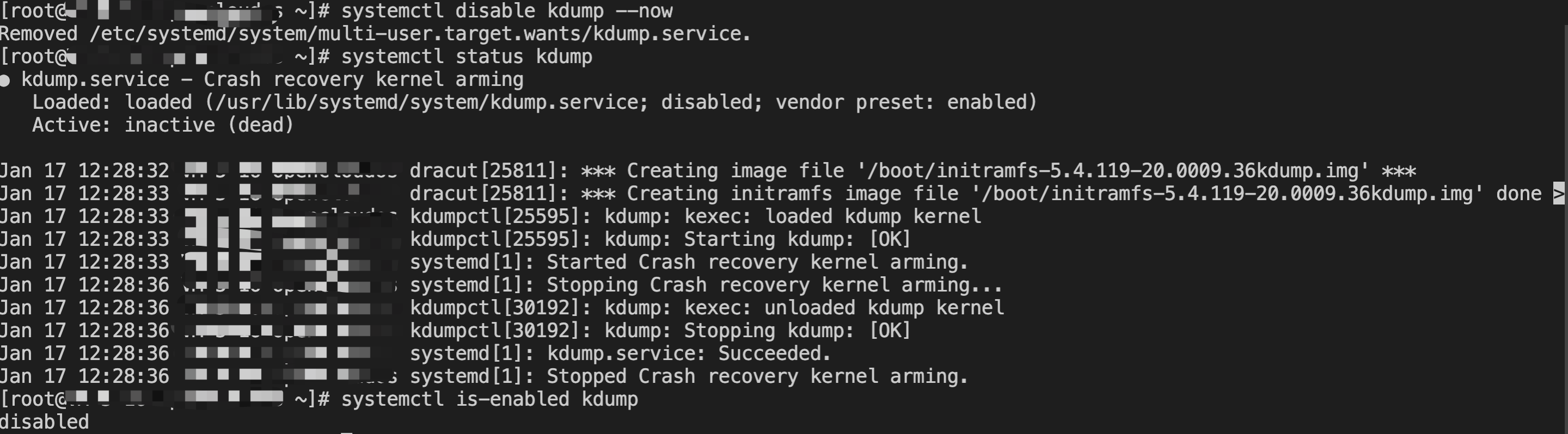
/etc/default/grub to remove the crashkernel configuration from GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX and update the configuration to the boot file./etc/default/grub file.cp /etc/default/grub /etc/default/grub.bak.$(date +%Y%m%d)
crashkernel=XXX configuration item (such as the content highlighted in red below) from the GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX line in the /etc/default/grub file and save the changes.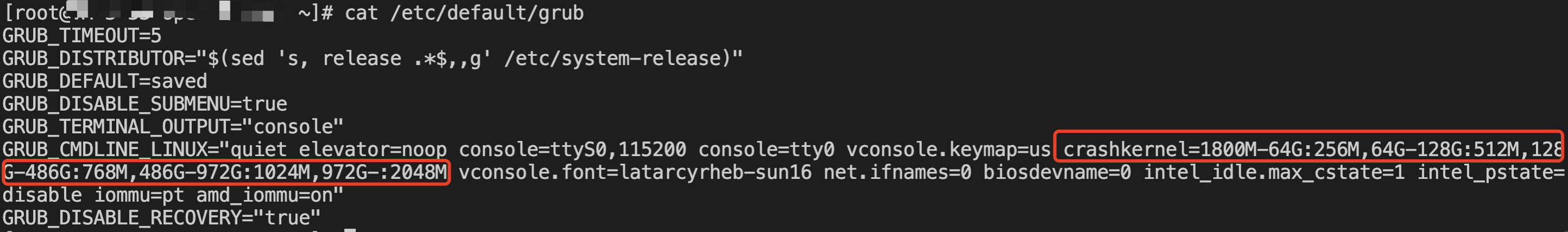
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
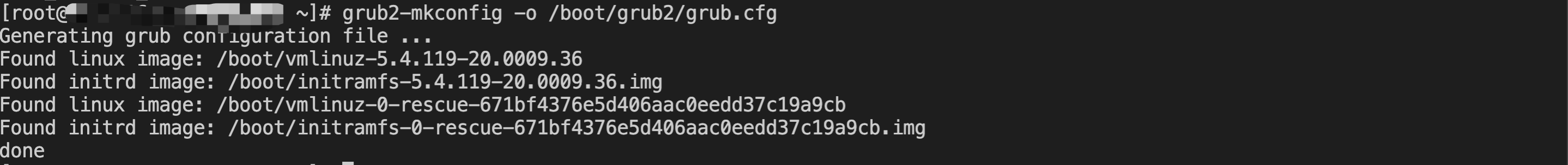
/sys/kernel/kexec_crash_size) is 0, and whether the Linux boot command line parameter /proc/cmdline contain configuration items related to crashkernel.uptimesystemctl status kdump.servicecat /sys/kernel/kexec_crash_sizecat /proc/cmdline
Operating System: Ubuntu 24.04.3 LTS / x86_64
Runtime Version: GNU bash, version 5.2.21(1)-release (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)
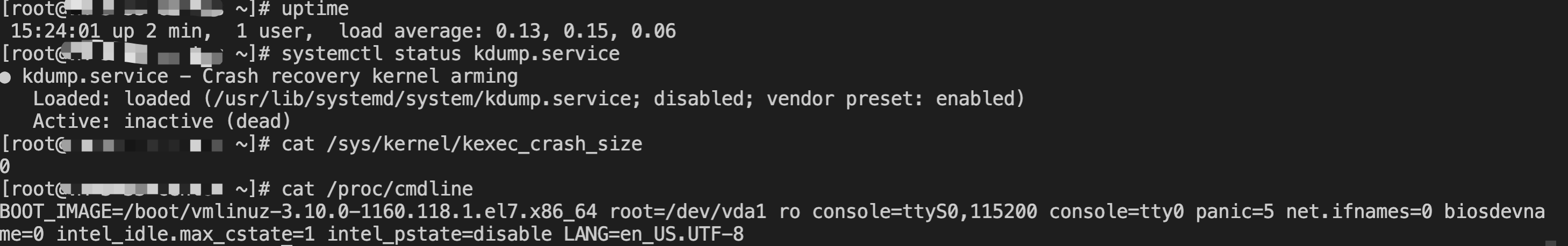
echo 0 >/sys/kernel/kexec_crash_size
cat /sys/kernel/kexec_crash_size
Operating System: Ubuntu 24.04.3 LTS / x86_64
Runtime Version: GNU bash, version 5.2.21(1)-release (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)
systemctl disable kdump-tools --nowsystemctl status kdump-toolssystemctl is-enabled kdump-tools
/etc/default/grub or /etc/default/grub.d to remove the crashkernel configuration from GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX or GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT, and update the configuration to the boot file./etc/default/grub file.cp /etc/default/grub /etc/default/grub.bak.$(date +%Y%m%d)
crashkernel=XXX configuration item
(such as the content highlighted in red below) from the GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX or GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT line in the /etc/default/grub file and save the changes.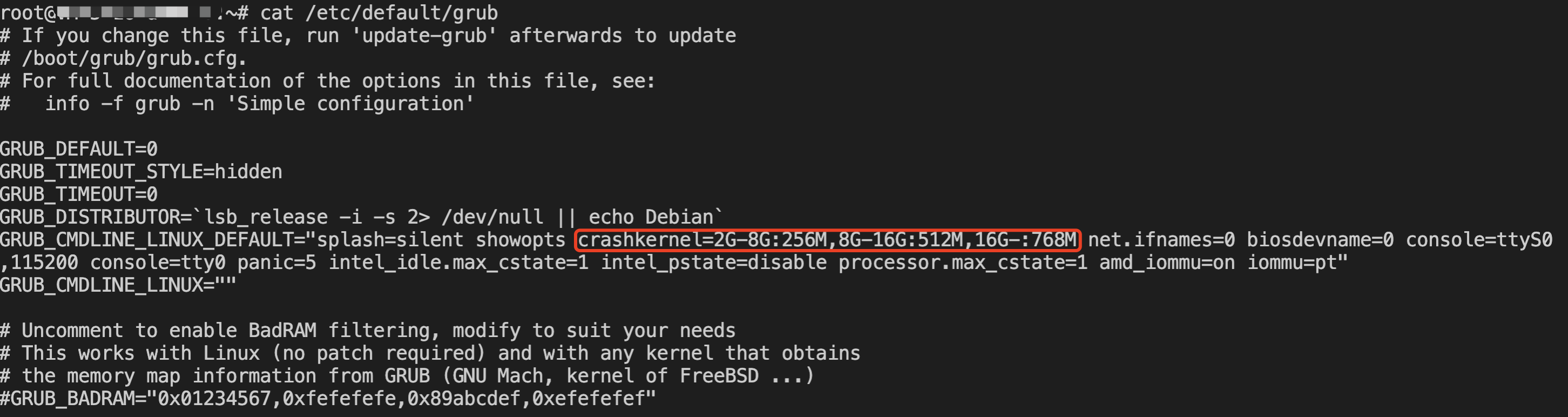
/etc/default/grub file, check whether the kdump-tools.cfg configuration file in /etc/default/grub.d contains the configuration item related to crashkernel (such as the content highlighted in red below). If it exists, remove the crashkernel=XXX configuration item.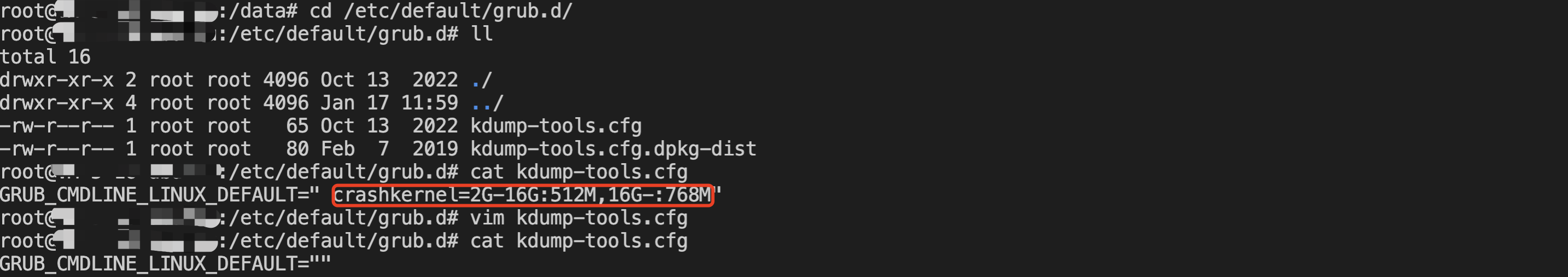
/etc/default/grub.d/ directory, check whether there is the kdump-tools.cfg file, check the kdump-tools.cfg configuration, back up the file, remove the configuration item related to crashkernel, and verify the modification result.cd /etc/default/grub.d/cat kdump-tools.cfgcp kdump-tools.cfg kdump-tools.cfg.bak.$(date +%Y%m%d)vim kdump-tools.cfgcat kdump-tools.cfg
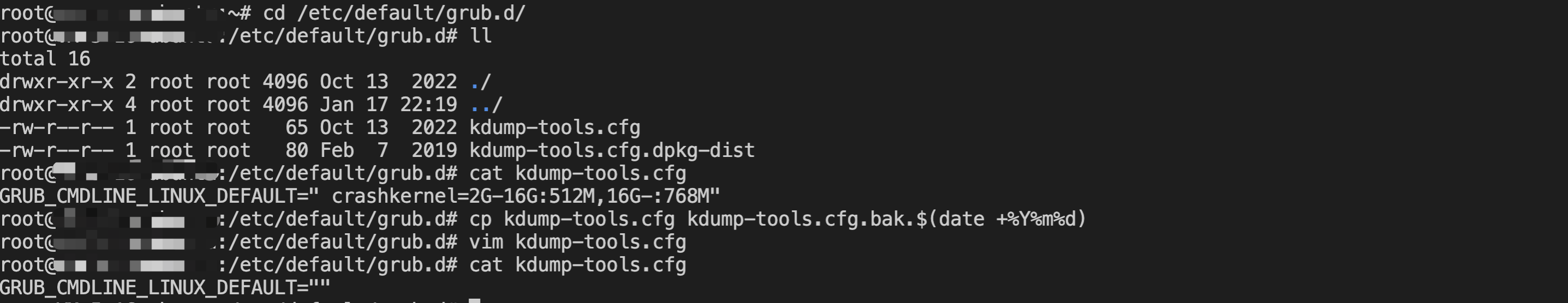
update-grub
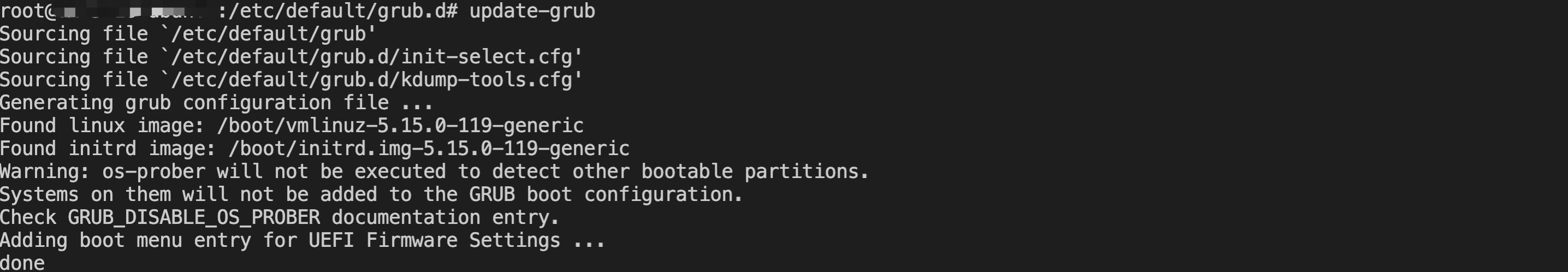
/sys/kernel/kexec_crash_size) is 0, and whether the Linux boot command line parameter /proc/cmdline contain configuration items related to crashkernel.uptimesystemctl status kdump-toolscat /sys/kernel/kexec_crash_sizecat /proc/cmdline
Operating System: Ubuntu 24.04.3 LTS / x86_64
Runtime Version: GNU bash, version 5.2.21(1)-release (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)
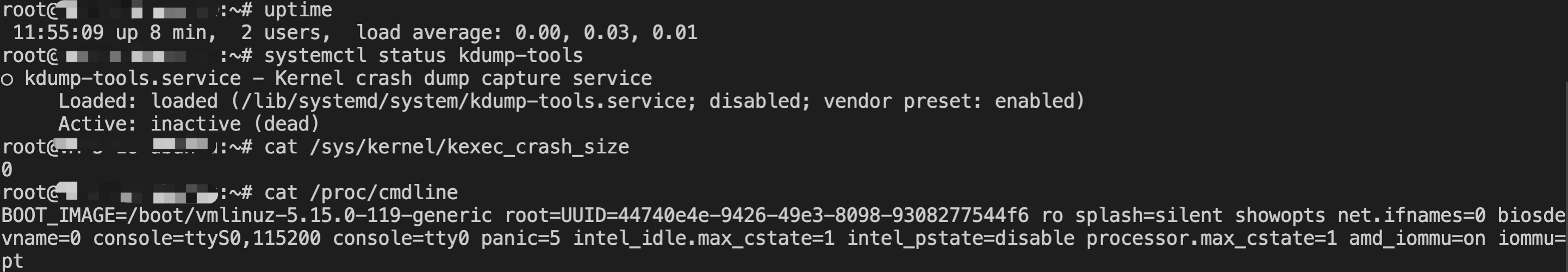
echo 0 >/sys/kernel/kexec_crash_size
cat /sys/kernel/kexec_crash_size
Operating System: Ubuntu 24.04.3 LTS / x86_64
Runtime Version: GNU bash, version 5.2.21(1)-release (x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)
/var/crash. The crash tool can be used to analyze the cause of the panic that occurs on the server. However, enabling kdump consumes part of the memory space of the operating system. Different Linux distributions have different methods for enabling kdump. Below are configuration methods for several Linux distributions:Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02
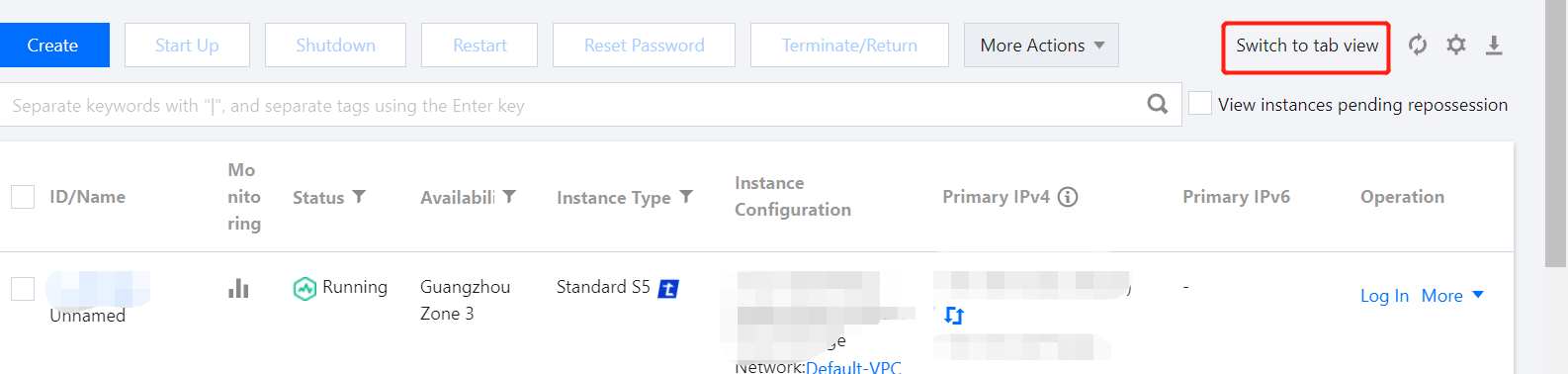
Last updated:2024-01-08 09:32:02